Kalmak on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Kalmyks (), archaically

 The contemporary Kalmyks are a branch of the
The contemporary Kalmyks are a branch of the  At the start of this 400-year era, the Western Mongols designated themselves as the
At the start of this 400-year era, the Western Mongols designated themselves as the  Together, these nomadic tribes roamed the grassy plains of western Inner Asia, between
Together, these nomadic tribes roamed the grassy plains of western Inner Asia, between

 At the beginning of the 17th century, the First Altan Khan drove the
At the beginning of the 17th century, the First Altan Khan drove the  Under the dynamic leadership of Erdeni Batur, the Dzungars stopped the expansion of the first
Under the dynamic leadership of Erdeni Batur, the Dzungars stopped the expansion of the first
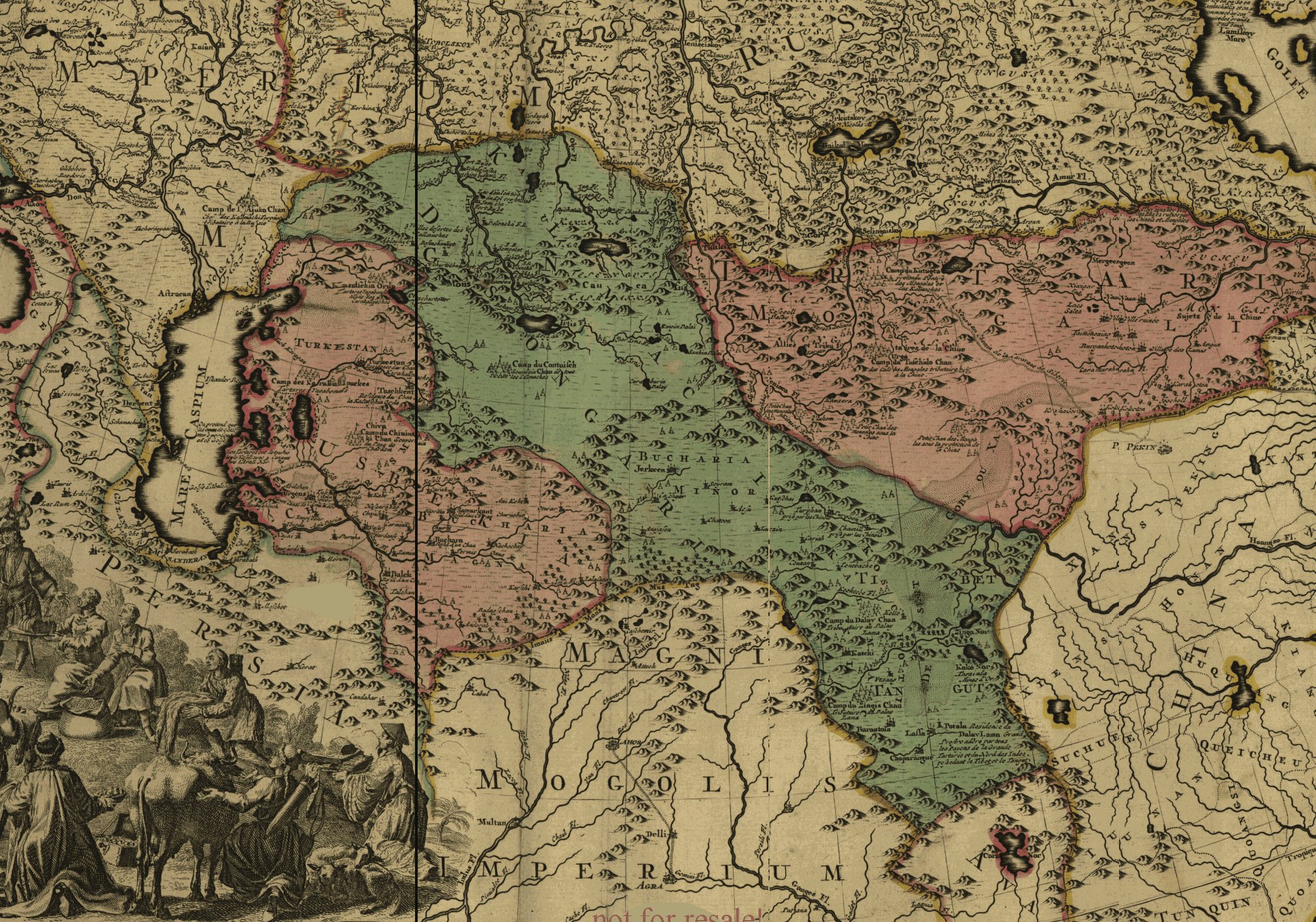
 Upon arrival to the lower Volga region in 1630, the Oirats encamped on land that was once part of the
Upon arrival to the lower Volga region in 1630, the Oirats encamped on land that was once part of the
 Historically, Oirat identified themselves by their respective sub-group names. In the 15th century, the three major groups of Oirat formed an alliance, adopting "Dörben Oirat" as their collective name. In the early 17th century, a second great Oirat Confederation emerged, which later became the Dzungar Empire. While the Dzungars (initially Choros, Dörbet and Khoit tribes) were establishing their empire in Central Eurasia, the Khoshuts were establishing the Khoshut Khanate in Tibet, protecting the Gelugpa sect from its enemies, and the Torghuts formed the Kalmyk Khanate in the lower Volga region.
After encamping, the Oirats began to identify themselves as "Kalmyk." This named was supposedly given to them by their Muslim neighbors and later used by the Russians to describe them. The Oirats used this name in their dealings with outsiders, viz., their Russian and Muslim neighbors. But they continued to refer to themselves by their tribal, clan, or other internal affiliations.
The name Kalmyk, however, wasn't immediately accepted by all of the Oirat tribes in the lower Volga region. As late as 1761, the Khoshut and Dzungars (refugees from the Manchu Empire) referred to themselves and the Torghuts exclusively as Oirats. The Torghuts, by contrast, used the name Kalmyk for themselves as well as the Khoshut and Dzungars.
Generally, European scholars have identified all western Mongolians collectively as Kalmyks, regardless of their location ( Ramstedt, 1935: v–vi). Such scholars (e.g. Sebastian Muenster) have relied on Muslim sources who traditionally used the word "Kalmyk" to describe western Mongolians in a derogatory manner and the western Mongols of China and Mongolia have regarded that name as a term of abuse. Instead, they use the name Oirat or they go by their respective tribal names, e.g., Khoshut, Dörbet, Choros, Torghut, Khoit, Bayid, Mingat, etc.
Over time, the descendants of the Oirat migrants in the lower Volga region embraced the name "Kalmyk" irrespective of their locations, viz., Astrakhan, the Don Cossack region, Orenburg, Stavropol, the Terek and the Ural Mountains. Another generally accepted name is ''Ulan Zalata'' or the "red-buttoned ones".
Historically, Oirat identified themselves by their respective sub-group names. In the 15th century, the three major groups of Oirat formed an alliance, adopting "Dörben Oirat" as their collective name. In the early 17th century, a second great Oirat Confederation emerged, which later became the Dzungar Empire. While the Dzungars (initially Choros, Dörbet and Khoit tribes) were establishing their empire in Central Eurasia, the Khoshuts were establishing the Khoshut Khanate in Tibet, protecting the Gelugpa sect from its enemies, and the Torghuts formed the Kalmyk Khanate in the lower Volga region.
After encamping, the Oirats began to identify themselves as "Kalmyk." This named was supposedly given to them by their Muslim neighbors and later used by the Russians to describe them. The Oirats used this name in their dealings with outsiders, viz., their Russian and Muslim neighbors. But they continued to refer to themselves by their tribal, clan, or other internal affiliations.
The name Kalmyk, however, wasn't immediately accepted by all of the Oirat tribes in the lower Volga region. As late as 1761, the Khoshut and Dzungars (refugees from the Manchu Empire) referred to themselves and the Torghuts exclusively as Oirats. The Torghuts, by contrast, used the name Kalmyk for themselves as well as the Khoshut and Dzungars.
Generally, European scholars have identified all western Mongolians collectively as Kalmyks, regardless of their location ( Ramstedt, 1935: v–vi). Such scholars (e.g. Sebastian Muenster) have relied on Muslim sources who traditionally used the word "Kalmyk" to describe western Mongolians in a derogatory manner and the western Mongols of China and Mongolia have regarded that name as a term of abuse. Instead, they use the name Oirat or they go by their respective tribal names, e.g., Khoshut, Dörbet, Choros, Torghut, Khoit, Bayid, Mingat, etc.
Over time, the descendants of the Oirat migrants in the lower Volga region embraced the name "Kalmyk" irrespective of their locations, viz., Astrakhan, the Don Cossack region, Orenburg, Stavropol, the Terek and the Ural Mountains. Another generally accepted name is ''Ulan Zalata'' or the "red-buttoned ones".
(Mongolian) As C.D Barkman notes, "It is quite clear that the Torghuts had not intended to surrender the Chinese, but had hoped to lead an independent existence in Dzungaria." Ubashi sent 30,000 cavalry in the first year of the Russo-Turkish War (1768–74) to gain weaponry before the migration. The 8th Dalai Lama was contacted to request his blessing and to set the date of departure. After consulting the astrological chart, he set a return date, but at the moment of departure, the weakening of the ice on the Volga River permitted only those Kalmyks (about 200,000 people) on the eastern bank to leave. Those 100,000–150,000 people on the western bank were forced to stay behind and
 In the aftermath of the
In the aftermath of the  The majority of the Don Kalmyks also sided with the White Movement to preserve their Cossack lifestyle and proud traditions. As
The majority of the Don Kalmyks also sided with the White Movement to preserve their Cossack lifestyle and proud traditions. As
 Around half of (97–98,000) Kalmyk people deported to Siberia died before being allowed to return home in 1957. The government of the Soviet Union forbade teaching
Around half of (97–98,000) Kalmyk people deported to Siberia died before being allowed to return home in 1957. The government of the Soviet Union forbade teaching
 The name "Kalmyk" is a word of Turkic origin that means "remnant" or "to remain". Turkic tribes may have used this name as early as the thirteenth century. Arab geographer Ibn al-Wardi is documented as the first person to use the term in referring to the Oirats in the fourteenth century. The
The name "Kalmyk" is a word of Turkic origin that means "remnant" or "to remain". Turkic tribes may have used this name as early as the thirteenth century. Arab geographer Ibn al-Wardi is documented as the first person to use the term in referring to the Oirats in the fourteenth century. The


 The Kalmyks are the only European ethnic group whose primary religion is
The Kalmyks are the only European ethnic group whose primary religion is
 ''Ethnologue'' classifies
''Ethnologue'' classifies
Антропологические характеристики калмыков по данным исследователей XVIII–XIX вв.
' // Вестник Прикаспия: археология, история, этнография. No. 1. Элиста: Изд-во КГУ, 2008. с. 220–243. * Хойт С.К.
Калмыки в работах антропологов первой половины XX вв
'. // Вестник Прикаспия: археология, история, этнография. No. 3, 2012. с. 215–245. * Хойт С.К.
Этническая история ойратских групп
'. Элиста, 2015. 199 с. (Khoyt S.K. Ethnic history of oyirad groups. Elista, 2015. 199 p). (in Russian) * Хойт С.К.
Данные фольклора для изучения путей этногенеза ойратских групп
' // Международная научная конференция «Сетевое востоковедение: образование, наука, культура», 7-10 декабря 2017 г.: материалы. Элиста: Изд-во Калм. ун-та, 2017. с. 286–289. {{DEFAULTSORT:Kalmyk People Ethnic groups in Kyrgyzstan Kalmyk people Buddhism in Russia Mongol diaspora in Europe Mongolian diaspora in Europe Ethnic groups in Russia East Asian diaspora Kalmyk Khanate
anglicised
Anglicisation or anglicization is a form of cultural assimilation whereby something non-English becomes assimilated into or influenced by the culture of England. It can be sociocultural, in which a non-English place adopts the English language ...
as Calmucks (), are the only Mongolic ethnic group living in Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
, residing in the easternmost part of the European Plain
The European Plain or the Great European Plain is a plain in Europe and is a major feature of one of four major topographical units of Europethe ''Central and Interior Lowlands''.
.
This dry steppe area, west of the lower Volga River, known among the nomads as Itil/Idjil, a basin on the northwest shore of the Caspian Sea, was the most suitable land for nomadic pastures. Itil or Idjil, the ancient name of the Volga River, written in the archaic Oirat script, means exactly that: the "pastures".
The ancestors of Kalmyks were nomadic groups of Oirat-speaking Mongols
Mongols are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, China ( Inner Mongolia and other 11 autonomous territories), as well as the republics of Buryatia and Kalmykia in Russia. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family o ...
, who migrated from Western Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by po ...
to Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural and socio-economic connotations. Its eastern boundary is marked by the Ural Mountain ...
three times: in early medieval times, establishing in the 6th–8th centuries the Avar Khanate
The Avar Khanate, the Avar Nutsaldom (; ), also known as Khundzia or Avaria, was a long-lived Avar state, which controlled mountainous parts of Dagestan (in the North Caucasus) from the early 13th century to the 19th century.
History of Avar ...
; in medieval times, establishing the Ulus of Juchi and Il-Kanate as Khuda-in-laws of Genghis Khan
Genghis Khan (born Temüjin; August 1227), also known as Chinggis Khan, was the founder and first khan (title), khan of the Mongol Empire. After spending most of his life uniting the Mongols, Mongol tribes, he launched Mongol invasions and ...
; and finally, in early modern times, establishing the Kalmyk Khanate in the 17th century.
The Oirat language belongs to the western branch of the Mongolic language family, whose speakers include numerous sub-ethnic groups (Derbet, Torgut, Khoshut, Olot, Dzungar (Zunghar), Bayad, Zakhchin, Khoton, Myangad, Buzava) across a wide geographical area of Uvs and Khovd provinces (aimags) of Western Mongolia (''N'' = 209,412), and in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China (''N'' = 194,891). Ethnic groups of Oirat speakers in the Republic of Kalmykia, Russia (''N'' = 162,740) include Torguts, Derbets and Buzavas, together with a smaller group called Khoshuts, who live in just two villages of Kalmykia. Up until today the Kalmyks have retained their distinguished sub-ethnic groups, being quite separated from their geographical neighbours in Russia and northeast Caucasus.
The Kalmyks are the only traditionally Buddhist
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
ethnic group
An ethnicity or ethnic group is a group of people with shared attributes, which they collectively believe to have, and long-term endogamy. Ethnicities share attributes like language, culture, common sets of ancestry, traditions, society, re ...
who are located inside Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
. Through emigration, small Kalmyk communities have been established in the United States, France, Germany, and the Czech Republic.
Origins and history
Early history of the Oirats

 The contemporary Kalmyks are a branch of the
The contemporary Kalmyks are a branch of the Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by po ...
n Oirats
Oirats (; ) or Oirds ( ; ), formerly known as Eluts and Eleuths ( or ; zh, 厄魯特, ''Èlǔtè'') are the westernmost group of Mongols, whose ancestral home is in the Altai Mountains, Altai region of Siberia, Xinjiang and western Mongolia.
...
, whose ancient grazing-lands spanned present-day parts of Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
, Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
, Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by po ...
and China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
. After the fall of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty ( ; zh, c=元朝, p=Yuáncháo), officially the Great Yuan (; Mongolian language, Mongolian: , , literally 'Great Yuan State'), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Div ...
of China in 1368, the Oirats
Oirats (; ) or Oirds ( ; ), formerly known as Eluts and Eleuths ( or ; zh, 厄魯特, ''Èlǔtè'') are the westernmost group of Mongols, whose ancestral home is in the Altai Mountains, Altai region of Siberia, Xinjiang and western Mongolia.
...
emerged as a formidable foe against the Khalkha Mongols
The Khalkha (; ) have been the largest subgroup of the Mongols in modern Mongolia since the 15th century. The Khalkha, together with Chahars, Ordos Mongols, Ordos and Tumed, were directly ruled by Borjigin khans until the 20th century. In cont ...
, the Han-led Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty, officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming was the last imperial dynasty of ...
and the Manchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic peoples, Tungusic East Asian people, East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized Ethnic minorities in China, ethnic minority in China and the people from wh ...
-led Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the ...
. For 400 years, the Oirats
Oirats (; ) or Oirds ( ; ), formerly known as Eluts and Eleuths ( or ; zh, 厄魯特, ''Èlǔtè'') are the westernmost group of Mongols, whose ancestral home is in the Altai Mountains, Altai region of Siberia, Xinjiang and western Mongolia.
...
conducted a military struggle for domination and control over both Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of China. Its border includes two-thirds of the length of China's China–Mongolia border, border with the country of Mongolia. ...
and Outer Mongolia
Outer Mongolia was the name of a territory in the Manchu-led Qing dynasty of China from 1691 to 1911. It corresponds to the modern-day independent state of Mongolia and the Russian republic of Tuva. The historical region gained ''de facto'' ...
. The struggle ended in 1757 with the defeat of the Oirats of the Dzungar Khanate
The Dzungar Khanate ( Mongolian: ), also known as the Zunghar Khanate or Junggar Khanate, was an Inner Asian khanate of Oirat Mongol origin. At its greatest extent, it covered an area from southern Siberia in the north to present-day Kyrgyz ...
against the Qing Empire
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the ...
, in the Dzungar–Qing Wars
The Dzungar–Qing Wars (, ) were a decades-long series of conflicts that pitted the Dzungar Khanate against the Qing dynasty and its Mongol vassals. Fighting took place over a wide swath of Inner Asia, from present-day central and eastern Mong ...
; they were the last of the Mongol groups to resist vassalage to Qing.
 At the start of this 400-year era, the Western Mongols designated themselves as the
At the start of this 400-year era, the Western Mongols designated themselves as the Four Oirat
The Four Oirats ( Written Oirat: , ; , ; ) or Oirat Confederation, formerly known as the Eleuths, was the confederation of the Oirat tribes which marked the rise of the Western Mongols in the history of the Mongolian Plateau.
Despite the univer ...
. The alliance comprised four major Western Mongol tribes: Khoshut
The Khoshut (Mongolian language, Mongolian: Хошууд,, qoşūd, ; literally "bannermen," from Middle Mongol language, Middle Mongolian ''qosighu'' "flag, banner") are one of the four major tribes of the Oirats, Oirat people. They established ...
, Choros, Torghut
The Torghut ( Mongolian: Торгууд, , Torguud, "Guardsman", ) are one of the four major subgroups of the Four Oirats. The Torghut nobles traced their descent to the Mongol Keraite ruler Toghrul, and many Torghuts descended from the Keraites.
...
and Dörbet. Collectively, the Four Oirat sought power as an alternative to the Mongols, who were the patrilineal heirs to Genghis Khan
Genghis Khan (born Temüjin; August 1227), also known as Chinggis Khan, was the founder and first khan (title), khan of the Mongol Empire. After spending most of his life uniting the Mongols, Mongol tribes, he launched Mongol invasions and ...
. The Four Oirat incorporated neighboring tribes or splinter groups at times, so there was a great deal of fluctuation in the composition of the alliance, with larger tribes dominating or absorbing the smaller ones. Smaller tribes belonging to the confederation included the Khoits, Zakhchin, Bayids and Khangal.
 Together, these nomadic tribes roamed the grassy plains of western Inner Asia, between
Together, these nomadic tribes roamed the grassy plains of western Inner Asia, between Lake Balkhash
Lake Balkhash, also spelt Lake Balqash (, , ), is a lake in southeastern Kazakhstan, one of the largest lakes in Asia and the 15th largest in the world. It is located in the eastern part of Central Asia and sits in the Balkhash-Alakol Basin, ...
in present-day eastern Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
and Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal is a rift lake and the deepest lake in the world. It is situated in southern Siberia, Russia between the Federal subjects of Russia, federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast, Irkutsk Oblasts of Russia, Oblast to the northwest and the Repu ...
in present-day Russia north of central Mongolia. They pitched their yurt
A yurt (from the Turkic languages) or ger (Mongolian language, Mongolian) is a portable, round tent covered and Thermal insulation, insulated with Hide (skin), skins or felt and traditionally used as a dwelling by several distinct Nomad, nomad ...
s and kept herds of cattle, flocks of sheep, horses, donkeys and camels.
Paul Pelliot
Paul Eugène Pelliot (28 May 187826 October 1945) was a French sinologist and Orientalist best known for his explorations of Central Asia and the Silk Road regions, and for his acquisition of many important Tibetan Empire-era manuscripts and ...
translated the name "Torghut" as ''garde de jour''. He wrote that the Torghuts owed their name either to the memory of the guard of Genghis Khan or, as descendants of the Keraites
The Keraites (also ''Kerait, Kereit, Khereid'', Kazakh: керейт; Kyrgyz: керей; Mongolian: Хэрэйд; Nogai: Кереит; Uzbek: ''Kerait''; Chinese: 克烈) were one of the five dominant Turco-Mongol tribal confederations ...
, to the old ''garde de jour''. This was documented among the Keraites in ''The Secret History of the Mongols
The ''Secret History of the Mongols'' is the oldest surviving literary work in the Mongolic languages. Written for the Borjigin, Mongol royal family some time after the death of Genghis Khan in 1227, it recounts his life and conquests, and parti ...
'' before Genghis Khan took over the region.
Period of open conflict
The ''Four Oirat'' was a political entity formed by the four major Oirat tribes. During the 15–17th centuries, they established under the name "10 tumen Mongols", a cavalry unit of 10,000 horsemen, including four Oirat tumen and six tumen composed of other Mongols. They reestablished their traditional pastoral nomadic lifestyle during the end of the Yuan dynasty. The Oirats formed this alliance to defend themselves against the Khalkha Mongols and to pursue the greater objective of reunifying Mongolia. Until the mid-17th century, when bestowal of the title of Khan was transferred to theDalai Lama
The Dalai Lama (, ; ) is the head of the Gelug school of Tibetan Buddhism. The term is part of the full title "Holiness Knowing Everything Vajradhara Dalai Lama" (圣 识一切 瓦齐尔达喇 达赖 喇嘛) given by Altan Khan, the first Shu ...
, all Mongol tribes recognized this claim and the political prestige attached to it. Although the Oirats could not assert this claim prior to the mid-17th century, they did in fact have a close connection to Genghis Khan by virtue of the fact that Genghis Khan
Genghis Khan (born Temüjin; August 1227), also known as Chinggis Khan, was the founder and first khan (title), khan of the Mongol Empire. After spending most of his life uniting the Mongols, Mongol tribes, he launched Mongol invasions and ...
's brother, Qasar
Khasar (; , ), was one of the three full brothers of the legendary Genghis Khan. According to the '' Jami' al-Tawarikh'', his given name was ''Jochi'' and he got the nickname ''Khasar'' after his distinguished bravery. He was also called Khabht ...
, was in command of the Khoshut tribe.
In response to the Western Mongols' self-designation as the Four Oirat, the Eastern Mongols began to refer to themselves as the "Forty Mongols", or the "Forty and Four". This means that the Khalkha Mongols claimed to have forty tümen to the four tümen maintained by the Four Oirat.
The Oirat alliance was decentralized, informal and unstable. For instance, the Four Oirat did not have a central location from which it was governed, and it was not governed by a central figure for most of its existence. The four Oirats did not establish a single military or a unified monastic system. Lastly, it was not until 1640 that the Four Oirat adopted uniform customary laws.
As pastoralist nomads, the Oirats were organized at the tribal level, where each tribe was ruled by a ''noyon'' or prince who also functioned as the chief ''taishi'' "chieftain". The chief taishi governed with the support of lesser noyons, who were also called taishi. These minor noyons controlled divisions of the tribe (''ulus'') and were politically and economically independent of the chief tayishi. Chief taishis sought to influence and dominate the chief taishis of the other tribes, causing intertribal rivalry, dissension and periodic skirmishes.
Under the leadership of Esen, Chief Taishi of the Choros, the Four Oirat unified Mongolia for a short period. After Esen's death in 1455, the political union of the Dörben Oirat dissolved quickly, resulting in two decades of Oirat-Eastern Mongol conflict. The deadlock ended during the reign of Batmunkh Dayan Khan
Dayan Khan (; ), born Batumöngke ( , ; ''Bātúméngkè''; 1472–1517) was a khagan of the Northern Yuan dynasty, reigning from 1480 to 1517. During his rule, he reunited the Mongols under Chinggisid supremacy. His reigning title, "Dayan" ...
, a five-year-old boy in whose name the loyal Eastern Mongol forces rallied. Mandukhai Khatun
Queen Mandukhai (; ), also fully known as Wise Queen Mandukhai (; – 1510) was a queen of the Northern Yuan. With her second husband Batmunkh Dayan Khan, she helped reunite the warring Mongols.
Early life
Mandukhai was the only daughter of ...
and Dayan Khan took advantage of Oirat disunity and weakness and brought Oirats back under Mongolian rule. In doing so, he regained control of the Mongol homeland and restored the hegemony of the Eastern Mongols.
After the death of Dayan in 1543, the Oirats and the Khalkhas resumed their conflict. The Oirat forces thrust eastward, but Dayan's youngest son, Geresenz, was given command of the Khalkha forces and drove the Oirats to Uvs Lake in northwest Mongolia. In 1552, after the Oirats once again challenged the Khalkha, Altan Khan
Altan Khan of the Tümed (2 January 1508 – 13 January 1582; ; Chinese: 阿勒坦汗), whose given name was Anda ( Mongolian: Алтан (Аньда); Chinese: 俺答), was the leader of the Tümed Mongols de facto ruler of the Right Wing, o ...
swept up from Inner Mongolia with Tümed and Ordos cavalry units, pushing elements of various Oirat tribes from Karakorum
Karakorum (Khalkha Mongolian: Хархорум, ''Kharkhorum''; Mongolian script:, ''Qaraqorum'') was the capital city, capital of the Mongol Empire between 1235 and 1260 and of the Northern Yuan, Northern Yuan dynasty in the late 14th and 1 ...
to the Khovd region in northwest Mongolia, reuniting most of Mongolia in the process.
The Oirats would later regroup south of the Altai Mountains in Dzungaria. But Geresenz's grandson, Sholoi Ubashi Khuntaiji, pushed the Oirats further northwest, along the steppes of the Ob and Irtysh Rivers. Afterwards, he established a Khalkha Khanate under the name, Altan Khan, in the Oirat heartland of Dzungaria.
In spite of the setbacks, the Oirats would continue their campaigns against the Altan Khanate, trying to unseat Sholoi Ubashi Khuntaiji from Dzungaria. The continuous, back-and-forth nature of the struggle, which defined this period, is captured in the Oirat epic song "The Rout of Mongolian Sholoi Ubashi Khuntaiji", recounting the Oirat victory over the Altan Khan of the Khalkha in 1587.
Resurgence of Oirat power

 At the beginning of the 17th century, the First Altan Khan drove the
At the beginning of the 17th century, the First Altan Khan drove the Oirats
Oirats (; ) or Oirds ( ; ), formerly known as Eluts and Eleuths ( or ; zh, 厄魯特, ''Èlǔtè'') are the westernmost group of Mongols, whose ancestral home is in the Altai Mountains, Altai region of Siberia, Xinjiang and western Mongolia.
...
westward to present-day eastern Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
. The Torghut
The Torghut ( Mongolian: Торгууд, , Torguud, "Guardsman", ) are one of the four major subgroups of the Four Oirats. The Torghut nobles traced their descent to the Mongol Keraite ruler Toghrul, and many Torghuts descended from the Keraites.
...
s became the westernmost Oirat tribe, encamped in the Tarbagatai Mountains region and along the northern stretches of the Irtysh
The Irtysh is a river in Russia, China, and Kazakhstan. It is the chief tributary of the Ob (river), Ob and is also the longest tributary in the world.
The river's source lies in the Altai Mountains, Mongolian Altai in Dzungaria (the northern p ...
, Ishim
Ishim may refer to:
*Ishim (river), a river in Kazakhstan and Russia
*Ishim, Tyumen Oblast, a town in Tyumen Oblast, Russia
*Ishim (angel), a rank of angels in the Jewish angelic hierarchy
See also
*Ishimsky (disambiguation)
*Ishimbay
{{Disam ...
and Tobol River
The Tobol (, ) is a river in Western Siberia (in Kazakhstan and Russia) and the main (left) tributary of the Irtysh. Its length is , and the area of its drainage basin is .
History
The Tobol River was one of the four important rivers of the ...
s.
Further west, the Kazakhs
The Kazakhs (Kazakh language, Kazakh: , , , ) are a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group native to Central Asia and Eastern Europe. They share a common Culture of Kazakhstan, culture, Kazakh language, language and History of Kazakhstan, history ...
– a Turco-Mongol
The Turco-Mongol or Turko-Mongol tradition was an ethnocultural synthesis that arose in Asia during the 14th century among the ruling elites of the Golden Horde and the Chagatai Khanate. The ruling Mongol elites of these khanates eventually ass ...
people – prevented the Torghut
The Torghut ( Mongolian: Торгууд, , Torguud, "Guardsman", ) are one of the four major subgroups of the Four Oirats. The Torghut nobles traced their descent to the Mongol Keraite ruler Toghrul, and many Torghuts descended from the Keraites.
...
s from sending its trading caravans to the Muslim towns and villages located along the Syr Darya
The Syr Darya ( ),; ; ; ; ; /. historically known as the Jaxartes ( , ), is a river in Central Asia. The name, which is Persian language, Persian, literally means ''Syr Sea'' or ''Syr River''. It originates in the Tian Shan, Tian Shan Mountain ...
river. As a result, the Torghuts established a trading relationship with the newly established outposts of the Tsarist government whose expansion into and exploration of Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states ...
was motivated mostly by the desire to profit from trade with Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
.
The Khoshut
The Khoshut (Mongolian language, Mongolian: Хошууд,, qoşūd, ; literally "bannermen," from Middle Mongol language, Middle Mongolian ''qosighu'' "flag, banner") are one of the four major tribes of the Oirats, Oirat people. They established ...
, by contrast, were the easternmost Oirat, encamped near the Lake Zaysan area and the Semey
Semey (; , formerly known as Semipalatinsk ( ) until 2007 and as Alash-Qala ( ) from 1917 to 1920, is a city in eastern Kazakhstan, in the Kazakh part of Siberia. When Abai Region was created in 2022, Semey became its administrative centre. I ...
region along the lower portions of the Irtysh River, where they built several steppe monasteries
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone ( hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer which m ...
. The Khoshut were adjacent to the Khalkha khanates of Altan Khan and Dzasagtu Khan. Both khanates prevented the Khoshut and the other Oirat from trading with Chinese border towns. The Khoshut were ruled by Baibagas Khan and then Güshi Khan
Güshi Khan (1582 – 14 January 1655) was a Khoshut prince and founder of the Khoshut Khanate, who supplanted the Tumed descendants of Altan Khan as the main benefactor of the Dalai Lama and the Gelug school of Tibetan Buddhism. In 1637, Güsh ...
, who were the first Oirat leaders to convert to the Gelug
file:DalaiLama0054 tiny.jpg, 240px, 14th Dalai Lama, The 14th Dalai Lama (center), the most influential figure of the contemporary Gelug tradition, at the 2003 Kalachakra ceremony, Bodh Gaya, Bodhgaya (India)
The Gelug (, also Geluk; 'virtuous' ...
school of Tibetan Buddhism
Tibetan Buddhism is a form of Buddhism practiced in Tibet, Bhutan and Mongolia. It also has a sizable number of adherents in the areas surrounding the Himalayas, including the Indian regions of Ladakh, Gorkhaland Territorial Administration, D ...
.
Locked in between both tribes were the Choros, Dörbet Oirat
The Dörbet (, ), known in English as The Fours, is the second largest subgroup of Mongols, Mongol people in modern Mongolia and was formerly one of the major tribes of the Four Oirat confederation in the 15th-18th centuries. In early times, the D� ...
and Khoid
The Khoid, also Khoyd or Khoit (; "Northern ones/people") people are an Oirat subgroup of the Choros clan. Once one of largest tribes of the Oirats.
File:Amursana.jpg, Amursana was a Khoid Oirat
File:Dzungar cavalry of Amursana, in the Battle ...
, collectively known as the "Dzungar people
The Dzungar people (also written as Zunghar or Junggar; from the Mongolian language, Mongolian words , meaning 'left hand') are the many Mongol Oirats, Oirat tribes who formed and maintained the Dzungar Khanate in the 17th and 18th centuries. H ...
", who were slowly rebuilding the base of power they enjoyed under the Four Oirat. The Choros were the dominant Oirat tribe of that era. Their leader, Erdeni Batur, attempted to follow Esen Khan in unifying the Oirats to challenge the Khalkha.
 Under the dynamic leadership of Erdeni Batur, the Dzungars stopped the expansion of the first
Under the dynamic leadership of Erdeni Batur, the Dzungars stopped the expansion of the first Altan Khan
Altan Khan of the Tümed (2 January 1508 – 13 January 1582; ; Chinese: 阿勒坦汗), whose given name was Anda ( Mongolian: Алтан (Аньда); Chinese: 俺答), was the leader of the Tümed Mongols de facto ruler of the Right Wing, o ...
and began planning the resurrection of the Four Oirat
The Four Oirats ( Written Oirat: , ; , ; ) or Oirat Confederation, formerly known as the Eleuths, was the confederation of the Oirat tribes which marked the rise of the Western Mongols in the history of the Mongolian Plateau.
Despite the univer ...
under the Dzungar banner. In furtherance of such plans, Erdeni Batur designed and built a capital city called Kubak-sari on the Emil River
The Emil (, ''Emıl''; ''Emel'') or Emin (), also spelled Emel, Imil, etc., is a river in China and Kazakhstan. It flows through Tacheng (Tarbagatay) Prefecture of China's Xinjiang Uighur Autonomous Region and the East Kazakhstan Province of K ...
near the modern city of Tacheng
TachengThe official spelling according to (), also known as Tarbagatay, Chuguchak or Qoqek, is a county-level city and the administrative seat of Tacheng Prefecture, in northern Ili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture, Xinjiang. The Chinese name "Tach ...
. During his attempt to build a nation, Erdeni Batur encouraged diplomacy, commerce and farming. He also sought to acquire modern weaponry and build small industry, such as metal works, to supply his military with weapons.
The attempted unification of the Oirat caused dissension among the tribes and their Chief Tayishis who were independent minded but also highly regarded leaders themselves. This dissension reputedly caused Kho Orluk to move the Torghut tribe and elements of the Dörbet tribe westward to the Volga region where his descendants formed the Kalmyk Khanate. In the east, Güshi Khan
Güshi Khan (1582 – 14 January 1655) was a Khoshut prince and founder of the Khoshut Khanate, who supplanted the Tumed descendants of Altan Khan as the main benefactor of the Dalai Lama and the Gelug school of Tibetan Buddhism. In 1637, Güsh ...
took part of the Khoshut to the Tsaidam and Qinghai
Qinghai is an inland Provinces of China, province in Northwestern China. It is the largest provinces of China, province of China (excluding autonomous regions) by area and has the third smallest population. Its capital and largest city is Xin ...
regions in the Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau, also known as the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau or Qingzang Plateau, is a vast elevated plateau located at the intersection of Central Asia, Central, South Asia, South, and East Asia. Geographically, it is located to the north of H ...
, where he formed the Khoshut Khanate
The Khoshut Khanate was a Mongols, Mongol Oirats, Oirat khanate based in the Tibetan Plateau from 1642 to 1717. Based in modern Qinghai, it was founded by Güshi Khan in 1642 after defeating the opponents of the Gelug school of Tibetan Buddhism in ...
to protect Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ), or Greater Tibet, is a region in the western part of East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are other ethnic groups s ...
and the Gelug from both internal and external enemies. Erdeni Batur and his descendants, by contrast, formed the Dzungar Khanate
The Dzungar Khanate ( Mongolian: ), also known as the Zunghar Khanate or Junggar Khanate, was an Inner Asian khanate of Oirat Mongol origin. At its greatest extent, it covered an area from southern Siberia in the north to present-day Kyrgyz ...
and came to dominate Central Eurasia.
Torghut migration
In 1618, the Torghut and a small contingent ofDörbet Oirat
The Dörbet (, ), known in English as The Fours, is the second largest subgroup of Mongols, Mongol people in modern Mongolia and was formerly one of the major tribes of the Four Oirat confederation in the 15th-18th centuries. In early times, the D� ...
s (200,000–250,000 people) chose to migrate from the upper Irtysh River region to the grazing pastures of the lower Volga region
The Volga region, known as the ( , ; rus, Поволжье, r=Povolžje, p=pɐˈvoɫʐje; ), is a historical region in Russia that encompasses the drainage basin of the Volga River, the longest river in Europe, in central and southern European ...
south of Saratov
Saratov ( , ; , ) is the largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and administrative center of Saratov Oblast, Russia, and a major port on the Volga River. Saratov had a population of 901,361, making it the List of cities and tow ...
and north of the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake and usually referred to as a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia: east of the Caucasus, ...
on both banks of the Volga River
The Volga (, ) is the longest river in Europe and the longest endorheic basin river in the world. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchment ...
. The Torghut were led by their taishi, Kho Orluk
Kho Orluk (; 1580-1644) was an Oirat prince and Taish of the Torghut- Oirat tribe. Around 1616, Kho Orluk persuaded the other Torghut princes and lesser nobility to move their tribe en masse westward through southern Siberia and southward along ...
. They were the largest Oirat tribe to migrate, bringing along nearly the entire tribe. The second-largest group was the Dörbet Oirats under their taishi, Dalai Batur. Together they moved west through southern Siberia and the southern Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ),; , ; , or simply the Urals, are a mountain range in Eurasia that runs north–south mostly through Russia, from the coast of the Arctic Ocean to the river Ural (river), Ural and northwestern Kazakhstan.
, avoiding the more direct route that would have taken them through the heart of the territory of their enemy, the Kazakhs. En route, they raided Russian settlements and Kazakh and Bashkir encampments.
Many theories have been advanced to explain the reasons for the migration. One generally accepted theory is that there may have been discontent among the Oirat tribes, which arose from the attempt by Kharkhul, taishi of the Dzungars, to centralize political and military control over the tribes under his leadership. Some scholars, however, believe that the Torghuts sought uncontested pastures as their territory was being encroached upon by the Russians from the north, the Kazakhs from the south and the Dzungars from the east. The encroachments resulted in overcrowding of people and livestock, thereby diminishing the food supply. Lastly, a third theory suggests that the Torghuts grew weary of the militant struggle between the Oirats and the Altan Khanate.
Kalmyk Khanate
Period of self rule, 1630–1724
 Upon arrival to the lower Volga region in 1630, the Oirats encamped on land that was once part of the
Upon arrival to the lower Volga region in 1630, the Oirats encamped on land that was once part of the Astrakhan Khanate
The Khanate of Astrakhan was a Tatar rump state of the Golden Horde. The khanate existed in the 15th and 16th centuries in the area adjacent to the mouth of the Volga river, around the modern city of Astrakhan. Its khans claimed patrilineal de ...
but was now claimed by the Tsardom of Russia
The Tsardom of Russia, also known as the Tsardom of Moscow, was the centralized Russian state from the assumption of the title of tsar by Ivan the Terrible, Ivan IV in 1547 until the foundation of the Russian Empire by Peter the Great in 1721.
...
. The region was lightly populated, from south of Saratov to the Russian garrison at Astrakhan and on both the east and the west banks of the Volga River. The Tsardom of Russia was not ready to colonize the area and was in no position to prevent the Oirats from encamping in the region, but it had a direct political interest in ensuring that the Oirats would not become allied with its Turkic-speaking neighbors. The Kalmyks became Russian allies and a treaty to protect the southern Russian border was signed between the Kalmyk Khanate and Russia.
The Oirats quickly consolidated their position by expelling the majority of the native inhabitants, the Nogai Horde
The Nogai Horde was a confederation founded by the Nogais that occupied the Pontic–Caspian steppe from about 1500 until they were pushed west by the Kalmyks and south by the Russians in the 17th century. The Mongol tribe called the Manghuds con ...
. Large groups of Nogais
The Nogais ( ) are a Kipchaks, Kipchak people who speak a Turkic languages, Turkic language and live in Southeastern Europe, North Caucasus, Volga region, Central Asia and Turkey. Most are found in Northern Dagestan and Stavropol Krai, as well ...
fled southeast to the northern Caucasian plain and west to the Black Sea steppe, lands claimed by the Crimean Khanate
The Crimean Khanate, self-defined as the Throne of Crimea and Desht-i Kipchak, and in old European historiography and geography known as Little Tartary, was a Crimean Tatars, Crimean Tatar state existing from 1441 to 1783, the longest-lived of th ...
, itself a vassal or ally of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
. Smaller groups of Nogais sought the protection of the Russian garrison at Astrakhan
Astrakhan (, ) is the largest city and administrative centre of Astrakhan Oblast in southern Russia. The city lies on two banks of the Volga, in the upper part of the Volga Delta, on eleven islands of the Caspian Depression, from the Caspian Se ...
. The remaining nomadic tribes became vassals of the Oirats.
The Kalmyks battled the Karakalpaks
The Karakalpaks or Qaraqalpaqs (; ), are a Kipchak languages, Kipchak-Nogai Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group native to Karakalpakstan in Northwestern Uzbekistan. During the 18th century, they settled in the lower reaches of the Amu Darya a ...
. The Mangyshlak Peninsula
Mangyshlak or Mangghyshlaq Peninsula (; ) is a large peninsula located in western Kazakhstan. It borders on the Caspian Sea in the west and with the Buzachi Peninsula, a marshy sub-feature of the main peninsula, in the northeast. The Tyuleniy Ar ...
was overtaken in 1639 by Kalmyks.
At first, an uneasy relationship existed between the Russians and the Oirats. Mutual raiding by the Oirats of Russian settlements and by the Cossacks
The Cossacks are a predominantly East Slavic languages, East Slavic Eastern Christian people originating in the Pontic–Caspian steppe of eastern Ukraine and southern Russia. Cossacks played an important role in defending the southern borde ...
and the Bashkirs
The Bashkirs ( , ) or Bashkorts (, ; , ) are a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group indigenous to Russia. They are concentrated in Bashkortostan, a Republics of Russia, republic of the Russian Federation and in the broader historical region of B ...
, Muslim vassals of the Russians, of Oirat encampments was commonplace. Numerous oaths and treaties were signed to ensure Oirat loyalty and military assistance. Although the Oirats became subjects of the Tsar, such allegiance by the Oirats was deemed to be nominal.
In reality, the Oirats governed themselves pursuant to a document known as the "Great Code of the Nomads" (''Iki Tsaadzhin Bichig''). The Code was promulgated in 1640 by them, their brethren in Dzungaria and some of the Khalkha who all gathered near the Tarbagatai Mountains in Dzungaria to resolve their differences and to unite under the banner of the Gelug school. Although the goal of unification was not met, the summit leaders did ratify the Code, which regulated all aspects of nomadic life.
In securing their position, the Oirats became a borderland power, often allying themselves with the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
against the neighboring Muslim population. During the era of Ayuka Khan
Ayuka or Ayuki Khan (; 1669–1724) was a Kalmyk leader under whose rule the Kalmyk Khanate reached its zenith in terms of economic, military, and politic power. On behalf of Russia, Ayuka Khan protected the southern borders of Russia, engaging ...
, the Oirats rose to political and military prominence as the Russian Empire sought the increased use of Oirat cavalry in support of its military campaigns against the Muslim powers in the south, such as Safavid Iran
The Guarded Domains of Iran, commonly called Safavid Iran, Safavid Persia or the Safavid Empire, was one of the largest and longest-lasting Iranian empires. It was ruled from 1501 to 1736 by the Safavid dynasty. It is often considered the begi ...
, the Ottoman Empire, the Nogais, the Tatars
Tatars ( )Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
of in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
Kuban
Kuban ( Russian and Ukrainian: Кубань; ) is a historical and geographical region in the North Caucasus region of southern Russia surrounding the Kuban River, on the Black Sea between the Don Steppe, the Volga Delta and separated fr ...
and the Crimean Khanate
The Crimean Khanate, self-defined as the Throne of Crimea and Desht-i Kipchak, and in old European historiography and geography known as Little Tartary, was a Crimean Tatars, Crimean Tatar state existing from 1441 to 1783, the longest-lived of th ...
. Ayuka Khan also waged wars against the Kazakhs, subjugated the Turkmens
Turkmens (, , , ) are a Turkic ethnic group native to Central Asia, living mainly in Turkmenistan, northern and northeastern regions of Iran and north-western Afghanistan. Sizeable groups of Turkmens are found also in Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, ...
of the Mangyshlak Peninsula
Mangyshlak or Mangghyshlaq Peninsula (; ) is a large peninsula located in western Kazakhstan. It borders on the Caspian Sea in the west and with the Buzachi Peninsula, a marshy sub-feature of the main peninsula, in the northeast. The Tyuleniy Ar ...
, and made multiple expeditions against the highlanders of the North Caucasus
The North Caucasus, or Ciscaucasia, is a subregion in Eastern Europe governed by Russia. It constitutes the northern part of the wider Caucasus region, which separates Europe and Asia. The North Caucasus is bordered by the Sea of Azov and the B ...
. These campaigns highlighted the strategic importance of the Kalmyk Khanate which functioned as a buffer zone, separating Russia and the Muslim world, as Russia fought wars in Europe to establish itself as a European power.
To encourage the release of Oirat cavalrymen in support of its military campaigns, the Russian Empire increasingly relied on the provision of monetary payments and dry goods to the Oirat Khan and the Oirat nobility. In that respect, the Russian Empire treated the Oirats as it did the Cossacks. The provision of monetary payments and dry goods, however, did not stop the mutual raiding, and, in some instances, both sides failed to fulfill its promises.
Another significant incentive the Russian Empire provided to the Oirats was tariff-free access to the markets of Russian border towns, where the Oirats were permitted to barter their herds and the items they obtained from Asia and their Muslim neighbors in exchange for Russian goods. Trade also occurred with neighboring Turkic tribes under Russian control, such as the Tatars and the Bashkirs. Intermarriage became common with such tribes. This trading arrangement provided substantial benefits, monetary and otherwise, to the Oirat tayishis, noyons and zaisangs.
Fred Adelman described this era as the "Frontier Period", lasting from the advent of the Torghut under Kho Orluk in 1630 to the end of the great khanate of Kho Orluk
Kho Orluk (; 1580-1644) was an Oirat prince and Taish of the Torghut- Oirat tribe. Around 1616, Kho Orluk persuaded the other Torghut princes and lesser nobility to move their tribe en masse westward through southern Siberia and southward along ...
's descendant, Ayuka Khan
Ayuka or Ayuki Khan (; 1669–1724) was a Kalmyk leader under whose rule the Kalmyk Khanate reached its zenith in terms of economic, military, and politic power. On behalf of Russia, Ayuka Khan protected the southern borders of Russia, engaging ...
, in 1724, a phase accompanied by little discernible acculturative change:
During the era of Ayuka Khan, the Kalmyk Khanate reached its peak of military and political power. The Khanate experienced economic prosperity from free trade with Russian border towns, China, Tibet and with their Muslim neighbors. During this era, Ayuka Khan also kept close contacts with his Oirat kinsmen in Dzungaria, as well as the Dalai Lama in Tibet.
From Oirat to Kalmyk
 Historically, Oirat identified themselves by their respective sub-group names. In the 15th century, the three major groups of Oirat formed an alliance, adopting "Dörben Oirat" as their collective name. In the early 17th century, a second great Oirat Confederation emerged, which later became the Dzungar Empire. While the Dzungars (initially Choros, Dörbet and Khoit tribes) were establishing their empire in Central Eurasia, the Khoshuts were establishing the Khoshut Khanate in Tibet, protecting the Gelugpa sect from its enemies, and the Torghuts formed the Kalmyk Khanate in the lower Volga region.
After encamping, the Oirats began to identify themselves as "Kalmyk." This named was supposedly given to them by their Muslim neighbors and later used by the Russians to describe them. The Oirats used this name in their dealings with outsiders, viz., their Russian and Muslim neighbors. But they continued to refer to themselves by their tribal, clan, or other internal affiliations.
The name Kalmyk, however, wasn't immediately accepted by all of the Oirat tribes in the lower Volga region. As late as 1761, the Khoshut and Dzungars (refugees from the Manchu Empire) referred to themselves and the Torghuts exclusively as Oirats. The Torghuts, by contrast, used the name Kalmyk for themselves as well as the Khoshut and Dzungars.
Generally, European scholars have identified all western Mongolians collectively as Kalmyks, regardless of their location ( Ramstedt, 1935: v–vi). Such scholars (e.g. Sebastian Muenster) have relied on Muslim sources who traditionally used the word "Kalmyk" to describe western Mongolians in a derogatory manner and the western Mongols of China and Mongolia have regarded that name as a term of abuse. Instead, they use the name Oirat or they go by their respective tribal names, e.g., Khoshut, Dörbet, Choros, Torghut, Khoit, Bayid, Mingat, etc.
Over time, the descendants of the Oirat migrants in the lower Volga region embraced the name "Kalmyk" irrespective of their locations, viz., Astrakhan, the Don Cossack region, Orenburg, Stavropol, the Terek and the Ural Mountains. Another generally accepted name is ''Ulan Zalata'' or the "red-buttoned ones".
Historically, Oirat identified themselves by their respective sub-group names. In the 15th century, the three major groups of Oirat formed an alliance, adopting "Dörben Oirat" as their collective name. In the early 17th century, a second great Oirat Confederation emerged, which later became the Dzungar Empire. While the Dzungars (initially Choros, Dörbet and Khoit tribes) were establishing their empire in Central Eurasia, the Khoshuts were establishing the Khoshut Khanate in Tibet, protecting the Gelugpa sect from its enemies, and the Torghuts formed the Kalmyk Khanate in the lower Volga region.
After encamping, the Oirats began to identify themselves as "Kalmyk." This named was supposedly given to them by their Muslim neighbors and later used by the Russians to describe them. The Oirats used this name in their dealings with outsiders, viz., their Russian and Muslim neighbors. But they continued to refer to themselves by their tribal, clan, or other internal affiliations.
The name Kalmyk, however, wasn't immediately accepted by all of the Oirat tribes in the lower Volga region. As late as 1761, the Khoshut and Dzungars (refugees from the Manchu Empire) referred to themselves and the Torghuts exclusively as Oirats. The Torghuts, by contrast, used the name Kalmyk for themselves as well as the Khoshut and Dzungars.
Generally, European scholars have identified all western Mongolians collectively as Kalmyks, regardless of their location ( Ramstedt, 1935: v–vi). Such scholars (e.g. Sebastian Muenster) have relied on Muslim sources who traditionally used the word "Kalmyk" to describe western Mongolians in a derogatory manner and the western Mongols of China and Mongolia have regarded that name as a term of abuse. Instead, they use the name Oirat or they go by their respective tribal names, e.g., Khoshut, Dörbet, Choros, Torghut, Khoit, Bayid, Mingat, etc.
Over time, the descendants of the Oirat migrants in the lower Volga region embraced the name "Kalmyk" irrespective of their locations, viz., Astrakhan, the Don Cossack region, Orenburg, Stavropol, the Terek and the Ural Mountains. Another generally accepted name is ''Ulan Zalata'' or the "red-buttoned ones".
Reduction in autonomy, 1724–1771
In January 1771 the oppression of Tsarist administration forced the larger part of Kalmyks (33 thousand households, or approximately 170,000–200,000 people) to migrate to Dzungaria.Ubashi Khan
Ubashi Khan (; ; 1744 – 1774) was a Torghut- Kalmyk prince and the last Khan of the Kalmyk Khanate. In January 1771, he led the return migration of the majority of the Kalmyk people from the Kalmyk steppe to Dzungaria, their ancestral hom ...
, the great-grandson of Ayuka Khan and the last Kalmyk Khan, decided to return his people to their ancestral homeland, Dzungaria, and restore the Dzungar Khanate and Mongolian independence.ТИВ ДАМНАСАН НҮҮДЭЛ(Mongolian) As C.D Barkman notes, "It is quite clear that the Torghuts had not intended to surrender the Chinese, but had hoped to lead an independent existence in Dzungaria." Ubashi sent 30,000 cavalry in the first year of the Russo-Turkish War (1768–74) to gain weaponry before the migration. The 8th Dalai Lama was contacted to request his blessing and to set the date of departure. After consulting the astrological chart, he set a return date, but at the moment of departure, the weakening of the ice on the Volga River permitted only those Kalmyks (about 200,000 people) on the eastern bank to leave. Those 100,000–150,000 people on the western bank were forced to stay behind and
Catherine the Great
Catherine II. (born Princess Sophie of Anhalt-Zerbst; 2 May 172917 November 1796), most commonly known as Catherine the Great, was the reigning empress of Russia from 1762 to 1796. She came to power after overthrowing her husband, Peter I ...
executed influential nobles from among them.
Approximately five-sixths of the Torghut followed Ubashi Khan. Most of the Khoshut, Choros, and Khoid also accompanied the Torghut on their journey to Dzungaria. The Dörbet Oirat, in contrast, elected not to go at all.
Catherine the Great asked the Russian army, Bashkirs, and Kazakh Khanate to stop all migrants. Beset by Kazakh raids, thirst and starvation, approximately 85,000 Kalmyks died on their way to Dzungaria. After failing to stop the flight, Catherine abolished the Kalmyk Khanate, transferring all governmental powers to the governor of Astrakhan. The title of Khan was abolished. The highest native governing office remaining was the Vice- Khan, who also was recognized by the government as the highest ranking Kalmyk prince. By appointing the Vice-Khan, the Russian Empire was now permanently the decisive force in Kalmyk government and affairs.
After seven months of travel, only one-third (66,073) of the original group reached Balkhash Lake
Lake Balkhash, also spelt Lake Balqash (, , ), is a lake in southeastern Kazakhstan, one of the largest lakes in Asia and the 15th largest in the world. It is located in the eastern part of Central Asia and sits in the Balkhash-Alakol Basin, ...
, the western border of Qing China
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty ...
. This migration became the topic of ''The Revolt of the Tartars'', by Thomas De Quincey
Thomas Penson De Quincey (; Thomas Penson Quincey; 15 August 17858 December 1859) was an English writer, essayist, and literary critic, best known for his ''Confessions of an English Opium-Eater'' (1821).Eaton, Horace Ainsworth, ''Thomas De Q ...
.
The Qing shifted the Kalmyks to five different areas to prevent their revolt and influential leaders of the Kalmyks soon died. The migrant Kalmyks became known as Torghut in Qing China. The Torghut were coerced by the Qing into giving up their nomadic lifestyle and to take up sedentary agriculture instead as part of a deliberate policy by the Qing to enfeeble them.
Life in the Russian Empire
After the 1771 exodus, the Kalmyks that remained part of the Russian Empire continued their nomadic pastoral lifestyle, ranging the pastures between the Don and the Volga Rivers, wintering in the lowlands along the shores of theCaspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake and usually referred to as a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia: east of the Caucasus, ...
as far as Sarpa Lake to the northwest and Lake Manych-Gudilo
Lake Manych-Gudilo () is a large salt lake, saltwater reservoir lake in Kalmykia, Russia. Part of the lake lies also in Rostov Oblast and Stavropol Krai. It has an area of about 344 km2 and average depth of only about 0.6 m.
Lake Manyc ...
to the west. In the spring, they moved along the Don River and the Sarpa lake system, attaining the higher grounds along the Don in the summer, passing the autumn in the Sarpa and Volga lowlands. In October and November they returned to their winter camps and pastures.
Despite their great loss in population, the Torghut still remained numerically superior, dominating the Kalmyks. The other Kalmyks in Russia included Dörbet Oirats and Khoshut. Elements of the Choros and Khoit also were present but were too few in number to retain their ''ulus'' (tribal division) as independent administrative units. As a result, they were absorbed by the ulus of the larger tribes.
The factors that caused the 1771 exodus continued to trouble the remaining Kalmyks. In the wake of the exodus, the Torghuts joined the Cossack rebellion of Yemelyan Pugachev
Yemelyan Ivanovich Pugachev (also spelled Pugachyov; ; ) was an ataman of the Yaik Cossacks and the leader of the Pugachev's Rebellion, a major popular uprising in the Russian Empire during the reign of Catherine the Great.
The son of a Do ...
in hopes that he would restore the independence of the Kalmyks. After Pugachev's Rebellion
Pugachev's Rebellion (; also called the Peasants' War 1773–1775 or Cossack Rebellion) of 1773–1775 was the principal revolt in a series of popular rebellions that took place in the Russian Empire after Catherine II seized power in 1762. It ...
was defeated, Catherine the Great transferred the office of the Vice-Khan from the Torghut tribe to the Dörbet, whose princes supposedly remained loyal to the government during the rebellion. Thus, the Torghut were removed from their role as the hereditary leaders of the Kalmyk people. The Khoshut could not challenge this political arrangement due to their smaller population size.
The disruptions to Kalmyk society caused by the exodus and the Torghut participation in the Pugachev Rebellion precipitated a major realignment in Kalmyk tribal structure. The government divided the Kalmyks into three administrative units attached, according to their respective locations, to the district governments of Astrakhan, Stavropol and the Don and appointed a special Russian official bearing the title of "Guardian of the Kalmyk People" for purposes of administration. The government also resettled some small groups of Kalmyks along the Ural, Terek and Kuma rivers and in Siberia.
The redistricting divided the now dominant Dörbet tribe into three separate administrative units. Those in the western Kalmyk Steppe were attached to the Astrakhan district government. They were called Baga (Lesser) Dörbet. By contrast, the Dörbets who moved to the northern part of the Stavropol province were called Ike (Greater) Dörbet even though their population was smaller. Finally, the Kalmyks of the Don became known as Buzava. Although they were composed of elements of all the Kalmyk tribes, the Buzava claimed descent from the Torghut tribe. Their name is derived from two tributaries of the Don River: Busgai and Busuluk. In 1798, Tsar Paul I recognized the Don Kalmyks as Don Cossacks. As such, they received the same rights and benefits as their Russian counterparts in exchange for providing national military services. At the end of the Napoleonic Wars
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Napoleonic Wars
, partof = the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars
, image = Napoleonic Wars (revision).jpg
, caption = Left to right, top to bottom:Battl ...
, Kalmyk cavalry units in Russian service entered Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
.
Over time, the Kalmyks gradually created fixed settlements with houses and temples, in place of transportable round felt yurt
A yurt (from the Turkic languages) or ger (Mongolian language, Mongolian) is a portable, round tent covered and Thermal insulation, insulated with Hide (skin), skins or felt and traditionally used as a dwelling by several distinct Nomad, nomad ...
s. In 1865, Elista
Elista (, ;"Большой энциклопедический словарь", под ред. А. М. Прохорова. Москва и Санкт-Петербург, 1997, стр. 1402 , ''Elst'', )The approximate pronunciation of the Cyr ...
, the future capital of the Kalmyk Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic was founded. This process lasted until well after the October Revolution
The October Revolution, also known as the Great October Socialist Revolution (in Historiography in the Soviet Union, Soviet historiography), October coup, Bolshevik coup, or Bolshevik revolution, was the second of Russian Revolution, two r ...
of 1917.
Russian Revolution and Civil War
 In the aftermath of the
In the aftermath of the February Revolution
The February Revolution (), known in Soviet historiography as the February Bourgeois Democratic Revolution and sometimes as the March Revolution or February Coup was the first of Russian Revolution, two revolutions which took place in Russia ...
, Kalmyk leaders believed that the Russian Provisional Government
The Russian Provisional Government was a provisional government of the Russian Empire and Russian Republic, announced two days before and established immediately after the abdication of Nicholas II on 2 March, O.S. New_Style.html" ;"title="5 ...
, which replaced the Tsarist government, would allow greater autonomy and freedom with respect to their culture, religion and economy. This enthusiasm, however, would soon dissolve after the Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks, led by Vladimir Lenin, were a radical Faction (political), faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) which split with the Mensheviks at the 2nd Congress of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party, ...
took control of the national government during the second revolution in November 1917.
After the Bolsheviks took control, various political and ethnic groups opposed to Communism organized in a loose political and military coalition known as the White movement
The White movement,. The old spelling was retained by the Whites to differentiate from the Reds. also known as the Whites, was one of the main factions of the Russian Civil War of 1917–1922. It was led mainly by the Right-wing politics, right- ...
. A volunteer "White Army" was raised to fight the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People ...
, the military arm of the Bolshevik government. Initially, this army was composed primarily of volunteers and Tsarist supporters but were later joined by the Cossacks
The Cossacks are a predominantly East Slavic languages, East Slavic Eastern Christian people originating in the Pontic–Caspian steppe of eastern Ukraine and southern Russia. Cossacks played an important role in defending the southern borde ...
, including Don Kalmyks, many of whom resisted the Bolshevik policy of decossackization
De-Cossackization () was the Bolshevik policy of systematic repression against the Cossacks in the former Russian Empire between 1919 and 1933, especially the Don and Kuban Cossacks in Russia, aimed at the elimination of the Cossacks as a dist ...
.
The second revolution split the Kalmyk people into opposing camps. Many were dissatisfied with the Tsarist government for its historic role in promoting the colonization of the Kalmyk steppe and in encouraging the russification of the Kalmyk people. But others also felt hostility towards Bolshevism for two reasons: (1) the loyalty of the Kalmyk people to their traditional leaders (i.e., nobility and clergy) – sources of anti-Communism – was deeply ingrained; and (2) the Bolshevik exploitation of the conflict between the Kalmyks and the local Russian peasants who seized Kalmyk land and livestock.
The Astrakhan Kalmyk nobility, led by Prince Danzan Tundutov of the Baga Dörbets and Prince Sereb-Djab Tiumen of the Khoshuts, expressed their anti-Bolshevik sentiments by seeking to integrate the Astrakhan Kalmyks into the military units of the Astrakhan Cossacks. But before a general mobilization of Kalmyk horsemen could occur, the Red Army seized power in Astrakhan and in the Kalmyk steppe thereby preventing the mobilization from occurring.
After the capture of Astrakhan, the Bolsheviks engaged in savage reprisals against the Kalmyk people, especially against Buddhist temples and the Buddhist clergy. Eventually the Bolsheviks would draft as many as 18,000 Kalmyk horsemen in the Red Army to prevent them from joining the White Army. This objective, however, failed to prevent many Red Army Kalmyk horsemen from defecting to the White side.
 The majority of the Don Kalmyks also sided with the White Movement to preserve their Cossack lifestyle and proud traditions. As
The majority of the Don Kalmyks also sided with the White Movement to preserve their Cossack lifestyle and proud traditions. As Don Cossacks
Don Cossacks (, ) or Donians (, ), are Cossacks who settled along the middle and lower Don River (Russia), Don. Historically, they lived within the former Don Cossack Host (, ), which was either an independent or an autonomous democratic rep ...
, the Don Kalmyks first fought under White army General Anton Denikin
Anton Ivanovich Denikin (, ; – 7 August 1947) was a Russian military leader who served as the Supreme Ruler of Russia, acting supreme ruler of the Russian State and the commander-in-chief of the White movement–aligned armed forces of Sout ...
and then under his successor, General Pyotr Nikolayevich Wrangel
Baron Pyotr Nikolayevich Wrangel (, ; ; 25 April 1928), also known by his nickname the Black Baron, was a Russian military officer of Baltic German origin in the Imperial Russian Army. During the final phase of the Russian Civil War, he was c ...
. Because the Don Cossack Host to which they belonged was the main center of the White Movement and of Cossack resistance, the battles were fought on Cossack lands and were disastrous for the Don Cossacks as villages and entire regions changed hands repeatedly in a fratricidal conflict in which both sides committed terrible atrocities. The Don Cossacks, including the Don Kalmyks, experienced heavy military and civilian losses, either from the fighting itself or from starvation and disease induced by the war. Some argue that the Bolsheviks were guilty of the mass extermination of the Don Cossack people, killing an estimated 70 percent (or 700,000 persons) of the Don Cossack population.
By October 1920, the Red Army smashed General Wrangel's resistance in the Crimea
Crimea ( ) is a peninsula in Eastern Europe, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, almost entirely surrounded by the Black Sea and the smaller Sea of Azov. The Isthmus of Perekop connects the peninsula to Kherson Oblast in mainland Ukrain ...
, forcing the evacuation of some 150,000 White army soldiers and their families to Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
, Turkey. A small group of Don Kalmyks managed to escape on the British and French vessels. The chaos at the Russian port city of Novorossiysk
Novorossiysk (, ; ) is a city in Krasnodar Krai, Russia. It is one of the largest ports on the Black Sea. It is one of the few cities designated by the Soviet Union as a Hero City. The population was
History
In antiquity, the shores of the ...
was described by Major H.N.H. Williamson of the British Military Mission to the Don Cossacks as follows:
From there, this group resettled in Europe, primarily in Belgrade (where they established the fourth Buddhist temple in Europe), Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia and France where its leaders remained active in the White movement. In 1922, several hundred Don Kalmyks returned home under a general amnesty. Some returnees, including Prince Dmitri Tundutov, were imprisoned and then executed soon after their return.
Formation of the Kalmyk Soviet Republic
The Soviet government established the Kalmyk Autonomous Oblast in November 1920. It was formed by merging the Stavropol Kalmyk settlements with a majority of the Astrakhan Kalmyks. A small number of Don Kalmyks (Buzava) from the Don Host migrated to this Oblast. The administrative center was Elista, a small village in the western part of the Oblast that was expanded in the 1920s to reflect its status as the capital of the Oblast. In October 1935, the Kalmyk Autonomous Oblast was reorganized into the Kalmyk Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic. The chief occupations of the Republic were cattle breeding, agriculture, including the growing of cotton and fishing. There was no industry.Collectivization and revolts
On 22 January 1922,Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by po ...
proposed to migrate the Kalmyks during famine in Kalmykia but Russia refused; 71–72,000 Kalmyks died during the famine. The Kalmyks revolted against Russia in 1926, 1930 and 1942–1943. In March 1927, Soviet deported 20,000 Kalmyks to Siberia, tundra
In physical geography, a tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. There are three regions and associated types of tundra: #Arctic, Arctic, Alpine tundra, Alpine, and #Antarctic ...
and Karelia
Karelia (; Karelian language, Karelian and ; , historically Коре́ла, ''Korela'' []; ) is an area in Northern Europe of historical significance for Russia (including the Soviet Union, Soviet era), Finland, and Sweden. It is currentl ...
. Soviet scientists attempted to convince the Kalmyks and Buryats
The Buryats are a Mongolic ethnic group native to southeastern Siberia who speak the Buryat language. They are one of the two largest indigenous groups in Siberia, the other being the Yakuts. The majority of the Buryats today live in their ti ...
that they were not Mongols during the 20th century under the demongolization policy.
In 1929, Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Dzhugashvili; 5 March 1953) was a Soviet politician and revolutionary who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, his death in 1953. He held power as General Secret ...
ordered the forced collectivization of agriculture, forcing the Astrakhan Kalmyks to abandon their traditional nomadic pastoralist lifestyle and to settle in villages. All Kalmyk herdsmen owning more than 500 sheep were deported to labor camps in Siberia.
World War II and exile
In June 1941 the German army invaded the Soviet Union, ultimately taking (some) control of the Kalmyk Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic. In December 1942, however, the Red Army in their turn re-invaded the Republic. On 28 December 1943, the Soviet government accused the Kalmyks of collaborating with the Germans and deported the entire population, including Kalmyk Red Army soldiers, to various locations in Central Asia and Siberia. Within 24 hours the population transfer occurred at night during winter without notice in unheated cattle cars. According to N. F. Bugai, the leading Russian expert on deportations, 4.9% of the Kalmyk population died during the first three months of 1944; 1.5% in the first three months of 1945; and 0.7% in the same period of 1946. From 1945 to 1950, 15,206 Kalmyks died and 7843 were born. The Kalmyk Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic was quickly dissolved. Its territory was divided and transferred to the adjacent regions, viz., the Astrakhan and Stalingrad Oblasts and Stavropol Krai. Since no Kalmyks lived there any longer the Soviet authorities changed the names of towns and villages from Kalmyk names to Russian names. For example, Elista became Stepnoi.Return from Siberian exile

 Around half of (97–98,000) Kalmyk people deported to Siberia died before being allowed to return home in 1957. The government of the Soviet Union forbade teaching
Around half of (97–98,000) Kalmyk people deported to Siberia died before being allowed to return home in 1957. The government of the Soviet Union forbade teaching Kalmyk Oirat
Kalmyk Oirat (, ), also known as the Kalmyk language () and formerly anglicized as Calmuck, is a variety of the Oirat language, natively spoken by the Kalmyk people of Kalmykia, a federal subject of Russia. In Russia, it is the standard f ...
during the deportation. The Kalmyks' main purpose was to migrate to Mongolia. Under the Law of the Russian Federation of April 26, 1991, "On Rehabilitation of Exiled Peoples", repressions against Kalmyks and other peoples were qualified as an act of genocide
Genocide is violence that targets individuals because of their membership of a group and aims at the destruction of a people. Raphael Lemkin, who first coined the term, defined genocide as "the destruction of a nation or of an ethnic group" by ...
.
In 1957, Soviet Premier Nikita Khrushchev
Nikita Sergeyevich Khrushchev (– 11 September 1971) was the General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, First Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1953 to 1964 and the Premier of the Soviet Union, Chai ...
permitted the Kalmyk people to return to their home. Upon return, however, the Kalmyks found their homeland had become settled by Russians
Russians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. Their mother tongue is Russian language, Russian, the most spoken Slavic languages, Slavic language. The majority of Russians adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church ...
and Ukrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary eth ...
, many of whom chose to remain. On January 9, 1957, Kalmykia once again became an autonomous oblast, and on 29 July 1958, an autonomous republic within the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (Russian SFSR or RSFSR), previously known as the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic and the Russian Soviet Republic, and unofficially as Soviet Russia,Declaration of Rights of the labo ...
.
In the following years bad planning of agricultural and irrigation projects resulted in widespread desertification
Desertification is a type of gradual land degradation of Soil fertility, fertile land into arid desert due to a combination of natural processes and human activities.
The immediate cause of desertification is the loss of most vegetation. This i ...
. In addition, industrial plants were constructed without an analysis of the economic viability of such plants.
In 1992, after the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Kalmykia chose to remain an autonomous republic of the successor government, the Russian Federation. The dissolution, however, facilitated the collapse of the economy at both the national and the local level, causing widespread economic and social hardship. The resulting upheaval caused many young Kalmyks to leave Kalmykia, especially in the rural areas, for economic opportunities in and outside the Russian Federation.
The local Supreme Soviet decided in 1992 to change the name of the republic to Khalmg Tangch. In June 1993, the Kalmyk authorities laid claim to the of the Volga delta that were not returned to Kalmyks when the Kalmyk ASSR was recreated in 1957. The Kalmyk authorities claimed that under the terms of the 1991 law On the Rehabilitation of Repressed Peoples, the lands, currently in the Astrakhan Oblast and Dagestan, would formally belong to Kalmykia with effect from July 1, 1993. The long-standing dispute over the delineation of Kalmykia's borders with Astrakhan oblast and Dagestan
Dagestan ( ; ; ), officially the Republic of Dagestan, is a republic of Russia situated in the North Caucasus of Eastern Europe, along the Caspian Sea. It is located north of the Greater Caucasus, and is a part of the North Caucasian Fede ...
resurfaced in 2005, but no border changes were made.
The Kalmyks' ability to maintain a mostly homogeneous existence contrasts with the Russian admixture with other similar people, "as there is evidence for Russian admixture with Yakuts
The Yakuts or Sakha (, ; , ) are a Turkic ethnic group native to North Siberia, primarily the Republic of Sakha in the Russian Federation. They also inhabit some districts of the Krasnoyarsk Krai. They speak Yakut, which belongs to the Si ...
," for example. Thus far, genetic analysis of the Kalmyks supports their Mongol roots that also shows that entire families of Kalmyks moved to the Volga region and not simply males as is generally the case with most nomadic tribal groups:
In modern times, Kalmykia has friendly diplomatic and cultural ties with Mongolia. In the context of the Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, , starting the largest and deadliest war in Europe since World War II, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, conflict between the two countries which began in 2014. The fighting has caused hundreds of thou ...
since 2022, the Kalmyks have been reported as one of Russia's ethnic minority
The term "minority group" has different meanings, depending on the context. According to common usage, it can be defined simply as a group in society with the least number of individuals, or less than half of a population. Usually a minority g ...
groups suffering from a disproportionally large casualty rate among Russian forces.
Etymology
 The name "Kalmyk" is a word of Turkic origin that means "remnant" or "to remain". Turkic tribes may have used this name as early as the thirteenth century. Arab geographer Ibn al-Wardi is documented as the first person to use the term in referring to the Oirats in the fourteenth century. The
The name "Kalmyk" is a word of Turkic origin that means "remnant" or "to remain". Turkic tribes may have used this name as early as the thirteenth century. Arab geographer Ibn al-Wardi is documented as the first person to use the term in referring to the Oirats in the fourteenth century. The khojas
The Khoja are a caste of Muslims mainly members of the Nizari Ismaʿiliyyah sect of Islam with a minority of followers of Shia Islam originating the western Indian subcontinent, and converted to Islam from Hinduism by the 14th century by the Pe ...
of Kashgaria
Yettishar ( Chagatai: ; ; ), also known as Kashgaria or the Kashgar Emirate, was a Uyghur state in Xinjiang that existed from 1864 to 1877, during the Dungan Revolt against the Qing dynasty. It was an Islamic monarchy ruled by Yakub Beg, a ...
applied the name to Oirats in the fifteenth century. Russian written sources mentioned the name "Kolmak Tatars" as early as 1530, and cartographer Sebastian Muenster (1488–1552) circumscribed the territory of the "Kalmuchi" on a map in his ''Cosmographia'', which was published in 1544. The Oirats themselves, however, did not accept the name as their own.
Subgroups
There are these main ethnic subgroups of Kalmyks: Baatud, Dörbet,Khoid
The Khoid, also Khoyd or Khoit (; "Northern ones/people") people are an Oirat subgroup of the Choros clan. Once one of largest tribes of the Oirats.
File:Amursana.jpg, Amursana was a Khoid Oirat
File:Dzungar cavalry of Amursana, in the Battle ...
, Khoshut
The Khoshut (Mongolian language, Mongolian: Хошууд,, qoşūd, ; literally "bannermen," from Middle Mongol language, Middle Mongolian ''qosighu'' "flag, banner") are one of the four major tribes of the Oirats, Oirat people. They established ...
, Olot
Olot (; ) is the capital city of the ''Catalonia/Comarques, comarca'' of Garrotxa, in the Province of Girona, Catalonia, Spain. The city is known for its natural landscape, including four volcanoes scattered around the city center. The municipali ...
, Torghut
The Torghut ( Mongolian: Торгууд, , Torguud, "Guardsman", ) are one of the four major subgroups of the Four Oirats. The Torghut nobles traced their descent to the Mongol Keraite ruler Toghrul, and many Torghuts descended from the Keraites.
...
and Buzava. The Torghuts and Dörbets are numerically dominant. The Buzavs are a small minority and are considered to be the most russified Kalmyks.
Demographics
Location
The Kalmyks live primarily in theRepublic of Kalmykia
Kalmykia, officially the Republic of Kalmykia,; , ''Khalmg Tanghch'' is a republic of Russia, located in the Volga region of European Russia. The republic is part of the Southern Federal District, and borders Dagestan to the south and Stavr ...
, a federal subject of Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
. Kalmykia is located in the southeast European part of Russia, between the Volga and the Don rivers. It has borders with the Republic of Dagestan
Dagestan ( ; ; ), officially the Republic of Dagestan, is a republic of Russia situated in the North Caucasus of Eastern Europe, along the Caspian Sea. It is located north of the Greater Caucasus, and is a part of the North Caucasian Fede ...
in the south; the Stavropol Krai in the southwest; and the Rostov Oblast
Rostov Oblast ( rus, Росто́вская о́бласть, r=Rostovskaya oblastʹ, p=rɐˈstofskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ) is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast), located in the Southern Federal District. The oblast ...
and the Volgograd Oblast
Volgograd Oblast ( rus, Волгоградская область, p=vəɫɡɐˈgratskəjə ˈobɫəsʲtʲ) is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject (an oblast) of Russia, located in the Volga region, lower Volga region of Southern Russia ...
in the west and the northwest, respectively. Its eastern border is the Astrakhan Oblast
Astrakhan Oblast (; ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast) located in southern Russia. Its administrative center is the city of Astrakhan. As of the 2010 Census, its population was 1,010,073.
Geography
Astrakhan's southern border is the ...
. The southeast border is the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake and usually referred to as a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia: east of the Caucasus, ...
.
After the collapse of the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
, a large number of Kalmyks, primarily the young, moved from Kalmykia to larger cities in Russia, such as Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
and St. Petersburg
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea. The city had a population of 5,601, ...
, and to the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
. The move was precipitated by the desire of these Kalmyks to pursue better educational and economic opportunities and continues today.
Currently, Kalmyks form a majority of the population in Kalmykia. According to the 2021 Russian census, there was a total of 159,138 Kalmyks who resided within Kalmykia. This represented 62.5% of the total population of the republic in 2021. In addition, Kalmyks have a much higher fertility rate than Russians and the other Slavic peoples, while the median age of the Kalmyk population is much lower than Russians. This ensures that the Kalmyk population will continue to grow for the foreseeable future.
Religion



 The Kalmyks are the only European ethnic group whose primary religion is
The Kalmyks are the only European ethnic group whose primary religion is Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
. They embraced Tibetan Buddhism
Tibetan Buddhism is a form of Buddhism practiced in Tibet, Bhutan and Mongolia. It also has a sizable number of adherents in the areas surrounding the Himalayas, including the Indian regions of Ladakh, Gorkhaland Territorial Administration, D ...
in the early part of the 17th century and belong to the Tibetan Buddhist
Tibetan Buddhism is a form of Buddhism practiced in Tibet, Bhutan and Mongolia. It also has a sizable number of adherents in the areas surrounding the Himalayas, including the Indian regions of Ladakh, Darjeeling, Sikkim, and Arunachal Prades ...
sect known as the Gelugpa
240px, The 14th Dalai Lama (center), the most influential figure of the contemporary Gelug tradition, at the 2003 Bodh_Gaya.html" ;"title="Kalachakra ceremony, Bodh Gaya">Bodhgaya (India)
The Gelug (, also Geluk; 'virtuous')Kay, David N. (20 ...
(Virtuous Way). The Gelugpa are commonly referred to as the Yellow Hat sect. This religion is derived from the India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
n Mahayana Buddhism
Mahāyāna ( ; , , ; ) is a term for a broad group of Buddhist traditions, texts, philosophies, and practices developed in ancient India ( onwards). It is considered one of the three main existing branches of Buddhism, the others being Thera ...
. In the West, it was formerly referred to as Lamaism, from the name of the Tibetan monks, the lama
Lama () is a title bestowed to a realized practitioner of the Dharma in Tibetan Buddhism. Not all monks are lamas, while nuns and female practitioners can be recognized and entitled as lamas. The Tibetan word ''la-ma'' means "high mother", ...
s.
Historically, Kalmyk clergy received their training either on the steppe or in Tibet. The pupils who received their religious training on the steppe joined Kalmyk monasteries, which were active centers of learning. Many of these monasteries operated out of felt tents, which accompanied the Kalmyk tribes as they migrated. The Oirats maintained tent monasteries throughout present-day eastern Kazakhstan and along the migratory route they took across southern Siberia to the Volga. They also maintained tent monasteries around Lake Issyk Kul in present-day Kyrgyzstan.
The Oirats also built stone monasteries in the regions of eastern Kazakhstan. For instance, the remains of stone Buddhist monasteries have been found at Almalik and at Kyzyl-Kent (See image to the right). In addition, there was a great Buddhist monastery in Semipalatinsk
Semey (; , formerly known as Semipalatinsk ( ) until 2007 and as Alash-Qala ( ) from 1917 to 1920, is a city in eastern Kazakhstan, in the Kazakh part of Siberia. When Abai Region was created in 2022, Semey became its administrative centre. I ...
(seven palaces), which derives its name from that seven-halled Buddhist temple. Further, remains of Buddhist monasteries have been found at Ablaiket near Ust Kamenogorsk and at Talgar, near Almaty, and at Sumbe in the Narynkol region, bordering China.
Upon completion of training, Kalmyk clergy dispensed not only spiritual guidance but also medical advice. As clergymen, the Kalmyk lamas enjoyed great political influence among the nobility and held a strong influence over the general tribal population. For many commoners, the only path to literacy and prestige was to join the Kalmyk monastic system.
As a matter of policy, the Tsarist
Tsarist autocracy (), also called Tsarism, was an autocracy, a form of absolute monarchy in the Grand Duchy of Moscow and its successor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire. In it, the Tsar possessed in principle authority and ...
government and the Russian Orthodox Church
The Russian Orthodox Church (ROC; ;), also officially known as the Moscow Patriarchate (), is an autocephaly, autocephalous Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox Christian church. It has 194 dioceses inside Russia. The Primate (bishop), p ...
sought to gradually absorb and convert any subject of another creed or nationality. The aim of the policy was to eliminate foreign influence and to entrench newly annexed areas. The baptized indigenous population would then become loyal to the Russian empire and would agree to be governed by Russian officials.
In the 1700s, some Kalmyks converted to Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
, however their numbers were insignificant compared to Kalmyk converts to Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
who were more numerous. One group of Kalmyk Muslims were known as the Tomuts who were formed as the offspring of mixed marriages between Kalmyk women and Kazakh and Bashkir communities who lived among the Kalmyks and by the end of the 1730s they numbered around 600 tents. Another group of Kalmyk Muslims was known as the Sherets, they consisted of 120 tents and in 1733 they fled from the Derbet tayishi Cheter and settled near Azov. Later they were transferred to Crimea where they converted to Islam. In 1744, 233 Kalmyk men and 413 Kalmyk women were converted to Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
by the Astrakhan Tatars
Astrakhan Tatars () are an ethnic subgroup of the Tatar.
In the 15th to 17th-centuries, the Astrakhan Tatars inhabited the Astrakhan Khanate (1459–1556), which was also inhabited by the Nogai Horde, and the Astrakhan Tatars exerted a profoun ...
. Today, Sart Kalmyks living in Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan, officially the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia lying in the Tian Shan and Pamir Mountains, Pamir mountain ranges. Bishkek is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Kyrgyzstan, largest city. Kyrgyz ...
are predominantly Sunni
Sunni Islam is the largest branch of Islam and the largest religious denomination in the world. It holds that Muhammad did not appoint any successor and that his closest companion Abu Bakr () rightfully succeeded him as the caliph of the Mu ...
Muslims
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
.
A small percentage of Kalmyk-Cossack families in Belarus converted to Judaism in the early 19th century.
The Kalmyks migrated to territory annexed by the Tsarist government and were subject to this policy of conversion as long as they remained in this territory, but the efforts of the Tsarist government remained unsuccessful for the most part. However, the policy did contribute to the conversion of some of the Kalmyk nobility. One of the earliest converts were the children of Donduk-Ombo, the sixth Khan of the Kalmyks who reigned between 1737 and 1741, and his Circassian-born wife (See Dondukov family). Another important convert was Baksaday-Dorji, the grandson of Ayuka Khan who adopted the Christian name, Peter Taishin. Each conversion was motivated by political ambition to become the Kalmyk Khan. Kalmyk Tayishis, by contrast, were given salaries and towns and settlements were established for them and their ulus. Kalmyk converts, however, often continued to follow Buddhist law instead of Christian law.
Later on, the Tsarist government policy of encouraging Russian and German settlements along the Volga indirectly pressured Kalmyks to convert for economic reasons. The settlers took the most fertile land along the river, leaving barren lands for the Kalmyks to graze their herds. The resulting reduction of herds led to impoverishment for Kalmyk Tayishis, some of whom led their ulus to Christianity to obtain economic benefits.
To discourage the monastic lifestyle, the government required the building of permanent structures at government determined construction sites while imposing Russian architects. This policy resulted in the suspension of Lamaist canonical regulations governing monastery construction and in Kalmyk temples resembling Russian Orthodox churches. For example, the Khosheutovsky khurul is modeled after the Kazan Cathedral in St. Petersburg, Russia.
Other policies the Tsarist government implemented after the abolition of the Kalmyk Khanate
The Kalmyk Khanate (, ''Xal'mg xana uls'') was an Oirat Mongol khanate on the Eurasian steppe. It extended over modern Kalmykia and surrounding areas in the North Caucasus, including Stavropol and Astrakhan. During their independence, the Kalm ...
in 1771, sought to gradually weaken the influence of the lamas. For instance, the government limited Kalmyk contact with Tibet. In addition, the Tsar began appointing the Šajin Lama (title of the High Lama of the Kalmyks). Further, the economic crises that resulted from settler encroachment forced many monasteries and temples to close and lamas to adopt a secularized lifestyle. The success of this policy is borne out by the decrease in the number of Kalmyk monasteries in the Volga
The Volga (, ) is the longest river in Europe and the longest endorheic basin river in the world. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchment ...
region during the 19th century.
::::
Like the Tsarist government, the Communist regime was aware of the influence the Kalmyk clergy held over the general population. In the 1920s and the 1930s, the Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
government implemented policies to eliminate religion through control and suppression. Towards that end, Kalmyk khurul
image:Khoshotovsky Khurul 1812.jpg, Khosheutovsky khurul
A khurul (; or ''hure'' or ''küriye'') is a Buddhist monastery (temple, abode) in Kalmyks, Kalmyk (Oirats, Mongol-Oirat) Tibetan Buddhism, Lamaism. Some of the most famous Kalmyk khuruls ...
s (temples) and monasteries
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone ( hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer which m ...
were destroyed and property confiscated; the clergy and many believers were harassed, killed, or sent to labor camps; religious artifacts and books were destroyed; and young men were prohibited from religious training.
In the 1920s and 1930s, Buddhist temples and monasteries were destroyed and almost all of the spiritual leaders were arrested. By 1940 all Kalmyk Buddhist temples were either closed or destroyed and the clergy systematically oppressed. Dr. Loewenthal writes that the policies were so enforced that the Kalmyk clergy and Buddhism were not mentioned in the work by B. Dzhimbinov, "Sovetskaya Kalmykiya," published in 1940. In 1944, the Soviet government exiled all Kalmyks not fighting in the Soviet army
The Soviet Ground Forces () was the land warfare service branch of the Soviet Armed Forces from 1946 to 1992. It was preceded by the Red Army.
After the Soviet Union ceased to exist in December 1991, the Ground Forces remained under th ...
to Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
and Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states ...
, accusing them of collaborating with Nazi Germany. Upon rehabilitation in 1957, the Kalmyks were permitted to return home from exile, but all attempts by them to restore their religion and to build a temple failed.
By the 1980s, the Soviet campaign against religion was so successful that a majority of the Kalmyks had never received any formal spiritual guidance. By the late 1980s, however, the Soviet government reversed course and implemented policies favoring the liberalization of religion. As a result, the first Buddhist community was organized in 1988. By 1995, there were 21 Buddhist temples, 17 places of worship for various Christian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
denominations, and 1 mosque in the Republic of Kalmykia.
On December 27, 2005, a new khurul opened in Elista, the capital of the Republic of Kalmykia. The khurul was named "Burkhan Bakshin Altan Sume
The Burkhan Bakshin Altan Sume ("The Golden Abode of the Buddha Sakyamuni", , ; ) is a Gelug Buddhist monastery in Elista, the capital of the Republic of Kalmykia, a federal subject of the Russian Federation. The temple is the largest Buddhist ...
". It is the largest Buddhist temple in Europe. The government of the Republic of Kalmykia sought to build a magnificent temple of a monumental scale in hopes of creating an international learning center for Buddhist scholars and students from all over the world. More significantly, the temple is a monument to the Kalmyk people who died in exile between 1944 and 1957.
The Kalmyks of Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan, officially the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia lying in the Tian Shan and Pamir Mountains, Pamir mountain ranges. Bishkek is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Kyrgyzstan, largest city. Kyrgyz ...
live primarily in the Karakol region of eastern Kyrgyzstan. They are referred to as "Sart Kalmyks." The origin of this name is unknown. Likewise, it is not known when, why and from where this small group of Kalmyks migrated to eastern Kyrgyzstan. Due to their minority status, the Sart Kalmyks have adopted the Turkic language and culture of the majority Kyrgyz population. As a result, nearly all now belong to the Muslim faith.
Although Sart Kalmyks are Muslims
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
, Kalmyks elsewhere by and large remain faithful to the Gelugpa
240px, The 14th Dalai Lama (center), the most influential figure of the contemporary Gelug tradition, at the 2003 Bodh_Gaya.html" ;"title="Kalachakra ceremony, Bodh Gaya">Bodhgaya (India)
The Gelug (, also Geluk; 'virtuous')Kay, David N. (20 ...
Order of Tibetan Buddhism
Tibetan Buddhism is a form of Buddhism practiced in Tibet, Bhutan and Mongolia. It also has a sizable number of adherents in the areas surrounding the Himalayas, including the Indian regions of Ladakh, Gorkhaland Territorial Administration, D ...
. In Kalmykia, for example, the Gelugpa Order with the assistance of the government has constructed numerous Buddhist temples. In addition, the Kalmyk people recognize Tenzin Gyatso, 14th Dalai Lama
The 14th Dalai Lama (born 6 July 1935; full spiritual name: Jetsun Jamphel Ngawang Lobsang Yeshe Tenzin Gyatso, shortened as Tenzin Gyatso; ) is the incumbent Dalai Lama, the highest spiritual leader and head of Tibetan Buddhism. He served a ...
as their spiritual leader and Erdne Ombadykow, a Kalmyk American, as the supreme lama of the Kalmyk people. The Dalai Lama has visited Elista on a number of occasions. Buddhism and Christianity have been given the status of state religions. In November 2004 the 14th Dalai Lama
The 14th Dalai Lama (born 6 July 1935; full spiritual name: Jetsun Jamphel Ngawang Lobsang Yeshe Tenzin Gyatso, shortened as Tenzin Gyatso; ) is the incumbent Dalai Lama, the highest spiritual leader and head of Tibetan Buddhism. He served a ...
visited Kalmykia. In October 2022, Erdne Ombadykow, the Supreme Lama of Kalmykia, condemned the Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, , starting the largest and deadliest war in Europe since World War II, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, conflict between the two countries which began in 2014. The fighting has caused hundreds of thou ...
and fled Russia to Mongolia. In January 2023, he was recognized in Russia as a foreign agent
A foreign agent is any person or entity actively carrying out the interests of a foreign principal while located in another host country, generally outside the Diplomatic immunity, protections offered to those working in their official capacity fo ...
.
Language
 ''Ethnologue'' classifies
''Ethnologue'' classifies Kalmyk Oirat
Kalmyk Oirat (, ), also known as the Kalmyk language () and formerly anglicized as Calmuck, is a variety of the Oirat language, natively spoken by the Kalmyk people of Kalmykia, a federal subject of Russia. In Russia, it is the standard f ...
as a member of the Eastern branch of the Mongolic languages: "Mongolic, Eastern, Oirat-Khalkha, Oirat-Kalmyk-Darkhat".Ethnologue:xal, Kalmyk-Oirat, in Gordon, Raymond G., Jr. (ed.), 2005. ''Ethnologue: Languages of the World'', 15th edition. Dallas, Tex.: SIL International This places Mongolian language, Standard Mongolian – which is essentially Khalkha Mongolian – and Kalmyk Oirat fairly close together.
Other linguists, such as Nicholas Poppe, have classified Kalmyk Oirat as belonging to the Western branch of the Mongolian language division and thus more distant from Khalkha and Standard Mongolian as spoken in modern Mongolia, since the language group developed separately and is distinct. Poppe also contends that Kalmyk and Oirat are two distinct languages in spite of little phonetic and morphological difference between them, and that the major distinction is in their lexicons. The Kalmyk language, for example, has adopted many words of Russian origin. Consequently, mainly on lexical grounds, Kalmyk is classified as a distinct language.
By population, the major dialects of Kalmyk are Torghut, Dörbet and Buzava. Minor dialects include Khoshut and Olöt. The Kalmyk dialects vary somewhat, but their differences are insignificant. Generally, the Russian language less influenced the dialects of the pastoral nomadic Kalmyk tribes of the Volga region.
In contrast, the Dörbets (and later on, Torghuts) who migrated from the Volga region to the of the Don Host Oblast took the name Buzava (or Don Kalmyks). The Buzava dialect developed from their close interaction with Russians. In 1798 the Tsarist government recognized the Buzava as Don Cossacks
Don Cossacks (, ) or Donians (, ), are Cossacks who settled along the middle and lower Don River (Russia), Don. Historically, they lived within the former Don Cossack Host (, ), which was either an independent or an autonomous democratic rep ...
, both militarily and administratively. As a result of their integration into the Don Host, the Buzava dialect incorporated many words of Russian origin.
In 1938, the Kalmyk literary language started using Cyrillic script.
During World War II, all Kalmyks not fighting in the Soviet Army were forcibly exiled to Siberia and Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
, where they were dispersed and not permitted to speak Kalmyk in public places. As a result, the Kalmyk language was not formally taught to the younger generation of Kalmyks.
Upon return from exile in 1957, the Kalmyks spoke and published primarily in Russian. Consequently, the younger generation of Kalmyks primarily speak Russian and not their own native language. This is a subject of popular concern. In recent years, the Kalmyk government has made attempts to revive the Kalmyk language. Some laws have been passed regarding the usage of Kalmyk on shop signs; for example, on entrance doors, the words 'Entrance' and 'Push-Pull' appear in Kalmyk.
According to UNESCO's 2010 edition of the ''Red Book of Endangered Languages'', the Kalmyk language classified as List of endangered languages in Russia, definitely endangered.
Writing system
In the 17th century, Zaya Pandita, a Khoshut bhikkhu, Buddhist monk, devised a writing system, Clear Script, based on the classical vertical Mongol script in order to phonetically capture the Oirat language. In the later part of the 19th and early part of the 20th centuries, Clear Script fell into disuse until the Kalmyks abandoned it in 1923 and introduced the Cyrillic script. In 1930, Kalmyk language scholars introduced a modified Latin alphabet, but it was not used for long.List of notable Kalmyks
*Maria Kirbasova, Russian human rights activist who founded the Committee of Soldiers' Mothers of Russia *Kristina Anna Evdokia Bange (1/2 Kalmyk) *Irina Kukanova (Kristina's mother) *Dinara Wagner - Russian chess grandmaster *Ngawang Wangyal - Buddhist lama and scholarPolitical figures
* Kirsan Ilyumzhinov - 1st President of Kalmykia, former President of FIDE * Vladimir Lenin (Possibly up to 1/4 Kalmyk) - Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist * Ilya Ulyanov (1/2 Kalmyk) * Oka Gorodovikov -Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People ...
cavalry general
* Lavr Kornilov - Imperial Russian Army general, commander of the anti-Bolshevik Volunteer Army
Khans of the Kalmyk Khanate
* Kho Orlok, Kho Erleg — 1580-1644 * — 1654–1661 * (Monchak) — 1661–1669 *Ayuka Khan
Ayuka or Ayuki Khan (; 1669–1724) was a Kalmyk leader under whose rule the Kalmyk Khanate reached its zenith in terms of economic, military, and politic power. On behalf of Russia, Ayuka Khan protected the southern borders of Russia, engaging ...
— 1669–1724
* — 1724-1735
* — 1735–1741
* — 1741–1761
* Ubashi Khan
Ubashi Khan (; ; 1744 – 1774) was a Torghut- Kalmyk prince and the last Khan of the Kalmyk Khanate. In January 1771, he led the return migration of the majority of the Kalmyk people from the Kalmyk steppe to Dzungaria, their ancestral hom ...
— 1761–1771
Athletes
* Sanan Sjugirov, Russian chess grandmaster * Batu Khasikov, Russian politician and kickboxer * Mingiyan Semenov, Russian wrestler * Sandje Ivanchukov, American soccer defender * Jean Djorkaeff (1/2 Kalmyk) * Youri Djorkaeff (one-quarter Kalmyk) * Lyudmila Bodniyeva, Liudmila Bodnieva, Russian handball playerSee also
* Kalmyk nameNotes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * Dzhimbinov, B. ''Sovetskaia Kalmykiia'', Moscow, 1940. * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Williamson, ''H.N.H. FAREWELL TO THE DON: The Russian Revolution in the Journals of Brigadier H.N.H. Williamson'', John Harris, Editor, The John Day Company, New York, 1970. * * * ''Санчиров В. П.'' О Происхождении этнонима торгут и народа, носившего это название // Монголо-бурятские этнонимы: cб. ст. – Улан-Удэ: БНЦ СО РАН, 1996. C. 31–50. * * * Хойт С.К.Антропологические характеристики калмыков по данным исследователей XVIII–XIX вв.
' // Вестник Прикаспия: археология, история, этнография. No. 1. Элиста: Изд-во КГУ, 2008. с. 220–243. * Хойт С.К.
Калмыки в работах антропологов первой половины XX вв
'. // Вестник Прикаспия: археология, история, этнография. No. 3, 2012. с. 215–245. * Хойт С.К.
Этническая история ойратских групп
'. Элиста, 2015. 199 с. (Khoyt S.K. Ethnic history of oyirad groups. Elista, 2015. 199 p). (in Russian) * Хойт С.К.
Данные фольклора для изучения путей этногенеза ойратских групп
' // Международная научная конференция «Сетевое востоковедение: образование, наука, культура», 7-10 декабря 2017 г.: материалы. Элиста: Изд-во Калм. ун-та, 2017. с. 286–289. {{DEFAULTSORT:Kalmyk People Ethnic groups in Kyrgyzstan Kalmyk people Buddhism in Russia Mongol diaspora in Europe Mongolian diaspora in Europe Ethnic groups in Russia East Asian diaspora Kalmyk Khanate