Flying-fox on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 ''Pteropus'' (suborder
''Pteropus'' (suborder
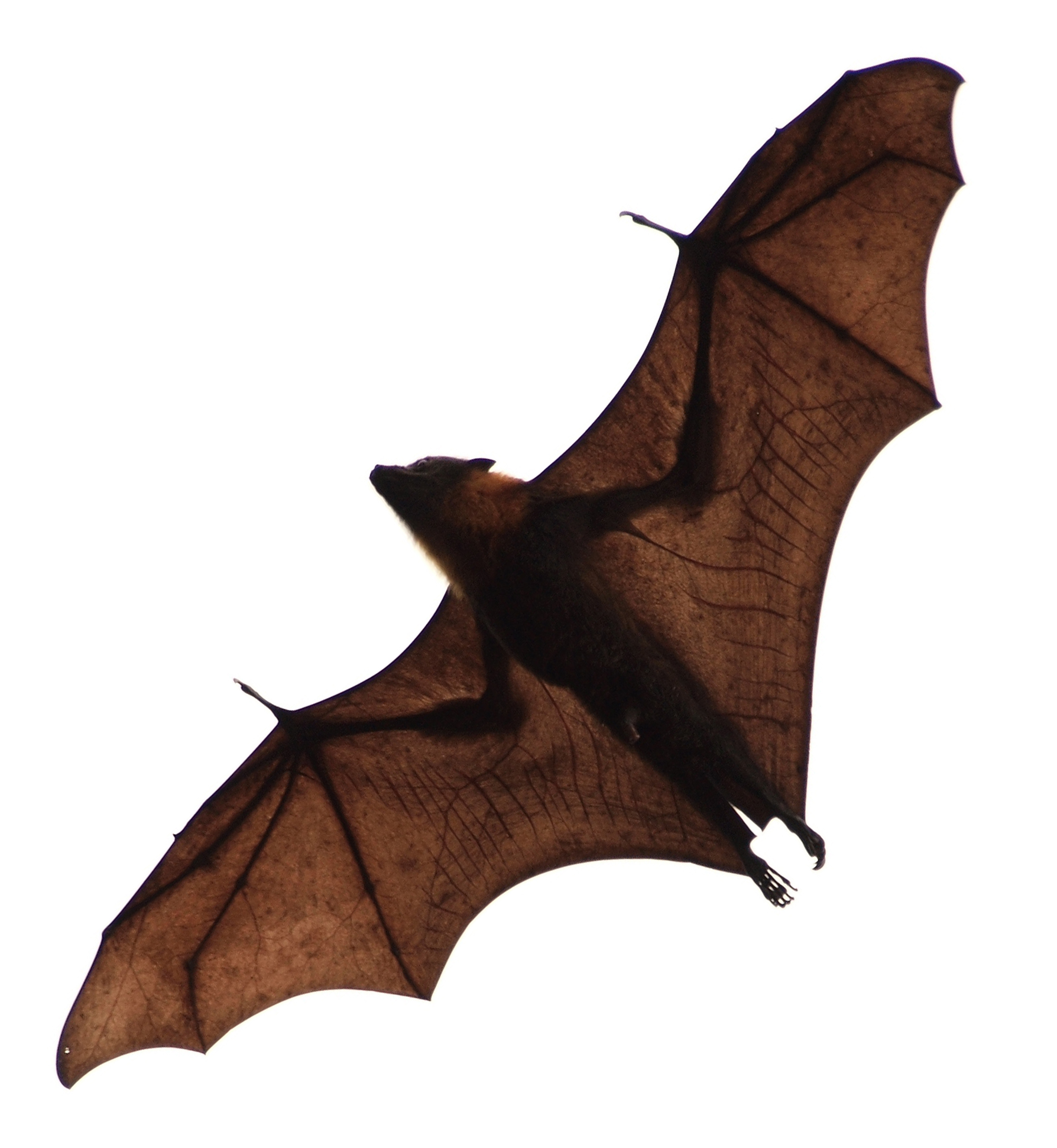 Flying fox species vary in body weight, ranging from . Across all species, males are usually larger than females.
The
Flying fox species vary in body weight, ranging from . Across all species, males are usually larger than females.
The
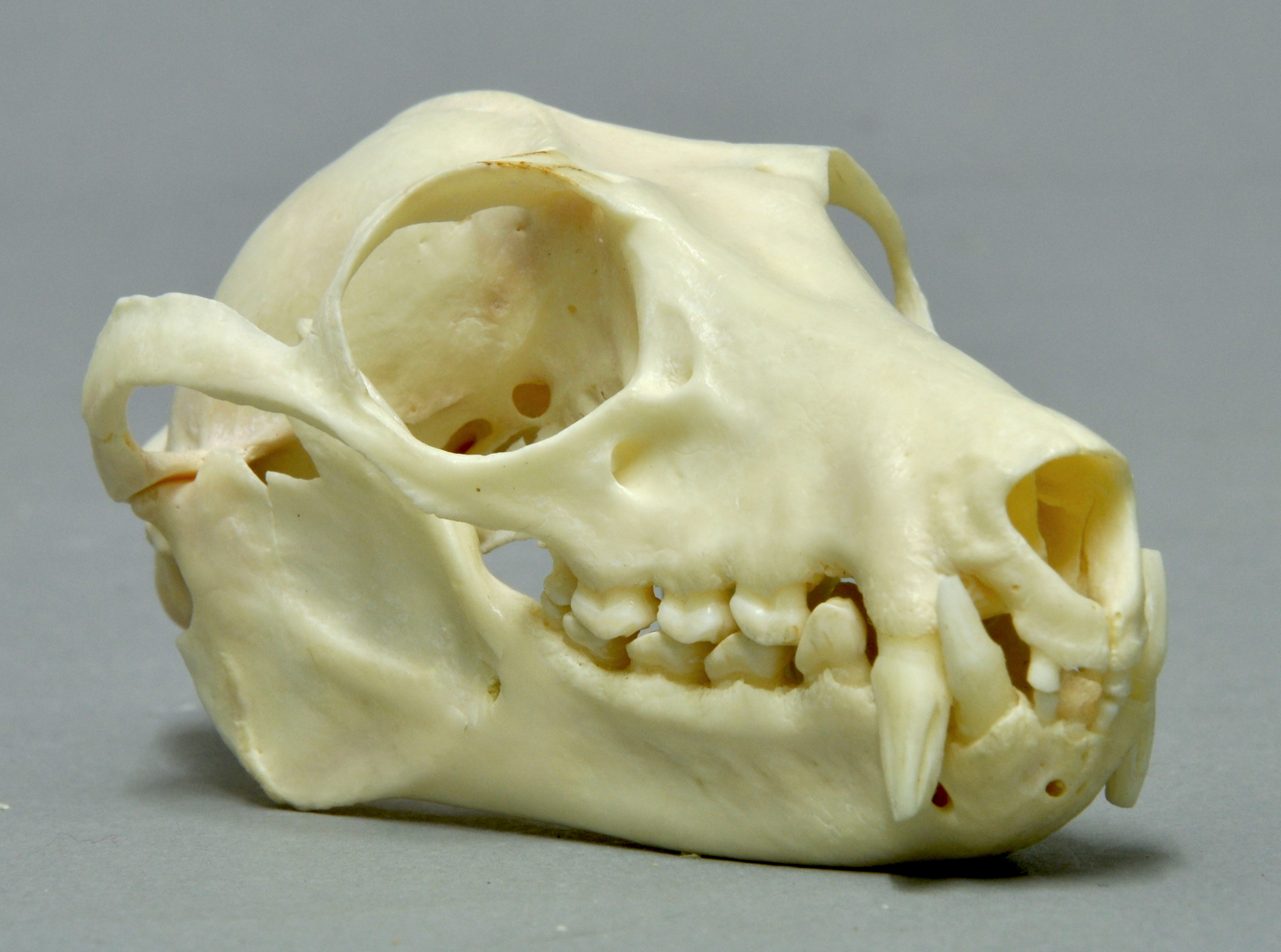 The skulls of ''Pteropus'' species are composed of 24 bones, the
The skulls of ''Pteropus'' species are composed of 24 bones, the
 Flying foxes rely heavily on their sense of smell.
They have large
Flying foxes rely heavily on their sense of smell.
They have large
 Many species of flying fox are
Many species of flying fox are
 Most flying fox species are
Most flying fox species are
 Of the 62 flying fox species evaluated by the
Of the 62 flying fox species evaluated by the
 Flying foxes species are declining or going extinct as a result of several human impacts to their environments, in addition to natural phenomena. Their populations are especially vulnerable to threats because the litter size is usually only individual and females generally only have one litter per year. Even when nearly every female (90%) successfully produces and raises young, if a population's
Flying foxes species are declining or going extinct as a result of several human impacts to their environments, in addition to natural phenomena. Their populations are especially vulnerable to threats because the litter size is usually only individual and females generally only have one litter per year. Even when nearly every female (90%) successfully produces and raises young, if a population's
 Several species of endangered flying fox are bred in captivity to augment their population sizes. Critically endangered Livingstone's fruit bats were taken from the wild starting in 1995 to create a
Several species of endangered flying fox are bred in captivity to augment their population sizes. Critically endangered Livingstone's fruit bats were taken from the wild starting in 1995 to create a
 Many flying foxes species are killed for
Many flying foxes species are killed for

 Flying foxes are the
Flying foxes are the
 Flying foxes are featured in many indigenous cultures and traditions.
A
Flying foxes are featured in many indigenous cultures and traditions.
A
 ''Pteropus'' (suborder
''Pteropus'' (suborder Yinpterochiroptera
The Yinpterochiroptera (or Pteropodiformes) is a suborder of the Chiroptera, which includes taxa formerly known as megabats and five of the microbat families: Rhinopomatidae, Rhinolophidae, Hipposideridae, Craseonycteridae, and Megadermatidae. T ...
) is a genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
of megabat
Megabats constitute the Family (biology), family Pteropodidae of the Order (biology), order Chiroptera. They are also called fruit bats, Old World fruit bats, or—especially the genus, genera ''Acerodon'' and ''Pteropus''—Pteropus, flyin ...
s which are among the largest bats in the world. They are commonly known as fruit bats or flying foxes, among other colloquial names.
They live in South Asia
South Asia is the southern Subregion#Asia, subregion of Asia that is defined in both geographical and Ethnicity, ethnic-Culture, cultural terms. South Asia, with a population of 2.04 billion, contains a quarter (25%) of the world's populatio ...
, Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
, East Africa
East Africa, also known as Eastern Africa or the East of Africa, is a region at the eastern edge of the Africa, African continent, distinguished by its unique geographical, historical, and cultural landscape. Defined in varying scopes, the regi ...
, and some oceanic islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans.
There are at least 60 extant
Extant or Least-concern species, least concern is the opposite of the word extinct. It may refer to:
* Extant hereditary titles
* Extant literature, surviving literature, such as ''Beowulf'', the oldest extant manuscript written in English
* Exta ...
species in the genus.
Flying foxes eat fruit and other plant matter, and occasionally consume insects as well. They locate resources with their keen sense of smell.
Most, but not all, are nocturnal
Nocturnality is a ethology, behavior in some non-human animals characterized by being active during the night and sleeping during the day. The common adjective is "nocturnal", versus diurnality, diurnal meaning the opposite.
Nocturnal creatur ...
. They navigate with keen eyesight, as they cannot echolocate.
They have long life spans and low reproductive outputs, with females of most species producing only one offspring per year. Their slow life history makes their populations vulnerable to threats such as overhunting
Overexploitation, also called overharvesting or ecological overshoot, refers to harvesting a renewable resource to the point of diminishing returns. Continued overexploitation can lead to the destruction of the resource, as it will be unable to ...
, culling
Culling is the process of segregating organisms from a group according to desired or undesired characteristics. In animal breeding, it is removing or segregating animals from a breeding stock based on a specific trait. This is done to exagge ...
, and natural disasters. Six flying fox species have been made extinct
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
in modern times by overhunting. Flying foxes are often persecuted for their real or perceived role in damaging crops. They are ecologically beneficial by assisting in the regeneration of forests via seed dispersal
In spermatophyte plants, seed dispersal is the movement, spread or transport of seeds away from the parent plant.
Plants have limited mobility and rely upon a variety of dispersal vectors to transport their seeds, including both abiotic vectors, ...
. They benefit ecosystems and human interests by pollinating
Pollination is the transfer of pollen from an anther of a plant to the stigma of a plant, later enabling fertilisation and the production of seeds. Pollinating agents can be animals such as insects, for example bees, beetles or butterflies; birds ...
plants.
Like other bats, flying foxes are relevant to humans as a source of disease, as they are the reservoirs
A reservoir (; ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam, usually built to store fresh water, often doubling for hydroelectric power generation.
Reservoirs are created by controlling a watercourse that drains an existing body of water, interrup ...
of rare but fatal disease agents including Australian bat lyssavirus
Australian bat lyssavirus (ABLV) is a enzootic virus closely related to the rabies virus. It was first identified in a 5-month-old juvenile black flying fox (''Pteropus alecto'') collected near Ballina, New South Wales, Ballina in northern New ...
, which causes rabies
Rabies is a viral disease that causes encephalitis in humans and other mammals. It was historically referred to as hydrophobia ("fear of water") because its victims panic when offered liquids to drink. Early symptoms can include fever and abn ...
, and Hendra virus
Hendra virus (''Henipavirus hendraense'') is a zoonotic virus found solely in Australia. First isolated in 1994, the virus has since been connected to numerous outbreaks of disease in domestic horses and seven human cases. Hendra virus belongs to ...
; seven known human deaths have resulted from these two diseases. Nipah virus
Nipah virus (''Henipavirus nipahense'') is a bat-borne, Zoonosis, zoonotic virus that causes Nipah virus infection in humans and other animals, a disease with a very high mortality rate (40-75%). Numerous disease outbreaks caused by Nipah virus ...
is also transmitted by flying foxes—it affects more people, with over 100 attributed fatalities. They have cultural significance to indigenous people, with appearances in traditional art, folklore, and weaponry. Their fur and teeth were used as currency in the past. Some cultures still use their teeth as currency today.
Taxonomy and etymology
The genus name ''Pteropus'', fromAncient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
'πτερόν' (pterón), meaning "wing", and 'πούς' (poús), meaning "foot", was coined by French zoologist Mathurin Jacques Brisson
Mathurin Jacques Brisson (; 30 April 1723 – 23 June 1806) was a French zoologist and natural philosophy, natural philosopher.
Brisson was born on 30 April 1723 at Fontenay-le-Comte in the Vendée department of western France. Note that page 14 ...
in 1762.
Prior to 1998, genus authority was sometimes given to German naturalist Johann Christian Polycarp Erxleben
Johann Christian Polycarp Erxleben (; 22 June 1744 – 19 August 1777) was a German naturalist from Quedlinburg.
Erxleben was professor of physics and veterinary medicine at the University of Göttingen
The University of Göttingen, officia ...
. Although the Brisson publication (1762) predated the Erxleben publication (1777), thus giving him preference under the Principle of Priority
Priority is a principle in Taxonomy (biology), biological taxonomy by which a valid scientific name is established based on the oldest available name. It is a decisive rule in Botanical nomenclature, botanical and zoological nomenclature to recogn ...
, some authors gave preference to Erxleben as genus authority because Brisson's publication did not consistently use binomial nomenclature
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammatical forms, altho ...
. In 1998, the International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature
The International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) is an organization dedicated to "achieving stability and sense in the scientific naming of animals". Founded in 1895, it currently comprises 26 commissioners from 20 countries.
Orga ...
(ICZN) decided that Brisson's 1762 publication was a "rejected work" for nomenclatural purposes. Despite rejecting the majority of the publication, the ICZN decided to conserve a dozen generic names from the work and retain Brisson as authority, including ''Pteropus''.
The type species
In International_Code_of_Zoological_Nomenclature, zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the spe ...
of the genus is the Mauritian flying fox
The Mauritian flying fox (''Pteropus niger''), also known as Greater Mascarene flying fox or Mauritius fruit bat is a large megabat species endemic to Mauritius and La Réunion
LA most frequently refers to Los Angeles, the second most populou ...
, ''Pteropus niger'' (described as ''Vespertilio vampyrus niger'' by Robert Kerr in 1792).
The decision to designate ''P. niger'' as the type species was made by the ICZN through their plenary power
A plenary power or plenary authority is a complete and absolute power to take action on a particular issue, with no limitations. It is derived from the Latin language, Latin term .
United States
In United States constitutional law, plenary powe ...
s over biological nomenclature. The phrase "flying fox" has been used to refer to ''Pteropus'' bats since at least 1759.
Species
Description
External characteristics
 Flying fox species vary in body weight, ranging from . Across all species, males are usually larger than females.
The
Flying fox species vary in body weight, ranging from . Across all species, males are usually larger than females.
The large flying fox
The large flying fox (''Pteropus vampyrus'', formerly ''Pteropus giganteus''), also known as the greater flying fox, Malayan flying fox, Malaysian flying fox, large fruit bat, kalang, or kalong, is a southeast Asian species of megabat in the fam ...
has the longest forearm length and reported wingspan of any bat species, but some bat species exceed it in weight.
Its wingspan is up to , and it can weigh up to . The Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Associated with India
* of or related to India
** Indian people
** Indian diaspora
** Languages of India
** Indian English, a dialect of the English language
** Indian cuisine
Associated with indigenous peoples o ...
and great
Great may refer to:
Descriptions or measurements
* Great, a relative measurement in physical space, see Size
* Greatness, being divine, majestic, superior, majestic, or transcendent
People
* List of people known as "the Great"
* Artel Great (bo ...
flying foxes are heavier, at , respectively.
Outside this genus, the giant golden-crowned flying fox
The giant golden-crowned flying fox (''Acerodon jubatus''), also known as the golden-capped fruit bat, is a species of megabat endemism, endemic to the Philippines. Since its description in 1831, three subspecies of the giant golden-crowned flyi ...
(genus ''Acerodon
''Acerodon'' (meaning: sharp-tooth) is a genus of bats in the family Pteropodidae containing five species, all native to forests in Southeast Asia, and all considered threatened. They are closely related to ''Pteropus''. These bats are consider ...
'') is the only bat with similar dimensions.
Most flying fox species are considerably smaller and generally weigh less than .
Smaller species such as the masked, Temminck's, Guam
Guam ( ; ) is an island that is an Territories of the United States, organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. Guam's capital is Hagåtña, Guam, Hagåtña, and the most ...
, and dwarf
Dwarf, dwarfs or dwarves may refer to:
Common uses
*Dwarf (folklore), a supernatural being from Germanic folklore
* Dwarf, a human or animal with dwarfism
Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities
* Dwarf (''Dungeons & Dragons''), a sh ...
flying foxes all weigh less than .
The pelage is long and silky with a dense underfur. In many species, individuals have a "mantle" of contrasting fur color on the back of their head, the shoulders, and the upper back. They lack tails. As the common name "flying fox" suggests, their heads resemble that of a small fox because of their small ears and large eyes. Females have one pair of mammae
A mammary gland is an exocrine gland that produces milk in humans and other mammals. Mammals get their name from the Latin word ''mamma'', "breast". The mammary glands are arranged in organs such as the breasts in primates (for example, humans ...
located in the chest region. Their ears are long and pointed at the tip and lack tragi, the outer margin of each ear forming an unbroken ring. The toes have sharp, curved claws. While microbat
Microbats constitute the suborder Microchiroptera within the order Chiroptera (bats). Bats have long been differentiated into Megachiroptera (megabats) and Microchiroptera, based on their size, the use of echolocation by the Microchiroptera an ...
s only have a claw on each thumb of their forelimbs, flying foxes additionally have a claw on each index finger.
Skull and dentition
 The skulls of ''Pteropus'' species are composed of 24 bones, the
The skulls of ''Pteropus'' species are composed of 24 bones, the snout
A snout is the protruding portion of an animal's face, consisting of its nose, mouth, and jaw. In many animals, the structure is called a muzzle, Rostrum (anatomy), rostrum, beak or proboscis. The wet furless surface around the nostrils of the n ...
is made of 7, the cranium
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
of 16 and the mandible
In jawed vertebrates, the mandible (from the Latin ''mandibula'', 'for chewing'), lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lowerand typically more mobilecomponent of the mouth (the upper jaw being known as the maxilla).
The jawbone i ...
is a single bone. It has a large and bulbous braincase
In human anatomy, the neurocranium, also known as the braincase, brainpan, brain-pan, or brainbox, is the upper and back part of the skull, which forms a protective case around the brain. In the human skull, the neurocranium includes the calv ...
. Like all mammals, flying foxes have three middle ear ossicles
The ossicles (also called auditory ossicles) are three irregular bones in the middle ear of humans and other mammals, and are among the smallest bones in the human body. Although the term "ossicle" literally means "tiny bone" (from Latin ''ossicu ...
which assist in transmitting sound to the brain. Flying fox skulls continue to develop after they are born. Compared to adults, young flying foxes have very short snouts; as they reach maturity, the maxilla
In vertebrates, the maxilla (: maxillae ) is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxil ...
elongates, gaining bone between the zygomatic process
The zygomatic processes (aka. malar) are three processes (protrusions) from other bones of the skull which each articulate with the zygomatic bone. The three processes are:
* Zygomatic process of frontal bone from the frontal bone
* Zygomatic ...
es and the canine teeth
In mammalian oral anatomy, the canine teeth, also called cuspids, dogteeth, eye teeth, vampire teeth, or fangs, are the relatively long, pointed teeth. In the context of the upper jaw, they are also known as '' fangs''. They can appear more fl ...
.
Based on the grey-headed flying fox
The grey-headed flying fox (''Pteropus poliocephalus'') is a megabat native to Australia. The species shares mainland Australia with three other members of the genus ''Pteropus'': the little red '' P. scapulatus'', spectacled '' P. conspicillat ...
's development, pups are born with some milk teeth
Milk Teeth (often stylised as MILK TEETH) were a British punk rock band from Stroud, Gloucestershire, which formed in May 2013. The band officially announced their breakup on Facebook and Twitter on 4 September 2020.
History Formation and earl ...
already erupted: canines and incisor
Incisors (from Latin ''incidere'', "to cut") are the front teeth present in most mammals. They are located in the premaxilla above and on the mandible below. Humans have a total of eight (two on each side, top and bottom). Opossums have 18, wher ...
s. By 9 days old, all the milk teeth have emerged, with a dental formula
Dentition pertains to the development of teeth and their arrangement in the mouth. In particular, it is the characteristic arrangement, kind, and number of teeth in a given species at a given age. That is, the number, type, and morpho-physiology ...
of and a total of 20 teeth. By 140 days old (4.6 months), all the milk teeth have fallen and been replaced by permanent teeth
Permanent teeth or adult teeth are the second set of teeth formed in diphyodont mammals. In humans and old world simians, there are thirty-two permanent teeth, consisting of six maxillary and six mandibular molars, four maxillary and four mandib ...
. The canines are usually replaced first, followed by the premolar
The premolars, also called premolar Tooth (human), teeth, or bicuspids, are transitional teeth located between the Canine tooth, canine and Molar (tooth), molar teeth. In humans, there are two premolars per dental terminology#Quadrant, quadrant in ...
s, incisors, and then molars
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat tooth, teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammal, mammals. They are used primarily to comminution, grind food during mastication, chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, '' ...
. The adult dental formula is for a total of 34 teeth. The occlusal surface of the molars is generally smooth but with longitudinal furrows.
Internal systems
Flying foxes have large hearts and a relatively fastheart rate
Heart rate is the frequency of the cardiac cycle, heartbeat measured by the number of contractions of the heart per minute (''beats per minute'', or bpm). The heart rate varies according to the body's Human body, physical needs, including the nee ...
: resting individuals have a heart rate of 100–400 beats per minute.
Flying foxes have simple digestive tracts; the time between ingestion and excretion is as short as 12 minutes. They lack both a cecum
The cecum ( caecum, ; plural ceca or caeca, ) is a pouch within the peritoneum that is considered to be the beginning of the large intestine. It is typically located on the right side of the body (the same side of the body as the appendix (a ...
and an appendix
Appendix (: appendices or appendixes) may refer to:
__NOTOC__ In documents
* Addendum, an addition made to a document by its author after its initial printing or publication
* Bibliography, a systematic list of books and other works
* Index (publis ...
. The stomach has marked cardiac and fundic regions.
Intelligence
The megabats, including flying foxes, have the greatestencephalization quotient
Encephalization quotient (EQ), encephalization level (EL), or just encephalization is a relative brain size measure that is defined as the ratio between observed and predicted brain mass for an animal of a given size, based on nonlinear regre ...
(brain size relative to body size) of any bat family at 1.20.
This value is equivalent to that of domestic dogs. Flying foxes display behaviors that indicate a reliance on long-term information storage. Though they have wide-ranging movements and cover thousands of square kilometers annually, they are consistently able to locate the same resource patches and roosts. They will visit these resource patches consistently in a strategy known as trap-lining
In ethology and behavioral ecology, trap-lining or traplining is a feeding strategy in which an individual visits food sources on a regular, repeatable sequence, much as Animal trapping, trappers check their lines of traps. Traplining is usually ...
. They can also be conditioned to perform behaviors, such as one study where spectacled flying fox
The spectacled flying fox (''Pteropus conspicillatus''), also known as the spectacled fruit bat, is a megabat that lives in Australia's north-eastern regions of Queensland. It is also found in New Guinea and on the offshore islands including Wood ...
es were trained to pull a lever using juice as a reinforcement
In Behaviorism, behavioral psychology, reinforcement refers to consequences that increase the likelihood of an organism's future behavior, typically in the presence of a particular ''Antecedent (behavioral psychology), antecedent stimulus''. Fo ...
. In a follow-up to the initial study, individuals who had learned to pull the lever to receive juice still did so 3.5 years later.
Senses
Smell
 Flying foxes rely heavily on their sense of smell.
They have large
Flying foxes rely heavily on their sense of smell.
They have large olfactory bulb
The olfactory bulb (Latin: ''bulbus olfactorius'') is a neural structure of the vertebrate forebrain involved in olfaction, the sense of smell. It sends olfactory information to be further processed in the amygdala, the orbitofrontal cortex (OF ...
s to process scents. They use scent to locate food, for mothers to locate their pups, and for mates to locate each other. Males have enlarged androgen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning ) is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This includes ...
-sensitive sebaceous gland
A sebaceous gland or oil gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in ...
s on their shoulders that they use for scent-marking
In ethology, territory is the sociographical area that an animal consistently defends against conspecificity, conspecific competition (biology), competition (or, occasionally, against animals of other species) using agonistic behaviors or (less ...
their territories, particularly during the mating season. The secretions of these glands vary by species—of the 65 chemical compounds identified from the glands of four species, no compound was found in all species. Males also engage in " urine washing", meaning that they coat themselves in their own urine.
Sight
Flying foxes do not echolocate, and therefore rely on sight to navigate. Their eyes are relatively large and positioned on the front of their heads, giving thembinocular vision Binocular vision is seeing with two eyes. The Field_of_view, field of view that can be surveyed with two eyes is greater than with one eye. To the extent that the visual fields of the two eyes overlap, #Depth, binocular depth can be perceived. Th ...
.
Like most mammals, though not primate
Primates is an order (biology), order of mammals, which is further divided into the Strepsirrhini, strepsirrhines, which include lemurs, galagos, and Lorisidae, lorisids; and the Haplorhini, haplorhines, which include Tarsiiformes, tarsiers a ...
s, they are dichromatic. They have both rods and cones
In geometry, a cone is a three-dimensional figure that tapers smoothly from a flat base (typically a circle) to a point not contained in the base, called the ''apex'' or '' vertex''.
A cone is formed by a set of line segments, half-lines, ...
; they have "blue" cones that detect short-wavelength light and "green" cones that detect medium-to-long-wavelengths. The rods greatly outnumber the cones, however, as cones comprise only 0.5% of photoreceptors. Flying foxes are adapted to seeing in low-light conditions.
Evolutionary history
Flying foxes are poorly represented in the fossil record. Relative to the current number of extant species, the Pteropodidae has one of the most incomplete fossil records of any bat group. As of 2014, no flying fox fossils are known from before theHolocene
The Holocene () is the current geologic time scale, geological epoch, beginning approximately 11,700 years ago. It follows the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene to ...
.
Many flying foxes live in the tropics
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the equator, where the sun may shine directly overhead. This contrasts with the temperate or polar regions of Earth, where the Sun can never be directly overhead. This is because of Earth's ax ...
, where conditions for fossilization are poor. Based on molecular evolution
Molecular evolution describes how Heredity, inherited DNA and/or RNA change over evolutionary time, and the consequences of this for proteins and other components of Cell (biology), cells and organisms. Molecular evolution is the basis of phylogen ...
, flying foxes diverged from a common ancestor with ''Rousettus
''Rousettus'' is a genus of Old World fruit bats or megabats, referred to as rousette bats. The genus is a member of the Family_(biology), family Pteropodidae. The genus consists of seven species that range over most of Africa to southeast Asia, ...
'' 28–18 million years ago and from their sister taxa
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree.
Definition
The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram:
Taxon A and ...
'' Neopteryx'' and ''Acerodon'' 6.6–10.6 million years ago. ''Neopteryx'', ''Acerodon'', '' Desmalopex'', ''Melonycteris
''Melonycteris'' (dark blossom bat) is a genus of megabat in the family Pteropodidae. Members are found in the Solomon Islands or in the case of the black-bellied fruit bat, in Papua New Guinea.
It contains the following species:
* Fardoulis's ...
'', ''Mirimiri
The Fijian monkey-faced bat (''Mirimiri acrodonta''), also known as the Fijian flying fox or Fijian flying monkey, is a megabat endemic to Fiji. It was discovered in old-growth cloud forest on Des Vœux Peak, the second highest mountain peak () ...
'', ''Pteralopex
''Pteralopex'' is a genus of large megabats in the family Pteropodidae. Species in this genus are commonly known as "monkey-faced bats". They are restricted to Solomon Islands rain forests in Melanesia, and all species are seriously threatened, b ...
'', and '' Styloctenium'' are all relatively closely related to the flying foxes, as they are the other members of its subfamily
In biological classification, a subfamily (Latin: ', plural ') is an auxiliary (intermediate) taxonomic rank, next below family but more inclusive than genus. Standard nomenclature rules end botanical subfamily names with "-oideae", and zo ...
Pteropodinae
The Pteropodinae are a subfamily of megabats. Taxa within this subfamily are:
* Genus '' Acerodon''
** Sulawesi flying fox, ''A. celebensis''
** Talaud flying fox, ''A. humilis''
** Giant golden-crowned flying fox, ''A. jubatus''
** Palawan frui ...
.
Phylogenetic analysis indicates that flying foxes diversified rapidly in an explosive evolutionary radiation
An evolutionary radiation is an increase in taxonomic diversity that is caused by elevated rates of speciation, that may or may not be associated with an increase in morphological disparity. A significantly large and diverse radiation within ...
, creating many taxa in a relatively short time frame. Most flying fox lineages emerged after the Zanclean
The Zanclean is the lowest stage or earliest age on the geologic time scale of the Pliocene. It spans the time between 5.332 ± 0.005 Ma (million years ago) and 3.6 ± 0.005 Ma. It is preceded by the Messinian Age of the Miocene Epoch, and f ...
, with two major clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach t ...
s created: one consisting of the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or approximately 20% of the water area of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia (continent), ...
species and the other of the Melanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from New Guinea in the west to the Fiji Islands in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.
The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, Vanu ...
n, Micronesia
Micronesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of approximately 2,000 small islands in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: Maritime Southeast Asia to the west, Poly ...
n, Australian, and insular Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
n species. Flying foxes likely originated on mainland Asia; molecular data suggests that there were at least three colonization events into the Indian Ocean. One event resulted in Livingstone's fruit bat and the Pemba flying fox, which are the westernmost flying foxes. A second colonization event resulted in the Rodrigues flying fox
The Rodrigues flying fox or Rodrigues fruit bat (''Pteropus rodricensis'') is a species of bat in the family Pteropodidae, the flying foxes or fruit bats. It is endemic to Rodrigues, an island in the Indian Ocean belonging to Mauritius. Its nat ...
to Rodrigues
Rodrigues ( ; Mauritian Creole, Creole: ) is a Autonomous administrative division, autonomous Outer islands of Mauritius, outer island of the Republic of Mauritius in the Indian Ocean, about east of Mauritius. It is part of the Mascarene Isl ...
Island; while a third event resulted in several species diverging to Mauritius
Mauritius, officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island country in the Indian Ocean, about off the southeastern coast of East Africa, east of Madagascar. It includes the main island (also called Mauritius), as well as Rodrigues, Ag ...
, the Seychelles
Seychelles (, ; ), officially the Republic of Seychelles (; Seychellois Creole: ), is an island country and archipelagic state consisting of 155 islands (as per the Constitution) in the Indian Ocean. Its capital and largest city, Victoria, ...
, Madagascar
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, f ...
, and Aldabra
Aldabra, the world's second-largest coral atoll (the largest is Kiritimati), is located east of the continent of Africa. It is part of the Aldabra Group of islands in the Indian Ocean that are part of the Outer Islands (Seychelles), Outer Islands ...
.
With one possible exception - the masked flying fox (''P. personatus''), flying foxes are likely monophyletic
In biological cladistics for the classification of organisms, monophyly is the condition of a taxonomic grouping being a clade – that is, a grouping of organisms which meets these criteria:
# the grouping contains its own most recent co ...
. There are over 60 extant species of flying fox. Flying foxes are now present from the western Indian Ocean midway through the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
as far east as the Cook Islands
The Cook Islands is an island country in Polynesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It consists of 15 islands whose total land area is approximately . The Cook Islands' Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) covers of ocean. Avarua is its ...
. They are found in tropical and subtropical climates.
Biology and ecology
Reproduction and life cycle
 Many species of flying fox are
Many species of flying fox are polygynandrous
Polygynandry is a mating system in which both males and females have multiple mating partners during a breeding season. In sexually reproducing diploid animals, different mating strategies are employed by males and females, because the cost of gam ...
, meaning that each individual will mate with several other individuals. The Samoa flying fox
The Samoa flying fox or Samoan flying fox (''Pteropus samoensis'') is a species of flying fox in the family Pteropodidae. It is found in American Samoa, Fiji, and Samoa (where it is known as ''pe'a'' and ''pe'a vao''). Its natural habitat is sub ...
is a notable exception because it is monogamous
Monogamy ( ) is a relationship of two individuals in which they form a mutual and exclusive intimate partnership. Having only one partner at any one time, whether for life or serial monogamy, contrasts with various forms of non-monogamy (e.g. ...
. Flying fox sexual behaviors include oral sex in addition to intercourse, with fellatio
Fellatio (also known as fellation, and in slang as blowjob, BJ, giving head, or sucking off) is an oral sex act consisting of the stimulation of a human penis, penis by using the mouth. Oral stimulation of the scrotum may also be termed ''fellat ...
and cunnilingus
Cunnilingus is an oral sex act consisting of the stimulation of a vulva by using the tongue and lips. The clitoris is the most sexually sensitive part of the vulva, and its stimulation may result in a woman becoming sexually aroused or achievi ...
observed between opposite sexes, as well as homosexual fellatio in at least one species, the Bonin flying fox
The Bonin flying fox (''Pteropus pselaphon''), also known as Bonin fruit bat, is a species of flying fox in the family Pteropodidae. It is endemic to four islands (Chichijima, Hahajima, North Iwo Jima, and South Iwo Jima) of the Bonin Island ...
. Opposite-sex oral sex is associated with increased duration of intercourse, while same-sex fellatio is hypothesized to encourage colony formation of otherwise-antagonistic males in colder climates.
Flying fox gestation length varies among species; gestation length is 140–190 days (4.6–6.3 months).
Females have a litter size of one young at a time, called a pup.
Twins have been occasionally documented in some species, however. Twins can be fraternal, identical
Identical may refer to:
* Identical, when two things are the same, see Identity (philosophy)
* Identical (Hopkins novel), ''Identical'' (Hopkins novel), a 2008 young adult novel by Ellen Hopkins
* Identical (Turow novel), ''Identical'' (Turow novel ...
, or the result of superfetation
Superfetation (also spelled superfoetation – see fetus) is the simultaneous occurrence of more than one stage of developing offspring in the same animal.
In mammals, it manifests as the formation of an embryo from a subsequent menstrual cycle, ...
. Pups are altricial
Precocial species in birds and mammals are those in which the young are relatively mature and mobile from the moment of birth or hatching. They are normally nidifugous, meaning that they leave the nest shortly after birth or hatching. Altricial ...
and sparsely furred at birth, thereby dependent on their mothers for care. Pups are relatively small at birth, weighing approximately 12% of the mother's weight. Bats in other genera can have pups that weigh as much as 30% of the mother's weight at birth. They cling to their mothers' abdomens, gripping her fur with their thumb claws and teeth; females carry the pups for the first several weeks of life. After this, the females may leave the pups behind at the roost at night while they forage. As with nearly all bat species, males do not assist females in parental care. While male flying foxes of at least one species, the Bismarck masked flying fox
The Bismarck masked flying fox (''Pteropus capistratus'') is a species of flying fox in the family Pteropodidae found in Papua New Guinea and named after the Bismarck Archipelago. It was once considered a subspecies of '' Pteropus temminckii'' ...
, can lactate, it is unclear if the lactation is functional and males actually nurse pups or if it is a result of stress or malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
. Pups fledge
Fledging is the stage in a flying animal's life between egg, hatching or birth and becoming capable of flight.
This term is most frequently applied to birds, but is also used for bats. For altricial birds, those that spend more time in vulnera ...
beginning at 3 months old, but may not be weaned
Weaning is the process of gradually introducing an infant human or other mammal to what will be its adult diet while withdrawing the supply of its mother's milk. In the UK, weaning primarily refers to the introduction of solid foods at 6 mont ...
until 4–6 months old. Pups may stay with their mothers until age one. Flying foxes do not reach sexual maturity
Sexual maturity is the capability of an organism to reproduce. In humans, it is related to both puberty and adulthood. ''Puberty'' is the biological process of sexual maturation, while ''adulthood'', the condition of being socially recognized ...
until 1.5–2 years old. Females can have up to two litters annually, though one is the norm due to the long weaning period. Most flying foxes are seasonal breeder
Seasonal breeders are animal species that successfully mate only during certain times of the year. These times of year allow for the optimization of survival of young due to factors such as ambient temperature, food and water availability, and ch ...
s and give birth in the spring
Spring(s) may refer to:
Common uses
* Spring (season), a season of the year
* Spring (device), a mechanical device that stores energy
* Spring (hydrology), a natural source of water
* Spring (mathematics), a geometric surface in the shape of a he ...
, though the Mariana fruit bat seems to have aseasonal breeding with new pups documented throughout the year. Females remain fertile
Fertility in colloquial terms refers the ability to have offspring. In demographic contexts, fertility refers to the actual production of offspring, rather than the physical capability to reproduce, which is termed fecundity. The fertility rate is ...
with no decrease in reproductive capability for at least the first 12 or 13 years of life.
Flying foxes, like all bats, are long-lived relative to their size. In the wild, average lifespans are likely 15 years. However, individuals part of populations that face excessive disturbance may have lifespans as short as 7.1 years. In captivity, individuals can live approximately 20–28 years. The longest-lived flying fox was an Indian flying fox named Statler, who was a resident at Bat World Sanctuary for his last few years. He was born at a zoo in 1987, and was 34 years old at the time of his death.
Social systems
gregarious
Sociality is the degree to which individuals in an animal population tend to associate in social groups (gregariousness) and form cooperative societies.
Sociality is a survival response to evolutionary pressures. For example, when a mother was ...
and form large aggregations of individuals called colonies
A colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule, which rules the territory and its indigenous peoples separated from the foreign rulers, the colonizer, and their '' metropole'' (or "mother country"). This separated rule was often or ...
or "camps." The large flying fox forms colonies of up to 15,000 individuals, while the little red flying fox
The little red flying-fox (''Pteropus scapulatus'') is a megachiropteran bat native to northern and eastern Australia. The species weighs about half a kilogram, one US pound, and is the smallest species of ''Pteropus'' in mainland Australia. '' ...
forms colonies of up to 100,000 individuals. A few species and subspecies, such as Orii's flying fox (''P. dasymallus inopinatus'') and the Ceram fruit bat, are solitary.
Colony size varies throughout the year in response to biological needs. The grey-headed flying fox forms harems
A harem is a domestic space that is reserved for the women of the house in a Muslim family. A harem may house a man's wife or wives, their pre-pubescent male children, unmarried daughters, female domestic Domestic worker, servants, and other un ...
during the breeding season consisting of one male and up to six females. These colonies break up after the breeding season is over. In the Bonin flying fox, colony formation is based on both the sex and age of individuals, as well as the season. In the winter breeding season, adult females will form colonies that include a few adult males (likely harems). Adult males who do not roost with females will form colonies with other adult and subadult
A juvenile is an individual organism (especially an animal) that has not yet reached its adult form, sexual maturity or size. Juveniles can look very different from the adult form, particularly in colour, and may not fill the same niche as t ...
males. Subadults will form mixed-sex "subadult groups" with each other. In the summer, however, individuals are solitary, with the exception of nursing
Nursing is a health care profession that "integrates the art and science of caring and focuses on the protection, promotion, and optimization of health and human functioning; prevention of illness and injury; facilitation of healing; and alle ...
females, who roost with their pups.
Diet and foraging
Flying foxes consume 25–35% of their body weight daily. They are generalists that will consume a variety of items to meet their nutritional needs. Food items include fruit, flowers, nectar, and leaves. They will sometimes deliberately consume insects such ascicada
The cicadas () are a superfamily, the Cicadoidea, of insects in the order Hemiptera (true bugs). They are in the suborder Auchenorrhyncha, along with smaller jumping bugs such as leafhoppers and froghoppers. The superfamily is divided into two ...
s as well.
In Australia, eucalypt
Eucalypt is any woody plant with Capsule (fruit), capsule fruiting bodies belonging to one of seven closely related genera (of the tribe Eucalypteae) found across Australia:
''Eucalyptus'', ''Corymbia'', ''Angophora'', ''Stockwellia'', ''Allosyn ...
blossoms and pollen are preferred food sources, followed by ''Melaleuca
''Melaleuca'' () is a genus of nearly 300 species of plants in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae, commonly known as paperbarks, honey-myrtles, bottlebrushes or tea-trees (although the last name is also applied to species of '' Leptospermum''). They ...
'' and ''Banksia
''Banksia'' is a genus of around 170 species of flowering plants in the family Proteaceae. These Australian wildflowers and popular garden plants are easily recognised by their characteristic flower spikes, and woody fruiting "cones" and head ...
'' flowers They feed on a wide variety of crop
A crop is a plant that can be grown and harvested extensively for profit or subsistence. In other words, a crop is a plant or plant product that is grown for a specific purpose such as food, Fiber, fibre, or fuel.
When plants of the same spe ...
s as well, causing conflicts with farmers. Crops eaten by flying foxes include sisal
Sisal (, ; ''Agave sisalana'') is a species of flowering plant native to southern Mexico, but widely cultivated and naturalized in many other countries. It yields a stiff fibre used in making rope and various other products. The sisal fiber is ...
, cashew
Cashew is the common name of a tropical evergreen tree ''Anacardium occidentale'', in the family Anacardiaceae. It is native to South America and is the source of the cashew nut and the cashew apple, an accessory fruit. The tree can grow as t ...
, pineapple
The pineapple (''Ananas comosus'') is a Tropical vegetation, tropical plant with an edible fruit; it is the most economically significant plant in the family Bromeliaceae.
The pineapple is indigenous to South America, where it has been culti ...
, areca
''Areca'' is a genus of 51 species of Arecaceae, palms in the family (biology), family Arecaceae, found in humid tropical forests from the islands of the Philippines and Malaysia, India, and across Southeast Asia to Melanesia. The generic name ' ...
, breadfruit
Breadfruit (''Artocarpus altilis'') is a species of flowering tree in the mulberry and jackfruit family ( Moraceae) believed to have been selectively bred in Polynesia from the breadnut ('' Artocarpus camansi''). Breadfruit was spread into ...
, jackfruit
The jackfruit or ''nangka'' (''Artocarpus heterophyllus'') is a species of tree in the Common fig, fig, mulberry, and breadfruit family (Moraceae).
The jackfruit is the largest tree fruit, reaching as much as in weight, in length, and in d ...
, neem
''Azadirachta indica'', commonly known as neem, margosa, nimtree or Indian lilac, is a tree in the mahogany family Meliaceae. It is one of the two species in the genus '' Azadirachta''. It is native to the Indian subcontinent and to parts of S ...
, papaya
The papaya (, ), papaw, () or pawpaw () is the plant species ''Carica papaya'', one of the 21 accepted species in the genus '' Carica'' of the family Caricaceae, and also the name of its fruit. It was first domesticated in Mesoamerica, within ...
, citrus
''Citrus'' is a genus of flowering trees and shrubs in the family Rutaceae. Plants in the genus produce citrus fruits, including important crops such as oranges, mandarins, lemons, grapefruits, pomelos, and limes.
''Citrus'' is nativ ...
, fig
The fig is the edible fruit of ''Ficus carica'', a species of tree or shrub in the flowering plant family Moraceae, native to the Mediterranean region, together with western and southern Asia. It has been cultivated since ancient times and i ...
, mango
A mango is an edible stone fruit produced by the tropical tree '' Mangifera indica''. It originated from the region between northwestern Myanmar, Bangladesh, and northeastern India. ''M. indica'' has been cultivated in South and Southeast As ...
, banana
A banana is an elongated, edible fruit – botanically a berry – produced by several kinds of large treelike herbaceous flowering plants in the genus '' Musa''. In some countries, cooking bananas are called plantains, distinguishing the ...
, avocado
The avocado, alligator pear or avocado pear (''Persea americana'') is an evergreen tree in the laurel family (Lauraceae). It is native to Americas, the Americas and was first domesticated in Mesoamerica more than 5,000 years ago. It was priz ...
, guava
Guava ( ), also known as the 'guava-pear', is a common tropical fruit cultivated in many tropical and subtropical regions. The common guava '' Psidium guajava'' (lemon guava, apple guava) is a small tree in the myrtle family (Myrtaceae), nativ ...
, sugar cane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fib ...
, tamarind
Tamarind (''Tamarindus indica'') is a Legume, leguminous tree bearing edible fruit that is indigenous to tropical Africa and naturalized in Asia. The genus ''Tamarindus'' is monotypic taxon, monotypic, meaning that it contains only this spe ...
, grape
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus ''Vitis''. Grapes are a non- climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters.
The cultivation of grapes began approximately 8,0 ...
s, and more.
In captivity, the recommended diet for flying foxes consists of two-thirds hard fruits like pears and apples and one-third soft fruits. Bananas and other high-fiber fruits should only be offered occasionally, as flying foxes are not adapted to high-fiber diets. Protein supplements are recommended for captive flying foxes; other supplements such as vitamin C
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits, berries and vegetables. It is also a generic prescription medication and in some countries is sold as a non-prescription di ...
, calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to it ...
, chondroitin sulfate
Chondroitin sulfate is a sulfated glycosaminoglycan (GAG) composed of a chain of alternating sugars (N-Acetylgalactosamine, N-acetylgalactosamine and glucuronic acid). It is usually found attached to proteins as part of a proteoglycan. A chondroit ...
, and glucosamine
Glucosamine (C6H13NO5) is an amino sugar and a prominent precursor in the biochemical synthesis of glycosylated proteins and lipids. Glucosamine is part of the structure of two polysaccharides, chitosan and chitin. Glucosamine is one of the mo ...
can be recommended periodically.
The majority of flying fox species are nocturnal
Nocturnality is a ethology, behavior in some non-human animals characterized by being active during the night and sleeping during the day. The common adjective is "nocturnal", versus diurnality, diurnal meaning the opposite.
Nocturnal creatur ...
and forage at night. A few island species and subspecies are diurnal, however, hypothesized as a response to a lack of predators. Diurnal taxa include '' P. melanotus natalis'', the Mauritian flying fox, the Caroline flying fox, '' P. p. insularis'', and the Seychelles fruit bat
The Seychelles fruit bat or Seychelles flying fox (''Pteropus seychellensis'') is a megabat found on the granitic islands of Seychelles, and on the Comoros and Mafia Island. It is a significant component of the ecosystems for the islands, dispers ...
. Foraging resources are often far from roosts, with individuals traveling up to to reach them. Flying foxes can travel at for three hours or more, and can reach top speeds of . Some colonial species will forage in groups, especially when resources are abundant. Less social species will forage alone. When they land on a tree with food, they will hang onto the branch with their clawed hind feet and use their clawed thumbs to pull branches bearing flowers or fruits towards them. As they forage on fruit, flying foxes will compress the fruit against the palate
The palate () is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity.
A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly sep ...
with the tongue to squeeze out and consume the juices. The rest of the fruit is then discarded in "ejecta pellets."
Role in ecosystems
Flying foxes have important roles as seed dispersers andpollinator
A pollinator is an animal that moves pollen from the male anther of a flower to the female carpel, stigma of a flower. This helps to bring about fertilization of the ovules in the flower by the male gametes from the pollen grains.
Insects are ...
s. They help spread the seeds in the fruit they eat by discarding them in ejecta pellets or through their guano
Guano (Spanish from ) is the accumulated excrement of seabirds or bats. Guano is a highly effective fertiliser due to the high content of nitrogen, phosphate, and potassium, all key nutrients essential for plant growth. Guano was also, to a le ...
. In Madagascar, fig seeds have better germination success if they have passed through the gut of a flying fox, which is important because fig trees are a vital pioneer species
Pioneer species are resilient species that are the first to colonize barren environments, or to repopulate disrupted biodiverse steady-state ecosystems as part of ecological succession. Various kinds of events can create good conditions for pi ...
in regenerating lost forest. Even though flying foxes can have a gut transit time as fast as 12 minutes, seeds can be retained in the gut for as long as 20 hours. As the flying foxes travel large distances, seeds can be deposited up to from the parent tree. They are particularly important in fragmented forests, as many other frugivores are terrestrial and often confined to forest fragments.
Flying foxes have the capability to spread seeds beyond the forest fragments through flight.
Flying foxes pollinate a variety of plants, including the economically valuable durian
The durian () is the edible fruit of several tree species belonging to the genus ''Durio''. There are 30 recognized species, at least nine of which produce edible fruit. ''Durio zibethinus'', native to Borneo and Sumatra, is the only species ...
. They forage on its nectar in such a way that the flowers (and eventual fruit production) are not usually harmed. Flying fox pollination has a positive effect on durian reproductive success, suggesting that both flying foxes and durian trees benefit from this relationship.
Conservation
Conservation status
 Of the 62 flying fox species evaluated by the
Of the 62 flying fox species evaluated by the IUCN
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. Founded in 1948, IUCN has become the global authority on the status ...
as of 2018, 3 are considered critically endangered
An IUCN Red List critically endangered (CR or sometimes CE) species is one that has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as facing an extremely high risk of extinction in the wild. As of December 2023, of t ...
: the Aru flying fox, Livingstone's fruit bat, and the Vanikoro flying fox
The Vanikoro flying fox (''Pteropus tuberculatus''), also known locally as the basapine, is a species of bat in the family Pteropodidae. It has only been found in the Vanikoro island group located in the southern Solomon Islands. The species a ...
. Another 7 species are listed as endangered
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching, inv ...
; 20 are listed as vulnerable, 6 as near threatened
A near-threatened species is a species which has been Conservation status, categorized as "Near Threatened" (NT) by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as that may be vulnerable to Endangered species, endangerment in the ne ...
, 14 as least concern
A least-concern species is a species that has been evaluated and categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as not being a focus of wildlife conservation because the specific species is still plentiful in the wil ...
, and 8 as data deficient
A data deficient (DD) species is one which has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as offering insufficient information for a proper assessment of conservation status to be made. This does not necessaril ...
. A further 4 are listed as extinct
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
: the dusky flying fox, the large Palau flying fox, the small Mauritian flying fox
The small Mauritian flying fox or dark flying fox (''Pteropus subniger''), known as a ''rougette'' to early French travelers, is an extinct species of megabat. It lived on the islands of Réunion and Mauritius in the Mascarene Islands of the Indi ...
, and the Guam flying fox. Over half of the species are threatened today with extinction, and in particular in the Pacific, a number of species have died out as a result of hunting, deforestation, and predation by invasive species. Six flying fox species are believed to have gone extinct from 1864 to 2014: the Guam, large Palau, small Mauritian, dusky, large Samoan, and the small Samoan flying foxes.
Legal status
All species of ''Pteropus'' are placed onAppendix II
CITES (shorter acronym for the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora, also known as the Washington Convention) is a multilateral treaty to protect endangered plants and animals from the threats of inte ...
of CITES
CITES (shorter acronym for the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora, also known as the Washington Convention) is a multilateral treaty to protect endangered plants and animals from the threats of inte ...
and 10 on Appendix I, which restricts international trade. Individual species have different legal protections from hunting and domestic trade that reflect the environmental laws of the countries where they are found.
In some countries such as Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, and Thailand, flying foxes are absolutely protected from harm under the Wildlife Preservation and Security Act of 2012, Fauna and Flora Protection Ordinance of 1937, and Wildlife Protection and Reservation Act of 1992, respectively. However, in Thailand, flying fox poaching and the illegal bushmeat trade still occurs outside of protected area
Protected areas or conservation areas are locations which receive protection because of their recognized natural or cultural values. Protected areas are those areas in which human presence or the exploitation of natural resources (e.g. firewood ...
s. The large flying fox and the small flying fox are particularly prone to poaching and roost disturbance.
In other countries, such as Australia, Japan, and the United States, some species of conservation concern are protected under national environmental legislation, while others are not. In Australia, two flying foxes are listed under the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act of 1999: the grey-headed and spectacled flying foxes are listed as "vulnerable." Farmers can apply for permits to kill flying foxes when they are causing crop damage.
Several flying fox species occur in Japan. The Bonin flying fox has been a Natural Monument
A natural monument is a natural or cultural feature of outstanding or unique value because of its inherent rarity, representative of aesthetic qualities, or cultural significance. They can be natural geological and geographical features such as w ...
of Japan since 1969, which means that it is illegal to capture or disturb them without appropriate permits. Two subspecies of the Ryukyu flying fox (''P. d. dasymallus'' and ''P. d. daitoensis'') are also listed as Natural Monuments.
Flying foxes are not designated game species in Japan, and therefore cannot be legally hunted per the Wildlife Protection and Hunting Law. The Bonin flying fox and ''P. d. daitoensis'' are also listed as National Endangered Species, meaning that they cannot be killed or harmed; furthermore, the sale or transfer of live or dead individuals in whole or part is also prohibited without permits.
Despite not occurring in the continental United States, several species and subspecies are listed under its Endangered Species Act of 1973
The Endangered Species Act of 1973 (ESA; 16 U.S.C. § 1531 et seq.) is the primary law in the United States for protecting and conserving imperiled species. Designed to protect critically imperiled species from extinction as a "consequence of e ...
. ''Pteropus mariannus mariannus''—a subspecies of the Mariana fruit bat—is listed as threatened
A threatened species is any species (including animals, plants and fungi) which is vulnerable to extinction in the near future. Species that are threatened are sometimes characterised by the population dynamics measure of ''critical depensatio ...
while the Rodrigues flying fox and Guam flying fox are listed as endangered
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching, inv ...
. Additionally, the U. S. government has been petitioned to list the Aru flying fox and Bonin flying fox as threatened or endangered.
In such countries as India and Pakistan, flying foxes explicitly have no legal protection. In India, they are listed as "vermin
Vermin (colloquially varmint(s) or varmit(s)) are pests or nuisance animals that spread diseases and destroy crops, livestock, and property. Since the term is defined in relation to human activities, which species are included vary by regi ...
" under the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972
The Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972 is an Act of the Parliament of India enacted for the protection of plants and animal species. Before 1972, India had only five designated national parks. Among other reforms, the Act established schedule ...
. Pakistan's only flying fox, the Indian flying fox, is listed under Schedule 4 of the Punjab Wildlife (Protection, Preservation, Conservation and Management) Act of 1974, meaning that it has no legal protections and can be hunted.
In Mauritius, flying foxes were formerly protected but are now legally culled at a large scale. In 2015, the Mauritian government passed the Native Terrestrial Biodiversity And National Parks Act, which legalized culling of the Mauritian flying fox. In Mauritius, over 40,000 Mauritian flying foxes were culled in a two-year period, reducing its population by an estimated 45%. This decision was viewed with controversy, with researchers stating "Because they spread seeds and pollinate flowers, flying foxes are vital for regenerating lost forests."
Legal protection can vary within a country as well, such as in Malaysia
Malaysia is a country in Southeast Asia. Featuring the Tanjung Piai, southernmost point of continental Eurasia, it is a federation, federal constitutional monarchy consisting of States and federal territories of Malaysia, 13 states and thre ...
. Under the 1990 Protection of Wild Life Amendment Order, flying foxes can be hunted with a permit; each permit is good for killing up to 50 flying foxes. Permits cost U.S.$8 each. However, under the Protection of WildLife Act of 1972, flying foxes can be killed without permits if they are causing damage or if there is "reason to believe that it is about to cause serious damage" to crops. In 2012, the Malaysian state of Terengganu
Terengganu (; Terengganu Malay: ''Tranung'', formerly spelled Trengganu or Tringganu) is a sultanate and States and federal territories of Malaysia, federal state of Malaysia. The state is also known by its Arabic honorific, ''Dāru l-Iman (c ...
issued a moratorium on hunting flying foxes.
In Sarawak
Sarawak ( , ) is a States and federal territories of Malaysia, state of Malaysia. It is the largest among the 13 states, with an area almost equal to that of Peninsular Malaysia. Sarawak is located in East Malaysia in northwest Borneo, and is ...
, all bat species are listed as "Protected" and hunting them is not legal.
Factors causing decline
Anthropogenic sources
 Flying foxes species are declining or going extinct as a result of several human impacts to their environments, in addition to natural phenomena. Their populations are especially vulnerable to threats because the litter size is usually only individual and females generally only have one litter per year. Even when nearly every female (90%) successfully produces and raises young, if a population's
Flying foxes species are declining or going extinct as a result of several human impacts to their environments, in addition to natural phenomena. Their populations are especially vulnerable to threats because the litter size is usually only individual and females generally only have one litter per year. Even when nearly every female (90%) successfully produces and raises young, if a population's mortality rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular Statistical population, population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically ...
exceeds 22% annually, then it will steadily decline.
Invasive species, such as the brown tree snake
The brown tree snake (''Boiga irregularis''), also known as the brown catsnake, is an arboreal rear-fanged colubrid snake native to eastern and northern coastal Australia, eastern Indonesia (Sulawesi to Papua), Papua New Guinea, and many island ...
, can seriously affect populations; the brown tree snake consumes so many pups that it reduced the recruitment
Recruitment is #Process, the overall process of identifying, sourcing, screening, shortlisting, and interviewing candidates for Job (role), jobs (either permanent or temporary) within an organization. Recruitment also is the process involved in ...
of the Guam
Guam ( ; ) is an island that is an Territories of the United States, organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. Guam's capital is Hagåtña, Guam, Hagåtña, and the most ...
population of the Mariana fruit bat to essentially zero.
Many flying fox species are threatened by overhunting. While they have long been a dietary component of indigenous people, expanding human population
Population growth is the increase in the number of people in a population or dispersed group. The global population has grown from 1 billion in 1800 to 8.2 billion in 2025. Actual global human population growth amounts to around 70 million annua ...
and more efficient weapons have resulted in population declines, local extinction
Local extinction, also extirpation, is the termination of a species (or other taxon) in a chosen geographic area of study, though it still exists elsewhere. Local extinctions are contrasted with extinction, global extinctions.
Local extinctions ...
s, and extinctions. Overhunting is believed to be the primary cause of extinction for the small Mauritian flying fox and the Guam flying fox.
Flying foxes are also threatened with excessive culling due to conflict with farmers. They are shot, beaten to death, or poisoned to reduce their populations. Mortality also occurs via accidental entanglement into netting
In law, set-off or netting is a legal technique applied between persons or businesses with mutual rights and Liability (financial accounting), liabilities, replacing gross positions with net positions. It permits the rights to be used to discharg ...
used to prevent the bats from eating fruit. Culling can dramatically reduce flying fox populations.
In Mauritius, over 40,000 Mauritian flying foxes were culled in a two-year period, reducing its population by an estimated 45%. Flying foxes are also killed by electrocution. In one Australian orchard, it is estimated that over 21,000 bats were electrocuted to death in an 8-week period. Farmers construct electrified grids over their fruit trees to kill flying foxes before they can consume their crop. The grids are questionably effective at preventing crop loss, with one farmer who operated such a grid estimating that they still lost of fruit to flying foxes in a year. Some electrocution deaths are also accidental, such as when bats fly into overhead power line
An overhead power line is a structure used in electric power transmission and distribution to transmit electrical energy along large distances. It consists of one or more conductors (commonly multiples of three) suspended by towers or poles. ...
s.
Climate change causes flying fox mortality and a source of concern for species persistence. Extreme heat waves in Australia have been responsible for the deaths of more than 30,000 Australian flying foxes from 1994 to 2008. Females and young bats are most susceptible to extreme heat, which affects a population's ability to recover. Flying foxes are threatened by sea level rise associated with climate change, as several taxa are endemic to low-lying atoll
An atoll () is a ring-shaped island, including a coral rim that encircles a lagoon. There may be coral islands or cays on the rim. Atolls are located in warm tropical or subtropical parts of the oceans and seas where corals can develop. Most ...
s.
Natural sources
Because many species are endemic to a single island, they are vulnerable to random events such astyphoon
A typhoon is a tropical cyclone that develops between 180° and 100°E in the Northern Hemisphere and which produces sustained hurricane-force winds of at least . This region is referred to as the Northwestern Pacific Basin, accounting for a ...
s. A 1979 typhoon halved the remaining population of the Rodrigues flying fox. Typhoons result in indirect mortality as well: Because they defoliate the trees, flying foxes are more visible and easily hunted by humans. Food resources for the bats become scarce after major storms, and flying foxes resort to riskier foraging strategies such as consuming fallen fruit off the ground. There, they are more vulnerable to depredation by domestic cats, dogs, and pigs.
Flying foxes are also threatened by disease such as tick paralysis
Tick paralysis is a type of paralysis caused by specific types of ticks. Unlike tick-borne diseases caused by infectious organisms, the illness is caused by a neurotoxin produced in the tick's salivary gland. After prolonged attachment, the en ...
. Tick paralysis affects the spectacled flying fox, and is responsible for an estimated 1% of its annual mortality.
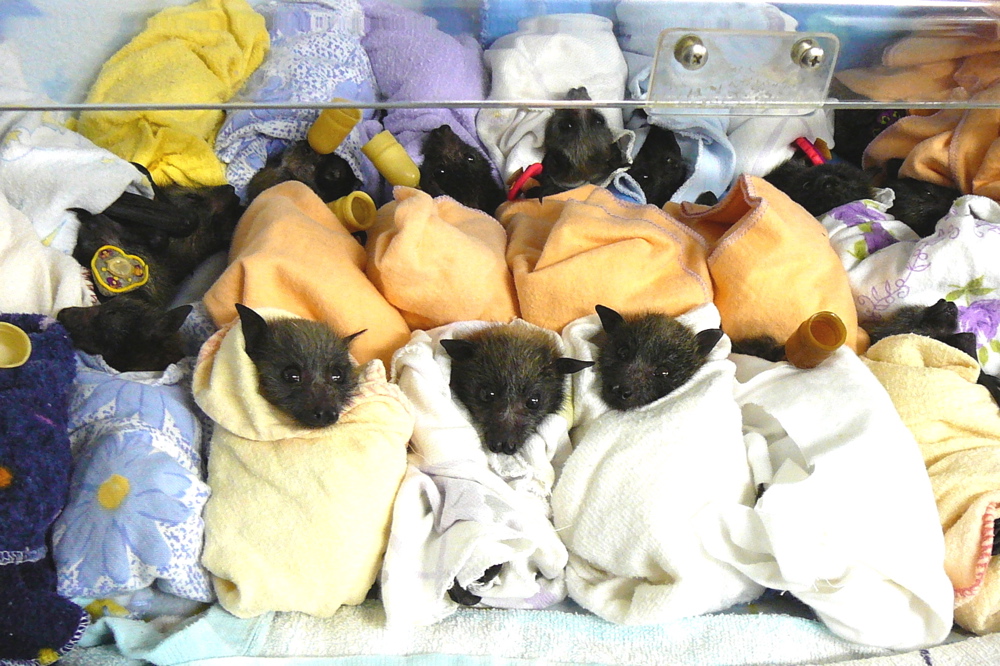
Captive breeding
 Several species of endangered flying fox are bred in captivity to augment their population sizes. Critically endangered Livingstone's fruit bats were taken from the wild starting in 1995 to create a
Several species of endangered flying fox are bred in captivity to augment their population sizes. Critically endangered Livingstone's fruit bats were taken from the wild starting in 1995 to create a captive breeding
Captive breeding, also known as captive propagation, is the process of keeping plants or animals in controlled environments, such as wildlife reserves, zoos, Botanical garden, botanic gardens, and other Conservation biology, conservation facilitie ...
program. All captive individuals remain the property of the Comorian government. 17 individuals were collected from the wild; with breeding, there are 71 in captivity as of 2017. Individuals are held at the Jersey Zoo
Jersey Zoo (formerly Durrell Wildlife Park) is a zoological park established in 1959 on the island of Jersey in the English Channel by naturalist and writer Gerald Durrell. It is operated by the Durrell Wildlife Conservation Trust. In 2023, th ...
and the Bristol Zoo
Bristol Zoo was a zoo in the city of Bristol in South West England. The zoo's stated mission was to "maintain and defend" biodiversity through breeding endangered species, conserving threatened species and habitats and promoting a wider underst ...
. Though the program has been successful in increasing the population, caretakers of the captive population have had to deal with husbandry
Animal husbandry is the branch of agriculture concerned with animals that are raised for meat, fibre, milk, or other products. It includes day-to-day care, management, production, nutrition, selective breeding, and the raising of livestock. ...
issues such as obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classifi ...
and cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy is a group of primary diseases of the heart muscle. Early on there may be few or no symptoms. As the disease worsens, shortness of breath, feeling tired, and swelling of the legs may occur, due to the onset of heart failure. A ...
. Relative to their wild counterparts, captive bats have a higher percentage of body fat and a lower percentage of muscle mass. The problem is pronounced in dominant males, which are the most sedentary
Sedentary lifestyle is a lifestyle type, in which one is physically inactive and does little or no physical movement and/or exercise. A person living a sedentary lifestyle is often sitting or lying down while engaged in an activity like soc ...
. Addressing these concerns involves increasing flight space so that the animals can exercise adequately. Keepers are also exploring ways of distributing food within enclosures to encourage exercise.
The endangered Rodrigues flying fox has been bred in captivity with great success. By 1979, only 70–100 individuals were left in the world. In 1976, 25 individuals were removed from the wild by Durrell Wildlife Conservation Trust
Durrell Wildlife Conservation Trust is a conservation organization with a mission to save species from extinction. Gerald Durrell founded the Jersey Wildlife Preservation Trust as a charitable institution in 1963 with the dodo as its symbol. Th ...
to begin a breeding program. In 1988, the breeding program was called "undoubtedly the most important chiropteran breeding project now in operation." By 2016, there were 180 individuals in 16 zoos across the United States alone. Worldwide, 46 zoos participate in the Rodrigues flying fox breeding program as of 2017.
Relationship to people
Food
bushmeat
Bushmeat is meat from wildlife species that are Hunting, hunted for human consumption. Bushmeat represents a primary source of animal protein and a cash-earning commodity in poor and rural communities of humid tropical forest regions of the worl ...
. The bushmeat harvest is often unsustainable, often resulting in severe population decline or local extinction
Local extinction, also extirpation, is the termination of a species (or other taxon) in a chosen geographic area of study, though it still exists elsewhere. Local extinctions are contrasted with extinction, global extinctions.
Local extinctions ...
. Flying foxes are killed and sold for bushmeat in several countries in Southeast Asia, South Asia
South Asia is the southern Subregion#Asia, subregion of Asia that is defined in both geographical and Ethnicity, ethnic-Culture, cultural terms. South Asia, with a population of 2.04 billion, contains a quarter (25%) of the world's populatio ...
, and Oceania
Oceania ( , ) is a region, geographical region including Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Outside of the English-speaking world, Oceania is generally considered a continent, while Mainland Australia is regarded as its co ...
, including Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
, Malaysia, Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is an island country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and offshore islands in Melanesia, a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean n ...
, the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
, Bangladesh, China, Fiji
Fiji, officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists of an archipelago of more than 330 islands—of which about ...
, and Guam. Flying fox consumption is particularly common in countries with low food security
Food security is the state of having reliable access to a sufficient quantity of affordable, healthy Human food, food. The availability of food for people of any class, gender, ethnicity, or religion is another element of food protection. Simila ...
and lack of environmental regulation. In some cultures in the region, however, eating flying fox meat is taboo
A taboo is a social group's ban, prohibition or avoidance of something (usually an utterance or behavior) based on the group's sense that it is excessively repulsive, offensive, sacred or allowed only for certain people.''Encyclopædia Britannica ...
. In Namoluk
Namoluk (meaning "lagoon in the middle") is an atoll and municipality in the state of Chuuk, Federated States of Micronesia.
It is the smallest atoll in Micronesia, with a total surface of only 13 km2 and a land mass of less than 1 km ...
, locals are repulsed by the idea of eating flying foxes because the flying foxes urinate on themselves. In predominately Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
regions such as much of Indonesia, flying foxes are rarely consumed because of halal
''Halal'' (; ) is an Arabic word that translates to in English. Although the term ''halal'' is often associated with Islamic dietary laws, particularly meat that is slaughtered according to Islamic guidelines, it also governs ethical practices ...
dietary restrictions.
North Sulawesi
North Sulawesi () is a Provinces of Indonesia, province of Indonesia. It is mainly located on the Minahasa Peninsula of the island of Sulawesi, south of the Philippines and southeast of Sabah, Malaysia, but also includes various small archipel ...
has the greatest demand for flying fox bushmeat. Despite being in Muslim-majority Indonesia, North Sulawesi is predominately Christian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
; therefore, many locals do not follow halal guidelines prohibiting flying fox consumption. In Manado
Manado (, ) is the capital City status in Indonesia, city of the Indonesian Provinces of Indonesia, province of North Sulawesi. It is the second largest city in Sulawesi after Makassar, with the 2020 census giving a population of 451,916,Badan ...
, most local people consume flying fox meat at least once a month. The frequency of flying fox consumption increases tenfold around holidays.
Locals believe that "unique meat" from undomesticated animals should be served on special occasions to "enliven the atmosphere." Suggestions to make the flying fox bushmeat trade more sustainable include enforcing a quota system for harvesting, encouraging hunters to release female and juvenile individuals, and providing economic alternatives to those who make a living selling flying fox bushmeat.
In Guam and the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands
The Northern Mariana Islands, officially the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI), is an unincorporated territory and commonwealth of the United States consisting of 14 islands in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.Lin, Tom C.W.Amer ...
, consumption of the Mariana fruit bat exposes locals to the neurotoxin
Neurotoxins are toxins that are destructive to nervous tissue, nerve tissue (causing neurotoxicity). Neurotoxins are an extensive class of exogenous chemical neurological insult (medical), insultsSpencer 2000 that can adversely affect function ...
beta-Methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA) which may later lead to neurodegenerative diseases
A neurodegenerative disease is caused by the progressive loss of neurons, in the process known as neurodegeneration. Neuronal damage may also ultimately result in their death. Neurodegenerative diseases include amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, mul ...
. BMAA may become biomagnified in humans who consume flying foxes; flying foxes are exposed to BMAA by eating cycad
Cycads are seed plants that typically have a stout and woody (ligneous) trunk (botany), trunk with a crown (botany), crown of large, hard, stiff, evergreen and (usually) pinnate leaves. The species are dioecious, that is, individual plants o ...
fruits.
Medicine
Flying foxes are killed for use in traditional medicine. The Indian flying fox, for example, has many perceived medical uses. Some believe that its fat is a treatment forrheumatism
Rheumatism or rheumatic disorders are conditions causing chronic, often intermittent pain affecting the joints or connective tissue. Rheumatism does not designate any specific disorder, but covers at least 200 different conditions, including a ...
. Tribes in the Attappadi
Attappadi (, HQ:Agali) is a one and only tribal taluk in Kerala state covering an area of . It was carved out of Mannarkkad taluk in Palakkad district in February 2021. Attappadi Reserve Forest is a Protected areas of Kerala, protected area comp ...
region of India eat the cooked flesh of the Indian flying fox to treat asthma and chest pain. Healers of the Kanda tribe of Bangladesh use hair from Indian flying foxes to create treatments for "fever with shivering."
Transmitting disease
 Flying foxes are the
Flying foxes are the natural reservoir
In Infection, infectious disease ecology and epidemiology, a natural reservoir, also known as a disease reservoir or a reservoir of infection, is the population of organisms or the specific environment in which an infectious pathogen naturally li ...
s of several viruses, some of which can be transmitted to humans. Notably, flying foxes can transmit lyssavirus
''Lyssavirus'' (from the Greek ''lyssa'' "rage, fury, rabies" and the Latin '' vīrus'') is a genus of RNA viruses in the family ''Rhabdoviridae'', order '' Mononegavirales''. Mammals, including humans, can serve as natural hosts. The genus ...
es, which cause rabies
Rabies is a viral disease that causes encephalitis in humans and other mammals. It was historically referred to as hydrophobia ("fear of water") because its victims panic when offered liquids to drink. Early symptoms can include fever and abn ...
. In Australia the rabies virus
Rabies virus (''Lyssavirus rabies'') is a neurotropic virus that causes rabies in animals, including humans. It can cause violence, hydrophobia, and fever. Rabies transmission can also occur through the saliva of animals and less commonly throu ...
is not naturally present; Australian bat lyssavirus
Australian bat lyssavirus (ABLV) is a enzootic virus closely related to the rabies virus. It was first identified in a 5-month-old juvenile black flying fox (''Pteropus alecto'') collected near Ballina, New South Wales, Ballina in northern New ...
is the only lyssavirus present. Australian bat lyssavirus was first identified in 1996; it is very rarely transmitted to humans. Transmission occurs from the bite or scratch of an infected animal, but can also occur from getting the infected animal's saliva in a mucous membrane
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It ...
or an open wound
A wound is any disruption of or damage to living tissue, such as skin, mucous membranes, or organs. Wounds can either be the sudden result of direct trauma (mechanical, thermal, chemical), or can develop slowly over time due to underlying diseas ...
. Exposure to flying fox blood, urine, or feces is not a risk of exposure to Australian bat lyssavirus.
Since 1994, there have been three records of people getting infected with it—all three were in Queensland
Queensland ( , commonly abbreviated as Qld) is a States and territories of Australia, state in northeastern Australia, and is the second-largest and third-most populous state in Australia. It is bordered by the Northern Territory, South Austr ...
and each case was fatal.
Flying foxes are also reservoirs of henipavirus
''Henipavirus'' is a genus of negative-strand RNA viruses in the family ''Paramyxoviridae'', order ''Mononegavirales'' containing five established species, and numerous others still under study. Henipaviruses are naturally harboured by several s ...
es such as Hendra virus
Hendra virus (''Henipavirus hendraense'') is a zoonotic virus found solely in Australia. First isolated in 1994, the virus has since been connected to numerous outbreaks of disease in domestic horses and seven human cases. Hendra virus belongs to ...
and Nipah virus
Nipah virus (''Henipavirus nipahense'') is a bat-borne, Zoonosis, zoonotic virus that causes Nipah virus infection in humans and other animals, a disease with a very high mortality rate (40-75%). Numerous disease outbreaks caused by Nipah virus ...
. Hendra virus was first identified in 1994; it also rarely occurs humans. From 1994 to 2013, there have been seven reported cases of Hendra virus affecting people, four of which were fatal. The hypothesized primary route of human infection is via contact with horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 mi ...
s that have come into contact with flying fox urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and many other animals. In placental mammals, urine flows from the Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder and exits the urethra through the penile meatus (mal ...
.
There are no documented instances of direct transmission between flying foxes and humans. As of 2012, there is a vaccine
A vaccine is a biological Dosage form, preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease, infectious or cancer, malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verifi ...
available for horses to decrease the likelihood of infection and transmission.
Nipah virus was first identified in 1998 in Malaysia. Since 1998, there have been several Nipah outbreaks in Malaysia, Singapore
Singapore, officially the Republic of Singapore, is an island country and city-state in Southeast Asia. The country's territory comprises one main island, 63 satellite islands and islets, and one outlying islet. It is about one degree ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
, and Bangladesh, resulting in over 100 casualties. A 2018 outbreak in Kerala, India resulted in 19 humans infected, of which 17 died. The overall fatality rate is 40–75%. Humans can contract Nipah virus from direct contact with flying foxes or their fluids, through exposure to an intermediate host
A host is a person responsible for guests at an event or for providing hospitality during it.
Host may also refer to:
Places
* Host, Pennsylvania, a village in Berks County
* Host Island, in the Wilhelm Archipelago, Antarctica
People
* ...
such as domestic pig
The pig (''Sus domesticus''), also called swine (: swine) or hog, is an omnivorous, domesticated, even-toed, hoofed mammal. It is named the domestic pig when distinguishing it from other members of the genus '' Sus''. Some authorities cons ...
s, or from contact with an infected person. A 2014 study of the Indian flying fox and Nipah virus found that while Nipah virus outbreaks are more likely in areas preferred by flying foxes, "the presence of bats in and of itself is not considered a risk factor for Nipah virus infection." Rather, the consumption of date palm sap is a significant route of transmission. The practice of date palm sap collection involves placing collecting pots at date palm trees. Indian flying foxes have been observed licking the sap as it flows into the pots, as well as defecating and urinating in proximity to the pots. In this way, humans who drink the palm sap can be exposed to the bats' viruses. The use of bamboo skirts on collecting pots lowers the risk of contamination from bat fluids.
Flying foxes can transmit several non-lethal diseases as well, such as Menangle virus
''Menangle pararubulavirus'', also called Menangle virus, is a virus that infects pigs, humans and bats.
History
Menangle virus was first identified in 1997 after a piggery in Menangle near Sydney, NSW, Australia experienced a high number of s ...
and Nelson Bay virus
''Nelson Bay orthoreovirus'', often called Nelson Bay virus (NBV) is a novel double-stranded RNA orthoreovirus species first isolated from a flying fox (Pteropus poliocephalus) near Nelson Bay in New South Wales, Australia.Gard G, Compans RW. Str ...
. These viruses rarely affect humans and few cases have been reported. While other bat species have been suspected or implicated as the reservoir of diseases such as SARS
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is a viral respiratory disease of zoonotic origin caused by the virus SARS-CoV-1, the first identified strain of the SARS-related coronavirus. The first known cases occurred in November 2002, and the ...
and Ebola
Ebola, also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) and Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF), is a viral hemorrhagic fever in humans and other primates, caused by ebolaviruses. Symptoms typically start anywhere between two days and three weeks after in ...
, flying foxes are not suspected as hosts for either causative virus.
Pests
Flying foxes are often consideredpests
PESTS was an anonymous American activist group formed in 1986 to critique racism, tokenism, and exclusion in the art world. PESTS produced newsletters, posters, and other print material highlighting examples of discrimination in gallery represent ...
due to the damage they cause to orchard
An orchard is an intentional plantation of trees or shrubs that is maintained for food production. Orchards comprise fruit tree, fruit- or nut (fruit), nut-producing trees that are generally grown for commercial production. Orchards are also so ...
crops. Flying foxes have been cited as particularly destructive to almond
The almond (''Prunus amygdalus'', Synonym (taxonomy)#Botany, syn. ''Prunus dulcis'') is a species of tree from the genus ''Prunus''. Along with the peach, it is classified in the subgenus ''Amygdalus'', distinguished from the other subgenera ...
s, guava
Guava ( ), also known as the 'guava-pear', is a common tropical fruit cultivated in many tropical and subtropical regions. The common guava '' Psidium guajava'' (lemon guava, apple guava) is a small tree in the myrtle family (Myrtaceae), nativ ...
s, and mango
A mango is an edible stone fruit produced by the tropical tree '' Mangifera indica''. It originated from the region between northwestern Myanmar, Bangladesh, and northeastern India. ''M. indica'' has been cultivated in South and Southeast As ...
es in the Maldives; lychee
Lychee ( , ; ''Litchi chinensis''; ) is a monotypic taxon and the sole member in the genus ''Litchi'' in the soapberry family, Sapindaceae.
There are three distinct subspecies of lychee. The most common is the Indochinese lychee found in So ...
in Mauritius; areca
''Areca'' is a genus of 51 species of Arecaceae, palms in the family (biology), family Arecaceae, found in humid tropical forests from the islands of the Philippines and Malaysia, India, and across Southeast Asia to Melanesia. The generic name ' ...
in India; and stone fruit
In botany, a drupe (or stone fruit) is a type of fruit in which an outer fleshy part (exocarp, or skin, and mesocarp, or flesh) surrounds a single shell (the ''pip'' (UK), ''pit'' (US), ''stone'', or ''pyrena'') of hardened endocarp with a seed ...
s in Australia. Orchard damages from other animals are often misattributed to flying foxes, though, and economic damage can be difficult to quantify or exaggerated. To prevent fruit damage, farmers may legally or illegally cull flying foxes. In the 1800s, the Australian government paid farmers bounties to kill flying foxes, though the practice has since been discontinued.
Alternatives to culling include placing barriers between the bats and fruit trees, such as netting, or harvesting fruit in a timely manner to avoid attracting as many flying foxes. Netting is the most effective way to prevent crop loss, though some farmers find it cost prohibitive. It costs US$4,400–44,000 to net of crops. Other methods of preventing fruit loss may also involve the use of scare guns, chemical deterrents, or night-time lights. Alternatively, planting Singapore cherry trees and other decoy crops next to an orchard can be effective, as flying foxes are much more attracted to their fruits than many other orchard crops.
The location of flying fox camps can be a disturbance to humans. In Batemans Bay, Australia, locals report being so disturbed by flying fox vocalizations in the morning that they lose sleep. Flying foxes can fly into power lines and cause electricity outages. Their guano and body odor are also unpleasant to smell. The presence of flying fox colonies can cause nearby property values to decline.
In culture
 Flying foxes are featured in many indigenous cultures and traditions.
A
Flying foxes are featured in many indigenous cultures and traditions.
A folklore
Folklore is the body of expressive culture shared by a particular group of people, culture or subculture. This includes oral traditions such as Narrative, tales, myths, legends, proverbs, Poetry, poems, jokes, and other oral traditions. This also ...
Dreamtime
The Dreaming, also referred to as Dreamtime, is a term devised by early anthropologists to refer to a religio-cultural worldview attributed to Australian Aboriginal religion and mythology, Australian Aboriginal mythology. It was originally u ...
story from the New South Wales North Coast
New South Wales North Coast or NSW North Coast, an interim Australian bioregion, is located in New South Wales
New South Wales (commonly abbreviated as NSW) is a States and territories of Australia, state on the Eastern states of Austral ...
in Australia features an impatient flying fox wanting the Great Spirit to teach him how to be a bird, only to be hung upside down on a branch. They were also featured in Aboriginal cave art, as evinced by several surviving examples.
In Tonga
Tonga, officially the Kingdom of Tonga, is an island country in Polynesia, part of Oceania. The country has 171 islands, of which 45 are inhabited. Its total surface area is about , scattered over in the southern Pacific Ocean. accordin ...
, flying foxes are considered sacred. All flying foxes are the property of the king, meaning non-royal persons cannot harm them in any way. Tongan legend states that a colony of flying foxes at Kolovai
Kolovai is a village on the Tongan island of Tongatapu. Its 2006 population was 4,098.
The village is notable for its lakalaka, the national dance of Tonga. A national monument has been proposed to preserve the site of the koka tree where members ...
are the descendants of a pair of flying foxes gifted to the King of Tonga by the Princess of Samoa.
In the Indian village of Puliangulam, a colony of Indian flying foxes roosts in a Banyan
A banyan, also spelled banian ( ), is a fig that develops accessory trunks from adjacent prop roots, allowing the tree to spread outwards indefinitely. This distinguishes banyans from other trees with a strangler habit that begin life as ...
tree. Villagers believe that the flying foxes are under the protection of Muni
Muni or Munni may refer to:
Municipal
* A common US abbreviation for municipal, municipal services, and the like
*Municipal bond
*Municipal Bridge, the former name of the George Rogers Clark Memorial Bridge in Louisville, Kentucky
*"Muni", slang ...
, and do not harm the bats. A shrine to Muni is beneath the tree.
If locals believe that they have offended Muni by failing to protect the bats, they will pray and perform puja after offering sweet rice, coconut, and bananas to those attending the ceremony.
Flying foxes are also featured in folk stories from Papua New Guinea. Stories with flying foxes include a legend about a cockatoo
A cockatoo is any of the 21 species of parrots belonging to the family Cacatuidae, the only family in the superfamily Cacatuoidea. Along with the Psittacoidea ( true parrots) and the Strigopoidea (large New Zealand parrots), they make up t ...
stealing feathers from the flying fox, resulting in it becoming nocturnal. Another story features a flying fox that could transform into a young man; the flying fox stole a woman away from her husband to take as his wife. Another legend states that a flying fox-man was responsible for introducing yams to their people.
Indigenous societies in Oceania used parts of flying foxes for functional and ceremonial weapons. In the Solomon Islands, people created barbs out of their bones for use in spears. In New Caledonia, ceremonial axes made of jade
Jade is an umbrella term for two different types of decorative rocks used for jewelry or Ornament (art), ornaments. Jade is often referred to by either of two different silicate mineral names: nephrite (a silicate of calcium and magnesium in t ...
were decorated with braids of flying fox fur. Flying fox wings were depicted on the war shields of the Asmat people
The Asmat are an ethnic group of New Guinea, residing in the province of South Papua, Indonesia. The Asmat inhabit a region on the island's southwestern coast bordering the Arafura Sea, with lands totaling approximately 18,000 km2 (7,336&n ...
of Indonesia; they believed that the wings offered protection to their warriors.
There are modern and historical references to flying fox byproducts used as currency. In New Caledonia, braided flying fox fur was once used as currency. On the island of Makira
The island of Makira (previously known as San Cristóbal) is the largest island of Makira-Ulawa Province in Solomon Islands. It is third most populous of the Solomon Islands after Malaita and Guadalcanal, with a population of 55,126 as of 2020 ...
, which is part of the Solomon Islands, indigenous peoples still hunt flying foxes for their teeth as well as for bushmeat. The canine teeth
In mammalian oral anatomy, the canine teeth, also called cuspids, dogteeth, eye teeth, vampire teeth, or fangs, are the relatively long, pointed teeth. In the context of the upper jaw, they are also known as '' fangs''. They can appear more fl ...
are strung together on necklaces that are used as currency
A currency is a standardization of money in any form, in use or circulation as a medium of exchange, for example banknotes and coins. A more general definition is that a currency is a ''system of money'' in common use within a specific envi ...
. Teeth of the insular flying fox
The insular flying fox or Pacific flying fox (''Pteropus tonganus'') is a species of flying fox in the family Pteropodidae. It is geographically widespread, the most widespread flying fox in the Pacific: it is found in American Samoa, the Cook I ...
are particularly prized, as they are usually large enough to drill holes in. The Makira flying fox
The Makira flying fox (''Pteropus cognatus'') is a species of megabat in the genus ''Pteropus'', found in the Solomon Islands.D.E. Wilson & D.M. Reeder, 2005: ''Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference''. Third Edition. Th ...
is also hunted, though, despite its smaller teeth. Deterring local peoples from using flying fox teeth as currency may be detrimental to the species, with Lavery and Fasi noting, "Species that provide an important cultural resource can be highly treasured." Emphasizing sustainable hunting Sustainable hunting is a conservation-based hunting approach that does not reduce the density of the game animal being hunted via the adherence to hunting limits. Sustainable hunting is a method of hunting that focuses on not degrading the environm ...
of flying foxes to preserve cultural currency may be more effective than encouraging the abandonment of cultural currency. Even if flying foxes were no longer hunted for their teeth, they would still be killed for bushmeat; therefore, retaining their cultural value may encourage sustainable hunting practices. Lavery stated, "It’s a positive, not a negative, that their teeth are so culturally valuable. The practice of hunting bats shouldn’t necessarily be stopped, it needs to be managed sustainably."
Other uses
Flying foxes and other bat species in Southeast Asia are often killed and sold as "mummies". The mummified bodies or skeletons of these bats are often shipped to the United States where they are sold in souvenir or curiosity shops or online through vendors such asEtsy
Etsy, Inc. is an American e-commerce company with an emphasis on the selling of handmade or vintage items and craft supplies. These items fall under a wide range of categories, including jewelry, bags, clothing, home decor, religious items, furni ...
or eBay
eBay Inc. ( , often stylized as ebay) is an American multinational e-commerce company based in San Jose, California, that allows users to buy or view items via retail sales through online marketplaces and websites in 190 markets worldwide. ...
. From 2000 to 2013, over 100,000 dead bats were imported to the United States. Bat conservationist Merlin Tuttle
Merlin Devere Tuttle (born August 26, 1941) is an American ecologist, conservationist, writer and wildlife photographer who has specialized in bat ecology, behavior, and conservation. He is credited with protecting the Austin Congress Avenue Br ...
wrote, "I've seen huge losses, mostly due to various kinds of over-harvesting, especially at cave entrances, either for food or for sale as mummies." Despite sometimes being advertised as "sustainable," the practice could lead to overharvesting and depletion of flying fox species, with Tuttle saying, "It is a virtual certainty that the bats you've seen advertised are not sustainably harvested."
References
{{good article Bats of Asia Bats of Africa Fauna of Southeast Asia Mammals of Thailand Articles containing video clips Bat genera Taxa named by Mathurin Jacques Brisson Taxa described in 1762