Increasing methane emissions are a major contributor to the rising concentration of
greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth. Unlike other gases, greenhouse gases absorb the radiations that a planet emits, resulting in the greenhouse effect. T ...
es in
Earth's atmosphere, and are responsible for up to one-third of near-term
global heating.
During 2019, about 60% (360 million tons) of
methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes ...
released globally was from human activities, while natural sources contributed about 40% (230 million tons).
Reducing methane emissions by capturing and utilizing the gas can produce simultaneous environmental and economic benefits.
Since the Industrial Revolution, concentrations of
methane in the atmosphere have more than doubled, and about 20 percent of the warming the planet has experienced can be attributed to the gas. About one-third (33%) of
anthropogenic
Anthropogenic ("human" + "generating") is an adjective that may refer to:
* Anthropogeny, the study of the origins of humanity
Anthropogenic may also refer to things that have been generated by humans, as follows:
* Human impact on the enviro ...
emissions are from gas release during the
extraction and delivery of
fossil fuels
A fossil fuel is a flammable carbon compound- or hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the buried remains of prehistoric organisms (animals, plants or microplanktons), a process that occurs within geologica ...
; mostly due to
gas venting
Gas venting, more specifically known as natural-gas venting or methane venting, is the intentional and controlled release of gases containing alkane hydrocarbons - predominately methane - into Earth's atmosphere.
It is a widely used method for ...
and
gas leak
A gas leak refers to a leak of natural gas or another gaseous product from a pipeline or other containment into any area where the gas should not be present. Gas leaks can be hazardous to health as well as the environment. Even a small leak into ...
s from both active fossil fuel infrastructure and
orphan wells. Russia is the world's top methane emitter from oil and gas. The International Energy Agency (IEA) highlights that abandoned coal mines and oil and gas wells have become significant sources of methane emissions. If considered a country, these emissions would rank as the fourth-largest globally, surpassing those of Iran. The IEA estimates that addressing over 8 million abandoned onshore oil and gas sites would cost about $100 billion.
Animal agriculture is a similarly large source (30%); primarily because of
enteric fermentation by
ruminant livestock such as cattle and sheep. According to the Global Methane Assessment published in 2021, methane emissions from livestock (including cattle) are the largest sources of
agricultural emissions worldwide A single cow can make up to 99 kg of methane gas per year. Ruminant livestock can produce 250 to 500 L of methane per day.
Human consumer waste flows, especially those passing through
landfill
A landfill is a site for the disposal of waste materials. It is the oldest and most common form of waste disposal, although the systematic burial of waste with daily, intermediate and final covers only began in the 1940s. In the past, waste was ...
s and
wastewater treatment
Wastewater treatment is a process which removes and eliminates contaminants from wastewater. It thus converts it into an effluent that can be returned to the water cycle. Once back in the water cycle, the effluent creates an acceptable impact on ...
, have grown to become a third major category (18%). Plant agriculture, including both food and
biomass
Biomass is a term used in several contexts: in the context of ecology it means living organisms, and in the context of bioenergy it means matter from recently living (but now dead) organisms. In the latter context, there are variations in how ...
production, constitutes a fourth group (15%), with
rice production being the largest single contributor.
The world's
wetland
A wetland is a distinct semi-aquatic ecosystem whose groundcovers are flooded or saturated in water, either permanently, for years or decades, or only seasonally. Flooding results in oxygen-poor ( anoxic) processes taking place, especially ...
s contribute about three-quarters (75%) of the enduring natural sources of methane.
Seepages from near-surface
hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and Hydrophobe, hydrophobic; their odor is usually fain ...
and
clathrate hydrate deposits,
volcanic releases,
wildfire
A wildfire, forest fire, or a bushfire is an unplanned and uncontrolled fire in an area of Combustibility and flammability, combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire may be more specifically identified as a ...
s, and
termite
Termites are a group of detritivore, detritophagous Eusociality, eusocial cockroaches which consume a variety of Detritus, decaying plant material, generally in the form of wood, Plant litter, leaf litter, and Humus, soil humus. They are dist ...
emissions account for much of the remainder.
Contributions from the surviving wild populations of ruminant mammals are vastly overwhelmed by those of cattle, humans, and other livestock animals.
''The Economist'' recommended setting methane emissions targets as a reduction in methane emissions would allow for more time to tackle the more challenging
carbon emissions".
Atmospheric concentration and warming influence
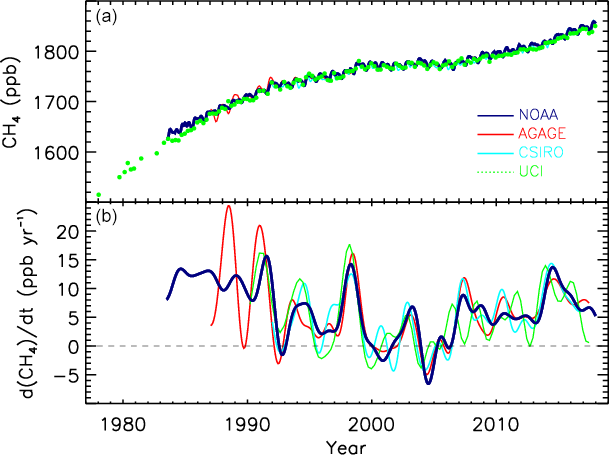
The
atmospheric methane (CH
4) concentration is increasing and exceeded 1860 parts per billion in 2019, equal to two-and-a-half times the pre-industrial level. The methane itself causes ''direct
radiative forcing'' that is second only to that of
carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
(CO
2).
Due to interactions with oxygen compounds stimulated by sunlight, CH
4 can also increase the atmospheric presence of shorter-lived
ozone
Ozone () (or trioxygen) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , break ...
and water vapour, themselves potent warming gases: atmospheric researchers call this amplification of methane's near-term warming influence ''indirect radiative forcing''. When such interactions occur, longer-lived and less-potent CO
2 is also produced. Including both the direct and indirect forcings, the increase in atmospheric methane is responsible for about one-third of near-term global heating.
Though methane causes far more heat to be trapped than the same mass of carbon dioxide, less than half of the emitted CH
4 remains in the atmosphere after a decade. On average, carbon dioxide warms for much longer, assuming no change in rates of carbon sequestration.
The
global warming potential
Global warming potential (GWP) is a measure of how much heat a greenhouse gas traps in the atmosphere over a specific time period, relative to carbon dioxide (). It is expressed as a multiple of warming caused by the same mass of carbon dioxide ( ...
(GWP) is a way of comparing the warming due to other gases to that from carbon dioxide, over a given time period. Methane's GWP
20 of 85 means that a ton of CH
4 emitted into the atmosphere creates approximately 85 times the atmospheric warming as a ton of CO
2 over a period of 20 years.
[Myhre, G., D. Shindell, F.-M. Bréon, W. Collins, J. Fuglestvedt, J. Huang, D. Koch, J.-F. Lamarque, D. Lee, B. Mendoza, T. Nakajima, A. Robock, G. Stephens, T. Takemura and H. Zhang (2013]
"Anthropogenic and Natural Radiative Forcing"
Table 8.7 on page 714. In: ''Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change''. Stocker, T.F., D. Qin, G.-K. Plattner, M. Tignor, S.K. Allen, J. Boschung, A. Nauels, Y. Xia, V. Bex and P.M. Midgley (eds.). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA
Anthropogenic and Natural Radiative Forcing
/ref> On a 100-year timescale, methane's GWP100 is in the range of 28–34.
Methane emissions are important as reducing them can buy time to tackle carbon emissions.
Overview of emission sources
Biogenic methane is actively produced by microorganisms in a process called methanogenesis. Under certain conditions, the process mix responsible for a sample of methane may be deduced from the ratio of the isotopes of carbon
Carbon (6C) has 14 known isotopes, from to as well as , of which only and are stable. The longest-lived radioisotope is , with a half-life of years. This is also the only carbon radioisotope found in nature, as trace quantities are formed ...
, and through analysis methods similar to carbon dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon.
The method was ...
.
Anthropogenic
 , emission volumes from some sources remain more uncertain than others; due in part to localized emission spikes not captured by the limited global measurement capability. The time required for a methane emission to become well-mixed throughout earth's
, emission volumes from some sources remain more uncertain than others; due in part to localized emission spikes not captured by the limited global measurement capability. The time required for a methane emission to become well-mixed throughout earth's troposphere
The troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere of Earth. It contains 80% of the total mass of the Atmosphere, planetary atmosphere and 99% of the total mass of water vapor and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. From the ...
is about 1–2 years.
Satellite data indicate over 80% of the growth of methane emissions during 2010–2019 are tropical terrestrial emissions.
There is accumulating research and data showing that oil and gas industry methane emissions – or from fossil fuel extraction, distribution and use – are much larger than thought.
Natural
 Natural sources have always been a part of the methane cycle. Wetland emissions have been declining due to draining for agricultural and building areas.
Natural sources have always been a part of the methane cycle. Wetland emissions have been declining due to draining for agricultural and building areas.
Methanogenesis
Most ecological emissions of methane relate directly to methanogens generating methane in warm, moist soils as well as in the digestive tracts of certain animals. Methanogens are methane producing microorganisms. In order to produce energy, they use an anaerobic process called methanogenesis. This process is used in lieu of aerobic, or with oxygen, processes because methanogens are unable to metabolise in the presence of even small concentrations of oxygen. When acetate is broken down in methanogenesis, the result is the release of methane into the surrounding environment.
'' Methanogenesis'', the scientific term for methane production, occurs primarily in anaerobic conditions because of the lack of availability of other oxidants. In these conditions, microscopic organisms called archaea
Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even thou ...
use acetate and hydrogen to break down essential resources in a process called fermentation
Fermentation is a type of anaerobic metabolism which harnesses the redox potential of the reactants to make adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and organic end products. Organic molecules, such as glucose or other sugars, are catabolized and reduce ...
.
''Acetoclastic methanogenesis'' – certain archaea cleave acetate
An acetate is a salt formed by the combination of acetic acid with a base (e.g. alkaline, earthy, metallic, nonmetallic, or radical base). "Acetate" also describes the conjugate base or ion (specifically, the negatively charged ion called ...
produced during anaerobic fermentation to yield methane and carbon dioxide.
: H3C-COOH → CH4 + CO2
''Hydrogenotrophic methanogenesis'' – archaea oxidize hydrogen with carbon dioxide to yield methane and water.
: 4H2 + CO2 → CH4 + 2H2O
While acetoclastic methanogenesis and hydrogenotrophic methanogenesis are the two major source reactions for atmospheric methane, other minor biological methane source reactions also occur. For example, it has been discovered that leaf surface wax exposed to UV radiation in the presence of oxygen is an aerobic source of methane.
Natural methane cycles
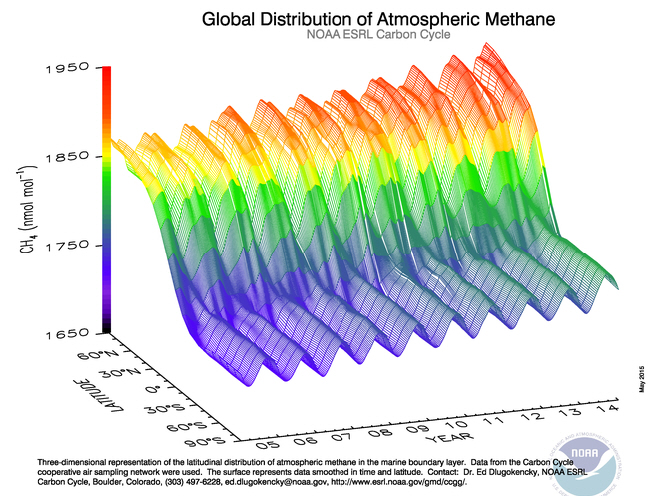 Its concentration is higher in the
Its concentration is higher in the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined by humans as being in the same celestial sphere, celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the Solar ...
since most sources (both natural and human) are located on land and the Northern Hemisphere has more land mass.
Wetlands
In wetlands, where the rate of methane production is high, plants help methane travel into the atmosphere—acting like inverted lightning rods as they direct the gas up through the soil and into the air. They are also suspected to produce methane themselves, but because the plants would have to use aerobic conditions to produce methane, the process itself is still unidentified, according to a 2014 ''Biogeochemistry'' article.
Human-caused methane emissions
The AR6 of the IPCC
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is an intergovernmental body of the United Nations. Its job is to "provide governments at all levels with scientific information that they can use to develop climate policies". The World M ...
said, "It is unequivocal that the increases in atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O) since the pre-industrial period are overwhelmingly caused by human activities."United Nations Environment Programme
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is responsible for coordinating responses to environmental issues within the United Nations system. It was established by Maurice Strong, its first director, after the Declaration of the United Nati ...
(UNEP) over 50% of global methane emissions are caused by human activities in fossil fuels
A fossil fuel is a flammable carbon compound- or hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the buried remains of prehistoric organisms (animals, plants or microplanktons), a process that occurs within geologica ...
(35%), waste (20%), and agriculture (40%). The oil and gas industry accounts for 23%, and coal mining for 12%. Twenty percent of global anthropogenic emissions stem from landfills and wastewater. Manure and enteric fermentation represent 32%, and rice cultivation represents 8%.
Emissions due to oil and gas extraction
A 2005 Wuppertal Institute for Climate, Environment and Energy article identified pipelines that transport natural gas as a source of methane emissions. The article cited the example of Trans-Siberian natural gas pipeline system to western and Central Europe from the Yamburg and Urengoy exist gas fields in Russia with a methane concentration of 97%.Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
humans have had a major impact on concentrations of atmospheric methane, increasing atmospheric concentrations roughly 250%.climate change mitigation
Climate change mitigation (or decarbonisation) is action to limit the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere that cause climate change. Climate change mitigation actions include energy conservation, conserving energy and Fossil fuel phase-out, repl ...
. An alliance of 107 countries, including Brazil, the EU and the US, have joined the pact known as the Global Methane Pledge, committing to a collective goal of reducing global methane emissions by at least 30% from 2020 levels by 2030.
The European Union adopted methane regulations in 2024. The law requires oil and gas developers to monitor, measure, and report methane emissions. Producers must stop flaring unused natural gas and use satellite imagery to detect leaks.
Animals and livestock
Ruminant
Ruminants are herbivorous grazing or browsing artiodactyls belonging to the suborder Ruminantia that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally through microb ...
animals, particularly cows and sheep, contain bacteria in their gastrointestinal
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascular system. ...
systems that help to break down plant material. Some of these microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic scale, microscopic size, which may exist in its unicellular organism, single-celled form or as a Colony (biology)#Microbial colonies, colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen ...
s use the acetate from the plant material to produce methane, and because these bacteria live in the stomachs and intestines of ruminants, whenever the animal "burps" or defecates, it emits methane as well. Based upon a 2012 study in the Snowy Mountains region, the amount of methane emitted by one cow is equivalent to the amount of methane that around 3.4 hectares of methanotrophic bacteria can consume.Termite
Termites are a group of detritivore, detritophagous Eusociality, eusocial cockroaches which consume a variety of Detritus, decaying plant material, generally in the form of wood, Plant litter, leaf litter, and Humus, soil humus. They are dist ...
s also contain methanogenic microorganisms in their gut. However, some of these microorganisms are so unique that they live nowhere else in the world except in the third gut of termites. These microorganisms also break down biotic components to produce ethanol
Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with its formula also written as , or EtOH, where Et is the ps ...
, as well as methane byproduct. However, unlike ruminants who lose 20% of the energy from the plants they eat, termites only lose 2% of their energy in the process.NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
researchers confirmed the vital role of enteric fermentation in livestock on global warming.nitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide (dinitrogen oxide or dinitrogen monoxide), commonly known as laughing gas, nitrous, or factitious air, among others, is a chemical compound, an Nitrogen oxide, oxide of nitrogen with the Chemical formula, formula . At room te ...
and 37% of anthropogenic methane. Since then, animal science and biotechnology researchers have focused research on methanogens in the rumen
The rumen, also known as a paunch, is the largest stomach compartment in ruminants. The rumen and the reticulum make up the reticulorumen in ruminant animals. The diverse microbial communities in the rumen allows it to serve as the primary si ...
of livestock and mitigation of methane emissions.
Nicholas Stern, the author of the 2006 '' Stern Review'' on climate change has stated "people will need to turn vegetarian if the world is to conquer climate change". In 2003, the National Academy of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, NGO, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the ...
's president, Ralph Ciceronean atmospheric scientistraised concerns about the increase in the number of methane-producing dairy and beef cattle was a "serious topic" as methane was the "second-most-important greenhouse gas in the atmosphere".
Approximately 5% of the methane is released via the flatus, whereas the other 95% is released via eructation. Vaccines are under development to reduce the amount introduced through eructation. Asparagopsis seaweed as a livestock feed additive has reduced methane emissions by more than 80%.
Waste
Landfills
Due to the large collections of organic matter and availability of anaerobic conditions, landfills are the third largest source of atmospheric methane in the United States, accounting for roughly 18.2% of methane emissions globally in 2014. When waste is first added to a landfill, oxygen is abundant and thus undergoes aerobic decomposition; during which time very little methane is produced. However, generally within a year oxygen levels are depleted and anaerobic conditions dominate the landfill allowing methanogens to takeover the decomposition process. These methanogens emit methane into the atmosphere and even after the landfill is closed, the mass amount of decaying matter allows the methanogens to continue producing methane for years.
Waste water treatment
Waste water treatment facilities act to remove organic matter, solids, pathogens, and chemical hazards as a result of human contamination. Methane emission in waste treatment facilities occurs as a result of anaerobic treatments of organic compounds and anaerobic biodegradation
Biodegradation is the breakdown of organic matter by microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. It is generally assumed to be a natural process, which differentiates it from composting. Composting is a human-driven process in which biodegrada ...
of sludge.
Release of stored methane from the Arctic


Others
Aquatic ecosystems
Natural and anthropogenic methane emissions from aquatic ecosystem
An aquatic ecosystem is an ecosystem found in and around a body of water, in contrast to land-based terrestrial ecosystems. Aquatic ecosystems contain communities of organisms—aquatic life—that are dependent on each other and on their environ ...
s are estimated to contribute about half of total global emissions.Urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation in British English) is the population shift from Rural area, rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. ...
and eutrophication
Eutrophication is a general term describing a process in which nutrients accumulate in a body of water, resulting in an increased growth of organisms that may deplete the oxygen in the water; ie. the process of too many plants growing on the s ...
are expected to lead to increased methane emissions from aquatic ecosystems.
Ecological conversion
Conversion of forests and natural environments into agricultural plots increases the amount of nitrogen in the soil, which inhibits methane oxidation, weakening the ability of the methanotrophic bacteria in the soil to act as sinks.
Rice agriculture
Rice agriculture is a significant source of methane. With warm weather and water-logged soil, rice paddies act like wetlands, but are generated by humans for the purpose of food production. Due to the swamp-like environment of rice fields, these paddies emitted about 30 of the 400 million metric tons of anthropogenic methane in 2022.
Biomass burning
Incomplete burning of both living and dead organic matter results in the emission of methane. While natural wildfires can contribute to methane emissions, the bulk majority of biomass burning occurs as a result of humans – including everything from accidental burnings by civilians to deliberate burnings used to clear out land to biomass burnings occurring as a result of destroying waste.
Oil and natural gas supply chain
Methane is a primary component of natural gas
Natural gas (also fossil gas, methane gas, and gas) is a naturally occurring compound of gaseous hydrocarbons, primarily methane (95%), small amounts of higher alkanes, and traces of carbon dioxide and nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide and helium ...
, and thus during the production, processing, storage, transmission, and distribution of natural gas, a significant amount of methane is lost into the atmosphere.
Coal mining
In 2014 NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
researchers reported the discovery of a methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes ...
cloud floating over the Four Corners region of the south-west United States. The discovery was based on data from the European Space Agency
The European Space Agency (ESA) is a 23-member International organization, international organization devoted to space exploration. With its headquarters in Paris and a staff of around 2,547 people globally as of 2023, ESA was founded in 1975 ...
's Scanning Imaging Absorption Spectrometer for Atmospheric Chartography instrument from 2002 to 2012.European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
's Emissions Database for Global Atmospheric Research.
Methane gas from methane clathrates
At high pressures, such as are found on the bottom of the ocean, methane forms a solid clathrate
A clathrate is a chemical substance consisting of a lattice (group), lattice that traps or contains molecules. The word ''clathrate'' is derived from the Latin language, Latin (), meaning 'with bars, Crystal structure, latticed'. Most clathrate ...
with water, known as methane hydrate. An unknown, but possibly very large quantity of methane is trapped in this form in ocean sediments. Researchers are investigating possible changes in this process ( clathrate gun hypothesis).
However, the 2021 IPCC Sixth Assessment Report
The Sixth Assessment Report (AR6) of the United Nations (UN) Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is the sixth in a series of reports which assess the available scientific information on climate change. Three Working Groups (WGI, II, ...
found that it was "very unlikely that gas clathrates (mostly methane) in deeper terrestrial permafrost and subsea clathrates will lead to a detectable departure from the emissions trajectory during this century".
Methane slip from gas engines
The use of natural gas and biogas
Biogas is a gaseous renewable energy source produced from raw materials such as agricultural waste, manure, municipal waste, plant material, sewage, green waste, Wastewater treatment, wastewater, and food waste. Biogas is produced by anaerobic ...
in internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal comb ...
s for such applications as electricity production, cogeneration and heavy vehicles or marine vessels such as LNG carrier
An LNG carrier is a tank ship designed for transporting liquefied natural gas (LNG).
Overview
The first oceangoing liquified natural gas tanker in the world was '' Methane Pioneer'', which entered service in 1959 with a carrying capacity of ...
s using the boil off gas for propulsion, emits a certain percentage of unburned hydrocarbons of which 85% is methane. The climate issues of using gas to fuel internal combustion engines may offset or even cancel out the advantages of less CO2 and particle emissions is described in thi
2016 EU Issue Paper on methane slip from marine engines
"Emissions of unburnt methane (known as the 'methane slip') were around 7 g per kg LNG at higher engine loads, rising to 23–36 g at lower loads. This increase could be due to slow combustion at lower temperatures, which allows small quantities of gas to avoid the combustion process". Road vehicles run more on low load than marine engines causing relatively higher methane slip.
Global methane emissions monitoring
 The Tropospheric Monitoring Instrument aboard the
The Tropospheric Monitoring Instrument aboard the European Space Agency
The European Space Agency (ESA) is a 23-member International organization, international organization devoted to space exploration. With its headquarters in Paris and a staff of around 2,547 people globally as of 2023, ESA was founded in 1975 ...
's Sentinel-5P spacecraft launched in October 2017 provides the most detailed methane emissions monitoring which is publicly available. It has a resolution of about 50 square kilometres.Harvard University
Harvard University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the History of the Puritans in North America, Puritan clergyma ...
, to monitor methane emissions with an improved resolution of 1 kilometer. MethaneSAT is designed to monitor 50 major oil and gas facilities, and could also be used for monitoring of landfills and agriculture. It receives funding from Audacious Project (a collaboration of TED and the Gates Foundation), and is projected to launch as soon as 2024.
GHGSat
for monitoring methane emissions.European Space Agency
The European Space Agency (ESA) is a 23-member International organization, international organization devoted to space exploration. With its headquarters in Paris and a staff of around 2,547 people globally as of 2023, ESA was founded in 1975 ...
can measure methane, sulphur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, carbon monoxide, aerosol, and ozone concentrations in earth's troposphere
The troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere of Earth. It contains 80% of the total mass of the Atmosphere, planetary atmosphere and 99% of the total mass of water vapor and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. From the ...
at resolutions of several kilometers.
CarbonMapper
Global maps combining satellite data to help identify and monitor major methane emission sources are being built.
The International Methane Emissions Observatory was created by the UN.
Quantifying the global methane budget
In order to mitigate climate change, scientists have been focusing on quantifying the global methane CH4 budget as the concentration of methane continues to increase—it is now second after carbon dioxide in terms of climate forcing.methane emissions
Increasing methane emissions are a major contributor to the rising concentration of greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere, and are responsible for up to one-third of near-term global heating. During 2019, about 60% (360 million tons) of methane r ...
:
National reduction policies
China implemented regulations requiring coal plants to either capture methane emissions or convert methane into in 2010. According to a Nature Communications
''Nature Communications'' is a peer-reviewed, open access, scientific journal published by Nature Portfolio since 2010. It is a multidisciplinary journal that covers the natural sciences, including physics, chemistry, earth sciences, medic ...
paper published in January 2019, methane emissions instead increased 50 percent between 2000 and 2015.
In March 2020, Exxon called for stricter methane regulations, which would include detection and repair of methane leaks, minimization of venting and releases of unburned methane, and reporting requirements for companies. However, in August 2020, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency rescinded a prior tightening of methane emission rules for the U.S. oil and gas industry.
Approaches to reduce emissions
Natural gas industries
About 40% of methane emissions from the fossil fuel industry could be "eliminated at no net cost for firms", according to the International Energy Agency
The International Energy Agency (IEA) is a Paris-based autonomous intergovernmental organization, established in 1974, that provides policy recommendations, analysis and data on the global energy sector. The 31 member countries and 13 associatio ...
(IEA) by using existing technologies.methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes ...
that would otherwise be released from the coal mine into the atmosphere.
Livestock
In order to counteract the amount of methane that ruminants give off, a type of drug called monensin (marketed as rumensin) has been developed. This drug is classified as an ionophore, which is an antibiotic that is naturally produced by a harmless bacteria strain. This drug not only improves feed efficiency but also reduces the amount of methane gas emitted from the animal and its manure.
Landfills
To counteract methane emissions from landfills, on March 12, 1996, the EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) added the "Landfill Rule" to the Clean Air Act. This rule requires large landfills that have ever accepted municipal solid waste
Municipal solid waste (MSW), commonly known as trash or garbage in the American English, United States and rubbish in British English, Britain, is a List of waste types, waste type consisting of everyday items that are discarded by the public. ...
, have been used as of November 8, 1987, can hold at least 2.5 million metric tons of waste with a volume greater than 2.5 million cubic meters, and/or have nonmethane organic compound (NMOC) emissions of at least 50 metric tons per year to collect and combust emitted landfill gas.
See also
*
*
*
*
*
*
Notes
References
External links
*
* {{cite web , title=Greenhouse Gas Emissions - Methane Emissions , website= EIA , date=2011-03-31 , url=https://www.eia.gov/environment/emissions/ghg_report/ghg_methane.php , ref={{sfnref , EIA , 2011 , access-date=2018-03-06
Greenhouse gas emissions
Methane
 The atmospheric methane (CH4) concentration is increasing and exceeded 1860 parts per billion in 2019, equal to two-and-a-half times the pre-industrial level. The methane itself causes ''direct radiative forcing'' that is second only to that of
The atmospheric methane (CH4) concentration is increasing and exceeded 1860 parts per billion in 2019, equal to two-and-a-half times the pre-industrial level. The methane itself causes ''direct radiative forcing'' that is second only to that of  , emission volumes from some sources remain more uncertain than others; due in part to localized emission spikes not captured by the limited global measurement capability. The time required for a methane emission to become well-mixed throughout earth's
, emission volumes from some sources remain more uncertain than others; due in part to localized emission spikes not captured by the limited global measurement capability. The time required for a methane emission to become well-mixed throughout earth's  Natural sources have always been a part of the methane cycle. Wetland emissions have been declining due to draining for agricultural and building areas.
Natural sources have always been a part of the methane cycle. Wetland emissions have been declining due to draining for agricultural and building areas.
 Its concentration is higher in the
Its concentration is higher in the 

 The Tropospheric Monitoring Instrument aboard the
The Tropospheric Monitoring Instrument aboard the