|
Barium
Barium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ba and atomic number 56. It is the fifth element in group 2 and is a soft, silvery alkaline earth metal. Because of its high chemical reactivity, barium is never found in nature as a free element. The most common minerals of barium are barite ( barium sulfate, BaSO4) and witherite ( barium carbonate, BaCO3). The name ''barium'' originates from the alchemical derivative "baryta", from Greek (), meaning 'heavy'. ''Baric'' is the adjectival form of barium. Barium was identified as a new element in 1772, but not reduced to a metal until 1808 with the advent of electrolysis. Barium has few industrial applications. Historically, it was used as a getter for vacuum tubes and in oxide form as the emissive coating on indirectly heated cathodes. It is a component of YBCO (high-temperature superconductors) and electroceramics, and is added to steel and cast iron to reduce the size of carbon grains within the microstructure. Barium compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barium Sulfate
Barium sulfate (or sulphate) is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ba SO4. It is a white crystalline solid that is odorless and insoluble in water. It occurs in nature as the mineral barite, which is the main commercial source of barium and materials prepared from it. Its opaque white appearance and its high density are exploited in its main applications.Holleman, A. F. and Wiberg, E. (2001) ''Inorganic Chemistry'', San Diego, CA. Academic Press, . Uses Drilling fluids About 80% of the world's barium sulfate production, mostly purified mineral, is consumed as a component of oil well drilling fluid. It increases the density of the fluid, increasing the hydrostatic pressure in the well and reducing the chance of a blowout. Radiocontrast agent Barium sulfate in suspension is often used medically as a radiocontrast agent for X-ray imaging and other diagnostic procedures. It is most often used in imaging of the GI tract during what is colloquially known as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barium Oxide
Barium oxide, also known as baria, is a white hygroscopic non-flammable chemical compound, compound with the formula BaO. It has a Cubic crystal system, cubic structure and is used in cathode-ray tubes, crown glass, and Catalysis, catalysts. It is harmful to human skin and if swallowed in large quantity causes irritation. Excessive quantities of barium oxide may lead to death. It is prepared by heating barium carbonate with coke (fuel), coke, carbon black or tar or by thermal decomposition of barium nitrate. Uses Barium oxide is used as a coating for hot cathodes, for example, those in cathode-ray tubes. It replaced lead(II) oxide in the production of certain kinds of glass such as optical crown glass (optics), crown glass. While lead oxide raised the refractive index, it also raised the optical dispersion, dispersive power, which barium oxide does not alter. Barium oxide also has use as an ethoxylation catalyst in the reaction of ethylene oxide and Alcohol (chemistry), alcohols ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaline Earth Metal
The alkaline earth metals are six chemical elements in group (periodic table), group 2 of the periodic table. They are beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra).. The elements have very similar properties: they are all shiny, silvery-white, somewhat reactivity (chemistry), reactive metals at standard temperature and pressure. Together with helium, these elements have in common an outer atomic orbital, s orbital which is full —that is, this orbital contains its full complement of two electrons, which the alkaline earth metals readily lose to form cations with electric charge, charge +2, and an oxidation state of +2. Helium is grouped with the noble gases and not with the alkaline earth metals, but it is theorized to have some similarities to beryllium when forced into bonding and has sometimes been suggested to belong to group 2. All the discovered alkaline earth metals occur in nature, although radium occurs only through the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barium Carbonate
Barium carbonate is the inorganic compound with the formula BaCO3. Like most alkaline earth metal carbonates, it is a white salt that is poorly soluble in water. It occurs as the mineral known as witherite. In a commercial sense, it is one of the most important barium compounds. Preparation Barium carbonate is made commercially from barium sulfide by treatment with sodium carbonate at 60 to 70 °C ( soda ash method) or, more commonly carbon dioxide at 40 to 90 °C: In the soda ash process, an aqueous solution of barium sulfide is treated with sodium carbonate: : Reactions Barium carbonate reacts with acids such as hydrochloric acid to form soluble barium salts, such as barium chloride: : Pyrolysis of barium carbonate gives barium oxide. Uses It is mainly used to remove sulfate impurities from feedstock of the chlor-alkali process. Otherwise it is a common precursor to barium-containing compounds such as ferrites. Other uses Barium carbonate is widely used in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yttrium Barium Copper Oxide
Yttrium barium copper oxide (YBCO) is a family of crystalline chemical compounds that display high-temperature superconductivity; it includes the first material ever discovered to become superconducting above the boiling point of liquid nitrogen [] at about . Many YBCO compounds have the general formula (also known as Y123), although materials with other Y:Ba:Cu ratios exist, such as (Y124) or (Y247). At present, there is no singularly recognised theory for high-temperature superconductivity. It is part of the more general group of rare-earth barium copper oxides (ReBCO) in which, instead of yttrium, other rare earths are present. History In April 1986, Georg Bednorz and Karl Müller, working at IBM in Zurich, discovered that certain semiconducting oxides became superconducting at relatively high temperature, in particular, a lanthanum barium copper oxide becomes superconducting at 35 K. This oxide was an oxygen-deficient perovskite-related material that proved pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
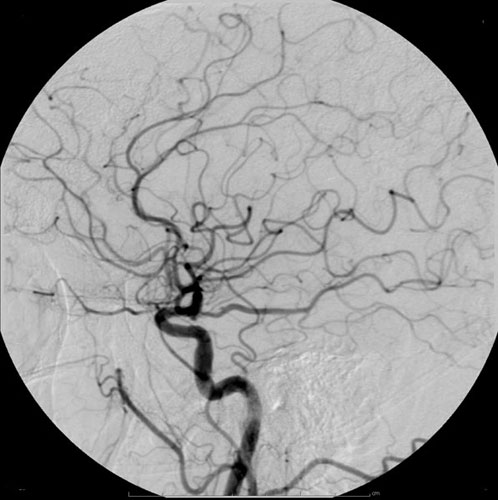
Radiocontrast Agent
Radiocontrast agents are substances used to enhance the visibility of internal structures in X-ray-based imaging techniques such as computed tomography (contrast CT), projectional radiography, and fluoroscopy. Radiocontrast agents are typically iodine, or more rarely barium sulfate. The contrast agents absorb external X-rays, resulting in decreased exposure on the X-ray detector. This is different from radiopharmaceuticals used in nuclear medicine which emit radiation. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) functions through different principles and thus MRI contrast agents have a different mode of action. These compounds work by altering the magnetic properties of nearby hydrogen nuclei. Types and uses Radiocontrast agents used in X-ray examinations can be grouped in positive (iodinated agents, barium sulfate), and negative agents (air, carbon dioxide, methylcellulose). Iodine (circulatory system) Iodinated contrast contains iodine. It is the main type of radiocontrast used for intra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body-centered Cubic
In crystallography, the cubic (or isometric) crystal system is a crystal system where the Crystal structure#Unit cell, unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals. There are three main varieties of these crystals: *Primitive cubic (abbreviated ''cP'' and alternatively called simple cubic) *Body-centered cubic (abbreviated ''cI'' or bcc) *Face-centered cubic (abbreviated ''cF'' or fcc) Note: the term fcc is often used in synonym for the Close-packing of equal spheres, ''cubic close-packed'' or ccp structure occurring in metals. However, fcc stands for a face-centered cubic Bravais lattice, which is not necessarily close-packed when a motif is set onto the lattice points. E.g. the diamond and the zincblende lattices are fcc but not close-packed. Each is subdivided into other variants listed below. Although the ''unit cells'' in these crystals are conventionally taken to be cubes, the primitive cell, primitiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
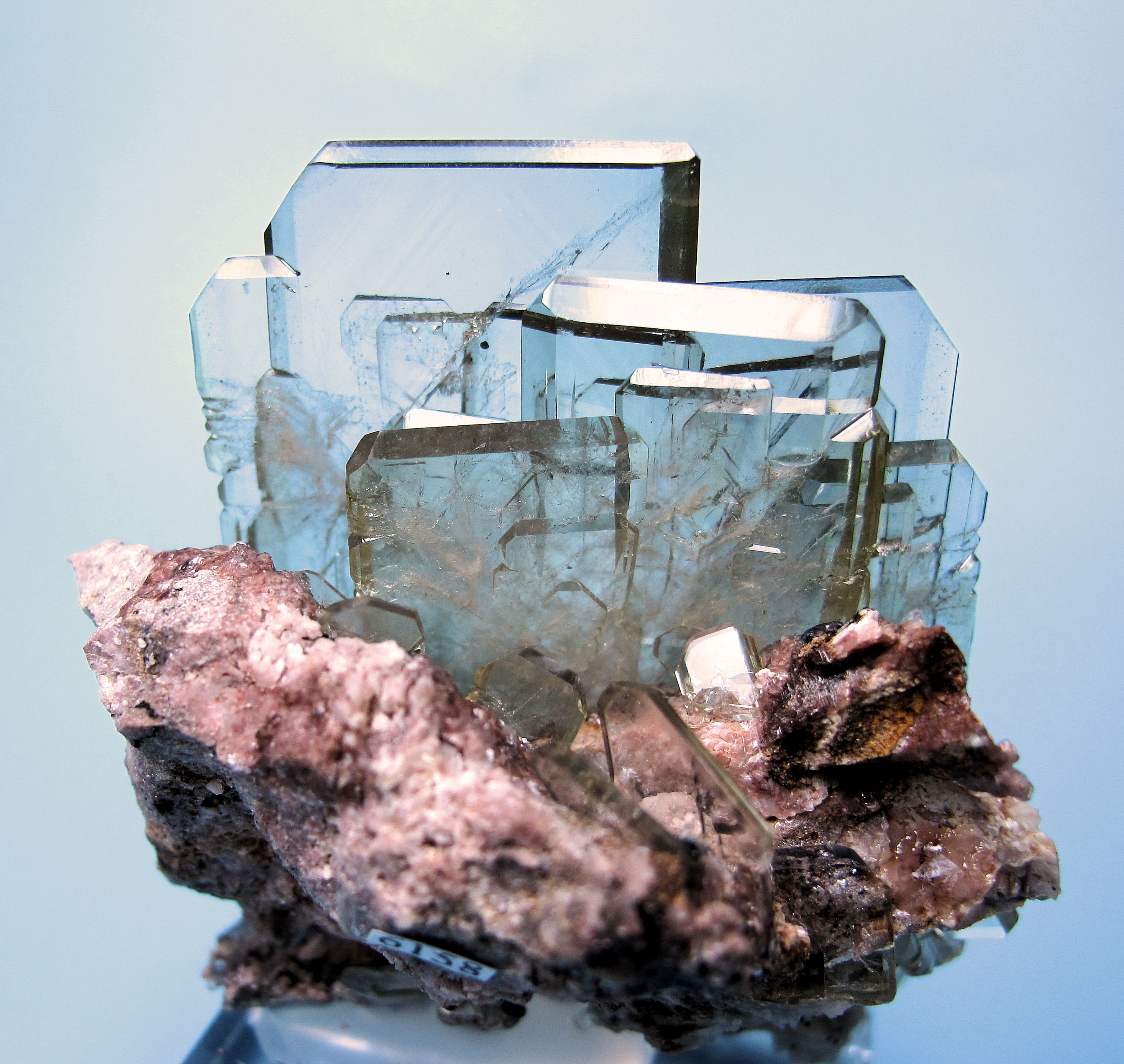
Barite
Baryte, barite or barytes ( or ) is a mineral consisting of barium sulfate (Ba S O4). Baryte is generally white or colorless, and is the main source of the element barium. The ''baryte group'' consists of baryte, celestine (strontium sulfate), anglesite (lead sulfate), and anhydrite (calcium sulfate). Baryte and celestine form a solid solution . Names and history The radiating form, sometimes referred to as ''Bologna Stone'', attained some notoriety among alchemists for specimens found in the 17th century near Bologna by Vincenzo Casciarolo. These became phosphorescent upon being calcined. Carl Scheele determined that baryte contained a new element in 1774, but could not isolate barium, only barium oxide. Johan Gottlieb Gahn also isolated barium oxide two years later in similar studies. Barium was first isolated by electrolysis of molten barium salts in 1808 by Sir Humphry Davy in England. The American Petroleum Institute specification API 13/ISO 13500, which governs '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
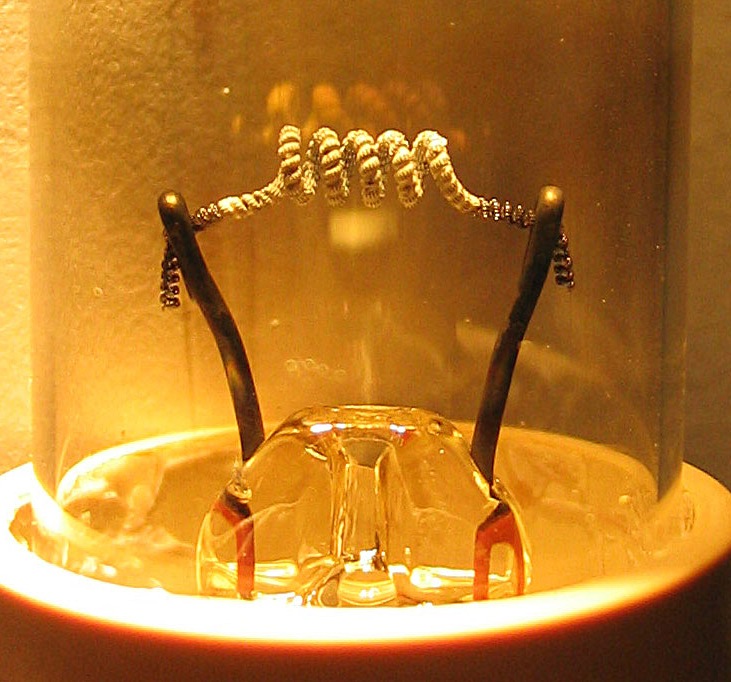
Hot Cathode
In vacuum tubes and gas-filled tubes, a hot cathode or thermionic cathode is a cathode electrode which is heated to make it emit electrons due to thermionic emission. This is in contrast to a cold cathode, which does not have a heating element. The heating element is usually an electrical filament heated by a separate electric current passing through it. Hot cathodes typically achieve much higher power density than cold cathodes, emitting significantly more electrons from the same surface area. Cold cathodes rely on field electron emission or secondary electron emission from positive ion bombardment, and do not require heating. There are two types of hot cathode. In a ''directly heated cathode'', the filament is the cathode and emits the electrons. In an ''indirectly heated cathode'', the filament or ''heater'' heats a separate metal cathode electrode which emits the electrons. From the 1920s to the 1960s, a wide variety of electronic devices used hot-cathode vacuum tubes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Witherite
Witherite is a barium carbonate mineral, Ba C O3, in the aragonite group. Witherite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system and virtually always is twinned. The mineral is colorless, milky-white, grey, pale-yellow, green, to pale-brown. The specific gravity is 4.3, which is high for a translucent mineral. It fluoresces light blue under both long- and short-wave UV light, and is phosphorescent under short-wave UV light. Witherite forms in low-temperature hydrothermal environments. It is commonly associated with fluorite, celestine, galena, barite, calcite, and aragonite. Witherite occurrences include: Cave-in-Rock, Illinois, US; Pigeon Roost Mine, Glenwood, Arkansas, US; Settlingstones Mine Northumberland; Alston Moor, Cumbria; Anglezarke, Lancashire and Burnhope, County Durham, England; Thunder Bay area, Ontario, Canada, Germany, and Poland ( Tarnowskie Góry and Tajno at Suwałki Region). Witherite was named after William Withering (1741–1799) an English physician ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |