lasers on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A laser is a device that emits

 A laser consists of a
A laser consists of a
 An electron in an atom can absorb energy from light (
An electron in an atom can absorb energy from light (
 The gain medium is put into an
The gain medium is put into an
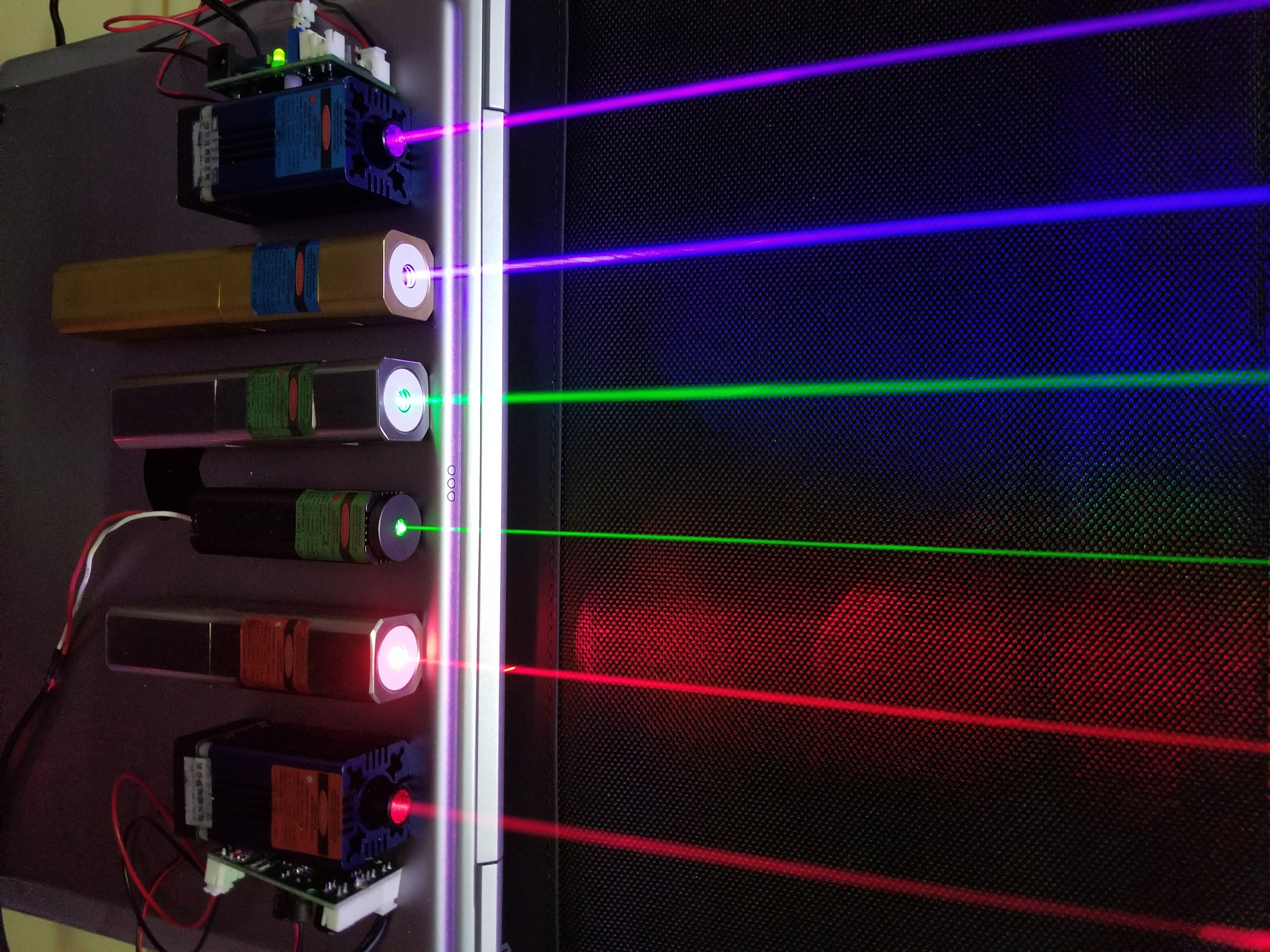 In most lasers, lasing begins with spontaneous emission into the lasing mode. This initial light is then amplified by stimulated emission in the gain medium. Stimulated emission produces light that matches the input signal in direction, wavelength, and polarization, whereas the
In most lasers, lasing begins with spontaneous emission into the lasing mode. This initial light is then amplified by stimulated emission in the gain medium. Stimulated emission produces light that matches the input signal in direction, wavelength, and polarization, whereas the


 A laser can be classified as operating in either continuous or pulsed mode, depending on whether the power output is essentially continuous over time or whether its output takes the form of pulses of light on one or another time scale. Of course, even a laser whose output is normally continuous can be intentionally turned on and off at some rate to create pulses of light. When the modulation rate is on time scales much slower than the cavity lifetime and the period over which energy can be stored in the lasing medium or pumping mechanism, then it is still classified as a "modulated" or "pulsed" continuous wave laser. Most laser diodes used in communication systems fall into that category.
A laser can be classified as operating in either continuous or pulsed mode, depending on whether the power output is essentially continuous over time or whether its output takes the form of pulses of light on one or another time scale. Of course, even a laser whose output is normally continuous can be intentionally turned on and off at some rate to create pulses of light. When the modulation rate is on time scales much slower than the cavity lifetime and the period over which energy can be stored in the lasing medium or pumping mechanism, then it is still classified as a "modulated" or "pulsed" continuous wave laser. Most laser diodes used in communication systems fall into that category.
 In 1951,
In 1951,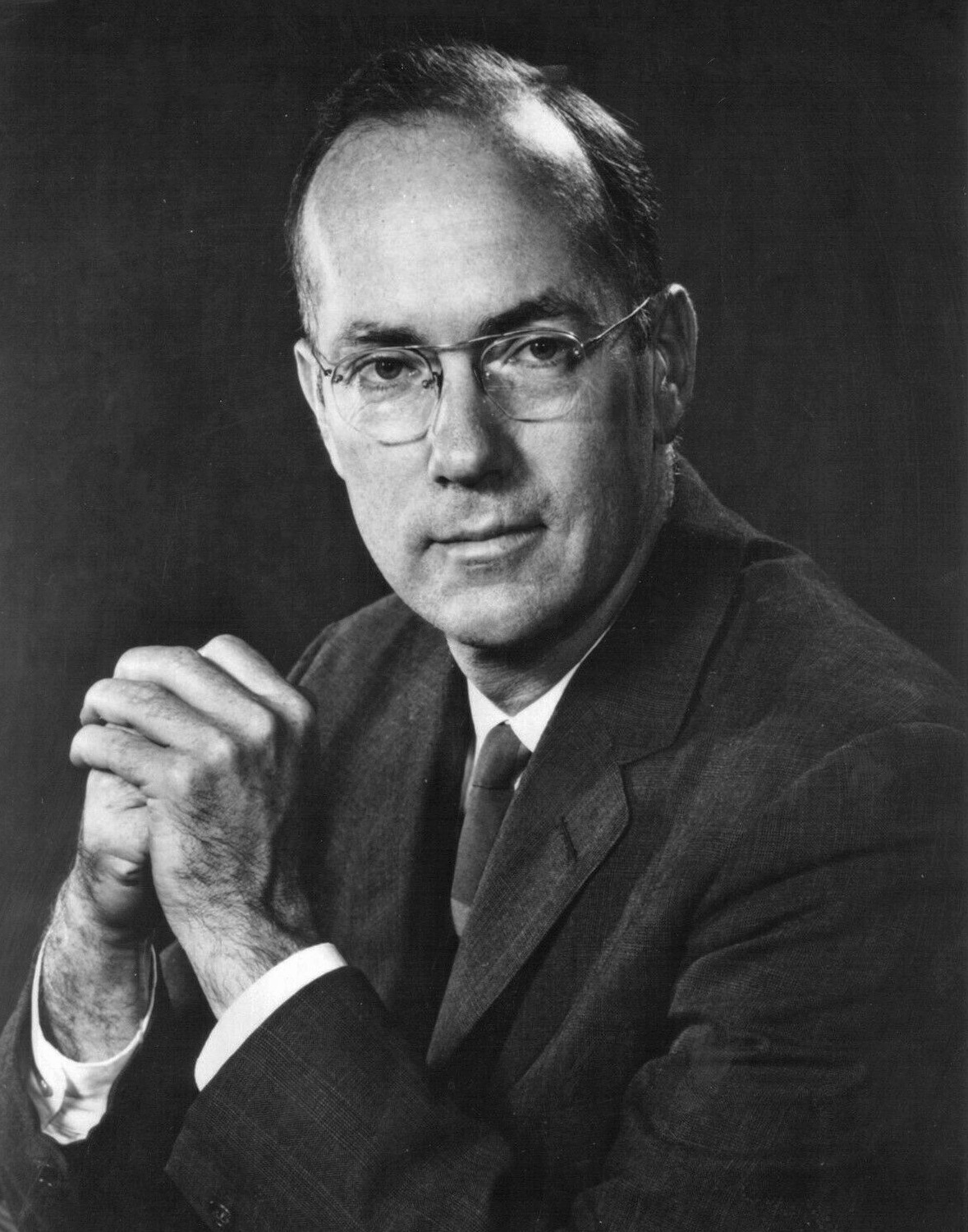  In 1953, Charles H. Townes and graduate students James P. Gordon and Herbert J. Zeiger produced the first microwave amplifier, a device operating on similar principles to the laser, but amplifying
In 1953, Charles H. Townes and graduate students James P. Gordon and Herbert J. Zeiger produced the first microwave amplifier, a device operating on similar principles to the laser, but amplifying
 Since the early period of laser history, laser research has produced a variety of improved and specialized laser types, optimized for different performance goals, including:
* new wavelength bands
* maximum average output power
* maximum peak pulse
Since the early period of laser history, laser research has produced a variety of improved and specialized laser types, optimized for different performance goals, including:
* new wavelength bands
* maximum average output power
* maximum peak pulse

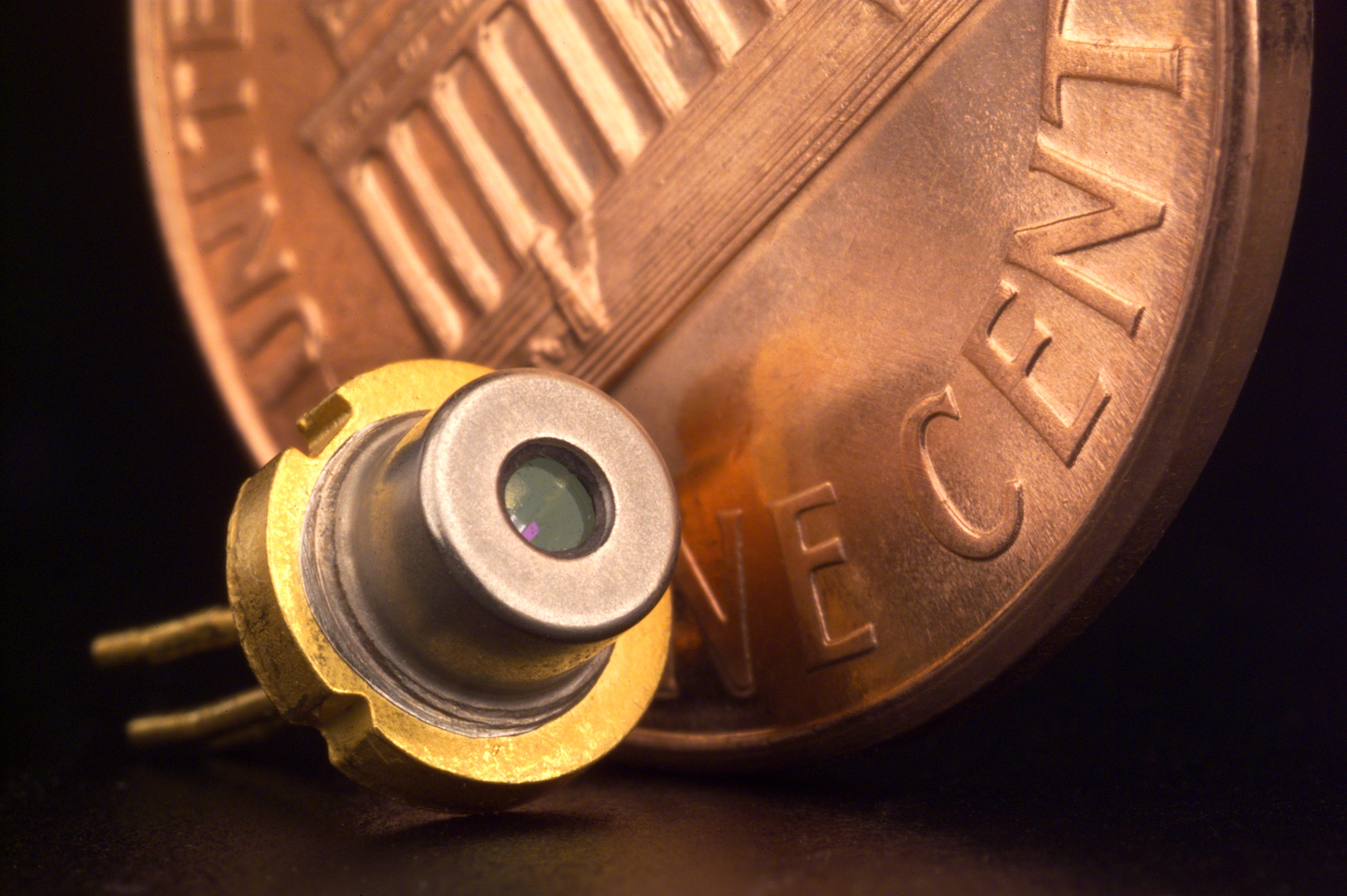 Semiconductor lasers are
Semiconductor lasers are


 When the laser was first invented, it was called "a solution looking for a problem", although Gould noted numerous possible applications in his notebook and patent applications. Since then, they have become ubiquitous, finding utility in thousands of highly varied applications in every section of modern society, including
When the laser was first invented, it was called "a solution looking for a problem", although Gould noted numerous possible applications in his notebook and patent applications. Since then, they have become ubiquitous, finding utility in thousands of highly varied applications in every section of modern society, including
 A
A  Lasers can be used as incapacitating
Lasers can be used as incapacitating
 Different applications need lasers with different output powers. Lasers that produce a continuous beam or a series of short pulses can be compared on the basis of their average power. Lasers that produce pulses can also be characterized based on the ''peak'' power of each pulse. The peak power of a pulsed laser is many
Different applications need lasers with different output powers. Lasers that produce a continuous beam or a series of short pulses can be compared on the basis of their average power. Lasers that produce pulses can also be characterized based on the ''peak'' power of each pulse. The peak power of a pulsed laser is many
Encyclopedia of laser physics and technology by Rüdiger Paschotta
* ttp://www.technology.niagarac.on.ca/staff/mcsele/lasers/index.html Homebuilt Lasers Page by Professor Mark Csele
Powerful laser is 'brightest light in the universe'
he world's most powerful laser as of 2008 might create supernova-like shock waves and possibly even antimatter *
an online course by F. Balembois and S. Forget.
* ttp://www.laserfest.org/ Website on Lasers 50th anniversary by APS, OSA, SPIE
Advancing the Laser anniversary site by SPIE: Video interviews, open-access articles, posters, DVDs
history of the invention, with audio interview clips.
Free software for Simulation of random laser dynamics
Video Demonstrations in Lasers and Optics
Produced by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Real-time effects are demonstrated in a way that would be difficult to see in a classroom setting.
MIT Video Lecture: Understanding Lasers and Fiberoptics
Virtual Museum of Laser History, from the touring exhibit by SPIE
website with animations, applications and research about laser and other quantum based phenomena
Universite Paris Sud {{Authority control 1960 introductions American inventions Articles containing video clips Photonics Quantum optics Russian inventions Soviet inventions
light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be visual perception, perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400– ...
through a process of optical amplification
An optical amplifier is a device that amplifies an optical signal directly, without the need to first convert it to an electrical signal. An optical amplifier may be thought of as a laser without an optical cavity, or one in which feedback from ...
based on the stimulated emission
Stimulated emission is the process by which an incoming photon of a specific frequency can interact with an excited atomic electron (or other excited molecular state), causing it to drop to a lower energy level. The liberated energy transfers to ...
of electromagnetic radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) is a self-propagating wave of the electromagnetic field that carries momentum and radiant energy through space. It encompasses a broad spectrum, classified by frequency or its inverse, wavelength ...
. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym
An acronym is a type of abbreviation consisting of a phrase whose only pronounced elements are the initial letters or initial sounds of words inside that phrase. Acronyms are often spelled with the initial Letter (alphabet), letter of each wor ...
for light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore Maiman
Theodore Harold Maiman (July 11, 1927 – May 5, 2007) was an American engineer and physicist who is widely credited with the invention of the laser.Johnson, John Jr. (May 11, 2008). "Theodore H. Maiman, at age 32; scientist created the first L ...
at Hughes Research Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles H. Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow
Arthur Leonard Schawlow (May 5, 1921 – April 28, 1999) was an American physicist who, along with Charles Townes, developed the theoretical basis for laser science. His central insight was the use of two mirrors as the resonant cavity to take m ...
and the optical amplifier patented by Gordon Gould
Richard Gordon Gould (July 17, 1920 – September 16, 2005) was an American physicist who is sometimes credited with the invention of the laser and the optical amplifier. (Credit for the invention of the laser is disputed, since Charles Towne ...
.
A laser differs from other sources of light in that it emits light that is ''coherent''. Spatial coherence allows a laser to be focused to a tight spot, enabling uses such as optical communication, laser cutting
Laser cutting is a technology that uses a laser to vaporize materials, resulting in a cut edge. While typically used for industrial manufacturing applications, it is now used by schools, small businesses, architecture, and hobbyists. Laser cutt ...
, and lithography
Lithography () is a planographic method of printing originally based on the miscibility, immiscibility of oil and water. The printing is from a stone (lithographic limestone) or a metal plate with a smooth surface. It was invented in 1796 by ...
. It also allows a laser beam to stay narrow over great distances (collimation
A collimated beam of light or other electromagnetic radiation has parallel rays, and therefore will spread minimally as it propagates. A laser beam is an archetypical example. A perfectly collimated light beam, with no divergence, would not disp ...
), used in laser pointer
A laser pointer or laser pen is a (typically battery-powered) handheld device that uses a laser diode to emit a narrow low-power visible laser beam (i.e. Coherence (physics), coherent light) to highlight something of interest with a small brigh ...
s, lidar
Lidar (, also LIDAR, an acronym of "light detection and ranging" or "laser imaging, detection, and ranging") is a method for determining ranging, ranges by targeting an object or a surface with a laser and measuring the time for the reflected li ...
, and free-space optical communication
Free-space optical communication (FSO) is an optical communication technology that uses light propagating in free space to wirelessly transmit data for telecommunications or computer networking over long distances. "Free space" means air, oute ...
. Lasers can also have high temporal coherence
Coherence expresses the potential for two waves to Wave interference, interfere. Two Monochromatic radiation, monochromatic beams from a single source always interfere. Wave sources are not strictly monochromatic: they may be ''partly coherent''. ...
, which permits them to emit light with a very narrow frequency spectrum
In signal processing, the power spectrum S_(f) of a continuous time signal x(t) describes the distribution of power into frequency components f composing that signal. According to Fourier analysis, any physical signal can be decomposed int ...
. Temporal coherence can also be used to produce ultrashort pulse
In optics, an ultrashort pulse, also known as an ultrafast event, is an electromagnetic pulse whose time duration is of the order of a picosecond (10−12 second) or less. Such pulses have a broadband optical spectrum, and can be created by ...
s of light with a broad spectrum but durations measured in attosecond
An attosecond (abbreviated as as) is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to 10−18 or 1⁄1 000 000 000 000 000 000 (one quintillionth) of a second.
An attosecond is to a second, as a second is to approximately 31.69 ...
s.
Lasers are used in fiber-optic
An optical fiber, or optical fibre, is a flexible glass or plastic fiber that can transmit light from one end to the other. Such fibers find wide usage in fiber-optic communications, where they permit transmission over longer distances and at ...
and free-space optical communications, optical disc drive
In computing, an optical disc drive (ODD) is a disc drive that uses laser light or electromagnetic waves within or near the visible light spectrum as part of the process of reading or writing data to or from optical discs. Some drives can on ...
s, laser printer
Laser printing is an electrostatic digital printing process. It produces high-quality text and graphics (and moderate-quality photographs) by repeatedly passing a laser beam back and forth over a Electric charge, negatively charged cylinder call ...
s, barcode scanner
A barcode reader or barcode scanner is an optical scanner that can read printed barcodes and send the data they contain to computer. Like a flatbed scanner, it consists of a light source, a lens, and a light sensor for translating optical impulses ...
s, semiconductor chip manufacturing (photolithography
Photolithography (also known as optical lithography) is a process used in the manufacturing of integrated circuits. It involves using light to transfer a pattern onto a substrate, typically a silicon wafer.
The process begins with a photosensiti ...
, etching
Etching is traditionally the process of using strong acid or mordant to cut into the unprotected parts of a metal surface to create a design in intaglio (incised) in the metal. In modern manufacturing, other chemicals may be used on other type ...
), laser surgery
Laser surgery is a type of surgery that cuts tissue using a laser in contrast to using a scalpel.
Soft-tissue laser surgery is used in a variety of applications in humans ( general surgery, neurosurgery, ENT, dentistry, orthodontics, and ...
and skin treatments, cutting and welding
Welding is a fabrication (metal), fabrication process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, primarily by using high temperature to melting, melt the parts together and allow them to cool, causing Fusion welding, fusion. Co ...
materials, military and law enforcement
Law enforcement is the activity of some members of the government or other social institutions who act in an organized manner to enforce the law by investigating, deterring, rehabilitating, or punishing people who violate the rules and norms gove ...
devices for marking targets and measuring range and speed, and in laser lighting displays for entertainment. The laser is regarded as one of the greatest inventions of the 20th century.
Terminology
The first device using amplification by stimulated emission operated atmicrowave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than other radio waves but longer than infrared waves. Its wavelength ranges from about one meter to one millimeter, corresponding to frequency, frequencies between 300&n ...
frequencies, and was called a ''maser
A maser is a device that produces coherent electromagnetic waves ( microwaves), through amplification by stimulated emission. The term is an acronym for microwave amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. Nikolay Basov, Alexander Pr ...
'', for "microwave amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". When similar optical
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultravio ...
devices were developed they were first called ''optical masers'', until "microwave" was replaced by "light" in the acronym, to become ''laser''.
Today, all such devices operating at frequencies higher than microwaves (approximately above 300 GHz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), often described as being equivalent to one event (or Cycle per second, cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose formal expression in ter ...
) are called lasers (e.g. ''infrared lasers'', ''ultraviolet lasers'', ''X-ray laser
An X-ray laser can be created by several methods either in hot, dense plasmas or as a free-electron laser in an accelerator. This article describes the x-ray lasers in plasmas, only.
The plasma x-ray lasers rely on stimulated emission to gener ...
s'', '' gamma-ray lasers''), whereas devices operating at microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than other radio waves but longer than infrared waves. Its wavelength ranges from about one meter to one millimeter, corresponding to frequency, frequencies between 300&n ...
or lower radio frequencies are called masers.
The back-formed verb " to lase" is frequently used in the field, meaning "to give off coherent light," especially about the gain medium
The active laser medium (also called a gain medium or lasing medium) is the source of optical gain within a laser. The gain results from the stimulated emission of photons through electronic or molecular transitions to a lower energy state from ...
of a laser; when a laser is operating, it is said to be " lasing". The terms ''laser'' and ''maser'' are also used for naturally occurring coherent emissions, as in ''astrophysical maser
An astrophysical maser is a naturally occurring source of Stimulated emission, stimulated spectral line emission, typically in the microwave portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. This emission may arise in molecular clouds, comets, planetary at ...
'' and ''atom laser
An atom laser is a coherent state of propagating atoms. They are created out of a Bose–Einstein condensate of atoms that are output coupled using various techniques. Much like an optical laser, an atom laser is a coherent beam that behaves lik ...
''.
A laser that produces light by itself is technically an optical oscillator rather than an optical amplifier
An optical amplifier is a device that amplifies an optical signal directly, without the need to first convert it to an electrical signal. An optical amplifier may be thought of as a laser without an optical cavity, or one in which feedback fro ...
as suggested by the acronym. It has been humorously noted that the acronym LOSER, for "light oscillation by stimulated emission of radiation", would have been more correct. Some sources refer to the word laser as an anacronym
An acronym is a type of abbreviation consisting of a phrase whose only pronounced elements are the initial letters or initial sounds of words inside that phrase. Acronyms are often spelled with the initial letter of each word in all caps wit ...
, meaning an acronym so widely used as a noun that it is no longer considered an abbreviation.
Fundamentals

Photons
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless particles that ...
, the quanta of electromagnetic radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) is a self-propagating wave of the electromagnetic field that carries momentum and radiant energy through space. It encompasses a broad spectrum, classified by frequency or its inverse, wavelength ...
, are released and absorbed from energy levels in atoms and molecules. In a lightbulb or a star, the energy is emitted from many different levels giving photons with a broad range of energies. This process is called thermal radiation
Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation emitted by the thermal motion of particles in matter. All matter with a temperature greater than absolute zero emits thermal radiation. The emission of energy arises from a combination of electro ...
.
The underlying physical process creating photons in a laser is the same as in thermal radiation, but the actual emission is not the result of random thermal processes. Instead, the release of a photon is triggered by the nearby passage of another photon. This is called stimulated emission
Stimulated emission is the process by which an incoming photon of a specific frequency can interact with an excited atomic electron (or other excited molecular state), causing it to drop to a lower energy level. The liberated energy transfers to ...
. For this process to work, the passing photon must be similar in energy, and thus wavelength, to the one that could be released by the atom or molecule, and the atom or molecule must be in the suitable excited state.
The photon that is emitted by stimulated emission is identical to the photon that triggered its emission, and both photons can go on to trigger stimulated emission in other atoms, creating the possibility of a chain reaction
A chain reaction is a sequence of reactions where a reactive product or by-product causes additional reactions to take place. In a chain reaction, positive feedback leads to a self-amplifying chain of events.
Chain reactions are one way that sys ...
. For this to happen, many of the atoms or molecules must be in the proper excited state so that the photons can trigger them. In most materials, atoms or molecules drop out of excited states fairly rapidly, making it difficult or impossible to produce a chain reaction. The materials chosen for lasers are the ones that have metastable states, which stay excited for a relatively long time. In laser physics
Laser science or laser physics is a branch of optics that describes the theory and practice of lasers.
Laser science is principally concerned with quantum electronics, laser construction, optical cavity design, the physics of producing a po ...
, such a material is called an active laser medium
The active laser medium (also called a gain medium or lasing medium) is the source of optical gain within a laser. The gain results from the stimulated emission of photons through electronic or molecular transitions to a lower energy state from ...
. Combined with an energy source that continues to "pump" energy into the material, it is possible to have enough atoms or molecules in an excited state for a chain reaction to develop.
Lasers are distinguished from other light sources by their coherence
Coherence is, in general, a state or situation in which all the parts or ideas fit together well so that they form a united whole.
More specifically, coherence, coherency, or coherent may refer to the following:
Physics
* Coherence (physics ...
. Spatial (or transverse) coherence is typically expressed through the output being a narrow beam, which is diffraction-limited
In optics, any optical instrument or systema microscope, telescope, or camerahas a principal limit to its resolution due to the physics of diffraction. An optical instrument is said to be diffraction-limited if it has reached this limit of res ...
. Laser beams can be focused to very tiny spots, achieving a very high irradiance
In radiometry, irradiance is the radiant flux ''received'' by a ''surface'' per unit area. The SI unit of irradiance is the watt per square metre (symbol W⋅m−2 or W/m2). The CGS unit erg per square centimetre per second (erg⋅cm−2⋅s−1) ...
, or they can have a very low divergence to concentrate their power at a great distance. Temporal (or longitudinal) coherence implies a polarized wave at a single frequency, whose phase is correlated over a relatively great distance (the coherence length) along the beam. A beam produced by a thermal or other incoherent light source has an instantaneous amplitude and phase
Phase or phases may refer to:
Science
*State of matter, or phase, one of the distinct forms in which matter can exist
*Phase (matter), a region of space throughout which all physical properties are essentially uniform
*Phase space, a mathematica ...
that vary randomly with respect to time and position, thus having a short coherence length.
Lasers are characterized according to their wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
in a vacuum
A vacuum (: vacuums or vacua) is space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective (neuter ) meaning "vacant" or "void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressur ...
. Most "single wavelength" lasers produce radiation in several ''modes'' with slightly different wavelengths. Although temporal coherence implies some degree of monochromaticity, some lasers emit a broad spectrum of light or emit different wavelengths of light simultaneously. Certain lasers are not single spatial mode and have light beams that diverge more than is required by the diffraction limit
In optics, any optical instrument or systema microscope, telescope, or camerahas a principal limit to its resolution due to the physics of diffraction. An optical instrument is said to be diffraction-limited if it has reached this limit of res ...
. All such devices are classified as "lasers" based on the method of producing light by stimulated emission. Lasers are employed where light of the required spatial or temporal coherence can not be produced using simpler technologies.
Design
gain medium
The active laser medium (also called a gain medium or lasing medium) is the source of optical gain within a laser. The gain results from the stimulated emission of photons through electronic or molecular transitions to a lower energy state from ...
, a mechanism to energize it, and something to provide optical feedback
Feedback occurs when outputs of a system are routed back as inputs as part of a chain of cause and effect that forms a circuit or loop. The system can then be said to ''feed back'' into itself. The notion of cause-and-effect has to be handle ...
. The gain medium is a material with properties that allow it to amplify light by way of stimulated emission. Light of a specific wavelength that passes through the gain medium is amplified (power increases). Feedback enables stimulated emission to amplify predominantly the optical frequency at the peak of the gain-frequency curve. As stimulated emission grows, eventually one frequency dominates over all others, meaning that a coherent beam has been formed.
The process of stimulated emission is analogous to that of an audio oscillator with positive feedback which can occur, for example, when the speaker in a public-address system is placed in proximity to the microphone. The screech one hears is audio oscillation at the peak of the gain-frequency curve for the amplifier.
For the gain medium to amplify light, it needs to be supplied with energy in a process called pumping. The energy is typically supplied as an electric current or as light at a different wavelength. Pump light may be provided by a flash lamp or by another laser.
The most common type of laser uses feedback from an optical cavity
An optical cavity, resonating cavity or optical resonator is an arrangement of mirrors or other optical elements that confines light waves similarly to how a cavity resonator confines microwaves. Optical cavities are a major component of lasers, ...
a pair of mirrors on either end of the gain medium. Light bounces back and forth between the mirrors, passing through the gain medium and being amplified each time. Typically one of the two mirrors, the output coupler, is partially transparent. Some of the light escapes through this mirror. Depending on the design of the cavity (whether the mirrors are flat or curved), the light coming out of the laser may spread out or form a narrow beam. In analogy to electronic oscillator
An electronic oscillator is an electronic circuit that produces a periodic, oscillating or alternating current (AC) signal, usually a sine wave, square wave or a triangle wave, powered by a direct current (DC) source. Oscillators are found ...
s, this device is sometimes called a ''laser oscillator''.
Most practical lasers contain additional elements that affect the properties of the emitted light, such as the polarization, wavelength, and shape of the beam.
Laser physics
Electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
s and how they interact with electromagnetic field
An electromagnetic field (also EM field) is a physical field, varying in space and time, that represents the electric and magnetic influences generated by and acting upon electric charges. The field at any point in space and time can be regarde ...
s are important in the understanding of chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules a ...
and physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge whi ...
.
Stimulated emission
In the classical view, the energy of an electron orbiting an atomic nucleus is larger for orbits further from thenucleus
Nucleus (: nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucleu ...
of an atom
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished fr ...
. However, quantum mechanical effects force electrons to take on discrete positions in orbitals. Thus, electrons are found in specific energy levels of an atom, two of which are shown below:
photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless particles that can ...
s) or heat (phonon
A phonon is a collective excitation in a periodic, elastic arrangement of atoms or molecules in condensed matter, specifically in solids and some liquids. In the context of optically trapped objects, the quantized vibration mode can be defined a ...
s) only if there is a transition between energy levels that match the energy carried by the photon or phonon. For light, this means that any given transition will only absorb one particular wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
of light. Photons with the correct wavelength can cause an electron to jump from the lower to the higher energy level. The photon is consumed in this process.
When an electron is excited from one state to that at a higher energy level with energy difference ΔE, it will not stay that way forever. Eventually, a photon will be spontaneously created from the vacuum having energy ΔE. Conserving energy, the electron transitions to a lower energy level that is not occupied, with transitions to different levels having different time constants. This process is called spontaneous emission
Spontaneous emission is the process in which a Quantum mechanics, quantum mechanical system (such as a molecule, an atom or a subatomic particle) transits from an excited state, excited energy state to a lower energy state (e.g., its ground state ...
. Spontaneous emission is a quantum-mechanical effect and a direct physical manifestation of the Heisenberg uncertainty principle
The uncertainty principle, also known as Heisenberg's indeterminacy principle, is a fundamental concept in quantum mechanics. It states that there is a limit to the precision with which certain pairs of physical properties, such as position a ...
. The emitted photon has a random direction, but its wavelength matches the absorption wavelength of the transition. This is the mechanism of fluorescence
Fluorescence is one of two kinds of photoluminescence, the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. When exposed to ultraviolet radiation, many substances will glow (fluoresce) with colore ...
and thermal emission
Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation emitted by the thermal motion of particles in matter. All matter with a temperature greater than absolute zero emits thermal radiation. The emission of energy arises from a combination of electro ...
.
A photon with the correct wavelength to be absorbed by a transition can also cause an electron to drop from the higher to the lower level, emitting a new photon. The emitted photon exactly matches the original photon in wavelength, phase, and direction. This process is called stimulated emission.
Gain medium and cavity
excited state
In quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical Scientific theory, theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Add ...
by an external source of energy. In most lasers, this medium consists of a population of atoms that have been excited into such a state using an outside light source, or an electrical field that supplies energy for atoms to absorb and be transformed into their excited states.
The gain medium of a laser is normally a material of controlled purity, size, concentration, and shape, which amplifies the beam by the process of stimulated emission described above. This material can be of any state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
: gas, liquid, solid, or plasma. The gain medium absorbs pump energy, which raises some electrons into higher energy (" excited") quantum state
In quantum physics, a quantum state is a mathematical entity that embodies the knowledge of a quantum system. Quantum mechanics specifies the construction, evolution, and measurement of a quantum state. The result is a prediction for the system ...
s. Particles can interact with light by either absorbing or emitting photons. Emission can be spontaneous or stimulated. In the latter case, the photon is emitted in the same direction as the light that is passing by. When the number of particles in one excited state exceeds the number of particles in some lower-energy state, population inversion
In physics, specifically statistical mechanics, a population inversion occurs when a system (such as a group of atoms or molecules) exists in a state in which more members of the system are in higher, excited states than in lower, unexcited energy ...
is achieved. In this state, the rate of stimulated emission is larger than the rate of absorption of light in the medium, and therefore the light is amplified. A system with this property is called an optical amplifier
An optical amplifier is a device that amplifies an optical signal directly, without the need to first convert it to an electrical signal. An optical amplifier may be thought of as a laser without an optical cavity, or one in which feedback fro ...
. When an optical amplifier is placed inside a resonant optical cavity, one obtains a laser.
For lasing media with extremely high gain, so-called superluminescence, light can be sufficiently amplified in a single pass through the gain medium without requiring a resonator. Although often referred to as a laser (see, for example, nitrogen laser
A nitrogen laser is a gas laser operating in the ultraviolet rangeC. S. Willett, ''Introduction to Gas Lasers: Population Inversion Mechanisms'' (Pergamon, New York,1974). (typically 337.1 nm) using molecular nitrogen as its gain medium, lase ...
), the light output from such a device lacks the spatial and temporal coherence achievable with lasers. Such a device cannot be described as an oscillator but rather as a high-gain optical amplifier that amplifies its spontaneous emission. The same mechanism describes so-called astrophysical maser
An astrophysical maser is a naturally occurring source of Stimulated emission, stimulated spectral line emission, typically in the microwave portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. This emission may arise in molecular clouds, comets, planetary at ...
s/lasers.
The optical resonator
A resonator is a device or system that exhibits resonance or resonant behavior. That is, it naturally oscillates with greater amplitude at some frequencies, called resonant frequencies, than at other frequencies. The oscillations in a reso ...
is sometimes referred to as an "optical cavity", but this is a misnomer: lasers use open resonators as opposed to the literal cavity that would be employed at microwave frequencies in a maser
A maser is a device that produces coherent electromagnetic waves ( microwaves), through amplification by stimulated emission. The term is an acronym for microwave amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. Nikolay Basov, Alexander Pr ...
.
The resonator typically consists of two mirrors between which a coherent beam of light travels in both directions, reflecting on itself so that an average photon will pass through the gain medium repeatedly before it is emitted from the output aperture or lost to diffraction or absorption.
If the gain (amplification) in the medium is larger than the resonator losses, then the power of the recirculating light can rise exponentially. But each stimulated emission event returns an atom from its excited state to the ground state, reducing the gain of the medium. With increasing beam power, the net gain (gain minus loss) reduces to unity and the gain medium is said to be saturated. In a continuous wave (CW) laser, the balance of pump power against gain saturation and cavity losses produces an equilibrium value of the laser power inside the cavity; this equilibrium determines the operating point of the laser. If the applied pump power is too small, the gain will never be sufficient to overcome the cavity losses, and laser light will not be produced. The minimum pump power needed to begin laser action is called the ''lasing threshold The lasing threshold is the lowest excitation level at which a laser's output is dominated by stimulated emission rather than by spontaneous emission. Below the threshold, the laser's output power rises slowly with increasing excitation. Above thr ...
''. The gain medium will amplify any photons passing through it, regardless of direction; but only the photons in a spatial mode supported by the resonator will pass more than once through the medium and receive substantial amplification.
The light emitted
phase
Phase or phases may refer to:
Science
*State of matter, or phase, one of the distinct forms in which matter can exist
*Phase (matter), a region of space throughout which all physical properties are essentially uniform
*Phase space, a mathematica ...
of the emitted light is 90 degrees in lead of the stimulating light. This, combined with the filtering effect of the optical resonator gives laser light its characteristic coherence, and may give it uniform polarization and monochromaticity, depending on the resonator's design. The fundamental laser linewidth
Laser linewidth is the spectral linewidth of a laser beam.
Two of the most distinctive characteristics of laser emission are spatial coherence and spectral coherence. While spatial coherence is related to the beam divergence of the laser, spec ...
of light emitted from the lasing resonator can be orders of magnitude narrower than the linewidth of light emitted from the passive resonator. Some lasers use a separate injection seeder to start the process off with a beam that is already highly coherent. This can produce beams with a narrower spectrum than would otherwise be possible.
In 1963, Roy J. Glauber showed that coherent states are formed from combinations of photon number states, for which he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics
The Nobel Prize in Physics () is an annual award given by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences for those who have made the most outstanding contributions to mankind in the field of physics. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the ...
. A coherent beam of light is formed by single-frequency quantum photon states distributed according to a Poisson distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the Poisson distribution () is a discrete probability distribution that expresses the probability of a given number of events occurring in a fixed interval of time if these events occur with a known const ...
. As a result, the arrival rate of photons in a laser beam is described by Poisson statistics.
Many lasers produce a beam that can be approximated as a Gaussian beam
In optics, a Gaussian beam is an idealized beam of electromagnetic radiation whose amplitude envelope in the transverse plane is given by a Gaussian function; this also implies a Gaussian intensity (irradiance) profile. This fundamental (or ...
; such beams have the minimum divergence possible for a given beam diameter. Some lasers, particularly high-power ones, produce multimode beams, with the transverse mode
A transverse mode of electromagnetic radiation is a particular electromagnetic field pattern of the radiation in the plane perpendicular (i.e., transverse) to the radiation's propagation direction. Transverse modes occur in radio waves and micr ...
s often approximated using Hermite–Gaussian
Carl Friedrich Gauss (1777–1855) is the eponym of all of the topics listed below.
There are over 100 topics all named after this German mathematician and scientist, all in the fields of mathematics, physics, and astronomy. The English eponymo ...
or Laguerre-Gaussian functions. Some high-power lasers use a flat-topped profile known as a " tophat beam". Unstable laser resonators (not used in most lasers) produce fractal-shaped beams. Specialized optical systems can produce more complex beam geometries, such as Bessel beams and optical vortexes.
Near the "waist" (or focal region) of a laser beam, it is highly ''collimated
A collimated beam of light or other electromagnetic radiation has parallel rays, and therefore will spread minimally as it propagates. A laser beam is an archetypical example. A perfectly collimated light beam, with no divergence, would not disp ...
'': the wavefronts are planar, normal to the direction of propagation, with no beam divergence
In electromagnetics, especially in optics, beam divergence is an angular measure of the increase in beam diameter or radius with distance from the optical aperture or antenna aperture from which the beam emerges. The term is relevant only in ...
at that point. However, due to diffraction
Diffraction is the deviation of waves from straight-line propagation without any change in their energy due to an obstacle or through an aperture. The diffracting object or aperture effectively becomes a secondary source of the Wave propagation ...
, that can only remain true well within the Rayleigh range. The beam of a single transverse mode (gaussian beam) laser eventually diverges at an angle that varies inversely with the beam diameter, as required by diffraction
Diffraction is the deviation of waves from straight-line propagation without any change in their energy due to an obstacle or through an aperture. The diffracting object or aperture effectively becomes a secondary source of the Wave propagation ...
theory. Thus, the "pencil beam" directly generated by a common helium–neon laser
A helium–neon laser or He–Ne laser is a type of gas laser whose high energetic gain medium consists of a mixture of helium and neon (ratio between 5:1 and 10:1) at a total pressure of approximately 1 Torr (133.322 Pa) inside a small electr ...
would spread out to a size of perhaps 500 kilometers when shone on the Moon (from the distance of the Earth). On the other hand, the light from a semiconductor laser
The laser diode chip removed and placed on the eye of a needle for scale
A laser diode (LD, also injection laser diode or ILD or semiconductor laser or diode laser) is a semiconductor device similar to a light-emitting diode in which a diode p ...
typically exits the tiny crystal with a large divergence: up to 50°. However even such a divergent beam can be transformed into a similarly collimated beam employing a lens
A lens is a transmissive optical device that focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements'') ...
system, as is always included, for instance, in a laser pointer
A laser pointer or laser pen is a (typically battery-powered) handheld device that uses a laser diode to emit a narrow low-power visible laser beam (i.e. Coherence (physics), coherent light) to highlight something of interest with a small brigh ...
whose light originates from a laser diode
file:Laser diode chip.jpg, The laser diode chip removed and placed on the eye of a needle for scale
A laser diode (LD, also injection laser diode or ILD or semiconductor laser or diode laser) is a semiconductor device similar to a light-emittin ...
. That is possible due to the light being of a single spatial mode. This unique property of laser light, spatial coherence, cannot be replicated using standard light sources (except by discarding most of the light) as can be appreciated by comparing the beam from a flashlight (torch) or spotlight to that of almost any laser.
A laser beam profiler is used to measure the intensity profile, width, and divergence of laser beams.
Diffuse reflection
Diffuse reflection is the reflection of light or other waves or particles from a surface such that a ray incident on the surface is scattered at many angles rather than at just one angle as in the case of specular reflection. An ''ideal'' dif ...
of a laser beam from a matte surface produces a speckle pattern
Speckle, speckle pattern, or speckle noise designates the granular structure observed in coherent light, resulting from random interference. Speckle patterns are used in a wide range of metrology techniques, as they generally allow high sensitivi ...
with interesting properties.
Quantum vs. classical emission processes
The mechanism of producing radiation in a laser relies onstimulated emission
Stimulated emission is the process by which an incoming photon of a specific frequency can interact with an excited atomic electron (or other excited molecular state), causing it to drop to a lower energy level. The liberated energy transfers to ...
, where energy is extracted from a transition in an atom or molecule. This is a quantum phenomenon that was predicted by Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein (14 March 187918 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist who is best known for developing the theory of relativity. Einstein also made important contributions to quantum mechanics. His mass–energy equivalence f ...
, who derived the relationship between the ''A'' coefficient, describing spontaneous emission, and the ''B'' coefficient which applies to absorption and stimulated emission. In the case of the free-electron laser
A free-electron laser (FEL) is a fourth generation light source producing extremely brilliant and short pulses of radiation. An FEL functions much as a laser but employs relativistic electrons as a active laser medium, gain medium instead of using ...
, atomic energy levels are not involved; it appears that the operation of this rather exotic device can be explained without reference to quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical Scientific theory, theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Addison-Wesley, 1989, It is ...
.
Modes of operation


 A laser can be classified as operating in either continuous or pulsed mode, depending on whether the power output is essentially continuous over time or whether its output takes the form of pulses of light on one or another time scale. Of course, even a laser whose output is normally continuous can be intentionally turned on and off at some rate to create pulses of light. When the modulation rate is on time scales much slower than the cavity lifetime and the period over which energy can be stored in the lasing medium or pumping mechanism, then it is still classified as a "modulated" or "pulsed" continuous wave laser. Most laser diodes used in communication systems fall into that category.
A laser can be classified as operating in either continuous or pulsed mode, depending on whether the power output is essentially continuous over time or whether its output takes the form of pulses of light on one or another time scale. Of course, even a laser whose output is normally continuous can be intentionally turned on and off at some rate to create pulses of light. When the modulation rate is on time scales much slower than the cavity lifetime and the period over which energy can be stored in the lasing medium or pumping mechanism, then it is still classified as a "modulated" or "pulsed" continuous wave laser. Most laser diodes used in communication systems fall into that category.
Continuous-wave operation
Some applications of lasers depend on a beam whose output power is constant over time. Such a laser is known as a ''continuous-wave
A continuous wave or continuous waveform (CW) is an electromagnetic wave of constant amplitude and frequency, typically a sine wave, that for mathematical analysis is considered to be of infinite duration. It may refer to e.g. a laser or particle ...
'' (''CW'') laser. Many types of lasers can be made to operate in continuous-wave mode to satisfy such an application. Many of these lasers lase in several longitudinal modes at the same time, and beats between the slightly different optical frequencies of those oscillations will produce amplitude variations on time scales shorter than the round-trip time (the reciprocal of the frequency spacing between modes), typically a few nanoseconds or less. In most cases, these lasers are still termed "continuous-wave" as their output power is steady when averaged over longer periods, with the very high-frequency power variations having little or no impact on the intended application. (However, the term is not applied to mode-locked lasers, where the ''intention'' is to create very short pulses at the rate of the round-trip time.)
For continuous-wave operation, the population inversion of the gain medium needs to be continually replenished by a steady pump source. In some lasing media, this is impossible. In some other lasers, it would require pumping the laser at a very high continuous power level, which would be impractical, or destroying the laser by producing excessive heat. Such lasers cannot be run in CW mode.
Pulsed operation
The pulsed operation of lasers refers to any laser not classified as a continuous wave so that the optical power appears in pulses of some duration at some repetition rate. This encompasses a wide range of technologies addressing many different motivations. Some lasers are pulsed simply because they cannot be run incontinuous
Continuity or continuous may refer to:
Mathematics
* Continuity (mathematics), the opposing concept to discreteness; common examples include
** Continuous probability distribution or random variable in probability and statistics
** Continuous ...
mode.
In other cases, the application requires the production of pulses having as large an energy as possible. Since the pulse energy is equal to the average power divided by the repetition rate, this goal can sometimes be satisfied by lowering the rate of pulses so that more energy can be built up between pulses. In laser ablation
Laser ablation or photoablation (also called laser blasting) is the process of removing material from a solid (or occasionally liquid) surface by irradiating it with a laser beam. At low laser flux, the material is heated by the absorbed laser ...
, for example, a small volume of material at the surface of a workpiece can be evaporated if it is heated in a very short time, while supplying the energy gradually would allow for the heat to be absorbed into the bulk of the piece, never attaining a sufficiently high temperature at a particular point.
Other applications rely on the peak pulse power (rather than the energy in the pulse), especially to obtain nonlinear optical
Nonlinear optics (NLO) is the branch of optics that describes the behaviour of light in nonlinear media, that is, media in which the polarization density P responds non-linearly to the electric field E of the light. The non-linearity is typicall ...
effects. For a given pulse energy, this requires creating pulses of the shortest possible duration utilizing techniques such as Q-switching
Q-switching, sometimes known as giant pulse formation or Q-spoiling, is a technique by which a laser can be made to produce a pulsed output beam. The technique allows the production of light pulses with extremely high (gigawatt) peak power, much h ...
.
The optical bandwidth of a pulse cannot be narrower than the reciprocal of the pulse width. In the case of extremely short pulses, that implies lasing over a considerable bandwidth, quite contrary to the very narrow bandwidths typical of CW lasers. The lasing medium in some ''dye lasers'' and ''vibronic solid-state lasers'' produces optical gain over a wide bandwidth, making a laser possible that can thus generate pulses of light as short as a few femtoseconds
A femtosecond is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to 10 or of a second; that is, one quadrillionth, or one millionth of one billionth, of a second.
A femtosecond is to a second, as a second is to approximately 31.6 ...
(10−15 s).
Q-switching
In a Q-switched laser, the population inversion is allowed to build up by introducing loss inside the resonator which exceeds the gain of the medium; this can also be described as a reduction of the quality factor or 'Q' of the cavity. Then, after the pump energy stored in the laser medium has approached the maximum possible level, the introduced loss mechanism (often an electro- or acousto-optical element) is rapidly removed (or that occurs by itself in a passive device), allowing lasing to begin which rapidly obtains the stored energy in the gain medium. This results in a short pulse incorporating that energy, and thus a high peak power.Mode locking
A mode-locked laser is capable of emitting extremely short pulses on the order of tens of picoseconds down to less than 10femtoseconds
A femtosecond is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to 10 or of a second; that is, one quadrillionth, or one millionth of one billionth, of a second.
A femtosecond is to a second, as a second is to approximately 31.6 ...
. These pulses repeat at the round-trip time, that is, the time that it takes light to complete one round trip between the mirrors comprising the resonator. Due to the Fourier limit (also known as energy–time uncertainty
Uncertainty or incertitude refers to situations involving imperfect or unknown information. It applies to predictions of future events, to physical measurements that are already made, or to the unknown, and is particularly relevant for decision ...
), a pulse of such short temporal length has a spectrum spread over a considerable bandwidth. Thus such a gain medium must have a gain bandwidth sufficiently broad to amplify those frequencies. An example of a suitable material is titanium
Titanium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in ...
-doped, artificially grown sapphire
Sapphire is a precious gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum, consisting of aluminium oxide () with trace amounts of elements such as iron, titanium, cobalt, lead, chromium, vanadium, magnesium, boron, and silicon. The name ''sapphire ...
( Ti:sapphire), which has a very wide gain bandwidth and can thus produce pulses of only a few femtoseconds duration.
Such mode-locked lasers are a most versatile tool for researching processes occurring on extremely short time scales (known as femtosecond physics, femtosecond chemistry and ultrafast science), for maximizing the effect of nonlinearity
In mathematics and science, a nonlinear system (or a non-linear system) is a system in which the change of the output is not proportional to the change of the input. Nonlinear problems are of interest to engineers, biologists, physicists, mathe ...
in optical materials (e.g. in second-harmonic generation
Second-harmonic generation (SHG), also known as frequency doubling, is the lowest-order wave-wave nonlinear interaction that occurs in various systems, including optical, radio, atmospheric, and magnetohydrodynamic systems. As a prototype behav ...
, parametric down-conversion
Spontaneous parametric down-conversion (also known as SPDC, parametric fluorescence or parametric scattering) is a nonlinear instant optical process that converts one photon of higher energy (namely, a ''pump'' photon) into a pair of photons (name ...
, optical parametric oscillators and the like). Unlike the giant pulse of a Q-switched laser, consecutive pulses from a mode-locked laser are phase-coherent; that is, the pulses (and not just their envelopes
An envelope is a common packaging item, usually made of thin, flat material. It is designed to contain a flat object, such as a letter or card.
Traditional envelopes are made from sheets of paper cut to one of three shapes: a rhombus, a sho ...
) are identical and perfectly periodic. For this reason, and the extremely large peak powers attained by such short pulses, such lasers are invaluable in certain areas of research.
Pulsed pumping
Another method of achieving pulsed laser operation is to pump the laser material with a source that is itself pulsed, either through electronic charging in the case of flash lamps, or another laser that is already pulsed. Pulsed pumping was historically used with dye lasers where the inverted population lifetime of a dye molecule was so short that a high-energy, fast pump was needed. The way to overcome this problem was to charge up largecapacitors
In electrical engineering, a capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy by accumulating electric charges on two closely spaced surfaces that are insulated from each other. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term st ...
which are then switched to discharge through flashlamps, producing an intense flash. Pulsed pumping is also required for three-level lasers in which the lower energy level rapidly becomes highly populated, preventing further lasing until those atoms relax to the ground state. These lasers, such as the excimer laser and the copper vapor laser, can never be operated in CW mode.
History
Foundations
In 1917,Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein (14 March 187918 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist who is best known for developing the theory of relativity. Einstein also made important contributions to quantum mechanics. His mass–energy equivalence f ...
established the theoretical foundations for the laser and the maser
A maser is a device that produces coherent electromagnetic waves ( microwaves), through amplification by stimulated emission. The term is an acronym for microwave amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. Nikolay Basov, Alexander Pr ...
in the paper "''Zur Quantentheorie der Strahlung''" ("On the Quantum Theory of Radiation") via a re-derivation of Max Planck
Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck (; ; 23 April 1858 – 4 October 1947) was a German Theoretical physics, theoretical physicist whose discovery of energy quantum, quanta won him the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1918.
Planck made many substantial con ...
's law of radiation, conceptually based upon probability coefficients ( Einstein coefficients) for the absorption, spontaneous emission, and stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. In 1928, Rudolf W. Ladenburg confirmed the existence of the phenomena of stimulated emission and negative absorption. In 1939, Valentin A. Fabrikant predicted using stimulated emission to amplify "short" waves. In 1947, Willis E. Lamb and R.C.Retherford found apparent stimulated emission in hydrogen spectra and effected the first demonstration of stimulated emission. In 1950, Alfred Kastler
Alfred Kastler (; 3 May 1902 – 7 January 1984) was a German-born French physicist and Nobel laureate in Physics. He is known for the development of optical pumping.
Biography
Kastler was born in Guebwiller (Alsace, at the time part of the Germ ...
(Nobel Prize for Physics 1966) proposed the method of optical pumping
Optical pumping is a process in which light is used to raise (or "pump") electrons from a lower energy level in an atom or molecule to a higher one. It is commonly used in laser construction to pump the active laser medium so as to achieve popu ...
, which was experimentally demonstrated two years later by Brossel, Kastler, and Winter.
Maser
 In 1951,
In 1951, Joseph Weber
Joseph Weber (May 17, 1919 – September 30, 2000) was an American physicist. He gave the earliest public lecture on the principles behind the laser and the maser and developed the first gravitational wave detectors, known as Weber bars.
Ear ...
submitted a paper on using stimulated emissions to make a microwave amplifier to the June 1952 Institute of Radio Engineers Vacuum Tube Research Conference in Ottawa
Ottawa is the capital city of Canada. It is located in the southern Ontario, southern portion of the province of Ontario, at the confluence of the Ottawa River and the Rideau River. Ottawa borders Gatineau, Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the cor ...
, Ontario, Canada. After this presentation, RCA
RCA Corporation was a major American electronics company, which was founded in 1919 as the Radio Corporation of America. It was initially a patent pool, patent trust owned by General Electric (GE), Westinghouse Electric Corporation, Westinghou ...
asked Weber to give a seminar on this idea, and Charles H. Townes asked him for a copy of the paper.
 In 1953, Charles H. Townes and graduate students James P. Gordon and Herbert J. Zeiger produced the first microwave amplifier, a device operating on similar principles to the laser, but amplifying
In 1953, Charles H. Townes and graduate students James P. Gordon and Herbert J. Zeiger produced the first microwave amplifier, a device operating on similar principles to the laser, but amplifying microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than other radio waves but longer than infrared waves. Its wavelength ranges from about one meter to one millimeter, corresponding to frequency, frequencies between 300&n ...
radiation rather than infrared or visible radiation. Townes's maser was incapable of continuous output. Meanwhile, in the Soviet Union, Nikolay Basov
Nikolay Gennadiyevich Basov (; 14 December 1922 – 1 July 2001) was a Russian Soviet physicist and educator. For his fundamental work in the field of quantum electronics that led to the development of laser and maser, Basov shared the 1964 Nobe ...
and Aleksandr Prokhorov were independently working on the quantum oscillator and solved the problem of continuous-output systems by using more than two energy levels. These gain media could release stimulated emission
Stimulated emission is the process by which an incoming photon of a specific frequency can interact with an excited atomic electron (or other excited molecular state), causing it to drop to a lower energy level. The liberated energy transfers to ...
s between an excited state and a lower excited state, not the ground state, facilitating the maintenance of a population inversion
In physics, specifically statistical mechanics, a population inversion occurs when a system (such as a group of atoms or molecules) exists in a state in which more members of the system are in higher, excited states than in lower, unexcited energy ...
. In 1955, Prokhorov and Basov suggested optical pumping of a multi-level system as a method for obtaining the population inversion, later a main method of laser pumping.
Townes reports that several eminent physicistsamong them Niels Bohr
Niels Henrik David Bohr (, ; ; 7 October 1885 – 18 November 1962) was a Danish theoretical physicist who made foundational contributions to understanding atomic structure and old quantum theory, quantum theory, for which he received the No ...
, John von Neumann
John von Neumann ( ; ; December 28, 1903 – February 8, 1957) was a Hungarian and American mathematician, physicist, computer scientist and engineer. Von Neumann had perhaps the widest coverage of any mathematician of his time, in ...
, and Llewellyn Thomas
Llewellyn Hilleth Thomas (21 October 1903 – 20 April 1992) was a British physicist and applied mathematician. He is best known for his contributions to atomic and molecular physics and solid-state physics. His key achievements include calculat ...
argued the maser violated Heisenberg's uncertainty principle
The uncertainty principle, also known as Heisenberg's indeterminacy principle, is a fundamental concept in quantum mechanics. It states that there is a limit to the precision with which certain pairs of physical properties, such as position a ...
and hence could not work. Others such as Isidor Rabi and Polykarp Kusch expected that it would be impractical and not worth the effort. In 1964, Charles H. Townes, Nikolay Basov, and Aleksandr Prokhorov shared the Nobel Prize in Physics
The Nobel Prize in Physics () is an annual award given by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences for those who have made the most outstanding contributions to mankind in the field of physics. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the ...
, "for fundamental work in the field of quantum electronics, which has led to the construction of oscillators and amplifiers based on the maser–laser principle".
Laser
In April 1957, Japanese engineerJun-ichi Nishizawa
was a Japanese engineer and inventor. He is known for his electronic inventions since the 1950s, including the PIN diode, static induction transistor, static induction thyristor, SIT/SITh. His inventions contributed to the development of ...
proposed the concept of a " semiconductor optical maser" in a patent application. That same year, Charles H. Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow, then at Bell Labs
Nokia Bell Labs, commonly referred to as ''Bell Labs'', is an American industrial research and development company owned by Finnish technology company Nokia. With headquarters located in Murray Hill, New Jersey, Murray Hill, New Jersey, the compa ...
, began a serious study of infrared "optical masers". As ideas developed, they abandoned infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those ...
radiation to instead concentrate on visible light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm ...
.
Simultaneously, Columbia University
Columbia University in the City of New York, commonly referred to as Columbia University, is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Churc ...
graduate student Gordon Gould
Richard Gordon Gould (July 17, 1920 – September 16, 2005) was an American physicist who is sometimes credited with the invention of the laser and the optical amplifier. (Credit for the invention of the laser is disputed, since Charles Towne ...
was working on a doctoral thesis
A thesis (: theses), or dissertation (abbreviated diss.), is a document submitted in support of candidature for an academic degree or professional qualification presenting the author's research and findings.International Standard ISO 7144: D ...
about the energy levels of excited thallium
Thallium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Tl and atomic number 81. It is a silvery-white post-transition metal that is not found free in nature. When isolated, thallium resembles tin, but discolors when exposed to air. Che ...
. Gould and Townes met and talked about radiation emission as a general subject, but not the specific work they were pursuing. Later, in November 1957, Gould noted his ideas for how a "laser" could be made, including using an open resonator
A resonator is a device or system that exhibits resonance or resonant behavior. That is, it naturally oscillates with greater amplitude at some frequencies, called resonant frequencies, than at other frequencies. The oscillations in a reso ...
(an essential laser-device component). His notebook included a diagram of an optically pumped laser. It also contained the first recorded use of the term "laser," an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation," along with suggestions for potential applications of the coherent light beams described.
In 1958, Bell Labs filed a patent application for Schawlow and Townes's proposed optical maser; and Schawlow and Townes published a paper with their theoretical calculations in the ''Physical Review
''Physical Review'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal. The journal was established in 1893 by Edward Nichols. It publishes original research as well as scientific and literature reviews on all aspects of physics. It is published by the Ame ...
''. That same year, Prokhorov independently proposed using an open resonator, the first published appearance of this idea.
At a conference in 1959, Gordon Gould first published the acronym "LASER" in the paper ''The LASER, Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation''. Gould's intention was that different "-ASER" acronyms should be used for different parts of the spectrum: "XASER" for x-rays, "UVASER" for ultraviolet, "RASER" for radio-wave, etc. Instead, the term "LASER" ended up being used for all devices operating at wavelengths shorter than microwaves.
Gould's notes included possible applications for a laser, such as optical telecommunications, spectrometry, interferometry
Interferometry is a technique which uses the ''interference (wave propagation), interference'' of Superposition principle, superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important inves ...
, radar
Radar is a system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), direction ( azimuth and elevation angles), and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It is a radiodetermination method used to detect and track ...
, and nuclear fusion
Nuclear fusion is a nuclear reaction, reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei combine to form a larger nuclei, nuclei/neutrons, neutron by-products. The difference in mass between the reactants and products is manifested as either the rele ...
. He continued developing the idea and filed a patent application
A patent application is a request pending at a patent office for the grant of a patent for an invention described in the patent specification and a set of one or more claim (patent), claims stated in a formal document, including necessary officia ...
in April 1959. The United States Patent and Trademark Office
The United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) is an List of federal agencies in the United States, agency in the United States Department of Commerce, U.S. Department of Commerce that serves as the national patent office and trademark ...
(USPTO) denied his application, and awarded a patent to Bell Labs
Nokia Bell Labs, commonly referred to as ''Bell Labs'', is an American industrial research and development company owned by Finnish technology company Nokia. With headquarters located in Murray Hill, New Jersey, Murray Hill, New Jersey, the compa ...
, in 1960. That provoked a twenty-eight-year legal fight over the rights to various laser technologies and applications. Gould won his first patent in 1977 for optically pumped laser amplifiers, yet it was not until 1987 that he won his first significant patent infringement claim. Many aspects of a working laser were patented by different people: the question of just how to assign credit for inventing the laser remains unresolved by historians.
On May 16, 1960, Theodore H. Maiman operated the first functioning laser at Hughes Research Laboratories, Malibu, California, ahead of several research teams, including those of Townes, at Columbia University
Columbia University in the City of New York, commonly referred to as Columbia University, is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Churc ...
, Arthur L. Schawlow, at Bell Labs
Nokia Bell Labs, commonly referred to as ''Bell Labs'', is an American industrial research and development company owned by Finnish technology company Nokia. With headquarters located in Murray Hill, New Jersey, Murray Hill, New Jersey, the compa ...
, and Gould, at the TRG (Technical Research Group) company. Maiman's functional laser used a flashlamp-pumped synthetic ruby
Ruby is a pinkish-red-to-blood-red-colored gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum ( aluminium oxide). Ruby is one of the most popular traditional jewelry gems and is very durable. Other varieties of gem-quality corundum are called sapph ...
crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macros ...
to produce red laser light at 694 nanometers wavelength. The device was only capable of pulsed operation, due to its three-level pumping design scheme. Later that year, the Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
ian physicist Ali Javan, and William R. Bennett Jr., and Donald R. Herriott, constructed the first gas laser, using helium
Helium (from ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, non-toxic, inert gas, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. Its boiling point is ...
and neon
Neon is a chemical element; it has symbol Ne and atomic number 10. It is the second noble gas in the periodic table. Neon is a colorless, odorless, inert monatomic gas under standard conditions, with approximately two-thirds the density of ...
that was capable of continuous operation in the infrared (U.S. Patent 3,149,290); later, Javan received the Albert Einstein World Award of Science
The Albert Einstein World Award for Science is an annual award given by the World Cultural Council "as a means of recognition and encouragement for scientific and technological research and development", with special consideration for researche ...
in 1993. In 1962, Robert N. Hall demonstrated the first semiconductor laser
The laser diode chip removed and placed on the eye of a needle for scale
A laser diode (LD, also injection laser diode or ILD or semiconductor laser or diode laser) is a semiconductor device similar to a light-emitting diode in which a diode p ...
, which was made of gallium arsenide
Gallium arsenide (GaAs) is a III-V direct band gap semiconductor with a Zincblende (crystal structure), zinc blende crystal structure.
Gallium arsenide is used in the manufacture of devices such as microwave frequency integrated circuits, monoli ...
and emitted in the near-infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those of ...
band of the spectrum at 850 nm. Later that year, Nick Holonyak Jr. demonstrated the first semiconductor laser with a visible emission. This first semiconductor laser could only be used in pulsed-beam operation, and when cooled to liquid nitrogen
Liquid nitrogen (LN2) is nitrogen in a liquid state at cryogenics, low temperature. Liquid nitrogen has a boiling point of about . It is produced industrially by fractional distillation of liquid air. It is a colorless, mobile liquid whose vis ...
temperatures (77 K). In 1970, Zhores Alferov
Zhores Ivanovich Alferov ( rus, Жоре́с Ива́нович Алфёров, , ʐɐˈrɛs ɨˈvanəvʲɪtɕ ɐlˈfʲɵrəf}; ; 15 March 19301 March 2019) was a Soviet and Russian physicist and academic who contributed significantly to the cr ...
, in the USSR, and Izuo Hayashi and Morton Panish of Bell Labs also independently developed room-temperature, continual-operation diode lasers, using the heterojunction
A heterojunction is an interface between two layers or regions of dissimilar semiconductors. These semiconducting materials have unequal band gaps as opposed to a homojunction. It is often advantageous to engineer the electronic energy bands in m ...
structure.
Recent innovations
energy
Energy () is the physical quantity, quantitative physical property, property that is transferred to a physical body, body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of Work (thermodynamics), work and in the form of heat and l ...
* maximum peak pulse power
Power may refer to:
Common meanings
* Power (physics), meaning "rate of doing work"
** Engine power, the power put out by an engine
** Electric power, a type of energy
* Power (social and political), the ability to influence people or events
Math ...
* minimum output pulse duration
* minimum linewidth
* maximum power efficiency
* minimum cost
Research on improving these aspects of lasers continues to this day.
In 2015, researchers made a white laser, whose light is modulated by a synthetic nanosheet made out of zinc, cadmium, sulfur, and selenium that can emit red, green, and blue light in varying proportions, with each wavelength spanning 191 nm.
In 2017, researchers at the Delft University of Technology
The Delft University of Technology (TU Delft; ) is the oldest and largest Dutch public university, public Institute of technology, technical university, located in Delft, Netherlands. It specializes in engineering, technology, computing, design, a ...
demonstrated an AC Josephson junction microwave laser. Since the laser operates in the superconducting regime, it is more stable than other semiconductor-based lasers. The device has the potential for applications in quantum computing
A quantum computer is a computer that exploits quantum mechanical phenomena. On small scales, physical matter exhibits properties of wave-particle duality, both particles and waves, and quantum computing takes advantage of this behavior using s ...
. In 2017, researchers at the Technical University of Munich
The Technical University of Munich (TUM or TU Munich; ) is a public research university in Munich, Bavaria, Germany. It specializes in engineering, technology, medicine, and applied and natural sciences.
Established in 1868 by King Ludwig II ...
demonstrated the smallest mode locking laser capable of emitting pairs of phase-locked picosecond laser pulses with a repetition frequency up to 200 GHz.
In 2017, researchers from the Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt
The Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB) is the national metrology institute of the Federal Republic of Germany, with scientific and technical service tasks. It is a higher federal authority and a public-law institution directly under fed ...
(PTB), together with US researchers from JILA, a joint institute of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the University of Colorado Boulder
The University of Colorado Boulder (CU Boulder, CU, or Colorado) is a public research university in Boulder, Colorado, United States. Founded in 1876, five months before Colorado became a state, it is the flagship university of the University o ...
, established a new world record by developing an erbium-doped fiber laser with a linewidth of only 10millihertz.
Types and operating principles
Gas lasers
Following the invention of the HeNe gas laser, many other gas discharges have been found to amplify light coherently. Gas lasers using many different gases have been built and used for many purposes. Thehelium–neon laser
A helium–neon laser or He–Ne laser is a type of gas laser whose high energetic gain medium consists of a mixture of helium and neon (ratio between 5:1 and 10:1) at a total pressure of approximately 1 Torr (133.322 Pa) inside a small electr ...
(HeNe) can operate at many different wavelengths, however, the vast majority are engineered to lase at 633 nm; these relatively low-cost but highly coherent lasers are extremely common in optical research and educational laboratories. Commercial carbon dioxide (CO2) lasers can emit many hundreds of watts in a single spatial mode which can be concentrated into a tiny spot. This emission is in the thermal infrared at 10.6 μm; such lasers are regularly used in industry for cutting and welding. The efficiency of a CO2 laser is unusually high: over 30%. Argon-ion lasers can operate at several lasing transitions between 351 and 528.7 nm. Depending on the optical design one or more of these transitions can be lasing simultaneously; the most commonly used lines are 458 nm, 488 nm and 514.5 nm. A nitrogen transverse electrical discharge in gas at atmospheric pressure (TEA) laser is an inexpensive gas laser, often home-built by hobbyists, which produces rather incoherent UV light at 337.1 nm. Metal ion lasers are gas lasers that generate deep ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of t ...
wavelengths. Helium
Helium (from ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, non-toxic, inert gas, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. Its boiling point is ...
-silver (HeAg) 224 nm and neon
Neon is a chemical element; it has symbol Ne and atomic number 10. It is the second noble gas in the periodic table. Neon is a colorless, odorless, inert monatomic gas under standard conditions, with approximately two-thirds the density of ...
-copper (NeCu) 248 nm are two examples. Like all low-pressure gas lasers, the gain media of these lasers have quite narrow oscillation linewidth
A spectral line is a weaker or stronger region in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum. It may result from emission or absorption of light in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies. Spectral lines are often used ...
s, less than 3 GHz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), often described as being equivalent to one event (or Cycle per second, cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose formal expression in ter ...
(0.5 picometers), making them candidates for use in fluorescence
Fluorescence is one of two kinds of photoluminescence, the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. When exposed to ultraviolet radiation, many substances will glow (fluoresce) with colore ...
suppressed Raman spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy () (named after physicist C. V. Raman) is a Spectroscopy, spectroscopic technique typically used to determine vibrational modes of molecules, although rotational and other low-frequency modes of systems may also be observed. Ra ...
.
Lasing without maintaining the medium excited into a population inversion was demonstrated in 1992 in sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the peri ...
gas and again in 1995 in rubidium
Rubidium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Rb and atomic number 37. It is a very soft, whitish-grey solid in the alkali metal group, similar to potassium and caesium. Rubidium is the first alkali metal in the group to have ...
gas by various international teams. This was accomplished by using an external maser to induce "optical transparency" in the medium by introducing and destructively interfering the ground electron transitions between two paths so that the likelihood for the ground electrons to absorb any energy has been canceled.
Chemical lasers
Chemical laser
A chemical laser is a laser that obtains its energy from a chemical reaction. Chemical lasers can reach continuous wave output with power reaching to megawatt levels. They are used in industry for cutting and drilling.
Common examples of chemical ...
s are powered by a chemical reaction permitting a large amount of energy to be released quickly. Such very high-power lasers are especially of interest to the military; however continuous wave chemical lasers at very high power levels, fed by streams of gasses, have been developed and have some industrial applications. As examples, in the hydrogen fluoride laser (2700–2900 nm) and the deuterium fluoride laser
The hydrogen fluoride laser is an infrared chemical laser. It is capable of delivering continuous output power in the megawatt range.
Hydrogen fluoride lasers operate at the wavelength of 2.7–2.9 μm. This wavelength is absorbed by the atm ...
(3800 nm) the reaction is the combination of hydrogen or deuterium gas with combustion products of ethylene
Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula or . It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon–carbon bond, carbon–carbon doub ...
in nitrogen trifluoride
Nitrogen trifluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula (). It is a colorless, non-flammable, toxic gas with a slightly musty odor. In contrast with ammonia, it is nonbasic. It finds increasing use within the manufacturing of flat-panel ...
.
The first chemical laser was demonstrated in 1965 by Jerome V. V. Kasper and George C. Pimentel at the University of California, Berkeley. It was a hydrogen chloride
The Chemical compound, compound hydrogen chloride has the chemical formula and as such is a hydrogen halide. At room temperature, it is a colorless gas, which forms white fumes of hydrochloric acid upon contact with atmospheric water vapor. Hyd ...
laser operating at 3.7 micrometers.
Excimer lasers
Excimer laser
An excimer laser, sometimes more correctly called an exciplex laser, is a form of ultraviolet laser which is commonly used in the production of microelectronic devices, semiconductor based integrated circuits or "chips", eye surgery, and micro ...
s are a special sort of gas laser powered by an electric discharge in which the lasing medium is an excimer
An excimer (originally short for excited dimer) is a short-lived polyatomic molecule formed from two species that do not form a stable molecule in the ground state. In this case, formation of molecules is possible only if such atom is in an elec ...
, or more precisely an exciplex
An excimer (originally short for excited dimer) is a short-lived polyatomic molecule formed from two species that do not form a stable molecule in the ground state. In this case, formation of molecules is possible only if such atom is in an elec ...
in existing designs. These are molecules that can only exist with one atom in an excited electronic state. Once the molecule transfers its excitation energy to a photon, its atoms are no longer bound to each other, and the molecule disintegrates. This drastically reduces the population of the lower energy state thus greatly facilitating a population inversion. Excimers currently used are all noble gas compounds; noble gasses are chemically inert and can only form compounds while in an excited state. Excimer lasers typically operate at ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
wavelengths, with major applications including semiconductor photolithography
Photolithography (also known as optical lithography) is a process used in the manufacturing of integrated circuits. It involves using light to transfer a pattern onto a substrate, typically a silicon wafer.
The process begins with a photosensiti ...
and LASIK
LASIK or Lasik (; "laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis"), commonly referred to as laser eye surgery or laser vision correction, is a type of refractive surgery for the correction of myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism. LASIK surgery is p ...
eye surgery. Commonly used excimer molecules include ArF (emission at 193 nm), KrCl (222 nm), KrF (248 nm), XeCl (308 nm), and XeF (351 nm).
The molecular fluorine
Fluorine is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists at Standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions as pale yellow Diatomic molecule, diatomic gas. Fluorine is extre ...
laser, emitting at 157 nm in the vacuum ultraviolet, is sometimes referred to as an excimer laser; however, this appears to be a misnomer since F2 is a stable compound.
Solid-state lasers
Solid-state laser
A solid-state laser is a laser that uses a active laser medium, gain medium that is a solid, rather than a liquid as in dye lasers or a gas as in gas lasers. Semiconductor-based lasers are also in the solid state, but are generally considered as ...
s use a crystalline or glass rod that is "doped" with ions that provide the required energy states. For example, the first working laser was a ruby laser
A ruby laser is a solid-state laser that uses a synthetic ruby crystal as its gain medium. The first working laser was a ruby laser made by Theodore H. "Ted" Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories on May 16, 1960.
Ruby lasers produce pulses of ...
, made from ruby
Ruby is a pinkish-red-to-blood-red-colored gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum ( aluminium oxide). Ruby is one of the most popular traditional jewelry gems and is very durable. Other varieties of gem-quality corundum are called sapph ...
(chromium
Chromium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6 element, group 6. It is a steely-grey, Luster (mineralogy), lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium ...
-doped corundum
Corundum is a crystalline form of aluminium oxide () typically containing traces of iron, titanium, vanadium, and chromium. It is a rock (geology), rock-forming mineral. It is a naturally transparency and translucency, transparent material, but ...
). The population inversion
In physics, specifically statistical mechanics, a population inversion occurs when a system (such as a group of atoms or molecules) exists in a state in which more members of the system are in higher, excited states than in lower, unexcited energy ...
is maintained in the dopant. These materials are pumped optically using a shorter wavelength than the lasing wavelength, often from a flash tube or another laser. The usage of the term "solid-state" in laser physics is narrower than in typical use. Semiconductor lasers (laser diodes) are typically ''not'' referred to as solid-state lasers.
Neodymium
Neodymium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Nd and atomic number 60. It is the fourth member of the lanthanide series and is considered to be one of the rare-earth element, rare-earth metals. It is a hard (physics), hard, sli ...
is a common dopant in various solid-state laser crystals, including yttrium orthovanadate
Yttrium orthovanadate (YVO4) is a transparent crystal. Undoped YVO4 is also used to make efficient high-power polarizing prisms similar to Glan–Taylor prisms.
There are two principal applications for doped yttrium orthovanadate:
*Doped with ...
( Nd:YVO4), yttrium lithium fluoride ( Nd:YLF) and yttrium aluminium garnet
Yttrium aluminium garnet (YAG, Yttrium, Y3Aluminium, Al5Oxygen, O12) is a synthetic crystalline material of the garnet group. It is a Crystal system, cubic yttrium aluminium oxide phase, with other examples being YAlO3 (YAP) in a Crystal system, ...
( Nd:YAG). All these lasers can produce high powers in the infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those ...
spectrum at 1064 nm. They are used for cutting, welding, and marking of metals and other materials, and also in spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets electromagnetic spectra. In narrower contexts, spectroscopy is the precise study of color as generalized from visible light to all bands of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Spectro ...
and for pumping dye laser
A dye laser is a laser that uses an organic dye as the lasing medium, usually as a liquid solution. Compared to gases and most solid state lasing media, a dye can usually be used for a much wider range of wavelengths, often spanning 50 to 100 n ...
s. These lasers are also commonly doubled, tripled or quadrupled in frequency to produce 532 nm (green, visible), 355 nm and 266 nm ( UV) beams, respectively. Frequency-doubled diode-pumped solid-state (DPSS) lasers are used to make bright green laser pointers.
Ytterbium
Ytterbium is a chemical element; it has symbol Yb and atomic number 70. It is a metal, the fourteenth and penultimate element in the lanthanide series, which is the basis of the relative stability of its +2 oxidation state. Like the other lanthani ...
, holmium
Holmium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ho and atomic number 67. It is a rare-earth element and the eleventh member of the lanthanide series. It is a relatively soft, silvery, fairly corrosion-resistant and malleable metal. Like many other ...
, thulium
Thulium is a chemical element; it has symbol Tm and atomic number 69. It is the thirteenth element in the lanthanide series of metals. It is the second-least abundant lanthanide in the Earth's crust, after radioactively unstable promethium. It i ...
, and erbium
Erbium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Er and atomic number 68. A silvery-white solid metal when artificially isolated, natural erbium is always found in chemical combination with other elements. It is a lanthanide, a rare- ...
are other common "dopants" in solid-state lasers. Ytterbium is used in crystals such as Yb:YAG, Yb:KGW, Yb:KYW, Yb:SYS, Yb:BOYS, Yb:CaF2, typically operating around 1020–1050 nm. They are potentially very efficient and high-powered due to a small quantum defect. Extremely high powers in ultrashort pulses can be achieved with Yb:YAG. Holmium
Holmium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ho and atomic number 67. It is a rare-earth element and the eleventh member of the lanthanide series. It is a relatively soft, silvery, fairly corrosion-resistant and malleable metal. Like many other ...
-doped YAG crystals emit at 2097 nm and form an efficient laser operating at infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those ...
wavelengths strongly absorbed by water-bearing tissues. The Ho-YAG is usually operated in a pulsed mode and passed through optical fiber surgical devices to resurface joints, remove rot from teeth, vaporize cancers, and pulverize kidney and gall stones.
Titanium
Titanium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in ...
-doped sapphire
Sapphire is a precious gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum, consisting of aluminium oxide () with trace amounts of elements such as iron, titanium, cobalt, lead, chromium, vanadium, magnesium, boron, and silicon. The name ''sapphire ...
( Ti:sapphire) produces a highly tunable infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those ...
laser, commonly used for spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets electromagnetic spectra. In narrower contexts, spectroscopy is the precise study of color as generalized from visible light to all bands of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Spectro ...
. It is also notable for use as a mode-locked laser producing ultrashort pulse
In optics, an ultrashort pulse, also known as an ultrafast event, is an electromagnetic pulse whose time duration is of the order of a picosecond (10−12 second) or less. Such pulses have a broadband optical spectrum, and can be created by ...
s of extremely high peak power.
Thermal limitations in solid-state lasers arise from unconverted pump power that heats the medium. This heat, when coupled with a high thermo-optic coefficient (d''n''/d''T'') can cause thermal lensing and reduce the quantum efficiency. Diode-pumped thin disk laser
A disk laser or active mirror (Fig.1) is a type of diode pumped solid-state laser characterized by a heat sink and laser output that are realized on opposite sides of a thin layer of active gain medium. Despite their name, disk lasers do not hav ...
s overcome these issues by having a gain medium that is much thinner than the diameter of the pump beam. This allows for a more uniform temperature in the material. Thin disk lasers have been shown to produce beams of up to one kilowatt.
Fiber lasers
Solid-state lasers or laser amplifiers where the light is guided due to thetotal internal reflection
In physics, total internal reflection (TIR) is the phenomenon in which waves arriving at the interface (boundary) from one medium to another (e.g., from water to air) are not refracted into the second ("external") medium, but completely refl ...
in a single mode optical fiber
An optical fiber, or optical fibre, is a flexible glass or plastic fiber that can transmit light from one end to the other. Such fibers find wide usage in fiber-optic communications, where they permit transmission over longer distances and at ...
are instead called fiber laser
A fiber laser (or fibre laser in Commonwealth English) is a laser in which the active gain medium is an optical fiber doped with rare-earth elements such as erbium, ytterbium, neodymium, dysprosium, praseodymium, thulium and holmium. They ar ...
s. Guiding of light allows extremely long gain regions, providing good cooling conditions; fibers have a high surface area to volume ratio which allows efficient cooling. In addition, the fiber's waveguiding properties tend to reduce thermal distortion of the beam. Erbium
Erbium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Er and atomic number 68. A silvery-white solid metal when artificially isolated, natural erbium is always found in chemical combination with other elements. It is a lanthanide, a rare- ...
and ytterbium
Ytterbium is a chemical element; it has symbol Yb and atomic number 70. It is a metal, the fourteenth and penultimate element in the lanthanide series, which is the basis of the relative stability of its +2 oxidation state. Like the other lanthani ...
ions are common active species in such lasers.
Quite often, the fiber laser is designed as a double-clad fiber
Double-clad fiber (DCF) is a class of optical fiber with a structure consisting of three layers of optical material instead of the usual two. The inner-most layer is called the ''core''. It is surrounded by the ''inner cladding'', which is surr ...
. This type of fiber consists of a fiber core, an inner cladding, and an outer cladding. The index of the three concentric layers is chosen so that the fiber core acts as a single-mode fiber for the laser emission while the outer cladding acts as a highly multimode core for the pump laser. This lets the pump propagate a large amount of power into and through the active inner core region while still having a high numerical aperture (NA) to have easy launching conditions.
Pump light can be used more efficiently by creating a fiber disk laser, or a stack of such lasers.
Fiber lasers, like other optical media, can suffer from the effects of photodarkening when they are exposed to radiation of certain wavelengths. In particular, this can lead to degradation of the material and loss in laser functionality over time. The exact causes and effects of this phenomenon vary from material to material, although it often involves the formation of color centers.
Photonic crystal lasers
Photonic crystal
A photonic crystal is an optical nanostructure in which the refractive index changes periodically. This affects the propagation of light in the same way that the structure of Crystal structure, natural crystals gives rise to X-ray crystallograp ...
lasers are lasers based on nano-structures that provide the mode confinement and the density of optical states (DOS) structure required for the feedback to take place. They are typical micrometer-sized and tunable on the bands of the photonic crystals.
Semiconductor lasers
 Semiconductor lasers are
Semiconductor lasers are diode
A diode is a two-Terminal (electronics), terminal electronic component that conducts electric current primarily in One-way traffic, one direction (asymmetric electrical conductance, conductance). It has low (ideally zero) Electrical resistance ...
s that are electrically pumped. Recombination of electrons and holes created by the applied current introduces optical gain. Reflection from the ends of the crystal forms an optical resonator, although the resonator can be external to the semiconductor in some designs.
Commercial laser diode
file:Laser diode chip.jpg, The laser diode chip removed and placed on the eye of a needle for scale
A laser diode (LD, also injection laser diode or ILD or semiconductor laser or diode laser) is a semiconductor device similar to a light-emittin ...
s emit at wavelengths from 375 nm to 3500 nm. Low to medium power laser diodes are used in laser pointer
A laser pointer or laser pen is a (typically battery-powered) handheld device that uses a laser diode to emit a narrow low-power visible laser beam (i.e. Coherence (physics), coherent light) to highlight something of interest with a small brigh ...
s, laser printer
Laser printing is an electrostatic digital printing process. It produces high-quality text and graphics (and moderate-quality photographs) by repeatedly passing a laser beam back and forth over a Electric charge, negatively charged cylinder call ...
s and CD/DVD players. Laser diodes are also frequently used to optically pump
A pump is a device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or sometimes Slurry, slurries, by mechanical action, typically converted from electrical energy into hydraulic or pneumatic energy.
Mechanical pumps serve in a wide range of application ...
other lasers with high efficiency. The highest-power industrial laser diodes, with power of up to 20 kW, are used in industry for cutting and welding. External-cavity semiconductor lasers have a semiconductor active medium in a larger cavity. These devices can generate high power outputs with good beam quality, wavelength-tunable narrow-linewidth
A spectral line is a weaker or stronger region in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum. It may result from emission or absorption of light in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies. Spectral lines are often used ...
radiation, or ultrashort laser pulses.
In 2012, Nichia and OSRAM
OSRAM Licht AG is a German company that makes electric lights, headquartered in Munich and Premstätten (Austria). OSRAM positions itself as a high-tech photonics company that is increasingly focusing on sensor technology, visualization and trea ...
developed and manufactured commercial high-power green laser diodes (515/520 nm), which compete with traditional diode-pumped solid-state lasers.
Vertical cavity surface-emitting lasers (VCSEL
The vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL ) is a type of semiconductor laser diode with laser beam emission perpendicular from the top surface, contrary to conventional edge-emitting semiconductor lasers (also called ''in-plane'' laser ...
s) are semiconductor lasers whose emission direction is perpendicular to the surface of the wafer. VCSEL devices typically have a more circular output beam than conventional laser diodes. As of 2005, only 850 nm VCSELs are widely available, with 1300 nm VCSELs beginning to be commercialized and 1550 nm devices being an area of research. VECSEL
A vertical-external-cavity surface-emitting-laser (VECSEL) is a small semiconductor laser similar to a vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL). VECSELs are used primarily as near infrared devices in laser cooling and spectroscopy, but hav ...
s are external-cavity VCSELs. Quantum cascade lasers are semiconductor lasers that have an active transition between energy ''sub-bands'' of an electron in a structure containing several quantum well
A quantum well is a potential well with only discrete energy values.
The classic model used to demonstrate a quantum well is to confine particles, which were initially free to move in three dimensions, to two dimensions, by forcing them to occup ...
s.
The development of a silicon
Silicon is a chemical element; it has symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic lustre, and is a tetravalent metalloid (sometimes considered a non-metal) and semiconductor. It is a membe ...
laser is important in the field of optical computing
Optical computing or photonic computing uses light waves produced by lasers or incoherent sources for data processing, data storage or data communication for computing. For decades, photons have shown promise to enable a higher bandwidth than the ...
. Silicon is the material of choice for integrated circuits
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
, and so electronic and silicon photonic components (such as optical interconnect
In integrated circuits, optical interconnects refers to any system of transmitting signals from one part of an integrated circuit to another using light. Optical interconnects have been the topic of study due to the high latency and power consumpt ...
s) could be fabricated on the same chip. Unfortunately, silicon is a difficult lasing material to deal with, since it has certain properties which block lasing. However, recently teams have produced silicon lasers through methods such as fabricating the lasing material from silicon and other semiconductor materials, such as indium(III) phosphide or gallium(III) arsenide
Gallium arsenide (GaAs) is a III-V direct band gap semiconductor with a zinc blende crystal structure.
Gallium arsenide is used in the manufacture of devices such as microwave frequency integrated circuits, monolithic microwave integrated cir ...
, materials that allow coherent light to be produced from silicon. These are called hybrid silicon lasers. Recent developments have also shown the use of monolithically integrated nanowire lasers directly on silicon for optical interconnects, paving the way for chip-level applications. These heterostructure nanowire lasers capable of optical interconnects in silicon are also capable of emitting pairs of phase-locked picosecond pulses with a repetition frequency up to 200 GHz, allowing for on-chip optical signal processing. Another type is a Raman laser, which takes advantage of Raman scattering
In chemistry and physics, Raman scattering or the Raman effect () is the inelastic scattering of photons by matter, meaning that there is both an exchange of energy and a change in the light's direction. Typically this effect involves vibrationa ...
to produce a laser from materials such as silicon.
Semiconductor quantum dot lasers use quantum dot
Quantum dots (QDs) or semiconductor nanocrystals are semiconductor particles a few nanometres in size with optical and electronic properties that differ from those of larger particles via quantum mechanical effects. They are a central topic i ...
s as the active laser medium. These lasers exhibit device performance that is closer to gas lasers and avoid some of the disadvantages of traditional semiconductor laser media. Improvements in modulation bandwidth, lasing threshold The lasing threshold is the lowest excitation level at which a laser's output is dominated by stimulated emission rather than by spontaneous emission. Below the threshold, the laser's output power rises slowly with increasing excitation. Above thr ...
, relative intensity noise, linewidth enhancement factor and temperature insensitivity have all been observed. The quantum dot active region may also be engineered to operate at different wavelengths by varying dot size and composition. This allows quantum dot lasers to be fabricated to operate at wavelengths previously not possible using semiconductor laser technology.
Dye lasers

Dye laser
A dye laser is a laser that uses an organic dye as the lasing medium, usually as a liquid solution. Compared to gases and most solid state lasing media, a dye can usually be used for a much wider range of wavelengths, often spanning 50 to 100 n ...
s use an organic dye as the gain medium. The wide gain spectrum of available dyes, or mixtures of dyes, allows these lasers to be highly tunable, or to produce very short-duration pulses ( on the order of a few femtosecond
A femtosecond is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to 10 or of a second; that is, one quadrillionth, or one millionth of one billionth, of a second.
A femtosecond is to a second, as a second is to approximately 31.6 ...
s). Although these tunable laser
A tunable laser is a laser whose wavelength of operation can be altered in a controlled manner. While all active laser medium, laser gain media allow small shifts in output wavelength, only a few types of lasers allow continuous tuning over a sign ...
s are mainly known in their liquid form, researchers have also demonstrated narrow-linewidth tunable emission in dispersive oscillator configurations incorporating solid-state dye gain media. In their most prevalent form, these solid-state dye lasers use dye-doped polymers as laser media.
Bubble laser
An ordinary Bubble_(physics), bubble can serve as an optofluidics, optofluidic laser. These bubble lasers have been made of dye-doped soap solutions and Liquid crystal#Smectic_phases, smectic liquid crystal. In a bubble laser, the bubble itself se ...
s are dye lasers that use a bubble
Bubble, Bubbles or The Bubble may refer to:
Common uses
* Bubble (physics), a globule of one substance in another, usually gas in a liquid
** Soap bubble
* Economic bubble, a situation where asset prices are much higher than underlying fundame ...
as the optical resonator. Whispering gallery modes in the bubble produce an output spectrum composed of hundreds of evenly spaced peaks: a frequency comb
A frequency comb or spectral comb is a spectrum made of discrete and regularly spaced spectral lines.
In optics, a frequency comb can be generated by certain laser sources.
A number of mechanisms exist for obtaining an optical frequency comb, i ...
. The spacing of the whispering gallery modes is directly related to the bubble circumference, allowing bubble lasers to be used as highly sensitive pressure sensors.
Free-electron lasers

Free-electron laser
A free-electron laser (FEL) is a fourth generation light source producing extremely brilliant and short pulses of radiation. An FEL functions much as a laser but employs relativistic electrons as a active laser medium, gain medium instead of using ...
s (FEL) generate coherent, high-power radiation that is widely tunable, currently ranging in wavelength from microwaves through terahertz radiation
Terahertz radiation – also known as submillimeter radiation, terahertz waves, tremendously high frequency
(THF), T-rays, T-waves, T-light, T-lux or THz – consists of electromagnetic waves within the International Telecommunicat ...
and infrared to the visible spectrum, to soft X-rays. They have the widest frequency range of any laser type. While FEL beams share the same optical traits as other lasers, such as coherent radiation, FEL operation is quite different. Unlike gas, liquid, or solid-state lasers, which rely on bound atomic or molecular states, FELs use a relativistic electron beam as the lasing medium, hence the term ''free-electron''.
Exotic media
The pursuit of a high-quantum-energy laser using transitions between isomeric states of anatomic nucleus
The atomic nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom, discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford at the Department_of_Physics_and_Astronomy,_University_of_Manchester , University of Manchester ...
has been the subject of wide-ranging academic research since the early 1970s. Much of this is summarized in three review articles. This research has been international in scope but mainly based in the former Soviet Union and the United States. While many scientists remain optimistic that a breakthrough is near, an operational gamma-ray laser is yet to be realized.
Some of the early studies were directed toward short pulses of neutrons exciting the upper isomer state in a solid so the gamma-ray transition could benefit from the line-narrowing of Mössbauer effect
The Mössbauer effect, or recoilless nuclear resonance fluorescence, is a physical phenomenon discovered by Rudolf Mössbauer in 1958. It involves the resonant and recoil-free emission and absorption of gamma radiation by atomic nuclei bound in a ...
. In conjunction, several advantages were expected from two-stage pumping of a three-level system. It was conjectured that the nucleus of an atom embedded in the near field of a laser-driven coherently-oscillating electron cloud would experience a larger dipole field than that of the driving laser. Furthermore, the nonlinearity of the oscillating cloud would produce both spatial and temporal harmonics, so nuclear transitions of higher multipolarity could also be driven at multiples of the laser frequency.
In September 2007, the BBC News
BBC News is an operational business division of the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) responsible for the gathering and broadcasting of news and current affairs in the UK and around the world. The department is the world's largest broad ...
reported that there was speculation about the possibility of using positronium
Positronium (Ps) is a system consisting of an electron and its antimatter, anti-particle, a positron, bound together into an exotic atom, specifically an onium. Unlike hydrogen, the system has no protons. The system is unstable: the two part ...
annihilation
In particle physics, annihilation is the process that occurs when a subatomic particle collides with its respective antiparticle to produce other particles, such as an electron colliding with a positron to produce two photons. The total energy a ...
to drive a very powerful gamma ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol ), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from high energy interactions like the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei or astronomical events like solar flares. It consists o ...
laser. David Cassidy of the University of California, Riverside
The University of California, Riverside (UCR or UC Riverside) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Riverside, California, United States. It is one of the ten campuses of the University of Cali ...
proposed that a single such laser could be used to ignite a nuclear fusion
Nuclear fusion is a nuclear reaction, reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei combine to form a larger nuclei, nuclei/neutrons, neutron by-products. The difference in mass between the reactants and products is manifested as either the rele ...
reaction, replacing the banks of hundreds of lasers currently employed in inertial confinement fusion
Inertial confinement fusion (ICF) is a fusion energy process that initiates nuclear fusion reactions by compressing and heating targets filled with fuel. The targets are small pellets, typically containing deuterium (2H) and tritium (3H).
Typical ...
experiments.
Space-based X-ray laser
An X-ray laser can be created by several methods either in hot, dense plasmas or as a free-electron laser in an accelerator. This article describes the x-ray lasers in plasmas, only.
The plasma x-ray lasers rely on stimulated emission to gener ...
s pumped by nuclear explosions have also been proposed as antimissile weapons. Such devices would be one-shot weapons.
Living cells have been used to produce laser light. The cells were genetically engineered to produce green fluorescent protein
The green fluorescent protein (GFP) is a protein that exhibits green fluorescence when exposed to light in the blue to ultraviolet range. The label ''GFP'' traditionally refers to the protein first isolated from the jellyfish ''Aequorea victo ...
, which served as the laser's gain medium. The cells were then placed between two 20-micrometer-wide mirrors, which acted as the laser cavity. When the cell was illuminated with blue light, it emitted intensely directed green laser light.
Natural lasers
Likeastrophysical maser
An astrophysical maser is a naturally occurring source of Stimulated emission, stimulated spectral line emission, typically in the microwave portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. This emission may arise in molecular clouds, comets, planetary at ...
s, irradiated planetary or stellar gases may amplify light producing a natural laser. Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
, Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is often called Earth's "twin" or "sister" planet for having almost the same size and mass, and the closest orbit to Earth's. While both are rocky planets, Venus has an atmosphere much thicker ...
, and MWC 349 exhibit this phenomenon.
Uses
 When the laser was first invented, it was called "a solution looking for a problem", although Gould noted numerous possible applications in his notebook and patent applications. Since then, they have become ubiquitous, finding utility in thousands of highly varied applications in every section of modern society, including
When the laser was first invented, it was called "a solution looking for a problem", although Gould noted numerous possible applications in his notebook and patent applications. Since then, they have become ubiquitous, finding utility in thousands of highly varied applications in every section of modern society, including consumer electronics
Consumer electronics, also known as home electronics, are electronic devices intended for everyday household use. Consumer electronics include those used for entertainment, Communication, communications, and recreation. Historically, these prod ...
, information technology, science, medicine, industry, law enforcement
Law enforcement is the activity of some members of the government or other social institutions who act in an organized manner to enforce the law by investigating, deterring, rehabilitating, or punishing people who violate the rules and norms gove ...
, entertainment, and the military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a d ...
. Fiber-optic communication
Fiber-optic communication is a form of optical communication for transmitting information from one place to another by sending pulses of infrared or visible light through an optical fiber. The light is a form of carrier wave that is modul ...
relies on multiplexed lasers in dense wave-division multiplexing (WDM) systems to transmit large amounts of data over long distances.
The first widely noticeable use of lasers was the supermarket barcode scanner
A barcode reader or barcode scanner is an optical scanner that can read printed barcodes and send the data they contain to computer. Like a flatbed scanner, it consists of a light source, a lens, and a light sensor for translating optical impulses ...
, introduced in 1974. The laserdisc
LaserDisc (LD) is a home video format and the first commercial optical disc storage medium. It was developed by Philips, Pioneer Corporation, Pioneer, and the movie studio MCA Inc., MCA. The format was initially marketed in the United State ...
player, introduced in 1978, was the first successful consumer product to include a laser, but the compact disc player was the first laser-equipped device to become common, commercialized in 1982, followed shortly by laser printer
Laser printing is an electrostatic digital printing process. It produces high-quality text and graphics (and moderate-quality photographs) by repeatedly passing a laser beam back and forth over a Electric charge, negatively charged cylinder call ...
s.
Some other uses are:
* Communications: besides fiber-optic communication
Fiber-optic communication is a form of optical communication for transmitting information from one place to another by sending pulses of infrared or visible light through an optical fiber. The light is a form of carrier wave that is modul ...
, lasers are used for free-space optical communication
Free-space optical communication (FSO) is an optical communication technology that uses light propagating in free space to wirelessly transmit data for telecommunications or computer networking over long distances. "Free space" means air, oute ...
, including laser communication in space
Laser communication in space is the use of free-space optical communication in outer space. Communication may be fully in space (an inter-satellite laser link) or in a ground-to-satellite or satellite-to-ground application. The main advantage o ...
* Medicine: see below
Below may refer to:
*Earth
*Ground (disambiguation)
*Soil
*Floor
* Bottom (disambiguation)
*Less than
*Temperatures below freezing
*Hell or underworld
People with the surname
* Ernst von Below (1863–1955), German World War I general
* Fred Belo ...
* Industry: cutting
Cutting is the separation or opening of a physical object, into two or more portions, through the application of an acutely directed force.
Implements commonly used for wikt:cut, cutting are the knife and saw, or in medicine and science the sca ...
including converting thin materials, welding
Welding is a fabrication (metal), fabrication process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, primarily by using high temperature to melting, melt the parts together and allow them to cool, causing Fusion welding, fusion. Co ...
, material heat treatment
Heat treating (or heat treatment) is a group of industrial, thermal and metalworking processes used to alter the physical, and sometimes chemical, properties of a material. The most common application is metallurgical. Heat treatments are a ...
, marking parts (engraving
Engraving is the practice of incising a design on a hard, usually flat surface by cutting grooves into it with a Burin (engraving), burin. The result may be a decorated object in itself, as when silver, gold, steel, or Glass engraving, glass ar ...
and bonding), additive manufacturing
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is the construction of a three-dimensional object from a CAD model or a digital 3D model. It can be done in a variety of processes in which material is deposited, joined or solidified under computer ...
or 3D printing
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is the construction of a three-dimensional object from a CAD model or a digital 3D model. It can be done in a variety of processes in which material is deposited, joined or solidified under computer ...
processes such as selective laser sintering
Selective laser sintering (SLS) is an additive manufacturing (AM) technique that uses a laser as the power and heat source to sinter powdered material (typically nylon or polyamide), aiming the laser automatically at points in space defined ...
and selective laser melting
Selective laser melting (SLM) is one of many proprietary names for a metal Additive Manufacturing, additive manufacturing (AM) technology that uses a bed of powder with a source of heat to create metal parts. Also known as direct metal laser sin ...
, laser metal deposition, and non-contact measurement of parts and 3D scanning
3D scanning is the process of analyzing a real-world object or environment to collect three dimensional data of its shape and possibly its appearance (e.g. color). The collected data can then be used to construct digital 3D models.
A 3D scanner ...
, and laser cleaning.
* Military: marking targets, guiding munition
Ammunition, also known as ammo, is the material fired, scattered, dropped, or detonated from any weapon or weapon system. The term includes both expendable weapons (e.g., bombs, missiles, grenades, land mines), and the component parts of oth ...
s, missile defense
Missile defense is a system, weapon, or technology involved in the detection, tracking, interception, and also the destruction of attacking missiles. Conceived as a defense against nuclear weapon, nuclear-armed intercontinental ballistic mi ...
, electro-optical countermeasures (EOCM), lidar
Lidar (, also LIDAR, an acronym of "light detection and ranging" or "laser imaging, detection, and ranging") is a method for determining ranging, ranges by targeting an object or a surface with a laser and measuring the time for the reflected li ...
, blinding troops, firearms sights. See below
Below may refer to:
*Earth
*Ground (disambiguation)
*Soil
*Floor
* Bottom (disambiguation)
*Less than
*Temperatures below freezing
*Hell or underworld
People with the surname
* Ernst von Below (1863–1955), German World War I general
* Fred Belo ...
* Law enforcement
Law enforcement is the activity of some members of the government or other social institutions who act in an organized manner to enforce the law by investigating, deterring, rehabilitating, or punishing people who violate the rules and norms gove ...
: LIDAR traffic enforcement. Lasers are used for latent fingerprint
A fingerprint is an impression left by the friction ridges of a human finger. The recovery of partial fingerprints from a crime scene is an important method of forensic science. Moisture and grease on a finger result in fingerprints on surfa ...
detection in the forensic identification
Forensic identification is the application of forensic science, or "forensics", and technology to identify specific objects from the trace evidence they leave, often at a crime scene or the scene of an accident. Forensic means "for the courts".
Hu ...
field
* Research: spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets electromagnetic spectra. In narrower contexts, spectroscopy is the precise study of color as generalized from visible light to all bands of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Spectro ...
, laser ablation
Laser ablation or photoablation (also called laser blasting) is the process of removing material from a solid (or occasionally liquid) surface by irradiating it with a laser beam. At low laser flux, the material is heated by the absorbed laser ...
, laser annealing, laser scattering
In physics, scattering is a wide range of physical processes where moving particles or radiation of some form, such as light or sound, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by localized non-uniformities (including particles and radiat ...
, laser interferometry
Interferometry is a technique which uses the ''interference (wave propagation), interference'' of Superposition principle, superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important inves ...
, lidar
Lidar (, also LIDAR, an acronym of "light detection and ranging" or "laser imaging, detection, and ranging") is a method for determining ranging, ranges by targeting an object or a surface with a laser and measuring the time for the reflected li ...
, laser capture microdissection
Laser capture microdissection (LCM), also called microdissection, laser microdissection (LMD), or laser-assisted microdissection (LMD or LAM), is a method for isolating specific cells of interest from microscopic regions of tissue/cells/organisms ...
, fluorescence microscopy
A fluorescence microscope is an optical microscope that uses fluorescence instead of, or in addition to, scattering, reflection, and attenuation or absorption, to study the properties of organic or inorganic substances. A fluorescence micro ...
, metrology
Metrology is the scientific study of measurement. It establishes a common understanding of Unit of measurement, units, crucial in linking human activities. Modern metrology has its roots in the French Revolution's political motivation to stan ...
, laser cooling
Laser cooling includes several techniques where atoms, molecules, and small mechanical systems are cooled with laser light. The directed energy of lasers is often associated with heating materials, e.g. laser cutting, so it can be counterintuit ...
* Commercial products: laser printer
Laser printing is an electrostatic digital printing process. It produces high-quality text and graphics (and moderate-quality photographs) by repeatedly passing a laser beam back and forth over a Electric charge, negatively charged cylinder call ...
s, barcode scanner
A barcode reader or barcode scanner is an optical scanner that can read printed barcodes and send the data they contain to computer. Like a flatbed scanner, it consists of a light source, a lens, and a light sensor for translating optical impulses ...
s, thermometer
A thermometer is a device that measures temperature (the hotness or coldness of an object) or temperature gradient (the rates of change of temperature in space). A thermometer has two important elements: (1) a temperature sensor (e.g. the bulb ...
s, laser pointer
A laser pointer or laser pen is a (typically battery-powered) handheld device that uses a laser diode to emit a narrow low-power visible laser beam (i.e. Coherence (physics), coherent light) to highlight something of interest with a small brigh ...
s, holograms, bubblegram
A bubblegram (also known as laser crystal, Subsurface Laser Engraving, 3D crystal engraving or vitrography) is a solid block of glass or transparent plastic that has been exposed to laser beams to generate three-dimensional space, three-dimensi ...
s
* Entertainment: optical discs
An optical disc is a flat, usuallyNon-circular optical discs exist for fashion purposes; see shaped compact disc. disc-shaped object that stores information in the form of physical variations on its surface that can be read with the aid of ...
, laser lighting displays, laser turntable
A laser turntable (or optical turntable) is a phonograph that plays standard LP records (and other gramophone records) using laser beams as the Phonograph cartridge, pickup instead of using a Phonograph#Stylus, stylus as in conventional phonograp ...
s.
* Informational markings: Laser lighting display technology can be used to project informational markings onto surfaces such as playing fields, roads, runways, or warehouse floors.
In 2004, excluding diode lasers, approximately 131,000 lasers were sold ,with a value of billion. In the same year, approximately 733 million diode lasers, valued at billion, were sold. Global Industrial laser sales in 2023 reached $21.85 billion.
In medicine
Lasers have many uses in medicine, includinglaser surgery
Laser surgery is a type of surgery that cuts tissue using a laser in contrast to using a scalpel.
Soft-tissue laser surgery is used in a variety of applications in humans ( general surgery, neurosurgery, ENT, dentistry, orthodontics, and ...
(particularly eye surgery
Eye surgery, also known as ophthalmic surgery or ocular surgery, is surgery performed on the eye or its adnexa. Eye surgery is part of ophthalmology and is performed by an ophthalmologist or eye surgeon. The eye is a fragile organ, and require ...
), laser healing (photobiomodulation therapy), kidney stone
Kidney stone disease (known as nephrolithiasis, renal calculus disease, or urolithiasis) is a crystallopathy and occurs when there are too many minerals in the urine and not enough liquid or hydration. This imbalance causes tiny pieces of cr ...
treatment, ophthalmoscopy
Ophthalmoscopy, also called funduscopy, is a test that allows a health professional to see inside the fundus of the eye and other structures using an ophthalmoscope (or funduscope). It is done as part of an eye examination and may be done as part ...
, and cosmetic skin treatments such as acne
Acne ( ), also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term Cutaneous condition, skin condition that occurs when Keratinocyte, dead skin cells and Sebum, oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include comedo, ...
treatment, cellulite
Cellulite () or gynoid lipodystrophy (GLD) is the herniation of subcutaneous fat within fibrous connective tissue that manifests as skin dimpling and nodularity, often on the pelvic region (specifically the buttocks), lower limbs, and abdomen. C ...
and striae reduction, and hair removal
Hair removal is the deliberate removal of body hair or head hair. This process is also known as epilation or depilation.
Hair is a common feature of the human body, exhibiting considerable variation in thickness and length across different po ...
.
Lasers are used to treat cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
by shrinking or destroying tumors
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
or precancerous growths. They are most commonly used to treat superficial cancers that are on the surface of the body or the lining of internal organs. They are used to treat basal cell skin cancer and the very early stages of others like cervical, penile, vaginal
In mammals and other animals, the vagina (: vaginas or vaginae) is the elastic, muscular reproductive organ of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vulval vestibule to the cervix (neck of the uterus). The vaginal introit ...
, vulvar, and non-small cell lung cancer
Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), or non-small-cell lung carcinoma, is any type of epithelial lung cancer other than small-cell lung cancer (SCLC). NSCLC accounts for about 85% of all lung cancers. As a class, NSCLCs are relatively insensitiv ...
. Laser therapy is often combined with other treatments, such as surgery
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery s ...
, chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
, or radiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a therapy, treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of treatment of cancer, cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignancy, malignant cell (biology), ...
. Laser-induced interstitial thermotherapy (LITT), or interstitial laser photocoagulation, uses lasers to treat some cancers using hyperthermia, which uses heat to shrink tumors by damaging or killing cancer cells. Lasers are more precise than traditional surgery methods and cause less damage, pain, bleeding
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethr ...
, swelling, and scarring. A disadvantage is that surgeons must acquire specialized training, and thus it will likely be more expensive than other treatments.
Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) is a treatment in which low-power light from lasers or light-emitting diode
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light (corre ...
s (LEDs) is applied to the surface of the body. This is claimed to stimulate healing, relieve pain, and enhance cell function. The effects appear to be limited to specific wavelengths of light. The effectiveness of this form of treatment is still under investigation. Repeated low-level red light therapy may be effective for controlling myopia
Myopia, also known as near-sightedness and short-sightedness, is an eye condition where light from distant objects focuses in front of, instead of on, the retina. As a result, distant objects appear blurry, while close objects appear normal. ...
in children. Several such devices are cleared by the United States Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respo ...
(FDA), and low level red light therapy is being tested for treating a range of medical problems including rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects synovial joint, joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and h ...
and oral mucositis.
As weapons
 A
A laser weapon
A laser weapon is a type of directed-energy weapon that uses lasers to inflict damage. Whether they will be deployed as practical, high-performance military weapons remains to be seen. One of the major issues with laser weapons is atmospheric ...
is a type of directed-energy weapon
A directed-energy weapon (DEW) is a ranged weapon that damages its target with highly focused energy without a solid projectile, including lasers, microwaves, particle beams, and sound beams. Potential applications of this technology include ...
that uses lasers
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radi ...
to inflict damage. Whether they will be deployed as practical, high-performance military weapons remains to be seen. One of the major issues with laser weapons is atmospheric thermal blooming, which is still largely unsolved. This issue is exacerbated when there is fog, smoke, dust, rain, snow, smog, foam, or purposely dispersed obscurant chemicals present. The United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the naval warfare, maritime military branch, service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest Displacement (ship), displacement, at 4.5 millio ...
has tested the very short range (1 mile), 30- kW Laser Weapon System or LaWS to be used against targets like small UAVs, rocket-propelled grenade
A rocket-propelled grenade (RPG), also known colloquially as a rocket launcher, is a Shoulder-fired missile, shoulder-fired anti-tank weapon that launches rockets equipped with a Shaped charge, shaped-charge explosive warhead. Most RPGs can ...
s, and visible motorboat
A motorboat or powerboat is a boat that is exclusively powered by an engine; faster examples may be called "speedboats".
Some motorboats are fitted with inboard engines, others have an outboard motor installed on the rear, containing the inter ...
or helicopter
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which Lift (force), lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning Helicopter rotor, rotors. This allows the helicopter to VTOL, take off and land vertically, to hover (helicopter), hover, and ...
engines. It has been described as "six welding lasers strapped together." A 60 kW system, HELIOS
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Helios (; ; Homeric Greek: ) is the god who personification, personifies the Sun. His name is also Latinized as Helius, and he is often given the epithets Hyperion ("the one above") an ...
, is being developed for destroyer-class ships .
 Lasers can be used as incapacitating
Lasers can be used as incapacitating non-lethal weapons
Non-lethal weapons, also called nonlethal weapons, less-lethal weapons, less-than-lethal weapons, non-deadly weapons, compliance weapons, or pain-inducing weapons are weapons intended to be lethality, less likely to kill a living target than c ...
. They can cause temporary or permanent vision loss when directed at the eyes. Even lasers with a power output of less than one watt can cause immediate and permanent vision loss under certain conditions, making them potentially non-lethal but incapacitating weapons. The use of such lasers is morally controversial due to the extreme handicap that laser-induced blindness represents. The Protocol on Blinding Laser Weapons bans the use of weapons designed to cause permanent blindness. Weapons designed to cause temporary blindness, known as dazzlers, are used by military and sometimes law enforcement organizations.
Hobbies
In recent years, some hobbyists have taken an interest in lasers. Lasers used by hobbyists are generally of class IIIa or IIIb , although some have made their own class IV types. However, due to the cost and potential dangers, this is an uncommon hobby. Some hobbyists salvage laser diodes from broken DVD players (red),Blu-ray
Blu-ray (Blu-ray Disc or BD) is a digital optical disc data storage format designed to supersede the DVD format. It was invented and developed in 2005 and released worldwide on June 20, 2006, capable of storing several hours of high-defin ...
players (violet), or even higher power laser diodes from CD or DVD burners.
Hobbyists have also used surplus lasers taken from retired military applications and modified them for holography
Holography is a technique that allows a wavefront to be recorded and later reconstructed. It is best known as a method of generating three-dimensional images, and has a wide range of other uses, including data storage, microscopy, and interfe ...
. Pulsed ruby and YAG lasers work well for this application.
Examples by power
 Different applications need lasers with different output powers. Lasers that produce a continuous beam or a series of short pulses can be compared on the basis of their average power. Lasers that produce pulses can also be characterized based on the ''peak'' power of each pulse. The peak power of a pulsed laser is many
Different applications need lasers with different output powers. Lasers that produce a continuous beam or a series of short pulses can be compared on the basis of their average power. Lasers that produce pulses can also be characterized based on the ''peak'' power of each pulse. The peak power of a pulsed laser is many orders of magnitude
In a ratio scale based on powers of ten, the order of magnitude is a measure of the nearness of two figures. Two numbers are "within an order of magnitude" of each other if their ratio is between 1/10 and 10. In other words, the two numbers are wi ...
greater than its average power. The average output power is always less than the power consumed.
Examples of pulsed systems with high peak power:
* 700 TW (700×1012 W)National Ignition Facility
The National Ignition Facility (NIF) is a laser-based inertial confinement fusion (ICF) research device, located at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in Livermore, California, United States. NIF's mission is to achieve fusion ignition wit ...
, a 192-beam, 1.8-megajoule laser system adjoining a 10-meter-diameter target chamber
* 10 PW (10×1015 W)world's most powerful laser as of 2019, located at the ELI-NP facility in Măgurele, Romania.
Safety
Even the first laser was recognized as being potentially dangerous.Theodore Maiman
Theodore Harold Maiman (July 11, 1927 – May 5, 2007) was an American engineer and physicist who is widely credited with the invention of the laser.Johnson, John Jr. (May 11, 2008). "Theodore H. Maiman, at age 32; scientist created the first L ...
characterized the first laser as having the power of one "Gillette", as it could burn through one Gillette
Gillette is an American brand of safety razors and other personal care products including shaving supplies, owned by the multi-national corporation Procter & Gamble (P&G). Based in Boston, Massachusetts, United States, it was owned by The Gil ...
razor
A razor is a bladed tool primarily used in the removal of body hair through the act of shaving. Kinds of razors include straight razors, safety razors, disposable razors, and electric razors.
While the razor has been in existence since be ...
blade. Today, it is accepted that even low-power lasers with only a few milliwatts of output power can be hazardous to human eyesight when the beam hits the eye directly or after reflection from a shiny surface. At wavelengths which the cornea
The cornea is the transparency (optics), transparent front part of the eyeball which covers the Iris (anatomy), iris, pupil, and Anterior chamber of eyeball, anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and Lens (anatomy), lens, the cornea ...
and the lens can focus well, the coherence and low divergence of laser light means that it can be focused by the eye
An eye is a sensory organ that allows an organism to perceive visual information. It detects light and converts it into electro-chemical impulses in neurons (neurones). It is part of an organism's visual system.
In higher organisms, the ey ...
into an extremely small spot on the retina
The retina (; or retinas) is the innermost, photosensitivity, light-sensitive layer of tissue (biology), tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some Mollusca, molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focus (optics), focused two-dimensional ...
, resulting in localized burning and permanent damage in seconds or even less time.
Lasers are usually labeled with a safety class number, which identifies how dangerous the laser is:
* Class 1 is inherently safe, usually because the light is contained in an enclosure, for example in CD players
* Class 2 is safe during normal use; the blink reflex
The corneal reflex, also known as the blink reflex or eyelid reflex, is an involuntary blinking of the eyelids elicited by stimulation of the cornea (such as by touching or by a foreign body), though it could result from any peripheral stimulus ...
of the eye will prevent damage. Usually up to 1 mW power, for example, laser pointers.
* Class 3R (formerly IIIa) lasers are usually up to 5 mW and involve a small risk of eye damage within the time of the blink reflex. Staring into such a beam for several seconds is likely to cause damage to a spot on the retina.
* Class 3B lasers (5–499 mW) can cause immediate eye damage upon exposure.
* Class 4 lasers (≥ 500 mW) can burn skin, and in some cases, even scattered light from these lasers can cause eye and/or skin damage. Many industrial and scientific lasers are in this class.
The indicated powers are for visible-light, continuous-wave lasers. For pulsed lasers and invisible wavelengths, other power limits apply. People working with class 3B and class 4 lasers can protect their eyes with safety goggles which are designed to absorb light of a particular wavelength.
Infrared lasers with wavelengths longer than about 1.4micrometers are often referred to as "eye-safe", because the cornea tends to absorb light at these wavelengths, protecting the retina from damage. The label "eye-safe" can be misleading, however, as it applies only to relatively low-power continuous wave beams; a high-power or Q-switched laser at these wavelengths can burn the cornea, causing severe eye damage, and even moderate-power lasers can injure the eye.
Lasers can be a hazard to both civil and military aviation, due to the potential to temporarily distract or blind pilots. See Lasers and aviation safety for more on this topic.
Cameras based on charge-coupled device
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a ...
s may be more sensitive to laser damage than biological eyes.
See also
* Coherent perfect absorber * Homogeneous broadening *Laser linewidth
Laser linewidth is the spectral linewidth of a laser beam.
Two of the most distinctive characteristics of laser emission are spatial coherence and spectral coherence. While spatial coherence is related to the beam divergence of the laser, spec ...
* List of laser articles
This is a list of laser topics.
A
* 3D printing, additive manufacturing
* Abnormal reflection
* Above-threshold ionization
* Absorption spectroscopy
* Accelerator physics
* Acoustic microscopy
* Acousto-optic deflector
* Acousto-optic mo ...
* List of light sources
This is a list of sources of light, the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Light sources produce photons from another energy source, such as heat, chemical reactions, or conversion of mass or a different frequency of electromagnetic ener ...
* Nanolaser
A nanolaser is a laser that has Nanoscopic scale, nanoscale dimensions and it refers to a micro-/nano- device which can emit light with light or electric excitation of nanowires or other nanomaterials that serve as resonators. A standard feature of ...
* Sound amplification by stimulated emission of radiation
Sound amplification by stimulated emission of radiation (SASER) refers to a device that emits acoustic radiation. It focuses sound waves in a way that they can serve as accurate and high-speed carriers of information in many kinds of applications ...
* Spaser
A spaser or plasmonic laser is a type of laser which aims to confine light at a subwavelength scale far below John William Strutt, 3rd Baron Rayleigh, Rayleigh's Diffraction limited beam, diffraction limit of light, by storing some of the light ene ...
* Fabry–Pérot interferometer
In optics, a Fabry–Pérot interferometer (FPI) or etalon is an optical cavity made from two parallel reflecting surfaces (i.e.: thin mirrors). Optical waves can pass through the optical cavity only when they are in resonance with it. It is ...
* Ultrashort pulse laser
References
Further reading
Books
* Bertolotti, Mario (1999, trans. 2004). ''The History of the Laser''. Institute of Physics. . * Bromberg, Joan Lisa (1991). ''The Laser in America, 1950–1970''. MIT Press. . * Csele, Mark (2004). ''Fundamentals of Light Sources and Lasers''. Wiley. . * Koechner, Walter (1992). ''Solid-State Laser Engineering''. 3rd ed. Springer-Verlag. . * Siegman, Anthony E. (1986). ''Lasers''. University Science Books. . * Silfvast, William T. (1996). ''Laser Fundamentals''. Cambridge University Press. . * Svelto, Orazio (1998). ''Principles of Lasers''. 4th ed. Trans. David Hanna. Springer. . * * * Wilson, J. & Hawkes, J.F.B. (1987). ''Lasers: Principles and Applications''. Prentice Hall International Series in Optoelectronics,Prentice Hall
Prentice Hall was a major American publishing#Textbook_publishing, educational publisher. It published print and digital content for the 6–12 and higher-education market. It was an independent company throughout the bulk of the twentieth cen ...
. .
* Yariv, Amnon (1989). ''Quantum Electronics''. 3rd ed. Wiley. .
Periodicals
* '' Applied Physics B: Lasers and Optics'' () * ''IEEE Journal of Lightwave Technology'' () * '' IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics'' () * '' IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics'' () * '' IEEE Photonics Technology Letters'' () * ''Journal of the Optical Society of America B: Optical Physics'' () * '' Laser Focus World'' () * ''Optics Letters
''Optics Letters'' is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Optica (formerly known as Optical Society of America). It was established in July 1977. The editor-in-chief is Miguel Alonso (University of Rochester). The journal cove ...
'' ()
* '' Photonics Spectra'' ()
External links
Encyclopedia of laser physics and technology by Rüdiger Paschotta
* ttp://www.technology.niagarac.on.ca/staff/mcsele/lasers/index.html Homebuilt Lasers Page by Professor Mark Csele
Powerful laser is 'brightest light in the universe'
he world's most powerful laser as of 2008 might create supernova-like shock waves and possibly even antimatter *
an online course by F. Balembois and S. Forget.
* ttp://www.laserfest.org/ Website on Lasers 50th anniversary by APS, OSA, SPIE
Advancing the Laser anniversary site by SPIE: Video interviews, open-access articles, posters, DVDs
history of the invention, with audio interview clips.
Free software for Simulation of random laser dynamics
Video Demonstrations in Lasers and Optics
Produced by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Real-time effects are demonstrated in a way that would be difficult to see in a classroom setting.
MIT Video Lecture: Understanding Lasers and Fiberoptics
Virtual Museum of Laser History, from the touring exhibit by SPIE
website with animations, applications and research about laser and other quantum based phenomena
Universite Paris Sud {{Authority control 1960 introductions American inventions Articles containing video clips Photonics Quantum optics Russian inventions Soviet inventions