|
Henipavirus
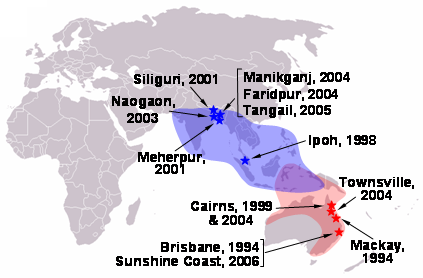
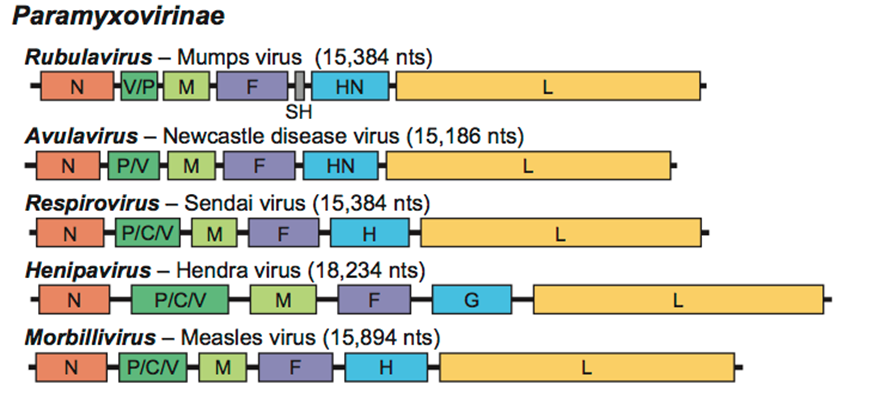
''Henipavirus'' is a genus of negative-strand RNA viruses in the family ''Paramyxoviridae'', order ''Mononegavirales'' containing five established species, and numerous others still under study. Henipaviruses are naturally harboured by several species of small mammals, notably Pteropus, pteropid fruit bats (flying foxes), microbats of several species, and shrews. Henipaviruses are characterised by long genomes and a wide host range. Their recent emergence as zoonosis, zoonotic pathogens capable of causing illness and death in domestic animals and humans is a cause of concern. In 2009, RNA sequences of three novel viruses in phylogenetic relationship to known henipaviruses were detected in African straw-colored fruit bats (''Eidolon helvum'') in Ghana. The finding of these novel henipaviruses outside Australia and Asia indicates that the region of potential endemicity of henipaviruses may be worldwide. These African henipaviruses are slowly being characterised. Nipah virus and He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nipah Virus
Nipah virus (''Henipavirus nipahense'') is a bat-borne, Zoonosis, zoonotic virus that causes Nipah virus infection in humans and other animals, a disease with a very high mortality rate (40-75%). Numerous disease outbreaks caused by Nipah virus have occurred in South East Africa and Southeast Asia. Nipah virus belongs to the genus ''Henipavirus'' along with the Hendra virus, which has also caused disease outbreaks. Virology Like other henipaviruses, the Nipah virus genome is a single (non-segmented) negative-sense, single-stranded RNA of over 18 kb, which is substantially longer than that of other Paramyxoviridae, paramyxoviruses. The viral envelope, enveloped virus particles are variable in shape, and can be filamentous or spherical; they contain a helical nucleocapsid. Six structural proteins are generated: N (nucleocapsid), P (phosphoprotein), M (matrix), F (fusion), G (glycoprotein) and L (RNA polymerase). The ''P'' open reading frame also encodes three nonstructural pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hendra Virus
Hendra virus (''Henipavirus hendraense'') is a zoonotic virus found solely in Australia. First isolated in 1994, the virus has since been connected to numerous outbreaks of disease in domestic horses and seven human cases. Hendra virus belongs to the genus '' Henipavirus'', which also contains the zoonotic Nipah virus. The reservoir species of Hendra virus are four species of bat within the genus ''Pteropus'' native to Australia. Pathology The Pteropus fruit-eating bats, commonly known as flying foxes, experimentally infected with the Hendra virus develop a viraemia and shed the virus in their urine, faeces and saliva for approximately one week. There is no other indication of an illness in them. Symptoms of Hendra virus infection of humans may be respiratory, including hemorrhage and edema of the lungs, or in some cases viral meningitis. In horses, infection usually causes one or more of pulmonary oedema, congestion and neurological signs. Ephrin B2 has been identified as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paramyxoviridae
''Paramyxoviridae'' (from Ancient Greek, Greek ''para-'' “by the side of” and ''myxa'' “mucus”) is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Vertebrates serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with this family include measles, mumps, and respiratory tract infections. The family has nine subfamilies that contain 23 genera. Structure Virions are enveloped and can be spherical or pleomorphic and capable of producing filamentous virions. The diameter is around 150 nm. Genomes are linear, around 15kb in length. Fusion proteins and attachment proteins appear as spikes on the virion surface. Matrix proteins inside the envelope stabilise virus structure. The nucleocapsid core is composed of the genomic RNA, nucleocapsid proteins, phosphoproteins and polymerase proteins. Genome The genome is non-segmented, negative-sense RNA, 15–19 kilobases in length, and contains six to 10 genes. Extracistronic (noncoding) regions include: * A 3’ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pteropus
''Pteropus'' (suborder Yinpterochiroptera) is a genus of megabats which are among the largest bats in the world. They are commonly known as fruit bats or flying foxes, among other colloquial names. They live in South Asia, Southeast Asia, Australia, East Africa, and some oceanic islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. There are at least 60 extant species in the genus. Flying foxes eat fruit and other plant matter, and occasionally consume insects as well. They locate resources with their keen sense of smell. Most, but not all, are nocturnal. They navigate with keen eyesight, as they cannot echolocate. They have long life spans and low reproductive outputs, with females of most species producing only one offspring per year. Their slow life history makes their populations vulnerable to threats such as overhunting, culling, and natural disasters. Six flying fox species have been made extinct in modern times by overhunting. Flying foxes are often persecuted for their real or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fruit Bat
Megabats constitute the family Pteropodidae of the order Chiroptera. They are also called fruit bats, Old World fruit bats, or—especially the genera ''Acerodon'' and ''Pteropus''—flying foxes. They are the only member of the superfamily Pteropodoidea, which is one of two superfamilies in the suborder Yinpterochiroptera. Internal divisions of Pteropodidae have varied since subfamilies were first proposed in 1917. From three subfamilies in the 1917 classification, six are now recognized, along with various tribes. As of 2018, 197 species of megabat had been described. The leading theory of the evolution of megabats has been determined primarily by genetic data, as the fossil record for this family is the most fragmented of all bats. They likely evolved in Australasia, with the common ancestor of all living pteropodids existing approximately 31 million years ago. Many of their lineages probably originated in Melanesia, then dispersed over time to mainland Asia, the Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoonosis
A zoonosis (; plural zoonoses) or zoonotic disease is an infectious disease of humans caused by a pathogen (an infectious agent, such as a virus, bacterium, parasite, fungi, or prion) that can jump from a non-human vertebrate to a human. When humans infect non-humans, it is called reverse zoonosis or anthroponosis. Major modern diseases such as Ebola and salmonellosis are zoonoses. HIV was a zoonotic disease transmitted to humans in the early part of the 20th century, though it has now evolved into a separate human-only disease. Human infection with animal influenza viruses is rare, as they do not transmit easily to or among humans. However, avian and swine influenza viruses in particular possess high zoonotic potential, and these occasionally recombine with human strains of the flu and can cause pandemics such as the 2009 swine flu. Zoonoses can be caused by a range of disease pathogens such as emergent viruses, bacteria, fungi and parasites; of 1,415 pathogens known t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EFNB2
Ephrin-B2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''EFNB2'' gene. Function This gene encodes a member of the ephrin (EPH) family. The ephrins and EPH-related receptors comprise the largest subfamily of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases and have been implicated in mediating developmental events, especially in the nervous system and in erythropoiesis. Based on their structures and sequence relationships, ephrins are divided into the ephrin-A (EFNA) class, which are anchored to the membrane by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol linkage, and the ephrin-B (EFNB) class, which are transmembrane proteins. This gene encodes an EFNB class ephrin which binds to the EPHB4 and EPHA3 receptors. Cancer EFNB2 gene has been observed progressively downregulated in Human papillomavirus-positive neoplastic keratinocytes derived from uterine cervical preneoplastic lesions at different levels of malignancy. For this reason, EFNB2 is likely to be associated with tumorigenesis and may be a pot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proceedings Of The National Academy Of Sciences
''Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America'' (often abbreviated ''PNAS'' or ''PNAS USA'') is a peer-reviewed multidisciplinary scientific journal. It is the official journal of the National Academy of Sciences, published since 1915, and publishes original research, scientific reviews, commentaries, and letters. According to ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2022 impact factor of 9.4. ''PNAS'' is the second most cited scientific journal, with more than 1.9 million cumulative citations from 2008 to 2018. In the past, ''PNAS'' has been described variously as "prestigious", "sedate", "renowned" and "high impact". ''PNAS'' is a delayed open-access journal, with an embargo period of six months that can be bypassed for an author fee ( hybrid open access). Since September 2017, open access articles are published under a Creative Commons license. Since January 2019, ''PNAS'' has been online-only, although print issues are available ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conserved Sequence
In evolutionary biology, conserved sequences are identical or similar sequences in nucleic acids ( DNA and RNA) or proteins across species ( orthologous sequences), or within a genome ( paralogous sequences), or between donor and receptor taxa ( xenologous sequences). Conservation indicates that a sequence has been maintained by natural selection. A highly conserved sequence is one that has remained relatively unchanged far back up the phylogenetic tree, and hence far back in geological time. Examples of highly conserved sequences include the RNA components of ribosomes present in all domains of life, the homeobox sequences widespread amongst eukaryotes, and the tmRNA in bacteria. The study of sequence conservation overlaps with the fields of genomics, proteomics, evolutionary biology, phylogenetics, bioinformatics and mathematics. History The discovery of the role of DNA in heredity, and observations by Frederick Sanger of variation between animal insulins in 194 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syncytia
A syncytium (; : syncytia; from Greek: σύν ''syn'' "together" and κύτος ''kytos'' "box, i.e. cell") or symplasm is a multinucleate cell that can result from multiple cell fusions of uninuclear cells (i.e., cells with a single nucleus), in contrast to a coenocyte, which can result from multiple nuclear divisions without accompanying cytokinesis. The muscle cell that makes up animal skeletal muscle is a classic example of a syncytium cell. The term may also refer to cells interconnected by specialized membranes with gap junctions, as seen in the heart muscle cells and certain smooth muscle cells, which are synchronized electrically in an action potential. The field of embryogenesis uses the word ''syncytium'' to refer to the coenocytic blastoderm embryos of invertebrates, such as ''Drosophila melanogaster''. Physiological examples Protists In protists, syncytia can be found in some rhizarians (e.g., chlorarachniophytes, plasmodiophorids, haplosporidians) and ace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |