|
Kingisepp
Kingisepp ( or ), formerly Yamburg (), Yam (), and Yama (; Votic language, Votic: Jaama), is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, town and the administrative center of Kingiseppsky District of Leningrad Oblast, Russia, located along the Luga River southwest of Saint Petersburg, St. Petersburg, east of Narva, and south of the Gulf of Finland. Population: History 14th century The town was first documented in 1384, when the Novgorod Republic, Novgorodians under Patrikas built there a Yam fortress, fortress against the Swedes. It was called Yama or Yamsky Gorodok, after the Izhorians, Izhorian (ethnic Baltic Finns, Finnic group) name Jaama. The environs of the town are still cited as the main location of speakers of the nearly extinct Ingrian language, Izhorian language. The citadel withstood sieges by the Swedes in 1395 and by the Teutonic Knights during the 1444–1448 war. 15-16th century The town became the most important economic center of the of the Novgor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingiseppsky District
Kingiseppsky District (, ) is an administrativeOblast Law #32-oz and municipalLaw #81-oz district (raion), one of the administrative divisions of Leningrad Oblast, seventeen in Leningrad Oblast, Russia. It is located in the southwest of the oblast and borders with Ida-Viru County of Estonia in the west, Lomonosovsky District, Leningrad Oblast, Lomonosovsky District in the northeast, Volosovsky District in the east, and with Slantsevsky District in the south. In the north and northwest it is washed by the waters of the Gulf of Finland. The area of the district is .Official website of Kingiseppsky District Its administrative center is the types of inhabited localities in Russia, town of Kingisepp. Population (excluding the administrative center): 20,408 (Russian Census (2002), 2002 Census); [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yam Fortress
Yam (Yama, Yamgorod, ) is a fortification, fortress and heritage site located on the eastern bank of the Luga (river), Luga river in Kingisepp, Leningrad Oblast, Russia. The fortress was built in 1384 by Ivan Fyodorovich, a boyar (noble) of the Novgorod republic, to protect the republic’s western borders. Thanks to it, Yam remained unconquered from the 14th to 15th centuries. The fortress was completely rebuilt after the Novgorod Republic was incorporated into the Grand Duchy of Moscow. Following the construction of Ivangorod Fortress, Yam Fortress lost its military significance. Between the end of the 16th century and the beginning of the 17th century, Yam Fortress was captured twice by the Swedish army, and the fortress was awarded to Sweden in 1612 by the Treaty of Stolbovo. Russians stormed the fortress in 1658 and captured most of it, however the Swedish garrison held out in the Detinets. Subsequently, the Swedish army demolished most of the fortress (except for the Det ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luga River
The Luga () is a river in Novgorodsky and Batetsky Districts of Novgorod Oblast and Luzhsky, Volosovsky, Slantsevsky, and Kingiseppsky Districts of Leningrad Oblast of Russia. The river flows into the Luga Bay of the Gulf of Finland. It freezes up in the early December and stays under the ice until early April. The length of the Luga is , and the area of its drainage basin is . Its main tributary is the Oredezh (right). The towns of Luga and Kingisepp, as well as the urban-type settlement of Tolmachyovo are located on the banks of the Luga. The mouth of the Luga is the site of the Ust-Luga container terminal. The source of the Luga is located in a peat production area in the northwest of Novgorod Oblast, several dozen kilometers northwest of the city of Veliky Novgorod. The river flows south, crosses into Batetsky District, and gradually turns west. A stretch of the Luga serves the border between Novgorod and Leningrad Oblasts. There, the Luga flows northwest, in the town ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leningrad Oblast
Leningrad Oblast (, ; ; ) is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast). The oblast has an area of and a population of 2,000,997 (2021 Russian census, 2021 Census); up from 1,716,868 recorded in the 2010 Russian census, 2010 Census. Leningrad Oblast is highly industrialized. Its administrative center and largest city is Gatchina. The oblast was established on 1 August 1927, although it was not until 1946 that the oblast's borders had been mostly settled in their present position. The oblast was named after the city of Saint Petersburg, Leningrad. In 1991, the city restored its original name, Saint Petersburg, but the oblast retains the name of Leningrad. It overlaps the historical region of Ingria, and is bordered by Finland (Kymenlaakso and South Karelia) in the northwest and Estonia (Ida-Viru County) in the west, as well as five federal subjects of Russia: the Republic of Karelia in the northeast, Vologda Oblast in the east, Novgorod Oblast in the sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Finland
The Gulf of Finland (; ; ; ) is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland to the north and Estonia to the south, to Saint Petersburg—the second largest city of Russia—to the east, where the river Neva drains into it. Other major cities around the gulf include Helsinki and Tallinn. The eastern parts of the gulf belong to Russia, and some of Russia's most important oil harbors are located there, including Primorsk, Leningrad Oblast, Primorsk. As the seaway to Saint Petersburg, the gulf is of considerable strategic importance to Russia. Some of the Baltic Sea#Environmental status, environmental problems affecting the Baltic Sea are at their most pronounced in the shallow gulf. Proposals for an undersea tunnel, undersea Helsinki–Tallinn Tunnel through the gulf have been made. Geography The Gulf of Finland has an area of . The length (from the Hanko Peninsula to Saint Petersburg) is and the width varies from near the entrance to on the meridian of Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
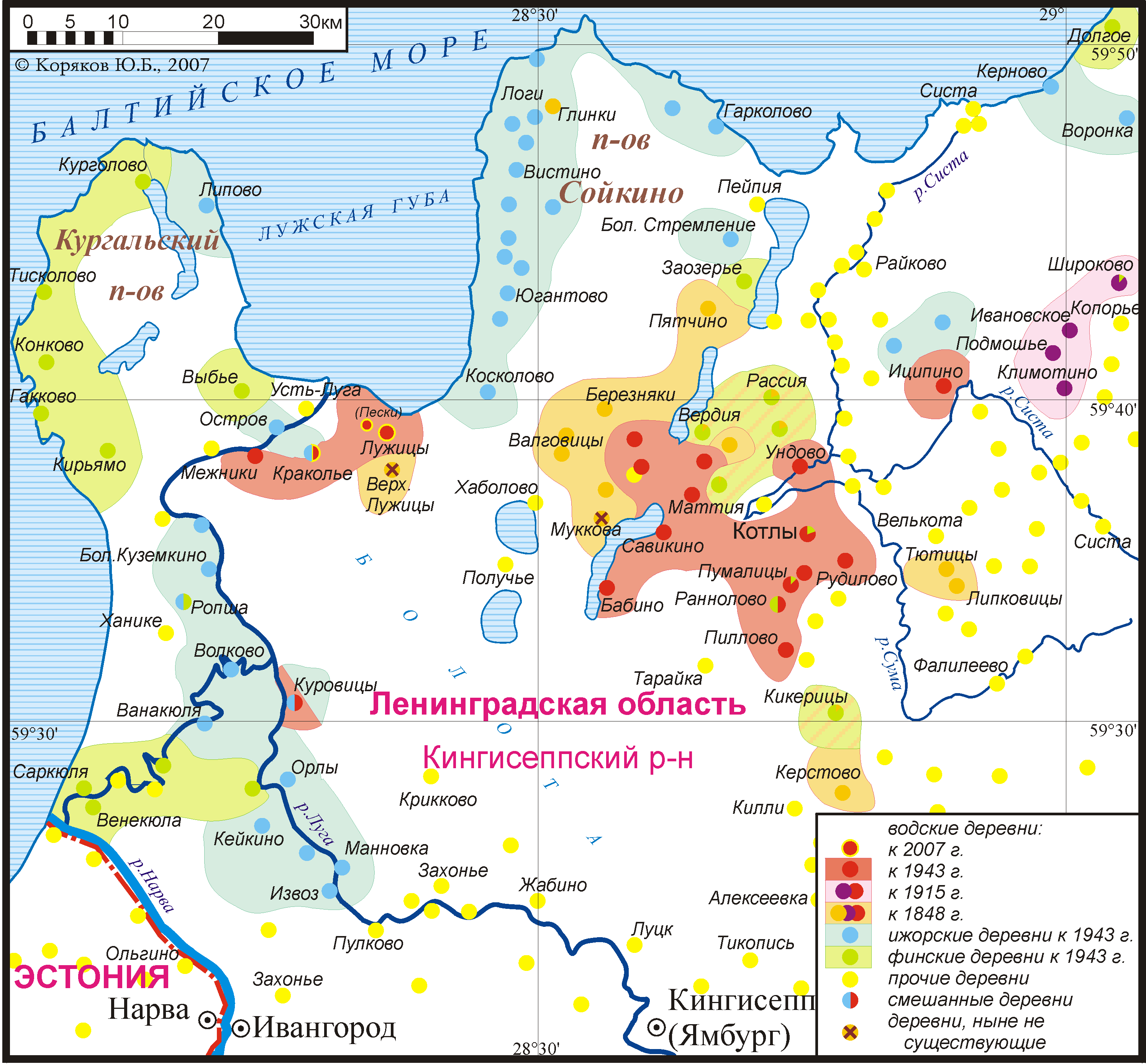
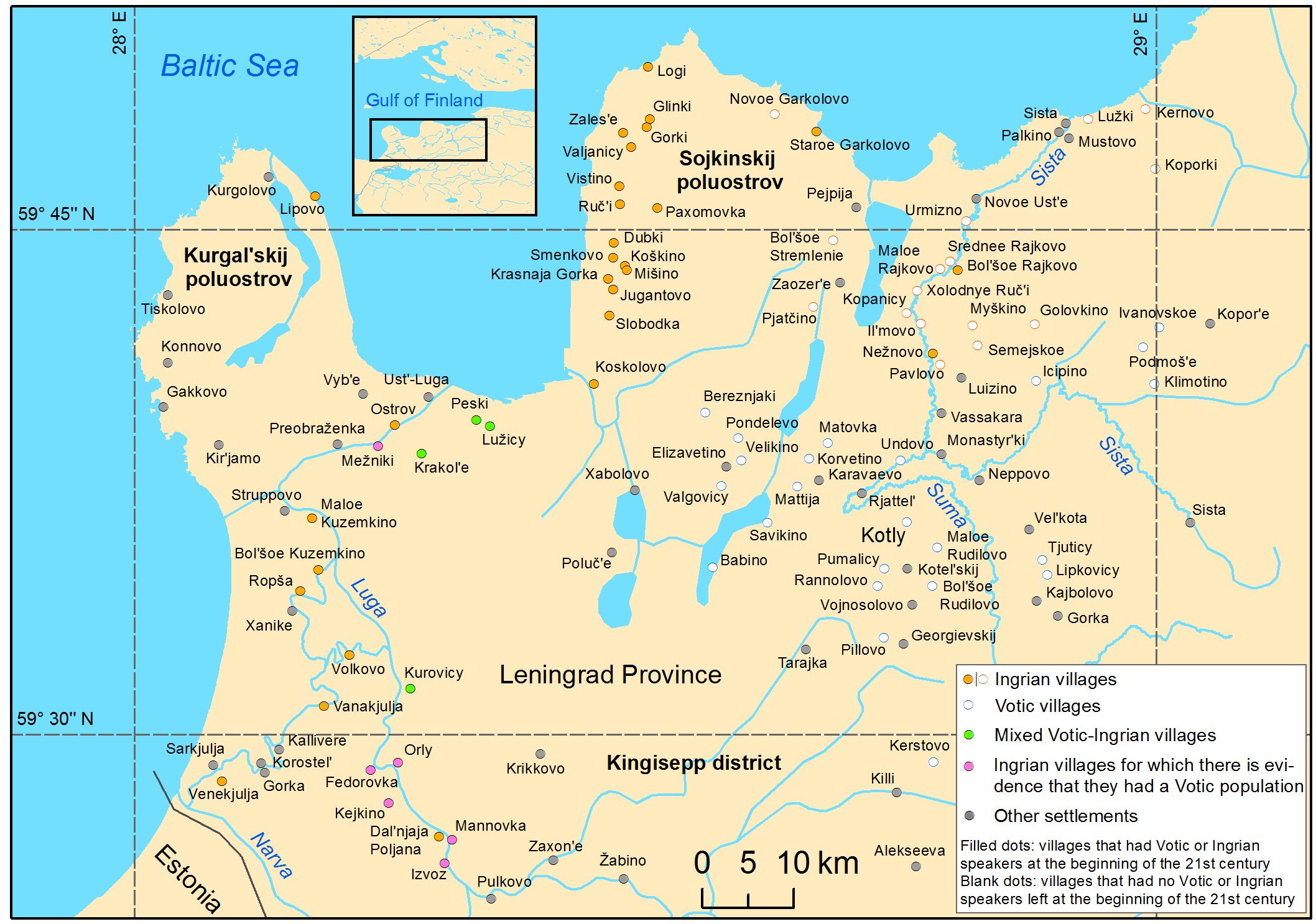
Ingria
Ingria (; ; ; ) is a historical region including, and adjacent to, what is now the city of Saint Petersburg in northwestern Russia. The region lies along the southeastern shore of the Gulf of Finland, bordered by Lake Ladoga on the Karelian Isthmus in the north and by the Narva river on the current international border with Estonia in the west. The earliest known inhabitants of the region were indigenous Finnic peoples, primarily the ancestors of modern Izhorians and Votians, who converted to Eastern Orthodox Christianity during the late Middle Ages. They were later joined by the Ingrian Finns, descendants of 17th century Lutheran Finnish immigrants. At that time, Ingria, the Karelian Isthmus, Estonia, and what is now Finland were all part of the Kingdom of Sweden. Ingria as a whole never formed a separate state; however, North Ingria was an independent state for just under two years in 1919–1920. The inhabitants of Ingria cannot be said to have comprised a distinct n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Izhorians
The Izhorians (; ; ; ) are a Finnic indigenous people native to Ingria. Small numbers can still be found in the western part of Ingria, between the Narva and Neva rivers in northwestern Russia. They are also referred to as Ingrians, although the term can also refer to the Ingrian Finns or the Baltic Finnic residents of Ingria in general. History The history of the Izhorians is bound to the history of Ingria. It is supposed that shortly after 1000 AD the Izhorians moved from Karelia to the west and south-west. In 1478, the Novgorod Republic, where Ingrians had settled, was united with the Grand Duchy of Moscow, and some of the Izhorians were transferred to the east. The establishment of St Petersburg in 1703 had a great influence on Izhorian culture. World War II had the biggest impact on Izhorians, as devastating battles (such as the Siege of Leningrad) took place on their territory. In 1848, P. von Köppen counted 17,800 Izhorians, and by 1926 there were 26,137 Izhorians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patrikas
Patrikey Glebovich or Patrikas Narimantaitis (, Finnish: ''Patrika Narimantinpoika'') was a grandson (or great-grandson) of Gediminas who exchanged his lands in and near Starodub in Siveria for the Korela and Oreshek fortresses in the Novgorod Republic. He also founded the town of Yamskaya krepost (Yamburg) (now Kingisepp) near Pskov. His male line descendants include the Golitsyn, Kurakin, and princely houses of Russia. Life Patrikas was born sometime around 1340 and died after 1408, which is the last time he is mentioned in any source. Genealogical literature usually reports that his mother was a khatun from Crimea. An 18th-century author claims that her father was khan Tokhta, Batu Khan's great-grandson, and her mother was Maria Palaiologina, a bastard daughter of Andronikos II Palaiologos. Patrikas' wife was named Helena (see ES by Schwennicke; and Ikonnikov). In 19th century genealogical literature about him there has arisen a controversy as to who was Patrikas' father ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Votic Language
Votic or Votian (, ) , is a Finnic language spoken by the Vots of Ingria, belonging to the Finnic branch of the Uralic languages. Votic is spoken only in Krakolye (now part of Ust-Luga) and Luzhitsy, two villages in Kingiseppsky District in Leningrad Oblast, Russia. In the 2020–2021 Russian census, 21 people claimed to speak Votic natively, which is an increase from 4 in 2010. Arvo Survo also estimated that around 100 people have knowledge of the language to some degree. History Votic is one of numerous Finnic varieties known from Ingria. Votic shares some similarities with and has acquired loanwords from the adjacent Ingrian language, but also has deep-reaching similarities with Estonian to the west, which is considered its closest relative. Some linguists, including Tiit-Rein Viitso and Paul Alvre, have claimed that Votic evolved specifically from northeastern dialects of ancient Estonian. Votic regardless exhibits several features that indicate its distinction from Es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ingrian Language
Ingrian (, ), also called Izhorian (, , ), is a Finnic language spoken by the (mainly Orthodox) Izhorians of Ingria. It has approximately 70 native speakers left, most of whom are elderly. The Ingrian language should be distinguished from the Ingrian dialect of the Finnish language, which became the majority language of Ingria in the 17th century with the influx of Lutheran Finnish immigrants; their descendants, the Ingrian Finns, are often referred to as Ingrians. The immigration of Lutheran Finns was promoted by Swedish authorities, who gained the area in 1617 from Russia, as the local population was (and remained) Orthodox. Dialects Four dialect groups of Ingrian have been attested, two of which are probably extinct by now: * Hevaha, spoken along Kovashi River and nearby coastal areas (†) * Soikkola, spoken on Soikinsky Peninsula and along Sista River * Ylä-Laukaa (Upper Luga or Oredezhi), spoken along Oredezh River and the upper Luga River (†) * Ala-Laukaa (Lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livonian War
The Livonian War (1558–1583) concerned control of Terra Mariana, Old Livonia (in the territory of present-day Estonia and Latvia). The Tsardom of Russia faced a varying coalition of the Denmark–Norway, Dano-Norwegian Realm, the Kingdom of Sweden (1523–1611), Kingdom of Sweden, and the Polish–Lithuanian union, Union (later Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Commonwealth) of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569), Kingdom of Poland. From 1558 to 1578, Russia dominated the region with early military successes at Tartu, Dorpat (Tartu) and Narva. The Russian dissolution of the Livonian Confederation brought Poland–Lithuania into the conflict, and Sweden and Denmark-Norway intervened between 1559 and 1561. Swedish Estonia was established despite constant invasion from Russia, and Frederick II of Denmark, Frederick II of Denmark-Norway bought the old Bishopric of Ösel–Wiek, which he placed under the control of his brother Magnus of Holstein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narva
Narva is a municipality and city in Estonia. It is located in the Ida-Viru County, at the Extreme points of Estonia, eastern extreme point of Estonia, on the west bank of the Narva (river), Narva river which forms the Estonia–Russia border, Estonia–Russia international border. As of January 1, 2025, the population of Narva, Estonia, was approximately 52,495, according to data compiled by national statistical bureaus in the Baltic region (source). Narva is Estonia's third largest city after capital Tallinn and Tartu. Narva was nearly completely destroyed in 1944 during World War II. During the Soviet era of Estonia in 1944–1991, the city's original inhabitants were not permitted to return, and immigrant workers from Soviet Russia and other parts of the former Soviet Union (USSR) were introduced. Narva’s population, 65% ethnic Estonian as of the 1934 census, became overwhelmingly non-Estonian in the second half of the 20th century. According to more recent data, 46.7% of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |