Italian Propaganda During World War I on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In Italy as in other countries the outbreak of the First World War created new opportunities and channels for propaganda. The unusual circumstances of Italy’s entry into the war meant that the government played no active role in propaganda work during the early years of the war. Public opinion was served by a pro-war nationalist press that avoided the unpleasant details of life on the front, while the army regarded discipline as more important than morale, leaving soldiers’ welfare to the Church. The momentous Italian defeat at
In Italy as in other countries the outbreak of the First World War created new opportunities and channels for propaganda. The unusual circumstances of Italy’s entry into the war meant that the government played no active role in propaganda work during the early years of the war. Public opinion was served by a pro-war nationalist press that avoided the unpleasant details of life on the front, while the army regarded discipline as more important than morale, leaving soldiers’ welfare to the Church. The momentous Italian defeat at
 In the UK, France, Germany and Austria-Hungary, propaganda was mainly a centrally managed effort by the government and the armed forces from the outbreak of hostilities in August 1914. Italy did not enter the war until May 1915, and before this there was no organised state propaganda relating to the war. Instead, business interests and the press themselves took the lead.
Between the end of 1914 and 1915 there was a sustained campaign in the Italian press for the country to enter the war. There were strong views in favour of intervention among the leading economic, industrial and financial interests, particularly those linked to heavy industry and war production, such as
In the UK, France, Germany and Austria-Hungary, propaganda was mainly a centrally managed effort by the government and the armed forces from the outbreak of hostilities in August 1914. Italy did not enter the war until May 1915, and before this there was no organised state propaganda relating to the war. Instead, business interests and the press themselves took the lead.
Between the end of 1914 and 1915 there was a sustained campaign in the Italian press for the country to enter the war. There were strong views in favour of intervention among the leading economic, industrial and financial interests, particularly those linked to heavy industry and war production, such as
 Although slow to mobilise public opinion through active propaganda, the government did act to censor the press. War correspondents were aware of the reality of the front and sent detailed reports to their editors. Nevertheless the reading public saw only articles that hid, and in some cases falsified, much of the truth, in a conscious process of disinformation in which much of the public did not seek objective information. Towards the end of 1915
Although slow to mobilise public opinion through active propaganda, the government did act to censor the press. War correspondents were aware of the reality of the front and sent detailed reports to their editors. Nevertheless the reading public saw only articles that hid, and in some cases falsified, much of the truth, in a conscious process of disinformation in which much of the public did not seek objective information. Towards the end of 1915
 Before 1917 propaganda, recreational and welfare initiatives for soldiers were scarce and poorly managed. Propaganda was understood in traditional forms, such as speeches given by officers and invited speakers. As these speakers were exempted from military service, they appeared "privileged" in the eyes of the infantry. These proclamations about the reasons for the war were entirely alien to the language and mentality of the soldiers, who regarded the requirement to stand and listen to them as a waste of time, which lowered their morale.
Before 1917 propaganda, recreational and welfare initiatives for soldiers were scarce and poorly managed. Propaganda was understood in traditional forms, such as speeches given by officers and invited speakers. As these speakers were exempted from military service, they appeared "privileged" in the eyes of the infantry. These proclamations about the reasons for the war were entirely alien to the language and mentality of the soldiers, who regarded the requirement to stand and listen to them as a waste of time, which lowered their morale.
 The defeat at
The defeat at
 Before 1918 Italy had made attempts to spread propaganda through Austria-Hungary, but these efforts had been fairly ineffective.Cornwall, ''The Undermining of Austria-Hungary'', pg. 202 In 1918 representatives from other
Before 1918 Italy had made attempts to spread propaganda through Austria-Hungary, but these efforts had been fairly ineffective.Cornwall, ''The Undermining of Austria-Hungary'', pg. 202 In 1918 representatives from other
Correspondence between Harukichi Shimoi and Giuseppe De Lorenzo
*Row, Thomas
Mobilizing the Nation: Italian Propaganda in the Great War
The Journal of Decorative and Propaganda Arts, Vol. 24, Design, Culture, Identity: The Wolfsonian Collection (2002), pp. 141-169 * Pesenti Campagnoni, Sarah
La guerra (in) tradotta. Informazione, propaganda e immagini dal fronte
Annali d'Italianistica, 2015, Vol. 33, THE GREAT WAR AND THE MODERNIST IMAGINATION IN ITALY (2015), pp. 241-258 * Pisa, Beatrice
Propaganda at Home (Italy)
in
1914-1918-online. International Encyclopedia of the First World War
* Cornwall, Mark. ''The Undermining of Austria-Hungary: The Battle for Hearts and Minds''. London: Macmillan, 2000. * Courriol, Marie-France. "Looking Back on the Myth of the Great War: Anti-rhetoric, War Culture and Film in Fascist Italy." ''Media, War and Conflict'', 7, 3 (2014): 342–64.
 In Italy as in other countries the outbreak of the First World War created new opportunities and channels for propaganda. The unusual circumstances of Italy’s entry into the war meant that the government played no active role in propaganda work during the early years of the war. Public opinion was served by a pro-war nationalist press that avoided the unpleasant details of life on the front, while the army regarded discipline as more important than morale, leaving soldiers’ welfare to the Church. The momentous Italian defeat at
In Italy as in other countries the outbreak of the First World War created new opportunities and channels for propaganda. The unusual circumstances of Italy’s entry into the war meant that the government played no active role in propaganda work during the early years of the war. Public opinion was served by a pro-war nationalist press that avoided the unpleasant details of life on the front, while the army regarded discipline as more important than morale, leaving soldiers’ welfare to the Church. The momentous Italian defeat at Caporetto
Kobarid (; ; ; ) is a settlement in Slovenia, the administrative centre of the Municipality of Kobarid.
Kobarid is known for the 1917 Battle of Caporetto, where the Italian retreat was documented by Ernest Hemingway in his novel ''A Farewell to A ...
saw an end to this laissez-faire approach and the beginnings of a more centralised and managed effort to motivate the public and the army to the national cause.
Pro-war propaganda to May 1915
 In the UK, France, Germany and Austria-Hungary, propaganda was mainly a centrally managed effort by the government and the armed forces from the outbreak of hostilities in August 1914. Italy did not enter the war until May 1915, and before this there was no organised state propaganda relating to the war. Instead, business interests and the press themselves took the lead.
Between the end of 1914 and 1915 there was a sustained campaign in the Italian press for the country to enter the war. There were strong views in favour of intervention among the leading economic, industrial and financial interests, particularly those linked to heavy industry and war production, such as
In the UK, France, Germany and Austria-Hungary, propaganda was mainly a centrally managed effort by the government and the armed forces from the outbreak of hostilities in August 1914. Italy did not enter the war until May 1915, and before this there was no organised state propaganda relating to the war. Instead, business interests and the press themselves took the lead.
Between the end of 1914 and 1915 there was a sustained campaign in the Italian press for the country to enter the war. There were strong views in favour of intervention among the leading economic, industrial and financial interests, particularly those linked to heavy industry and war production, such as Ansaldo
Ansaldo Energia S.p.A. is an Italian power engineering company based in Genoa, Italy. The original parent company, Gio. Ansaldo & C., was founded in 1853, and merged with Finmeccanica in 1993 (now Leonardo S.p.A.).
In 2024, the company's share ...
and Fiat
Fiat Automobiles S.p.A., commonly known as simply Fiat ( , ; ), is an Italian automobile manufacturer. It became a part of Fiat Chrysler Automobiles in 2014 and, in 2021, became a subsidiary of Stellantis through its Italian division, Stellant ...
, who financed Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (29 July 188328 April 1945) was an Italian politician and journalist who, upon assuming office as Prime Minister of Italy, Prime Minister, became the dictator of Fascist Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 un ...
’s pro-war paper Avanti!
''Avanti!'' (; Italian interjection – 'come in!') is a 1972 comedy film produced and directed by Billy Wilder, and starring Jack Lemmon and Juliet Mills. The screenplay by Wilder and I. A. L. Diamond is based on Samuel A. Taylor's pla ...
and the Banca Italiana di Sconto
Banca may refer to:
Places
* Bangka Island, an island lying east of Sumatra, part of Indonesia
* Banca, Pyrénées-Atlantiques, a commune of the Pyrénées-Atlantiques ''département'', France
* Banca, Tasmania, a locality in Tasmania, Australia
* ...
. These financed the press to urge the government to enter the war alongside the Entente
Entente, meaning a diplomatic "understanding", may refer to a number of agreements:
History
* Entente (alliance), a type of treaty or military alliance where the signatories promise to consult each other or to cooperate with each other in case o ...
. Most intellectuals were in favor of entering the war and many actively argued for it. The culmination of this campaign was Radiosomaggismo
''Radiosomaggismo'' (Italian language, Italian for the "Radiant days of May") describes a brief period of popular demonstrations in a number of Italian cities in May 1915, demanding the country’s entry into the First World War.
Background
Althou ...
.
In fact the majority of the Italian people did not support entering the war, but the government of Antonio Salandra
Antonio Salandra (; 13 August 1853 – 9 December 1931) was a conservative Italian politician, journalist, and writer who served as the 21st prime minister of Italy between 1914 and 1916. He ensured the entry of Italy in World War I on the side o ...
made little attempt to involve parliament in the decision. It was widely expected that the war would be short and produce substantial territorial gains for Italy, so there appeared to be little need for an organised propaganda effort.
Government and private initiatives after May 1915
Once war was declared, it was considered unnecessary to make the case for war beyondirredentism
Irredentism () is one State (polity), state's desire to Annexation, annex the territory of another state. This desire can be motivated by Ethnicity, ethnic reasons because the population of the territory is ethnically similar to or the same as the ...
and "sacred selfishness”. It was generally believed that the conflict would be short, and the conservative leaders Antonio Salandra
Antonio Salandra (; 13 August 1853 – 9 December 1931) was a conservative Italian politician, journalist, and writer who served as the 21st prime minister of Italy between 1914 and 1916. He ensured the entry of Italy in World War I on the side o ...
and Sidney Sonnino
Sidney Costantino, Baron Sonnino (; 11 March 1847 – 24 November 1922) was an Italian statesman, 19th prime minister of Italy and twice served briefly as one, in 1906 and again from 1909 to 1910. In 1901, he founded a new major newspaper, '' Il ...
did not consider public opinion or support for the war to be essential. For these reasons government involvement in propaganda activities remained sporadic. It was not until the government of Paolo Boselli
Paolo Boselli (; 8 June 1838 – 10 March 1932) was an Italian politician who served as the 34th prime minister of Italy during World War I.
Biography
Boselli was born in Savona, Liguria. Boselli was the first professor of science at the Uni ...
in 1916 that some form of ministerial responsibility for propaganda was first established. Two ministries without portfolio were created; one was for propaganda under Vittorio Scialoja
Vittorio Giulio Ippolito Camillo Scialoja (; 24 April 1856 – 19 November 1933) was an influential Italian Professor of Jurisprudence. His early focus was on Roman law, but he later broadened the scope of his research and teaching to embrace o ...
who in 1915 had founded the Unione Generale degli Insegnanti d’Italia ("General Union of Italian Teachers") aimed at involving teachers in promoting the mobilisation of society on the home front. The other was for civil assistance, under Ubaldo Comandini
Ubaldo Comandini (Cesena, 25 March 1869 – Rome, 1 March 1925) was an Italian lawyer, publicist and politician, several times a parliamentary deputy and minister for the Italian Republican Party.
Background an early life
Ubaldo Comandini was bo ...
. From July 1917 Comandini was in charge of internal propaganda, and from February 1918, of the new Commissariato Generale per l'Assistenza Civile e la Propaganda Interna (General Commission for Civil Assistance and Internal Propaganda).
Numerous private associations made up for the lack of state-directed propaganda and took on the burden of civil assistance; some of them arose in the early months of 1915 with the aim of national education and assistance to the working classes most affected by the mobilization. As the war went on they became more numerous, and many of these were brought together in the summer of 1917 in the Opere Federate di Assistenza e Propaganda Nazionale (Federation of National Assistance and Propaganda Organizations), directed by Comandini himself. This was a single private body, made up of 80 provincial secretaries and 4,500 commissioners, and it became the main organization used by the government for assistance and patriotic propaganda directed at the civilian population. Subsequently, the Federation provided the "P officers" with material for the troops at the front and supported the soldiers on leave. Both the Opere Federate and P Service
The P Service () was an organization set up for propaganda, surveillance and troop welfare within the Royal Italian Army. It was commissioned at the beginning of 1918 by the Italian High Command. Under the leadership of Luigi Cadorna it was not tho ...
collaborated with a wide range of partners, printed internal bulletins, and organised conferences to mobilise support for the war. They published talking points for conversations with soldiers and while the Opere Federate put on propaganda plays for the popular theatre, the P Service staged them for the troops.
Press censorship
 Although slow to mobilise public opinion through active propaganda, the government did act to censor the press. War correspondents were aware of the reality of the front and sent detailed reports to their editors. Nevertheless the reading public saw only articles that hid, and in some cases falsified, much of the truth, in a conscious process of disinformation in which much of the public did not seek objective information. Towards the end of 1915
Although slow to mobilise public opinion through active propaganda, the government did act to censor the press. War correspondents were aware of the reality of the front and sent detailed reports to their editors. Nevertheless the reading public saw only articles that hid, and in some cases falsified, much of the truth, in a conscious process of disinformation in which much of the public did not seek objective information. Towards the end of 1915 Giovanni Papini
Giovanni Papini (9 January 18818 July 1956) was an Italian journalist, essayist, novelist, short story writer, poet, literary critic, and Italian philosophy, philosopher. A controversial literary figure of the early and mid-twentieth century, he ...
wrote in Il Resto del Carlino that people limited themselves to looking at the official headlines and press releases and that soon, perhaps, they would not even read these anymore. This was probably due to the fact that readers, despite having the vague feeling of being deceived, sought in the newspapers only the confirmation of their illusions. Those lucky enough to escape the horrors of war preferred not to see them described in detail in the newspapers. As the historian Antonio Monti wrote in 1922, with the passage of time this meant that the press had served to deepen and widen the fatal division of the country into the two camps - the troops in the trenches on one hand and "imboscati" (draft-dodgers) on the other. This division greatly embittered the feelings of the soldiers towards "imboscati" and towards the journalists themselves. In the writings of officers and soldiers, it was common to find harsh and contemptuous judgments on the press, who were regarded as guilty of distorting the reality of battle by reducing the struggle of millions of men to mere spectacle, falsifying the soldiers' feelings and state of mind.
Restrictions on soldiers
The army censored the post of soldiers writing to their families, and only rarely granted home leave. The winter of 1915 saw a number of soldiers allowed to return home for the first time, with the intention that this would raise morale. In fact it had the opposite effect. The soldiers realized that the country was unaware of the realities of the war that the newspapers and the military were trying to hide. Hoping for a short war, the Salandra government did not want it to become unpopular so they took no measures to limit general consumption or impose austerity. The soldiers did not find their home towns proud of their sacrifices, ready to welcome them as heroes. The High Command not only forbade them from revealing anything about what was happening at the front, but they also made sure thecarabinieri
The Carabinieri (, also , ; formally ''Arma dei Carabinieri'', "Arm of Carabineers"; previously ''Corpo dei Carabinieri Reali'', "Royal Carabineers Corps") are the national gendarmerie of Italy who primarily carry out domestic and foreign poli ...
stopped the soldiers from entering cafes or from walking with a girl on their arm. Corrado De Vita
Corrado De Vita (1905, Noto – 21 September 1987, Rome), was an Italian journalist and writer.
Early life
He was born in Noto but completed his studies in Naples, graduating in Literature, a pupil of the Dante scholar :it:Francesco Torraca. His ...
wrote "I saw so many of those young people enjoying themselves in theaters and cafes that I felt like punching them and hating them more than the Austrians."
Propaganda at the front before Caporetto
 Before 1917 propaganda, recreational and welfare initiatives for soldiers were scarce and poorly managed. Propaganda was understood in traditional forms, such as speeches given by officers and invited speakers. As these speakers were exempted from military service, they appeared "privileged" in the eyes of the infantry. These proclamations about the reasons for the war were entirely alien to the language and mentality of the soldiers, who regarded the requirement to stand and listen to them as a waste of time, which lowered their morale.
Before 1917 propaganda, recreational and welfare initiatives for soldiers were scarce and poorly managed. Propaganda was understood in traditional forms, such as speeches given by officers and invited speakers. As these speakers were exempted from military service, they appeared "privileged" in the eyes of the infantry. These proclamations about the reasons for the war were entirely alien to the language and mentality of the soldiers, who regarded the requirement to stand and listen to them as a waste of time, which lowered their morale. Giuseppe Prezzolini
Giuseppe Prezzolini (27 January 1882 – 14 July 1982) was an Italian literary critic, journalist, editor and writer. He later became an American citizen.
Biography
Prezzolini was born in Perugia in January 1882, to Tuscan parents from Siena, L ...
wrote in his essay ''Vittorio Veneto'': "It was called propaganda to order soldiers to attention in a courtyard, after eight hours on duty, and there, taking away an hour of freedom, forcing them to listen to the chatter of a lawyer unused to the fatigue of war." For the vast majority of soldiers, their willingness to fight was not secured through effective propaganda or strong patriotic motivations, but despite this the Italian army gave proof of its reliability, commitment and obedience throughout the three and a half years of war. Only a few Italian soldiers fought with clear ideas and personal conviction, while most did so without understanding the reasons for the war. This was partly due to a very low level of education, and partly due to how the High Command managed the troops. From Luigi Cadorna
Marshal of Italy Luigi Cadorna, (4 September 1850 – 21 December 1928) was an Italian people, Italian general, Marshal of Italy and Count, most famous for being the Chief of Staff of the Italian Army from 1914 until 1917 during World War I ...
downwards, commanders were less concerned about motivation and more interested in maintaining discipline through corporal punishment.
Up to 1917 troop welfare activities were left to priests who operated with the permission of the High Command but without their involvement. Parish priests had always been important and trusted cultural mediators in peasant communities. One of them, Don :it:Giovanni Minozzi established a network of “Case del Soldato”, rest houses behind the front where infantrymen could relax, read, listen to music, attend theatrical performances, and obtain help writing letters home. Minozzi sensed that morale and willingness to fight required more subtle methods than lectures imposed by officers, and had to be based on the creation of welcoming and reassuring environments for the soldiers. To convince, it was first necessary to assist and instill trust. Patriotic and ideological discourse was not completely ignored in the Case del Soldato, but it was not imposed.
Before Caporetto organised propaganda initiatives took place only in the 2nd Army under Luigi Capello
Luigi Capello (14 April 1859 – 25 June 1941) was an Italian general, distinguished in both the Italo-Turkish War (1911–12) and World War I. During the Italo-Turkish War he served in Cyrenaica and took part in operations near Derna, comman ...
. Army documents from June 1917 show that there was an internal propaganda office, while material and moral assistance was generally left to priests, as for the rest of the army. Capello intended to use propaganda to raise the morale of his troops, which had been undermined by the battles of the Isonzo
The Battles of the Isonzo (also known as the Isonzo Front by historians, or the Soča Front - ) were a series of twelve battles between the Austria-Hungary, Austro-Hungarian and Italian armies in World War I mostly on the territory of present-d ...
and established a Propaganda and Education Office. Its first major change was to replace the figures invited to address the men at patriotic meetings. Until then, these had been lawyers, politicians, or senior officers; now they invited with lower officers "since the soldier prefers to listen to his officer with whom he is in daily contact, tied by the esteem and affection that arise from the community of deprivation and risks" and even with ordinary soldiers. To do this, Capello and his collaborator in the Office, Alessandro Casati
Alessandro Casati (5 March 1881 – 4 June 1955) was an Italian academic, commentator, and politician. He served as a Senate of the Kingdom of Italy, senator :it:Senatori della XXVI legislatura del Regno d'Italia#1923, between 1923 and 1924 and ...
, chose eighty men, half of whom were officers, explaining to them the themes and techniques to be adopted. With these men, the soldiers had the impression of actively participating in a discussion rather than passively attending a meeting. On 24 July Capello confirmed the usefulness of these new meetings, which resumed on 11 September after being interrupted by the eleventh battle of the Isonzo. Capello then decided to employ the interventionist artist Ardengo Soffici
Ardengo Soffici (7 April 1879 – 19 August 1964) was an Italian writer, painter, poet, sculptor and intellectual.
Early life
Soffici was born in Rignano sull'Arno, near Florence. In 1893 his family moved to the latter city, where he stud ...
to support propaganda work by illustrating brochures and magazines aimed at the soldier. The experiment was not followed up due to the breakthrough of Caporetto, but Capello's experiments were subsequently used in a decisive way by the new Servizio P (P Service).
Propaganda at the front after Caporetto
 The defeat at
The defeat at Caporetto
Kobarid (; ; ; ) is a settlement in Slovenia, the administrative centre of the Municipality of Kobarid.
Kobarid is known for the 1917 Battle of Caporetto, where the Italian retreat was documented by Ernest Hemingway in his novel ''A Farewell to A ...
marked a turning point in army practice. A new Propaganda Office ( Servizio P) was set up with the task of actively persuading men of the need to fight. The main activities of the P service at the front were preparing conversational talking points, which reached the soldiers through new trench newspapers, which described life at the front, without denying its hardship, in a playful, moving and reassuring tone, with new visual and verbal communication techniques. This was the first large-scale operation to condition and form popular opinion in a national-patriotic direction, and it drew on scholars, writers, designers, graphic designers and pedagogues who were effectively the mass media experts of the time, headed by Giuseppe Lombardo Radice
Giuseppe Lombardo Radice (Catania, June 24, 1879 - Cortina d'Ampezzo, August 16, 1938) was an Italian pedagogist and philosopher.
Early life and career
He was born in Catania on June 24, 1879 (but his birth was registered late, on June 28) to Luci ...
. Radice had aimed at modernizing the authoritarian methods used in schools, and in the same way he considered the soldiers as children to be taught, enjoying themselves as they learned the Italian language and national ideology.
Shaping public opinion after Caporetto
Defeat at the battle of Caporetto in October 1917 brought about a revolution in Italian wartime propaganda under a new prime minister,Vittorio Emanuele Orlando
Vittorio Emanuele Orlando (; 19 May 1860 – 1 December 1952) was an Italian statesman, who served as the prime minister of Italy from October 1917 to June 1919. Orlando is best known for representing Italy in the 1919 Paris Peace Conference with ...
and a new commander more sensitive to the morale of his men, Armando Diaz
Armando Diaz, 1st Duke della Vittoria, (5 December 1861 – 28 February 1928) was an Italian general and a Marshal of Italy. He is mostly known for his role as Chief of Staff of the Regio Esercito during World War I from November 1917. He ...
, who replaced Cadorna. The country's citizens and industries had to be mobilized in the face of Austrian invasion and the government realized that a major propaganda effort was now needed both on the home front and on the battlefield. The country and the army began to feel greater solidarity. As enemy soldiers entered Italian territory for the first time, the war took on the character of defense of homeland and family. It seemed to many that the defeat had worked a real "miracle" both among the troops and in public opinion.
Before these initiatives began to take effect, many gloomy forecasts circulated around the country. In the months after Caporetto there was speculation about a further retreat beyond Piave to the Mincio
The Mincio (; ; ; ; ) is a river in the Lombardy region of northern Italy.
The river is the main outlet of Lake Garda. It is a part of the ''Sarca-Mincio'' river system which also includes the river Sarca and the Lake Garda. The river starts ...
or even beyond the Po, and the possibility of concluding a separate peace with Austria-Hungary was discussed. To try to raise the morale of the country, the editor of Corriere della Sera, Luigi Albertini
Luigi Albertini (19 October 1871 – 29 December 1941) was an influential Italian newspaper editor, member of the Italian Parliament, and historian of the First World War. As editor of one of Italy's best-known newspapers, of Milan, he was a cha ...
, published several long articles on how and why Italy should not withdraw from the war. Luigi Einaudi
Luigi Numa Lorenzo Einaudi (; 24 March 1874 – 30 October 1961) was an Italian politician, economist and banker who served as President of Italy from 1948 to 1955 and is considered one of the founding fathers of the 1946 Italian institutional ...
contributed articles demonstrating the impossibility of a separate peace since Italy depended economically on its allies. The most ardent interventionists, led by the Comandini, formed the "fascia for national defense", in order to fight what they called the "parliamentary defeatism" of the new Orlando government. Throughout the country, groups and action committees multiplied with the aim of mobilizing citizens against defeatists, traitors and spies.
In the wake of this crisis, in November 1917 many of the most notable Italian intellectuals joined in the "Committee for National Self-Examination” in order to rewrite the whole history of Italy, from the Renaissance to the Great War, in the light of Caporetto. This committee, joined by the philosophers Benedetto Croce
Benedetto Croce, ( , ; 25 February 1866 – 20 November 1952)
was an Italian idealist philosopher, historian, and politician who wrote on numerous topics, including philosophy, history, historiography, and aesthetics. A Cultural liberalism, poli ...
and Giovanni Gentile
Giovanni Gentile ( , ; 30 May 1875 – 15 April 1944) was an Italian pedagogue, philosopher, and politician.
He, alongside Benedetto Croce, was one of the major exponents of Italian idealism in Italian philosophy, and also devised his own sys ...
, embarked on a wholesale critical review of Italian history, highlighting how Caporetto was a moral defeat to which an educational and ideological explanation was required. However it was very difficult to define what the Italian people really thought or expected. Censorship did not allow the press to expose the events around the defeat freely, or to share its readers’ opinions about them, concerning the war with a certain freedom, nor the opinion that readers had about it. While reports on the mood of the population generally indicated good levels of national cohesion, there were some instances of discontent. Ferdinando Martini
Ferdinando Martini (30 July 1840 – 24 April 1928) was an Italian writer and politician. He was governor of Eritrea for from late 1897 to early 1907.
Biography
Born in Florence, he worked as journalist and writer. He collaborated with '' Il F ...
, a member of the "National Defence Group", said that in Valdinievole
Valdinievole or Val di Nievole (; "Valley of the Nievole (River)") is an area in the south-western part of the province of Pistoia, Tuscany, Italy.
Geography
The area is made up of 11 comuni: Buggiano, Chiesina Uzzanese, Larciano, Lamporecchi ...
the peasants were shouting "Long live the Germans!", While on December 15 Croce wrote a letter to Orlando, warning him that the "Neapolitan populace was spreading plans for revolt".
Many factors contributed to popular attitudes towards the war. Public assemblies were forbidden during the war; workers could be moved to where they were needed for war production and many women had taken up waged work for the first time; long working hours, food shortages and inflation led to sporadic strikes and occasional riots. After Caporetto the government took new steps to try and keep the public onside with the war, promising that after the war there would be land for the peasants and the right to vote.
Italian propaganda in Allied countries
Before the Orlando government to took office, the efforts of Italian government propaganda in other countries were as limited as they were at home. In the main, advocacy for Italy was led by local associations of expatriate Italians. In Britain, these included the "Pro Italia" committee set up in London in June 1915, who organised fundraising charity sales and similar events. There was also a British Italian League and a Society of the Friends of Italy. At a more official level, there was also the Italian Chamber of Commerce and theDante Alighieri Society
The Dante Alighieri Society () is a society that promotes Italian culture and language around the world. Today this society is present in more than 60 countries.
It was formed in Italy in July 1889. The society was named after Dante Alighieri (12 ...
with offices in London, Glasgow and Cardiff. In addition, a group of correspondents from major Italian newspapers based in Britain had established a press office, the Italian Information Bureau, that worked closely with the Italian embassy and disseminated news from the Italian front in war bulletins.
On 1 November 1917 Orlando established an Undersecretariat for Propaganda under :it:Romeo Gallenga Stuart with a particular focus on overseas work. Its main purpose was to build public support for Italian territorial claims at the end of the war, and securing British public support was seen as critically important. Within days, the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
published all the secret treaties
''Secret Treaties'' is the third studio album by American rock band Blue Öyster Cult, released on April 5, 1974 by Columbia. It features the same band members and production team as their previous album.
The album spent 14 weeks in the US a ...
to which Tsarist Russia had been party, exposing to the world for the first time the provisions of the 1915 Treaty of London
The Treaty of London (; ) or the Pact of London (, ) was a secret agreement concluded on 26 April 1915 by the United Kingdom, France, and Russia on the one part, and Kingdom of Italy, Italy on the other, in order to entice the last to enter ...
including Italy's territorial demands in the Balkans. In January 1918 US President Wilson published his Fourteen Points
The Fourteen Points was a statement of principles for peace that was to be used for peace negotiations in order to end World War I. The principles were outlined in a January 8, 1918 speech on war aims and peace terms to the United States Congress ...
, emphasising the national rights of what was later the Kingdom of Yugoslavia
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia was a country in Southeast Europe, Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 1918 to 1929, it was officially called the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes, but the term "Yugoslavia" () h ...
, which were at odds with Italy's demands.
A series of informal contacts began in London which gave rise to the idea of drafting an informal agreement on which any official negotiations could be based. The goal was achieved, during the meetings held on 14 and 18 December 1917 at the home of Wickham Steed
Henry Wickham Steed (10 October 1871 – 13 January 1956) was an English journalist and historian. He was editor of ''The Times'' from 1919 to 1922.
Early life
Born in Long Melford, England, Steed was educated at Sudbury Grammar School ...
, where the Yugoslav Committee
The Yugoslav Committee (, , ) was a World War I-era, unelected, '' ad-hoc'' committee. It largely consisted of émigré Croat, Slovene, and Bosnian Serb politicians and political activists whose aim was the detachment of Austro-Hungarian l ...
met the men responsible for Italian propaganda in England: the Corriere della Sera journalist :it:Guglielmo Emanuel and Colonel Filippo De Filippi. These meetings eventually led to the Torre- Trumbić agreement (7 March 1918), an important step towards the convening of the congress of oppressed nationalities in Rome in April 1918.
The Italian Foreign Action Bureau still faced difficulties. A lot of the material sent to it in London was not suitable for use; sometimes pamphlets were delivered translated into Spanish, or things just arrived too late to be used as planned. One of the materials it published was a translation of a soldier’s letters to his family, ''Letters and Drawings of Enzo Valentini''. Distributed to schools and universities, it was intended to evoke sympathy among the British public. A large number of general interest materials were issued - posters, photographs and postcards - which appeared in clubs, hospitals, and theatres. Supporting a drive to create general positive views about Italy, there were film and theatrical performances, while
De Filippi continued to organize meetings and conferences. From 13 to 23 January 1918 he was in Leeds, Sheffield and Manchester explaining Italy’s war aims, and the essential nature of continued Allied support so that Italy could continue in the common task. Between 300 and 500 people attended each meeting.
Meanwhile the British Italian League and the Royal Society of Literature organised a visit by a group of Italian scholars to the main English and Scottish universities. In May 1918 the "Italian university mission" of important Italian academics, visited the universities of Oxford, Cambridge, Manchester, Sheffield, Leeds, Edinburgh and Glasgow. The British-Italian League also hosted a charity exhibition at the Mendoza Galleries of London featuring the art of the Cascella brothers, who had served in Albania and in Trentino.
Italy still held the initiative on territorial claims when it convened The congress of the oppressed nationalities of Austria-Hungary in Rome from 8 to 10 April. At the end of this the parties agreed the right of the Italian, Yugoslav, Polish, Czech and Romanian peoples to freedom in the “Pact of Rome”. The commitments in the Torre-Trumbić agreement were restated, while the areas of disagreement were left unresolved. The Congress was attended by figures from across the range of Italian politics, but their failure to do anything after the Congress to back up their declarations in support of other nationalities meant that nothing substantive was gained by holding it. As the ambiguities of Italy’s stance towards its neighbours remained unresolved, Britain, France and the United States grew stronger and clearer in their support for the creation of a Yugoslav state.
A conference of the Allies was held in London 14 to 17 August 1918, in London, under Lord Northcliffe
Alfred Charles William Harmsworth, 1st Viscount Northcliffe (15 July 1865 – 14 August 1922), was a British newspaper and publishing magnate. As owner of the ''Daily Mail'' and the ''Daily Mirror'', he was an early developer of popular journal ...
. This meeting put pressure on Italy to make a clear declaration in favour of Yugoslav independence and unity. Foreign Minister Sonnino
Sonnino is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Latina, in the Lazio region of central Italy.
It is the birthplace of Italian national team footballer Alessandro Altobelli, and Roman Catholic archbishop Velasio de Paolis.
History
Originati ...
was not willing to be pushed into this. He was already encouraging much more nationalist propaganda overseas, through the Dante Alighieri Society. Thus while much of the quasi-official Italian propaganda in Britain aimed to build sympathy and support, government channels took a different and much harder line. After the London meeting Sonnino demanded that all propaganda activities abroad should immediately be placed in the charge of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
The Italian victory at Vittorio Veneto
Vittorio Veneto is a city and ''comune'' situated in the Province of Treviso, in the region of Veneto, Italy, in the Cardinal direction, northeast of Italy, between the Piave and the Livenza rivers, borders with the following municipalities:
Alpa ...
only hardened attitudes further, with Italy’s territorial demands being asserted more clearly, and obviously at odds with the wishes of the other Allies. Ambassador Imperiali reported from London that “we are undoubtedly losing ground here". ''The Observer
''The Observer'' is a British newspaper published on Sundays. First published in 1791, it is the world's oldest Sunday newspaper.
In 1993 it was acquired by Guardian Media Group Limited, and operated as a sister paper to ''The Guardian'' ...
'', which had always been friendly, now criticized Italian politics. Steed's magazine, ''The New Europe'', was openly against Italy. By the time the armistice was signed therefore, Italy’s propaganda efforts had gained her nothing because of the ambiguity of her positions and lack of trust in her statements.
Italian propaganda in Austria-Hungary
 Before 1918 Italy had made attempts to spread propaganda through Austria-Hungary, but these efforts had been fairly ineffective.Cornwall, ''The Undermining of Austria-Hungary'', pg. 202 In 1918 representatives from other
Before 1918 Italy had made attempts to spread propaganda through Austria-Hungary, but these efforts had been fairly ineffective.Cornwall, ''The Undermining of Austria-Hungary'', pg. 202 In 1918 representatives from other Allies of World War I
The Allies or the Entente (, ) was an international military coalition of countries led by the French Republic, the United Kingdom, the Russian Empire, the United States, the Kingdom of Italy, and the Empire of Japan against the Central Powers ...
met with Italy to help it come up with propaganda techniques
Propaganda techniques are methods used in propaganda to convince an audience to believe what the propagandist wants them to believe. Many propaganda techniques are based on social psychology, socio-psychological research. Many of these same tech ...
against Austria-Hungary. This resulted in the Padua Commission, a military-civilian agency led mostly by Italians, formed to co-ordinate a propaganda offensive. One of the commission's leaders was :it:Ugo Ojetti who worked together with the Yugoslav Committee
The Yugoslav Committee (, , ) was a World War I-era, unelected, '' ad-hoc'' committee. It largely consisted of émigré Croat, Slovene, and Bosnian Serb politicians and political activists whose aim was the detachment of Austro-Hungarian l ...
and came up with a plan to appeal to the minority groups within Austria-Hungary. The plan included the spread of pamphlets, manifestos and flyers to promote an independent Yugoslavia. The intention as to weaken the loyalty of troops from Slavic ethnic groups, encouraging them to surrender to Italy or turn on Austria-Hungary from within its borders.Cornwall, ''The Undermining of Austria-Hungary'', pg. 204
Between May 15 and early November 1918, around 60 million copies of 643 different manifestos and almost 2 million copies of 80 news sheets were spread over Austria-Hungary; three times more than the volume of propaganda spread over Germany by the British during the entire war.Cornwall, ''The Undermining of Austria-Hungary'', pg. 209 Soon, pro-independence leaflets were finding their way to the front lines. Soldiers then took the leaflets home and shared them with their household or community. Austria-Hungary immediately grew concerned over the disturbances that might be caused on the front lines and domestically, and was forced to divert some of its attention from active propaganda directed at Italy to establishing defensive anti-propaganda campaigns. The majority of the leaflets were aimed at Croats, Slovenes and Serbs to rise against the Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is ...
and to establish their own independent nation. One leaflet, targeting Slovenes and Croats, stated, "The decisive battle has begun. Either justice will conquer and the sun of freedom for all nations will shine, or the coarse, brutal force of German militaristic barbarism will conquer, which would signify: further slavery. At this greatest moment it is the duty of every Serb, Croat and Slovene not only not to fight on the Austrian side, but to thrust their bayonets into Magyar and German chests". The Yugoslav Committee praised the way the Italians treated their prisoners-of-war and affirmed Italy's support for an independent Yugoslavia. On the battlefield, Austro-Hungarian soldiers began surrendering to the Italian military, carrying the pamphlets with them in the hope of better treatment. Most soldiers said they were surrendering because of hunger and the lack of supplies, but the propaganda was an prompt for them to abscond. The Austro-Hungary military pursued a tough campaign of investigations into any propaganda it discovered.
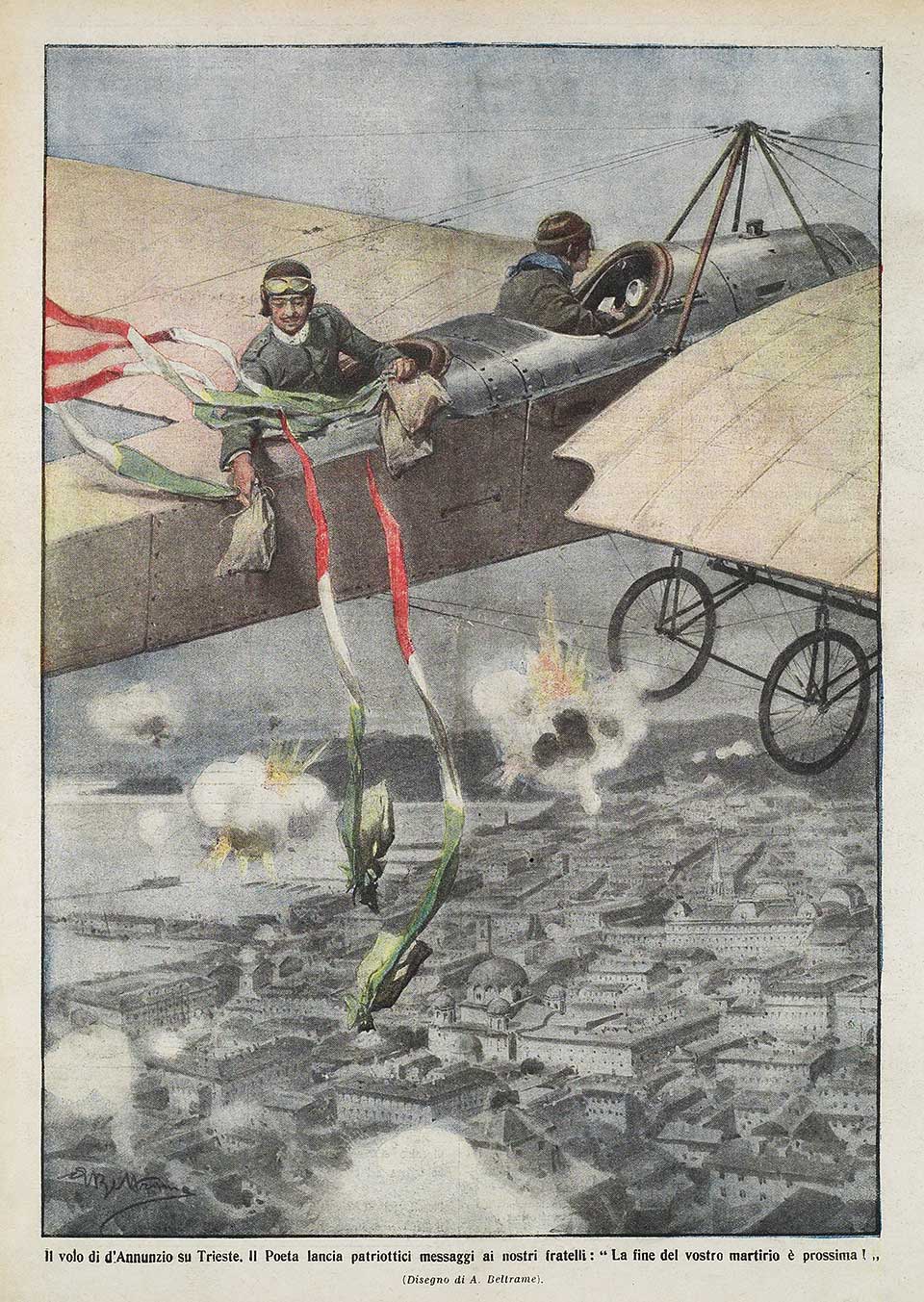
German military support to Austria-Hungary had made a decisive difference on the Italian front at Caporetto. When Germany pulled back its troops in 1918 to move them to the Western Front, Austria-Hungary was left more exposed. To demoralise its troops, Italy spread news from the Western Front describing the Germans as being obliterated by the British, French, and Americans. Italian propaganda stating that 'an awful abyss yawns under the feet of the German people', and that Habsburg soldiers ought to break their own chains immediately if they were not to suffer the same dismal fate".Cornwall, ''The Undermining of Austria-Hungary'', pg. 344 In the summer of 1918 Gabriele D'Annunzio’s flight over Vienna
The Flight over Vienna was an air raid during World War I undertaken by Italian poet and nationalist Gabriele D'Annunzio on 9 August 1918. With 11 Ansaldo SVA aircraft from his team, the 87ma ''squadriglia'' (squadron) called ''La Serenissim ...
to drop propaganda leaflets was a high profile exercise to demoralise Austria-Hungary's civilian population.
Italian propaganda in Japan
Despite having very few economic, cultural, or political commonalities, the Japanese poetHarukichi Shimoi
was a Japanese poet, translator and writer. Shimoi lived in Italy for many years and was an important promoter of cultural exchange between Japan and Italy.
Shimoi translated works from Yosano Akiko and Matsuo Bashō into Italian, and conver ...
was extremely energetic in promoting Japanese-Italian relationships. He joined the Arditi
Arditi (from the Italian verb ''ardire'', 'to dare', and translates as "The Daring nes) was the name adopted by a Royal Italian Army elite special force of World War I. They and the opposing German '' Stormtroopers'' were the first modern s ...
to help in the war effort, acted as a liaison between Gabrielle D'Annunzio and then-newspaper editor Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (29 July 188328 April 1945) was an Italian politician and journalist who, upon assuming office as Prime Minister of Italy, Prime Minister, became the dictator of Fascist Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 un ...
, and published a book of wartime correspondences in Italian and Japanese to promote the Italian struggle abroad. This cross cultural promotion would eventually culminate in the Rome-Tokyo Raid of Arturo Ferrarin
Arturo Ferrarin (13 February 1895 – 18 July 1941) was an Italian pioneer aviator. His exploits included winning the "Rome-Tokyo Raid" air race in 1920 and a non-stop flight from Italy to Brazil in 1928 with fellow aviator Carlo Del Prete. The l ...
.Reto Hofmann, The Fascist Effect: Japan and Italy, 1915-1952
Further reading
*Shimoi, HarukichiCorrespondence between Harukichi Shimoi and Giuseppe De Lorenzo
*Row, Thomas
Mobilizing the Nation: Italian Propaganda in the Great War
The Journal of Decorative and Propaganda Arts, Vol. 24, Design, Culture, Identity: The Wolfsonian Collection (2002), pp. 141-169 * Pesenti Campagnoni, Sarah
La guerra (in) tradotta. Informazione, propaganda e immagini dal fronte
Annali d'Italianistica, 2015, Vol. 33, THE GREAT WAR AND THE MODERNIST IMAGINATION IN ITALY (2015), pp. 241-258 * Pisa, Beatrice
Propaganda at Home (Italy)
in
1914-1918-online. International Encyclopedia of the First World War
* Cornwall, Mark. ''The Undermining of Austria-Hungary: The Battle for Hearts and Minds''. London: Macmillan, 2000. * Courriol, Marie-France. "Looking Back on the Myth of the Great War: Anti-rhetoric, War Culture and Film in Fascist Italy." ''Media, War and Conflict'', 7, 3 (2014): 342–64.
References
{{Propaganda in Europe Italy in World War I World War I propaganda Propaganda in Italy