|
Colonisation (biology)
Colonisation or colonization is the spread and development of an organism in a new area or habitat. Colonization comprises the physical arrival of a species in a new area, but also its successful establishment within the local community. In ecology, it is represented by the symbol ''λ'' (lowercase lambda) to denote the long-term intrinsic growth rate of a population. Surrounding theories and applicable process have been introduced below. These include dispersal, colonisation-competition trade off and prominent examples that have been previously studied. One classic scientific model in biogeography posits that a species must continue to colonize new areas through its Biological life cycle, life cycle (called a ''taxon cycle'') in order to persist. Accordingly, colonisation and extinction are key components of island biogeography, a theory that has many applications in ecology, such as Metapopulation, metapopulations. Another factor included in this scientific model is the compet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progeny (genetic Descendant)
In biology, offspring are the young creation of living organisms, produced either by sexual or asexual reproduction. Collective offspring may be known as a brood or progeny. This can refer to a set of simultaneous offspring, such as the chicks hatched from one clutch of eggs, or to all offspring produced over time, as with the honeybee. Offspring can occur after mating, artificial insemination, or as a result of cloning. Human offspring ( descendants) are referred to as children; male children are sons and female children are daughters (see Kinship). Overview Offspring contains many parts and properties that are precise and accurate in what they consist of, and what they define. As the offspring of a new species, also known as a child or f1 generation, consist of genes of the father and the mother, which is also known as the parent generation. Each of these offspring contains numerous genes which have coding for specific tasks and properties. Males and females both contrib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recent African Origin Of Modern Humans
The recent African origin of modern humans or the "Out of Africa" theory (OOA) is the most widely accepted paleoanthropology, paleo-anthropological model of the geographic origin and Early human migrations, early migration of early modern human, anatomically modern humans (''Human, Homo sapiens''). It follows the early expansions of hominins out of Africa, accomplished by ''Homo erectus'' and then ''Neanderthal, Homo neanderthalensis''. The model proposes a "monogenism, single origin" of ''Human, Homo sapiens'' in the taxonomic sense, precluding parallel evolution in other regions of traits considered anatomically modern humans, anatomically modern, but not precluding multiple Archaic human admixture with modern humans, admixture between ''H. sapiens'' and archaic humans in Europe and Asia. ''H. sapiens'' most likely developed in the Horn of Africa between 300,000 and 200,000 years ago, although an alternative hypothesis argues that diverse morphological features of ''H. sap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
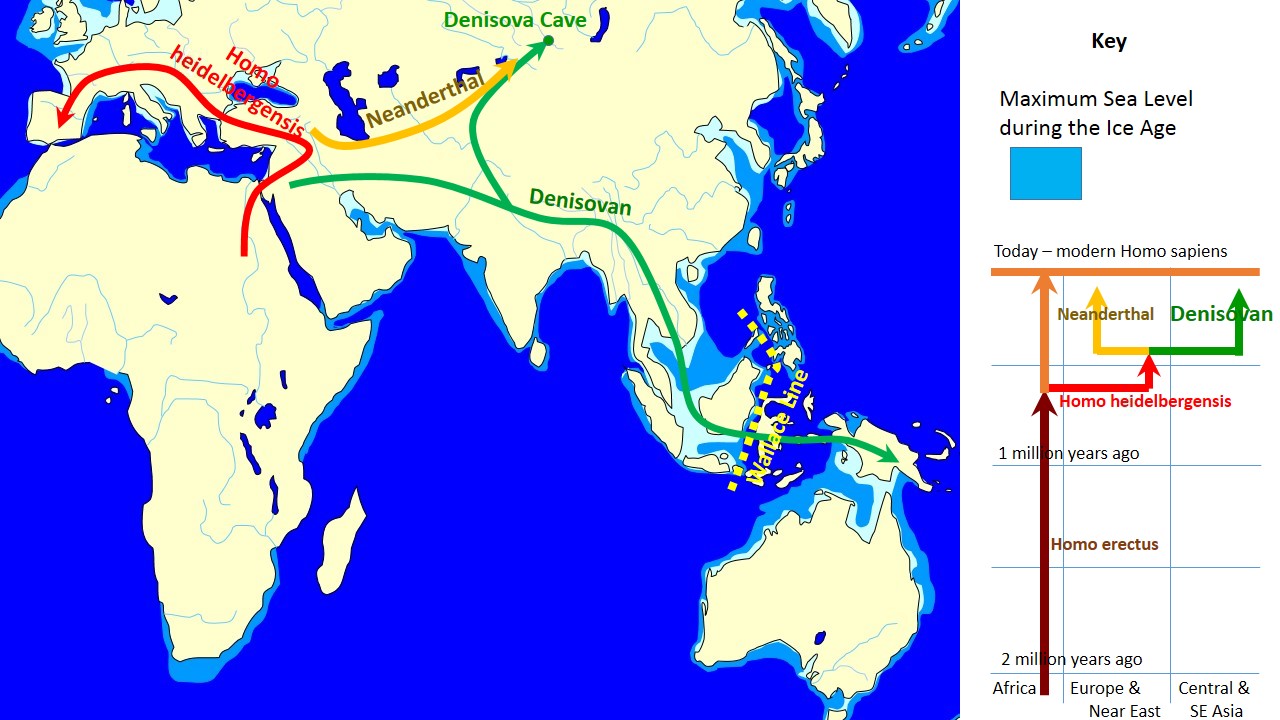
Early Human Migration
Early human migrations are the earliest Human migration, migrations and expansions of Homo, archaic and modern humans across continents. They are believed to have begun approximately 2 million years ago with the early expansions of hominins out of Africa, early expansions out of Africa by ''Homo erectus''. This initial migration was followed by other archaic humans including ''Homo heidelbergensis, H. heidelbergensis'', which lived around 500,000 years ago and was the likely ancestor of Denisovans and Neanderthals as well as modern humans. Early hominids had likely crossed land bridges that have now sunk. Within Africa, ''Homo sapiens'' dispersed around the time of its speciation, roughly 300,000 years ago. The Recent African origin of modern humans, recent African origin theory suggests that the anatomically modern humans outside of Africa descend from a population of ''Homo sapiens'' migrating from East Africa roughly 70–50,000 years ago and spreading Southern Dispersal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millipede
Millipedes (originating from the Latin , "thousand", and , "foot") are a group of arthropods that are characterised by having two pairs of jointed legs on most body segments; they are known scientifically as the class Diplopoda, the name derived from this feature. Each double-legged segment is a result of two single segments fused together. Most millipedes have very elongated cylindrical or flattened bodies with more than 20 segments, while pill millipedes are shorter and can roll into a tight ball. Although the name "millipede" derives from Latin for "thousand feet", no species was known to have 1,000 or more until the discovery in 2020 of '' Eumillipes persephone'', which can have over 1,300 legs. There are approximately 12,000 named species classified into 16 orders and around 140 families, making Diplopoda the largest class of myriapods, an arthropod group which also includes centipedes and other multi-legged creatures. Most millipedes are slow-moving detritivores, eat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metamerism (biology), metameric) Segmentation (biology), segments, and paired jointed appendages. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. They form an extremely diverse group of up to ten million species. Haemolymph is the analogue of blood for most arthropods. An arthropod has an open circulatory system, with a body cavity called a haemocoel through which haemolymph circulates to the interior Organ (anatomy), organs. Like their exteriors, the internal organs of arthropods are generally built of repeated segments. They have ladder-like nervous systems, with paired Anatomical terms of location#Dorsal and ventral, ventral Ventral nerve cord, nerve cord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egretta Garzetta Tree Greece
''Egretta'' is a genus of medium-sized herons, mostly breeding in warmer climates. Representatives of this genus are found in most of the world, and the little egret, as well as being widespread throughout much of the Old World, has now started to colonise the Americas. These are typical egrets in shape, long-necked and long-legged. A few plumage features are shared, although several have plumes in breeding plumage; a number of species are either white in all plumages, have a white morph (e.g. reddish egret), or have a white juvenile plumage (little blue heron). The breeding habitat of ''Egretta'' herons is marshy wetlands in warm regions. They nest in colonies, often with other wading birds, usually on platforms of sticks in trees or shrubs. These herons feed on insects, fish, and amphibians, caught normally by cautious stalking. Taxonomy The genus ''Egretta'' was introduced in 1817 by the German naturalist Johann Reinhold Forster with the little egret as the type species. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasive Species
An invasive species is an introduced species that harms its new environment. Invasive species adversely affect habitats and bioregions, causing ecological, environmental, and/or economic damage. The term can also be used for native species that become harmful to their native environment after human alterations to its food web. Since the 20th century, invasive species have become serious economic, social, and environmental threats worldwide. Invasion of long-established ecosystems by organisms is a natural phenomenon, but human-facilitated introductions have greatly increased the rate, scale, and geographic range of invasion. For millennia, humans have served as both accidental and deliberate dispersal agents, beginning with their earliest migrations, accelerating in the Age of Discovery, and accelerating again with the spread of international trade. Notable invasive plant species include the kudzu vine, giant hogweed (''Heracleum mantegazzianum''), Japanese knotw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species Translocation
Translocation is the human action of moving an organism from one area and releasing it in another. In terms of wildlife conservation, its objective is to improve the conservation status of the translocated organism or to restore the function and processes of the ecosystem the organism is entering. Two overarching goals of translocation are population restoration and conservation introduction.''Guidelines for reintroductions and other conservation translocations'' (PDF). IUCN. Retrieved 06 October 2023. Population restoration includes reinforcing existing populations and reintroducing populations to areas where they have disappeared. Conservation introduction involves assisted colonization of organism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Introduced Species
An introduced species, alien species, exotic species, adventive species, immigrant species, foreign species, non-indigenous species, or non-native species is a species living outside its native distributional range, but which has arrived there by human activity, directly or indirectly, and either deliberately or accidentally. Non-native species can have various effects on the local ecosystem. Introduced species that become established and spread beyond the place of introduction are considered naturalized. The process of human-caused introduction is distinguished from biological colonization, in which species spread to new areas through "natural" (non-human) means such as storms and rafting. The Latin expression neobiota captures the characteristic that these species are ''new'' biota to their environment in terms of established biological network (e.g. food web) relationships. Neobiota can further be divided into neozoa (also: neozoons, sing. neozoon, i.e. animals) and ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pioneer Species Colonization Leading To Primary Sucession
Pioneer commonly refers to a person who is among the first at something that is new to a community. A pioneer as a settler is among the first settling at a place that is new to the settler community. A historic example are American pioneers, persons in American history who migrated westward to settle in what is now the Western and Midwestern United States. Pioneer, The Pioneer, or pioneering may also refer to: Companies and organizations *Pioneer Aerospace Corporation *Pioneer Chicken, an American fast-food restaurant chain *Pioneer Club Las Vegas, a casino in Las Vegas, Nevada, U.S. *Pioneer Corporation, a Japanese electronics manufacturer *Pioneer Energy, a Canadian gas station chain *Pioneer Entertainment, a Japanese anime company *Pioneer Fund, racist foundation, 1937 *Pioneer Hi-Bred, a U.S.-based agriculture company *Pioneer Hotel & Gambling Hall, Laughlin, Nevada, U.S. *Pioneer Instrument Company, an American aeronautical instrument manufacturer *Pioneer movement, a commu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predation
Predation is a biological interaction in which one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common List of feeding behaviours, feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill the Host (biology), host) and parasitoidism (which always does, eventually). It is distinct from Scavenger, scavenging on dead prey, though many predators also scavenge; it overlaps with Herbivore, herbivory, as Seed predation, seed predators and destructive frugivores are predators. Predation behavior varies significantly depending on the organism. Many predators, especially carnivores, have evolved distinct hunting strategy, hunting strategies. Pursuit predation involves the active search for and pursuit of prey, whilst ambush predation, ambush predators instead wait for prey to present an opportunity for capture, and often use stealth or aggressive mimicry. Other predators are opportunism, opportunistic or om ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |