|
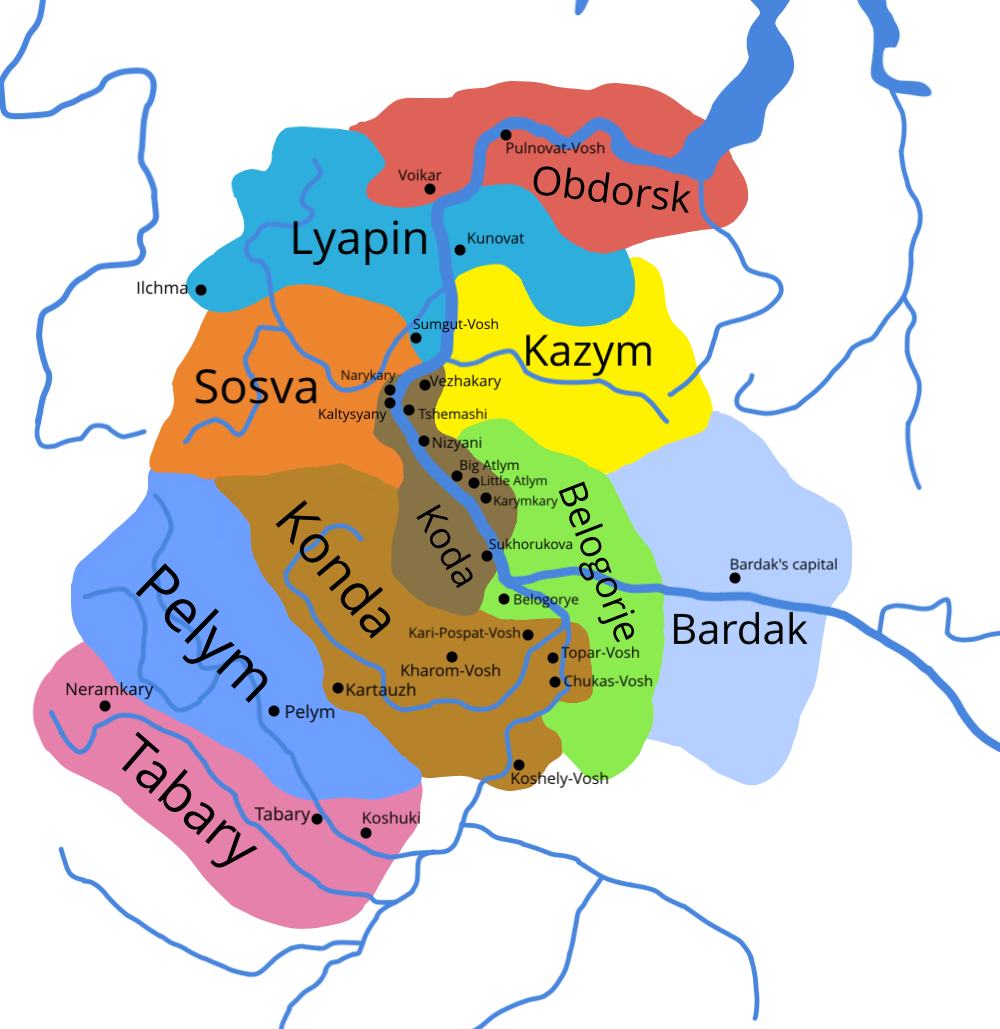
Yugra
Yugra or Yugor Land (; also spelled ''Iuhra'' in contemporary sources) was a collective name for lands and peoples in the region east of the northern Ural Mountains in modern Russia given by Russian chroniclers in the 12th to 17th centuries. During this period, the region was inhabited by the Khanty (Ostyaks) and Mansi (Voguls) peoples. In a modern context, the term ''Yugra'' generally refers to a political constituent of the Russian Federation formally known as Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug–Yugra, located in the lands historically known as Ioughoria. In modern Russian, this word is rendered "Югория" (''Yugoria''), and is used as a poetic synonym of the region. At the beginning of the 16th century, the similarity between ''Yugria'' (the latinized form of the name) and ''ugry'', an old Russian ethnonym for the Hungarians, was noted by scholars such as Maciej Miechowita. The modern name of the Ugric language family, which includes Khanty and Mansi together with H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug–Yugra
Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug–Yugra, also known as Khanty-Mansia (Khantia-Mansia), is a federal subject of Russia (an autonomous okrug of Tyumen Oblast). It has a population of 1,532,243 as of the 2010 Census. Its administrative center is located at Khanty-Mansiysk. The peoples native to the region are the Khanty and the Mansi, known collectively as Ob-Ugric peoples, but today the two groups only constitute 2.5% of the region's population. The local languages, Khanty and Mansi, are part of the Ugric branch of the Finno-Ugric language family, and enjoy a special status in the autonomous okrug. Russian remains the only official language. In 2012, the majority (51%) of the oil produced in Russia came from Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug, giving the region great economic importance in Russia and the world. It borders Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug to the north, Komi Republic to the northwest, Sverdlovsk Oblast to the west, Tyumen Oblast to the south, Tomsk Oblast to the south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mansi People
The Mansi (Mansi language, Mansi: Мāньси / Мāньси мāхум, ''Māńsi / Māńsi māhum'', ) are an Ob-Ugrians, Ob-Ugric Indigenous people living in Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug, Khanty–Mansia, an Autonomous okrugs of Russia, autonomous okrug within Tyumen Oblast in Russia. In Khanty–Mansia, the Khanty language, Khanty and Mansi language, Mansi languages have co-official status with Russian. The Mansi language is one of the postulated Ugric languages of the Uralic languages, Uralic family. The Mansi people were formerly known as the Voguls. Together with the Khanty, Khanty people, the Mansi are politically represented by the Association to Save Yugra, an organisation founded during Perestroika in the late 1980s. This organisation was among the first regional indigenous associations in Russia. Demographics According to the 2021 census, there were 12,228 Mansi in Russia. History The ancestors of the Mansi people populated the areas west of the Urals. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states since the lengthy conquest of Siberia, which began with the fall of the Khanate of Sibir in 1582 and concluded with the annexation of Chukotka in 1778. Siberia is vast and sparsely populated, covering an area of over , but home to roughly a quarter of Russia's population. Novosibirsk, Krasnoyarsk, and Omsk are the largest cities in the area. Because Siberia is a geographic and historic concept and not a political entity, there is no single precise definition of its territorial borders. Traditionally, Siberia spans the entire expanse of land from the Ural Mountains to the Pacific Ocean, with the Ural River usually forming the southernmost portion of its western boundary, and includes most of the drainage basin of the Arctic Ocean. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khanty People
The Khanty (), also known in older literature as Ostyaks (), are a Ob-Ugric languages, Ugric Indigenous people, living in Khanty–Mansi Autonomous Okrug, a region historically known as "Yugra" in Russia, together with the Mansi people, Mansi. In the autonomous okrug, the Khanty language, Khanty and Mansi languages are given co-official status with Russian language, Russian. In the Russian Census (2021), 2021 Census, 31,467 persons identified themselves as Khanty. Of those, 30,242 were resident in Tyumen Oblast, of whom 19,568 were living in Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug and 9,985—in Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug. 495 were residents of neighbouring Tomsk Oblast, and 109 lived in Sverdlovsk Oblast. Ethnonym Since the Khanty language has about 10 dialects which can be united in 3 main branches, there are several slightly different words used by these people to describe themselves: *''Khanti, Khante'' (in Northern Khanty language, North) *''Khande'' (in Southern Khanty lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ),; , ; , or simply the Urals, are a mountain range in Eurasia that runs north–south mostly through Russia, from the coast of the Arctic Ocean to the river Ural (river), Ural and northwestern Kazakhstan.Ural Mountains , Encyclopædia Britannica on-line The mountain range forms part of the Boundaries between the continents of Earth, conventional boundary between the continents of Europe and Asia, marking the separation between European Russia and Siberia. Vaygach Island and the islands of Novaya Zemlya form a further continuation of the chain to the north into the Arctic Ocean. The average altitudes of the Urals are around , the highest point being Mount Narodnaya, which reaches a height of . The mountains lie within the Ural (region), Ural geographical region and significantl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fur Trade
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal ecosystem, boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals have been the most valued. Historically the trade stimulated the exploration and colonization of Siberia, northern North America, and the South Shetland Islands, South Shetland and South Sandwich Islands. Today the importance of the fur trade has diminished; it is based on pelts produced at fur farms and regulated fur-bearer trapping, but has become controversial. Animal rights organizations oppose the fur trade, citing that animals are brutally killed and sometimes skinned alive. Fur has been replaced in some clothing by synthetic fiber, synthetic imitations, for example, as in ruffs on hoods of parkas. Continental fur trade Russian fur trade Before the European colonization of the Americas, Russia was a major supplier of fur pelts to W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novgorod Republic
The Novgorod Republic () was a medieval state that existed from the 12th to 15th centuries in northern Russia, stretching from the Gulf of Finland in the west to the northern Ural Mountains in the east. Its capital was the city of Novgorod. The republic prospered as the easternmost trading post of the Hanseatic League, and its people were much influenced by the culture of the Byzantines, with the Novgorod school of icon painting producing many fine works. Novgorod won its independence in 1136 after the Novgorodians deposed their prince and the Novgorod ''veche'' began to elect and dismiss princes at its own will. The ''veche'' also elected the '' posadnik'', who was the chief executive of the city, and the archbishop of Novgorod, subject to approval by the Russian metropolitan. The '' tysyatsky'' was also elected by the ''veche'', who was originally the military commander, and served the interests of the common people. Novgorodian nobles known as boyars dominated the ''vech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
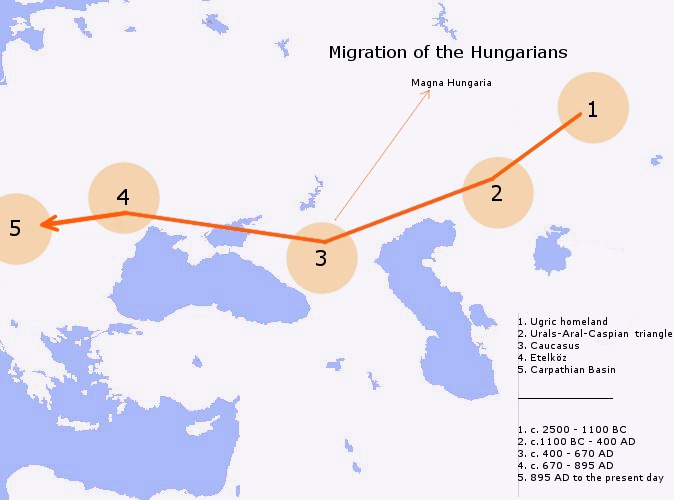
Ugric Languages
The Ugric or Ugrian languages ( or ) are a branch of the Uralic language family. Ugric includes three subgroups: Hungarian, Khanty, and Mansi. The latter two are traditionally considered to be single languages, though they are sometimes considered to be small subdivisions of the Ugric language family due to considerable dialectical differences. A common Proto-Ugric language is posited to have been spoken from the end of the 3rd millennium BC until the first half of the 1st millennium BC, in Western Siberia, east of the southern Ural Mountains. Of the three languages, Khanty and Mansi have sometimes been set apart from Hungarian as Ob-Ugric, though features uniting Mansi and Hungarian in particular are known as well. The name Ugric is derived from ''ugry'' (), a Russian exonym of the Magyars (Hungarians) and also the name of the historical northern Russian region of Yugra. A connection between these words was first suggested in the beginning of 16th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ob (river)
The Ob (; ) is a major river in Russia. It is in western Siberia, and with its tributary the Irtysh forms the world's seventh-longest river system, at . The Ob forms at the confluence of the Biya and Katun which have their origins in the Altai Mountains. It is the westernmost of the three great Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean (the other two being the Yenisei and the Lena). Its flow is north-westward, then northward. The main city on its banks is Novosibirsk, the largest city in Siberia, and the third-largest city in Russia. It is where the Trans-Siberian Railway crosses the river. The Gulf of Ob is the world's longest estuary. Names The internationally known name of the river is based on the Russian name ''Обь'' (''Obʹ'', ). Possibly from Proto-Indo-Iranian '' *Hā́p-'', "river, water" (compare Vedic Sanskrit ''áp-'', Persian ''āb'', Tajik ''ob'', and Pashto ''obə'', "water"). Katz (1990) proposes Komi ''ob'' 'river' as the immediate source o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an Ethnicity, ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common Culture of Hungary, culture, Hungarian language, language and History of Hungary, history. They also have a notable presence in former parts of the Kingdom of Hungary. The Hungarian language belongs to the Ugric languages, Ugric branch of the Uralic languages, Uralic language family, alongside the Khanty languages, Khanty and Mansi languages, Mansi languages. There are an estimated 14.5 million ethnic Hungarians and their descendants worldwide, of whom 9.6 million live in today's Hungary. About 2 million Hungarians live in areas that were part of the Kingdom of Hungary before the Treaty of Trianon in 1920 and are now parts of Hungary's seven neighbouring countries, Hungarians in Slovakia, Slovakia, Hungarians in Ukraine, Ukraine, Hungarians in Romania, Romania, Hungarians in Serbia, Serbia, Hungarians of Croatia, Croatia, Prekmurje, Slovenia, and Hungarians in Austria, Aust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu Hamid Al-Gharnati
Abu Hamid al-Gharnati (full name: Abu Hamid Muhammad ibn Abd al-Rahman ibn Sulayman ibn Rabi al-Māzinī al-Qaysi; c. 1080 – 1170) was an Andalusian traveller from Granada who travelled around eastern and central Europe, and wrote about his travels in an Arabic travelogue, ''Tuhfat al-Albab'' ("Gift of Hearts"). He also wrote about spectacular places and things in ''al''-''Mu’rib ‘an ba’d ‘aja’ib al-Maghreb'' (''Praise of Some of the Wonders of North Africa''), and established a genre of books of wonder in Arabic. Many of the things he saw and wrote about were embellished with fantastic details. Al-Gharnati's family is thought to have fled Granada to escape the reign of the Almoravid emir Yusuf ibn Tashfin. He travelled from Iberia to Egypt and Syria in 1106, reaching Alexandria in 1115 via Sardinia and Sicily, writing about Mount Etna. He moved to Baghdad in 1123. He lived with the Volga Bulgarians from 1131 to 1150 and travelled to Hungary, where he worked as an adviso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kara Sea
The Kara Sea is a marginal sea, separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and from the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya archipelago. Ultimately the Kara, Barents and Laptev Seas are all extensions of the Arctic Ocean north of Siberia. The Kara Sea's northern limit is marked geographically by a line running from Cape Kohlsaat in Graham Bell Island, Franz Josef Land, to Cape Molotov (Arctic Cape), the northernmost point of Komsomolets Island in Severnaya Zemlya. The Kara Sea is roughly long and wide with an area of around and a mean depth of . Its main ports are Novy Port and Dikson and it is important as a fishing ground although the sea is ice-bound for all but two months of the year. The Kara Sea contains the East-Prinovozemelsky field (an extension of the West Siberian Oil Basin), containing significant undeveloped petroleum and natural gas. In 2014, US government sanctions resulted in Exxon having unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |