Katowice (, ) is the capital city of the
Silesian Voivodeship
Silesian Voivodeship ( ) is an administrative province in southern Poland. With over 4.2 million residents and an area of 12,300 square kilometers, it is the second-most populous, and the most-densely populated and most-urbanized region of Poland ...
in southern
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
and the central city of the
Katowice urban area
The Katowice urban area (, ), also known as the Upper Silesian urban area (, ), is an urban area/conurbation in southern Poland, centered on Katowice. It is located in the Silesian Voivodeship. The Katowice urban area is the largest urban are ...
. As of 2021, Katowice has an official population of 286,960, and a resident population estimate of around 315,000. Katowice is a central part of the
Metropolis GZM
The Metropolis GZM (, formally in Polish (Upper Silesian-Dąbrowa Basin Metropolis)) is a metropolitan association () composed of 41 contiguous gminas, with a total population of over 2 million, covering most of the Katowice metropolitan area i ...
, with a population of 2.3 million, and a part of a larger
Katowice-Ostrava metropolitan area
The Katowice-Ostrava metropolitan areaBrookings Institutionbr>Redefining global cities: The seven types of global metro economies(2016), p. 16. European Spatial Planning Observation Network (ESPON"''Metroborder: Cross-border Polycentric Metropol ...
that extends into the Czech Republic and has a population of around 5 million people, making it
one of the most populous metropolitan areas in the European Union.
["''Study on Urban Functions (Project 1.4.3)''"](_blank)
– , 2007
Katowice was founded as a village in the 16th century, whereas several modern districts of Katowice were founded as villages in the
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
. Throughout the mid-18th century, Katowice grew following the discovery of rich
coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal i ...
reserves in the area. In the first half of the 19th century, intensive
industrialization
Industrialisation (British English, UK) American and British English spelling differences, or industrialization (American English, US) is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an i ...
transformed local mills and farms into industrial
steelworks
A steel mill or steelworks is an industrial plant for the manufacture of steel. It may be an integrated steel works carrying out all steps of steelmaking from smelting iron ore to rolled product, but may also be a plant where steel semi-fini ...
, mines,
foundries and artisan workshops. The city has since reshaped its economy from a heavy industry-based one to professional services, education and healthcare. The entire metropolitan area is the
16th most economically powerful city by GDP in the
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
with an output amounting to $114.5 billion.
Katowice Special Economic Zone is ranked fourth on the list of the TOP10 Global Free Zones.
[Global Free Zones of the Year 2023](_blank)
– fDi Intelligence
''fDi Intelligence'' is an English-language bi-monthly news and foreign direct investment (FDI) publication, providing an up-to-date review of global investment activity. The A4 glossy pages reach a circulation of 15,488 ABC audited, active corp ...
, 2023
Katowice has been classified as a
Gamma – global city by the
Globalization and World Cities Research Network
The Globalization and World Cities Research Network (GaWC) is a British think tank that studies the relationships between world cities in the context of globalization. It is based in the geography department of Loughborough University in Leic ...
and is a centre of commerce, business, transportation, and culture in
southern Poland, with numerous public companies headquartered in the city or in its suburbs including energy group
Tauron and metal industry corporation
Fasing, important cultural institutions such as
Polish National Radio Symphony Orchestra, award-winning music festivals such as
Off Festival
OFF Festival is an alternative music festival series held annually since 2006. Until 2009 it was held at Słupna Park in Mysłowice, Poland in August and lasts four days. OFF Festival from 2010 takes place in Katowice in Dolina Trzech Stawow.
Th ...
and
Tauron New Music, and transportation infrastructure such as
Katowice Korfanty Airport. It also hosts the finals of
Intel Extreme Masters
The Intel Extreme Masters (IEM) is a series of international esports tournaments held in countries around the world. These Electronic Sports League (ESL) sanctioned events, sponsored by Intel, currently host events in ''Counter-Strike 2''. Oth ...
, an
Esports
Esports (), short for electronic sports, is a form of competition using video games. Esports often takes the form of organized, multiplayer video game competitions, particularly between professional players, played individually or as teams. ...
video game tournament. Katowice is also home to several institutions of higher learning, notably the
University of Silesia, the
Silesian University of Technology
The Silesian University of Technology (Polish language, Polish name: Politechnika Śląska; ) is a university located in the Polish province of Silesia, with most of its facilities in the city of Gliwice. It was founded in 1945 by Polish profes ...
and the
Karol Szymanowski Academy of Music. The city is a member of the
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
Creative Cities Network
The UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN) is a flagship city programme of UNESCO launched in 2004 to promote cooperation among cities which have recognized culture and creativity as strategic drivers of sustainable urban development
Urban means ...
having been recognized as a
City of Music.
History
Before the industrial revolution
The area around Katowice, in
Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( ; ; ; ; Silesian German: ; ) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, located today mostly in Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic. The area is predominantly known for its heav ...
, has been inhabited by
Lechitic Silesian tribes from its earliest documented history.
While the name Katowice (''Katowicze'') is mentioned for the first time in 1598, other villages and settlements that would eventually become parts of modern Katowice have been established earlier, with ''Dąb'' being the oldest, mentioned in 1299 for the first time in a document issued by Duke
Casimir of Bytom.
Bogucice, Ligota, Szopenice and Podlesie were all established in early 14th century. Aside from farming, people living in the area would also work in hammer mills: the first one, ''Kuźnica Bogucka'', is mentioned in 1397.
The area which would become Katowice was initially ruled by the Polish
Silesian Piast dynasty until its extinction.
From 1327, the region was under administration of the
Kingdom of Bohemia
The Kingdom of Bohemia (), sometimes referenced in English literature as the Czech Kingdom, was a History of the Czech lands in the High Middle Ages, medieval and History of the Czech lands, early modern monarchy in Central Europe. It was the pr ...
under the
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
. As part of the
Bohemian Crown, it was passed to the
Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is ...
of
Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
in 1526. In 1742, along with most of
Silesia
Silesia (see names #Etymology, below) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at 8, ...
, it was seized by
Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
following the
First Silesian War
The First Silesian War () was a war between Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia and Habsburg monarchy, Austria that lasted from 1740 to 1742 and resulted in Prussia's seizing most of the region of Silesia (now in south-western Poland) from Austria. The ...
. The two subsequent
Silesian Wars
The Silesian Wars () were three wars fought in the mid-18th century between Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia (under King Frederick the Great) and Habsburg monarchy, Habsburg Austria (under Empress Maria Theresa) for control of the Central European ...
left the area severely depopulated and with an economy in ruins. In 1838, Franz von Winckler bought Katowice from Karl Friedrich Lehmann and in 1841, he made it the headquarters of his estate.
Emergence as an industrial centre

On 3 October 1846, the works of the final stage of the
Breslau-
Myslowitz (''Wrocław-Mysłowice'') rail line ended, built and operated by the
Upper Silesian Railway. It was opened by king
Frederick William IV of Prussia
Frederick William IV (; 15 October 1795 – 2 January 1861), the eldest son and successor of Frederick William III of Prussia, was King of Prussia from 7 June 1840 until his death on 2 January 1861. Also referred to as the "romanticist on the th ...
. A year later, on 6 August 1847, the first train arrived at the new
Katowice station.
The railway connection with major European cities (Katowice gained connections to
Berlin
Berlin ( ; ) is the Capital of Germany, capital and largest city of Germany, by both area and List of cities in Germany by population, population. With 3.7 million inhabitants, it has the List of cities in the European Union by population withi ...
,
Kraków
, officially the Royal Capital City of Kraków, is the List of cities and towns in Poland, second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city has a population of 804,237 ...
,
Vienna
Vienna ( ; ; ) is the capital city, capital, List of largest cities in Austria, most populous city, and one of Federal states of Austria, nine federal states of Austria. It is Austria's primate city, with just over two million inhabitants. ...
and
Warsaw
Warsaw, officially the Capital City of Warsaw, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the Vistula, River Vistula in east-central Poland. Its population is officially estimated at ...
, among others, between 1847 and 1848) fostered economic and population growth. The population grew enough to erect the first
Lutheran
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched ...
church on 29 September 1858 (
Church of the Resurrection), and the first
Catholic church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
two years later, on 11 November 1860. Katowice (then called Kattowitz) gained
city status
City status is a symbolic and legal designation given by a monarch, national or subnational government. A municipality may receive city status because it already has the qualities of a city, or because it has some special purpose.
Historically, ci ...
on 11 September 1865 in the Prussian
Province of Silesia
The Province of Silesia (; ; ) was a province of Prussia from 1815 to 1919. The Silesia region was part of the Prussian realm since 1742 and established as an official province in 1815, then became part of the German Empire in 1871. In 1919, as ...
, by the act of the king
Wilhelm I Hohenzollern.
The city flourished due to large mineral (especially coal) deposits in the area. Extensive city growth and prosperity depended on the coal mining and steel industries, which took off during the
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
. The city was inhabited mainly by
Germans
Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution of Germany, imple ...
,
Poles
Pole or poles may refer to:
People
*Poles (people), another term for Polish people, from the country of Poland
* Pole (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Pole (musician) (Stefan Betke, born 1967), German electronic music artist
...
incl.
Silesians
Silesians (; Silesian German: ''Schläsinger'' ''or'' ''Schläsier''; ; ; ) is both an ethnic as well as a geographical term for the inhabitants of Silesia, a historical region in Central Europe divided by the current national boundaries o ...
, and
Jews
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
. In 1884, 36 Jewish
Zionist
Zionism is an Ethnic nationalism, ethnocultural nationalist movement that emerged in History of Europe#From revolution to imperialism (1789–1914), Europe in the late 19th century that aimed to establish and maintain a national home for the ...
delegates met here, forming the
Hovevei Zion movement. Previously part of the Beuthen district, in 1873 it became the capital of the new
Kattowitz district. On 1 April 1899, the city was separated from the district, becoming an
independent city
An independent city or independent town is a city or town that does not form part of another general-purpose local government entity (such as a province).
Historical precursors
In the Holy Roman Empire, and to a degree in its successor states ...
.
In 1882, the Upper Silesian Coal and Steelworks Company (''Oberschlesischer Berg- und Hüttenmännischer Verein'') moved its headquarters to Katowice, followed by creation of the Upper Silesian Coal Convention (''Oberschlesische Kohlen-Konvention'') in 1898. Civic development followed industrial development: in 1851, the first post office opens in Katowice, and in 1893 the current regional post office headquarters have been opened; in 1871 the first middle school was opened (later expanded to high school); in 1889, Katowice got a district court; in 1895, the city bath opened and regional headquarters of the
Prussian state railways
The term Prussian state railways (German: ''Preußische Staatseisenbahnen'') encompasses those railway organisations that were owned or managed by the state of Prussia. The words "state railways" are not capitalized because Prussia did not have a ...
has been established in the city; in 1907, the city theater (currently the
Silesian Theatre) opened.
Under the
Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was a peace treaty signed on 28 June 1919. As the most important treaty of World War I, it ended the state of war between Germany and most of the Allies of World War I, Allied Powers. It was signed in the Palace ...
after
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, the
Upper Silesia plebiscite was organised by the
League of Nations
The League of Nations (LN or LoN; , SdN) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920), Paris Peace ...
. Though Kattowitz proper voted 22,774 to remain in Germany and 3,900 for Poland,
it was attached to Poland as the larger district voted 66,119 for Poland and 52,992 for Germany. Following the
Silesian Uprisings of 1918–21 Katowice became part of the
Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 7 October 1918 and 6 October 1939. The state was established in the final stage of World War I ...
with some autonomy for the
Silesian Parliament as a constituency and the Silesian Voivodeship Council as the executive body. In 1924, the surrounding villages and towns were incorporated into Katowice, and the number of inhabitants increased to over 112,000, since then the number of Poles exceeded the number of Germans – throughout the interwar period, the number of Germans decreased (in 1925 they constituted 12% of the inhabitants of Katowice, and in 1939 only 6%, while Poles constituted 93%). At the end of the interwar period, the number of inhabitants exceeded 134,000.
From 1926 to 1933, Katowice and the Polish part of Upper Silesia were connected with
Gdynia
Gdynia is a city in northern Poland and a seaport on the Baltic Sea coast. With an estimated population of 257,000, it is the List of cities in Poland, 12th-largest city in Poland and the second-largest in the Pomeranian Voivodeship after Gdańsk ...
and the Polish part of
Pomerania
Pomerania ( ; ; ; ) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The central and eastern part belongs to the West Pomeranian Voivodeship, West Pomeranian, Pomeranian Voivod ...
through the
Polish Coal Trunk-Line ().
World War II
During the early stages of
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
and the
Poland Campaign, Katowice was essentially abandoned by the
Polish Land Forces
The Land Forces () are the land forces of the Polish Armed Forces. They currently contain some 110,000 active personnel and form many components of the European Union and NATO deployments around the world. Poland's recorded military history str ...
, which had to position itself around
Kraków
, officially the Royal Capital City of Kraków, is the List of cities and towns in Poland, second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city has a population of 804,237 ...
. Nevertheless, the city was
defended by local Poles, and the invading Germans immediately carried out
massacres of captured Polish defenders. In the following weeks the German ''
Einsatzkommando
During World War II, the Nazi German ' were a sub-group of the ' (mobile killing squads) – up to 3,000 men total – usually composed of 500–1,000 functionaries of the SS and Gestapo, whose mission was to exterminate Jews, Polish intellect ...
1'' was stationed in the city, and its units were responsible for many
crimes against Poles committed in the region.
Under
German occupation many of the city's historical and iconic monuments were destroyed, most notably the
Great Katowice Synagogue, which was burned to the ground on 4 September 1939. This was followed by the alteration of street names and the introduction of strict rules. Additionally, the use of
Polish in public conversations was banned. The German administration was also infamous for organising public executions of civilians and by the middle of 1941, most of the Polish and Jewish population was
expelled. The Germans established and operated a Nazi prison in the city, and multiple
forced labour
Forced labour, or unfree labour, is any work relation, especially in modern or early modern history, in which people are employed against their will with the threat of destitution, detention, or violence, including death or other forms of ...
camps within present-day city limits, including two camps solely for Poles (''
Polenlager''), four camps solely for Jews, two subcamps (E734, E750) of the
Stalag VIII-B
Stalag VIII-B was most recently a German Army (Wehrmacht), German Army administered prisoner-of-war camp#Military District VIII (Breslau), POW camp during World War II, later renumbered Stalag-344, located near the village of Lamsdorf (now Łambin ...
/344
prisoner-of-war camp
A prisoner-of-war camp (often abbreviated as POW camp) is a site for the containment of enemy fighters captured as Prisoner of war, prisoners of war by a belligerent power in time of war.
There are significant differences among POW camps, inte ...
, and a
subcamp of the
Auschwitz concentration camp
Auschwitz, or Oświęcim, was a complex of over 40 Nazi concentration camps, concentration and extermination camps operated by Nazi Germany in Polish areas annexed by Nazi Germany, occupied Poland (in a portion annexed into Germany in 1939) d ...
. Eventually, Katowice was captured by the
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People ...
in January 1945. Significant parts of the downtown and inner suburbs were demolished during the occupation. As a result, the authorities were able to preserve the central district in its prewar character.
Postwar period
The postwar period of Katowice was characterised by the time of heavy industry development in the Upper Silesian region, which helped the city in regaining its status as the most industrialised Polish city and a major administrative centre. As the city developed so briskly, the 1950s marked a significant increase in its population and an influx of migrants from the
Eastern Borderlands, the so-called ''Kresy''. The city area began to quickly expand by incorporating the neighbouring communes and counties. However, the thriving industrial city also had a dark period in its short but meaningful history. Most notably, between 7 March 1953 and 10 December 1956, Katowice was called ''Stalinogród'' in honour of
Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Dzhugashvili; 5 March 1953) was a Soviet politician and revolutionary who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, his death in 1953. He held power as General Secret ...
, leader of the
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
. The change was brought upon by an issued decree of the State Council. The date of the alteration of the city name was neither a coincidence or accidental as it happened on the day of Stalin's death. In this way, the
Polish United Workers' Party
The Polish United Workers' Party (, ), commonly abbreviated to PZPR, was the communist party which ruled the Polish People's Republic as a one-party state from 1948 to 1989. The PZPR had led two other legally permitted subordinate minor parti ...
and the socialist authority wanted to pay tribute to the dictator. The new name
never got accepted by the citizens and in 1956 the former Polish name was restored.
The following decades were more memorable in the history of Katowice. Regardless of its industrial significance, it started to become an important cultural and educational centre in Central and Eastern Europe. In 1968, the
University of Silesia in Katowice, the largest and most valued college in the area, was founded. Simultaneously the construction of large housing estates began to evolve. Furthermore, many representative structures were erected at that time, including the
Silesian Insurgents' Monument (1967) and
Spodek
Spodek is a multipurpose arena complex in Katowice, Poland, opened on 9 May 1971. Aside from the main dome, the complex includes a gym, an ice rink, a hotel and three large car parks. It was the largest indoor venue of its kind in Poland until ...
(1971), which have become familiar landmarks and tourist sights. The 1960s and 1970s saw the evolution of
modernist architecture
Modern architecture, also called modernist architecture, or the modern movement, is an architectural architectural movement, movement and architectural style, style that was prominent in the 20th century, between the earlier Art Deco Architectu ...
and
functionalism. Katowice eventually developed into one of the most modernist post-war cities of Poland.
One of the most dramatic events in the history of the city occurred on 16 December 1981. It was then that 9 protesters died (7 were shot dead; 2 died from injury complications) and another 21 were
wounded in the pacification of Wujek Coal Mine. The
Special Platoon of the Motorized Reserves of the Citizens' Militia (''ZOMO'') was responsible for the brutal handling of strikers protesting against
Wojciech Jaruzelski
Wojciech Witold Jaruzelski ( ; ; 6 July 1923 – 25 May 2014) was a Polish military general, politician and ''de facto'' leader of the Polish People's Republic from 1981 until 1989. He was the First Secretary of the Polish United Workers' Party ...
's declaration of
martial law
Martial law is the replacement of civilian government by military rule and the suspension of civilian legal processes for military powers. Martial law can continue for a specified amount of time, or indefinitely, and standard civil liberties ...
and the arrest of
Solidarity trade union officials. On the 10th anniversary of the event, a memorial was unveiled by the President of Poland
Lech Wałęsa
Lech Wałęsa (; ; born 29 September 1943) is a Polish statesman, dissident, and Nobel Peace Prize laureate who served as the president of Poland between 1990 and 1995. After winning the 1990 Polish presidential election, 1990 election, Wałę ...
.
In 1990, the first democratic local elections that took place marked a new period in the city's history. The economy of Katowice has been transforming from the heavy industry of steel and coal mines into "one of the most attractive investment areas for modern economy branches in Central Europe".
21st century
In 2008, Katowice was awarded the
Europe Prize by the
Parliamentary Assembly of the
Council of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; , CdE) is an international organisation with the goal of upholding human rights, democracy and the Law in Europe, rule of law in Europe. Founded in 1949, it is Europe's oldest intergovernmental organisation, represe ...
for having made exceptional efforts to spread the ideal of European unity.
The city's efficient infrastructure, rapid progress in the overall development and an increase in office space has made Katowice a popular venue for conducting business. The Katowice Expo Centre (''Katowickie Centrum Wystawiennicze'') organises trade fairs or exhibitions and attracts investors from all over the world. In 2018, the city was the host of the 24th Session of the Conference of the Parties to the
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) is the UN process for negotiating an agreement to limit dangerous climate change. It is an international treaty among countries to combat "dangerous human interference with th ...
(UNFCCC
COP24). In 2022, the city hosted the 11th edition of the
World Urban Forum, the world's most important conference on sustainable urbanization and development of cities.

Geography
Katowice encompasses an area of . The city is situated in the
Silesian Highlands, about north of the
Silesian Beskids (part of the
Carpathian Mountains
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe and Southeast Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Ural Mountains, Urals at and the Scandinav ...
).
Kłodnica and
Rawa (tributaries of the
Oder
The Oder ( ; Czech and ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and its largest tributary the Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows through wes ...
and the
Vistula
The Vistula (; ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest in Europe, at in length. Its drainage basin, extending into three other countries apart from Poland, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra i ...
respectively) are the largest rivers in Katowice, and the border between catchment areas of Oder and Vistula goes through the city. With a minimal elevation of and median elevation of above sea level, Katowice has the highest elevation among large cities in Poland.
Climate
Katowice has a temperate, ocean-moderated
humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers, and cold ...
(
Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (te ...
: ''Dfb/Cfb''). The average temperature is 8.2 °Celsius ( in January and up to in July). Yearly rainfall averages at . Characteristic weak winds blow at about from the southwest, through the
Moravian Gate.
Neighborhoods
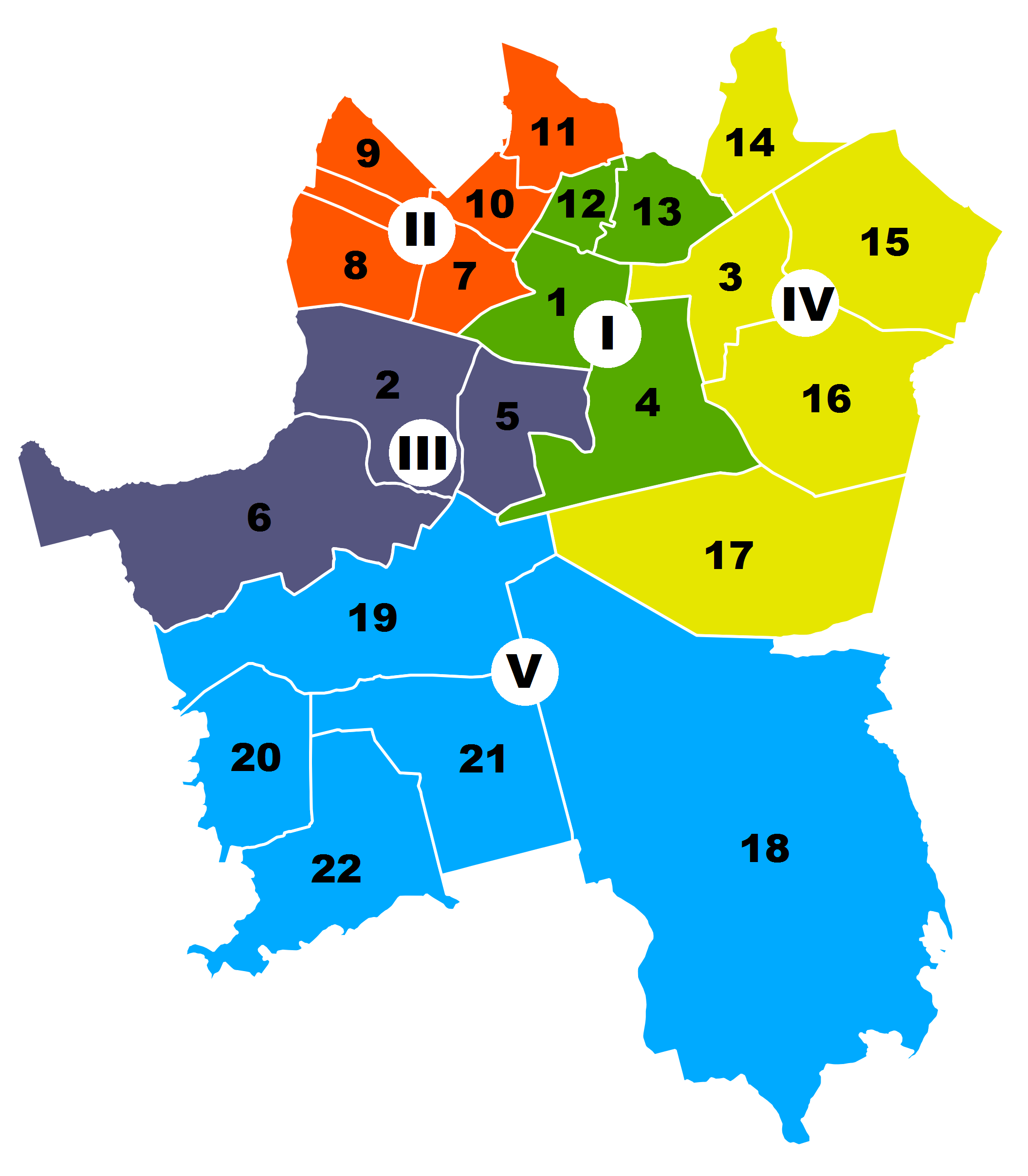
Katowice has 22 officially recognized neighborhoods.
Śródmieście,
Osiedle Paderewskiego-Muchowiec,
Zawodzie and
Koszutka form the dense central urban core where most cultural and educational institutions, businesses and administrative buildings are located.
Most Northern and Eastern neighborhoods around the downtown core are more working-class and developed from worker's estates build around large industry such as coal mines, manufactures and steelworks. Each of these neighborhoods has its own dense commercial strip surrounded by mid-rise apartment buildings and some single-family homes.
Szopienice, located between downtown Katowice and Mysłowice, used to be a separate town until mid-1960s.
Nikiszowiec, a former mine's town, has undergone strong
gentrification
Gentrification is the process whereby the character of a neighborhood changes through the influx of more Wealth, affluent residents (the "gentry") and investment. There is no agreed-upon definition of gentrification. In public discourse, it has ...
in recent years, and emerged as a major tourist attraction in the region thanks to its unique architecture and art galleries.
Western and Southern neighborhoods (with the exception of Brynów-Załęska Hałda, which is a working-class neighborhood built around a coal mine) are more suburban in nature, concentrating the city's middle and upper middle classes.
Metropolitan area
Katowice lies in the centre of
the largest conurbation in Poland,
one of the largest in the European Union, numbering about 2.7 million. The
Katowice metropolitan area
Katowice metropolitan area, also known as Upper Silesian metropolitan area[Katowice-Ostrava metropolitan area
The Katowice-Ostrava metropolitan areaBrookings Institutionbr>Redefining global cities: The seven types of global metro economies(2016), p. 16. European Spatial Planning Observation Network (ESPON"''Metroborder: Cross-border Polycentric Metropol ...](_blank)
(mostly within the
Upper Silesian Coal Basin) over 50 cities or towns and a population of 5,008,000. In 2006, Katowice and 14 adjacent cities united as the Metropolitan Association of Upper Silesia (predecessor to the current
Metropolis GZM
The Metropolis GZM (, formally in Polish (Upper Silesian-Dąbrowa Basin Metropolis)) is a metropolitan association () composed of 41 contiguous gminas, with a total population of over 2 million, covering most of the Katowice metropolitan area i ...
). Its population was 2 million and its area was 1,104 km
2. In 2006–2007 the union planned to unite these cities in one city under the name "Silesia", but this proved unsuccessful.
The Katowice conurbation comprises settlements which have evolved because of the mining of metal ores, coal and raw rock materials. The establishment of mining and heavy industry which have developed for the past centuries has resulted in the unique character of the cityscape; its typical aspects are the
red brick housing estates constructed for the poorer working class, factory chimneys, manufacturing plants, power stations and
quarries. The inhabitants of a large mining community like Katowice, and local administrations within the conurbation, which have only evolved due to mining, are a subject to overall decline after the liquidation of coal mines and factories. This is one of the reasons which led to the development of the service sector, including office spaces, shopping centres and tourism.
Demographics
The
Polish Statistical Office estimates Katowice's population to be 292,774 with a population density of . There were 139,274 males and 153,500 females. Age breakdown of people in Katowice is: 12.9% 0–14 years old, 13.7% 15–29 years old, 23.8% 30–44 years old, 19.5% 45–59 years old, 20.1% 60–74 years old, and 9.9% 75 years and older.
Katowice is a centre of the
Katowice-Ostrava metropolitan area
The Katowice-Ostrava metropolitan areaBrookings Institutionbr>Redefining global cities: The seven types of global metro economies(2016), p. 16. European Spatial Planning Observation Network (ESPON"''Metroborder: Cross-border Polycentric Metropol ...
, with a population of approx. 5.3 million. This metropolitan area extends into the neighboring
Czechia, where the other centre is the city of
Ostrava
Ostrava (; ; ) is a city in the north-east of the Czech Republic and the capital of the Moravian-Silesian Region. It has about 283,000 inhabitants. It lies from the border with Poland, at the confluences of four rivers: Oder, Opava (river), Opa ...
. 41 municipalities that constitute the core of the metropolitan area created the
Metropolis GZM
The Metropolis GZM (, formally in Polish (Upper Silesian-Dąbrowa Basin Metropolis)) is a metropolitan association () composed of 41 contiguous gminas, with a total population of over 2 million, covering most of the Katowice metropolitan area i ...
association, which has 2.3 million people
Historical population
Katowice's population grew very fast between 1845 and 1960, fueled by the expansion of heavy industry and administrative functions. In the 60s, 70s and 80s, the city grew by another 100,000 people, reaching a height of 368,621 in 1988. Since then, the decline of heavy industry, emigration, and
suburbanization
Suburbanization (American English), also spelled suburbanisation (British English), is a population shift from historic core cities or rural areas into suburbs. Most suburbs are built in a formation of (sub)urban sprawl. As a consequence ...
reversed the population development; Katowice lost approx. 75,000 people (20%) since the fall of communism in Poland.
Before World War II, Katowice was mainly inhabited by Poles and Germans. The 1905 Silesian demographic census has shown that Germans made up nearly 70–75% of the total population (including German Jews) and Poles constituted 25–30% of inhabitants of Katowice. After the plebiscite in Upper Silesia,
Silesian uprisings and the incorporation of Katowice into Poland in 1922, and then the incorporation of several nearby villages and towns into the city, the number of inhabitants of Katowice increased significantly, but the number of Germans in Katowice fell to 12% in 1925 and to 6% in 1939 (most Germans left Poland, many ethnic Silesians who used to identify as Germans switched their identification to Poles, and areas with a Polish majority were incorporated). Thus, in 1939 the ethnic breakdown of the city was: 93% Poles, 6% Germans, and 1% Jews.
After the German aggression against Poland in 1939, some Poles were
displaced from Katowice and Germans were settled in their place. During the war, the Nazi occupiers committed severe crimes against the local
Roma and Jewish communities, either killing them on the spot or transporting them to
concentration camps
A concentration camp is a prison or other facility used for the internment of political prisoners or politically targeted demographics, such as members of national or ethnic minority groups, on the grounds of national security, or for exploit ...
such as
Auschwitz
Auschwitz, or Oświęcim, was a complex of over 40 concentration and extermination camps operated by Nazi Germany in occupied Poland (in a portion annexed into Germany in 1939) during World War II and the Holocaust. It consisted of Auschw ...
for complete extermination. This led to a wartime population drop. In 1945, practically the entire German minority has either left fleeing the Red Army or was forced to leave after Poland regained control of the city, and Poles from
Kresy
Eastern Borderlands (), often simply Borderlands (, ) was a historical region of the eastern part of the Second Polish Republic. The term was coined during the interwar period (1918–1939). Largely agricultural and extensively multi-ethnic with ...
(Eastern Borderlands of interwar Poland that were annexed by USSR after the war) and other parts of the country started to come to settle in the city. Katowice enjoyed a population boom after World War II, driven primarily by internal economic migration from less developed parts of the country.
Since the late 1960s, Katowice and the surrounding area experiences low birth rates, which, paired with the decline of heavy industry and reduced job opportunities, caused the population of Katowice to start decreasing in the late 1980s. As of recent years, increased economic activity in the area has stopped outward migration but the negative natural change (more deaths than births) continues to fuel population decline.
Ethnic diversity
Katowice is one of the more diverse cities in Poland. In the 2021 census, 93.87% of inhabitants declared a Polish nationality while 19.38% declared a nationality other than Polish (in the Polish census, respondents are allowed to declare up to two nationalities or ethnicities). Indigenous Silesians were the largest minority, at 17.8%, followed by Germans (0.43%), Ukrainians (0.18%), the English (0.12%), Jews (0.07%) and Italians (0.07%).
In addition, Katowice is home to a large immigrant population that is largely unaccounted for in the official population data in Poland. According to the Polish Ministry of Development, Labor and Technology, there have been 20,527 foreigners (7% of official population figure) on a special worker permit for citizens of
Belarus
Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Belarus spans an a ...
,
Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
,
Moldova
Moldova, officially the Republic of Moldova, is a Landlocked country, landlocked country in Eastern Europe, with an area of and population of 2.42 million. Moldova is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. ...
,
Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
,
Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg
, national_motto =
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map =
, map_caption = Location of Serbia (gree ...
and
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
in Katowice in 2020, 19,003 of them from Ukraine. By the end of 2021, this number has increased to 26,990, with 23,207 of them from Ukraine. Additionally, 11,568
refugees
A refugee, according to the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR), is a person "forced to flee their own country and seek safety in another country. They are unable to return to their own country because of feared persecution as ...
settled in Katowice since the start of the
Russian invasion on Ukraine. By the December 2024, the number has increased to 11,894.
Socioeconomics
According to the 2021 census, 32.3% of the population aged 13 and older had a college degree, 34.3% had a high school diploma or some college, 17.9% completed a vocational secondary school, 2.4% only completed a gimnazjum, 8.4% only completed a primary school while 2.1% did not complete primary school. In 2011, in the 25–34 age group, college graduates share is 44.9%, and an additional 31.8% has a high school degree. According to
Eurostat
Eurostat ("European Statistical Office"; also DG ESTAT) is a department of the European Commission ( Directorate-General), located in the Kirchberg quarter of Luxembourg City, Luxembourg. Eurostat's main responsibilities are to provide statist ...
data, Katowice and its surrounding
Silesian region had one of the highest share of people who have attained at least an upper secondary level of education (more than 90%), and one of the lowest share of school dropouts in Europe (less than 5%).
There were 120,869 households in Katowice as of the 2021 census, a drop from 134,199 in the 2011 census. Average household size was 2.33, virtually unchanged from the 2.3 reported in the previous census. 32.4% households were single-person households, 31.2% had two people, 18.5% had three people, 11.5% had four people and 6.4% had five people or more. Compared to the 2011 census, the largest difference was an increase in households with 5 and more people (from 4.9%).
As of 2022, Katowice placed third in the country among cities with the highest average salaries, at PLN 8,017.49, behind Warsaw and Kraków. Poverty rate places Katowice on average with other big cities in Poland, at 4.09% of inhabitants eligible for welfare benefits
Religion
Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
is the main religion in Katowice; Polish census, 60.52% (172,915 people) of Katowice residents declared to be Roman Catholic, representing a significant drop from the 2011 census when Roman Catholics were 82.43% of the population.
No other denomination had at least 1,000 followers as of the 2021 census. In the 2011 census, denominations with at least 1,000 worshippers included the
Lutheran Church in Poland – 0.43% (1,336 people) and
Jehovah's Witnesses
Jehovah's Witnesses is a Christian denomination that is an outgrowth of the Bible Student movement founded by Charles Taze Russell in the nineteenth century. The denomination is nontrinitarian, millenarian, and restorationist. Russell co-fou ...
– 0.42% (1,311 people). Other religions with presence and places of worship in the city include
Judaism
Judaism () is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic, Monotheism, monotheistic, ethnic religion that comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Jews, Jewish people. Religious Jews regard Judaism as their means of o ...
,
Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
, and
Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
, as well as other
Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
denominations.
Christianity

Katowice is the seat of the
Roman Catholic Archdiocese, with the suffragan bishoprics of
Gliwice
Gliwice (; , ) is a city in Upper Silesia, in southern Poland. The city is located in the Silesian Highlands, on the Kłodnica river (a tributary of the Oder River, Oder). It lies approximately 25 km west from Katowice, the regional capital ...
and
Opole
Opole (; ; ; ) is a city located in southern Poland on the Oder River and the historical capital of Upper Silesia. With a population of approximately 127,387 as of the 2021 census, it is the capital of Opole Voivodeship (province) and the seat of ...
, and around 1,477,900 Catholics. The
Cathedral of Christ the King, constructed between 1927 and 1955 in a classicist style, is the largest cathedral in Poland. There are 36
Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
churches in Katowice (including two
basilicas
In Ancient Roman architecture, a basilica (Greek Basiliké) was a large public building with multiple functions that was typically built alongside the town's forum. The basilica was in the Latin West equivalent to a stoa in the Greek East ...
), as well as 18
monasteries
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone ( hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer which m ...
. Katowice is also a seat of a diocesan Catholic seminary, as well as one of the
Order of Friars Minor
The Order of Friars Minor (commonly called the Franciscans, the Franciscan Order, or the Seraphic Order; Post-nominal letters, postnominal abbreviation OFM) is a Mendicant orders, mendicant Catholic religious order, founded in 1209 by Francis ...
. Katowice Archdiocese owns several media companies headquartered in Katowice: ''Księgarnia św. Jacka'', a Catholic publishing company, and ''Instytut Gość Media'', a multi-channeled media company that owns ''Radio eM'', a regional Catholic radio, and a few magazines.
Gość Niedzielny, owned by ''Instytut Gość Media'' and published in Katowice, is currently the most-popular Catholic magazine in the country with approx. 120,000 copies sold weekly.
Katowice is also the seat of a
Lutheran Diocese which covers
Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( ; ; ; ; Silesian German: ; ) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, located today mostly in Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic. The area is predominantly known for its heav ...
,
Lesser Poland
Lesser Poland, often known by its Polish name ''Małopolska'' (; ), is a historical region situated in southern and south-eastern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Kraków. Throughout centuries, Lesser Poland developed a separate cult ...
and
Subcarpathian region and has 12,934 adherents Lutherans have two churches in Katowice, including a cathedral, which is the oldest church built originally in Katowice, completed on 29 September 1858. Historically, Lutheran population in Katowice was mostly
German, and with the expulsion of Germans from Poland after the Second World War, number of Lutherans dropped in Katowice.
Other denominations with churches or praying houses in Katowice include
Seventh Day Adventists,
Baptists
Baptists are a Christian denomination, denomination within Protestant Christianity distinguished by baptizing only professing Christian believers (believer's baptism) and doing so by complete Immersion baptism, immersion. Baptist churches ge ...
, Christ Church in Poland,
Pentecostals
Pentecostalism or classical Pentecostalism is a movement within the broader Evangelical wing of Protestant Christianity that emphasizes direct personal experience of God through baptism with the Holy Spirit. The term ''Pentecostal'' is derived ...
and other
evangelical
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide, interdenominational movement within Protestantism, Protestant Christianity that emphasizes evangelism, or the preaching and spreading of th ...
groups.
Judaism

Judaism has historically been present in Katowice since at least 1702.
First
synagogue
A synagogue, also called a shul or a temple, is a place of worship for Jews and Samaritans. It is a place for prayer (the main sanctuary and sometimes smaller chapels) where Jews attend religious services or special ceremonies such as wed ...
, designed by a local architect Ignatz Grünfeld, was consecrated on 4 September 1862, while the Jewish cemetery was established in 1868. Dr. Jacob Cohn was the first
rabbi
A rabbi (; ) is a spiritual leader or religious teacher in Judaism. One becomes a rabbi by being ordained by another rabbi—known as ''semikha''—following a course of study of Jewish history and texts such as the Talmud. The basic form of t ...
of Katowice, appointed to this function on 6 January 1872 and holding it until 1920s.
Zionism
Zionism is an Ethnic nationalism, ethnocultural nationalist movement that emerged in History of Europe#From revolution to imperialism (1789–1914), Europe in the late 19th century that aimed to establish and maintain a national home for the ...
was strong in Katowice, and in 1884 the city was the place of the
Katowice Conference, the first public Zionist meeting in history. On 12 September 1900, the
Great Synagogue was opened.
Following World War I and subsequent creation of the
Polish state, most Katowice Jews, who identified with Germany, left the city and settled primarily in
Bytom
Bytom (Polish pronunciation: ; Silesian language, Silesian: ''Bytōm, Bytōń'', ) is a city in Upper Silesia, in southern Poland. Located in the Silesian Voivodeship, the city is 7 km northwest of Katowice, the regional capital.
It is one ...
, a nearby city that was still part of Germany. They were partially replaced by Jews moving from the East, particularly the neighboring
Dąbrowa Basin region that had a large Jewish population. In 1931, 60% of 5,716 Jews in Katowice were recent immigrants from other parts of Poland.
On 1 September 1939, Poland was attacked by
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
, and Katowice, a border city, surrendered on 3 September. The Great Synagogue was burned by the German army the same day, and in the following months, Katowice Jews were deported to
ghettos in Dąbrowa Basin (primarily
Sosnowiec and
Będzin
Będzin (; also seen spelled ''Bendzin''; ) is a city in the Dąbrowa Basin, in southern Poland. It lies in the Silesian Highlands, on the Czarna Przemsza River (a tributary of the Vistula River, Vistula). Even though part of Silesian Voivodeship ...
) or directly to various
concentration
In chemistry, concentration is the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Several types of mathematical description can be distinguished: '' mass concentration'', '' molar concentration'', '' number concentration'', ...
and
death camps where most of them were murdered in
the Holocaust
The Holocaust (), known in Hebrew language, Hebrew as the (), was the genocide of History of the Jews in Europe, European Jews during World War II. From 1941 to 1945, Nazi Germany and Collaboration with Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy ...
. After the war, around 1,500 Jews were living in Katowice, but most of them left Poland and emigrated to the
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
and other Western countries.
Currently, Katowice has one
Qahal with approximately 200 members. It owns houses of prayer in Katowice (along with a
kosher
(also or , ) is a set of dietary laws dealing with the foods that Jewish people are permitted to eat and how those foods must be prepared according to Jewish law. Food that may be consumed is deemed kosher ( in English, ), from the Ashke ...
cafeteria) and nearby Gliwice, and the current rabbi is Yehoshua Ellis.
Other religions
There are two buddhist groups in Katowice:
Kwan Um School of Zen, first registered in 1982, and the Diamond Road of Karma Kagyu line association. Jehovah's Witnesses maintain 13 houses of prayer and one
Kingdom Hall in Katowice. Aside from Polish-language congregations, there is one for
English speakers and one for
Ukrainian speakers.
Architecture and urban design
Late 19th/early 20th century
Unlike most other large Polish cities, Katowice did not originate as a medieval town, therefore it does not have an old town with a street layout and architectural styles characteristic to cities founded on
Magdeburg rights
Magdeburg rights (, , ; also called Magdeburg Law) were a set of town privileges first developed by Otto I, Holy Roman Emperor (936–973) and based on the Flemish Law, which regulated the degree of internal autonomy within cities and villages gr ...
. Katowice's urban layout is a result of expansion and annexation of various towns, industrial worker estates, and villages.
Katowice city centre has an axis design, along the main railway line, developed by an industrialist Friedrich Grundman in mid-19th century.
Most of the city centre in Katowice developed in late 19th and early 20th century, when it was part of the
Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (, ) was a German state that existed from 1701 to 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It played a signif ...
and had a German-speaking majority. As a result, architectural styles of that era are similar to those in other Prussian cities such as
Berlin
Berlin ( ; ) is the Capital of Germany, capital and largest city of Germany, by both area and List of cities in Germany by population, population. With 3.7 million inhabitants, it has the List of cities in the European Union by population withi ...
or
Wrocław
Wrocław is a city in southwestern Poland, and the capital of the Lower Silesian Voivodeship. It is the largest city and historical capital of the region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the Oder River in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Eu ...
(then Breslau); primarily
renaissance revival and
baroque revival, with some buildings in
gothic revival
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic or neo-Gothic) is an Architectural style, architectural movement that after a gradual build-up beginning in the second half of the 17th century became a widespread movement in the first half ...
,
romanesque revival
Romanesque Revival (or Neo-Romanesque) is a style of building employed beginning in the mid-19th century inspired by the 11th- and 12th-century Romanesque architecture. Unlike the historic Romanesque style, Romanesque Revival buildings tended t ...
, and
art nouveau
Art Nouveau ( ; ; ), Jugendstil and Sezessionstil in German, is an international style of art, architecture, and applied art, especially the decorative arts. It was often inspired by natural forms such as the sinuous curves of plants and ...
styles.
Interwar architecture
In 1922, Katowice and the eastern portion of Upper Silesia were reintegrated with reborn Poland, and an
autonomous Silesian Voivodeship was established, with Katowice as its capital. This event has marked the beginning of a period of unprecedented architectural development in the city. Since most traditional styles, especially
gothic and gothic revival, were perceived as connected to imperial Germany by the new Polish authorities, all new development was to be built in, at first in the
neoclassical, and later in
functionalist/
Bauhaus
The Staatliches Bauhaus (), commonly known as the , was a German art school operational from 1919 to 1933 that combined Decorative arts, crafts and the fine arts.Oxford Dictionary of Art and Artists (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 4th edn., ...
style. The city, which needed to build administrative buildings for the new authorities and housing for people working in regional administration, began expansion southward creating one of the largest complexes of modern architecture in Poland, comparable to Warsaw and
Gdynia
Gdynia is a city in northern Poland and a seaport on the Baltic Sea coast. With an estimated population of 257,000, it is the List of cities in Poland, 12th-largest city in Poland and the second-largest in the Pomeranian Voivodeship after Gdańsk ...
(newly built port on the
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
) only.
The modernist district is centered around the monumental
Silesian Parliament building (1923–1929), which architecture is mostly neoclassical, albeit with early modernist influences. During World War II, the building became headquarters of the
Reichsgau Oberschlesien and part of the interior was redesigned by
Albert Speer
Berthold Konrad Hermann Albert Speer (; ; 19 March 1905 – 1 September 1981) was a German architect who served as Reich Ministry of Armaments and War Production, Minister of Armaments and War Production in Nazi Germany during most of W ...
,
Hitler
Adolf Hitler (20 April 1889 – 30 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his suicide in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the lea ...
's favorite architect, to resemble the interior of the
Reich Chancellery
The Reich Chancellery () was the traditional name of the office of the Chancellor of Germany (then called ''Reichskanzler'') in the period of the German Reich from 1878 to 1945. The Chancellery's seat, selected and prepared since 1875, was the fo ...
. The nearby
Cathedral of Christ the King (1927–1955, with dome lowered by 34 meters compared to original design) is also neoclassical but with an ascetic, modernist-inspired interior (including a
tabernacle
According to the Hebrew Bible, the tabernacle (), also known as the Tent of the Congregation (, also Tent of Meeting), was the portable earthly dwelling of God used by the Israelites from the Exodus until the conquest of Canaan. Moses was instru ...
and a golden mosaic funded by future pope,
Joseph Ratzinger). Other buildings, designed in mid-to-late 1920s and 1930s, are mostly modernist or functionalist. A symbol of the city in the interwar period,
Drapacz Chmur (literally: ''The Skyscraper''), was the first skyscraper built in Poland after World War I, and the first building in the country to be based on a steel frame.
Post-war architecture

After
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, Katowice again expected a period of rapid growth, particularly under the regional leadership of
Marshall Jerzy Ziętek. Pałac Młodzieży (''Youth Palace'') became the first major new building completed in Katowice after the war, erected in the
socrealist style with elements of
late modernism in 1949–1951. The largest development of the 1950s in Katowice was the expansion of the
Koszutka neighborhood, also in the
socialist realist style, in early 1950s.
Following the death of
Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Dzhugashvili; 5 March 1953) was a Soviet politician and revolutionary who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, his death in 1953. He held power as General Secret ...
in 1956, and the end of socrealism, Jerzy Ziętek and city authorities commissioned a group of young architects and urbanists to create a project of the new urban design of Katowice. The collective, named ''Miastoprojekt Katowice'', came up with a design heavily influenced by
Le Corbusier's ideas. The project was centered around a grand avenue (current ''Aleja Korfantego'') surrounded by simple, modern blocks and monuments, scattered in distance to each other according to modernist ideals of preserving space and light for the masses. The most important buildings from that time include:
*
Spodek Arena (1964–1971), widely considered the symbol of Katowice and ranked among the finest achievements of modern architecture in Poland; one of the first buildings in the world with a
tensegrity
Tensegrity, tensional integrity or floating compression is a structural principle based on a system of isolated components under compression (physical), compression inside a network of continuous tension (mechanics), tension, and arranged in s ...
rooftop. Arena's unique design, resembling a typical depiction of a UFO at the time, gave it its Polish name (literally meaning "a saucer", a shorthand for UFO in Polish).
*
Katowice Railway Station (1959–1972), considered to be the most outstanding example of brutalism in Poland, controversially demolished in 2010 and partially rebuilt as an addition to the Galeria Katowicka shopping centre.
*
Superjednostka (1967–1972), a massive (187.5 meters length, 51 meters high) residential block heavily inspired by Le Corbusier's
Unite d'habitation
Unite may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Music Albums
*Unite (1GN album), ''Unite'' (1GN album), 2016
*Unite (A Friend in London album), ''Unite'' (A Friend in London album), 2013
*Unite (Kool & the Gang album), ''Unite'' (Kool & the ...
in
Marseille
Marseille (; ; see #Name, below) is a city in southern France, the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Departments of France, department of Bouches-du-Rhône and of the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur Regions of France, region. Situated in the ...
* Osiedle Gwiazdy (1978–1985), a housing estate of eight 27-floor residential buildings on a plan resembling a star
* Osiedle Tysiąclecia (1961–1982, later expanded), a large housing estate connecting to the
Silesian Park, built with modernist principles (separation of foot and automobile traffic, vast green spaces, self-sufficiency in terms of schools, basic shops and healthcare). Later expansion of the estate includes Kukurydze high-rises, a group of 26-floor high residential towers inspired by
Marina City
Marina City is a mixed-use residential-commercial building complex in Chicago, Illinois, United States, North America, designed by architect Bertrand Goldberg. The multi-building complex on State Street on the north bank of the Chicago River o ...
in
Chicago
Chicago is the List of municipalities in Illinois, most populous city in the U.S. state of Illinois and in the Midwestern United States. With a population of 2,746,388, as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the List of Unite ...
*
Stalexport Towers (1979–1982), twin office towers with 22 and 20 floors, a prime example of early
postmodernism
Postmodernism encompasses a variety of artistic, Culture, cultural, and philosophical movements that claim to mark a break from modernism. They have in common the conviction that it is no longer possible to rely upon previous ways of depicting ...
in Poland
Contemporary architecture
Following the collapse of communism in Poland and other Eastern Bloc countries, and the centrally-planned economy with it, Poland's economy suffered a downturn, and construction slowed down. One of the most significant buildings of the 1990s was the new branch of the
Silesian Library, in postmodernism style.
The situation changed in the early aughts, when several new notable developments were completed:
* Chorzowska 50 (1999–2001) – first modern, A-grade office building in Katowice; currently owned and occupied by
ING Bank Śląski
*
Altus, previously known as Uni Centrum (2001–2003) – for many years the highest skyscraper in Poland outside of Warsaw, at 125 meters (410 ft) high.
*
Silesia City Center (2003–2005), the flagship brownfield development of the era, built in place a defunct coal mine Gottwald. It remains one of the largest shopping centres in Poland, at , and also includes a housing estate and a chapel.
* Dom z Ziemi Śląskiej (2001–2002), a modern suburban villa, nominated to
Mies van der Rohe Award in 2002
* Department of Law at the
University of Silesia (2001–2003), a postmodernist building aiming to resemble industrial installations of the region
* Department of Theology at the University of Silesia (2002–2004), built in the style resembling early Christian hermitages
Another wave of architectural revival came after Poland joined the
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
in 2004. European
cohesion funds, along with private capital investment, flew into the city resulting in a number of architecturally acclaimed buildings and complexes, including:
* Strefa Kultury (''Zone of Culture'', a brownfield urban redevelopment in downtown Katowice):
**
National Polish Radio Symphony Orchestra (NOSPR) building (2012–2014) contains two concert halls (for an audience of 1,800 or 300). Nominated to
Mies van der Rohe Award in 2014, first prize in European Commercial Property Awards.
** Katowice
International Conference Centre (2012–2015), the largest conference centre in Poland (capacity up to 12,000 people), connected to the Spodek Arena. The design of the centre, with a distinct canyon going through it in order to remove any obstruction from view of Spodek, has been hailed and the building was nominated to
Mies van der Rohe award in 2017
**
New Silesian Museum (2011–2013) located in place of a former coal mine, most of the museum is located underground, with only glass cubes that provide daylight, visible above ground. Shortlisted for Mies van der Rohe award in 2015.
* CINiBA (2009–2011) – academic library of the
University of Silesia and
Katowice University of Economics, shortlisted to Mies van der Rohe award in 2013.
*
Krzysztof Kieślowski Film School at the
University of Silesia (2014–2017) – awarded with Wienerberger Brick Award in 2020, shortlisted to Mies van der Rohe award in 2019. Located in a decayed neighborhood, the building aims at kick-starting an urban renewal process there.
*
KTW (2018–2022) – the taller tower, KTW II, is
the tallest building in Katowice and
one of the tallest in Poland at .
* Global Office Park (2022–2023) – mixed-use complex featuring four buildings, with two office towers reaching .
Tourist attractions

*
Market square
A market square (also known as a market place) is an urban square meant for trading, in which a market is held. It is an important feature of many towns and cities around the world. A market square is an open area where market stalls are tradit ...
and adjacent streets:
Warszawska, Teatralna, Dyrekcyjna, Staromiejska, Dworcowa, św. Jana, Pocztowa, Wawelska, 3 Maja, Stawowa, Mielęckiego, Starowiejska and Mickiewicza, the so-called "Great Market Square of Katowice" or "Old town of Katowice"—many historic (monument) buildings. This is a group of functional-architectural. On the market square and most of the above-mentioned streets are prohibitions or restrictions on cars. Streets: Staromiejska, Dyrekcyjna, Wawelska, Stawowa and Warszawska is lined decorative
cobblestone
Cobblestone is a natural building material based on Cobble (geology), cobble-sized stones, and is used for Road surface, pavement roads, streets, and buildings. Sett (paving), Setts, also called ''Belgian blocks'', are often referred to as " ...
creating a
pedestrian zone
Pedestrian zones (also known as auto-free zones and car-free zones, as pedestrian precincts in British English, and as pedestrian malls in the United States and Australia) are areas of a city or town restricted to use by people on foot or ...
. The authority plans to Katowice—Quarter streets: św. Jana, Dworcowa, Mariacka, Mielęckiego, Stanisława and Starowiejska is to become so "small market square".
*
Nikiszowiec – historical settlement of Katowice, candidate to UNESCO
*
Cathedral of Christ the King
*
St Mary's Church
*
Church of the Resurrection, Evangelical-Augsburg, built in 1856–1858
*
Church of St Michael Archangel, the oldest church in the city, built in 1510
*
Drapacz Chmur, one of the first skyscrapers in Europe
*
Silesian Parliament, built in 1925–1929. For a very long time, it was the biggest structure in Poland
*Modernist old town
*
Spodek
Spodek is a multipurpose arena complex in Katowice, Poland, opened on 9 May 1971. Aside from the main dome, the complex includes a gym, an ice rink, a hotel and three large car parks. It was the largest indoor venue of its kind in Poland until ...
(a large
sports centre/
concert hall
A concert hall is a cultural building with a stage (theatre), stage that serves as a performance venue and an auditorium filled with seats.
This list does not include other venues such as sports stadia, dramatic theatres or convention ...
, whose name translates as the 'saucer', from its distinctive shape resembling a
UFO flying saucer)
*
Silesian Insurgents Monument (Polish: ''Pomnik Powstańców Śląskich''), the largest and heaviest monument in Poland. It is a harmonious combination of architecture and sculpture with appropriate symbolism: the wings symbolize the three
Silesian Uprisings (1920–1921) while the names of places that were battlefields are etched on the vertical slopes. The monument, which was funded by the people of Warsaw for Upper Silesia, is considered Katowice's landmark.
*
Silesian Theater, built in 1907
*
Rialto Cinetheater, built in 1912
*
Silesian Museum, built in 1899
*
Old train station in Katowice, built in 1906
*The
Goldstein Palace
*The
Załęże Palace
*
Parachute Tower, a tall lattice tower was built in 1937 for training parachutists. It was used in the first days of World War II and is the only parachute tower in Poland.
Other:
*
Franciscan Monastery in Panewniki
*
Church of St Joseph (Załęże)
*
St Stephen's Church
*
Church of Christ Resurrection
*The Monument to Marshal
Piłsudski by Croatian sculptor
Antun Augustinčić, 1937–39. It was commissioned in 1936 but brought to Poland in 1991
*
Monopol Hotel
*
Katowice Rondo, the large
square
In geometry, a square is a regular polygon, regular quadrilateral. It has four straight sides of equal length and four equal angles. Squares are special cases of rectangles, which have four equal angles, and of rhombuses, which have four equal si ...
/
roundabout
A roundabout, a rotary and a traffic circle are types of circular intersection or junction in which road traffic is permitted to flow in one direction around a central island, and priority is typically given to traffic already in the junct ...
, reconstructed recently, with the semi-circular Galeria Rondo Sztuki in the centre.
Economy
Katowice has been classified as a
Gamma – global city by the
Globalization and World Cities Research Network
The Globalization and World Cities Research Network (GaWC) is a British think tank that studies the relationships between world cities in the context of globalization. It is based in the geography department of Loughborough University in Leic ...
and is considered as an emerging metropolis. Katowice's metropolitan area is the
16th most economically powerful urban area in the
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
by GDP, with an output amounting to $114.5 billion.
The city is one of the major industrial, commerce and financial hubs of Poland and has successfully transformed its economy from heavy industry-based to knowledge-based one.
Employment and incomes

As of August 2024, 252,841 people are employed in Katowice, which makes the city the 7th largest job market in Poland, slightly ahead of
Gdańsk
Gdańsk is a city on the Baltic Sea, Baltic coast of northern Poland, and the capital of the Pomeranian Voivodeship. With a population of 486,492, Data for territorial unit 2261000. it is Poland's sixth-largest city and principal seaport. Gdań ...
. Main sectors include professional services (including the IT sector and finance) at 15.8%, retail (13.7%), and government (12.6%). Unemployment rate is extremely low at 1%, as of June 2024.
Median monthly income for residents of Katowice stood at PLN 7,220.00 while median monthly income for those employed in Katowice was higher at PLN 8,053.30 as of August 2024, both above the country's median of PLN 6,697.52.
Business and commerce
Katowice is a large business, convention and
trade fair
A trade show, also known as trade fair, trade exhibition, or trade exposition, is an exhibition organized so that companies in a specific Industry (economics), industry can showcase and demonstrate their latest Product (business), products and se ...
centre. As of 2012, 44,050 businesses were registered in Katowice. 13 of them are traded on the
Warsaw Stock Exchange
The Warsaw Stock Exchange (WSE) () is a stock exchange in Warsaw, Poland. Founded in 1817, it was located in the Saxon Palace until 1877 when it was moved to the Exchange Building at the Saxon Garden. Currently, it is located at ul. Książęca ...
, with ING Bank Śląski being the largest one by far, while 11 are traded on the NewConnect floor.
Largest private corporations headquartered in Katowice include Polska Grupa Górnicza (coal mining and energy), Farmacol (pharmaceuticals), Famur (mining equipment manufacturing), Mistal (steel products manufacturing), Emiternet (renewable energy systems). Major international corporations with regional headquarters in Katowice include
IBM
International Business Machines Corporation (using the trademark IBM), nicknamed Big Blue, is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company headquartered in Armonk, New York, and present in over 175 countries. It is ...
,
Unilever
Unilever PLC () is a British multinational consumer packaged goods company headquartered in London, England. It was founded on 2 September 1929 following the merger of Dutch margarine producer Margarine Unie with British soap maker Lever B ...
,
PwC
PricewaterhouseCoopers, also known as PwC, is a Multinational corporation, multinational professional services network based in London, United Kingdom.
It is the second-largest professional services network in the world and is one of the Big Fo ...
,
Deloitte
Deloitte is a multinational professional services network based in London, United Kingdom. It is the largest professional services network in the world by revenue and number of employees, and is one of the Big Four accounting firms, along wi ...
,
Groupon
Groupon, Inc. is an American global e-commerce marketplace connecting subscribers with local merchants by offering activities, travel, goods and services in 13 countries. Based in Chicago, Groupon was launched there in November 2008, launching ...
,
Eurofins,
Capgemini
Capgemini SE is a French Multinational corporation, multinational information technology (IT) services and consulting company, headquartered in Paris, France.
History
Capgemini was founded by Serge Kampf in 1967 as an enterprise management and d ...
,
Sopra Steria,
Accenture
Accenture plc is a global multinational professional services company originating in the United States and headquartered in Dublin, Ireland, that specializes in information technology (IT) services and management consulting. It was founded in 1 ...
,
Fujitsu,
Citibank
Citibank, N.A. ("N. A." stands for "National bank (United States), National Association"; stylized as citibank) is the primary U.S. banking subsidiary of Citigroup, a financial services multinational corporation, multinational corporation. Ci ...
,
HSBC
HSBC Holdings plc ( zh, t_hk=滙豐; initialism from its founding member The Hongkong and Shanghai Banking Corporation) is a British universal bank and financial services group headquartered in London, England, with historical and business li ...
,
KPMG
KPMG is a multinational professional services network, based in London, United Kingdom. As one of the Big Four accounting firms, along with Ernst & Young (EY), Deloitte, and PwC. KPMG is a network of firms in 145 countries with 275,288 emplo ...
,
RSM,
Baker Tilly, and others.
Katowice is also the seat of
Katowice Special Economic Zone (Katowicka Specjalna Strefa Ekonomiczna).
Heavy industry and manufacturing
Since its creation, Katowice's development was tightly connected to heavy industry, especially coal mining, steelworks and machine production. In 1931, 49.5% of inhabitants worked in industry, and 12.5% in coal mining alone. In 1989 industry accounted for 36% of all jobs in the city (112,000 employees). As of 2018, 34,294 people worked in industry in Katowice, 20.4% of total, below the national average.
The first reported coal mine in Katowice (''Murcki'' coal mine) was established in 1740, and in 1769 construction on ''Emanuelssegen'' mine started. As the demand for coal kept rising in the
Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (, ) was a German state that existed from 1701 to 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It played a signif ...
, further mines were opened: ''Beata'' (1801), ''Ferdinand'' (1823), ''Kleofas'' (1845). Later in 19th and early 20th century additional mines were opened: ''Katowice'', ''Wujek'', ''Eminenz'' (later renamed ''Gottwald'' and merged with ''Kleofas''), ''Wieczorek'', ''Boże Dary'', ''Staszic'' and renewed ''Murcki''. Currently only one (''Murcki-Staszic'') remains in operation. Katowice is also the seat of
Polska Grupa Górnicza, the largest coal mining corporation in Europe. Metallurgy was another important part of Katowice's economy. In 1863 a dozen zinc metallurgy facilities were reported in Katowice, with ''Wilhelmina'' (founded in 1834) being the largest. In early 1900s, ''Wilhelmina'' (later renamed ''Huta Metali Niezależnych Szopienice'') was enlarged and became the largest Silesian producer of
non-ferrous metal
In metallurgy, non-ferrous metals are metals or alloys that do not contain iron ( allotropes of iron, ferrite, and so on) in appreciable amounts.
Generally more costly than ferrous metals, non-ferrous metals are used because of desirable pro ...
s and world's largest producer of
cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, silvery-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12 element, group 12, zinc and mercury (element), mercury. Like z ...
. Two major steelworks existed in the city: ''Huta Baildon'', established in 1823 by the Scottish engineer and industrialist
John Baildon (declared bankruptcy in 2001), and ''
Huta Ferrum'', established in 1874 and operating to this date in limited capacity.
Culture
Vibrant and progressive artistic communities, particularly around musical arts, make Katowice one of the leading cultural spots in Poland.
Since mid-2000s, Katowice has established a strategy to redevelop the post-industrial areas using culture – the pinnacle of which was a massive development on the site of a former coal mine known as
Strefa Kultury (the "Zone of Culture"), where numerous cultural and convention institutions are located.
Performing arts
Katowice's status as the UNESCO
City of Music, designated when Katowice joined
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
Creative Cities Network
The UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN) is a flagship city programme of UNESCO launched in 2004 to promote cooperation among cities which have recognized culture and creativity as strategic drivers of sustainable urban development
Urban means ...
in 2015, comes from a long and rich history of musical arts. Katowice is the seat of an internationally renowned
Karol Szymanowski Academy of Music, whose faculty and graduates created the nationally important informal group called the Silesian school of composers.
Polish National Radio Symphony Orchestra has been located in Katowice since 1945 and has gotten a new internationally acclaimed concert hall in 2014, built on a site of a former coal mine near Katowice's city center. The
Silesian Philharmonic also has its seat in Katowice. The city is a venue for numerous classical concerts and festivals, such as: the International Festival of Young Music Competition Laureates,
Grzegorz Fitelberg International Competition for Conductors, Chamber Music Festival, Ars Cameralis Festival and Katowice's opera, operettas and most of all ballet.
There are currently 6 theater buildings in Katowice, and some theater groups without a permanent location.
Teatr Śląski is the oldest still-functioning theater in Katowice, first opened for audience in 1907 and located on the main square. It was the first theater to give plays in
Silesian dialect of Polish. Every first Monday of the month, the
Silesian Opera
Silesian Opera in Bytom () is an opera company in Bytom, Silesia, Poland, that was founded in 1945. Its home is the former City Theatre, designed by architect Albert Bohm,
that was built in Neoclassical style
Neoclassicism, also spelled Neo- ...
singers from nearby
Bytom
Bytom (Polish pronunciation: ; Silesian language, Silesian: ''Bytōm, Bytōń'', ) is a city in Upper Silesia, in southern Poland. Located in the Silesian Voivodeship, the city is 7 km northwest of Katowice, the regional capital.
It is one ...
give a performance there, as Katowice does not have an opera house of its own. Teatr Ateneum is an important puppetry theater, while Teatr Korez was one of the first non-public theaters in post-war Poland.
Katowice is home to many nationally and internationally renowned popular music festivals.
Rawa Blues, named after a stream that passes through Katowice's city center, is one of the largest blues festivals in Europe. Electronic music's
Mayday Festival takes place every year in early November and is a sister event to its namesake in
Dortmund
Dortmund (; ; ) is the third-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia, after Cologne and Düsseldorf, and the List of cities in Germany by population, ninth-largest city in Germany. With a population of 614,495 inhabitants, it is the largest city ...
.
OFF Festival
OFF Festival is an alternative music festival series held annually since 2006. Until 2009 it was held at Słupna Park in Mysłowice, Poland in August and lasts four days. OFF Festival from 2010 takes place in Katowice in Dolina Trzech Stawow.
Th ...
, dedicated to alternative music, moved to Katowice in 2010 and has been held every August. Tauron Nowa Muzyka festival, oriented more towards dance and techno has been named one of the major European festivals to attend. Other music festivals, such as the Silesian Jazz Festival, KatoHej (dedicated to chants and touristic music), and Gardens of Sound, are also organized. In 2019, 475,806 people attended various big cultural events such as concerts and festivals, which gave the city the third place in Poland, behind Warsaw and Kraków. Nearby
Chorzów
Chorzów ( ; ; ) is a city in the Silesia region of southern Poland, near Katowice. Chorzów is one of the central cities of the Metropolis GZM – a metropolis with a population of 2 million. It is located in the Silesian Highlands, on the Rawa ...
, with the
Silesian Stadium
The Silesian Stadium (; Polish: ) is a sport stadium located on the premises of Silesian Park in Chorzów, Poland. The stadium has a fully covered capacity of 54,378, after refurbishment completed in October 2017. The stadium hosted many Poland ...
right across the street from Katowice, gathered another 319,783 attendees.
Museums and art galleries

The
Silesian Museum is the largest and most-important museum in Katowice. It originally opened in 1929, and its radically modern,
Bauhaus
The Staatliches Bauhaus (), commonly known as the , was a German art school operational from 1919 to 1933 that combined Decorative arts, crafts and the fine arts.Oxford Dictionary of Art and Artists (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 4th edn., ...
-style new building was demolished immediately after the Nazis seized Katowice in 1939, considering it too degenerate and too Polish. The museum has been placed in temporary buildings with its collections dispersed until 2015, when a new, mostly underground building has been constructed in the Zone of Culture. The museum exhibits works by famous and renowned Polish artists like
Józef Chełmoński
Józef Marian Chełmoński (7 November 1849 – 6 April 1914) was a Polish painter of the Realism (art movement), realist school with roots in the historical and social context of the late Romanticism in Poland, Romantic period in partitioned Pol ...
,
Artur Grottger,
Tadeusz Makowski,
Jacek Malczewski
Jacek Malczewski (; 15 July 1854 – 8 October 1929) was a Polish symbolist painter who was one of the central figures of the patriotic Young Poland movement.
His works combined the predominant style of his time with historical motifs of Pol ...
,
Jan Matejko
Jan Alojzy Matejko (; also known as Jan Mateyko; 24 June 1838 – 1 November 1893) was a Polish painter, a leading 19th-century exponent of history painting, known for depicting nodal events from Polish history. His works include large scale ...
,
Józef Mehoffer and
Stanisław Wyspiański
Stanisław Mateusz Ignacy Wyspiański (; 15 January 1869 – 28 November 1907) was a Polish playwright, painter, poet, and interior and furniture designer. A patriotic writer, he created symbolic national dramas accordant with the artisti ...
.
It is also well known for its collection of
naïve art
Naïve art is usually defined as visual art that is created by a person who lacks the formal education and training that a professional artist undergoes (in anatomy, art history, technique, perspective, ways of seeing). When this aesthetic is ...
paintings, including local coal miners from Katowice area. The museum has a number of sketches of globally recognizable artists such as
Albrecht Dürer
Albrecht Dürer ( , ;; 21 May 1471 – 6 April 1528),Müller, Peter O. (1993) ''Substantiv-Derivation in Den Schriften Albrecht Dürers'', Walter de Gruyter. . sometimes spelled in English as Durer or Duerer, was a German painter, Old master prin ...
and
Rembrandt
Rembrandt Harmenszoon van Rijn (; ; 15 July 1606 – 4 October 1669), mononymously known as Rembrandt was a Dutch Golden Age painter, printmaker, and Drawing, draughtsman. He is generally considered one of the greatest visual artists in ...
.
The City History Museum of Katowice exhibitions include: immersive typical urban apartments from early 20th century,
naïve art
Naïve art is usually defined as visual art that is created by a person who lacks the formal education and training that a professional artist undergoes (in anatomy, art history, technique, perspective, ways of seeing). When this aesthetic is ...
paintings from local artists and the history of Katowice from a village to an industrial center. Other museums in Katowice include Museum of the History of Computers and Informatics and the Museum of Smallest Books in the World.
The BWA Contemporary Art Gallery in Katowice, established in 1949, is a notable institution concerning the
Contemporary art
Contemporary art is a term used to describe the art of today, generally referring to art produced from the 1970s onwards. Contemporary artists work in a globally influenced, culturally diverse, and technologically advancing world. Their art is a ...
s. Every three years, it is responsible for organizing the Polish Graphic Art Triennial. Several other galleries feature exhibitions of the works by artists from abroad along with film screenings, workshops for children and public fairs.
Media
:''TV stations:''
*
TVP 3 Katowice
*
TVS (TV Silesia)
*
TVN24
TVN24 is a Polish 24-hour commercial news channel, launched on 9 August 2001. Being a part of the TVN Network, TVN24 has been owned since 2018 by US-based media company Warner Bros. Discovery ( Discovery, Inc. before 2022). It gained broade ...
– department Katowice (TVN24 – oddział Katowice)
:''radio stations:''
*
Radio Katowice
*
Antyradio
:''newspapers:''
*
Dziennik Zachodni
''Dziennik Zachodni'' (, Western Daily, DZ) is a regional Polish newspaper distributed in Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( ; ; ; ; Silesian German: ; ) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, located to ...
* – Katowice section
*
Fakt – Katowice section
*
Metro International
Metro International is a Swedish media company based in Luxembourg that publishes the freesheet newspaper ''Metro''.
The company was founded by Per Andersson, and started as a subsidiary of the Modern Times Group along with Viasat Broadcast ...
– Katowice
*Nowy Przegląd Katowicki
Festivals and events
*
 Rawa Blues Festiwal
Rawa Blues Festiwal –
Spodek
Spodek is a multipurpose arena complex in Katowice, Poland, opened on 9 May 1971. Aside from the main dome, the complex includes a gym, an ice rink, a hotel and three large car parks. It was the largest indoor venue of its kind in Poland until ...
*
Metalmania – Spodek
*
Off Festival
OFF Festival is an alternative music festival series held annually since 2006. Until 2009 it was held at Słupna Park in Mysłowice, Poland in August and lasts four days. OFF Festival from 2010 takes place in Katowice in Dolina Trzech Stawow.
Th ...
*
Mayday
Mayday is an emergency procedure word used internationally as a distress signal in voice-procedure radio communications.
It is used to signal a life-threatening emergency primarily by aviators and mariners, but in some countries local organiz ...
– Spodek
*International Competition of Conductors by Fitelberg
*
International Cycling Film Festival
*International Festival of Military Orchestras
*International Exhibition of
Graphic arts
A category of fine art, graphic art covers a broad range of visual artistic expression, typically two-dimensional graphics, i.e. produced on a flat surface,[Esports
Esports (), short for electronic sports, is a form of competition using video games. Esports often takes the form of organized, multiplayer video game competitions, particularly between professional players, played individually or as teams. ...]
tournament
ESL One Katowice Tournament in 2015.
*Esports tournament
Intel Extreme Masters
The Intel Extreme Masters (IEM) is a series of international esports tournaments held in countries around the world. These Electronic Sports League (ESL) sanctioned events, sponsored by Intel, currently host events in ''Counter-Strike 2''. Oth ...
World Championship, one of the biggest esports events in the world
*Poland hosted the 24th Session of the Conference of the Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC
COP24), with the meeting held in Katowice.
*
Wikimania 2024 was held at the
International Congress Centre August 7–10, 2024.
Parks and squares
:''parks:''
*
Silesian Park (Wojewódzki Park Kultury i Wypoczynku)
*
Kościuszko Park (Park im. Tadeusza Kościuszki)
*
Forest Park of Katowice (Katowicki Park Leśny)
*
Valley of Three Ponds (Dolina Trzech Stawów)
*
Zadole Park
:''squares:''
*
 Katowice market square
Katowice market square (Rynek w Katowicach)
*Freedom Square (Plac Wolności)
*Andrzej Square (Plac Andrzeja)
*Miarka Square (Plac Miarki)
*Council of Europe Square (Plac Rady Europy)
*Alfred Square (Plac Alfreda)
*A. Budniok Square (Plac A. Brudnioka)
*J. Londzin Square (Plac J. Londzina)
*A. Hlond Square (Plac A. Hlonda)
Nature reserves and ecological areas

*Nature reserve Las Murckowski
*Nature reserve Ochojec
*Szopienice-Borki
*Źródła Kłodnicy
*Staw Grunfeld
*Stawy Na Tysiącleciu
*Płone Bagno
Education and science

Katowice is a large scientific centre and has been designated as the European City of Science 2024 by
EuroScience (ESOF). It has over 20 schools of higher education, at which over 100,000 people study.
*
University of Silesia in Katowice
*
University of Economics in Katowice
*
Medical University of Silesia
*
Silesian University of Technology
The Silesian University of Technology (Polish language, Polish name: Politechnika Śląska; ) is a university located in the Polish province of Silesia, with most of its facilities in the city of Gliwice. It was founded in 1945 by Polish profes ...
*
University of Social Sciences and Humanities
*
Karol Szymanowski Academy of Music
*
Akademia Lospuma Training Institute
*
Academy of Fine Arts in Katowice
*
Academy of Physical Education im. Jerzy Kukuczka in Katowice
*
Higher Silesian Seminary in Katowice
There are also:
*around 80
high school
A secondary school, high school, or senior school, is an institution that provides secondary education. Some secondary schools provide both ''lower secondary education'' (ages 11 to 14) and ''upper secondary education'' (ages 14 to 18), i.e., ...
s
*around 35
gimnasia
*around 55 primary schools
*around 50
libraries
A library is a collection of Book, books, and possibly other Document, materials and Media (communication), media, that is accessible for use by its members and members of allied institutions. Libraries provide physical (hard copies) or electron ...
, including the
Silesian Library
Transportation
Public transportation

The public
transportation system of the Katowice consists of commuter and long-distance trains, trams, buses and city bikes. Around 38 percent of people in Katowice use trams and buses on their daily commute (40 percent if counted those using the park-and-ride facilities), 10 percent walk, 4 percent cycle, and 2 percent takes the train, according to a 2020 report.
There are also three park-and-ride centers in Katowice with over 1,000 parking spaces.
Tram and bus lines
The transit authority of the
Metropolis GZM
The Metropolis GZM (, formally in Polish (Upper Silesian-Dąbrowa Basin Metropolis)) is a metropolitan association () composed of 41 contiguous gminas, with a total population of over 2 million, covering most of the Katowice metropolitan area i ...
, Zarząd Transportu Metropolitalnego (ZTM), operates the city trams and buses.
The
Silesian Interurban tram system is one of the largest and oldest in Europe, in operation since 1894 and covering over 200 km of rails, including 62 km in Katowice proper. The network in Katowice is mostly located in the northern part of the city has a star-like shape, with most lines converging on the Rynek square and expanding to all directions. There are 13 tram lines in Katowice, all but 2 expanding into neighboring cities. 116 tram stops are located in Katowice proper, as of 2020. A new tram line is planned to the southern suburbs since 2016.

In addition to trams, bus lines are organized by ZTM. There are currently 63 regular lines in Katowice (including night lines), and additional 10 express metropolitan lines, with 609 bus stops as of 2020. ZTM organizes a bus line to their airport as well, which runs every 30 minutes between 4am and 9:30pm and every hour at night.
Commuter trains
Koleje Śląskie (Silesian Railways), a regional railway authority, connects Katowice with its suburbs and other major cities in
Silesian and
Lesser Poland voivodeships:
Gliwice
Gliwice (; , ) is a city in Upper Silesia, in southern Poland. The city is located in the Silesian Highlands, on the Kłodnica river (a tributary of the Oder River, Oder). It lies approximately 25 km west from Katowice, the regional capital ...
,
Rybnik
Rybnik (Polish pronunciation: ; ) is a city in southern Poland, in the Silesian Voivodeship, around 38 km (24 mi) southwest of Katowice, the region's capital, and around 19 km (11 mi) from the Czech Republic, Czech border. It i ...
,
Częstochowa
Częstochowa ( , ) is a city in southern Poland on the Warta with 214,342 inhabitants, making it the thirteenth-largest city in Poland. It is situated in the Silesian Voivodeship. However, Częstochowa is historically part of Lesser Poland, not Si ...
,
Bielsko-Biała
Bielsko-Biała (; ; , ; ) is a city in southern Poland, with a population of approximately 166,765 as of December 2022, making it the List of cities and towns in Poland#Largest cities and towns by population, 22nd largest city in Poland, and an a ...
,
Kraków
, officially the Royal Capital City of Kraków, is the List of cities and towns in Poland, second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city has a population of 804,237 ...
, and
Oświęcim
Oświęcim (; ; ; ) is a town in the Lesser Poland Voivodeship in southern Poland, situated southeast of Katowice, near the confluence of the Vistula (''Wisła'') and Soła rivers.
Oświęcim dates back to the 12th century, when it was an im ...
, among others. It operates 9 regular lines and 1 tourist weekend line (to
Zakopane
Zakopane (Gorals#Language, Podhale Goral: ''Zokopane'') is a town in the south of Poland, in the southern part of the Podhale region at the foot of the Tatra Mountains. From 1975 to 1998, it was part of Nowy Sącz Voivodeship; since 1999, it has ...
).
Polregio operates commuter trains from Katowice to cities and towns in
Lesser Poland
Lesser Poland, often known by its Polish name ''Małopolska'' (; ), is a historical region situated in southern and south-eastern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Kraków. Throughout centuries, Lesser Poland developed a separate cult ...
and
Świętokrzyskie voivodeships:
Trzebinia,
Olkusz
Olkusz ( ''Elkish'') is a town in southern Poland with 36,607 inhabitants (2014). Situated in the Lesser Poland Voivodeship (since 1999), previously in Katowice Voivodeship (1975–1998), it is the capital of Olkusz County. Olkusz is known for its ...
, and
Kielce
Kielce (; ) is a city in south-central Poland and the capital of the Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship. In 2021, it had 192,468 inhabitants. The city is in the middle of the Świętokrzyskie Mountains (Holy Cross Mountains), on the banks of the Silnic ...
, among others.
Long-haul trains
Katowice is the main railway hub in southern Poland. Katowice's main railway station is the fifth-busiest train station in Poland as of 2019 (and third outside Warsaw), with 17.6 million passengers and growing 47 percent since 2015. 16% of the passengers travelled on
PKP Intercity train, the main long-distance train operator in Poland.
Katowice has a direct
Express Intercity Premium (high-speed) connection to
Warsaw
Warsaw, officially the Capital City of Warsaw, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the Vistula, River Vistula in east-central Poland. Its population is officially estimated at ...
through the
Centralna Magistrala Kolejowa, with a run time of 2 hours 21 minutes.
PKP Intercity also offers direct standard connections to Kraków (under 1 hour),
Wrocław
Wrocław is a city in southwestern Poland, and the capital of the Lower Silesian Voivodeship. It is the largest city and historical capital of the region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the Oder River in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Eu ...
, Kielce and
Ostrava
Ostrava (; ; ) is a city in the north-east of the Czech Republic and the capital of the Moravian-Silesian Region. It has about 283,000 inhabitants. It lies from the border with Poland, at the confluences of four rivers: Oder, Opava (river), Opa ...
(under 2 hours), Warsaw,
Rzeszów
Rzeszów ( , ) is the largest city in southeastern Poland. It is located on both sides of the Wisłok River in the heartland of the Sandomierz Basin. Rzeszów is the capital of the Subcarpathian Voivodeship and the county seat, seat of Rzeszów C ...
,
Olomouc
Olomouc (; ) is a city in the Czech Republic. It has about 103,000 inhabitants, making it the Statutory city (Czech Republic), sixth largest city in the country. It is the administrative centre of the Olomouc Region.
Located on the Morava (rive ...
, and
Łódź
Łódź is a city in central Poland and a former industrial centre. It is the capital of Łódź Voivodeship, and is located south-west of Warsaw. Łódź has a population of 655,279, making it the country's List of cities and towns in Polan ...
(under 3 hours),
Poznań
Poznań ( ) is a city on the Warta, River Warta in west Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business center and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint John's ...
(under 4 hours),
Brno
Brno ( , ; ) is a Statutory city (Czech Republic), city in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. Located at the confluence of the Svitava (river), Svitava and Svratka (river), Svratka rivers, Brno has about 403,000 inhabitants, making ...
,
Vienna
Vienna ( ; ; ) is the capital city, capital, List of largest cities in Austria, most populous city, and one of Federal states of Austria, nine federal states of Austria. It is Austria's primate city, with just over two million inhabitants. ...
and
Bratislava
Bratislava (German: ''Pressburg'', Hungarian: ''Pozsony'') is the Capital city, capital and largest city of the Slovakia, Slovak Republic and the fourth largest of all List of cities and towns on the river Danube, cities on the river Danube. ...
(under 5 hours), as well as
Prague
Prague ( ; ) is the capital and List of cities and towns in the Czech Republic, largest city of the Czech Republic and the historical capital of Bohemia. Prague, located on the Vltava River, has a population of about 1.4 million, while its P ...
,
Budapest
Budapest is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns of Hungary, most populous city of Hungary. It is the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, tenth-largest city in the European Union by popul ...
, and
Berlin
Berlin ( ; ) is the Capital of Germany, capital and largest city of Germany, by both area and List of cities in Germany by population, population. With 3.7 million inhabitants, it has the List of cities in the European Union by population withi ...
.
Long-haul coach lines
Katowice has a modern international bus station located close to the city center. There are over 400 connections on a typical weekday, with the most-popular ones being domestic destinations in Poland and cities in
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
.
Cycling, walking and other
Cycling is becoming a more popular mode of transportation in Katowice. As of 2021, the city had of dedicated bicycle lanes, up from in 2015.
The metropolitan bicycle system is operated by
Nextbike and has 924 stations with over 7000 bicycles in Katowice and in surrounding cities.
Rides under 30 minutes costs PLN 1, less than 1 hour costs PLN 2.50 and each additional hour becomes more expensive.
Bolt and Blinkee operate commercial systems of scooter share. Traficar and Panek Car Share operate commercial carshare systems.
Freeways, roads and streets
Katowice has an extensive network of freeways, roads and streets, totaling over 1,120 km in length. The well-developed network supports over 200,000 cars registered in Katowice, and 49 percent of commuters that drive alone, a high share compared to other major cities in Poland.
Several freeways in Katowice are among the busiest in Poland:
expressway S86 between
Sosnowiec and Katowice's city center and
highway A4 between Murckowska and Mikołowska interchanges both see over 100,000 cars passing each day.
Katowice has a ring around its city center, consisting of highway A4, Murckowska freeway,
Drogowa Trasa Średnicowa (a freeway-style road connecting downtowns of cities in the Katowice urban area) that partly goes in a tunnel underground and Bocheńskiego road. Many of the roads and freeways in Katowice expand radially from the city center and replaced old local roads.
Main roads
European route E40
European route E40 is the longest European route, more than long, connecting Calais in France via Belgium, Germany, Poland, Ukraine, Russia, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, and Kyrgyzstan, with Ridder in Kazakhstan near the border with ...
passes through Katowice as
highway A4. It enters the city from Chorzów and continues eastward, with three lanes in each direction on the main road and two to three lanes in parallel access roads. It meets Bocheńskiego road and continues towards Mikołowska interchange, which is one of the only
combination interchanges in Poland and the main exit towards the city center. After that interchange, the highway loses its access roads due to lack of space in the dense urban area and continues east with four lanes in each direction. Access roads appear again (only on the south side, though) after around 500 meters and there is an exit towards Francuska Street. After another 1.5 kilometer, access roads appear again on the north side, too, and there is a tight exit towards Pułaskiego Street. The highway then runs into Murckowska interchange, before exiting the city.
National road 79 (DK79) enters Katowice from
Chorzów
Chorzów ( ; ; ) is a city in the Silesia region of southern Poland, near Katowice. Chorzów is one of the central cities of the Metropolis GZM – a metropolis with a population of 2 million. It is located in the Silesian Highlands, on the Rawa ...
and separates the
Silesian Park and
Osiedle Tysiąclecia in Katowice. It then merges with Drogowa Trasa Średnicowa (DTŚ) at the junction with Bocheńskiego road and Złota Street. It continues with DTŚ through the Katowice city center and descents into a tunnel under the Rondo roundabout. It then emerges overground again, right before an interchange with DK86. The road continues eastward as a freeway with exits towards
Zawodzie and
Szopienice neighborhoods for several more kilometers, before entering
Mysłowice and becoming a standard-access road.
National road 81 (DK81) enters Katowice from
Mikołów and runs through the southern residential neighborhoods as an arterial road with two lanes in each direction, named
Kościuszki Street. In the Brynów neighborhood, Kościuszki Street continues towards Katowice's city center while NR 81 turns east, to run through the forest towards the interchange with DK86.
National road 86 (DK86) enters Katowice from
Sosnowiec as expressway S86 up until Roździeńskiego interchange where it meets DK79 and loses its expressway status. It then continues south as Murckowska freeway east of the city center. It meets highway A4 and then passes by
Giszowiec neighborhood and continues through the woods southward, with exits towards
Murcki neighborhood (from which it gets its name) and
Kostuchna. It bypasses Murcki from the east and continues south towards
Tychy
Tychy (Polish pronunciation: ; ) is a city in Silesia in southern Poland, approximately south of Katowice. Situated on the southern edge of the Upper Silesian industrial district, the city borders Katowice to the north, Mikołów to the west, Bie ...
.
Tempo 30 Zone
In 2015, Katowice designated most of its city center as a zone, in an effort to curb traffic fatalities and crashes. Within 3 years of operation, the number of accidents dropped by 41 percent, including 37 percent drop in accidents involving pedestrians and cyclists. The accidents are also less severe: there was a 55 percent drop in injured pedestrians and cyclists.
Airports

Located approximately north of the city center,
Katowice Airport is the main airport serving Katowice. The airport is a focus city for
LOT Polish Airlines,
Ryanair
Ryanair is an Irish Low-cost carrier#Ultra low-cost carrier, ultra low-cost airline group headquartered in Swords, County Dublin, Ireland. The parent company, Ryanair Holdings plc, includes subsidiaries Ryanair , Malta Air, Buzz (Ryanair), Buzz ...
and its subsidiary
Buzz,
Wizz Air
{{Infobox airline
, airline = Wizz Air Holdings Plc.
, IATA =
, ICAO =
, callsign =
, aoc =
, hubs =
, focus_cities =
, frequent_flyer = {{ubl, class=nowrap
, Wizz All You Can Fly
, Wizz Discount Club
, Wizz Privilege Pass
, ...
,
Smartwings, and
Enter Air
Enter Air S.A._(corporation), S.A. is a Polish charter airline with its head office in Warsaw, Poland, and main base at Warsaw Chopin Airport and Katowice Airport. It operates holiday and charter flights out of its hubs in Poznań–Ławica Ai ...
. The busiest routes are:
London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
,
Dortmund
Dortmund (; ; ) is the third-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia, after Cologne and Düsseldorf, and the List of cities in Germany by population, ninth-largest city in Germany. With a population of 614,495 inhabitants, it is the largest city ...
,
Antalya
Antalya is the fifth-most populous city in Turkey and the capital of Antalya Province. Recognized as the "capital of tourism" in Turkey and a pivotal part of the Turkish Riviera, Antalya sits on Anatolia's southwest coast, flanked by the Tau ...
,
Eindhoven
Eindhoven ( ; ) is a city and List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality of the Netherlands, located in the southern Provinces of the Netherlands, province of North Brabant, of which it is the largest municipality, and is also locat ...
,
Warsaw
Warsaw, officially the Capital City of Warsaw, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the Vistula, River Vistula in east-central Poland. Its population is officially estimated at ...
and
Frankfurt
Frankfurt am Main () is the most populous city in the States of Germany, German state of Hesse. Its 773,068 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the List of cities in Germany by population, fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located in the forela ...
. Katowice is the largest leisure travel airport in Poland.
Long-haul flights are operated from Katowice to
Varadero
Varadero (), also referred to as ''Playa Azul'' (Blue Beach), is a resort town in the province of Matanzas, Cuba, and one of the largest resort areas in the Caribbean. Varadero Beach is rated one of the world's best beaches in TripAdvisor's Travel ...
in
Cuba
Cuba, officially the Republic of Cuba, is an island country, comprising the island of Cuba (largest island), Isla de la Juventud, and List of islands of Cuba, 4,195 islands, islets and cays surrounding the main island. It is located where the ...
,
Bangkok
Bangkok, officially known in Thai language, Thai as Krung Thep Maha Nakhon and colloquially as Krung Thep, is the capital and most populous city of Thailand. The city occupies in the Chao Phraya River delta in central Thailand and has an estim ...
in
Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
,
Cancún
Cancún is the most populous city in the Mexican state of Quintana Roo, located in southeast Mexico on the northeast coast of the Yucatán Peninsula. It is a significant tourist destination in Mexico and the seat of the municipality of Benito J ...
in
Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
,
Malé
Malé is the capital and most populous city of the Maldives. With a population of 211,908 in 2022 within its administrative area and coterminous geographical area of , Malé is one of the most densely populated cities in the world. The city i ...
in
Maldives
The Maldives, officially the Republic of Maldives, and historically known as the Maldive Islands, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in South Asia located in the Indian Ocean. The Maldives is southwest of Sri Lanka and India, abou ...
and to
Puerto Plata as well as
Punta Cana
Punta Cana is a resort town in the easternmost region of the Dominican Republic. It was politically incorporated as the "Verón–Punta Cana township" in 2006, and it is subject to the municipality of Higüey (La Altagracia Province). According ...
in
Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles of the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean. It shares a Maritime boundary, maritime border with Puerto Rico to the east and ...
. Katowice is also the second-largest cargo airport, after Warsaw Chopin. The airport is accessed through a metropolitan express bus line, running every 30 minutes between 4am and 9:30pm and every hour at night. A new train station at the airport is under construction, scheduled to be operational in 2023.
Katowice is also within an hour drive from
Kraków Airport, which offers additional destinations and airlines such as
Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , ; ; ) is the capital of the Netherlands, capital and Municipalities of the Netherlands, largest city of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. It has a population of 933,680 in June 2024 within the city proper, 1,457,018 in the City Re ...
(
KLM),
Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
(
Air France
Air France (; legally ''Société Air France, S.A.''), stylised as AIRFRANCE, is the flag carrier of France, and is headquartered in Tremblay-en-France. The airline is a subsidiary of the Air France-KLM Group and is one of the founding members ...
),
Helsinki
Helsinki () is the Capital city, capital and most populous List of cities and towns in Finland, city in Finland. It is on the shore of the Gulf of Finland and is the seat of southern Finland's Uusimaa region. About people live in the municipali ...
(
Finnair
Finnair Plc (, ) is the flag carrier and largest full-service legacy airline of Finland, with headquarters in Vantaa on the grounds of Helsinki Airport, its airline hub, hub. Finnair and its subsidiaries dominate both domestic and international ...
),
Chicago
Chicago is the List of municipalities in Illinois, most populous city in the U.S. state of Illinois and in the Midwestern United States. With a population of 2,746,388, as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the List of Unite ...
and
Newark (
LOT Polish Airlines),
Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a population of 1.4 million in the Urban area of Copenhagen, urban area. The city is situated on the islands of Zealand and Amager, separated from Malmö, Sweden, by the ...
and
Stockholm
Stockholm (; ) is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in Sweden by population, most populous city of Sweden, as well as the List of urban areas in the Nordic countries, largest urban area in the Nordic countries. Approximately ...
(
SAS) and
Zurich
Zurich (; ) is the list of cities in Switzerland, largest city in Switzerland and the capital of the canton of Zurich. It is in north-central Switzerland, at the northwestern tip of Lake Zurich. , the municipality had 448,664 inhabitants. The ...
(
Swiss
Swiss most commonly refers to:
* the adjectival form of Switzerland
* Swiss people
Swiss may also refer to: Places
* Swiss, Missouri
* Swiss, North Carolina
* Swiss, West Virginia
* Swiss, Wisconsin
Other uses
* Swiss Café, an old café located ...
). The airport can be accessed through scheduled buses leaving from Katowice bus station every 30–60 minutes.
Sports

Katowice has a long sporting tradition and hosted the final of
EuroBasket 2009 and
1975 European Athletics Indoor Championships,
1975 European Amateur Boxing Championships,
1976 World Ice Hockey Championships, 1957, 1985
European Weightlifting Championships, 1974, 1982
World Wrestling Championships
The World Wrestling Championships for Greco-Roman wrestling (men, since 1904) and freestyle wrestling (men since 1951, women since 1987) are organized by United World Wrestling (UWW).
Unofficial editions
Several World Greco-Roman Championships h ...
, 1991 World Amateur Bodybuilding Championships,
2011 Women's European Union Amateur Boxing Championships,
2014 FIVB Men's World Championship and others.
The
Stadion Śląski is between Chorzów and Katowice. It was a
national stadium
Many countries have a national sport stadium, which typically serves as the primary or exclusive home for one or more of a country's national representative sports teams. The term is most often used in reference to an association football ...
of Poland, with more than 50 international matches of the
Poland national football team
The Poland national football team () represents Poland in men's international Association football, football competitions since their first match in 1921. It is governed by the Polish Football Association (PZPN), the governing body for football ...
played here and around 30 matches in
UEFA
The Union of European Football Associations (UEFA ; ; ) is one of six continental bodies of governance in association football. It governs football, futsal and beach soccer, beach football in Europe and the List of transcontinental countries#A ...
competitions. There were also a
Speedway World Championship,
Speedway Grand Prix of Europe and many concerts featuring international stars.
Tourists can relax playing tennis or squash, doing
water sports
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms ...
also sailing (for example—in
Dolina Trzech Stawów), horse-riding (in
Wesoła Fala and
Silesian Park), cycling or going to one of numerous excellently equipped fitness clubs. Near the city centre are sporting facilities like swimming pools (for example "Bugla", "Rolna") and in neighbourhood—
Golf
Golf is a club-and-ball sport in which players use various Golf club, clubs to hit a Golf ball, ball into a series of holes on a golf course, course in as few strokes as possible.
Golf, unlike most ball games, cannot and does not use a standa ...
courses (in
Siemianowice Śląskie
Siemianowice Śląskie (; ; ) also known as Siemianowice is a city in Upper Silesia in southern Poland, near Katowice, in the core of the Metropolis GZM - a metropolis with a population of 2 million people and is located in the Silesian Highlands, ...
).
Sports clubs
*
GKS Katowice – men's
football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kick (football), kicking a football (ball), ball to score a goal (sports), goal. Unqualified, football (word), the word ''football'' generally means the form of football t ...
,
ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey in North America) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an Ice rink, ice skating rink with Ice hockey rink, lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. Tw ...
,
volleyball
Volleyball is a team sport in which two teams of six players are separated by a net. Each team tries to score points by grounding a ball on the other team's court under organized rules. It has been a part of the official program of the Summ ...
,
women's football club (
Polish Football League Runners-Up (4): 1988, 1989, 1992, 1994
Polish Cup
The Polish Cup in Association football, football ( ) is an annual Single-elimination tournament, knockout football competition for Polish football club (association football), football clubs, held continuously since 1950, and is the second most i ...
Winners (3): 1986, 1991, 1993;
Polish Super Cup
The Polish Super Cup (, ) is an annually held match between the champions of the Ekstraklasa and the Polish Cup winners or, if the Ekstraklasa champions also win the Polish Cup, the Cup's runners-up. As of 2024, the Polish Super Cup has been ...
Winners (2): 1991, 1995;
Polish Ice Hockey League Champions (8): 1958, 1960, 1962, 1965, 1968, 1970, 2022, 2023;
Polish Women's Football League Winners (1): 2023, Runners-Up (1): 2024,
Polish Women’s Cup Winners (1): 2024.
*
1. FC Katowice - men’s and women’s football club
*
AZS AWF Katowice – various sports, women's
handball
Handball (also known as team handball, European handball, Olympic handball or indoor handball) is a team sport in which two teams of seven players each (six outcourt players and a goalkeeper) pass a ball using their hands with the aim of thr ...
team playing in
Polish Women's Handball Superleague, men's
basketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams, most commonly of five players each, opposing one another on a rectangular Basketball court, court, compete with the primary objective of #Shooting, shooting a basketball (ball), basketball (appro ...
team playing in the second league, fencing section – many medals in the Polish Championship
*
Naprzód Janów
Naprzód Janów is an ice hockey team from the Janów neighbourhood of Katowice, Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mo ...
Katowice – hockey club playing in
Polish Hockey Superleague, vice-champion of Poland (5x): 1971, 1973, 1977, 1989, 1992; bronze medal (7x): 1972, 1974, 1976, 1978, 1982, 1986, 1987; Polish Cup (1x): 1970.
*AZS US Katowice – various sports, many medals in the Polish Championship in various sports
*HKS Szopienice – various sports, many medals in the Polish and Europe and World Championship in
weightlifting
Weightlifting or weight lifting generally refers to physical exercises and sports in which people lift weights, often in the form of dumbbells, barbells or machines. People engage in weightlifting for a variety of different reasons. These can ...
*
Silesia Miners –
American football
American football, referred to simply as football in the United States and Canada and also known as gridiron football, is a team sport played by two teams of eleven players on a rectangular American football field, field with goalposts at e ...
club playing in
Polish American Football League, Polish champion in 2009, vice-champion in 2007
*Jango Katowice –
futsal
Futsal is a variant of association football played between two teams of five players each on a court smaller than a football pitch. Its rules are based on the Laws of the Game (association football), Laws of the Game of association football, and i ...
club playing in Polish Futsal Superleague; Polish Cup (1x): 2007; bronze medal Polish Championship (2x): 2001, 2007
*
Rozwój Katowice – football club playing in
Polish Third League
*MK Katowice – football club playing in
Polish Fourth League
*Hetman Szopienice – chess club, many medals in the Polish Championship
*Sparta Katowice – various sports, many medals in the Polish Championship in various sports
*
Policyjny Klub Sportowy Katowice – various sports, many medals in the Polish Championship in various sports
*AWF Mickiewicz Katowice – basketball club
*Silesian
Flying club
A flying club or aero club is a non-profit organization, not-for-profit, member-run organization that provides its members with affordable access to aircraft.
Many clubs also provide flight training, flight planning facilities, pilot supplies and ...
(Aeroklub Śląski)
Defunct sports clubs:
*
Diana Kattowitz – football club
*
1. FC Kattowitz – football club, vice-champion of Poland: 1927; champion of Upper Silesia: 1907, 1908, 1909, 1913, 1922, 1932, 1945
*
Germania Kattowitz – football club
*KS Baildon Katowice – various sports, many medals in the Polish Championship in various sports
*Pogoń Katowice – various sports, many medals in the Polish Championship in various sports
Sports events
*
1975 European Athletics Indoor Championships
*
1976 World Ice Hockey Championships
*
FIVB World League 2001
*
FIVB World League 2007
*
Eurobasket 2009
*
Tour de Pologne 2010
*
BNP Paribas Katowice Open
*
EMS One Katowice 2014
Electronic Sports League Major Series One Katowice 2014, also known as EMS One Katowice 2014, was the second ''Counter-Strike: Global Offensive'' Counter-Strike: Global Offensive Major Championships, Major Championship. The tournament was held f ...
(
CS:GO Major Championship)
*
IEM World Championship Katowice 2015
*
ESL One Katowice 2015
ESL One Katowice 2015, also known as Katowice 2015, was the fifth '' Counter-Strike: Global Offensive'' Major Championship, held from March 12 to March 15, 2015, at the Spodek Arena in Katowice, Poland. It was the first ''CS:GO'' Major of 2015. ...
(
CS:GO Major Championship)
*
IEM World Championship Katowice 2016
*
IEM World Championship Katowice 2017
*
Overwatch World Cup 2017 Qualifier
*
IEM World Championship Katowice 2018
*
IEM World Championship Katowice 2019 (
CS:GO Major Championship)
*ESL One Katowice 2019
*BWF World Senior Badminton Championships 2019
*IEM Katowice 2020
*IEM Katowice 2021
*
Intel Extreme Masters
The Intel Extreme Masters (IEM) is a series of international esports tournaments held in countries around the world. These Electronic Sports League (ESL) sanctioned events, sponsored by Intel, currently host events in ''Counter-Strike 2''. Oth ...
Season XVI – Katowice
*
Intel Extreme Masters
The Intel Extreme Masters (IEM) is a series of international esports tournaments held in countries around the world. These Electronic Sports League (ESL) sanctioned events, sponsored by Intel, currently host events in ''Counter-Strike 2''. Oth ...
Katowice 2023
Notable people
*
Hans Sachs
Hans Sachs (5 November 1494 – 19 January 1576) was a German ''Meistersinger'' ("mastersinger"), poetry, poet, playwright, and shoemaking, shoemaker.
Biography
Hans Sachs was born in Nuremberg (). As a child he attended a singing school that w ...
(1877–1945), serologist
*
Kurt Goldstein
Kurt Goldstein (November 6, 1878 – September 19, 1965) was a German neurologist and psychiatrist who created a holistic theory of the organism. Educated in medicine, Goldstein studied under Carl Wernicke and Ludwig Edinger where he focused on ...
(1878–1965), neurologist
*
Erich Przywara (1889–1972), priest
*
Hans Mikosch (1898–1993), general
*
Hans Källner (1898–1945), general
*
Franz Leopold Neumann (1900–1954), politician
*
Willy Fritsch (1901–1973), actor
*
Hans Bellmer (1902–1975), surrealist photographer
*
Hans-Christoph Seebohm (1903–1967), politician
*
Maria Goeppert-Mayer (1906–1972), physicist, Nobel Prize winner
*
Gwendoline Jarczyk (1927–2021), philosopher and historian
*
Kurt Schwaen (1909–2007), composer
*
Rudolf Schnackenburg (1914–2002), priest
*
Georg Thomalla (1915–1999), actor
*
Ernst Wilimowski (1916–1997), football player
*
Ernst Plener (1919–2007), football player
*
Anneli Cahn Lax (1922–1999), mathematician
*
Richard Herrmann (1923–1962), football player
*
Chaskel Besser (1923–2010),
Orthodox rabbi
*
Kazimierz Kutz (1929–2018), film director and politician
*
Waldemar Świerzy (1931–2013), artist, illustrator and cartoonist
*
Wojciech Kilar (1932–2013), classical and
film music
A film score is original music written specifically to accompany a film. The score comprises a number of orchestral, instrumental, or choral pieces called cues, which are timed to begin and end at specific points during the film in order to ...
composer
*
Henryk Górecki (1933–2010),
classical composer
*
Władysław Masłowski (1933–1986), journalist and press researcher
*
Janusz Sidło (1933–1993), javelin thrower
*
Josef Kompalla (born 1936), ice hockey player and referee
*
Henryk Broder (born 1946), journalist
*
Krzysztof Krawczyk
Krzysztof January Krawczyk (; 8 September 1946 – 5 April 2021) was a Polish baritone Pop music, pop singer, guitarist and composer. He was the vocalist of a popular Polish band, Trubadurzy ("the Troubadours"), from 1963 to 1973 when he sta ...
(1946–2021), singer, guitarist and composer
*
Jerzy Kukuczka
Józef Jerzy Kukuczka (; 24 March 1948 – 24 October 1989) was a Polish mountaineer, regarded as one of the greatest high-altitude climbers in history. In 1987, he became the second man (after Reinhold Messner) to climb all 14 eight-thousand ...
(1948–1989), alpine and
high altitude
Altitude is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context (e.g., aviation, geometry, geographical s ...
climber
*
Joanna Kluzik-Rostkowska (born 1963), politician
*
Elżbieta Bieńkowska (born 1964), politician
*
Robert Konieczny (born 1969), architect
*
Anna Kańtoch (born 1976), writer
*
Alicja Kwade (born 1979), contemporary visual artist
*
Jan P. Matuszyński (born 1984), film director
*
Grzegorz Kosok (born 1986),
volleyball
Volleyball is a team sport in which two teams of six players are separated by a net. Each team tries to score points by grounding a ball on the other team's court under organized rules. It has been a part of the official program of the Summ ...
player
*
Zuzanna Bijoch (born 1994), fashion model
*
Mateusz Musiałowski (born 2003), footballer
International relations
Consulates
There are 15 honorary consulates in Katowice, of
Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
,
Belarus
Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Belarus spans an a ...
,
Benin
Benin, officially the Republic of Benin, is a country in West Africa. It was formerly known as Dahomey. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso to the north-west, and Niger to the north-east. The majority of its po ...
,
Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
,
Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in western South America. It is the southernmost country in the world and the closest to Antarctica, stretching along a narrow strip of land between the Andes, Andes Mountains and the Paci ...
,
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
,
Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
,
Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
,
Latvia
Latvia, officially the Republic of Latvia, is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is one of the three Baltic states, along with Estonia to the north and Lithuania to the south. It borders Russia to the east and Belarus to t ...
,
Lithuania
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, P ...
,
Luxembourg
Luxembourg, officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, is a landlocked country in Western Europe. It is bordered by Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France on the south. Its capital and most populous city, Luxembour ...
,
Peru
Peru, officially the Republic of Peru, is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the south and west by the Pac ...
,
Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg
, national_motto =
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map =
, map_caption = Location of Serbia (gree ...
,
Slovenia
Slovenia, officially the Republic of Slovenia, is a country in Central Europe. It borders Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the south and southeast, and a short (46.6 km) coastline within the Adriati ...
and
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
.
Twin towns – sister cities
Katowice is
twinned with:
*
Cologne
Cologne ( ; ; ) is the largest city of the States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with nearly 1.1 million inhabitants in the city pr ...
, Germany
*
Groningen
Groningen ( , ; ; or ) is the capital city and main municipality of Groningen (province), Groningen province in the Netherlands. Dubbed the "capital of the north", Groningen is the largest place as well as the economic and cultural centre of ...
, Netherlands
*
Košice
Košice is the largest city in eastern Slovakia. It is situated on the river Hornád at the eastern reaches of the Slovak Ore Mountains, near the border with Hungary. With a population of approximately 230,000, Košice is the second-largest cit ...
, Slovakia
*
Lviv
Lviv ( or ; ; ; see #Names and symbols, below for other names) is the largest city in western Ukraine, as well as the List of cities in Ukraine, fifth-largest city in Ukraine, with a population of It serves as the administrative centre of ...
, Ukraine
*
Miskolc
Miskolc ( , ; ; Czech language, Czech and ; ; ; ) is a city in northeastern Hungary, known for its heavy industry. With a population of 161,265 as of 1 January 2014, Miskolc is the List of cities and towns in Hungary#Largest cities in Hungary, ...
, Hungary
*
Mobile, United States
*
Opava
Opava (; , ) is a city in the Moravian-Silesian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 55,000 inhabitants. It lies on the Opava (river), Opava River. Opava is one of the historical centres of Silesia and was a historical capital of Czech Sile ...
, Czech Republic
*
Ostrava
Ostrava (; ; ) is a city in the north-east of the Czech Republic and the capital of the Moravian-Silesian Region. It has about 283,000 inhabitants. It lies from the border with Poland, at the confluences of four rivers: Oder, Opava (river), Opa ...
, Czech Republic
*
Pula
Pula, also known as Pola, is the largest city in Istria County, west Croatia, and the List of cities and towns in Croatia, seventh-largest city in the country, situated at the southern tip of the Istria, Istrian peninsula in western Croatia, wi ...
, Croatia
*
Saint-Étienne
Saint-Étienne (; Franco-Provençal: ''Sant-Etiève''), also written St. Etienne, is a city and the prefecture of the Loire département, in eastern-central France, in the Massif Central, southwest of Lyon, in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes regi ...
, France
*
Shenyang
Shenyang,; ; Mandarin pronunciation: ; formerly known as Fengtian formerly known by its Manchu language, Manchu name Mukden, is a sub-provincial city in China and the list of capitals in China#Province capitals, provincial capital of Liaonin ...
, China
See also
*
List of mayors of Katowice
*
List of tallest buildings in Katowice
*
Wojciech Korfanty Avenue
Notes
References
External links
The Municipal Council of the City of KatowiceKatowice Portal in English
{{Authority control
Cities and towns in Silesian Voivodeship
Cities in Silesia
City counties of Poland
Sites of Nazi war crimes during the Invasion of Poland
Holocaust locations in Poland
 On 3 October 1846, the works of the final stage of the Breslau- Myslowitz (''Wrocław-Mysłowice'') rail line ended, built and operated by the Upper Silesian Railway. It was opened by king
On 3 October 1846, the works of the final stage of the Breslau- Myslowitz (''Wrocław-Mysłowice'') rail line ended, built and operated by the Upper Silesian Railway. It was opened by king  Katowice has 22 officially recognized neighborhoods. Śródmieście, Osiedle Paderewskiego-Muchowiec, Zawodzie and Koszutka form the dense central urban core where most cultural and educational institutions, businesses and administrative buildings are located.
Most Northern and Eastern neighborhoods around the downtown core are more working-class and developed from worker's estates build around large industry such as coal mines, manufactures and steelworks. Each of these neighborhoods has its own dense commercial strip surrounded by mid-rise apartment buildings and some single-family homes. Szopienice, located between downtown Katowice and Mysłowice, used to be a separate town until mid-1960s. Nikiszowiec, a former mine's town, has undergone strong
Katowice has 22 officially recognized neighborhoods. Śródmieście, Osiedle Paderewskiego-Muchowiec, Zawodzie and Koszutka form the dense central urban core where most cultural and educational institutions, businesses and administrative buildings are located.
Most Northern and Eastern neighborhoods around the downtown core are more working-class and developed from worker's estates build around large industry such as coal mines, manufactures and steelworks. Each of these neighborhoods has its own dense commercial strip surrounded by mid-rise apartment buildings and some single-family homes. Szopienice, located between downtown Katowice and Mysłowice, used to be a separate town until mid-1960s. Nikiszowiec, a former mine's town, has undergone strong  Katowice is the seat of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese, with the suffragan bishoprics of
Katowice is the seat of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese, with the suffragan bishoprics of  Judaism has historically been present in Katowice since at least 1702. First
Judaism has historically been present in Katowice since at least 1702. First  After
After  As of August 2024, 252,841 people are employed in Katowice, which makes the city the 7th largest job market in Poland, slightly ahead of
As of August 2024, 252,841 people are employed in Katowice, which makes the city the 7th largest job market in Poland, slightly ahead of  The Silesian Museum is the largest and most-important museum in Katowice. It originally opened in 1929, and its radically modern,
The Silesian Museum is the largest and most-important museum in Katowice. It originally opened in 1929, and its radically modern,  Rawa Blues Festiwal –
Rawa Blues Festiwal –  Katowice market square (Rynek w Katowicach)
*Freedom Square (Plac Wolności)
*Andrzej Square (Plac Andrzeja)
*Miarka Square (Plac Miarki)
*Council of Europe Square (Plac Rady Europy)
*Alfred Square (Plac Alfreda)
*A. Budniok Square (Plac A. Brudnioka)
*J. Londzin Square (Plac J. Londzina)
*A. Hlond Square (Plac A. Hlonda)
Katowice market square (Rynek w Katowicach)
*Freedom Square (Plac Wolności)
*Andrzej Square (Plac Andrzeja)
*Miarka Square (Plac Miarki)
*Council of Europe Square (Plac Rady Europy)
*Alfred Square (Plac Alfreda)
*A. Budniok Square (Plac A. Brudnioka)
*J. Londzin Square (Plac J. Londzina)
*A. Hlond Square (Plac A. Hlonda)
 *Nature reserve Las Murckowski
*Nature reserve Ochojec
*Szopienice-Borki
*Źródła Kłodnicy
*Staw Grunfeld
*Stawy Na Tysiącleciu
*Płone Bagno
*Nature reserve Las Murckowski
*Nature reserve Ochojec
*Szopienice-Borki
*Źródła Kłodnicy
*Staw Grunfeld
*Stawy Na Tysiącleciu
*Płone Bagno
 Katowice is a large scientific centre and has been designated as the European City of Science 2024 by EuroScience (ESOF). It has over 20 schools of higher education, at which over 100,000 people study.
* University of Silesia in Katowice
* University of Economics in Katowice
* Medical University of Silesia
*
Katowice is a large scientific centre and has been designated as the European City of Science 2024 by EuroScience (ESOF). It has over 20 schools of higher education, at which over 100,000 people study.
* University of Silesia in Katowice
* University of Economics in Katowice
* Medical University of Silesia
*  Located approximately north of the city center, Katowice Airport is the main airport serving Katowice. The airport is a focus city for LOT Polish Airlines,
Located approximately north of the city center, Katowice Airport is the main airport serving Katowice. The airport is a focus city for LOT Polish Airlines,  Katowice has a long sporting tradition and hosted the final of EuroBasket 2009 and 1975 European Athletics Indoor Championships, 1975 European Amateur Boxing Championships, 1976 World Ice Hockey Championships, 1957, 1985 European Weightlifting Championships, 1974, 1982
Katowice has a long sporting tradition and hosted the final of EuroBasket 2009 and 1975 European Athletics Indoor Championships, 1975 European Amateur Boxing Championships, 1976 World Ice Hockey Championships, 1957, 1985 European Weightlifting Championships, 1974, 1982