|
Demetrius Poliorcetes
Demetrius I Poliorcetes (; , , ; ) was a Macedonian Greek nobleman and military leader who became king of Asia between 306 and 301 BC, and king of Macedon between 294 and 288 BC. A member of the Antigonid dynasty, he was the son of its founder, Antigonus I Monophthalmus, and his wife Stratonice, as well as the first member of the family to rule Macedon in Hellenistic Greece. In 307 BC, Demetrius successfully ousted Cassander's governor of Athens and after defeating Ptolemy I at the Battle of Salamis (306 BC) he gave his father the title of ''basileus'' ("king") over a land spanning from the Aegean Sea to the Middle East. He acquired the title ''Poliorcetes'' ("the besieger") after the unsuccessful siege of Rhodes in 305. While Antigonus I and Demetrius planned a revival of the Hellenic League with themselves as dual hegemons, a coalition of the diadochi; Cassander, Seleucus I, Ptolemy I, and Lysimachus defeated the two at the Battle of Ipsus in 301 BC, in which Antigon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Of Macedonia
Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedonia, also called Macedon, was ruled continuously by kings from its inception around the middle of the seventh century BC until its conquest by the Roman Republic in 168 BC. Government of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Kingship in Macedonia, its earliest attested political institution, was hereditary, exclusively male, and characterized by dynastic politics. Information regarding the origins of the Argead dynasty, Argeads, Macedonia's founding dynasty, is very scarce and often contradictory. The Argeads themselves claimed descent from the royal house of Argos, Peloponnese, Argos, the Temenus, Temenids, but this story is viewed with skepticism by some scholars as a fifth century BC fiction invented by the Argead court "to 'prove' Greek lineage". It is more likely that the Argeads first surfaced either as part of a tribe living near Vermio Mountains, Mount Bermion who, possibly under the authority of Perdiccas I of Macedon, Perdiccas, subjugated neigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
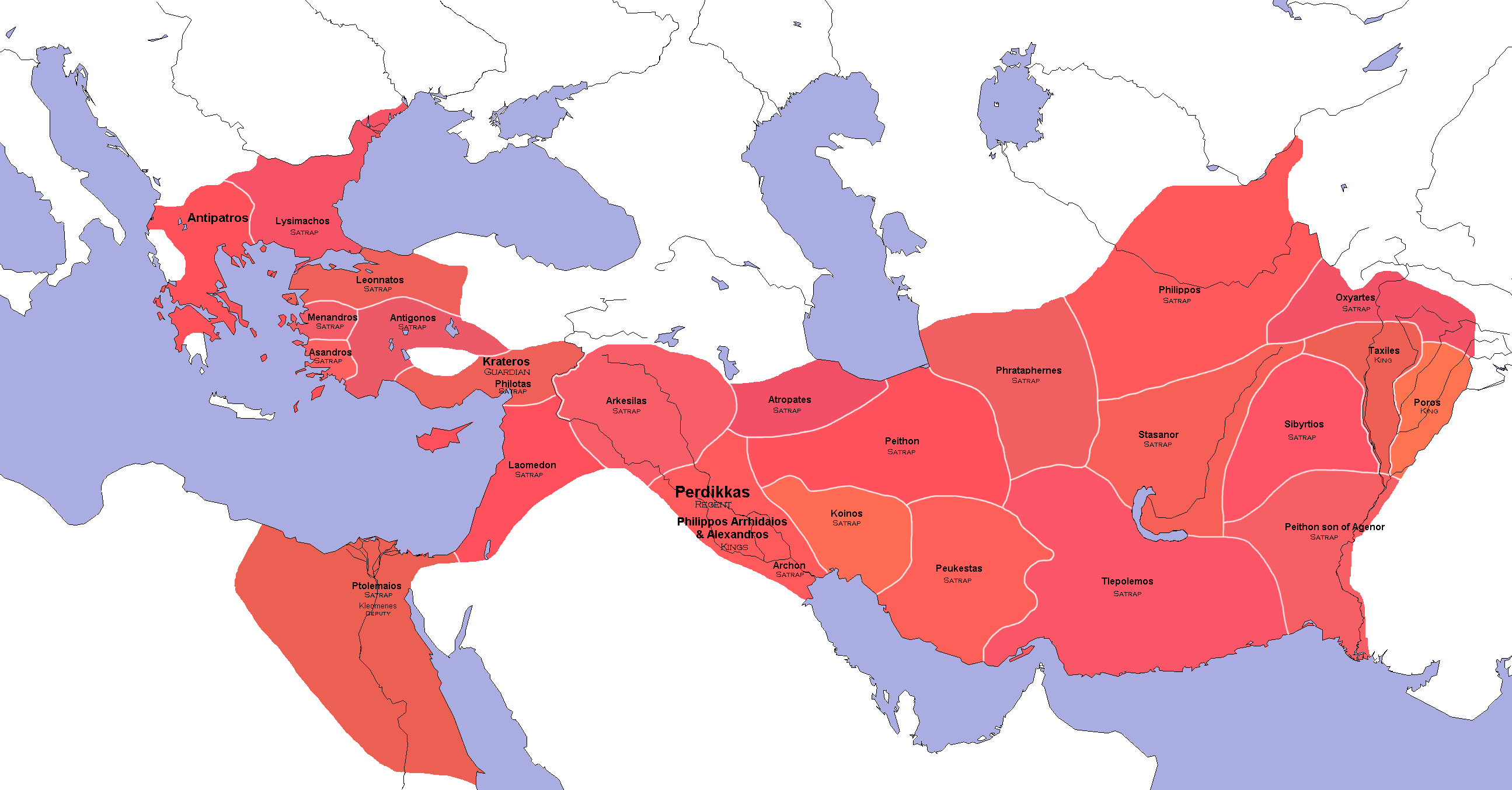
Second War Of The Diadochi
The Second War of the Diadochi was the conflict between the coalition of Polyperchon (as Regent of the Empire), Olympias and Eumenes and the coalition of Cassander, Antigonus, Ptolemy and Lysimachus following the death of Cassander's father, Antipater (the old Regent). Background The unexpected death of Alexander the Great left his vast, and newly created, empire without a clear successor. This lack of a clear arrangement for succession eventually led to war between his top generals, the Diadochi. In a series of shifting alliances they proceeded to carve out kingdoms and independent empires from Alexander's conquests. Following the first conflict, Antipater became the de facto ruler of Alexander's European territories, while Antigonus gained a similar position in Asia, a position Antigonus had to attain through hard campaigning and numerous battles (see: the battles of Orkynia and Cretopolis). In 319 BC, when Antipater died, he left his domain in the hands of his lieutenant, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macedon
Macedonia ( ; , ), also called Macedon ( ), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, which later became the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by the royal Argead dynasty, which was followed by the Antipatrid and Antigonid dynasties. Home to the ancient Macedonians, the earliest kingdom was centered on the northeastern part of the Greek peninsula,. and bordered by Epirus to the southwest, Illyria to the northwest, Paeonia to the north, Thrace to the east and Thessaly to the south. Before the 4th century BC, Macedonia was a small kingdom outside of the area dominated by the great city-states of Athens, Sparta and Thebes, and briefly subordinate to Achaemenid Persia. During the reign of the Argead king PhilipII (359–336 BC), Macedonia subdued mainland Greece and the Thracian Odrysian kingdom through conquest and diplomacy. With a reformed army containing phalanxes wielding the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asia (Roman Province)
Asia () was a Roman province covering most of western Asia Minor (Anatolia), which was created following the Roman Republic's annexation of the Attalid Kingdom in 133 BC. After the establishment of the Roman Empire by Augustus, it was the most prestigious senatorial province and was governed by a proconsul. That arrangement endured until the province was subdivided in the fourth century AD. The province was one of the richest of the Empire and was at peace for most of the Imperial period. It contained hundreds of largely self-governing Greek city-states, who competed fiercely with one another for status, through appeals to the Imperial authorities and the cultivation of prestigious cultural institutions such as festival games, religious cults, and oratory. Geography The province of Asia originally consisted of the territories of Mysia, the Troad, Aeolis, Lydia, Ionia, Caria, and the land corridor through Pisidia to Pamphylia. The Aegean islands, with the exception of Crete, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Macedonians
The Macedonians (, ) were an ancient tribe that lived on the alluvial plain around the rivers Haliacmon and lower Vardar, Axios in the northeastern part of Geography of Greece#Mainland, mainland Greece. Essentially an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek people,; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; . they gradually expanded from their homeland along the Haliacmon valley on the northern edge of the Greek world, absorbing or driving out neighbouring non-Greek tribes, primarily Thracians, Thracian and Illyrians, Illyrian.. They spoke Ancient Macedonian language, Ancient Macedonian, which is usually classified by scholars as a dialect of Northwest Greek, Northwest Doric Greek, and occasionally as a distinct sister language of Greek language, Greek or an Aeolic Greek dialect. However, the Lingua franca, prestige language of the region during the Classical Greece, Classical era was Attic Greek, replaced by Koine Greek during the Hellenistic era. Their religious beliefs mirrored those of Lis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Athens (287 BC)
The siege of Athens lasted through 287 BC when the city was put under siege by King Demetrius I of Macedon. Athens revolted in that year against Demetrius' rule and elected Olympiodorus as strategos. Olympiodorus raised a force among the Athenian citizens, including old men and children, and attacked the Macedonian garrison that had retreated to the fort at the Mouseion Hill which he took with the loss of just 13 of his men.Hammond ; Walbank 1988, p. 230 On receiving news of the revolt Demetrius gathered forces from the cities he still held and put Athens under siege.Hammond ; Walbank 1988, p. 231 The Athenians sent the philosopher Crates to negotiate with Demetrius. In the treaty signed Demetrius received some fortresses in Attica but Athens was freed from a Macedonian garrison. The Athenians resisted, but asked for help from Pyrrhus, king of Epirus. Pyrrhus arrived with his army behind Demetrius, forcing him to retreat. Following the victory, Pyrrhus was welcomed into the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Thebes (292–291 BC)
The siege of Thebes lasted from 292 until 291 BC. The city was put under siege by King Demetrius I of Macedon after it had revolted against Macedonian rule. History In 293, the Boeotians had revolted against Demetrius' rule but the revolt was quickly put down. In 292, the region revolted again, led by the same man, Peisis of Thespiae, whom Demetrius had pardoned the previous year. Demetrius besieged the city, but left for Thrace when he heard the news that Lysimachus had been taken prisoner by the Getae, hoping to rip the spoils from his undefended kingdom. Antigonus commanded the siege in his father's absence. Demetrius returned after Lysimachus was released from captivity. Although he had brought his siege engines, including his famous Helepolis Helepolis (, meaning: "Taker of Cities") is the Greek name for a movable siege tower. The most famous was that invented by Polyidus of Thessaly, and improved by Demetrius I of Macedon and Epimachus of Athens, for the Siege of Rho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Ipsus
The Battle of Ipsus () was fought between some of the Diadochi (the successors of Alexander the Great) in 301 BC near the town of Ipsus in Phrygia. Antigonus I Monophthalmus, the Macedonian ruler of large parts of Asia, and his son Demetrius were pitted against the coalition of three other successors of Alexander: Cassander, ruler of Macedon; Lysimachus, ruler of Thrace; and Seleucus I Nicator, ruler of Babylonia and Persia. Sources Diodorus Siculus is the principal source for the history of the Diadochi, in his 'Library of history' (''Bibliotheca historica''). Diodorus is often derided by modern historians for his style and inaccuracies, but he preserves many details of the ancient period found nowhere else. Diodorus worked primarily by epitomizing the works of other historians, omitting many details where they did not suit his purpose, which was to illustrate moral lessons from history.Buckler, p. ''xiv''. However, since Diodorus provides the only continuous narrative for the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
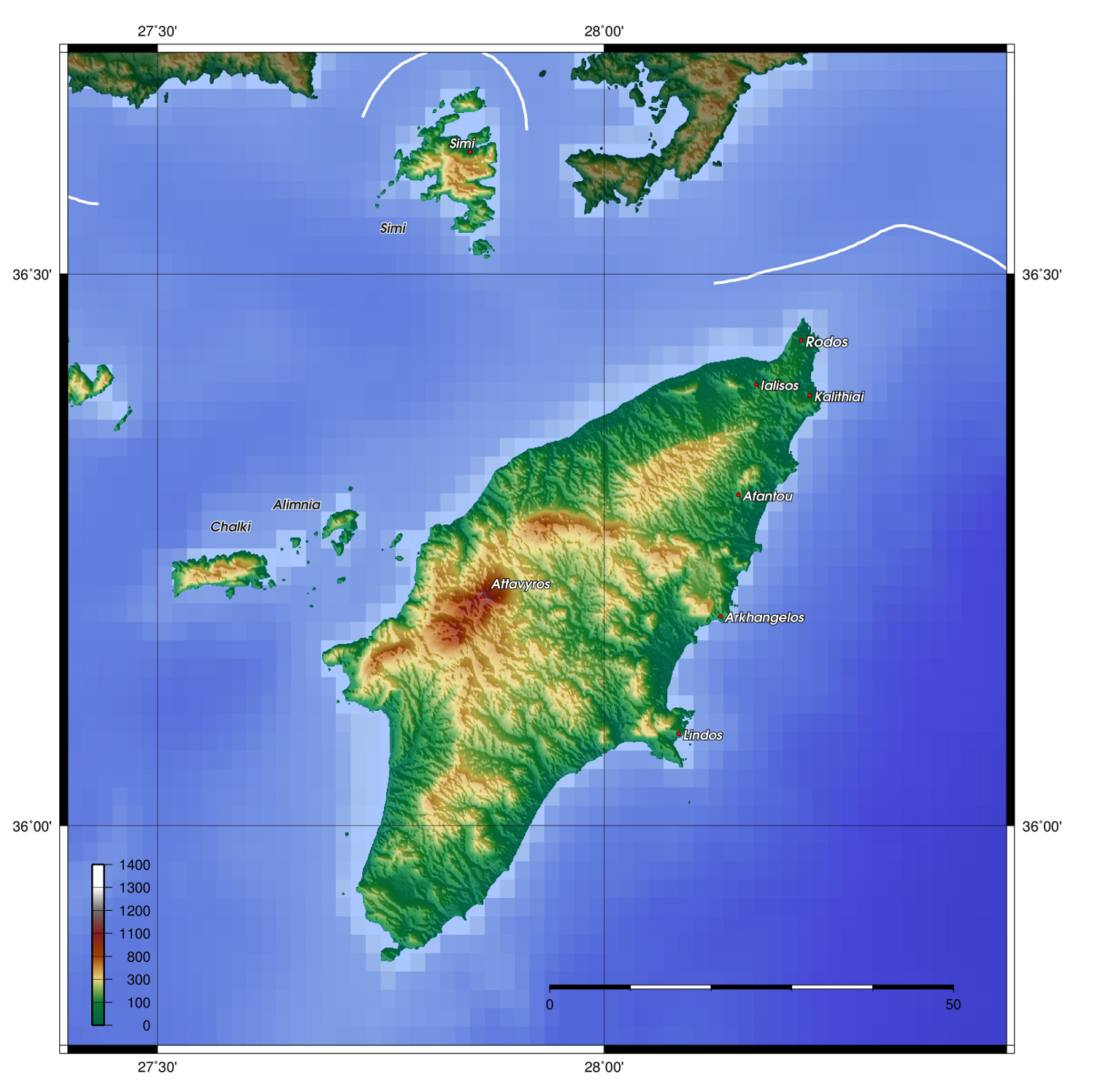
Siege Of Rhodes (305–304 BC)
The siege of Rhodes in 305–304 BC was one of the most notable sieges of antiquity, when Demetrius Poliorcetes, son of Antigonus I, besieged Rhodes in an attempt to make it abandon its neutrality and end its close relationship with Ptolemy I. The attempt ultimately proved unsuccessful, but the scale of the siege, along with the logistical, strategic, and engineering efforts of Demetrius Poliorcetes, cemented his reputation as a military engineer and city conqueror. The significant defense mounted by the Rhodians was also noted by the sources, and thus the siege gradually established itself, within Greek and Roman antiquity, as one of the most notable sieges of their shared past. To celebrate their victory, the Rhodians erected the Colossus of Rhodes, usually considered one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. Background The island of Rhodes was a mercantile republic with a large navy which controlled the entrance to the Aegean Sea. Rhodes maintained treaties of neut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Salamis (306 BC)
The naval Battle of Salamis in 306 BC took place off Salamis, Cyprus between the fleets of Ptolemy I of Egypt and Antigonus I Monophthalmus, two of the Diadochi, the generals who, after the death of Alexander the Great, fought each other for control of his empire. Cyprus had been seized by Ptolemy, and was used as a base for operations against the Antigonid territories in Asia Minor and the Levant. In 306 BC, Antigonus sent his son Demetrius to invade the island, which was defended by Ptolemy's brother Menelaus. After landing on the northeastern part of the island, Demetrius marched to Salamis, defeated Menelaus in a battle, and laid siege to the city. This was the first time where Demetrius demonstrated his flair for siege warfare, which would later earn him the sobriquet Poliorcetes, "the Besieger". Nevertheless, Menelaus was able to hold off Demetrius' attacks until the arrival of reinforcements. Ptolemy led a large-scale rescue expedition in person, hoping to catch Demetri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourth War Of The Diadochi
The Wars of the Diadochi (, romanized: ', ''War of the Crown Princes'') or Wars of Alexander's Successors were a series of conflicts fought between the generals of Alexander the Great, known as the Diadochi, over who would rule his empire following his death. The fighting occurred between 322 and 281 BC. Background Alexander the Great died on June 10, 323 BC, leaving behind an empire that stretched from Macedon and the rest of Greece in Europe to the Indus valley in South Asia. The empire had no clear successor, with the Argead dynasty, Argead family, at this point, consisting of Alexander's mentally disabled half-brother, Philip III of Macedon, Arrhidaeus; his unborn son Alexander IV of Macedon, Alexander IV; his reputed illegitimate son Heracles, son of Alexander, Heracles; his mother Olympias; his sister Cleopatra of Macedon, Cleopatra; and his half-sisters Thessalonike of Macedon, Thessalonike and Cynane. Alexander's death was the catalyst for the disagreements that ensued b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
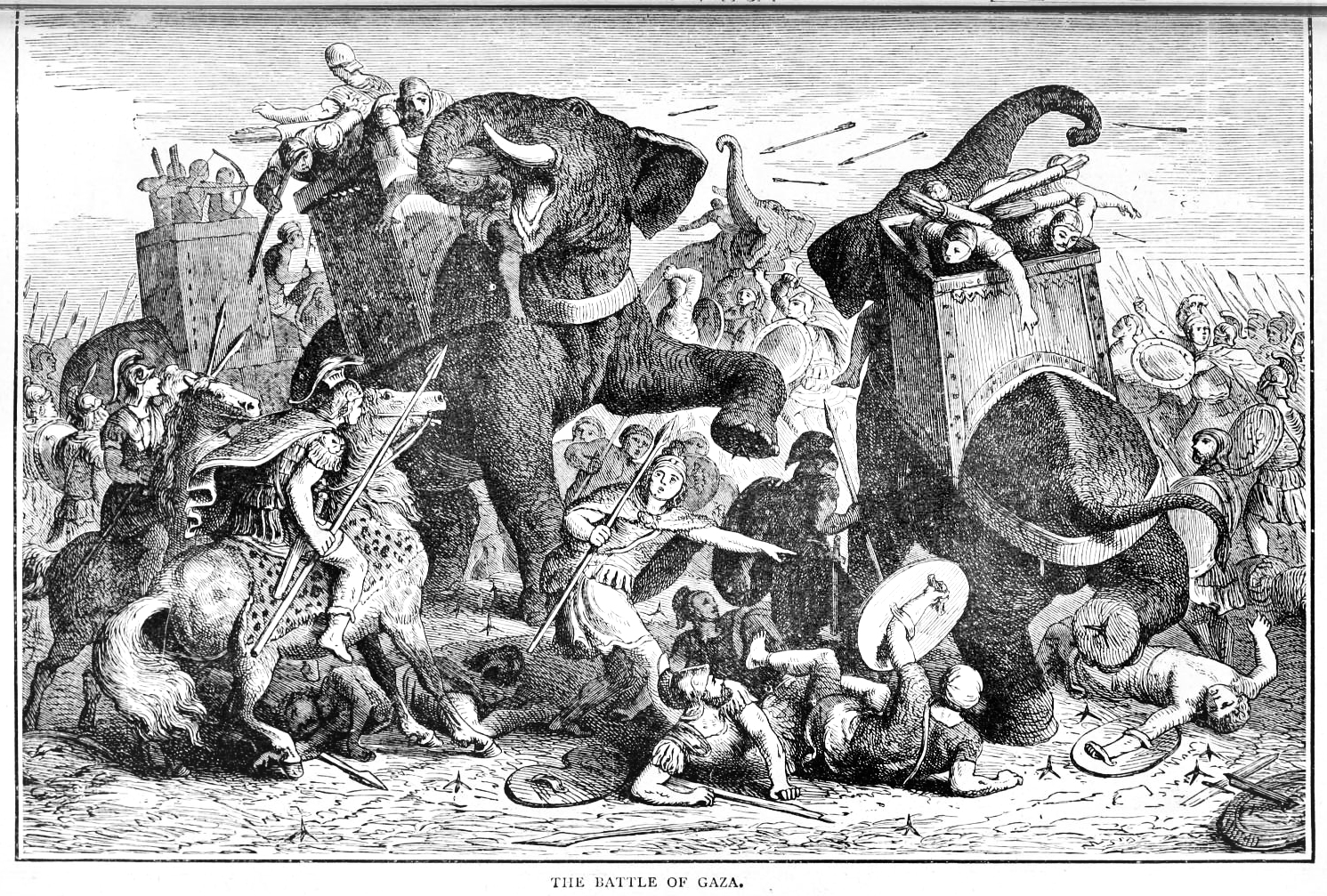
Battle Of Gaza (312 BC)
The Battle of Gaza of 312 BC, was fought between the invading army of Ptolemy I Soter and his ally Seleucus I Nicator and the defending army of Demetrius I of Macedon, son of Antigonus I Monophthalmus. The battle was part of the Wars of the Diadochi, Third War of the Diadochi and was fought near the city of Gaza City, Gaza. In late 312 BC, Ptolemy launched an invasion into the Levant from Ancient Egypt, Egypt, he marched with 18,000 infantry and 4,000 cavalry along the northern edge of the Sinai Peninsula. Receiving timely intelligence, Demetrius recalled his troops from their winter quarters and concentrated them at Gaza. Demetrius' advisors had apparently told him to avoid a military confrontation with Ptolemy and Seleucus, who had more military experience, but he ignored their advice; the conflict ended in a decisive defeat for Demetrius, subsequently enabling the absorption of his controlled territory by Ptolemy and Seleucus. Armies and deployment Troop strength Demetr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |