|
Artaxerxes II
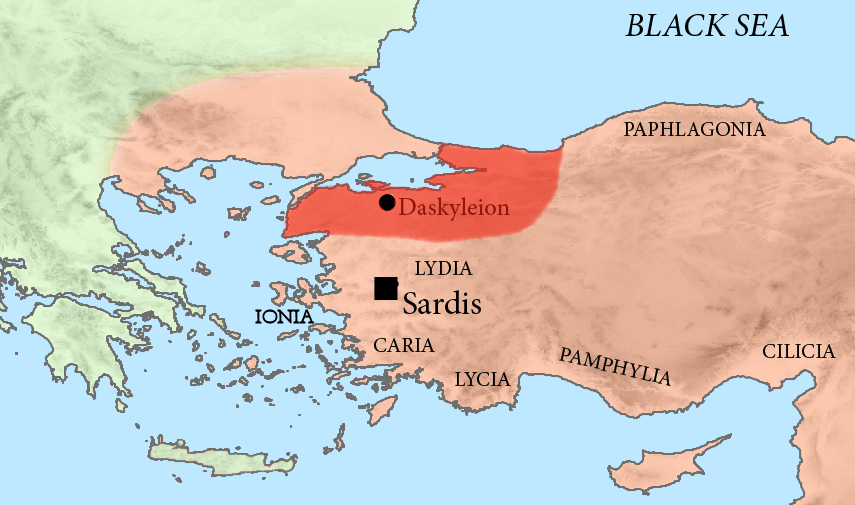
Arses (; 445 – 359/8 BC), known by his regnal name Artaxerxes II ( ; ), was King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire from 405/4 BC to 358 BC. He was the son and successor of Darius II () and his mother was Parysatis. Soon after his accession, Artaxerxes II faced opposition from his younger brother Cyrus the Younger, who assembled an army composed of troops from his Lydian and Ionians, Ionian satrapies as well as Greek mercenaries in his bid for the throne. The forces of the brothers clashed at Battle of Cunaxa, Cunaxa in 401 BC, which resulted in the defeat and death of Cyrus. Following this, Artaxerxes II had to contend with several other revolts; a revolt by Evagoras I () in Cyprus between 391–380 BC, by the Phoenicians in , and most importantly, the revolts by the western satraps (known as the Great Satraps' Revolt) in the 360s and 350s BC, led by distinguished figures such as Datames, Ariobarzanes of Phrygia, Ariobarzanes, and Autophradates. The rulers of the Parthian Empir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock Relief
A rock relief or rock-cut relief is a relief, relief sculpture carved on solid or "living rock" such as a cliff, rather than a detached piece of stone. They are a category of rock art, and sometimes found as part of, or in conjunction with, rock-cut architecture. However, they tend to be omitted in most works on rock art, which concentrate on engravings and paintings by prehistoric peoples. A few such works exploit the natural contours of the rock and use them to define an image, but they do not amount to man-made reliefs. Rock reliefs have been made in many cultures throughout human history, and were especially important in the art of the ancient Near East. Rock reliefs are generally fairly large, as they need to be in order to have an impact in the open air. Most of those discussed here have figures that are over life-size, and in many the figures are multiples of life-size. Stylistically they normally relate to other types of sculpture from the culture and period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evagoras I
Evagoras or Euagoras () was the king of Salamis (411–374 BC) in Cyprus, known especially from the work of Isocrates, who presents him as a model ruler. History He claimed descent from Teucer, the son of Telamon and half-brother of Ajax, and his family had long been rulers of Salamis, although during his childhood, Salamis came under Phoenician control, which resulted in his exile. While in Cilicia, Evagoras gathered the support of 50 followers and returned secretly in 410 BC, to gain possession of the throne. Expecting an eventual Persian response to recapture Cyprus, he cultivated the friendship of the Athenians, and after Conon's defeat at the Battle of Aegospotami he provided him with a refuge. For a time, he also maintained friendly relations with the Achaemenid Empire, and secured the aid of Artaxerxes II for Athens against Lacedaemon. He took part in the Battle of Cnidus of 394 BC which he provided most of the resources for and in which the Lacedaemonian fleet was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plutarch
Plutarch (; , ''Ploútarchos'', ; – 120s) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo (Delphi), Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''Parallel Lives'', a series of biographies of illustrious Greeks and Romans, and ''Moralia'', a collection of essays and speeches. Upon becoming a Roman citizen, he was possibly named Lucius Mestrius Plutarchus (). Family Plutarch was born to a prominent family in the small town of Chaeronea, about east of Delphi, in the Greek region of Boeotia. His family was long established in the town; his father was named Autobulus and his grandfather was named Lamprias. His brothers, Timon and Lamprias, are frequently mentioned in his essays and dialogues, which speak of Timon in particular in the most affectionate terms. Studies and life Plutarch studied mathematics and philosophy in Athens under Ammonius of Athens, Ammonius from AD 66 to 67. He attended th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Persian
Old Persian is one of two directly attested Old Iranian languages (the other being Avestan) and is the ancestor of Middle Persian (the language of the Sasanian Empire). Like other Old Iranian languages, it was known to its native speakers as (Iranian).''cf.'' , p. 2. Old Persian is close to both Avestan and Vedic Sanskrit, and all three languages are highly inflected. Old Persian appears primarily in the inscriptions, clay tablets and seals of the Achaemenid era ( to 300 BCE). Examples of Old Persian have been found in what is now Iran, Romania ( Gherla), Armenia, Bahrain, Iraq, Turkey and Egypt, with the most important attestation by far being the contents of the Behistun Inscription (dated to 522 BCE). In 2007, research into the vast Persepolis Administrative Archives at the Oriental Institute at the University of Chicago unearthed Old Persian tablets, which suggest Old Persian was a written language in use for practical recording and not only for royal display. Orig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akkadian Language
Akkadian ( ; )John Huehnergard & Christopher Woods, "Akkadian and Eblaite", ''The Cambridge Encyclopedia of the World's Ancient Languages''. Ed. Roger D. Woodard (2004, Cambridge) Pages 218–280 was an East Semitic language that is attested in ancient Mesopotamia ( Akkad, Assyria, Isin, Larsa, Babylonia and perhaps Dilmun) from the mid- third millennium BC until its gradual replacement in common use by Old Aramaic among Assyrians and Babylonians from the 8th century BC. Akkadian, which is the earliest documented Semitic language, is named after the city of Akkad, a major centre of Mesopotamian civilization during the Akkadian Empire (–2154 BC). It was written using the cuneiform script, originally used for Sumerian, but also used to write multiple languages in the region including Eblaite, Hurrian, Elamite, Old Persian and Hittite. The influence of Sumerian on Akkadian went beyond just the cuneiform script; owing to their close proximity, a lengthy span of con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek (, ; , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language, constituting an independent Hellenic languages, Hellenic branch within the Indo-European language family. It is native to Greece, Cyprus, Italy (in Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, Caucasus, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the list of languages by first written accounts, longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting importance in the European canon. Greek is also the language in which many of the foundational texts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progenitor
In genealogy, a progenitor (rarer: primogenitor; or ''Ahnherr'') is the founder (sometimes one that is legendary) of a family, line of descent, gens, clan, tribe, noble house, or ethnic group.. Ebenda''Ahnherr:''"Stammvater eines Geschlechts". Genealogy (commonly known as family history) understands a progenitor to be the earliest recorded ancestor of a consanguineous family group of descendants. Progenitors are sometimes used to describe the status of a genealogical research project, or in order to compare the availability of genealogical data in different times and places. Often, progenitors are implied to be patrilineal. If a patrilineal dynasty is considered, each such dynasty has exactly one progenitor. Aristocratic and dynastic families often look back to an ancestor who is seen as the founder and progenitor of their house (i.e. family line). Even the old Roman legal concept of agnates (Latin for "descendants") was based on the idea of the unbroken family lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parthian Empire
The Parthian Empire (), also known as the Arsacid Empire (), was a major Iranian political and cultural power centered in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe in conquering the region of Parthia in Iran's northeast, then a satrapy (province) under Andragoras, who was rebelling against the Seleucid Empire. Mithridates I ( BC) greatly expanded the empire by seizing Media and Mesopotamia from the Seleucids. At its height, the Parthian Empire stretched from the northern reaches of the Euphrates, in what is now central-eastern Turkey, to present-day Afghanistan and western Pakistan. The empire, located on the Silk Road trade route between the Roman Empire in the Mediterranean Basin and the Han dynasty of China, became a center of trade and commerce. The Parthians largely adopted the art, architecture, religious beliefs, and regalia of their culturally heterogeneous empire, which encompassed Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autophradates
Autophradates (; , lived 4th century BC) was a Persian people, Persian Satrap of Lydia, who also distinguished himself as a general in the reign of Artaxerxes III of Persia, Artaxerxes III and Darius III of Persia, Darius III. Rule as a satrap of Lydia During the reign of the Artaxerxes II of Persia, Artaxerxes II, Autophradates captured Artabazos II of Phrygia, Artabazus, the satrap of Lydia and Ionia who had revolted against the Persian king, and made him his prisoner, but afterwards was forced to set him free. Autophradates was also directed by Artaxerxes to put down the rebellion of the satrap of Cappadocia (satrapy), Cappadocia Datames. He went with a large army, but was obliged to retreat with heavy loss. Autophradates later joined the Revolt of the Satraps. Resistance to Alexander the Great Autophradates participated to the Achaemenid resistance against the campaigns of Alexander the Great in Asia Minor. Together with Pharnabazus III he supported militarily and financia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ariobarzanes Of Phrygia
Ariobarzanes (; ; death: crucified in c. 362 BCE), sometimes known as Ariobarzanes I of Cius, was a Persian Satrap of Phrygia and military commander, leader of an independence revolt, and the first known of the line of rulers of the Greek town of Cius who eventually were to stem the kings of Pontus in the 3rd century BCE. Ariobarzanes was apparently a cadet member of the Achaemenid dynasty, possibly son of Pharnabazus II, and part of the Pharnacid dynasty which had settled to hold Dascylium of Hellespont in the 470s BCE. Cius is located near Dascylium, and Cius seemingly was a share of family holdings for the branch of Ariobarzanes. Ariobarzanes' one predecessor was a (kinsman) named Mithradates (possibly Mithradates, Satrap of Cappadocia). The archaeologist Walther Judeich claims that Ariobarzanes was that Mithradates' son, but Brian C. McGing refutes that specific filiation. Seemingly, no classical source itself calls them son and father, the filiation being a later reconstr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Datames
Datames (Old Persian: ''Dātama'' or ''Dātāma'', Aramaic: ''Tadanmu'', ; 407 BC – 362 BC), also known as Tarkamuwa, was an Iranian military leader, who served as the governor (satrap) of the Achaemenid satrapy of Cappadocia (or Cilicia; the evidence is contradictory) from the 380s BC to 362 BC. A Carian by birth, he was the son of Camissares by a Paphlagonian mother. His father being satrap of Cilicia under Artaxerxes II, and high in the favour of that monarch, Datames became one of the king's bodyguards; and having in this capacity distinguished himself in the war against the Cadusii, was appointed to succeed his father (who had fallen in that war) in the government of his province. Here he distinguished himself both by his military abilities and his zeal in the service of the king; and reduced to subjection two officials who had revolted from Artaxerxes, Thyus, governor of Paphlagonia, and Aspis of Cataonia. Name "Datames" is the Hellenized form of the Old Iranian ''* ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |