Mica group on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
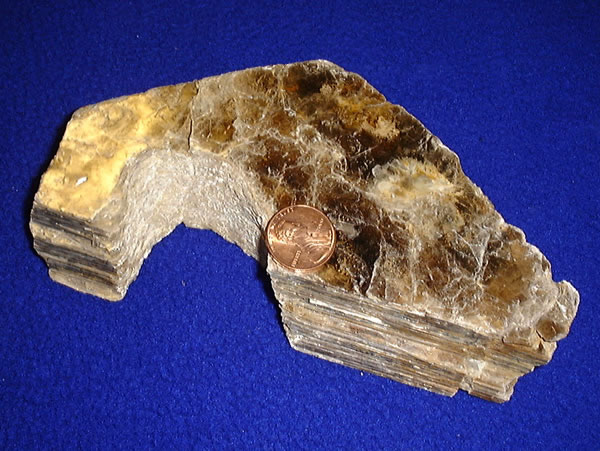 Micas ( ) are a group of
Micas ( ) are a group of
File:Mica T.png, View of tetrahedral sheet structure of mica. The apical oxygen ions are tinted pink.
File:Mica tO.png, View of trioctahedral sheet structure of mica. The binding sites for apical oxygen are shown as white spheres.
File:Mica tOs.png, View of trioctahedral sheet structure of mica emphasizing octahedral sites
File:Mica dO.png, View of dioctahedral sheet structure of mica. The binding sites for apical oxygen are shown as white spheres.
File:Mica dOs.png, View of dioctahedral sheet structure of mica emphasizing octahedral sites
File:Mica tri.png, View of trioctahedral mica structure looking at surface of a single layer
File:Mica tri side.png, View of trioctahedral mica structure looking along sheets


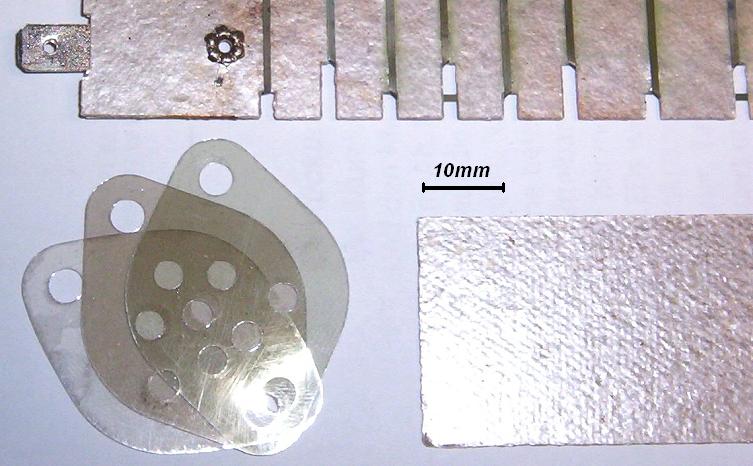
 Muscovite and phlogopite splittings can be fabricated into various built-up mica products, also known as ''micanite''. Produced by mechanized or hand setting of overlapping splittings and alternate layers of binders and splittings, built-up mica is used primarily as an electrical insulation material. Mica insulation is used in high-temperature and fire-resistant power cables in aluminium plants,
Muscovite and phlogopite splittings can be fabricated into various built-up mica products, also known as ''micanite''. Produced by mechanized or hand setting of overlapping splittings and alternate layers of binders and splittings, built-up mica is used primarily as an electrical insulation material. Mica insulation is used in high-temperature and fire-resistant power cables in aluminium plants,
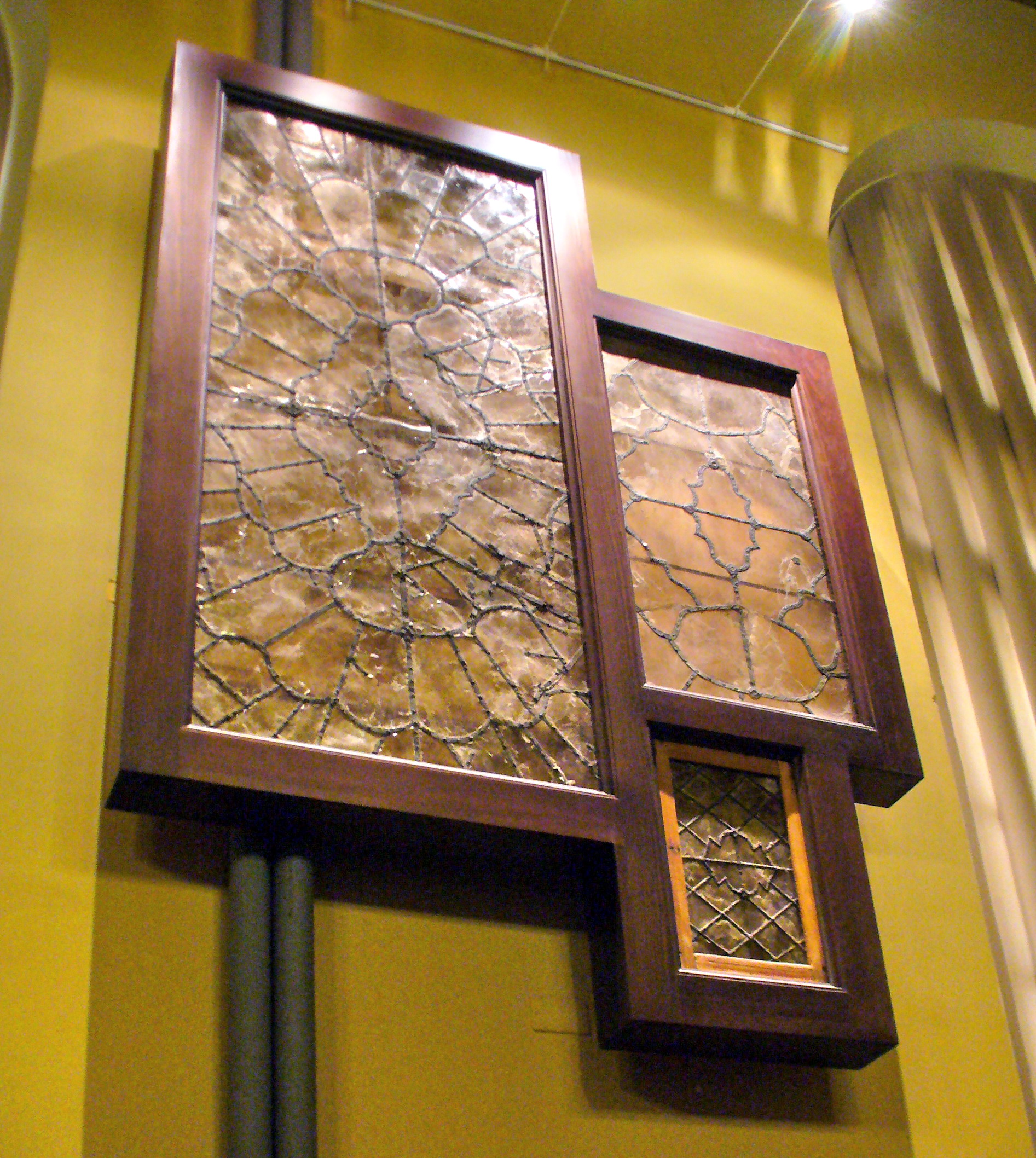 Sheet mica is a versatile and durable material widely used in electrical and thermal insulation applications. It exhibits excellent electrical properties, heat resistance, and chemical stability.
Technical grade sheet mica is used in electrical components, electronics, atomic force microscopy and as window sheets. Other uses include diaphragms for oxygen-breathing equipment, marker dials for navigation compasses,
Sheet mica is a versatile and durable material widely used in electrical and thermal insulation applications. It exhibits excellent electrical properties, heat resistance, and chemical stability.
Technical grade sheet mica is used in electrical components, electronics, atomic force microscopy and as window sheets. Other uses include diaphragms for oxygen-breathing equipment, marker dials for navigation compasses,
 Sheet mica is used principally in the electronic and electrical industries. Its usefulness in these applications is derived from its unique electrical and thermal properties and its mechanical properties, which allow it to be cut, punched, stamped, and machined to close tolerances. Specifically, mica is unusual in that it is a good electrical insulator at the same time as being a good thermal conductor. The leading use of block mica is as an electrical insulator in electronic equipment. High-quality block mica is processed to line the gauge glasses of high-pressure steam boilers because of its flexibility, transparency, and resistance to heat and chemical attack. Only high-quality muscovite film mica, which is variously called India ruby mica or ruby muscovite mica, is used as a dielectric in
Sheet mica is used principally in the electronic and electrical industries. Its usefulness in these applications is derived from its unique electrical and thermal properties and its mechanical properties, which allow it to be cut, punched, stamped, and machined to close tolerances. Specifically, mica is unusual in that it is a good electrical insulator at the same time as being a good thermal conductor. The leading use of block mica is as an electrical insulator in electronic equipment. High-quality block mica is processed to line the gauge glasses of high-pressure steam boilers because of its flexibility, transparency, and resistance to heat and chemical attack. Only high-quality muscovite film mica, which is variously called India ruby mica or ruby muscovite mica, is used as a dielectric in
mica
' is derived from the
 Human use of mica dates back to
Human use of mica dates back to
Mineral Galleries data
* *
Mica
, 22-Oct-1881, pp. 257 {{Authority control Phyllosilicates Dielectrics Articles containing video clips Industrial minerals
 Micas ( ) are a group of
Micas ( ) are a group of silicate
A silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is also used ...
mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid substance with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): Mi ...
s whose outstanding physical characteristic is that individual mica crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macros ...
s can easily be split into fragile elastic plates. This characteristic is described as ''perfect basal cleavage''. Mica is common in igneous
Igneous rock ( ), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava.
The magma can be derived from partial ...
and metamorphic rock
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock ( protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, caus ...
and is occasionally found as small flakes in sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock (geology), rock formed by the cementation (geology), cementation of sediments—i.e. particles made of minerals (geological detritus) or organic matter (biological detritus)—that have been accumulated or de ...
. It is particularly prominent in many granite
Granite ( ) is a coarse-grained (phanerite, phaneritic) intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly coo ...
s, pegmatite
A pegmatite is an igneous rock showing a very coarse texture, with large interlocking crystals usually greater in size than and sometimes greater than . Most pegmatites are composed of quartz, feldspar, and mica, having a similar silicic c ...
s, and schist
Schist ( ) is a medium-grained metamorphic rock generally derived from fine-grained sedimentary rock, like shale. It shows pronounced ''schistosity'' (named for the rock). This means that the rock is composed of mineral grains easily seen with a l ...
s, and "books" (large individual crystals) of mica several feet across have been found in some pegmatites.
Micas are used in products such as drywall
Drywall (also called plasterboard, dry lining, wallboard, sheet rock, gib board, gypsum board, buster board, turtles board, slap board, custard board, gypsum panel and gyprock) is a panel made of calcium sulfate dihydrate (gypsum), with or with ...
s, paint
Paint is a material or mixture that, when applied to a solid material and allowed to dry, adds a film-like layer. As art, this is used to create an image or images known as a painting. Paint can be made in many colors and types. Most paints are ...
s, and fillers, especially in parts for automobiles, roofing, and in electronics. The mineral is used in cosmetics and food to add "shimmer" or "frost".
Properties and structure
The mica group comprises 37 phyllosilicate minerals. All crystallize in themonoclinic
In crystallography, the monoclinic crystal system is one of the seven crystal systems. A crystal system is described by three Vector (geometric), vectors. In the monoclinic system, the crystal is described by vectors of unequal lengths, as in t ...
system, with a tendency towards pseudohexagonal crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macros ...
s, and are similar in structure but vary in chemical composition. Micas are translucent to opaque with a distinct vitreous or pearly luster, and different mica minerals display colors ranging from white to green or red to black. Deposits of mica tend to have a flaky or platy appearance.
The crystal structure of mica is described as ''TOT-c'', meaning that it is composed of parallel ''TOT'' layers weakly bonded to each other by cation
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
s (''c''). The ''TOT'' layers in turn consist of two tetrahedral sheets (''T'') strongly bonded to the two faces of a single octahedral sheet (''O''). The relatively weak ionic bonding between ''TOT'' layers gives mica its perfect basal cleavage.
The tetrahedral sheets consist of silica tetrahedra, each silicon ion surrounded by four oxygen ions. In most micas, one in four silicon ions is replaced by an aluminium ion, while aluminium ions replace half the silicon ions in brittle micas. The tetrahedra share three of their four oxygen ions with neighbouring tetrahedra to produce a hexagonal sheet. The remaining oxygen ion (the ''apical'' oxygen ion) is available to bond with the octahedral sheet.
The octahedral sheet can be dioctahedral or trioctahedral. A trioctahedral sheet has the structure of a sheet of the mineral brucite
Brucite is the mineral form of magnesium hydroxide, with the chemical formula Magnesium, Mg(hydroxyl, OH)2. It is a common alteration product of periclase in marble; a low-temperature hydrothermal Vein (geology), vein mineral in metamorphosed li ...
, with magnesium or ferrous iron being the most common cation. A dioctahedral sheet has the structure and (typically) the composition of a gibbsite sheet, with aluminium being the cation. Apical oxygens take the place of some of the hydroxyl ions that would be present in a brucite or gibbsite sheet, bonding the tetrahedral sheets tightly to the octahedral sheet.
Tetrahedral sheets have a strong negative charge since their bulk composition is . The octahedral sheet has a positive charge, since its bulk composition is (for a dioctahedral sheet with the apical sites vacant) or (for a trioctahedral site with the apical sites vacant; M represents a divalent ion such as ferrous iron or magnesium) The combined TOT layer has a residual negative charge, since its bulk composition is or . The remaining negative charge of the TOT layer is neutralized by the interlayer cations (typically sodium, potassium, or calcium ions).
Because the hexagons in the T and O sheets are slightly different in size, the sheets are slightly distorted when they bond into a TOT layer. This breaks the hexagonal symmetry and reduces it to monoclinic symmetry. However, the original hexahedral symmetry is discernible in the pseudohexagonal character of mica crystals. The short-range order of K+ ions on cleaved muscovite mica has been resolved.
Classification
Chemically, micas can be given the general formula :''X''2''Y''4–6''Z''8 O20( OH, F)4, in which :''X'' is K, Na, or Ca or less commonly Ba, Rb, or Cs; :''Y'' is Al, Mg, or Fe or less commonly Mn, Cr, Ti, Li, etc.; :''Z'' is chiefly Si or Al, but also may include Fe3+ or Ti. Structurally, micas can be classed as dioctahedral (''Y'' = 4) and trioctahedral (''Y'' = 6). If the ''X'' ion is K or Na, the mica is a ''common'' mica, whereas if the ''X'' ion is Ca, the mica is classed as a ''brittle'' mica.Dioctahedral micas
*Muscovite
Muscovite (also known as common mica, isinglass, or potash mica) is a hydrated phyllosilicate mineral of aluminium and potassium with formula KAl2(Al Si3 O10)( F,O H)2, or ( KF)2( Al2O3)3( SiO2)6( H2O). It has a highly perfect basal cleavage y ...
* Paragonite
Brittle micas:
* Margarite
Trioctahedral micas
Common micas: *Biotite
Biotite is a common group of phyllosilicate minerals within the mica group, with the approximate chemical formula . It is primarily a solid-solution series between the iron- endmember annite, and the magnesium-endmember phlogopite; more al ...
* Lepidolite
* Phlogopite
Phlogopite is a yellow, greenish, or reddish-brown member of the mica family of phyllosilicates. It is also known as magnesium mica.
Phlogopite is the magnesium endmember of the biotite solid solution series, with the chemical formula KMg3AlSi3 ...
* Zinnwaldite
Brittle micas:
* Clintonite
Interlayer-deficient micas
Very fine-grained micas, which typically show more variation in ion and water content, are informally termed "clay micas". They include: * Hydro-muscovite with H3O+ along with K in the ''X'' site; *Illite
Illite, also called hydromica or hydromuscovite, is a group of closely related non-expanding clay minerals. Illite is a secondary mineral precipitate, and an example of a phyllosilicate, or layered alumino-silicate. Its structure is a 2:1 sandw ...
with a K deficiency in the ''X'' site and correspondingly more Si in the ''Z'' site;
* Phengite with Mg or Fe2+ substituting for Al in the ''Y'' site and a corresponding increase in Si in the ''Z'' site.
Sericite
Sericite is the name given to very fine, ragged grains and Aggregate (geology), aggregates of white (colourless) micas, typically made of muscovite, illite, or paragonite. Sericite is produced by the alteration of orthoclase or plagioclase feldsp ...
is the name given to very fine, ragged grains and aggregates of white (colorless) micas.
Occurrence and production
Mica is widely distributed and occurs inigneous
Igneous rock ( ), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava.
The magma can be derived from partial ...
, metamorphic
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock (protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, causi ...
and sedimentary
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock formed by the cementation of sediments—i.e. particles made of minerals (geological detritus) or organic matter (biological detritus)—that have been accumulated or deposited at Earth's surface. Sedime ...
regimes. Large crystals of mica used for various applications are typically mined from granitic
A granitoid is a broad term referring to a diverse group of coarse-grained igneous rocks that are widely distributed across the globe, covering a significant portion of the Earth's exposed surface and constituting a large part of the continental ...
pegmatite
A pegmatite is an igneous rock showing a very coarse texture, with large interlocking crystals usually greater in size than and sometimes greater than . Most pegmatites are composed of quartz, feldspar, and mica, having a similar silicic c ...
s.
The largest documented single crystal of mica (phlogopite
Phlogopite is a yellow, greenish, or reddish-brown member of the mica family of phyllosilicates. It is also known as magnesium mica.
Phlogopite is the magnesium endmember of the biotite solid solution series, with the chemical formula KMg3AlSi3 ...
) was found in Lacey Mine, Ontario
Ontario is the southernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Located in Central Canada, Ontario is the Population of Canada by province and territory, country's most populous province. As of the 2021 Canadian census, it ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
; it measured and weighed about . Similar-sized crystals were also found in Karelia
Karelia (; Karelian language, Karelian and ; , historically Коре́ла, ''Korela'' []; ) is an area in Northern Europe of historical significance for Russia (including the Soviet Union, Soviet era), Finland, and Sweden. It is currentl ...
, Russia.
Scrap and flake mica is produced all over the world. In 2010, the major producers were Russia (100,000 tonnes), Finland (68,000 t), the United States (53,000 t), South Korea (50,000 t), France (20,000 t) and Canada (15,000 t). The total global production was 350,000 t, although no reliable data were available for China. Most sheet mica was produced in India (3,500 t) and Russia (1,500 t). Flake mica comes from several sources: the metamorphic rock called schist
Schist ( ) is a medium-grained metamorphic rock generally derived from fine-grained sedimentary rock, like shale. It shows pronounced ''schistosity'' (named for the rock). This means that the rock is composed of mineral grains easily seen with a l ...
as a byproduct of processing feldspar and kaolin resources, from placer deposits, and pegmatites. Sheet mica is considerably less abundant than flake and scrap mica, and is occasionally recovered from mining scrap and flake mica. The most important sources of sheet mica are pegmatite deposits. Sheet mica prices vary with grade and can range from less than $1 per kilogram for low-quality mica to more than $2,000 per kilogram for the highest quality.
In Madagascar and India, it is also mined artisanally, in poor working conditions and with the help of child labour
Child labour is the exploitation of children through any form of work that interferes with their ability to attend regular school, or is mentally, physically, socially and morally harmful. Such exploitation is prohibited by legislation w ...
.
Uses
The commercially important micas aremuscovite
Muscovite (also known as common mica, isinglass, or potash mica) is a hydrated phyllosilicate mineral of aluminium and potassium with formula KAl2(Al Si3 O10)( F,O H)2, or ( KF)2( Al2O3)3( SiO2)6( H2O). It has a highly perfect basal cleavage y ...
and phlogopite
Phlogopite is a yellow, greenish, or reddish-brown member of the mica family of phyllosilicates. It is also known as magnesium mica.
Phlogopite is the magnesium endmember of the biotite solid solution series, with the chemical formula KMg3AlSi3 ...
, which are used in a variety of applications.
Useful properties
Mica's value is based on its unique physical properties: the crystalline structure of mica forms layers that can be split or delaminated into thin sheets usually causingfoliation
In mathematics (differential geometry), a foliation is an equivalence relation on an topological manifold, ''n''-manifold, the equivalence classes being connected, injective function, injectively immersed submanifolds, all of the same dimension ...
in rocks. These sheets are chemically inert, dielectric
In electromagnetism, a dielectric (or dielectric medium) is an Insulator (electricity), electrical insulator that can be Polarisability, polarised by an applied electric field. When a dielectric material is placed in an electric field, electric ...
, elastic, flexible, hydrophilic, insulating, lightweight, platy, reflective, refractive, resilient, and range in opacity from transparent to opaque. Mica is stable when exposed to electricity, light, moisture, and extreme temperatures. It has superior electrical properties as an insulator and as a dielectric, and can support an electrostatic field while dissipating minimal energy in the form of heat; it can be split very thin (0.025 to 0.125 millimeters or thinner) while maintaining its electrical properties, has a high dielectric breakdown, is thermally stable to , and is resistant to corona discharge
A corona discharge is an electrical discharge caused by the ionization of a fluid such as air surrounding a conductor (material), conductor carrying a high voltage. It represents a local region where the air (or other fluid) has undergone ...
. Muscovite, the principal mica used by the electrical industry, is used in capacitors that are ideal for high frequency and radio frequency. Phlogopite mica remains stable at higher temperatures (to ) and is used in applications in which a combination of high-heat stability and electrical properties is required. Muscovite and phlogopite are used in sheet and ground forms.
Ground mica
The leading use of dry-ground mica in the US is in the joint compound for filling and finishing seams and blemishes ingypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate Hydrate, dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, drywall and blackboard or sidewalk ...
wallboard (drywall
Drywall (also called plasterboard, dry lining, wallboard, sheet rock, gib board, gypsum board, buster board, turtles board, slap board, custard board, gypsum panel and gyprock) is a panel made of calcium sulfate dihydrate (gypsum), with or with ...
). The mica acts as a filler and extender, provides a smooth consistency, improves the workability of the compound, and provides resistance to cracking. In 2008, joint compounds accounted for 54% of dry-ground mica consumption. In the paint industry, ground mica is used as a pigment
A pigment is a powder used to add or alter color or change visual appearance. Pigments are completely or nearly solubility, insoluble and reactivity (chemistry), chemically unreactive in water or another medium; in contrast, dyes are colored sub ...
extender that also facilitates suspension, reduces chalking, prevents shrinking and shearing of the paint film, increases the resistance of the paint film to water penetration and weathering and brightens the tone of colored pigments. Mica also promotes paint adhesion in aqueous and oleoresinous formulations. Consumption of dry-ground mica in paint, the second-ranked use, accounted for 22% of the dry-ground mica used in 2008.
Ground mica is used in the well-drilling industry as an additive to drilling fluid
In geotechnical engineering, drilling fluid, also known as drilling mud, is used to aid the drilling of boreholes into the earth. Used while drilling oil and natural gas wells and on exploration drilling rigs, drilling fluids are also use ...
s. The coarsely ground mica flakes help prevent the loss of circulation by sealing porous sections of the drill hole. Well-drilling muds accounted for 15% of dry-ground mica use in 2008. The plastics industry
The plastics industry manufactures polymer materials—commonly called plastics—and offers services in plastics important to a range of industries, including packaging, building and construction, electronics, aerospace, manufacturing and transpo ...
used dry-ground mica as an extender and filler, especially in parts for automobiles as lightweight insulation to suppress sound and vibration. Mica is used in plastic automobiles fascia
A fascia (; : fasciae or fascias; adjective fascial; ) is a generic term for macroscopic membranous bodily structures. Fasciae are classified as superficial, visceral or deep, and further designated according to their anatomical location.
...
and fenders as a reinforcing material, providing improved mechanical properties and increased dimensional stability, stiffness, and strength. Mica-reinforced plastics also have high-heat dimensional stability, reduced warpage, and the best surface properties of any filled plastic composite. In 2008, consumption of dry-ground mica in plastic applications accounted for 2% of the market. The rubber industry used ground mica as an inert filler and mold release compound in the manufacture of molded rubber products such as tires and roofing. The platy texture acts as an anti-blocking, anti-sticking agent. Rubber mold lubricant accounted for 1.5% of the dry-ground mica used in 2008. As a rubber additive, mica reduces gas permeation and improves resiliency.
Dry-ground mica is used in the production of rolled roofing and asphalt
Asphalt most often refers to:
* Bitumen, also known as "liquid asphalt cement" or simply "asphalt", a viscous form of petroleum mainly used as a binder in asphalt concrete
* Asphalt concrete, a mixture of bitumen with coarse and fine aggregates, u ...
shingles
Shingles, also known as herpes zoster or zona, is a viral disease characterized by a painful skin rash with blisters in a localized area. Typically the rash occurs in a single, wide mark either on the left or right side of the body or face. T ...
, where it serves as a surface coating to prevent sticking of adjacent surfaces. The coating is not absorbed by freshly manufactured roofing because mica's platy structure is unaffected by the acid in asphalt or by weather conditions. Mica is used in decorative coatings on wallpaper, concrete, stucco
Stucco or render is a construction material made of aggregates, a binder, and water. Stucco is applied wet and hardens to a very dense solid. It is used as a decorative coating for walls and ceilings, exterior walls, and as a sculptural and ...
, and tile surfaces. It also is used as an ingredient in flux coatings on welding rods, in some special greases, and as coatings for core and mold release compounds, facing agents, and mold washes in foundry applications. Dry-ground phlogopite mica is used in automotive brake linings and clutch plates to reduce noise and vibration (asbestos
Asbestos ( ) is a group of naturally occurring, Toxicity, toxic, carcinogenic and fibrous silicate minerals. There are six types, all of which are composed of long and thin fibrous Crystal habit, crystals, each fibre (particulate with length su ...
substitute); as sound-absorbing insulation for coatings and polymer
A polymer () is a chemical substance, substance or material that consists of very large molecules, or macromolecules, that are constituted by many repeat unit, repeating subunits derived from one or more species of monomers. Due to their br ...
systems; in reinforcing additives for polymers to increase strength and stiffness and to improve stability to heat, chemicals, and ultraviolet (UV) radiation; in heat shields and temperature insulation; in industrial coating additive to decrease the permeability of moisture and hydrocarbons; and in polar polymer formulations to increase the strength of epoxies, nylons, and polyester
Polyester is a category of polymers that contain one or two ester linkages in every repeat unit of their main chain. As a specific material, it most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyesters include some natura ...
s.

Paints and cosmetics
Wet-ground mica, which retains the brilliance of its cleavage faces, is used primarily in pearlescent paints by the automotive industry. Many metallic-looking pigments are composed of a substrate of mica coated with another mineral, usuallytitanium dioxide
Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium(IV) oxide or titania , is the inorganic compound derived from titanium with the chemical formula . When used as a pigment, it is called titanium white, Pigment White 6 (PW6), or Colour Index Internationa ...
(TiO2). The resultant pigment produces a reflective color depending on the thickness of the coating. These products are used to produce automobile paint, shimmery plastic containers, and high-quality inks used in advertising and security applications. In the cosmetics industry, its reflective and refractive properties make mica an important ingredient in blushes, eye liner
An eye is a sensory organ that allows an organism to perceive visual perception, visual information. It detects light and converts it into electro-chemical impulses in neurons (neurones). It is part of an organism's visual system.
In higher ...
, eye shadow, foundation, hair and body glitter, lipstick
Lipstick is a cosmetics, cosmetic product used to apply coloration and texture to lips, often made of wax and oil. Different pigments are used to produce color, and minerals such as silica may be used to provide texture. The use of lipstick ...
, lip gloss
Lip gloss is a cosmetic used primarily to give lips a glossy luster, and sometimes to add a subtle color. It is distributed as a fluid or a soft solid (not to be confused with lip balm, which generally has medical or soothing purposes, or lips ...
, mascara
Mascara (, ) is a Cosmetics, cosmetic commonly used to enhance the upper and lower eyelashes. It is used to darken, thicken, lengthen, and/or define the eyelashes. Normally in one of three forms—liquid, powder, or cream—the modern mascara p ...
, moisturizing lotions, and nail polish. Some brands of toothpaste include powdered white mica. This acts as a mild abrasive to aid the polishing of the tooth surface and also adds a cosmetically pleasing, glittery shimmer to the paste. Mica is added to latex balloons to provide a colored shiny surface.

Built-up mica

 Muscovite and phlogopite splittings can be fabricated into various built-up mica products, also known as ''micanite''. Produced by mechanized or hand setting of overlapping splittings and alternate layers of binders and splittings, built-up mica is used primarily as an electrical insulation material. Mica insulation is used in high-temperature and fire-resistant power cables in aluminium plants,
Muscovite and phlogopite splittings can be fabricated into various built-up mica products, also known as ''micanite''. Produced by mechanized or hand setting of overlapping splittings and alternate layers of binders and splittings, built-up mica is used primarily as an electrical insulation material. Mica insulation is used in high-temperature and fire-resistant power cables in aluminium plants, blast furnace
A blast furnace is a type of metallurgical furnace used for smelting to produce industrial metals, generally pig iron, but also others such as lead or copper. ''Blast'' refers to the combustion air being supplied above atmospheric pressure.
In a ...
s, critical wiring circuits (for example, defence systems, fire and security alarm systems, and surveillance systems), heaters and boilers, lumber kiln
A kiln is a thermally insulated chamber, a type of oven, that produces temperatures sufficient to complete some process, such as hardening, drying, or Chemical Changes, chemical changes. Kilns have been used for millennia to turn objects m ...
s, metal smelters, and tanks and furnace wiring. Specific high-temperature mica-insulated wire and cable are rated to work for up to 15 minutes in molten aluminium, glass, and steel. Major products are bonding materials; flexible, heater, molding, and segment plates; mica paper; and tape.
Flexible plate is used in electric motor and generator armatures, field coil insulation, and magnet and commutator
In mathematics, the commutator gives an indication of the extent to which a certain binary operation fails to be commutative. There are different definitions used in group theory and ring theory.
Group theory
The commutator of two elements, ...
core insulation. Mica consumption in flexible plates was about 21 tonnes in 2008 in the US. A heater plate is used where high-temperature insulation is required. The molding plate is sheet mica from which V-rings are cut and stamped for use in insulating the copper segments from the steel shaft ends of a commutator. The molding plate is also fabricated into tubes and rings for insulation in armatures, motor starters, and transformers. Segment plate acts as insulation between the copper commutator segments of direct-current universal motors and generators. Phlogopite built-up mica is preferred because it wears at the same rate as the copper segments. Although muscovite has a greater resistance to wear, it causes uneven ridges that may interfere with the operation of a motor or generator. Consumption of segment plates was about 149 t in 2008 in the US. Some types of built-up mica have bonded splittings reinforced with cloth, glass, linen
Linen () is a textile made from the fibers of the flax plant.
Linen is very strong and absorbent, and it dries faster than cotton. Because of these properties, linen is comfortable to wear in hot weather and is valued for use in garments. Lin ...
, muslin, plastic, silk, or special paper. These products are very flexible and are produced in wide, continuous sheets that are either shipped, rolled, or cut into ribbons or tapes, or trimmed to specified dimensions. Built-up mica products may also be corrugated or reinforced by multiple layering. In 2008, about 351 t of built-up mica was consumed in the US, mostly for molding plates (19%) and segment plates (42%).
Sheet mica
 Sheet mica is a versatile and durable material widely used in electrical and thermal insulation applications. It exhibits excellent electrical properties, heat resistance, and chemical stability.
Technical grade sheet mica is used in electrical components, electronics, atomic force microscopy and as window sheets. Other uses include diaphragms for oxygen-breathing equipment, marker dials for navigation compasses,
Sheet mica is a versatile and durable material widely used in electrical and thermal insulation applications. It exhibits excellent electrical properties, heat resistance, and chemical stability.
Technical grade sheet mica is used in electrical components, electronics, atomic force microscopy and as window sheets. Other uses include diaphragms for oxygen-breathing equipment, marker dials for navigation compasses, optical filters
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultravio ...
, pyrometers, thermal regulators, stove and kerosene heater windows, radiation aperture covers for microwave ovens, and micathermic heater elements. Mica is birefringent
Birefringence, also called double refraction, is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are described as birefring ...
and is therefore commonly used to make quarter and half wave plates. Specialized applications for sheet mica are found in aerospace components in air-, ground-, and sea-launched missile systems, laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radi ...
devices, medical electronics and radar systems. Mica is mechanically stable in micrometer-thin sheets which are relatively transparent to radiation (such as alpha particle
Alpha particles, also called alpha rays or alpha radiation, consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium-4 nucleus. They are generally produced in the process of alpha decay but may also be produce ...
s) while being impervious to most gases. It is therefore used as a window on radiation detectors such as Geiger–Müller tube
The Geiger–Müller tube or G–M tube is the sensing element of the Geiger counter instrument used for the detection of ionizing radiation. It is named after Hans Geiger, who invented the principle in 1908, and Walther Müller, who collaborate ...
s.
In 2008, mica splittings represented the largest part of the sheet mica industry in the United States. Consumption of muscovite and phlogopite splittings was about 308 t in 2008. Muscovite splittings from India accounted for essentially all US consumption. The remainder was primarily imported from Madagascar.
Small squared pieces of sheet mica are also used in the traditional Japanese ''Kōdō
is the art of appreciating Japanese incense, and involves using incense within a structure of codified conduct. ''Kōdō'' includes all aspects of the incense process, from the , to activities such as the incense-comparing games and . ''Kōdō ...
'' ceremony to burn incense: A burning piece of coal is placed inside a cone made of white ash. The sheet of mica is placed on top, acting as a separator between the heat source and the incense, to spread the fragrance without burning it.
Electrical and electronic
 Sheet mica is used principally in the electronic and electrical industries. Its usefulness in these applications is derived from its unique electrical and thermal properties and its mechanical properties, which allow it to be cut, punched, stamped, and machined to close tolerances. Specifically, mica is unusual in that it is a good electrical insulator at the same time as being a good thermal conductor. The leading use of block mica is as an electrical insulator in electronic equipment. High-quality block mica is processed to line the gauge glasses of high-pressure steam boilers because of its flexibility, transparency, and resistance to heat and chemical attack. Only high-quality muscovite film mica, which is variously called India ruby mica or ruby muscovite mica, is used as a dielectric in
Sheet mica is used principally in the electronic and electrical industries. Its usefulness in these applications is derived from its unique electrical and thermal properties and its mechanical properties, which allow it to be cut, punched, stamped, and machined to close tolerances. Specifically, mica is unusual in that it is a good electrical insulator at the same time as being a good thermal conductor. The leading use of block mica is as an electrical insulator in electronic equipment. High-quality block mica is processed to line the gauge glasses of high-pressure steam boilers because of its flexibility, transparency, and resistance to heat and chemical attack. Only high-quality muscovite film mica, which is variously called India ruby mica or ruby muscovite mica, is used as a dielectric in capacitor
In electrical engineering, a capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy by accumulating electric charges on two closely spaced surfaces that are insulated from each other. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term st ...
s. The highest quality mica film is used to manufacture capacitors for calibration standards. The next lower grade is used in transmitting capacitors. Receiving capacitors use a slightly lower grade of high-quality muscovite.
Mica sheets are used to provide structure for heating wire (such as in Kanthal or Nichrome
Nichrome (also known as NiCr, nickel-chromium or chromium-nickel) is a family of alloys of nickel and chromium (and occasionally iron) commonly used as resistance wire, heating elements in devices like toasters, electrical kettles and space he ...
) in heating element
A heating element is a device used for conversion of electric energy into heat, consisting of a heating resistor and accessories. Heat is generated by the passage of electric current through a resistor through a process known as Joule heating. He ...
s and can withstand up to .
Single-ended self-starting lamps are insulated with a mica disc and contained in a borosilicate glass
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass with silica and boron trioxide as the main glass-forming constituents. Borosilicate glasses are known for having very low coefficients of thermal expansion (≈3 × 10−6 K−1 at 20 °C), ma ...
gas discharge tube (arc tube) and a metal cap. They include the sodium-vapor lamp that is the gas-discharge lamp
Gas-discharge lamps are a family of artificial light sources that generate light by sending an electric discharge through an ionization, ionized gas, a plasma (physics), plasma.
Typically, such lamps use a
noble gas (argon, neon, krypton, and x ...
in street lighting.
Atomic force microscopy
Another use of mica is as a substrate in the production of ultra-flat, thin-film surfaces, e.g. gold surfaces. Although the deposited film surface is still rough due to deposition kinetics, the back side of the film at the mica-film interface is ultra-flat once the film is removed from the substrate. Freshly-cleaved mica surfaces have been used as clean imaging substrates inatomic force microscopy
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) or scanning force microscopy (SFM) is a very-high-resolution type of scanning probe microscopy (SPM), with demonstrated resolution on the order of fractions of a nanometer, more than 1000 times better than the opti ...
, enabling for example the imaging of bismuth
Bismuth is a chemical element; it has symbol Bi and atomic number 83. It is a post-transition metal and one of the pnictogens, with chemical properties resembling its lighter group 15 siblings arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth occurs nat ...
films, plasma glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide (sugar) chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known a ...
s, membrane bilayers, and DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
molecules.
Peepholes
Thin transparent sheets of mica were used for peepholes in boilers, lanterns,stove
A stove or range is a device that generates heat inside or on top of the device, for - local heating or cooking. Stoves can be powered with many fuels, such as natural gas, electricity, gasoline, wood, and coal.
Due to concerns about air pollu ...
s, and kerosene heaters because they were less likely to shatter than glass when exposed to extreme temperature gradients. Such peepholes were also fitted in horse-drawn carriage
A carriage is a two- or four-wheeled horse-drawn vehicle for passengers. In Europe they were a common mode of transport for the wealthy during the Roman Empire, and then again from around 1600 until they were replaced by the motor car around 1 ...
s and early 20th-century cars, where they were called '' isinglass curtains''.
Etymology
The wordmica
' is derived from the
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
word ', meaning ''a crumb'', and probably influenced by ', to glitter.
Early history
 Human use of mica dates back to
Human use of mica dates back to prehistoric
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use o ...
times. Mica was known to ancient Indian, Egyptian
''Egyptian'' describes something of, from, or related to Egypt.
Egyptian or Egyptians may refer to:
Nations and ethnic groups
* Egyptians, a national group in North Africa
** Egyptian culture, a complex and stable culture with thousands of year ...
, Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
, Roman, and Chinese civilizations, as well as the Aztec
The Aztecs ( ) were a Mesoamerican civilization that flourished in central Mexico in the Post-Classic stage, post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different Indigenous peoples of Mexico, ethnic groups of central ...
civilization of the New World
The term "New World" is used to describe the majority of lands of Earth's Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas, and sometimes Oceania."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: ...
.
The earliest use of mica has been found in cave painting
In archaeology, cave paintings are a type of parietal art (which category also includes petroglyphs, or engravings), found on the wall or ceilings of caves. The term usually implies prehistoric art, prehistoric origin. These paintings were often c ...
s created during the Upper Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic ( years ago) ( ), also called the Old Stone Age (), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehist ...
period (40,000 BC to 10,000 BC). The first hues were red (iron oxide
An iron oxide is a chemical compound composed of iron and oxygen. Several iron oxides are recognized. Often they are non-stoichiometric. Ferric oxyhydroxides are a related class of compounds, perhaps the best known of which is rust.
Iron ...
, hematite
Hematite (), also spelled as haematite, is a common iron oxide compound with the formula, Fe2O3 and is widely found in rocks and soils. Hematite crystals belong to the rhombohedral lattice system which is designated the alpha polymorph of . ...
, or red ochre
Ochre ( ; , ), iron ochre, or ocher in American English, is a natural clay earth pigment, a mixture of ferric oxide and varying amounts of clay and sand. It ranges in colour from yellow to deep orange or brown. It is also the name of the colou ...
) and black (manganese dioxide
Manganese dioxide is the inorganic compound with the formula . This blackish or brown solid occurs naturally as the mineral pyrolusite, which is the main ore of manganese and a component of manganese nodules. The principal use for is for dry-cel ...
, pyrolusite
Pyrolusite is a mineral consisting essentially of manganese dioxide ( Mn O2) and is important as an ore of manganese.. It is a black, amorphous appearing mineral, often with a granular, fibrous, or columnar structure, sometimes forming reniform ...
), though black from juniper or pine carbons has also been discovered. White from kaolin or mica was used occasionally.
A few kilometers northeast of Mexico City
Mexico City is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Mexico, largest city of Mexico, as well as the List of North American cities by population, most populous city in North America. It is one of the most important cultural and finan ...
stands the ancient site of Teotihuacan
Teotihuacan (; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Teotihuacán'', ; ) is an ancient Mesoamerican city located in a sub-valley of the Valley of Mexico, which is located in the State of Mexico, northeast of modern-day Mexico City.
Teotihuacan is ...
. Mica was found in the noble palace complex "Viking Group" during an excavation led by Pedro Armillas between 1942 and 1944. Later, a second deposit was located in the Xalla Complex, another palatial structure east of Street of the Dead. There is a claim mica was found within the Pyramid of the Sun, which originates from Peter Tompkins in his book ''Mysteries of the Mexican Pyramids''. But it is not yet proven.
Natural mica was and still is used by the Taos and Picuris Pueblos Indians in north-central New Mexico to make pottery. The pottery is made from weathered Precambrian
The Precambrian ( ; or pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pC, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of t ...
mica schist
Schist ( ) is a medium-grained metamorphic rock generally derived from fine-grained sedimentary rock, like shale. It shows pronounced ''schistosity'' (named for the rock). This means that the rock is composed of mineral grains easily seen with a l ...
and has flecks of mica throughout the vessels. Tewa Pueblo Pottery is made by coating the clay with mica to provide a dense, glittery micaceous finish over the entire object.
Mica flakes (called ''abrak'' in Urdu and written as ابرک) are also used in Pakistan to embellish women's summer clothes, especially ''dupattas'' (long light-weight scarves, often colorful and matching the dress). Thin mica flakes are added to a hot starch water solution, and the ''dupatta'' is dipped in this water mixture for 3–5 minutes. Then it is hung to air dry.
Mica powder
Throughout the ages, fine powders of mica have been used for various purposes, including decorations. Powdered mica glitter is used to decorate traditional water clay pots in India, Pakistan and Bangladesh; it is also used on traditionalPueblo
Pueblo refers to the settlements of the Pueblo peoples, Native American tribes in the Southwestern United States, currently in New Mexico, Arizona, and Texas. The permanent communities, including some of the oldest continually occupied settlement ...
pottery, though not restricted to use on water pots in this case. The ''gulal'' and '' abir'' (colored powders) used by North Indian Hindus
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ...
during the festive season of Holi
Holi () is a major Hindu festival celebrated as the Festival of Colours, Love and Spring.The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) p. 874 "Holi /'həʊli:/ noun a Hindu spring festival ...".Yudit Greenberg, Encyclopedia of Love in World ...
contain fine crystals of mica to create a sparkling effect. The majestic Padmanabhapuram Palace, from Trivandrum
Thiruvananthapuram ( ), also known as Trivandrum, is the capital city of the Indian state of Kerala. As of 2011, the Thiruvananthapuram Municipal Corporation had a population of 957,730 over an area of 214.86 sq. km, making it the largest and ...
in India, has colored mica windows.
Mica powder is also used as a decoration in traditional Japanese woodblock printmaking, as when applied to wet ink with gelatin
Gelatin or gelatine () is a translucent, colorless, flavorless food ingredient, commonly derived from collagen taken from animal body parts. It is brittle when dry and rubbery when moist. It may also be referred to as hydrolyzed collagen, coll ...
as thickener using '' kirazuri'' technique and allowed to dry, it sparkles and reflects light. Earlier examples are found among paper decorations, with the height as the Nishi Honganji 36 Poets Collection, codices of illuminated manuscripts in and after ACE 1112. For metallic glitter, ''Ukiyo-e
is a genre of Japanese art that flourished from the 17th through 19th centuries. Its artists produced woodblock printing, woodblock prints and Nikuhitsu-ga, paintings of such subjects as female beauties; kabuki actors and sumo wrestlers; scenes ...
'' prints employed very thick solution either with or without color pigments stencilled on hairpins, sword blades or fish scales on .
The soil around Nishio in central Japan is rich in mica deposits, which were already mined in the Nara period
The of the history of Japan covers the years from 710 to 794. Empress Genmei established the capital of Heijō-kyō (present-day Nara). Except for a five-year period (740–745), when the capital was briefly moved again, it remained the capita ...
. Yatsuomote ware is a type of local Japanese pottery
is one of the oldest Japanese crafts and Japanese art, art forms, dating back to the Neolithic period. Types have included earthenware, pottery, stoneware, porcelain, and Blue and white porcelain, blue-and-white ware. Japan has an exception ...
from there. After an incident at Mount Yatsuomote a small bell was offered to soothe the ''kami
are the Deity, deities, Divinity, divinities, Spirit (supernatural entity), spirits, mythological, spiritual, or natural phenomena that are venerated in the traditional Shinto religion of Japan. ''Kami'' can be elements of the landscape, forc ...
''. Katō Kumazō started a local tradition where small ceramic zodiac
The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8° north and south celestial latitude of the ecliptic – the apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year. Within this zodiac ...
bell
A bell /ˈbɛl/ () is a directly struck idiophone percussion instrument. Most bells have the shape of a hollow cup that when struck vibrates in a single strong strike tone, with its sides forming an efficient resonator. The strike may be m ...
s (きらら鈴) were made out of local mica kneaded into the clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolinite, ). Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impuriti ...
, and after burning in the kiln the bell would make a pleasing sound when rung.
Medicine
Ayurveda
Ayurveda (; ) is an alternative medicine system with historical roots in the Indian subcontinent. It is heavily practised throughout India and Nepal, where as much as 80% of the population report using ayurveda. The theory and practice of ayur ...
, the Hindu system of ancient medicine prevalent in India, includes the purification and processing of mica in preparing Abhraka bhasma, which is claimed as a treatment for diseases of the respiratory and digestive tracts.
Health impact
Mica dust in the workplace is regarded as a hazardous substance for respiratory exposure above certain concentrations.United States
TheOccupational Safety and Health Administration
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA; ) is a regulatory agency of the United States Department of Labor that originally had federal visitorial powers to inspect and examine workplaces. The United States Congress established ...
(OSHA) has set the legal limit (permissible exposure limit
The permissible exposure limit (PEL or OSHA PEL) is a legal limit in the United States for exposure of an employee to a chemical substance or physical agents such as high level noise. Permissible exposure limits were established by the Occupational ...
) for mica exposure in the workplace as 20 million parts per cubic foot (706,720,000 parts per cubic meter) over an 8-hour workday. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH, ) is the List of United States federal agencies, United States federal agency responsible for conducting research and making recommendations for the prevention of work-related occ ...
(NIOSH) has set a recommended exposure limit (REL) of 3 mg/m3 respiratory exposure over an 8-hour workday. At levels of 1,500 mg/m3, mica is immediately dangerous to life and health.Ireland
The Irish defective block crisis relates to mica in construction blocks.Substitutes
Some lightweight aggregates, such asdiatomite
Diatomaceous earth ( ), also known as diatomite ( ), celite, or kieselguhr, is a naturally occurring, soft, siliceous sedimentary rock that can be crumbled into a fine white to off-white powder. It has a particle size ranging from more than 3 ...
, perlite
Perlite is an amorphous volcanic glass that has a relatively high water content, typically formed by the Hydrate, hydration of obsidian. It occurs naturally and has the unusual property of greatly expanding when heated sufficiently. It is an indu ...
, and vermiculite
Vermiculite is a hydrous phyllosilicate mineral which undergoes significant expansion when heated. Exfoliation occurs when the mineral is heated sufficiently; commercial furnaces can routinely produce this effect. Vermiculite forms by the weathe ...
, may be substituted for ground mica when used as filler. Ground synthetic ''fluorophlogopite'', a fluorine-rich mica, may replace natural ground mica for uses that require thermal and electrical properties of mica. Many materials can be substituted for mica in numerous electrical, electronic, and insulation uses. Substitutes include acrylate polymer
An acrylate polymer (also known as acrylic or polyacrylate) is any of a group of polymers prepared from acrylate monomers. These plastics are noted for their transparency, resistance to breakage, and elasticity.
Acrylate polymer is commonly used ...
s, cellulose acetate
In biochemistry, cellulose acetate refers to any acetate ester of cellulose, usually cellulose diacetate. It was first prepared in 1865. A bioplastic, cellulose acetate is used as a film base in photography, as a component in some coatings, and ...
, fiberglass
Fiberglass (American English) or fibreglass (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English) is a common type of fibre-reinforced plastic, fiber-reinforced plastic using glass fiber. The fibers may be randomly arranged, flattened i ...
, fishpaper, nylon
Nylon is a family of synthetic polymers characterised by amide linkages, typically connecting aliphatic or Polyamide#Classification, semi-aromatic groups.
Nylons are generally brownish in color and can possess a soft texture, with some varieti ...
, phenolics, polycarbonate
Polycarbonates (PC) are a group of thermoplastic polymers containing carbonate ester, carbonate groups in their chemical structures. Polycarbonates used in engineering are strong, toughness, tough materials, and some grades are optically transp ...
, polyester
Polyester is a category of polymers that contain one or two ester linkages in every repeat unit of their main chain. As a specific material, it most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyesters include some natura ...
, styrene
Styrene is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH=CH2. Its structure consists of a vinyl group as substituent on benzene. Styrene is a colorless, oily liquid, although aged samples can appear yellowish. The compound evaporates easi ...
, vinyl-PVC, and vulcanized fiber. Mica paper made from scrap mica can be substituted for sheet mica in electrical and insulation applications.
See also
* Mica fish *References
Sources
External links
*Mineral Galleries data
* *
Scientific American
''Scientific American'', informally abbreviated ''SciAm'' or sometimes ''SA'', is an American popular science magazine. Many scientists, including Albert Einstein and Nikola Tesla, have contributed articles to it, with more than 150 Nobel Pri ...
,Mica
, 22-Oct-1881, pp. 257 {{Authority control Phyllosilicates Dielectrics Articles containing video clips Industrial minerals