Eurasian Land Bridge on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Eurasian Land Bridge (), sometimes called the New Silk Road (, ), is the
The Eurasian Land Bridge (), sometimes called the New Silk Road (, ), is the
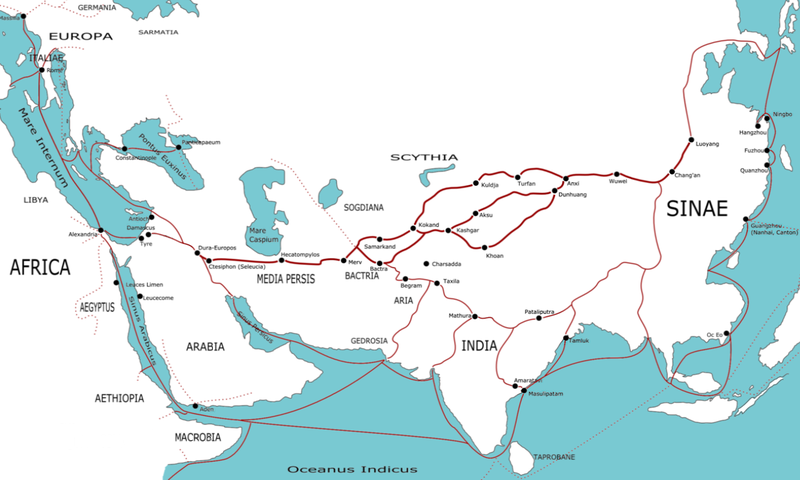 Commercial traffic between Europe and Asia took place along the
Commercial traffic between Europe and Asia took place along the
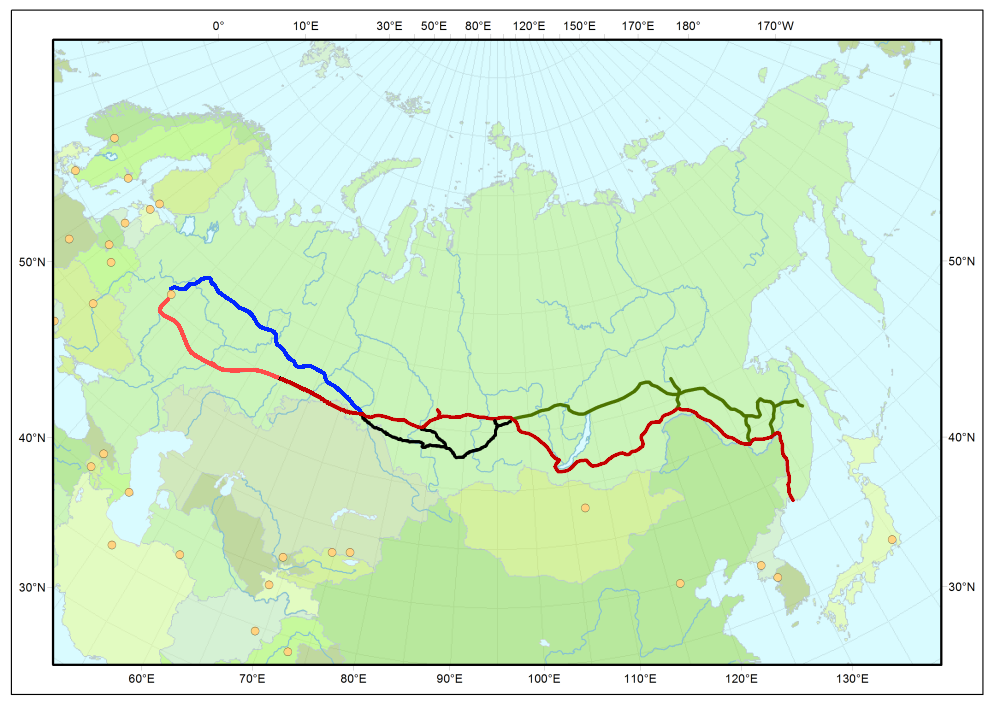 The Trans-Siberian Railway and its various associated branches and supporting lines, completed in 1916, established the first rail connection between Europe and Asia, from Moscow to Vladivostok. The line, at , is the longest rail line in the world.
The Trans-Siberian connects the Russian Pacific ports of
The Trans-Siberian Railway and its various associated branches and supporting lines, completed in 1916, established the first rail connection between Europe and Asia, from Moscow to Vladivostok. The line, at , is the longest rail line in the world.
The Trans-Siberian connects the Russian Pacific ports of
''
 The original Moscow–Vladivostok route, completed in 1904, cut across China's northeastern provinces, or
The original Moscow–Vladivostok route, completed in 1904, cut across China's northeastern provinces, or
("Reconstruction of the bogie exchange facility: workers at Zabaykalsk Station of the Transbaikalian Railway are working round the clock, renovating the passenger railcar bogie exchange facility"). (Transbaikalian Railway official web site, 8 June 2008 The eastern border point of the former Chinese Eastern Railway, at Suifenhe/ Grodekovo, sees significant use as well, with over 8 million tons of freight crossing the border there in 2007, and regular cross-border passenger service. A third, little-known and less used, rail connection between Russia and China was built farther south, between
 While the USSR had long been connected with China via the rail links in Northeastern China and
While the USSR had long been connected with China via the rail links in Northeastern China and
 The transportation authorities in another industrial center of central China,
The transportation authorities in another industrial center of central China,
 The Baku–Tbilisi–Kars railway also provides a route via the Caspian Sea by bypassing Iran, Uzbekistan and Turkmenistan. The new railway lines constructed in Kazakhstan will make it shorter. The new route, in this case, is China–Kazakhstan–Azerbaijan–Georgia–Turkey.
The Baku–Tbilisi–Kars railway also provides a route via the Caspian Sea by bypassing Iran, Uzbekistan and Turkmenistan. The new railway lines constructed in Kazakhstan will make it shorter. The new route, in this case, is China–Kazakhstan–Azerbaijan–Georgia–Turkey.
 The former countries of the Russian Empire and USSR, including Finland (which was once part of Russia), as well as Mongolia, use a
The former countries of the Russian Empire and USSR, including Finland (which was once part of Russia), as well as Mongolia, use a
 On 10 March 2004 the Kazakhstan Railway Company Ltd announced that it was looking for investors to fund the construction of a railway stretching from China across Kazakhstan to the Caspian Sea that would be the same gauge as Chinese railways. Thus, the railway would allow trains from China to cross Kazakhstan without having to change bogies. The reported construction cost of the new railway was $3.5 billion. Chinese media reported that the railway would complete the link between China and Europe via central Asia, but it is unclear where the actual link to Europe would be. Also unclear is whether construction has yet to begin on the project.
The governments of India and
On 10 March 2004 the Kazakhstan Railway Company Ltd announced that it was looking for investors to fund the construction of a railway stretching from China across Kazakhstan to the Caspian Sea that would be the same gauge as Chinese railways. Thus, the railway would allow trains from China to cross Kazakhstan without having to change bogies. The reported construction cost of the new railway was $3.5 billion. Chinese media reported that the railway would complete the link between China and Europe via central Asia, but it is unclear where the actual link to Europe would be. Also unclear is whether construction has yet to begin on the project.
The governments of India and
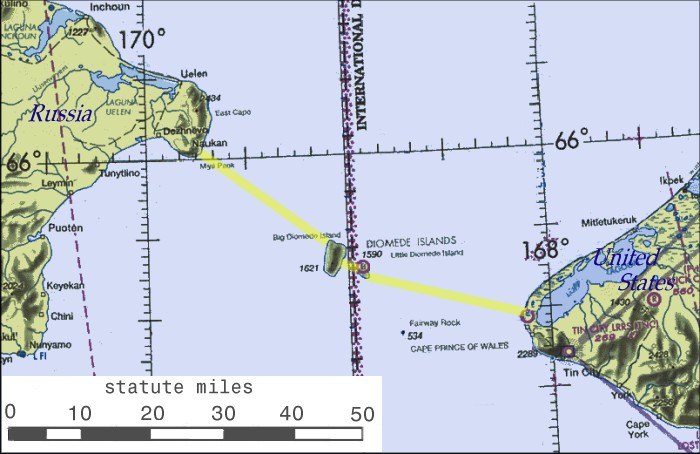 In April 2007 the Russian government announced that it was considering building a double track
In April 2007 the Russian government announced that it was considering building a double track
Vice premier: high-speed railway project, new highlight of Sino-Kazakh co-op
"
The Central People's Government of the People's Republic of China
22 February 2011; retrieved 25 February 2011.
Print
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
 The Eurasian Land Bridge (), sometimes called the New Silk Road (, ), is the
The Eurasian Land Bridge (), sometimes called the New Silk Road (, ), is the rail transport
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport using wheeled vehicles running in railway track, tracks, which usually consist of two parallel steel railway track, rails. Rail transport is one of the two primary means of ...
route for moving freight and passengers overland between Pacific seaports in the Russian Far East
The Russian Far East ( rus, Дальний Восток России, p=ˈdalʲnʲɪj vɐˈstok rɐˈsʲiɪ) is a region in North Asia. It is the easternmost part of Russia and the Asia, Asian continent, and is coextensive with the Far Easte ...
and China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
and seaports in Europe. The route, a transcontinental railroad
A transcontinental railroad or transcontinental railway is contiguous rail transport, railroad trackage that crosses a continent, continental land mass and has terminals at different oceans or continental borders. Such networks may be via the Ra ...
and rail land bridge, comprises the Trans-Siberian Railway
The Trans-Siberian Railway, historically known as the Great Siberian Route and often shortened to Transsib, is a large railway system that connects European Russia to the Russian Far East. Spanning a length of over , it is the longest railway ...
, which runs through Russia and is sometimes called the Northern East-West Corridor, and the New Eurasian Land Bridge or Second Eurasian Continental Bridge, running through China and Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
. As of November 2007, about one percent of the $600 billion in goods shipped from Asia to Europe each year were delivered by inland transport routes.
Completed in 1916, the Trans-Siberian connects Moscow with Russian Pacific seaports such as Vladivostok
Vladivostok ( ; , ) is the largest city and the administrative center of Primorsky Krai and the capital of the Far Eastern Federal District of Russia. It is located around the Zolotoy Rog, Golden Horn Bay on the Sea of Japan, covering an area o ...
. From the 1960s until the early 1990s the railway served as the primary land bridge between Asia and Europe, until several factors caused the use of the railway for transcontinental freight to dwindle. One factor is use of a wider rail gauge
In rail transport, track gauge is the distance between the two rails of a railway track. All vehicles on a rail network must have wheelsets that are compatible with the track gauge. Since many different track gauges exist worldwide, gauge dif ...
by the railways of the former Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
and Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
than most of the rest of Europe and China.
China's rail system had long linked to the Trans-Siberian via northeastern China
Northeast China () is a geographical region of China, consisting officially of three provinces Liaoning, Jilin and Heilongjiang. The heartland of the region is the Northeast China Plain, the largest plain in China with an area of over . The regi ...
and Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by po ...
. In 1990, China added a link between its rail system and the Trans-Siberian via Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
. China calls its uninterrupted rail link between the port city of Lianyungang
Lianyungang () is a prefecture-level city in northeastern Jiangsu province of China, province, China. It borders Yancheng to its southeast, Huai'an and Suqian to its south, Xuzhou to its southwest, and the province of Shandong to its north. Its ...
and Kazakhstan the New Eurasian Land Bridge or Second Eurasian Continental Bridge. In addition to Kazakhstan, the railways connect with other countries in Central Asia and the Middle East, including Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
. With the October 2013 completion of the rail link across the Bosphorus
The Bosporus or Bosphorus Strait ( ; , colloquially ) is a natural strait and an internationally significant waterway located in Istanbul, Turkey. The Bosporus connects the Black Sea to the Sea of Marmara and forms one of the continental bo ...
under the Marmaray project, the New Eurasian Land Bridge now theoretically connects to Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
via Central and South Asia
South Asia is the southern Subregion#Asia, subregion of Asia that is defined in both geographical and Ethnicity, ethnic-Culture, cultural terms. South Asia, with a population of 2.04 billion, contains a quarter (25%) of the world's populatio ...
.
Proposed expansion of the Eurasian Land Bridge includes construction of a railway across Kazakhstan that is the same gauge as Chinese and European railways (standard gauge
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of . The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), international gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge in Europe, and SGR in East Africa. It is the ...
, as opposed to 1,520 mm gauge in the former Russian Empire and the Soviet Union), rail links to India, Burma
Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar; and also referred to as Burma (the official English name until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and ha ...
, Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
, Malaysia
Malaysia is a country in Southeast Asia. Featuring the Tanjung Piai, southernmost point of continental Eurasia, it is a federation, federal constitutional monarchy consisting of States and federal territories of Malaysia, 13 states and thre ...
and elsewhere in Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
, construction of a rail tunnel and highway bridge across the Bering Strait to connect the Trans-Siberian to the North American rail system, and construction of a rail tunnel between South Korea and Japan. The United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
has proposed further expansion of the Eurasian Land Bridge, including the Trans-Asian Railway project.
History
 Commercial traffic between Europe and Asia took place along the
Commercial traffic between Europe and Asia took place along the Silk Road
The Silk Road was a network of Asian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over , it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and religious interactions between the ...
from at least the 2nd millennium BC. The Silk Road was not a specific thoroughfare, but a general route used by traders to travel, much of it by land, between the two continents along the Eurasian Steppe
The Eurasian Steppe, also called the Great Steppe or The Steppes, is the vast steppe ecoregion of Eurasia in the temperate grasslands, savannas and shrublands biome. It stretches through Manchuria, Mongolia, Xinjiang, Kazakhstan, Siberia, Europea ...
s through Central Asia. The route was used to exchange goods, ideas and people primarily between China and India and the Mediterranean and helped create a single-world system of trade between the civilisations of Europe and Asia.Christian; Ōtsuka, p. 42.
Exports from Asia transported along the Silk Road included fabrics, carpets, furs, weapons, utensils, metals, farm produce, livestock and slaves. Civilisations active in trading during the road's history included Scythia
Scythia (, ) or Scythica (, ) was a geographic region defined in the ancient Graeco-Roman world that encompassed the Pontic steppe. It was inhabited by Scythians, an ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic people.
Etymology
The names ...
, Ancient
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history through late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the development of Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient h ...
and Byzantine Greece, the Han and Tang dynasties, Parthia
Parthia ( ''Parθava''; ''Parθaw''; ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Medes during the 7th century BC, was incorporated into the subsequent Achaemeni ...
, Rouran
The Rouran Khaganate ( Chinese: zh, c=, p=Róurán, label=no), also known as Ruanruan or Juan-juan ( zh, c=, p=Ruǎnruǎn, label=no) (or variously ''Jou-jan'', ''Ruruan'', ''Ju-juan'', ''Ruru'', ''Ruirui'', ''Rouru'', ''Rouruan'' or ''Tantan'') ...
, Sogdiana
Sogdia () or Sogdiana was an ancient Iranian civilization between the Amu Darya and the Syr Darya, and in present-day Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan. Sogdiana was also a province of the Achaemenid Empire, and l ...
, Göktürks
The Göktürks (; ), also known as Türks, Celestial Turks or Blue Turks, were a Turkic people in medieval Inner Asia. The Göktürks, under the leadership of Bumin Qaghan (d. 552) and his sons, succeeded the Rouran Khaganate as the main powe ...
, Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of Nomad, nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese historiography, Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, t ...
, Yuezhi
The Yuezhi were an ancient people first described in China, Chinese histories as nomadic pastoralists living in an arid grassland area in the western part of the modern Chinese province of Gansu, during the 1st millennium BC. After a major defea ...
and the Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire was the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in human history, history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Euro ...
.Christian.
Beginning in the 5th century AD, new land routes between Asia and Europe developed further to the north. Many of these routes passed through Yugra and extended to the Baltic region
The Baltic Sea Region, alternatively the Baltic Rim countries (or simply the Baltic Rim), and the Baltic Sea countries/states, refers to the general area surrounding the Baltic Sea, including parts of Northern, Central and Eastern Europe. Un ...
. The Khazars
The Khazars ; 突厥可薩 ''Tūjué Kěsà'', () were a nomadic Turkic people who, in the late 6th century CE, established a major commercial empire covering the southeastern section of modern European Russia, southern Ukraine, Crimea, a ...
, Volga Bulgaria
Volga Bulgaria or Volga–Kama Bulgaria (sometimes referred to as the Volga Bulgar Emirate) was a historical Bulgar state that existed between the 9th and 13th centuries around the confluence of the Volga and Kama River, in what is now Europea ...
, and the Rus' Khaganate
Rus' Khaganate (, ''Russkiy kaganat'', , ''Ruśkyj kahanat''), or Kaganate of Rus is a name applied by some modern historians to a hypothetical polity suggested to have existed during a poorly documented period in the history of Eastern Europe b ...
were active in trading along the northern trade routes.
Traffic along the southern Silk Road routes greatly diminished with the fall of Constantinople
The Fall of Constantinople, also known as the Conquest of Constantinople, was the capture of Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire by the Ottoman Empire. The city was captured on 29 May 1453 as part of the culmination of a 55-da ...
in the 15th century and development of the sea route around the Cape of Good Hope
The Cape of Good Hope ( ) is a rocky headland on the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast of the Cape Peninsula in South Africa.
A List of common misconceptions#Geography, common misconception is that the Cape of Good Hope is the southern tip of Afri ...
in the 16th century. By the 18th century, European influence on trade and new national boundaries severely restricted the movement of traders along all land routes between Europe and China, and overland trade between East Asia and Europe virtually disappeared.
Trans-Siberian Railway
 The Trans-Siberian Railway and its various associated branches and supporting lines, completed in 1916, established the first rail connection between Europe and Asia, from Moscow to Vladivostok. The line, at , is the longest rail line in the world.
The Trans-Siberian connects the Russian Pacific ports of
The Trans-Siberian Railway and its various associated branches and supporting lines, completed in 1916, established the first rail connection between Europe and Asia, from Moscow to Vladivostok. The line, at , is the longest rail line in the world.
The Trans-Siberian connects the Russian Pacific ports of Vladivostok
Vladivostok ( ; , ) is the largest city and the administrative center of Primorsky Krai and the capital of the Far Eastern Federal District of Russia. It is located around the Zolotoy Rog, Golden Horn Bay on the Sea of Japan, covering an area o ...
and Nakhodka with Moscow. Rail links at Moscow allow passengers and freight to connect to train lines running further west into Europe. By making further transfers, passengers and freight can eventually reach Western European seaports. The Trans-Siberian also connects with North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders China and Russia to the north at the Yalu River, Yalu (Amnok) an ...
(e.g. via Dandong
Dandong ( zh, s=丹东 , t=丹東 , p=Dāndōng; lit. "Red East"), formerly known as Andong, is a coastal prefecture-level city in southeastern Liaoning province, in the northeastern region of the People's Republic of China.
It is the largest ...
in Northeastern China, or directly at Khasan south of Vladivostok).
A fully electrified and double-tracked line, the Trans-Siberian Railway line is capable of transporting around 100 million tons of freight annually. The line can handle up to 200,000 TEU of containerized international transit freight per year.
A more northerly east–west route across Siberia, parallel to the Trans-Siberian line and known as the Baikal–Amur Mainline was mostly completed in 1989. It terminates at the Pacific ports of Vanino and Sovetskaya Gavan. Although this line is comparatively little used (the management mentions 6 million tons of freight per year, not indicating the year), the management expects the line to be fully used in the foreseeable future for oil and copper ore export, and has plans to double-track it.
While the Trans-Siberian has always been used by the Tsarist, Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
and modern Russian government to project political power into their territories in Asia, in the 1960s it was opened by the USSR as an international trade route connecting the Western Pacific with Europe. Freight shipments on the Trans-Siberian, however, experienced increasing problems over time with dilapidated rail infrastructures, theft, damaged freight, late trains, inflated freight fees, uncertain scheduling for return of containers and geopolitical tension. As a result, use of the railway for international trade had declined to almost zero by the 1990s.
According to Hofstra University
Hofstra University is a Private university, private research university in Hempstead, New York, United States. It originated in 1935 as an extension of New York University and became an independent college in 1939. Comprising ten schools, includ ...
, as of 2001 there was renewed interest in using the Trans-Siberian as a route across Asia to Europe. Also, the Trans-Siberian links directly to railways which ultimately connect, via Finland and Sweden, to the year-round ice-free port of Narvik
() is the third-largest List of municipalities of Norway, municipality in Nordland Counties of Norway, county, Norway, by population. The administrative centre of the municipality is the Narvik (town), town of Narvik. Some of the notable villag ...
in Norway. At Narvik, freight can be transshipped to ships to cross the Atlantic to North America. Rail links from Russia also connect to Rotterdam
Rotterdam ( , ; ; ) is the second-largest List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city in the Netherlands after the national capital of Amsterdam. It is in the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of South Holland, part of the North S ...
, but may encounter greater congestion along this route with resulting delays. The trade route between the east coast of North America and eastern Russia using the Trans-Siberian is often called the Northern East West Freight Corridor.
In an effort to attract use of the Trans-Siberian to transport goods from Japan, China, and Korea to Europe, in the mid-1990s Russia lowered tariffs on freight using the railway. As a result, freight volume over the rail line doubled in 1999 and 2000.
In February and March 2011, Japan's Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism
The , abbreviated MLIT, is a ministry of the Japanese government.国土交通省設置法
sponsored a test of the route by shipping roof tiles to Europe via the Trans-Siberian. The tiles were transported by ship from Hamada, Shimane to Vladivostok, then by the railway to Moscow. The transit time was expected to be 30 days, in comparison with the 50 days on average it takes to ship cargo by ship from Hamada to ports in western Russia. If successful, the ministry would use the results of the test to encourage other Japanese companies to use the Trans-Siberian over the sea route.
In 2011, a direct container rail service began carrying car parts from Leipzig
Leipzig (, ; ; Upper Saxon: ; ) is the most populous city in the States of Germany, German state of Saxony. The city has a population of 628,718 inhabitants as of 2023. It is the List of cities in Germany by population, eighth-largest city in Ge ...
, Germany, to inland Shenyang
Shenyang,; ; Mandarin pronunciation: ; formerly known as Fengtian formerly known by its Manchu language, Manchu name Mukden, is a sub-provincial city in China and the list of capitals in China#Province capitals, provincial capital of Liaonin ...
, China, through Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states ...
in 23 days, every day.DB Schenker to launch daily freight train to China''
Railway Gazette International
''Railway Gazette International'' is a British monthly business magazine and news website covering the railway, metro, light rail and tram industries worldwide. Available by annual subscription, the magazine is read in over 140 countries by tran ...
'', 30 September 2011. Accessed: 4 October 2011.
In 2013 a direct container, pallet, and general cargo rail service began, from Łódź
Łódź is a city in central Poland and a former industrial centre. It is the capital of Łódź Voivodeship, and is located south-west of Warsaw. Łódź has a population of 655,279, making it the country's List of cities and towns in Polan ...
, Poland, to inland Chengdu
Chengdu; Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ; Chinese postal romanization, previously Romanization of Chinese, romanized as Chengtu. is the capital city of the Chinese province of Sichuan. With a ...
, China, through Siberia in 14 days, 3 days each week.
According to Russian statistics, the amount of international container shipments transiting annually through Russia over the Trans-Siberian grew by a factor of 7 between 2009 and 2014, reaching 131,000 TEU (55,000 physical containers) in 2014.
Belarusian Railways reported similar statistics: in 2014, the volume of direct container traffic from China to Western Europe crossing Belarus amounted to 40,600 TEU, on 25 direct container train routes. This constituted over 20% of Belarusian Railway's entire volume of container transportation that year, 193,100 TEU. This was still much less than 0.1% of the number of containers that travel via China's sea ports (some 170 million TEU).
China and the land bridge
Direct connections between Russia and China
 The original Moscow–Vladivostok route, completed in 1904, cut across China's northeastern provinces, or
The original Moscow–Vladivostok route, completed in 1904, cut across China's northeastern provinces, or Manchuria
Manchuria is a historical region in northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day northeast China and parts of the modern-day Russian Far East south of the Uda (Khabarovsk Krai), Uda River and the Tukuringra-Dzhagdy Ranges. The exact ...
; the section of the railway located within China was known as the Chinese Eastern Railway
The Chinese Eastern Railway or CER (, , or , ''Kitaysko-Vostochnaya Zheleznaya Doroga'' or ''KVZhD''), is the historical name for a railway system in Northeast China (also known as Manchuria).
The Russian Empire constructed the line from 1897 ...
. While the more northerly Trans-Siberian route, located entirely on Russian soil, was completed in 1916, the former Chinese Eastern Railway route continues as an important connector between the two countries' railway networks.
The western border point ( Zabaykalsk/ Manzhouli) and the line connecting it to the Trans-Siberian main line, are now being upgraded, with the goal of enabling the railway by 2010 to pass 30 freight trains in each direction across the border, each one up to 71 cars long. The cross-border freight volume at this rail crossing is expected to reach 25.5 million tons by 2010. Besides cargo (principally, Russian oil exported to China), this crossing sees a direct weekly passenger train, Moscow–Beijing, as well as some local passenger trains.Реконструкция пункта перестановки вагонов: В круглосуточном режиме на станции Забайкальск Забайкальской железной дороги ведется реконструкция пункта перестановки пассажирских вагонов("Reconstruction of the bogie exchange facility: workers at Zabaykalsk Station of the Transbaikalian Railway are working round the clock, renovating the passenger railcar bogie exchange facility"). (Transbaikalian Railway official web site, 8 June 2008 The eastern border point of the former Chinese Eastern Railway, at Suifenhe/ Grodekovo, sees significant use as well, with over 8 million tons of freight crossing the border there in 2007, and regular cross-border passenger service. A third, little-known and less used, rail connection between Russia and China was built farther south, between
Hunchun
Hunchun is a county-level city in the Yanbian Korean Autonomous Prefecture within Jilin province to the far east. It borders North Hamgyong Province in North Korea and Primorsky Krai in Russia, has over 250,000 inhabitants, and covers 5,145&nbs ...
(in China's Jilin
)
, image_skyline = Changbaishan Tianchi from western rim.jpg
, image_alt =
, image_caption = View of Heaven Lake
, image_map = Jilin in China (+all claims hatched).svg
, mapsize = 275px
, map_al ...
province) and Russian Makhalino (a station on the Ussuriysk
Ussuriysk () is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city in Primorsky Krai, Russia, in the valley of the Razdolnaya River. The city is north of Vladivostok, the administrative center of the krai, and about from both the China–Russia bo ...
– Khasan–North Korean border line, before Khasan). It began operating in February 2000, and saw only a minor amount of traffic (678 railcars of lumber) over the next two years. The line was closed in 2002–03, briefly reopened in 2003, and closed again in September 2004. On 15 February 2011, the two companies who own the line, Northeast Asia Railway Group, a Chinese company, and JSC Golden Link, a Russian company, signed an agreement to resume operations on the line in May 2011.
In November 2008, the transport ministries of Russia and the China signed an agreement about creating one more link between the railway systems of the two countries. It will involve a railway bridge between across the Amur (Heilong) River, connecting Tongjiang in China's Heilongjiang
Heilongjiang is a province in northeast China. It is the northernmost and easternmost province of the country and contains China's northernmost point (in Mohe City along the Amur) and easternmost point (at the confluence of the Amur and Us ...
province with Nizhneleninskoye in Russia's Jewish Autonomous Oblast
The Jewish Autonomous Oblast (JAO) is a federal subject of Russia in the far east of the country, bordering Khabarovsk Krai and Amur Oblast in Russia and Heilongjiang province in China. Its administrative center is the town of Birobidzhan.
...
. On 4 November 2010, the project director, Wang Jin, told Xinhua News Agency
Xinhua News Agency (English pronunciation: ),J. C. Wells: Longman Pronunciation Dictionary, 3rd ed., for both British and American English or New China News Agency, is the official state news agency of the People's Republic of China. It is a ...
that construction on the bridge would begin in January 2011.
Russia to China via Mongolia
The Trans-Mongolian line, connectingUlan-Ude
Ulan-Ude (; , ; , ) is the capital city of Buryatia, Russia, located about southeast of Lake Baikal on the Uda River, Buryatia, Uda River at its confluence with the Selenga River, Selenga. According to the Russian Census (2021), 2021 Census, 43 ...
on the Trans-Siberian with China's Erenhot
Erenhot ( ; zh, s=二连浩特, p=Èrliánhàotè, commonly shortened to Ereen or Erlian) is a county-level city under jurisdiction of the Xilingol League, Inner Mongolia, China, located in the Gobi Desert along the Sino-Mongolian border, ac ...
via the Mongolian capital Ulaanbaatar
Ulaanbaatar is the Capital (political), capital and List of cities in Mongolia, most populous city of Mongolia. It has a population of 1.6 million, and it is the coldest capital city in the world by average yearly temperature. The municipa ...
, both serves as a crucial link to the outside world for landlocked Mongolia, and the shortest connection between the Trans-Siberian Railway and Beijing. This line's capacity, however, is limited by its being single-track.
Kazakhstan to China
 While the USSR had long been connected with China via the rail links in Northeastern China and
While the USSR had long been connected with China via the rail links in Northeastern China and Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by po ...
, since the 1950s plans existed to connect the two countries' rail networks at the Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
/Xinjiang
Xinjiang,; , SASM/GNC romanization, SASM/GNC: Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Sinkiang, officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People' ...
border. The Soviets completed their line from Aktogay (a station on the Turksib in eastern Kazakhstan) to their border station Druzhba (now Dostyk), but the construction on the Chinese side stopped because of the Sino-Soviet split
The Sino-Soviet split was the gradual worsening of relations between the People's Republic of China (PRC) and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) during the Cold War. This was primarily caused by divergences that arose from their ...
of the 1960s. In 1985 construction commenced on the Northern Xinjiang Railway to link the Chinese and Russian rail networks via Kazakhstan. The section between Ürümqi
Ürümqi, , is the capital of the Xinjiang, Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in Northwestern China. With a census population of 4 million in 2020, Ürümqi is the second-largest city in China's northwestern interior after Xi'an, also the ...
and Alashankou was completed on 16 September 1990, linking the railway lines of the two countries at Dostyk. In July 1991 the first goods train traveled along the line from China to Kazakhstan's then-capital of Almaty
Almaty, formerly Alma-Ata, is the List of most populous cities in Kazakhstan, largest city in Kazakhstan, with a population exceeding two million residents within its metropolitan area. Located in the foothills of the Trans-Ili Alatau mountains ...
. In December 2009, a second rail link from China was built to the Kazakhstan border at Khorgos. The Jinghe–Yining–Khorgos Railway forks off of the Northern Xinjiang Railway at Jinghe and approaches Kazakhstan from the Ili River Valley. A rail link on Kazakh side will extend the line to Saryozek by 2013. The rail link through the Korgas Pass was completed in December 2012.
Because Kazakhstan was once in the Russian Empire and then a member of the USSR, its rail system connects with and carries the same rail gauge as the Russian rail system, as well as the other Central Asian republics of Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan is a landlocked country in Central Asia bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the south and southwest and the Caspian Sea to the west. Ash ...
, Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan, officially the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia lying in the Tian Shan and Pamir Mountains, Pamir mountain ranges. Bishkek is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Kyrgyzstan, largest city. Kyrgyz ...
and Tajikistan
Tajikistan, officially the Republic of Tajikistan, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Dushanbe is the capital city, capital and most populous city. Tajikistan borders Afghanistan to the Afghanistan–Tajikistan border, south, Uzbekistan to ...
.
From Kazakhstan, four major north–south railways connect with the Russian rail system. Two connect with the Trans-Siberian Railway (the Turksib and the Shu–Nur-Sultan
Astana is the capital city of Kazakhstan. With a population of 1,423,726 within the city limits, it is the second-largest in the country after Almaty, which had been the capital until 1997. The city lies on the banks of the Ishim (river), Ishim ...
–Petropavl
Petropavl ( ; ) is a city on the Ishim River in northern Kazakhstan close to the border with Russia. It is the capital of the North Kazakhstan Region. Population: 218,956.
Petropavl is about from Kökşetau, northwest of the national cap ...
meridional line) while the other two (the Trans-Aral Railway
The Trans-Aral Railway, also known as the Tashkent Railway, is a railway built in 1906 to connect Kinel and Tashkent, both then within the Russian Empire. For much of the early 20th century, it was the only railway link between European Russia a ...
, and the connection via Atyrau and Astrakhan Oblast
Astrakhan Oblast (; ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast) located in southern Russia. Its administrative center is the city of Astrakhan. As of the 2010 Census, its population was 1,010,073.
Geography
Astrakhan's southern border is the ...
) go directly to European Russia. These links to the Russian rail system are sometimes called the Eurasian Railway. Kazakhstan plays an important role in the "New Silk Road" initiative, known as "One Belt, One Road" linking China and Europe through Central Asia and Russia.
A new direction of the Silk Road was launched in January 2016 and included the Ukraine – Georgia – Azerbaijan – Kazakhstan – China route.
Kazakhstan's infrastructure development program Nurly Zhol was developed in line with the New Silk Road Initiative. President of Kazakhstan Nursultan Nazarbayev even noted that Nurly zhol was a part of the New Silk Road Economic Belt.
Through service between China and Western Europe
There are three main routes for container services from China to Europe: Eastern route from Vostochny Port (Russia), northern route from west China via Manzhouli/Zabaikalsk border stations and southern route from east China via Dostyk border station, through which totally 25k TEU has been transported on rail by 2014. In January 2008 China and Germany inaugurated a long-distance freight train service between Beijing andHamburg
Hamburg (, ; ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg,. is the List of cities in Germany by population, second-largest city in Germany after Berlin and List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, 7th-lar ...
. Travelling a total of , the train uses the China Railways and the Trans-Mongolian line to travel from Xiangtan
Xiangtan ( zh, s=湘潭) is a prefecture-level city in east-central Hunan province, south-central China. The hometowns of several founding leaders of the Chinese Communist Party, including Chairman Mao Zedong, President Liu Shaoqi, and Marshal P ...
(in Hunan
Hunan is an inland Provinces of China, province in Central China. Located in the middle reaches of the Yangtze watershed, it borders the Administrative divisions of China, province-level divisions of Hubei to the north, Jiangxi to the east, Gu ...
Province) to Ulaanbaatar
Ulaanbaatar is the Capital (political), capital and List of cities in Mongolia, most populous city of Mongolia. It has a population of 1.6 million, and it is the coldest capital city in the world by average yearly temperature. The municipa ...
, where it then continues north to the Trans-Siberian. After reaching the end of the Trans-Siberian at Moscow the train continues to Germany via rail links in Belarus
Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Belarus spans an a ...
and Poland. Total transit time is 15 days, as compared with the 30 days average it would take for the freight to make the same journey by ship. The first train of 50 containers, carrying a mixed load of clothes, ceramics and electronics (for the Fujitsu company), travelled on tracks operated by six different railways.
Hartmut Mehdorn
Hartmut Mehdorn (born 31 July 1942 in Warsaw) is a German manager and mechanical engineer. Until May 2009 he was CEO of Deutsche Bahn, Germany's biggest railway company. He was CEO of Germany's second largest airline Air Berlin until he stepped ...
, chairman of Deutsche Bahn
(, ; abbreviated as DB or DB AG ) is the national railway company of Germany, and a state-owned enterprise under the control of the German government. Headquartered in the Bahntower in Berlin, it is a joint-stock company ( AG).
DB was fou ...
(DB), stated in March 2008 that regularly scheduled, weekly China-Germany freight services should be in operation by 2010. In April 2009, however, DB postponed the service indefinitely because of the global economic crisis.
Another test run, from Chongqing
ChongqingPostal Romanization, Previously romanized as Chungking ();. is a direct-administered municipality in Southwestern China. Chongqing is one of the four direct-administered municipalities under the State Council of the People's Republi ...
to Duisburg
Duisburg (; , ) is a city in the Ruhr metropolitan area of the western States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. Lying on the confluence of the Rhine (Lower Rhine) and the Ruhr (river), Ruhr rivers in the center of the Rhine-Ruh ...
via Alashankou crossing, Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
, Russia, Belarus
Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Belarus spans an a ...
, and Poland took place in March–April 2011, covering in 16 days. It was again said by DB that if there is enough demand, the service can be made regular already in 2011, As of March 2014, the Chongqing-Duisburg route makes three weekly services carrying up to 50 forty-foot-long containers.
 The transportation authorities in another industrial center of central China,
The transportation authorities in another industrial center of central China, Wuhan
Wuhan; is the capital of Hubei, China. With a population of over eleven million, it is the most populous city in Hubei and the List of cities in China by population, eighth-most-populous city in China. It is also one of the nine National cent ...
, plan to organize regular runs of direct freight train between Wuhan and European destinations (Czech Republic, Poland, Germany) starting in April 2014. Plans call for the service starting from 1–2 trains per month in April–June 2014, gradually increasing the frequency to 1–2 trains per week in 2015. A new customs facility is under construction in Wuhan's Wujiashan (吴家山) industrial area; after its planned opening in October 2015, exports from the Wuhan region will be able to clear Chinese customs there, instead of Alashankou.
By 2016, the freight rail service between a number of container terminals in China and their counterparts in Europe has become fairly regular. Between some city pairs, there is one train per week.
Both with respect to cost and speed, the China-Europe direct train service is in between the air and sea options. While it is estimated that the overall volume of goods moving between China and Europe by rail is not going to surpass 1–2% of the sea cargo volume, it may eat significantly into the air cargo volume.
The service is typically used for valuable and somewhat time-sensitive cargo where the time advantage of rail over ship is essential, which, however, is heavy enough to make the cost saving vs. air transport noticeable. Typical cargoes include complex machinery and spare parts (in both directions), as well as high-end groceries and consumer goods (primarily toward China). While major customers ship their products by full container load, freight forwarders also make it possible to send less-than-container shipments.
On the European end of the freight route, the rail terminal near Duisburg
Duisburg (; , ) is a city in the Ruhr metropolitan area of the western States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. Lying on the confluence of the Rhine (Lower Rhine) and the Ruhr (river), Ruhr rivers in the center of the Rhine-Ruh ...
's river port ( Ruhrort) is a major destination. According to a 2018 report, Duisburg is either the destination, or one of the destinations, of some 80% of all direct China-Western Europe cargo trains.
New Eurasian Land Bridge
The New Eurasian Land Bridge, also called the New Eurasian Continental Bridge, is the name given to China's rail link with Central Asia. The route includes China's east–west railways which, in addition to the Beijiang line, are the Longhai Railway and the Lanzhou–Xinjiang Railway. Together, the railways create an uninterrupted rail link between the port city ofLianyungang
Lianyungang () is a prefecture-level city in northeastern Jiangsu province of China, province, China. It borders Yancheng to its southeast, Huai'an and Suqian to its south, Xuzhou to its southwest, and the province of Shandong to its north. Its ...
in Jiangsu
Jiangsu is a coastal Provinces of the People's Republic of China, province in East China. It is one of the leading provinces in finance, education, technology, and tourism, with its capital in Nanjing. Jiangsu is the List of Chinese administra ...
province and Kazakhstan. In 1995 the Chinese and Kazakhstan governments signed an agreement which allows the latter to use Lianyungang as its primary seaport for exports and imports, and the former intends for Lianyungang to serve as the designated starting point for the New Eurasian Land Bridge.
From Almaty in Kazakhstan, the railway extends to Tashkent
Tashkent (), also known as Toshkent, is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Uzbekistan, largest city of Uzbekistan. It is the most populous city in Central Asia, with a population of more than 3 million people as of April 1, 2024. I ...
and Samarkand
Samarkand ( ; Uzbek language, Uzbek and Tajik language, Tajik: Самарқанд / Samarqand, ) is a city in southeastern Uzbekistan and among the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities in Central As ...
, Uzbekistan and then to Tejen, Turkmenistan. From Tejen, another line continues to Ashgabat
Ashgabat (Turkmen language, Turkmen: ''Aşgabat'') is the capital city, capital and largest city of Turkmenistan. It lies between the Karakum Desert and the Kopet Dag, Kopetdag mountain range in Central Asia, approximately 50 km (30 ...
, the capital of Turkmenistan. After Ashgabat, the line ends at Türkmenbaşy, Turkmenistan
Türkmenbaşy, previously known as Shagadam (), Krasnovodsk () and Kyzyl-Su, is a city in Balkan Region, Balkan Province in western Turkmenistan, on the Türkmenbaşy Gulf of the Caspian Sea. It sits at an elevation of . The population (est 2004 ...
, a port on the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake and usually referred to as a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia: east of the Caucasus, ...
.Ōtsuka, p. 44.
Since 2013, the Trans-Caspian International Transport Route has been operating, which goes through the territory of Kazakhstan to the Port Kuryk, then through the Caspian Sea to Azerbaijan (Ələt
Ələt (also, Älät, Aliat, Aljat, Aliaty, Alyat, Alyat-Pristan’, Alyati-Pristan’, Alyaty, and Alyaty-Pristan’) is a settlement and municipality in Baku, Azerbaijan. It has a population of 12,765. The municipality consists of the settleme ...
), then to Georgia, and from the Georgian Poti Sea Port
The Poti Sea Port ( ka, ფოთის საზღვაო ნავსადგური, ) is a major seaport and harbor off the eastern Black Sea coast at the mouth of the Rioni River in Poti, Georgia. Its UN/LOCODE is GEPTI and is located ...
through the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
to the countries of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
. After the Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, , starting the largest and deadliest war in Europe since World War II, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, conflict between the two countries which began in 2014. The fighting has caused hundreds of thou ...
and the disruption of previous routes, this route became more relevant.
In 1996 a branch railway from Tejen was constructed across the border with Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
(at Serakhs) and linked to the Islamic Republic of Iran Railways
The Islamic Republic of Iran Railways (abbreviated as IRIR, or sometimes as RAI, or as IRI Railway) () is the national state-owned railway system of Iran. The Raja Passenger Train Company is an associate of the IR, and manages its passenger t ...
. The link potentially enables rail freight from China to reach ports on the Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf, sometimes called the Arabian Gulf, is a Mediterranean seas, mediterranean sea in West Asia. The body of water is an extension of the Arabian Sea and the larger Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.Un ...
and via other train lines, to reach into the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region spanning Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is situated between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, comprising parts of Southern Russia, Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. The Caucasus Mountains, i ...
and Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
. In 2016, direct container train service was inaugurated on this route, between Yiwu (Zhejiang
)
, translit_lang1_type2 =
, translit_lang1_info2 = ( Hangzhounese) ( Ningbonese) (Wenzhounese)
, image_skyline = 玉甑峰全貌 - panoramio.jpg
, image_caption = View of the Yandang Mountains
, image_map = Zhejiang i ...
Province) and Teheran
Tehran (; , ''Tehrân'') is the capital and largest city of Iran. It is the capital of Tehran province, and the administrative center for Tehran County and its Central District. With a population of around 9.8 million in the city as of 2025, ...
; the trip takes 14 days.
The central Asian route did not extend all the way into Europe until October 2013 when the rail link across the Bosphorus
The Bosporus or Bosphorus Strait ( ; , colloquially ) is a natural strait and an internationally significant waterway located in Istanbul, Turkey. The Bosporus connects the Black Sea to the Sea of Marmara and forms one of the continental bo ...
though the Marmaray link was opened. Iranian rail lines use gauge, requiring freight cars transiting from China into Iran to change wheel gauges twice. The train ferry across Lake Van
Lake Van (; ; ) is the largest lake in Turkey. It lies in the Eastern Anatolia Region of Turkey in the provinces of Van Province, Van and Bitlis Province, Bitlis, in the Armenian highlands. It is a Salt lake, saline Soda lake, soda lake, receiv ...
is also a capacity restriction.
Chinese state media claims that the New Eurasian Land/Continental Bridge extends from Lianyungang to Rotterdam
Rotterdam ( , ; ; ) is the second-largest List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city in the Netherlands after the national capital of Amsterdam. It is in the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of South Holland, part of the North S ...
, a distance of . The exact route used to connect the two cities, whether through Mongolia or Kazakhstan, however, is unclear.
Iron Silk Road via Turkey
An alternative way from China to Europe is via Turkey. The route from China follows Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Iran, Turkey. Due to longer distance, insufficient service, and border crossings, this route has not regularly been used for direct transport from China to Europe. However, work is underway to improve the viability of this route, such as the Marmaray project to connect Europe and Asia via a tunnel under theBosphorus
The Bosporus or Bosphorus Strait ( ; , colloquially ) is a natural strait and an internationally significant waterway located in Istanbul, Turkey. The Bosporus connects the Black Sea to the Sea of Marmara and forms one of the continental bo ...
. After the completion of the project, a continuous run of trains will be possible between Asia and Europe, which is now done by rail ferry service. But the Marmaray tunnel may give a limited service to freight trains due to dense usage by public transport. On 7 November 2019 the first Chinese freight train through the Marmaray tunnel to Europe ran, from Xi’an using a Chinese locomotive. This demonstrated a China to Turkey transportation time reduced from a month to 12 days.
 The Baku–Tbilisi–Kars railway also provides a route via the Caspian Sea by bypassing Iran, Uzbekistan and Turkmenistan. The new railway lines constructed in Kazakhstan will make it shorter. The new route, in this case, is China–Kazakhstan–Azerbaijan–Georgia–Turkey.
The Baku–Tbilisi–Kars railway also provides a route via the Caspian Sea by bypassing Iran, Uzbekistan and Turkmenistan. The new railway lines constructed in Kazakhstan will make it shorter. The new route, in this case, is China–Kazakhstan–Azerbaijan–Georgia–Turkey.
Break of gauge issues
 The former countries of the Russian Empire and USSR, including Finland (which was once part of Russia), as well as Mongolia, use a
The former countries of the Russian Empire and USSR, including Finland (which was once part of Russia), as well as Mongolia, use a track gauge
In rail transport, track gauge is the distance between the two rails of a railway track. All vehicles on a rail network must have Wheelset (rail transport), wheelsets that are compatible with the track gauge. Since many different track gauges ...
of . The international standard gauge
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of . The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), international gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge in Europe, and SGR in East Africa. It is the ...
used in most of Europe and China is . As a result, trains cannot run from China or European countries into or out of the former USSR without changing bogies. Large facilities to carry out this procedure exist at most border crossing between the " Russian" and " standard" gauge territories (e.g., at Zabaykalsk or Erenhot
Erenhot ( ; zh, s=二连浩特, p=Èrliánhàotè, commonly shortened to Ereen or Erlian) is a county-level city under jurisdiction of the Xilingol League, Inner Mongolia, China, located in the Gobi Desert along the Sino-Mongolian border, ac ...
)
Changing the bogie
A bogie ( ) (or truck in North American English) comprises two or more Wheelset (rail transport), wheelsets (two Railroad wheel, wheels on an axle), in a frame, attached under a vehicle by a pivot. Bogies take various forms in various modes ...
s on a rail car takes hours and special, heavy equipment. In many cases (especially, containerized freight), freight is transshipped from one train to another instead of changing the bogies. As of 2016, this is the usual procedure with China-Europe container trains at places such as Khorgos; it is reported that containers can be moved from one train to another in as little as 47 minutes. In the case of liquids, frozen goods and hazardous materials, however, the bogies are usually changed.
It has been suggested that on some lines variable-gauge axles would achieve significant time savings in comparison to bogie exchange. However, their implementation would involve a much higher capital cost, requiring either retrofitting
Retrofitting is the addition of new technology or features to older systems. Retrofits can happen for a number of reasons, for example with big capital expenditures like naval vessels, military equipment or manufacturing plants, businesses or go ...
or replacement of existing bogies.
Proposed development
Expansion projects
 On 10 March 2004 the Kazakhstan Railway Company Ltd announced that it was looking for investors to fund the construction of a railway stretching from China across Kazakhstan to the Caspian Sea that would be the same gauge as Chinese railways. Thus, the railway would allow trains from China to cross Kazakhstan without having to change bogies. The reported construction cost of the new railway was $3.5 billion. Chinese media reported that the railway would complete the link between China and Europe via central Asia, but it is unclear where the actual link to Europe would be. Also unclear is whether construction has yet to begin on the project.
The governments of India and
On 10 March 2004 the Kazakhstan Railway Company Ltd announced that it was looking for investors to fund the construction of a railway stretching from China across Kazakhstan to the Caspian Sea that would be the same gauge as Chinese railways. Thus, the railway would allow trains from China to cross Kazakhstan without having to change bogies. The reported construction cost of the new railway was $3.5 billion. Chinese media reported that the railway would complete the link between China and Europe via central Asia, but it is unclear where the actual link to Europe would be. Also unclear is whether construction has yet to begin on the project.
The governments of India and Burma
Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar; and also referred to as Burma (the official English name until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and ha ...
have proposed building, with China's cooperation, a link to the Eurasian Land Bridge that would start in India or Burma and connect to the Chinese rail system in Yunnan
Yunnan; is an inland Provinces of China, province in Southwestern China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 47.2 million (as of 2020). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the Chinese provinces ...
. The route would allow freight from India and Burma to travel overland to Europe. The link would also give rail access for China to the Indian Ocean. One proposed starting point for the route is Kyaukpyu. The governments of Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
and Malaysia
Malaysia is a country in Southeast Asia. Featuring the Tanjung Piai, southernmost point of continental Eurasia, it is a federation, federal constitutional monarchy consisting of States and federal territories of Malaysia, 13 states and thre ...
are also studying the feasibility of establishing rail links with China.
Both Russia and China are seeking to establish a permanent rail link with South Korea by way of North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders China and Russia to the north at the Yalu River, Yalu (Amnok) an ...
to allow South Korean goods to be shipped to Europe via the Eurasian Land Bridge. According to Choi Yeon-Hye, a professor of marketing and management at the Korea National Railway College, a rail connection from Busan
Busan (), officially Busan Metropolitan City, is South Korea's second list of cities in South Korea by population, most populous city after Seoul, with a population of over 3.3 million as of 2024. Formerly romanized as Pusan, it is the economi ...
to Rotterdam would cut shipping time from 26 to 16 days and save $800 per container of freight. As part of its plan to link the Trans-Siberian to North and South Korea, Russia rebuilt its rail link from Khasan to Rajin, finishing in October 2011.
The South Korean government announced on 2 December 2009 that it would conduct an economic and technical study on the feasibility of constructing undersea tunnels for transporting goods and people to and from the country directly to Kyushu
is the third-largest island of Japan's Japanese archipelago, four main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands (i.e. excluding Okinawa Island, Okinawa and the other Ryukyu Islands, Ryukyu (''Nansei'') Ryukyu Islands, Islands ...
, Japan and Shandong
Shandong is a coastal Provinces of China, province in East China. Shandong has played a major role in Chinese history since the beginning of Chinese civilization along the lower reaches of the Yellow River. It has served as a pivotal cultural ...
, China.
The United Nations Development Programme
The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) is a United Nations agency tasked with helping countries eliminate poverty and achieve sustainable economic growth and human development. The UNDP emphasizes on developing local capacity towar ...
has advocated greater regional integration along the Eurasian Land Bridge, including development of rail links between the countries of South and Southeast Asia and Central Asia, called the Trans-Asian Railway project. Chinese leaders have called for the establishment of free trade zone
A free-trade zone (FTZ) is a class of special economic zone. It is a geographic area where goods may be imported, stored, handled, manufactured, or reconfigured and re- exported under specific customs regulation and generally not subject t ...
s at both ends of the Eurasian Land Bridge to facilitate development. Said Khalid Malik, United Nations Resident Coordinator in China, "If this comes true, it will enable the continental bridge to play its due role in enhancing co-operation between Asia and Europe, and promoting world peace and development."
In 2010 and 2011, China announced plans to finance expansion of the rail systems in Laos, Thailand, Myanmar, Cambodia, and Vietnam and connect them to China's rail system via Kunming
Kunming is the capital and largest city of the province of Yunnan in China. The political, economic, communications and cultural centre of the province, Kunming is also the seat of the provincial government. During World War II, Kunming was a Ch ...
. The plans include construction of a high-speed rail line from Kunming to Vientiane
Vientiane (, ) is the capital city, capital and largest city of Laos. Situated on the banks of the Mekong, Mekong River at the Thailand, Thai border, it comprises the five urban districts of Vientiane Prefecture and had a population of 840,000 ...
, beginning in April 2011, with a possible future extension to Bangkok
Bangkok, officially known in Thai language, Thai as Krung Thep Maha Nakhon and colloquially as Krung Thep, is the capital and most populous city of Thailand. The city occupies in the Chao Phraya River delta in central Thailand and has an estim ...
.
On 15 December 2011, Russian Prime Minister Vladimir Putin announced that a rail link was being considered between Sakhalin Island and Japan. The rail line, constructed in an undersea tunnel, would link Japan to the Trans-Siberian.
Bering Strait link
 In April 2007 the Russian government announced that it was considering building a double track
In April 2007 the Russian government announced that it was considering building a double track broad gauge
A broad-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge (the distance between the rails) broader than the used by standard-gauge railways.
Broad gauge of , more known as Russian gauge, is the dominant track gauge in former Soviet Union countries ...
rail tunnel under the Bering Strait
The Bering Strait ( , ; ) is a strait between the Pacific and Arctic oceans, separating the Chukchi Peninsula of the Russian Far East from the Seward Peninsula of Alaska. The present Russia–United States maritime boundary is at 168° 58' ...
between Chukotka and Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
. The tunnel, as projected, would be long and would include oil and gas pipelines, fiber optic
An optical fiber, or optical fibre, is a flexible glass or plastic fiber that can transmit light from one end to the other. Such fibers find wide usage in fiber-optic communications, where they permit transmission over longer distances and at ...
cables and power lines. The tunnel project was estimated to cost $65 billion and take between 15 and 20 years to build. In addition to the Russian government, sponsors of the project apparently include Transneft
Joint Stock Company Transneft () is a state-controlled pipeline transport company headquartered in Moscow, Russia. It is the largest oil pipeline company in the world. The company is operating over of trunk pipelines and transports about 80% ...
and RAO United Energy Systems.
The project, as envisioned, would connect the Trans-Siberian via Komsomolsk-on-Amur
Komsomolsk-on-Amur ( rus, Комсомольск-на-Амуре, r=Komsomolsk-na-Amure, p=kəmsɐˈmolʲsk nɐ‿ɐˈmurʲə) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city in Khabarovsk Krai, Russia, located on the west bank of the Amur R ...
/Yakutsk
Yakutsk ( ) is the capital and largest city of Sakha, Russia, located about south of the Arctic Circle. Fueled by the mining industry, Yakutsk has become one of Russia's most rapidly growing regional cities, with a population of 355,443 at the ...
in Siberian Russia with the North American rail network (gauge to be widened) at Fort Nelson, British Columbia, Canada, a distance of . A significant hurdle for the project is that the nearest major road to the Russian end of the tunnel is away. In addition, Alaska has no direct rail link to either Canada or the contiguous United States
The contiguous United States, also known as the U.S. mainland, officially referred to as the conterminous United States, consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the District of Columbia of the United States in central North America. The te ...
. Other leaders, including Wally Hickel, Lyndon LaRouche
Lyndon Hermyle LaRouche Jr. (September 8, 1922 – February 12, 2019) was an American political activist who founded the LaRouche movement and its main organization, the National Caucus of Labor Committees (NCLC). He was a prominent conspiracy ...
, Sun Myung Moon
Sun Myung Moon (; born Moon Yong-myeong; 6 January 1920 – 3 September 2012) was a Korean religious leader, also known for his business ventures and support for conservative political causes. A messiah claimant, he was the founder of the ...
, and the 14th Dalai Lama
The 14th Dalai Lama (born 6 July 1935; full spiritual name: Jetsun Jamphel Ngawang Lobsang Yeshe Tenzin Gyatso, shortened as Tenzin Gyatso; ) is the incumbent Dalai Lama, the highest spiritual leader and head of Tibetan Buddhism. He served a ...
have also advocated the construction of a tunnel or bridge across the strait.
High-speed rail
It was reported in the press in March 2007 that China intends to build a high-speed rail link between China and Western Europe with the possibility of a high-speed rail journey from Beijing to London taking just two days. In February 2011, the Chinese government announced that it would jointly sponsor the construction of a high-speed rail line between Astana and Almaty in Kazakhstan. The announced completion date was 2015.An Lu (Xinhua
Xinhua News Agency (English pronunciation: ),J. C. Wells: Longman Pronunciation Dictionary, 3rd ed., for both British and American English or New China News Agency, is the official State media, state news agency of the China, People's Republic ...
),Vice premier: high-speed railway project, new highlight of Sino-Kazakh co-op
"
The Central People's Government of the People's Republic of China
22 February 2011; retrieved 25 February 2011.
See also
*Belt and Road Initiative
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI or B&R), known in China as the One Belt One Road and sometimes referred to as the New Silk Road, is a global infrastructure development strategy adopted by the government of China in 2013 to invest in more t ...
* Eurasia Continental Bridge corridor
* List of international bridges
An international bridge is a structure that provides transportation across border
Borders are generally defined as geography, geographical boundaries, imposed either by features such as oceans and terrain, or by polity, political entities such a ...
Citations
General references
Web
* * * * * * * *Further information
* * {{Good article Economic history of Russia Economic integration Economy of Siberia Economy of the Russian Far East Economy of Vladivostok History of foreign trade in China History of rail transport International bridges in China International railway lines in Asia International railway lines in Europe International railway lines Belt and Road Initiative Passenger rail transport Rail cooperatives Rail freight transport Rail transport in Asia Rail transport in China Rail transport in Europe Rail transport in Kazakhstan Rail transport in Russia Transnationalism Transport in the Russian Far East International bridges in Russia