|
International Methane Emissions Observatory
The International Methane Emissions Observatory (IMEO) of the UN Environment Programme is an initiative which tackles the problem of methane emissions by collecting, integrating, and reconciling methane data from different sources, including scientific measurement studies, satellites, industry reporting through the Oil and Gas Methane Partnership 2.0, and national inventories. It was presented by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) at the G20 Leaders' Summit in 2021. IMEO creates a public global dataset of empirically verified methane emissions, with an initial focus on fossil fuel sources, and interconnects this data with actions on research, reporting, and regulation. Manfredi Caltagirone is the Head of IMEO since its creation. IMEO serves as an implementing vehicle for the Global Methane Pledge and has the European Commission as one of its founding members. Methane emissions Methane is an important greenhouse gas, and its atmospheric concentration has nearly tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methane Emissions
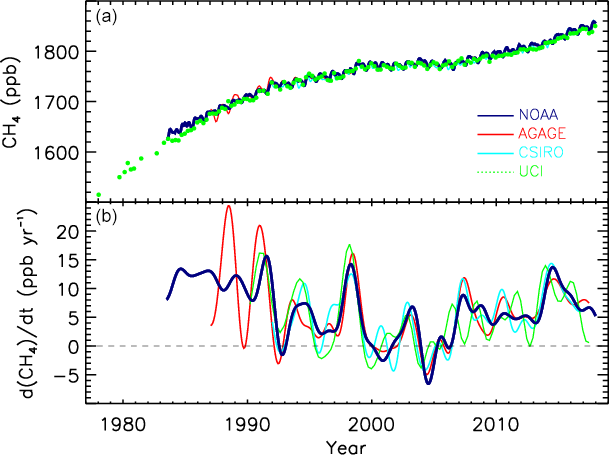
Increasing methane emissions are a major contributor to the rising concentration of greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere, and are responsible for up to one-third of near-term global heating. During 2019, about 60% (360 million tons) of methane released globally was from human activities, while natural sources contributed about 40% (230 million tons). Reducing methane emissions by capturing and utilizing the gas can produce simultaneous environmental and economic benefits. Since the Industrial Revolution, concentrations of Atmospheric methane, methane in the atmosphere have more than doubled, and about 20 percent of the warming the planet has experienced can be attributed to the gas. About one-third (33%) of anthropogenic greenhouse gases, anthropogenic emissions are from gas release during the mining, extraction and delivery of fossil fuels; mostly due to gas venting and gas leaks from both active fossil fuel infrastructure and orphan wells. Russia is the world's top methane e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations Environment Programme
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is responsible for coordinating responses to environmental issues within the United Nations system. It was established by Maurice Strong, its first director, after the Declaration of the United Nations Conference on the Human Environment, United Nations Conference on the Human Environment in Stockholm in June 1972. Its mandate is to provide leadership, deliver science and develop solutions on a wide range of issues, including climate change, the management of marine and terrestrial ecosystems, and green economic development. The organization also develops international environmental agreements; publishes and promotes environmental science and helps national governments achieve environmental targets. As a member of the United Nations Development Group, UNEP aims to help the world meet the 17 Sustainable Development Goals. UNEP hosts the secretariats of several multilateral environmental agreements and research bodies, including Conven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Fuel
A fossil fuel is a flammable carbon compound- or hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the buried remains of prehistoric organisms (animals, plants or microplanktons), a process that occurs within geological formations. Reservoirs of such compound mixtures, such as coal, petroleum and natural gas, can be extracted and burnt as fuel for human consumption to provide energy for direct use (such as for cooking, heating or lighting), to power heat engines (such as steam or internal combustion engines) that can propel vehicles, or to generate electricity via steam turbine generators. Some fossil fuels are further refined into derivatives such as kerosene, gasoline and diesel, or converted into petrochemicals such as polyolefins ( plastics), aromatics and synthetic resins. The origin of fossil fuels is the anaerobic decomposition of buried dead organisms. The conversion from these organic materials to high-carbon fossil fuels is ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Methane Pledge
Global may refer to: General *Globe, a spherical model of celestial bodies *Earth, the third planet from the Sun Entertainment * ''Global'' (Paul van Dyk album), 2003 * ''Global'' (Bunji Garlin album), 2007 * ''Global'' (Humanoid album), 1989 * ''Global'' (Todd Rundgren album), 2015 * Bruno J. Global, a character in the anime series ''The Super Dimension Fortress Marcoss'' Companies and brands Television * Global Television Network, in Canada ** Canwest Global, former parent company of Global Television Network ** Global BC, on-air brand of CHAN-TV, a television station in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada ** Global Calgary ** Global Edmonton ** Global Halifax ** Global Montreal ** Global News, the news division of the Global Television Network ** Global Okanagan, on-air brand of CHBC-TV, a television station in Kelowna, British Columbia, Canada ** Global Toronto, a television station in Toronto * Global TV (Venezuela) Global TV is a Venezuelan regional televisio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the primary Executive (government), executive arm of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with a number of European Commissioner, members of the Commission (directorial system, informally known as "commissioners") corresponding to two thirds of the number of Member state of the European Union, member states, unless the European Council, acting unanimously, decides to alter this number. The current number of commissioners is 27, including the president. It includes an administrative body of about 32,000 European civil servants. The commission is divided into departments known as Directorate-General, Directorates-General (DGs) that can be likened to departments or Ministry (government department), ministries each headed by a director-general who is responsible to a commissioner. Currently, there is one member per European Union member state, member state, but members are bound by their oath of office to represent the genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intergovernmental Panel On Climate Change
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is an intergovernmental body of the United Nations. Its job is to "provide governments at all levels with scientific information that they can use to develop climate policies". The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) set up the IPCC in 1988. The United Nations General Assembly, United Nations endorsed the creation of the IPCC later that year. It has a secretariat in Geneva, Switzerland, hosted by the WMO. It has 195 Member states of the United Nations, member states who govern the IPCC. The member states elect a bureau of scientists to serve through an assessment cycle. A cycle is usually six to seven years. The bureau selects experts in their fields to prepare IPCC reports. There is a formal nomination process by governments and observer organizations to find these experts. The IPCC has three working groups and a task force, which carry out its scientific work. The IPCC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IPCC Sixth Assessment Report
The Sixth Assessment Report (AR6) of the United Nations (UN) Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is the sixth in a series of reports which assess the available scientific information on climate change. Three Working Groups (WGI, II, and III) covered the following topics: The Physical Science Basis (WGI); Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability (WGII); Mitigation of Climate Change (WGIII). Of these, the first study was published in 2021, the second report February 2022, and the third in April 2022. The final synthesis report was finished in March 2023. It includes a summary for policymakers and was the basis for the 2023 United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP28) in Dubai. The first of the three working groups published its report on 9 August 2021, ''Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis''.IPCC, 2021Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decarbonisation
Climate change mitigation (or decarbonisation) is action to limit the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere that cause climate change. Climate change mitigation actions include conserving energy and replacing fossil fuels with clean energy sources. Secondary mitigation strategies include changes to land use and removing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. Current climate change mitigation policies are insufficient as they would still result in global warming of about 2.7 °C by 2100, significantly above the 2015 Paris Agreement's goal of limiting global warming to below 2 °C. Solar energy and wind power can replace fossil fuels at the lowest cost compared to other renewable energy options.IPCC (2022Summary for policy makersiClimate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes it an economically attractive fuel, although capturing and storing it is difficult because it is a gas at standard temperature and pressure. In the Earth's atmosphere methane is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. Methane is an Organic chemistry, organic Organic compound, compound, and among the simplest of organic compounds. Methane is also a hydrocarbon. Naturally occurring methane is found both below ground and under the seafloor and is formed by both geological and biological processes. The largest reservoir of methane is under the seafloor in the form of methane clathrates. When methane reaches the surface and the Atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere, it is known as atmospheric methane. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |