|
Phenolic Resin
Phenol formaldehyde resins (PF), also called phenolic resins or phenoplasts, are synthetic polymers obtained by the reaction of phenol or substituted phenol with formaldehyde. Used as the basis for Bakelite, PFs were the first commercial synthetic resins. They have been widely used for the production of molded products including billiard balls, laboratory countertops, and as coatings and adhesives. They were at one time the primary material used for the production of circuit boards but have been largely replaced with epoxy resins and fiberglass cloth, as with fire-resistant FR-4 circuit board materials. There are two main production methods. One reacts phenol and formaldehyde directly to produce a thermosetting network polymer, while the other restricts the formaldehyde to produce a prepolymer known as novolac which can be moulded and then cured with the addition of more formaldehyde and heat.A. Gardziella, L.A. Pilato, A. Knop, Phenolic Resins: Chemistry, Applications, Standard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenol
Phenol (also known as carbolic acid, phenolic acid, or benzenol) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile and can catch fire. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () bonded to a hydroxy group (). Mildly acidic, it requires careful handling because it can cause chemical burns. It is acutely toxic and is considered a health hazard. Phenol was first extracted from coal tar, but today is produced on a large scale (about 7 million tonnes a year) from petroleum-derived feedstocks. It is an important industrial commodity as a precursor to many materials and useful compounds, and is a liquid when manufactured. It is primarily used to synthesize plastics and related materials. Phenol and its chemical derivatives are essential for production of polycarbonates, epoxies, explosives such as picric acid, Bakelite, nylon, detergents, herbicides such as phenoxy herbicides, and numerous pharmaceuti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bisphenol F
Bisphenol F (BPF; 4,4′-dihydroxydiphenylmethane) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is structurally related to bisphenol A (BPA), a popular precursor for forming plastics, as both belong to the category of molecules known as bisphenols, which feature two phenol groups connected via a linking group. In BPF, the two aromatic rings are linked by a methylene connecting group. In response to concern about the health effects of BPA, BPF is increasingly used as a substitute for BPA. Uses BPF is used in the manufacture of plastics and epoxy resins. It is used in the production of tank and pipe linings, industrial flooring, road and bridge deck toppings, structural adhesives, grouts, coatings and electrical varnishes. BPF is also utilized in liners, lacquers, adhesives, plastics, and the coating of drinks and food cans. BPF is found in dental materials, such as restorative materials, liners, adhesives, oral prosthetic devices and tissue substitutes. Biological effec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
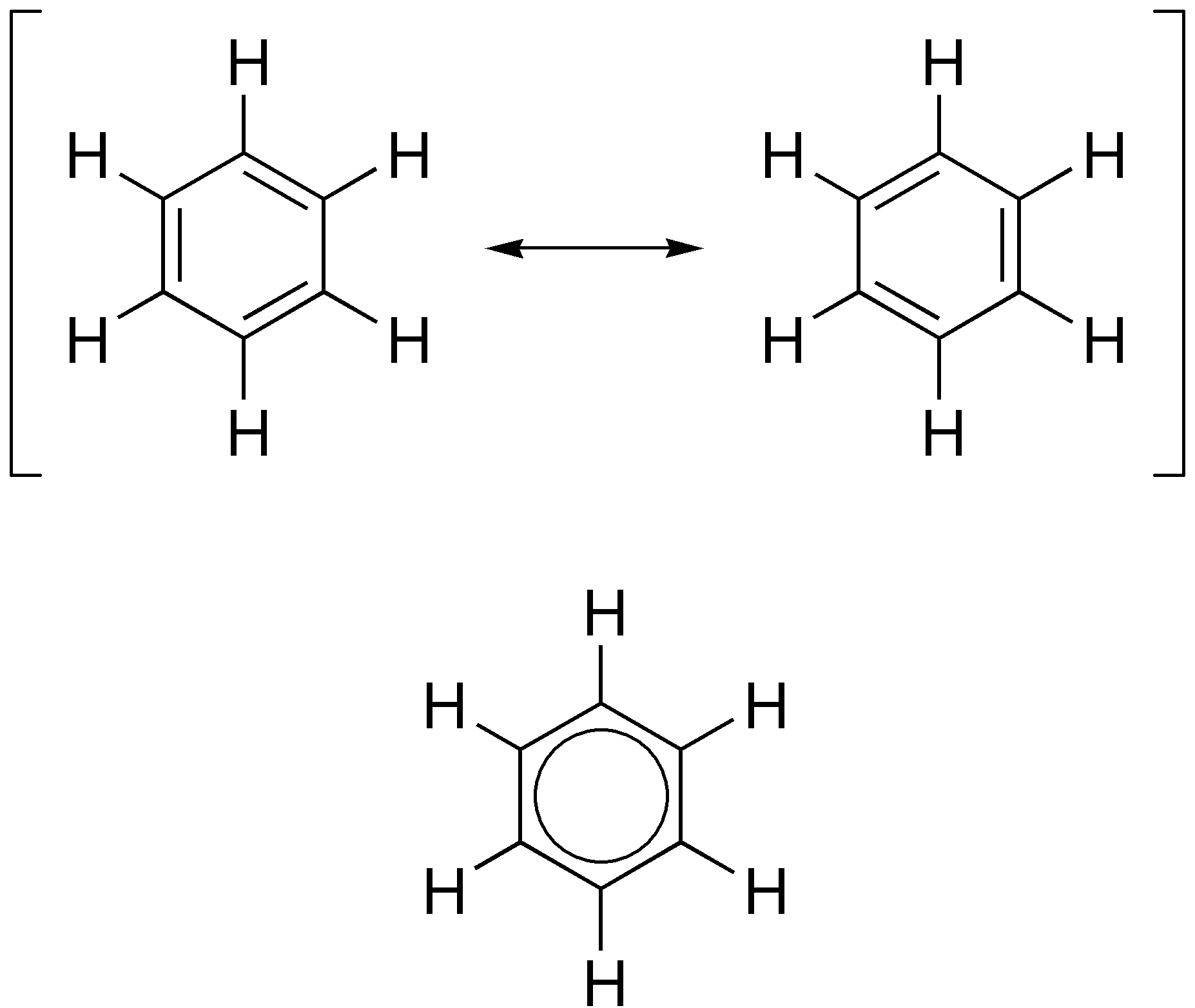
Aromatic Ring
In organic chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property describing the way in which a conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs, or empty orbitals exhibits a stabilization stronger than would be expected from conjugation alone. The earliest use of the term was in an article by August Wilhelm Hofmann in 1855. There is no general relationship between aromaticity as a chemical property and the olfactory properties of such compounds. Aromaticity can also be considered a manifestation of cyclic delocalization and of resonance. This is usually considered to be because electrons are free to cycle around circular arrangements of atoms that are alternately single- and double- bonded to one another. This commonly seen model of aromatic rings, namely the idea that benzene was formed from a six-membered carbon ring with alternating single and double bonds (cyclohexatriene), was developed by Kekulé (see History section below). Each bond may be seen as a hybrid of a single bond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delocalised
In chemistry, delocalized electrons are electrons in a molecule, ion or solid metal that are not associated with a single atom or a covalent bond.IUPAC Gold Boo''delocalization''/ref> The term delocalization is general and can have slightly different meanings in different fields: * In organic chemistry, it refers to resonance in conjugated systems and aromatic compounds. * In solid-state physics, it refers to free electrons that facilitate electrical conduction. * In quantum chemistry, it refers to molecular orbital electrons that have extended over several adjacent atoms. Resonance In the simple aromatic ring of benzene, the delocalization of six π electrons over the C6 ring is often graphically indicated by a circle. The fact that the six C-C bonds are equidistant is one indication that the electrons are delocalized; if the structure were to have isolated double bonds alternating with discrete single bonds, the bond would likewise have alternating longer and shorter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoresist
A photoresist (also known simply as a resist) is a light-sensitive material used in several processes, such as photolithography and photoengraving, to form a patterned coating on a surface. This process is crucial in the electronics industry. The process begins by coating a substrate with a light-sensitive organic material. A patterned mask is then applied to the surface to block light, so that only unmasked regions of the material will be exposed to light. A solvent, called a developer, is then applied to the surface. In the case of a positive photoresist, the photo-sensitive material is degraded by light and the developer will dissolve away the regions that were exposed to light, leaving behind a coating where the mask was placed. In the case of a negative photoresist, the photosensitive material is strengthened (either polymerized or cross-linked) by light, and the developer will dissolve away only the regions that were not exposed to light, leaving behind a coating in areas w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tackifier
Tackifiers are chemical compounds used in formulating adhesives to increase tack, the stickiness of the surface of the adhesive. They are usually low-molecular weight compounds with high glass transition temperature. At low strain rate, they provide higher stress compliance, and become stiffer at higher strain rates. Tackifiers tend to have low molecular weight, and glass transition and softening temperature above room temperature, providing them with suitable viscoelastic properties. Tackifiers frequently represent most of both weight percentage and cost of hot melt adhesives and pressure-sensitive adhesives. In hot melt adhesives they can comprise up to about 40% of total mass. Tackifiers are usually resins (e.g. rosins and their derivates, terpenes and modified terpenes, aliphatic, cycloaliphatic and aromatic resins (C5 aliphatic resins, C9 aromatic resins, and C5/C9 aliphatic/aromatic resins), hydrogenated hydrocarbon resins, and their mixtures, terpene-phenol resins (TPR, u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexamethylenetetramine
Hexamethylenetetramine (HMTA), also known as 1,3,5,7-tetraazaadamantane, is a heterocyclic organic compound with diverse applications. It has the chemical formula (CH2)6N4 and is a white crystalline compound that is highly soluble in water and polar organic solvents. It is useful in the synthesis of other organic compounds, including plastics, pharmaceuticals, and rubber additives. The compound is also used medically for certain conditions. It sublimes in vacuum at 280°C. It has a tetrahedral cage-like structure similar to adamantane. The four vertices are occupied by nitrogen atoms, which are linked by methylene groups. Although the molecular shape defines a cage, no void space is available at the interior. Synthesis, structure, reactivity Hexamethylenetetramine was discovered by Aleksandr Butlerov in 1859. In this article, Butlerov discovered formaldehyde, which he called "dioxymethylen" (methylene dioxide) age 247because his empirical formula for it was incorrect (C4H4O4) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermosetting Polymer
In materials science, a thermosetting polymer, often called a thermoset, is a polymer that is obtained by irreversibly hardening (" curing") a soft solid or viscous liquid prepolymer (resin). Curing is induced by heat or suitable radiation and may be promoted by high pressure or mixing with a catalyst. Heat is not necessarily applied externally, and is often generated by the reaction of the resin with a curing agent (''catalyst'', '' hardener''). Curing results in chemical reactions that create extensive cross-linking between polymer chains to produce an infusible and insoluble polymer network. The starting material for making thermosets is usually malleable or liquid prior to curing, and is often designed to be molded into the final shape. It may also be used as an adhesive. Once hardened, a thermoset cannot be melted for reshaping, in contrast to thermoplastic polymers which are commonly produced and distributed in the form of pellets, and shaped into the final product form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfonic Acid
In organic chemistry, sulfonic acid (or sulphonic acid) refers to a member of the class of organosulfur compounds with the general formula , where R is an organic alkyl or aryl group and the group a sulfonyl hydroxide. As a substituent, it is known as a sulfo group. A sulfonic acid can be thought of as sulfuric acid with one hydroxyl group replaced by an organic substituent. The parent compound (with the organic substituent replaced by hydrogen) is the parent sulfonic acid, , a tautomer of sulfurous acid, . Salt (chemistry), Salts or esters of sulfonic acids are called sulfonates. Preparation Aryl sulfonic acids are produced by the process of sulfonation. Usually the sulfonating agent is sulfur trioxide. A large scale application of this method is the production of alkylbenzenesulfonic acids: : In this reaction, sulfur trioxide is an electrophile and the arene is the nucleophile. The reaction is an example of electrophilic aromatic substitution. In a related process, carboxyli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrochloric Acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid or spirits of salt, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride (HCl). It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungency, pungent smell. It is classified as a acid strength, strong acid. It is a component of the gastric acid in the digestive systems of most animal species, including humans. Hydrochloric acid is an important laboratory reagent and industrial chemical. Etymology Because it was produced from halite, rock salt according to the methods of Johann Rudolph Glauber, hydrochloric acid was historically called by European alchemists ''spirits of salt'' or ''acidum salis'' (salt acid). Both names are still used, especially in other languages, such as , , , , , , , , , , (''ensan''), zh, 盐酸 (''yánsuān''), and (''yeomsan''). Gaseous HCl was called ''marine acid air''. The name ''muriatic acid'' has the same origin (''muriatic'' means "pertaining to brine or salt", hence ''muriate'' means hydrochloride), and this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxalic Acid
Oxalic acid is an organic acid with the systematic name ethanedioic acid and chemical formula , also written as or or . It is the simplest dicarboxylic acid. It is a white crystalline solid that forms a colorless solution in water. Its name is derived from early investigators who isolated oxalic acid from flowering plants of the genus '' Oxalis'', commonly known as wood-sorrels. It occurs naturally in many foods. Excessive ingestion of oxalic acid or prolonged skin contact can be dangerous. Oxalic acid is a much stronger acid than acetic acid. It is a reducing agent and its conjugate bases hydrogen oxalate () and oxalate () are chelating agents for metal cations. It is used as a cleaning agent, especially for the removal of rust, because it forms a water-soluble ferric iron complex, the ferrioxalate ion. Oxalic acid typically occurs as the dihydrate with the formula . History The preparation of salts of oxalic acid from plants had been known since at least 1745, when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |