|
Trans-Caspian International Transport Route
The Middle Corridor, also called TITR (''Trans-Caspian International Transport Route''), is a trade route from Southeast Asia and China to Europe via Kazakhstan, Caspian Sea, Azerbaijan, Georgia (country), Georgia and Turkey (optional). It is an alternative to the Northern Corridor to the north through Russia, and the Ocean Route to the south, via the Suez Canal. Geographically, the Middle Corridor is the shortest route between Western China and Europe. It is undergoing major developments in parts, with the Trans-Kazakhstan railroad completed in 2014 and the Baku–Tbilisi–Kars railway, Baku–Tbilisi–Kars (BTK) railway operational in 2017. In 2022, the Middle Corridor's cargo doubled to 1.5 million tons, while the Northern Route's shipping volume declined by 34%. However, obstacles to the further use of the Middle Corridor include the limited capacities of Port, seaports and railways, the absence of a unified tariff structure and single operator, and the alignment of geopoli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Corridor Logo
Middle or The Middle may refer to: * Centre (geometry), the point equally distant from the outer limits. Places * Middle (sheading), a subdivision of the Isle of Man * Middle Bay (other) * Middle Brook (other) * Middle Creek (other) * Middle Island (other) * Middle Lake (other) * Middle Mountain, California * Middle Peninsula, Chesapeake Bay, Virginia * Middle Range, a former name of the Xueshan Range on Taiwan Island * Middle River (other) * Middle Rocks, two rocks at the eastern opening of the Straits of Singapore * Middle Sound, a bay in North Carolina * Middle Township (other) * Middle East Music * "Middle" (song), 2015 * "The Middle" (Jimmy Eat World song), 2001 * "The Middle" (Zedd, Maren Morris and Grey song), 2018 *"Middle", a song by Rocket from the Crypt from their 1995 album '' Scream, Dracula, Scream!'' *"The Middle", a song by Demi Lovato from their debut album '' Don't Forget'' *"The Middle", a so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Hamburg, Manchester and Duluth; these access the sea via rivers or canals. Because of their roles as ports of entry for immigrants as well as soldiers in wartime, many port cities have experienced dramatic multi-ethnic and multicultural changes throughout their histories. Ports are extremely important to the global economy; 70% of global merchandise trade by value passes through a port. For this reason, ports are also often densely populated settlements that provide the labor for processing and handling goods and related services for the ports. Today by far the greatest growth in port development is in Asia, the continent with some of the world's largest and busiest ports, such as Singapore and the Chinese ports of Shanghai and Ning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
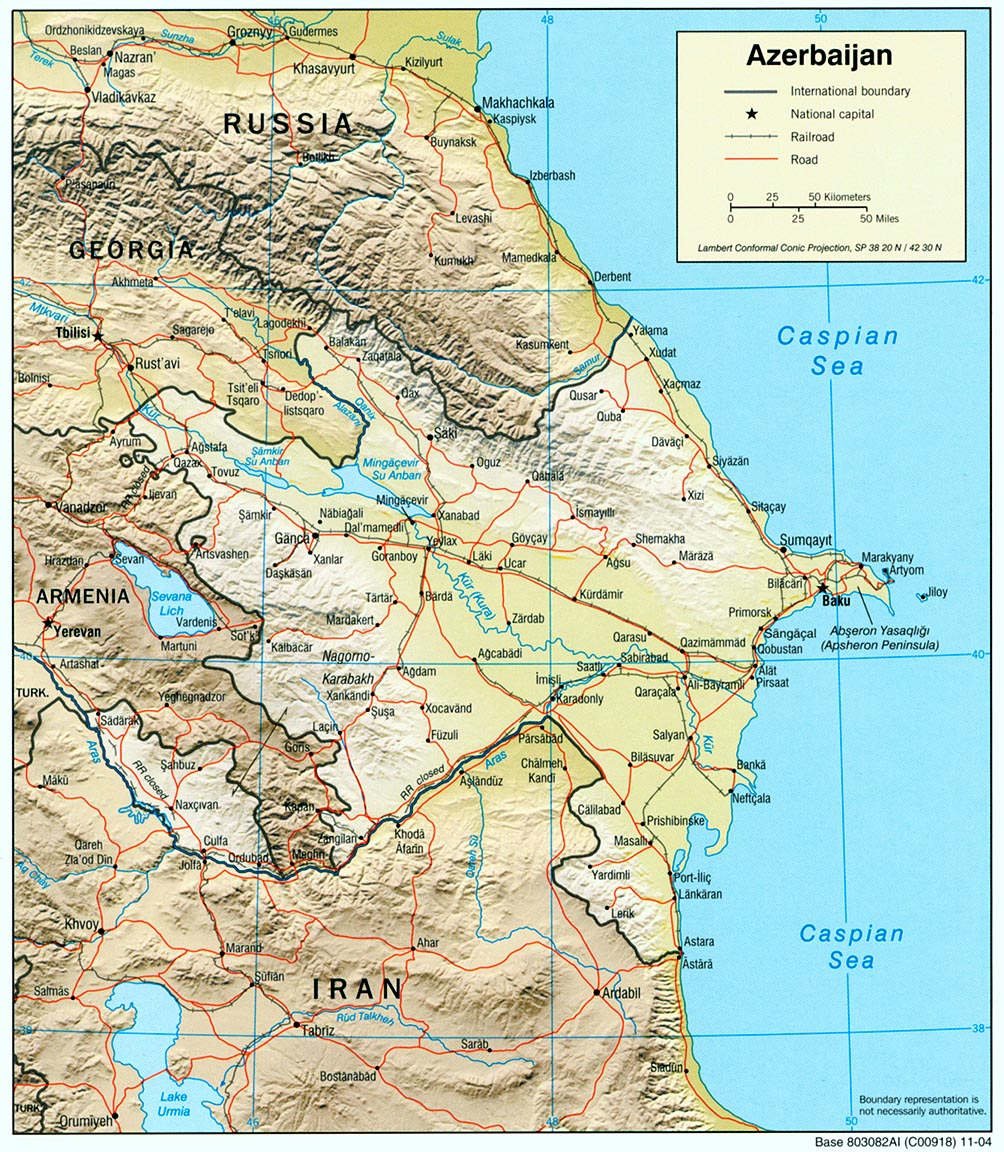
Transport In Azerbaijan
The transport in Azerbaijan involves air traffic, waterways and railroads. All transportation services in Azerbaijan except for oil and gas pipelines are regulated by the Ministry of Transportation of Azerbaijan Republic. * For Soviet transportation, see Transport in the Soviet Union. Railways There are of rail tracks out of which only are in common carrier service and are industrial lines. ''Total:'' (2013) ''Country comparison to the world:'' 59 ''Broad gauge:'' gauge Railway links with adjacent countries Timeline Metro System Currently, the only metro system in Azerbaijan is the Baku Metro, located in Baku, the country's capital. New plans to open metro systems in the most populated and developed cities of Azerbaijan were unveiled. Sumgayit, Nakhchivan and Ganja all plan to have subway systems in the future. Suburban Railway Roadways There are about 25,000 kilometres of roads in Azerbaijan, serving domestic cargo traffic and giving access to in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transport In Kazakhstan
The vast territory of Kazakhstan spans across . The population density is low in Kazakhstan, and the centers of industry and agriculture are spread out and remote from world markets. Railways Railways provide 68% of all cargo and passenger traffic to over 57% of the country. There are in common carrier service, excluding industrial lines. All railway lines in Kazakhstan are built in gauge, of which is electrified (2012). Kazakhstan Temir Zholy (KTZ) is the national railway company. KTZ cooperates with French loco manufacturer Alstom in developing Kazakhstan's railway infrastructure. Alstom has more than 600 staff and two joint ventures with KTZ and its subsidiary in Kazakhstan. In July 2017, Alstom opened its first locomotive repairing center in Kazakhstan. It is the only repairing center in Central Asia and the Caucasus. As the Kazakhstani rail system was designed during the Soviet era, rail routes were designed ignoring inter-Soviet borders, based on the needs of Sovie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transport In Southeast Asia
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land ( rail and road), water, cable, pipeline, and space. The field can be divided into infrastructure, vehicles, and operations. Transport enables human trade, which is essential for the development of civilizations. Transport infrastructure consists of both fixed installations, including roads, railways, airways, waterways, canals, and pipelines, and terminals such as airports, railway stations, bus stations, warehouses, trucking terminals, refueling depots (including fueling docks and fuel stations), and seaports. Terminals may be used both for interchange of passengers and cargo and for maintenance. Means of transport are any of the different kinds of transport facilities used to carry people or cargo. They may include vehicles, riding animals, and pack an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transport In China
Transport in China has experienced major growth and expansion in recent years. Although China's transport system comprises a vast network of transport nodes across its huge territory, the nodes tend to concentrate in the more economically developed coastal areas and inland cities along major rivers. The physical state and comprehensiveness of China's transport infrastructure tend to vary widely by geography. While remote, rural areas still largely depend on non-mechanized means of transport, a modern maglev system was built in China to connect the city center of Shanghai with Shanghai Pudong International Airport. Airports, roads, and railway construction will provide a massive employment boost in China over the next decade. Much of contemporary China's transport systems have been built since the establishment of the People's Republic in 1949. The railway, which is the primary mode of long distance transport, has seen rapid growth reaching of railway lines making it the secon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trade Routes
A trade route is a logistical network identified as a series of pathways and stoppages used for the commercial transport of cargo. The term can also be used to refer to trade over bodies of water. Allowing goods to reach distant markets, a single trade route contains long-distance arteries, which may further be connected to smaller networks of commercial and noncommercial transportation routes. Among notable trade routes was the Amber Road, which served as a dependable network for long-distance trade. Maritime trade along the Spice Route became prominent during the Middle Ages, when nations resorted to military means for control of this influential route. During the Middle Ages, organizations such as the Hanseatic League, aimed at protecting interests of the merchants and trade became increasingly prominent. In modern times, commercial activity shifted from the major trade routes of the Old World to newer routes between modern nation-states. This activity was sometimes c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China–Central Asia–West Asia Economic Corridor
The China–Central Asia–West Asia Economic Corridor (abbreviated as CCAWEC) is an economic and transportation corridor of the Belt and Road Initiative, a global economic connectivity program led by China. The corridor was one of the 6 land corridors articulated in the initial vision for the BRI in 2015. It has since the 2nd Belt and Road Forum in 2019 become one of 35 corridors and project officially included in the BRI. Countries Academic researchers have variously included the countries of Central Asia, the Caucasus, Middle East, Balkans and Turkey as part of the corridor. A report on the BRI by the OECD in 2018 classifies the following long list of countries as part of the corridor: Albania, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Bosnia, Bulgaria, Georgia, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Kyrgyzstan, Lebanon, Macedonia, Moldova, Montenegro, the Palestinian Authority, Romania, Serbia, Syria, Tajikistan, Turkey, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. Freight route The China Railways Express, the first freigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TRACECA
TRACECA (acronym: Transport Corridor Europe-Caucasus-Asia) is an international transport programme involving the European Union and 12 member states of the Eastern European, Caucasus and Central Asian region."TRACECA Member Countries" Traceca.org, accessed 30 January 2017 The programme aim is to strengthen economic relations, trade and transport in the regions of the basin, South Caucasus and Central Asia. It has a permanent Secretariat, originally financed by the , in Baku [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organization Of Turkic States
The Organization of Turkic States (OTS), formerly called the Turkic Council or the Cooperation Council of Turkic Speaking States, is an international organization comprising prominent independent Turkic countries: Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Turkey and Uzbekistan. It is an intergovernmental organization whose overarching aim is promoting comprehensive cooperation among Turkic-speaking states. First proposed by Kazakh President Nursultan Nazarbayev in 2006, it was founded on 3 October 2009, in Nakhchivan. The General Secretariat is in Istanbul. Hungary, Northern Cyprus and Turkmenistan are the observer states. During the 8th summit in Istanbul in 2021, the council reformed into an organization, with the name Turkic Council being changed to Organization of Turkic States. History The organization was established on 3 October 2009 as the Cooperation Council of the Turkic Speaking States (Turkic Council), by the Nakhchivan Agreement signed among Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trade Route
A trade route is a logistical network identified as a series of pathways and stoppages used for the commercial transport of cargo. The term can also be used to refer to trade over bodies of water. Allowing goods to reach distant markets, a single trade route contains long-distance arteries, which may further be connected to smaller networks of commercial and noncommercial transportation routes. Among notable trade routes was the Amber Road, which served as a dependable network for long-distance trade. Maritime trade along the Spice Route became prominent during the Middle Ages, when nations resorted to military means for control of this influential route. During the Middle Ages, organizations such as the Hanseatic League, aimed at protecting interests of the merchants and trade became increasingly prominent. In modern times, commercial activity shifted from the major trade routes of the Old World to newer routes between modern nation-states. This activity was sometimes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geopolitics
Geopolitics (from Greek γῆ ''gê'' "earth, land" and πολιτική ''politikḗ'' "politics") is the study of the effects of Earth's geography (human and physical) on politics and international relations. While geopolitics usually refers to countries and relations between them, it may also focus on two other kinds of states: ''de facto'' independent states with limited international recognition and relations between sub-national geopolitical entities, such as the federated states that make up a federation, confederation, or a quasi-federal system. At the level of international relations, geopolitics is a method of studying foreign policy to understand, explain, and predict international political behavior through geographical variables. These include area studies, climate, topography, demography, natural resources, and applied science of the region being evaluated. Geopolitics focuses on political power linked to geographic space. In particular, territorial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |