|
Kashgaria
Yettishar ( Chagatai: ; ; ), also known as Kashgaria or the Kashgar Emirate, was a Uyghur state in Xinjiang that existed from 1864 to 1877, during the Dungan Revolt against the Qing dynasty. It was an Islamic monarchy ruled by Yakub Beg, a Kokandi who secured power in Kashgar (later made Yettishar's capital) through a series of military and political manoeuvres. Yettishar's eponymous seven cities were Kashgar, Khotan, Yarkand, Yengisar, Aksu, Kucha, and Korla. In 1873, the Ottoman Empire recognised Yettishar as a vassal state and Yakub Beg as its emir. The Ottoman flag flew over Kashgar from 1873 to 1877. On 18 December 1877, the Qing army entered Kashgar and brought the state to an end. Background By the 1860s, Xinjiang had been under Qing rule for a century. The area had been conquered in 1759 from the Dzungar Khanate whose core population, the Oirats, subsequently became the targets of genocide. However, Xinjiang consisted mostly of semi-arid or desert land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
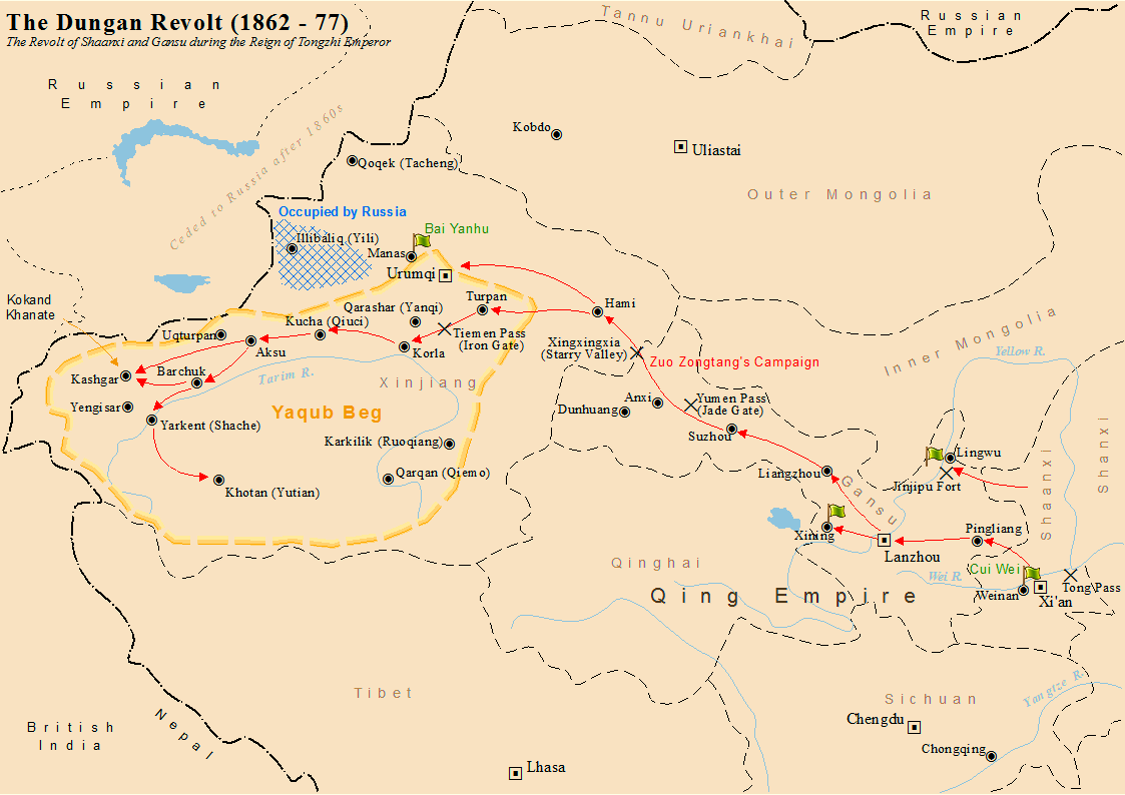
Dungan Revolt (1862–1877)
The Dungan Revolt (1862–1877), also known as the Tongzhi Hui Revolt (, Xiao'erjing: تُجِ خُوِ لُوًا, ) or Hui (Muslim) Minorities War, was a war fought in 19th-century western China, mostly during the reign of the Tongzhi Emperor (r. 1861–1875) of the Qing dynasty. The term sometimes includes the Panthay Rebellion in Yunnan, which occurred during the same period. However, this article refers specifically to two waves of uprising by various Chinese Muslims, mostly Hui people, Hui people, in Shaanxi, Gansu and Ningxia Province of China, provinces in the first wave, and then in Xinjiang in the second wave, between 1862 and 1877. The uprising was eventually suppressed by Qing forces led by Zuo Zongtang. The conflict began with riots by the Hui people, Hui and massacres of the Han Chinese, followed by the revenge massacres of the Hui by the Han. It resulted in massive demographic shifts in Northwest China, and led to a population loss of 21 million people from a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xinjiang Under Qing Rule
The Manchu-led Qing dynasty of China ruled over Xinjiang from the late 1750s to 1912. In the history of Xinjiang, the Qing rule was established in the final phase of the Dzungar–Qing Wars when the Dzungar Khanate was conquered by the Qing dynasty, and lasted until the fall of the Qing dynasty in 1912. The post of General of Ili was established to govern the whole of Xinjiang and reported to the Lifan Yuan, a Qing government agency that oversaw the empire's frontier regions. Xinjiang was turned into a province in 1884. Terminology Xinjiang The name "Xinjiang" () was introduced during the reign of the Qianlong Emperor (r. 1735–1796) as "Xiyu Xinjiang" (). Xinjiang became the common designation for the region under the General of Ili Songyun in the late 18th century. It was split between ''Zhunbu'' (Dzungaria) in the north, also known as ''Tianshan Beilu'' (Northern March), ''Huibu'' (Muslim Region) in the south, also known as ''Tianshan Nanlu'' (Southern March) or ''Huijian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yarkant County
Yarkant County,, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency also Shache County,, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency also transliterated from Uyghur as Yakan County, is a county in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, China, located on the southern rim of the Taklamakan Desert in the Tarim Basin. It is one of 11 counties administered under Kashgar Prefecture. The county, usually referred to as Yarkand in English, was the seat of an ancient Buddhist kingdom on the southern branch of the Silk Road and the Yarkand Khanate. The county sits at an altitude of and had a population of . The fertile oasis is fed by the Yarkand River, which flows north down from the Karakorum mountains and passes through the Kunlun Mountains, known historically as the Congling mountains (lit. 'Onion Mountains' - from the abundance of wild onions found there). The oasis now covers , but was likely far more extensive before a period of desiccation affected the region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Reconquest Of Xinjiang
The Qing reconquest of Xinjiang () was the event when the Qing dynasty reconquered Xinjiang after the Dungan Revolt in the late 19th century. After a century of Qing rule, the Uzbek adventurer Yakub Beg conquered almost all of Xinjiang during the revolt, but was eventually defeated by the Qing General Zuo Zongtang (also known as General Tso). Furthermore, Qing China recovered the Gulja region through diplomatic negotiations with the Russian Empire and the Treaty of Saint Petersburg in 1881. Xinjiang was converted into a province in 1884. Background The Qing dynasty under the Qianlong Emperor conquered Xinjiang from the Dzungar Khanate during the final stage of the Dzungar–Qing Wars in the late 1750s and put Xinjiang under its rule. However, Qing China declined in the late 19th century following the Opium War. A major revolt known as the Dungan Revolt occurred in the 1860s and 1870s in Northwest China, and Qing rule almost collapsed in all of Xinjiang except for pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yakub Beg Of Yettishar
Muhammad Yakub Beg (30 May 1877), later known as Yakub Padishah, was the Khanate of Kokand, Kokandi ruler of Yettishar (Kashgaria), a state he established in Xinjiang from 1865 to 1877. He was recognized as Emir of Yettishar by the Ottoman Empire and held the title of "Champion Father of the Faithful". Spelling variants In English-language literature, the name Yakub Beg has also been spelt as Yaqub Beg, Yakoob Beg or Yaʿqūb Beg. Authors using Russian sources have also used the spelling Yakub-bek. A few publications in English written by Chinese authors transcribe his name as ''Āgǔbó'', which is the pinyin transcription his name in Chinese, , a shortened form of . The first name, Muhammad, is subject to the usual variations in spelling. ''Yaʿqūb'' is an Jacob in Islam, Arabic analogue of Jacob, and ''Bey, Beg'' is a Turkic noble title. His noble title ''Beg'' was later elevated to ''Padishah'' after his rise to power. He was also given the title ''Atalıq Ghazi (warrior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xinjiang
Xinjiang,; , SASM/GNC romanization, SASM/GNC: Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Sinkiang, officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the Northwest China, northwest of the country at the crossroads of Central Asia and East Asia. Being the List of Chinese administrative divisions by area, largest province-level division of China by area and the List of the largest country subdivisions by area, 8th-largest country subdivision in the world, Xinjiang spans over and has about 25 million inhabitants. Xinjiang Borders of China, borders the countries of Afghanistan, India, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Mongolia, Pakistan, Russia, and Tajikistan. The rugged Karakoram, Kunlun Mountains, Kunlun and Tian Shan mountain ranges occupy much of Xinjiang's borders, as well as its western and southern regions. The Aksai Chin and Trans-Karakoram Tract regions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kashgar
Kashgar () or Kashi ( zh, c=喀什) is a city in the Tarim Basin region of southern Xinjiang, China. It is one of the westernmost cities of China, located near the country's border with Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan. For over 2,000 years, Kashgar was a strategically important oasis on the Silk Road between China, the Middle East, and Europe. It is one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world and has a population of 711,300 people (). Kashgar's urban area covers , although its administrative area extends over . At the convergence point of widely varying cultures and empires, Kashgar has been under the rule of the Chinese, Turkic, Mongol and Tibetan empires. The city has also been the site of a number of battles between various groups of people on the steppes. Now administered as a county-level city, Kashgar is the administrative centre of Kashgar Prefecture, which has an area of and a population of approximately 4 million . Kashgar was declared a Special Economic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khotan
Hotan (also known by #Etymology, other names) is a major oasis town in southwestern Xinjiang, an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region in Northwestern China. The city proper of Hotan broke off from the larger Hotan County to become an administrative area in its own right in August 1984. It is the seat of Hotan Prefecture. With a population of 408,900 (2018 census), Hotan is situated in the Tarim Basin some southwest of the regional capital, Ürümqi. It lies just north of the Kunlun Mountains, which are crossed by the Sanju Pass, Sanju, Hindutash and Ilchi passes. The town, located southeast of Yarkant County and populated almost exclusively by Uyghurs, is a minor agricultural center. An important station on the southern branch of the historic Silk Road, Hotan has always depended on two strong rivers, the Karakash River and the White Jade River, to provide the water needed to survive on the southwestern edge of the vast Taklamakan Desert. The White Jade River still pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uyghurs
The Uyghurs,. alternatively spelled Uighurs, Uygurs or Uigurs, are a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the general region of Central Asia and East Asia. The Uyghurs are recognized as the titular nationality of the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in Northwest China. They are one of Ethnic minorities in China, China's 55 officially recognized ethnic minorities. The Uyghurs have traditionally inhabited a series of Oasis, oases scattered across the Taklamakan Desert within the Tarim Basin. These oases have historically existed as independent states or were controlled by many civilizations including History of China, China, the Mongol Empire, Mongols, the Tibetan Empire, Tibetans, and various Turkic polities. The Uyghurs gradually started to become Islamized in the 10th century, and most Uyghurs identified as Muslims by the 16th century. Islam has since played an important role in Uyghur culture and identity. An estimated 80% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yengisar
Yengisar County, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (formerly transliterated as Yangi Hissar, from , United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency), also known as Yingjisha County, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency ( zh, s=英吉沙县), is a county of Kashgar Prefecture in southwest Xinjiang, China. It covers an area of . As of the 2002 census, it had a population of 230,000. The county seat is the city of Yengisar, a town well known among the local Uyghurs for its handmade knives. The finely-tuned skill of knife-making used to be passed down among generations in Yengisar, but it is slowly dying due to China's strict response to deadly clashes in Xinjiang. History In 1499, Ahmad Alaq seized Kashgar and Yengisar from Mirza Abu Bakr Dughlat. In 1847 and again in 1857, Kashgar and Yengisar were captured. In 1882, Yengisar Independent Subprefecture () was created. In 1913, Yengisar Independent Subprefecture became Yengisa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aksu City
Aksu (, ; zh, s=阿克苏, p=Ākèsū) is a city in and the seat of Aksu Prefecture, Xinjiang, lying at the northern edge of the Tarim Basin. The name Aksu literally means "white water" (in Turkic) and is used for both the oasis town and the Aksu River. The economy of Aksu is mostly agricultural, with cotton, in particular long-staple cotton (''Gossypium hirsutum''), as the main product. Also produced are grain, fruits, oils and beets. The industry mostly consists of weaving, cement and chemical industries. The land currently under the administration of the Aksu City is divided in two parts, separated by the Aral City. The northern part hosts the city center, while the southern part is occupied by the Taklamakan Desert. Aksu airport is considered a military airport in China (although also available for civil usage). Only aircraft registered in China can land in Aksu. This means if you are flying to Aksu from international origins you have to land in a major airport in China ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kucha
Kucha or Kuche (also: ''Kuçar'', ''Kuchar''; , Кучар; zh, t= 龜茲, p=Qiūcí, zh, t= 庫車, p=Kùchē; ) was an ancient Buddhist kingdom located on the branch of the Silk Road that ran along the northern edge of what is now the Taklamakan Desert in the Tarim Basin and south of the Muzat River. The former area of Kucha now lies in present-day Aksu Prefecture, Xinjiang, China. Kuqa town is the county seat of Aksu Prefecture's Kuqa County. Its population was given as 74,632 in 1990. Etymology The history of toponyms for modern Kucha remains somewhat problematic; however, it is clear that Kucha (''Kuchar'', in Turkic languages) and ''Kuché'' (modern Chinese)Elias (1895): ''The Tarikh-i-Rashidi of Mirza Muhammad Haidar, Dughlát: A History of the Moghuls of Central Asia. An English Version Edited, with Commentary, Notes, and Map by N. Elias''. Translation by E. Denison Ross. London. Sampson, Low, Marston and Company Ltd.), p. 124, n. 1., ''et passim'' both co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |