|
Dungan Revolt (1862–1877)
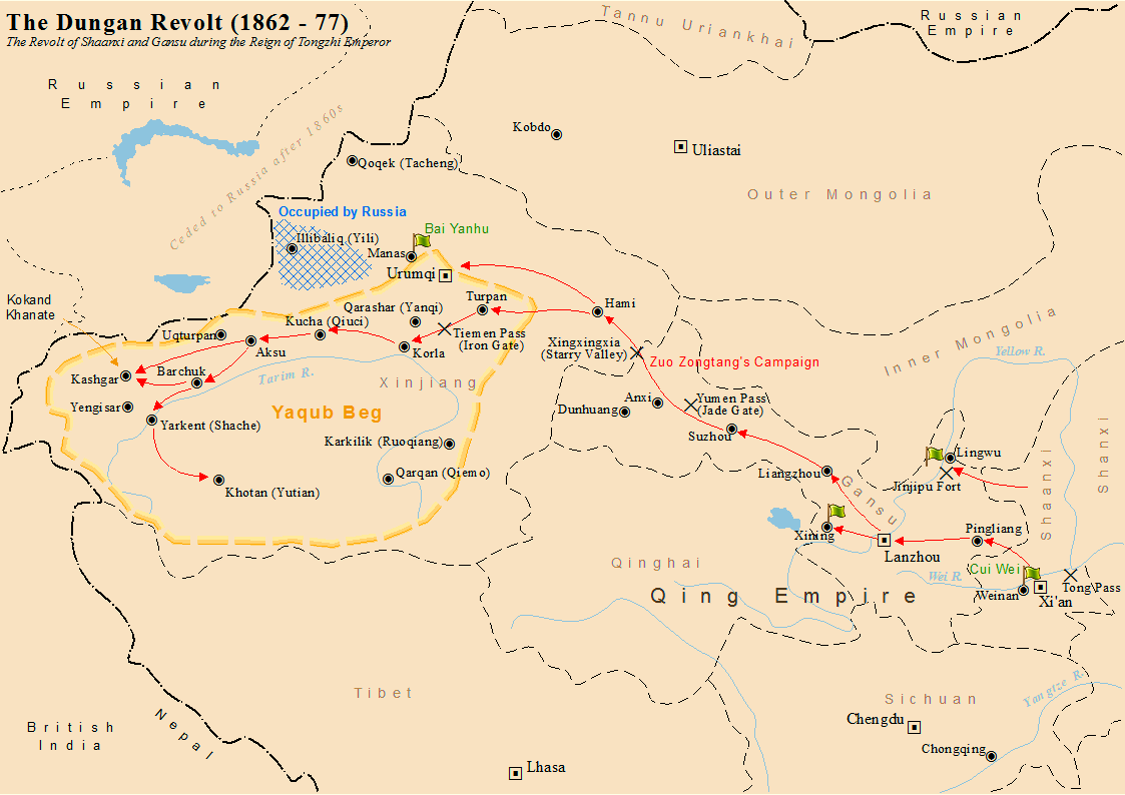
The Dungan Revolt (1862–1877), also known as the Tongzhi Hui Revolt (, Xiao'erjing: تُجِ خُوِ لُوًا, ) or Hui (Muslim) Minorities War, was a war fought in 19th-century western China, mostly during the reign of the Tongzhi Emperor (r. 1861–1875) of the Qing dynasty. The term sometimes includes the Panthay Rebellion in Yunnan, which occurred during the same period. However, this article refers specifically to two waves of uprising by various Chinese Muslims, mostly Hui people, Hui people, in Shaanxi, Gansu and Ningxia Province of China, provinces in the first wave, and then in Xinjiang in the second wave, between 1862 and 1877. The uprising was eventually suppressed by Qing forces led by Zuo Zongtang. The conflict began with riots by the Hui people, Hui and massacres of the Han Chinese, followed by the revenge massacres of the Hui by the Han. It resulted in massive demographic shifts in Northwest China, and led to a population loss of 21 million people from a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yakub Beg Of Yettishar
Muhammad Yakub Beg (30 May 1877), later known as Yakub Padishah, was the Khanate of Kokand, Kokandi ruler of Yettishar (Kashgaria), a state he established in Xinjiang from 1865 to 1877. He was recognized as Emir of Yettishar by the Ottoman Empire and held the title of "Champion Father of the Faithful". Spelling variants In English-language literature, the name Yakub Beg has also been spelt as Yaqub Beg, Yakoob Beg or Yaʿqūb Beg. Authors using Russian sources have also used the spelling Yakub-bek. A few publications in English written by Chinese authors transcribe his name as ''Āgǔbó'', which is the pinyin transcription his name in Chinese, , a shortened form of . The first name, Muhammad, is subject to the usual variations in spelling. ''Yaʿqūb'' is an Jacob in Islam, Arabic analogue of Jacob, and ''Bey, Beg'' is a Turkic noble title. His noble title ''Beg'' was later elevated to ''Padishah'' after his rise to power. He was also given the title ''Atalıq Ghazi (warrior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tacheng
TachengThe official spelling according to (), also known as Tarbagatay, Chuguchak or Qoqek, is a county-level city and the administrative seat of Tacheng Prefecture, in northern Ili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture, Xinjiang. The Chinese name "Tacheng" is an abbreviation of "Tarbagatay City", a reference to the Tarbagatay Mountains. Tacheng is located in the Dzungarian Basin, some from the Chinese border with Kazakhstan. For a long time it has been a major center for trade with Central Asia because it is an agricultural hub. Its industries include food processing, textiles, and utilities. History In the mid-19th century, Chuguchak was considered the most important commercial center of Western China after Ghulja (Yining), being an important center of trade between China and Russia, in particular in tea. The city, surrounded by an earth wall, was the residence of two Qing ambans and had a garrison of some 1,000 Chinese soldiers and 1,500 Manchu and Mongol soldiers. Chuguchak suffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hui People
The Hui people are an East Asian ethnoreligious group predominantly composed of Islam in China, Chinese-speaking adherents of Islam. They are distributed throughout China, mainly in the Northwest China, northwestern provinces and in the Zhongyuan region. According to the 2010 census, China is home to approximately 10.5 million Hui people. Outside China, the 170,000 Dungan people of Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan, the Panthays in Myanmar, and many of the Chin Haws in Thailand are also considered part of the Hui ethnicity. The Hui were referred to as Hanhui during the Qing dynasty to be distinguished from the Turkic peoples, Turkic Muslims, which were referred to as Chanhui. The Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China government also recognised the Hui as a branch of the Han Chinese rather than a separate ethnic group. In the National Assembly (Republic of China), National Assembly of the Republic of China, the Hui were referred to as 1947 Chinese National Assembly election ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khafiya
Ma Laichi (1681? – 1766?; ), also known as Abu 'l-Futūh Ma Laichi, was a Chinese Sufi master who brought the Khufiyya movement to China and created the Huasi '' menhuan'' ( Sufi order) - the earliest and most important Naqshbandi (نقشبندية,納克什班迪) order in Chinese Muslim history.Gladney (1996), pp. 47-48Lipman (1998), p. 65-67 Life Afaq Khoja's blessing Ma Laichi came from a Chinese Muslim family with a military background. His grandfather, Ma Congshan, was a general under the Ming dynasty; his father, Ma Jiujun, passed imperial examinations on the military track under the Qing, but instead of joining government service, made a fortune in business. His home was in Hezhou (now called Linxia), one of the main Muslim centers of Gansu. According to the legend told by Ma Laichi's followers, Ma Jiajun was still childless at the age of forty, and, desirous to have a son, he went to Xining, to ask for a blessing from Afaq Khoja, a Naqshbandi ''shayk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chu Army
The Chu Army () was a standing regional army organized by Zuo Zongtang. The name is taken from the Hunan region where the Army was raised. The Army was financed through local nobles and gentry, as opposed to the central government. The Chu Army was one of two armies known as the Hunan Army. Another Hunan Army, called the Xiang Army, was created by Zeng Guofan to fight in the Taiping Rebellion. Remnants of the Xiang Army that fought the Taiping were then known as the "Old Hunan Army". Dungan Revolt (1862–1877) The Xiang Army was an example of the regional Yong Ying armies that emerged in late Qing dynasty China, separate from the Manchu Eight Banners and Green Standard Army. The main points of difference were in their regional affiliations, since these forces were often raised and led via kinship and local networks; and their contravention of the normal Chinese military policy where army generals were frequently rotated to prevent ambitious commanders building power bases. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ma Hualong
Ma Hualong () (died March 2, 1871), was the fifth leader (, ''jiaozhu'') of the Jahriyya, a Sufi order (''menhuan'') in northwestern China.Dillon (1999), pp. 124–126 From the beginning of the anti-Qing Muslim Rebellion in 1862, and until his surrender and death in 1871, he was one of the main leaders of the rebellion. Biography Ma Hualong became the leader of the Jahriyya ca. 1849, succeeding the ''menhuans fourth ''shaykh'', Ma Yide (late 1770s – 1849). Although the Jahriyya had been originally created by Ma Mingxin in the central Gansu, by the time of Ma Hualong's succession to the leadership position the order was centered in the northern Ningxia (which in the 19th century was also part of Gansu Province), its headquarters being located in Jinjipu (), a few kilometers south from today's Wuzhong City. Lipman (1998), p. 125 The town of Jinjipu became an important religious and commercial center, and the ''menhuans leaders grew wealthy thanks to the order's profitable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ma Haiyan
Ma Haiyan (1837–1900) was a Chinese Muslim general of the Qing Dynasty. Originally a rebel, he defected to Qing during the Dungan revolt and helped crush rebel Muslims. He was the father of Ma Qi and Ma Lin and of Ma Feng. Dong Fuxiang, Ma Anliang and Ma Haiyan were originally called to Beijing during the First Sino-Japanese War in 1894, but the Dungan Revolt (1895) broke out and they were subsequently sent to crush the rebels. During the Hundred Days' Reform in 1898 Dong Fuxiang, Ma Anliang, and Ma Haiyan were called to Beijing and helped put an end to the reform movement along with Ma Fulu and Ma Fuxiang. He fought against the foreign Eight Nation alliance in the Boxer Rebellion The Boxer Rebellion, also known as the Boxer Uprising, was an anti-foreign, anti-imperialist, and anti-Christian uprising in North China between 1899 and 1901, towards the end of the Qing dynasty, by the Society of Righteous and Harmonious F ... with his nephew Ma Biao serving under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ma Qianling
Ma Qianling (, Xiao'erjing: ; 1826–1910) was a Chinese Muslim General who defected to the Qing Dynasty in 1872 during the Dungan revolt along with his superior General Ma Zhanao and General Ma Haiyan. He then assisted General Zuo Zongtang in crushing the rebel Muslims. In 1877 he and Ma Zhanao expelled Muslim rebels who refused to give up the fight from the hills around Hezhou. His four sons were, Ma Fucai, Ma Fulu, Ma Fushou, and Ma Fuxiang. His grandsons were Ma Hongbin and Ma Hongkui Ma Hongkui ( zh, s=马鸿逵 , t=馬鴻逵 , p=Mǎ Hóngkuí , w=Ma Hung-k'uei , first=t, Xiao'erjing: ; March 14, 1892 – January 14, 1970) was a prominent Hui people, Chinese Muslim warlord during the Republic of China (1912–1949), R .... He had three wives, one was a Muslim convert. His sons Ma Fulu and Ma Fuxiang inherited his army. References 19th-century Chinese military personnel 20th-century Chinese people 1826 births 1910 deaths People from Linxia Hui peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ma Anliang
Ma Anliang (, French romanization: Ma-ngan-leang, Xiao'erjing: ; 1855 – November 24, 1918) was a Hui people, Hui born in Linxia City, Hezhou, Gansu, China. He became a general in the Qing dynasty army, and of the Republic of China (1912–49), Republic of China. His father was Ma Zhan'ao, and his younger brothers were Ma Guoliang and Ma Suiliang (Ma Sui-liang) 馬遂良. Ma was educated in Chinese and Islamic education. His Muslim name was Abdul Majid ( zh, 阿卜都里默直底). Military career He defected to Qing in 1872 during the Dungan revolt (1862–77), along with several other Hui Muslims, including his father, Ma Zhan'ao, Ma Haiyan, and Ma Qianling. They belonged to the Huasi menhuan, of the Khafiya Naqshbandi Sufi order. They assisted the Qing Han Chinese general Zuo Zongtang in suppressing the Muslim revolt. In 1877, his father Ma Zhanao defeated a group of Muslim rebels who continued fighting near Linxia City, Hezhou. General Ma Anliang joined the Qing Gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ma Zhan'ao
Ma Zhan’ao (1830–1886) (, Xiao'erjing: ) was a Chinese Muslim General who defected to the Qing Dynasty in 1872 during the Dungan revolt along with his General Ma Qianling and General Ma Haiyan who served under him during the revolt. He first sent Ma Chun (Ma Jun) to negotiate a surrender with General Zuo, but Zuo suspected a ruse. Ma then sent his son, Ma Anliang, to negotiate. He then assisted General Zuo Zongtang in crushing the rebel Muslims. In 1877 he and Ma Qianling expelled Muslim rebels who refused to give up from the hills surrounding Hezhou. He had three sons, Ma Anliang Ma Anliang (, French romanization: Ma-ngan-leang, Xiao'erjing: ; 1855 – November 24, 1918) was a Hui people, Hui born in Linxia City, Hezhou, Gansu, China. He became a general in the Qing dynasty army, and of the Republic of China (1912 ..., Ma Guoliang, and Ma Suiliang (Ma Sui-liang) 馬遂良. The escape of Han people from Hezhou during the rebellion was assisted by Ma Zhan'ao. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dong Fuxiang
Dong Fuxiang (1839–1908), courtesy name Xingwu (), was a Chinese general who lived in the late Qing dynasty. He was born in the Western Chinese province of Gansu. He commanded an army of Hui soldiers, which included the later Ma clique generals Ma Anliang and Ma Fuxiang. According to the Western calendar, his birth date is in 1839. Religion Dong Fuxiang was a non-Muslim Han Chinese general who commanded Muslim Hui soldiers. Conflicting accounts were given about his religion and ethnicity. Contemporaneous Western sources claim he was Muslim, which was a mistake, but modern Western sources either say he was not Muslim, or did not mention his religion at all when talking about him, and some mistakenly still say he is Muslim. The only thing that was clear about him was that he was familiar with the Muslim militia of Gansu, and commanded Muslim troops in battle. The British consular officer Erich Teichman traveling in Gansu was repeatedly told that Dong Fuxiang was Han Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |