Eschaton (board Game) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
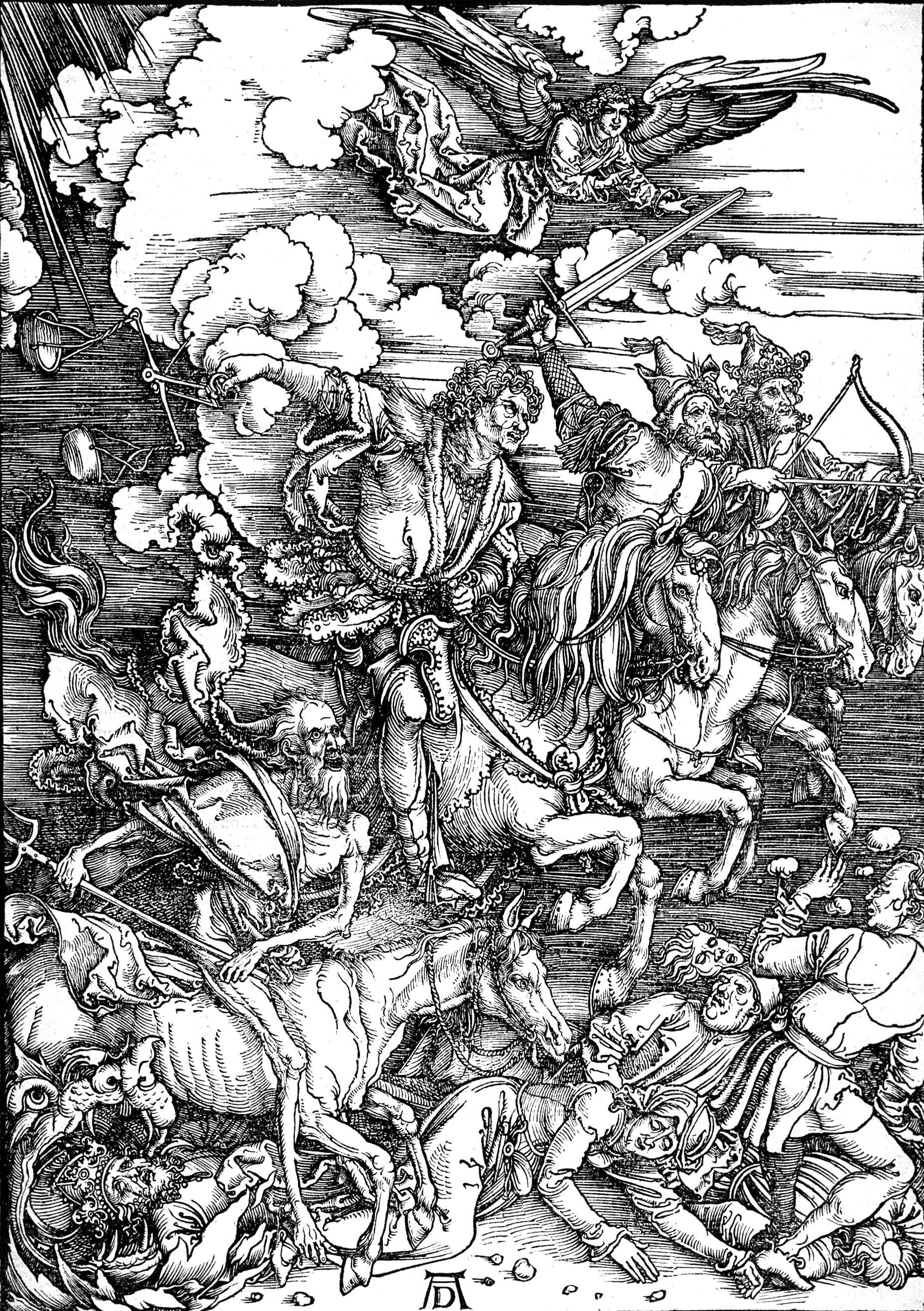 Eschatology (; ) concerns expectations of the end of the present age,
Eschatology (; ) concerns expectations of the end of the present age,
 Eschatology (; ) concerns expectations of the end of the present age,
Eschatology (; ) concerns expectations of the end of the present age, human history
Human history, also called world history, is the narrative of humanity's past. It is understood and studied through anthropology, archaeology, genetics, and linguistics. Since the invention of writing, human history has been studied t ...
, or of the world itself. The end of the world or end times is predicted by several world religion
World religions is a category used in the study of religion to demarcate the five—and in some cases more—largest and most internationally widespread religious movements. Hinduism, Buddhism, Judaism, Christianity, and Islam are always inclu ...
s (both Abrahamic
The Abrahamic religions are a group of religions centered around worship of the God of Abraham. Abraham, a Hebrew patriarch, is extensively mentioned throughout Abrahamic religious scriptures such as the Bible and the Quran.
Jewish tradition ...
and non-Abrahamic), which teach that negative world events will reach a climax. Belief that the end of the world is imminent is known as apocalypticism
Apocalypticism is the religious belief that the end of the world is imminent, even within one's own lifetime. This belief is usually accompanied by the idea that civilization will soon come to a tumultuous end due to some sort of catastrophic ...
, and over time has been held both by members of mainstream religions and by doomsday cults. In the context of mysticism
Mysticism is popularly known as becoming one with God or the Absolute, but may refer to any kind of ecstasy or altered state of consciousness which is given a religious or spiritual meaning. It may also refer to the attainment of insight in u ...
, the term refers metaphorically to the end of ordinary reality
Reality is the sum or aggregate of all that is real or existent within a system, as opposed to that which is only imaginary. The term is also used to refer to the ontological status of things, indicating their existence. In physical terms, r ...
and to reunion with the divine. Various religions
Religion is usually defined as a social-cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatural, tran ...
treat eschatology as a future event prophesied in sacred text
Religious texts, including scripture, are texts which various religions consider to be of central importance to their religious tradition. They differ from literature by being a compilation or discussion of beliefs, mythologies, ritual pract ...
s or in folklore
Folklore is shared by a particular group of people; it encompasses the traditions common to that culture, subculture or group. This includes oral traditions such as Narrative, tales, legends, proverbs and jokes. They include material culture, r ...
.
The Abrahamic religions maintain a linear cosmology
Cosmology () is a branch of physics and metaphysics dealing with the nature of the universe. The term ''cosmology'' was first used in English in 1656 in Thomas Blount's ''Glossographia'', and in 1731 taken up in Latin by German philosophe ...
, with end-time scenarios containing themes of transformation and redemption
Redemption may refer to:
Religion
* Redemption (theology), an element of salvation to express deliverance from sin
* Redemptive suffering, a Roman Catholic belief that suffering can partially remit punishment for sins if offered to Jesus
* Pi ...
. In later Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in the ...
, the term "end of days" makes reference to the Messianic Age
In Abrahamic religions, the Messianic Age is the future period of time on Earth in which the messiah will reign and bring universal peace and brotherhood, without any evil. Many believe that there will be such an age; some refer to it as the cons ...
and includes an in-gathering of the exiled Jewish diaspora
The Jewish diaspora ( he, תְּפוּצָה, təfūṣā) or exile (Hebrew: ; Yiddish: ) is the dispersion of Israelites or Jews out of their ancient ancestral homeland (the Land of Israel) and their subsequent settlement in other parts of ...
, the coming of the Messiah
In Abrahamic religions, a messiah or messias (; ,
; ,
; ) is a saviour or liberator of a group of people. The concepts of '' mashiach'', messianism, and of a Messianic Age originated in Judaism, and in the Hebrew Bible, in which a ''mashiach ...
, the resurrection of the righteous, and the world to come
The world to come, age to come, heaven on Earth, and the Kingdom of God are eschatological phrases reflecting the belief that the current world or current age is flawed or cursed and will be replaced in the future by a better world, age, or pa ...
. Some forms of Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesu ...
depict the end time as a period of tribulation
In Christian eschatology, the Great Tribulation ( grc, θλῖψις μεγάλη, thlîpsis megálē) is a period mentioned by Jesus in the Olivet Discourse as a sign that would occur in the time of the end.
At Revelation 7:14, "the Great Tri ...
that precedes the second coming
The Second Coming (sometimes called the Second Advent or the Parousia) is a Christian (as well as Islamic and Baha'i) belief that Jesus will return again after his ascension to heaven about two thousand years ago. The idea is based on messi ...
of Christ
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religi ...
, who will face the rise of the Antichrist
In Christian eschatology, the Antichrist refers to people prophesied by the Bible to oppose Jesus Christ and substitute themselves in Christ's place before the Second Coming. The term Antichrist (including one plural form)1 John ; . 2 John ...
along with his power structure and false prophet
In religion, a false prophet is a person who falsely claims the gift of prophecy or divine inspiration, or to speak for God, or who makes such claims for evil ends. Often, someone who is considered a "true prophet" by some people is simulta ...
s, and usher in the Kingdom of God
The concept of the kingship of God appears in all Abrahamic religions, where in some cases the terms Kingdom of God and Kingdom of Heaven are also used. The notion of God's kingship goes back to the Hebrew Bible, which refers to "his kingdom" ...
. In Islam, the Day of Judgment
The Last Judgment, Final Judgment, Day of Reckoning, Day of Judgment, Judgment Day, Doomsday, Day of Resurrection or The Day of the Lord (; ar, یوم القيامة, translit=Yawm al-Qiyāmah or ar, یوم الدین, translit=Yawm ad-Dīn, ...
is preceded by the appearance of the Masīḥ ad-Dajjāl, and followed by the descending of ʿĪsā
In Islam, Jesus ( ar, عِيسَى ٱبْنُ مَرْيَمَ, lit= Isa, son of Maryam, translit=ʿĪsā ibn Maryam) is believed to be the penultimate prophet and messenger of God and the Messiah. He is also considered to be the prophet se ...
(Jesus), which shall triumph over the false Messiah or Antichrist; his defeat will lead to a sequence of events that will end with the sun rising from the west and the beginning of the Qiyāmah (Judgment Day).
Dharmic religions
Indian religions, sometimes also termed Dharmic religions or Indic religions, are the religions that originated in the Indian subcontinent. These religions, which include Hinduism, Jainism, Buddhism, and Sikhism,Adams, C. J."Classification of ...
tend to have more cyclical worldviews, with end-time eschatologies characterized by decay, redemption, and rebirth (though some believe transitions between cycles are relatively uneventful). In Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or ''dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global po ...
, the end time occurs when Kalki
Kalki ( sa, कल्कि), also called Kalkin or Karki, is the prophesied tenth and final incarnation of the Hindu god Vishnu. He is described to appear in order to end the Kali Yuga, one of the four periods in the endless cycle of exis ...
, the final incarnation of Vishnu
Vishnu ( ; , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism.
Vishnu is known as "The Preserver" within ...
, descends atop a white horse and brings an end to the current ''Kali Yuga
''Kali Yuga'', in Hinduism, is the fourth and worst of the four '' yugas'' (world ages) in a '' Yuga Cycle'', preceded by ''Dvapara Yuga'' and followed by the next cycle's '' Krita (Satya) Yuga''. It is believed to be the present age, which ...
'', completing a cycle that starts again with the regeneration of the world. In Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
, the Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism.
According to Buddhist tradition, he was born in ...
predicted his teachings would be forgotten after 5,000 years, followed by turmoil. It says a ''bodhisattva
In Buddhism, a bodhisattva ( ; sa, 𑀩𑁄𑀥𑀺𑀲𑀢𑁆𑀢𑁆𑀯 (Brahmī), translit=bodhisattva, label=Sanskrit) or bodhisatva is a person who is on the path towards bodhi ('awakening') or Buddhahood.
In the Early Buddhist schoo ...
'' named Maitreya will appear and rediscover the teachings of the ''Buddha Dharma
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gra ...
'', and that the ultimate destruction of the world will then come through seven suns.
Since the development of the concept of deep time
Deep time is a term introduced and applied by John McPhee to the concept of geologic time in his book ''Basin and Range'' (1981), parts of which originally appeared in the '' New Yorker'' magazine.
The philosophical concept of geological time ...
in the 18th century and the calculation of the estimated age of planet Earth, scientific discourse about end times has considered the ultimate fate of the universe
The ultimate fate of the universe is a topic in physical cosmology, whose theoretical restrictions allow possible scenarios for the evolution and ultimate fate of the universe to be described and evaluated. Based on available observational ev ...
. Theories have included the Big Rip, Big Crunch
The Big Crunch is a hypothetical scenario for the ultimate fate of the universe, in which the expansion of the universe eventually reverses and the universe recollapses, ultimately causing the cosmic scale factor to reach zero, an event potent ...
, Big Bounce, and Big Freeze ( heat death). Social and scientific commentators also worry about global catastrophic risks
A global catastrophic risk or a doomsday scenario is a hypothetical future event that could damage human well-being on a global scale, even endangering or destroying modern civilization. An event that could cause human extinction or permanen ...
and scenarios that could result in human extinction
Human extinction, also known as omnicide, is the hypothetical end of the human species due to either natural causes such as population decline from sub-replacement fertility, an asteroid impact, or large-scale volcanism, or to anthropoge ...
.
Etymology
The word "eschatology" arises from theAncient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
term (''éschatos''), meaning "last", and ''-logy
''-logy'' is a suffix in the English language, used with words originally adapted from Ancient Greek ending in ('). The earliest English examples were anglicizations of the French '' -logie'', which was in turn inherited from the Latin '' -log ...
'', meaning "the study of", and first appeared in English around 1844. The ''Oxford English Dictionary
The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') is the first and foundational historical dictionary of the English language, published by Oxford University Press (OUP). It traces the historical development of the English language, providing a com ...
'' defines eschatology as "the part of theology concerned with death, judgment, and the final destiny of the soul and of humankind".
Linear cosmology
Judaism
The main tenets of modern Jewish eschatology, in no particular order, include: * God will redeem Israel from the captivity that began during theBabylonian Exile
The Babylonian captivity or Babylonian exile is the period in Jewish history during which a large number of Judeans from the ancient Kingdom of Judah were captives in Babylon, the capital city of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, following their def ...
in a new Exodus
Exodus or the Exodus may refer to:
Religion
* Book of Exodus, second book of the Hebrew Torah and the Christian Bible
* The Exodus, the biblical story of the migration of the ancient Israelites from Egypt into Canaan
Historical events
* Exo ...
.
* God will return the Jewish people to the Land of Israel.
* God will restore the House of David and the Temple in Jerusalem
The Temple in Jerusalem, or alternatively the Holy Temple (; , ), refers to the two now-destroyed religious structures that served as the central places of worship for Israelites and Jews on the modern-day Temple Mount in the Old City of Jeru ...
.
* God will raise up a regent from the House of David, the Jewish Messiah
The Messiah in Judaism () is a savior and liberator figure in Jewish eschatology, who is believed to be the future redeemer of the Jewish people. The concept of messianism originated in Judaism, and in the Hebrew Bible a messiah is a king or Hig ...
, to lead the Jewish people and the world and to usher in an age of justice and peace, the Messianic Age
In Abrahamic religions, the Messianic Age is the future period of time on Earth in which the messiah will reign and bring universal peace and brotherhood, without any evil. Many believe that there will be such an age; some refer to it as the cons ...
.
* Nations will recognize that the God of Israel is the only true god.
* God will resurrect the dead.
* God will create a new heaven and earth.
Judaism usually refers to the end times as the "end of days" (''aḥarit ha-yamim'', אחרית הימים), a phrase that appears several times in the Tanakh
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
''
 Protestants are divided between
Protestants are divided between
 In 1843, William Miller made the first of several predictions that the world would end in only a few months. As his predictions did not come true (referred to as the
In 1843, William Miller made the first of several predictions that the world would end in only a few months. As his predictions did not come true (referred to as the
 The eschatology of
The eschatology of
July 15, 1894, p. 1677
: "We see no reason for changing the figures—nor could we change them if we would. They are, we believe, God's dates, not ours. But bear in mind that the end of 1914 is not the date for the beginning, but for the end of the time of trouble." 19181 September 1916 ''The Watchtower'', page
264–265
and 1925''Millions Now Living Will Never Die'', 1920, page 97, "Based upon the argument heretofore set forth, then, that the old order of things, the old world, is ending and is therefore passing away, and that the new order is coming in, and that 1925 shall mark the resurrection of the faithful worthies of old and the beginning of reconstruction, it is reasonable to conclude that millions of people now on the earth will be still on the earth in 1925. Then, based upon the promises set forth in the divine Word, we must reach the positive and indisputable conclusion that millions now living will never die." made in the Watch Tower Society's publications between 1879 and 1924. Claims about the significance of those years, including the presence of Jesus Christ, the beginning of the "last days", the destruction of worldly governments and the earthly resurrection of Jewish patriarchs, were successively abandoned. In 1922 the society's principal magazine, ''
KJV They also believe there will be increasing war, earthquakes, hurricanes, and man-made disasters prior to the Second Coming. Disasters of all kind will happen before Christ comes. Upon the return of Jesus Christ, all people will be resurrected, the righteous in a first resurrection and the unrighteous in a second, later resurrection. Christ shall reign for a period of 1000 years, after which the Final Judgement will occur.

 Rastafari have a unique interpretation of end times, based on the
Rastafari have a unique interpretation of end times, based on the
 Notable teaching he will rediscover is that of the ten non-virtuous deeds—killing, stealing, sexual misconduct, lying, divisive speech, abusive speech, idle speech, covetousness, harmful intent and wrong views. The ten virtuous deeds will replace them with the abandonment of each of these practices.
Notable teaching he will rediscover is that of the ten non-virtuous deeds—killing, stealing, sexual misconduct, lying, divisive speech, abusive speech, idle speech, covetousness, harmful intent and wrong views. The ten virtuous deeds will replace them with the abandonment of each of these practices.


 Researchers in
Researchers in
An overview of models of technological singularity
/ref> Occasionally the term "physical eschatology" is applied to the long-term predictions of astrophysics about the
''
Book of Daniel
The Book of Daniel is a 2nd-century BC biblical apocalypse with a 6th century BC setting. Ostensibly "an account of the activities and visions of Daniel, a noble Jew exiled at Babylon", it combines a prophecy of history with an eschatology ...
and in numerous other prophetic passages in the Hebrew scriptures, and also in the Talmud
The Talmud (; he, , Talmūḏ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law ('' halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the cen ...
, particularly Tractate Avodah Zarah
''Avodah Zarah'' ( Hebrew: , or "foreign worship", meaning "idolatry" or "strange service") is the name of a tractate of the Talmud, located in '' Nezikin'', the fourth Order of the Talmud dealing with damages. The main topic of the tractate ...
.
The idea of a Messianic Age, an era of global peace and knowledge of the Creator, has a prominent place in Jewish thought, and is incorporated as part of the end of days. A well-known passage from the Book of Isaiah describes this future condition of the world: "They shall beat their swords into plowshares and their spears into pruning hooks; nation will not lift sword against nation and they will no longer study warfare" (2:4). Maimonides
Musa ibn Maimon (1138–1204), commonly known as Maimonides (); la, Moses Maimonides and also referred to by the acronym Rambam ( he, רמב״ם), was a Sephardic Jewish philosopher who became one of the most prolific and influential Torah ...
(1135–1204) further describes the Messianic Era in the Mishneh Torah
The ''Mishneh Torah'' ( he, מִשְׁנֵה תּוֹרָה, , repetition of the Torah), also known as ''Sefer Yad ha-Hazaka'' ( he, ספר יד החזקה, , book of the strong hand, label=none), is a code of Rabbinic Jewish religious law (''h ...
: "And at that time there will be no hunger or war, no jealousy or rivalry. For the good will be plentiful, and all delicacies available as dust. The entire occupation of the world will be only to know God;... the people Israel will be of great wisdom; they will perceive the esoteric truths and comprehend their Creator's wisdom as is the capacity of man. As it is written (Isaiah 11:9): 'For the earth shall be filled with the knowledge of God, as the waters cover the sea.'"
Kabbalah
InKabbalah
Kabbalah ( he, קַבָּלָה ''Qabbālā'', literally "reception, tradition") is an esoteric method, discipline and school of thought in Jewish mysticism. A traditional Kabbalist is called a Mekubbal ( ''Məqūbbāl'' "receiver"). The de ...
, the Zohar
The ''Zohar'' ( he, , ''Zōhar'', lit. "Splendor" or "Radiance") is a foundational work in the literature of Jewish mystical thought known as Kabbalah. It is a group of books including commentary on the mystical aspects of the Torah (the five ...
maintains that the seven days of the week, based on the seven days of creation, correspond to the seven millennia of creation. The seventh day of the week, the Shabbat day of rest, corresponds to the seventh millennium, the age of universal rest, or the Messianic Era. The seventh millennium begins with the year 6000 AM, and is the latest time the Messiah can come. A number of early and late Jewish scholars have written in support of this, including the Ramban, Isaac Abrabanel, Abraham Ibn Ezra, Rabbeinu Bachya, the Vilna Gaon
Elijah ben Solomon Zalman, ( he , ר' אליהו בן שלמה זלמן ''Rabbi Eliyahu ben Shlomo Zalman'') known as the Vilna Gaon ( Yiddish: דער װילנער גאון ''Der Vilner Gaon'', pl, Gaon z Wilna, lt, Vilniaus Gaonas) or Elijah of ...
, the Lubavitcher Rebbe, the Ramchal
Moshe Chaim Luzzatto ( he, משה חיים לוצאטו, also ''Moses Chaim'', ''Moses Hayyim'', also ''Luzzato'') (1707 – 16 May 1746 (26 ''Iyar'' 5506)), also known by the Hebrew acronym RaMCHaL (or RaMHaL, ), was a prominent Italia ...
, Aryeh Kaplan
Aryeh Moshe Eliyahu Kaplan ( he, אריה משה אליהו קפלן; October 23, 1934 – January 28, 1983) was an American Orthodox rabbi, author, and translator, best known for his Living Torah edition of the Torah. He became well known as ...
and Rebbetzin Esther Jungreis
Esther Jungreis (April 27, 1936 – August 23, 2016, 19 Menachem Av, 5776) was a Jewish, Hungarian-born, American author, and public speaker. She was the founder of the international Hineni organization in the United States. A Holocaust survivor ...
.
Zoroastrianism
Frashokereti is theZoroastrian
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheistic ...
doctrine of a final renovation of the universe when evil will be destroyed, and everything else will then be in perfect unity with God (Ahura Mazda
Ahura Mazda (; ae, , translit=Ahura Mazdā; ), also known as Oromasdes, Ohrmazd, Ahuramazda, Hoormazd, Hormazd, Hormaz and Hurmuz, is the creator deity in Zoroastrianism. He is the first and most frequently invoked spirit in the '' Yasna ...
). The doctrinal premises are:
# Good will eventually prevail over evil.
# Creation, initially perfectly good, was subsequently corrupted by evil.
# The world will ultimately be restored to the perfection it had at the time of creation.
# The "salvation for the individual depended on the sum of hat person'sthoughts, words and deeds, and there could be no intervention, whether compassionate or capricious, by any divine being to alter this". Thus each human bears the responsibility for the fate of his own soul, and simultaneously shares in the responsibility for the fate of the world.
.
Zoroastrian eschatology is considered one of the oldest in recorded history. The birth of its founder, Zoroaster
Zoroaster,; fa, زرتشت, Zartosht, label= Modern Persian; ku, زەردەشت, Zerdeşt also known as Zarathustra,, . Also known as Zarathushtra Spitama, or Ashu Zarathushtra is regarded as the spiritual founder of Zoroastrianism. He is ...
, is unknown, with scholarly dates ranging from sixth century BCE to 5,500 years earlier. Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ...
even suggests there were two Zoroasters. However, with beliefs paralleling and possibly predating the framework of the major Abrahamic faiths, a fully developed concept of the end of the world was not established in Zoroastrianism until 500 BCE. The Bahman Yasht
The ''Zand-i Wahman Yasn'' is a medieval Zoroastrian apocalyptical text in Middle Persian. It professes to be a prophetical work, in which Ahura Mazda gives Zoroaster an account of what was to happen to the ''behdin'' (those of the "good religion ...
describes:
At the end of thy tenth hundredth winter, the sun is more unseen and more spotted; the year, month, and day are shorter; and the earth is more barren; and the crop will not yield the seed. And men become more deceitful and more given to vile practices. They will have no gratitude. Honorable wealth will proceed to those of perverted faith. And a dark cloud makes the whole sky night, and it will rain more noxious creatures than water.A
Manichaean
Manichaeism (;
in New Persian ; ) is a former major religionR. van den Broek, Wouter J. Hanegraaff ''Gnosis and Hermeticism from Antiquity to Modern Times''SUNY Press, 1998 p. 37 founded in the 3rd century AD by the Parthian prophet Mani (A ...
battle between the righteous and wicked will be followed by the Frashokereti. On earth, the Saoshyant will arrive as the final savior of mankind, and bring about the resurrection of the dead
General resurrection or universal resurrection is the belief in a resurrection of the dead, or resurrection from the dead ( Koine: , ''anastasis onnekron''; literally: "standing up again of the dead") by which most or all people who have died ...
. The ''yazata''s Airyaman and Atar will melt the metal in the hills and mountains, which will flow as lava across the earth and all mankind, both the living and resurrected, will be required to wade through it. '' Ashavan'' will pass through the molten river as if it were warm milk, but the sinful will burn. It will then flow down to hell, where it will annihilate Angra Mainyu
Angra Mainyu (; Avestan: 𐬀𐬢𐬭𐬀⸱𐬨𐬀𐬌𐬥𐬌𐬌𐬎 ''Aŋra Mainiiu'') is the Avestan-language name of Zoroastrianism's hypostasis of the "destructive/evil spirit" and the main adversary in Zoroastrianism either of the ...
and the last vestiges of wickedness.
The righteous will partake of the ''parahaoma'', which will confer immortality upon them. Humanity will become like the Amesha Spentas, living without food, hunger, thirst, weapons or injury. Bodies will become so light as to cast no shadow. All humanity will speak a single language, and belong to a single nation with no borders. All will share a single purpose and goal, joining with Ahura Mazda
Ahura Mazda (; ae, , translit=Ahura Mazdā; ), also known as Oromasdes, Ohrmazd, Ahuramazda, Hoormazd, Hormazd, Hormaz and Hurmuz, is the creator deity in Zoroastrianism. He is the first and most frequently invoked spirit in the '' Yasna ...
for a perpetual and divine exaltation.
Gnosticism
TheGnostic
Gnosticism (from grc, γνωστικός, gnōstikós, , 'having knowledge') is a collection of religious ideas and systems which coalesced in the late 1st century AD among Jewish and early Christian sects. These various groups emphasized pe ...
codex On the Origin of the World states that during what is called the consummation of the age, the Sun and Moon will become dark as the stars change their ordinary course. Kings will make war with each other, and thunder will cause the world to be shaken. The corrupt Archons
''Archon'' ( gr, ἄρχων, árchōn, plural: ἄρχοντες, ''árchontes'') is a Greek word that means "ruler", frequently used as the title of a specific public office. It is the masculine present participle of the verb stem αρχ-, mean ...
will mourn. The sea will be troubled by fighting of the kings who became drunk from the flaming sword. Finally, great thunder will come from Sophia
Sophia means "wisdom" in Greek. It may refer to:
*Sophia (wisdom)
*Sophia (Gnosticism)
*Sophia (given name)
Places
*Niulakita or Sophia, an island of Tuvalu
*Sophia, Georgetown, a ward of Georgetown, Guyana
*Sophia, North Carolina, an unincorpor ...
, the woman in the firmament
In biblical cosmology, the firmament is the vast solid dome created by God during his creation of the world to divide the primal sea into upper and lower portions so that the dry land could appear. The concept was adopted into the subsequent ...
above the forces of Chaos. She will cast the corrupt gods into the abyss where they will fight each other until only their chief Yaldabaoth remains and destroys himself. Next the heavens of the Archons will collapse on each other before the Earth sinks into the abyss. Light will cover the darkness and eliminate it then form into something greater than anything that ever existed before. The source of the darkness will dissolve, and the deficiency will be taken from its root. Those who were not perfected in the unconceived one will receive glories in their realms and kingdoms of the immortals, but those who were will enter a kingless realm. All will be judged according to their deeds and gnosis
Gnosis is the common Greek noun for knowledge ( γνῶσις, ''gnōsis'', f.). The term was used among various Hellenistic religions and philosophies in the Greco-Roman world. It is best known for its implication within Gnosticism, where it s ...
.
Christianity
Christian eschatology is the study concerned with the ultimate destiny of the individualsoul
In many religious and philosophical traditions, there is a belief that a soul is "the immaterial aspect or essence of a human being".
Etymology
The Modern English noun '':wikt:soul, soul'' is derived from Old English ''sāwol, sāwel''. The ea ...
and of the entire created order, based primarily upon biblical
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a ...
texts within the Old and New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Christ ...
s.
Christian eschatological research looks to study and discuss matters such as the nature of the divine and the divine nature of Jesus Christ
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious ...
, death and the afterlife, Heaven
Heaven or the heavens, is a common religious cosmological or transcendent supernatural place where beings such as deities, angels, souls, saints, or venerated ancestors are said to originate, be enthroned, or reside. According to the bel ...
and Hell, the Second Coming of Jesus
The Second Coming (sometimes called the Second Advent or the Parousia) is a Christian (as well as Islamic and Baha'i) belief that Jesus will return again after his ascension to heaven about two thousand years ago. The idea is based on messia ...
, the resurrection of the dead
General resurrection or universal resurrection is the belief in a resurrection of the dead, or resurrection from the dead ( Koine: , ''anastasis onnekron''; literally: "standing up again of the dead") by which most or all people who have died ...
, the rapture
The rapture is an eschatological position held by some Christians, particularly those of American evangelicalism, consisting of an end-time event when all Christian believers who are alive, along with resurrected believers, will rise "in the c ...
, the Tribulation
In Christian eschatology, the Great Tribulation ( grc, θλῖψις μεγάλη, thlîpsis megálē) is a period mentioned by Jesus in the Olivet Discourse as a sign that would occur in the time of the end.
At Revelation 7:14, "the Great Tri ...
, millennialism
Millennialism (from millennium, Latin for "a thousand years") or chiliasm (from the Ancient Greek, Greek equivalent) is a belief advanced by some religious denominations that a Golden Age or Paradise will occur on Earth prior to the Last judgm ...
, the end of the world, the Last Judgment
The Last Judgment, Final Judgment, Day of Reckoning, Day of Judgment, Judgment Day, Doomsday, Day of Resurrection or The Day of the Lord (; ar, یوم القيامة, translit=Yawm al-Qiyāmah or ar, یوم الدین, translit=Yawm ad-Dīn, ...
, and the New Heaven and New Earth in the world to come
The world to come, age to come, heaven on Earth, and the Kingdom of God are eschatological phrases reflecting the belief that the current world or current age is flawed or cursed and will be replaced in the future by a better world, age, or pa ...
.
Eschatological passages occur in many places in the Bible, in both the Old and the New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Christ ...
s. In the Old Testament, apocalyptic eschatology can be found notably in Isaiah
Isaiah ( or ; he, , ''Yəšaʿyāhū'', "God is Salvation"), also known as Isaias, was the 8th-century BC Israelite prophet after whom the Book of Isaiah is named.
Within the text of the Book of Isaiah, Isaiah himself is referred to as "th ...
24–27, Isaiah 56–66, Joel, Zechariah
Zechariah most often refers to:
* Zechariah (Hebrew prophet), author of the Book of Zechariah
* Zechariah (New Testament figure), father of John the Baptist
Zechariah or its many variant forms and spellings may also refer to:
People
*Zechariah ...
9–14 as well as in the closing chapters of Daniel
Daniel is a masculine given name and a surname of Hebrew origin. It means "God is my judge"Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 68. (cf. Gabriel—"God is my strength" ...
, and in Ezekiel
Ezekiel (; he, יְחֶזְקֵאל ''Yəḥezqēʾl'' ; in the Septuagint written in grc-koi, Ἰεζεκιήλ ) is the central protagonist of the Book of Ezekiel in the Hebrew Bible.
In Judaism, Christianity, and Islam, Ezekiel is ackn ...
.Bauckham, R. J. (1996). "Apocalyptic". In D. R. W. Wood, I. H. Marshall, A. R. Millard, J. I. Packer, & D. J. Wiseman (Eds.), ''New Bible Dictionary'' (3rd ed., p. 53). Leicester, England; Downers Grove, IL: InterVarsity Press. In the New Testament, applicable passages include Matthew 24
Matthew 24 is the twenty-fourth chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament of the Christian Bible. It commences the Olivet Discourse or "Little Apocalypse" spoken by Jesus Christ, also described as the Eschatological Discourse, which ...
, Mark 13
Mark 13 is the thirteenth chapter of the Gospel of Mark in the New Testament of the Christianity, Christian Bible. It contains Jesus' predictions of the destruction of the Temple in Jerusalem and disaster for Iudaea Province, Judea, as well as hi ...
, the parable
A parable is a succinct, didactic story, in prose or verse, that illustrates one or more instructive lessons or principles. It differs from a fable in that fables employ animals, plants, inanimate objects, or forces of nature as characters, ...
of " The Sheep and the Goats" and the Book of Revelation
The Book of Revelation is the final book of the New Testament (and consequently the final book of the Christian Bible). Its title is derived from the first word of the Koine Greek text: , meaning "unveiling" or "revelation". The Book o ...
—Revelation often occupies a central place in Christian eschatology.
The Second Coming of Christ is the central event in Christian eschatology within the broader context of the fullness of the Kingdom of God
The concept of the kingship of God appears in all Abrahamic religions, where in some cases the terms Kingdom of God and Kingdom of Heaven are also used. The notion of God's kingship goes back to the Hebrew Bible, which refers to "his kingdom" ...
. Most Christians believe that death and suffering will continue to exist until Christ's return. There are, however, various views concerning the order and significance of other eschatological events.
The Book of Revelation stands at the core of much of Christian eschatology. The study of Revelation is usually divided into four interpretative methodologies or hermeneutic
Hermeneutics () is the theory and methodology of interpretation, especially the interpretation of biblical texts, wisdom literature, and philosophical texts. Hermeneutics is more than interpretative principles or methods used when immediate c ...
s:
* The Futurist approach treats the Book of Revelation mostly as unfulfilled prophecy taking place in some yet undetermined future.
* The Preterist approach interprets Revelation chiefly as having had prophetic fulfillment in the past, principally in the events of the first century CE.
* The Historicist approach places Revelation within the context of history, identifying figures and passages in Revelation with major historical people and events. This view was commonly held by the early Christian church, then among the predecessors to Protestantism
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
, such as John Wycliffe
John Wycliffe (; also spelled Wyclif, Wickliffe, and other variants; 1328 – 31 December 1384) was an English scholastic philosopher, theologian, biblical translator, reformer, Catholic priest, and a seminary professor at the University o ...
, Joachim of Fiore and later by the majority of Protestant Reformers
Protestant Reformers were those theologians whose careers, works and actions brought about the Protestant Reformation of the 16th century.
In the context of the Reformation, Martin Luther was the first reformer (sharing his views publicly in ...
, such as Martin Luther
Martin Luther (; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, theologian, author, hymnwriter, and professor, and Augustinian friar. He is the seminal figure of the Protestant Reformation and the namesake of Luther ...
, John Calvin
John Calvin (; frm, Jehan Cauvin; french: link=no, Jean Calvin ; 10 July 150927 May 1564) was a French theologian, pastor and reformer in Geneva during the Protestant Reformation. He was a principal figure in the development of the system ...
, and John Wesley. Further supporters of this view included Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726/27) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author (described in his time as a " natural philosopher"), widely recognised as one of the g ...
(1642-1727), among others.
* The Idealist approach sees the events of Revelation as neither past nor future actualities, but as purely symbolic accounts, dealing with the ongoing struggle and ultimate triumph of good over evil.
Date
First-century Christians believed Jesus would return during their lifetime. When the converts of Paul inThessalonica
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area, and the capital of the geographic region ...
were persecuted by the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Medite ...
, they believed the end of days to be imminent. Scholarly consensus would hold that Jesus, and following him the early Christians, understood the endtime as being imminent.
While some who believe in the literal interpretation of the Bible insist the prediction of dates or times is futile, others believe Jesus foretold signs of the end of days. The precise time, however, will come like a "thief in the night" (). They may also refer to in which Jesus is quoted as saying:
Great Tribulation
In the New Testament, Jesus refers to this period preceding the end times as the "Great Tribulation" (), "Affliction" (), and "days of vengeance" (). The Book of Matthew describes the devastation: The resulting chaos will affect pregnancies, newborns, and a scourge will spread throughout the flesh, save for the elect. The vivid imagery of this section is repeated closely in . The Gospel of Luke describes a complete unraveling of the social fabric, with widespread calamity and war: In the Book of Revelation, the "great tribulation" (Rev. 7:14b) refers to a time of affliction upon God's people.Catholicism and Orthodoxy
The Profession of Faith addresses Catholic beliefs concerning the last days. Catholicism adheres to theamillennial
Amillennialism or amillenarism is a chillegoristic eschatological position in Christianity which holds that there will be no millennial reign of the righteous on Earth. This view contrasts with both postmillennial and, especially, with premill ...
school of thought, promoted by Augustine of Hippo
Augustine of Hippo ( , ; la, Aurelius Augustinus Hipponensis; 13 November 354 – 28 August 430), also known as Saint Augustine, was a theologian and philosopher of Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia, Roman North A ...
in his work ''The City of God''.
Protestantism
Contemporary use of the term ''End Times'' has evolved from literal belief in Christianmillennialism
Millennialism (from millennium, Latin for "a thousand years") or chiliasm (from the Ancient Greek, Greek equivalent) is a belief advanced by some religious denominations that a Golden Age or Paradise will occur on Earth prior to the Last judgm ...
. In this tradition, Biblical
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a ...
apocalypse
Apocalypse () is a literary genre in which a supernatural being reveals cosmic mysteries or the future to a human intermediary. The means of mediation include dreams, visions and heavenly journeys, and they typically feature symbolic imager ...
is believed to be imminent, with various current events as omen
An omen (also called ''portent'') is a phenomenon that is believed to foretell the future, often signifying the advent of change. It was commonly believed in ancient times, and still believed by some today, that omens bring divine messages fr ...
s of impending Armageddon
According to the Book of Revelation in the New Testament of the Christian Bible, Armageddon (, from grc, Ἁρμαγεδών ''Harmagedōn'', Late Latin: , from Hebrew: ''Har Məgīddō'') is the prophesied location of a gathering of armies ...
. These beliefs have been put forward by the Adventist movement ( Millerites), Jehovah's Witnesses
Jehovah's Witnesses is a millenarian restorationist Christian denomination with nontrinitarian beliefs distinct from mainstream Christianity. The group reports a worldwide membership of approximately 8.7 million adherents involved ...
, and dispensational premillennialists. In 1918 a group of eight, well-known preachers produced the London Manifesto
The Pan-African Congress was a series of eight meetings, held in 1919 in Paris (1st Pan-African Congress), 1921 in London, Brussels and Paris (2nd Pan-African Congress), 1923 in London (3rd Pan-African Congress), 1927 in New York City (4th Pan-Afr ...
, warning of an imminent second coming of Christ shortly after the 1917 liberation of Jerusalem by the British.
=Millennialists and Amillennialists
= Protestants are divided between
Protestants are divided between Millennialists
Millenarianism or millenarism (from Latin , "containing a thousand") is the belief by a religious, social, or political group or movement in a coming fundamental transformation of society, after which "all things will be changed". Millenariani ...
and Amillennialists. Millennialists concentrate on the issue of whether the true believers will see the Great Tribulation
In Christian eschatology, the Great Tribulation ( grc, θλῖψις μεγάλη, thlîpsis megálē) is a period mentioned by Jesus in the Olivet Discourse as a sign that would occur in the time of the end.
At Revelation 7:14, "the Great Tri ...
or be removed from it by what is referred to as a Pre-Tribulation rapture
The rapture is an eschatological position held by some Christians, particularly those of American evangelicalism, consisting of an end-time event when all Christian believers who are alive, along with resurrected believers, will rise "in the c ...
.
Amillennialists believe the end times encompass the time from Christ's ascension to the last day, and maintain that the mention of the "thousand years" in the Book of Revelation
The Book of Revelation is the final book of the New Testament (and consequently the final book of the Christian Bible). Its title is derived from the first word of the Koine Greek text: , meaning "unveiling" or "revelation". The Book o ...
is meant to be taken metaphor
A metaphor is a figure of speech that, for rhetorical effect, directly refers to one thing by mentioning another. It may provide (or obscure) clarity or identify hidden similarities between two different ideas. Metaphors are often compared wit ...
ically (i.e., not literally), a view which continues to cause divisions within Protestant Christianity
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
.
There is a range of eschatological belief in Protestant Christianity. Christian premillennialists who believe the end times are occurring now, are usually specific about timelines that climax in the end of the world. For some, Israel, the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been ...
, or the United Nations are seen as major players whose roles were foretold in scripture. Within dispensational premillennialist writing, there is the belief that Christians will be summoned to Heaven
Heaven or the heavens, is a common religious cosmological or transcendent supernatural place where beings such as deities, angels, souls, saints, or venerated ancestors are said to originate, be enthroned, or reside. According to the bel ...
by Christ at the rapture
The rapture is an eschatological position held by some Christians, particularly those of American evangelicalism, consisting of an end-time event when all Christian believers who are alive, along with resurrected believers, will rise "in the c ...
, occurring before a Great Tribulation prophesied in Matthew 24–25; Mark 13 and Luke 21. The Tribulation is described in the Book of Revelation.
"End times" may also refer to the passing of an age or long period in the relationship between man and God. Adherents to this view cite the Second Epistle to Timothy
The Second Epistle to Timothy is one of the three pastoral epistles traditionally attributed to Paul the Apostle.. Addressed to Timothy, a fellow missionary, it is traditionally considered to be the last epistle he wrote before his death.
Alt ...
and draw analogies to the late twentieth and early twenty-first centuries.
Post-Exilic Hebrew books of prophecy
In religion, a prophecy is a message that has been communicated to a person (typically called a '' prophet'') by a supernatural entity. Prophecies are a feature of many cultures and belief systems and usually contain divine will or law, or pre ...
such as Daniel
Daniel is a masculine given name and a surname of Hebrew origin. It means "God is my judge"Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 68. (cf. Gabriel—"God is my strength" ...
and Ezekiel
Ezekiel (; he, יְחֶזְקֵאל ''Yəḥezqēʾl'' ; in the Septuagint written in grc-koi, Ἰεζεκιήλ ) is the central protagonist of the Book of Ezekiel in the Hebrew Bible.
In Judaism, Christianity, and Islam, Ezekiel is ackn ...
are given new interpretations in this Christian tradition, while apocalyptic forecasts appear in the Judeo-Christian Sibylline Oracles which include the Book of Revelation ascribed to John, the apocrypha
Apocrypha are works, usually written, of unknown authorship or of doubtful origin. The word ''apocryphal'' (ἀπόκρυφος) was first applied to writings which were kept secret because they were the vehicles of esoteric knowledge considered ...
l Apocalypse of Peter
The Apocalypse of Peter (or Revelation of Peter) is an early Christian text of the 2nd century and an example of apocalyptic literature with Hellenistic overtones. It is not included in the standard canon of the New Testament, but is mentioned ...
, and the Second Book of Esdras
2 Esdras (also called 4 Esdras, Latin Esdras, or Latin Ezra) is an apocalyptic book in some English versions of the Bible. Tradition ascribes it to Ezra, a sofer, scribe and kohen, priest of the , but scholarship places its composition between ...
.
=Fundamentalists
= Most fundamentalist Christians anticipate biblical prophecy to be literally fulfilled. They see current wars, natural disaster and famine as the birth pangs which Jesus described in Matthew and Mark . They believe mankind began in thegarden of Eden
In Abrahamic religions, the Garden of Eden ( he, גַּן־עֵדֶן, ) or Garden of God (, and גַן־אֱלֹהִים ''gan-Elohim''), also called the Terrestrial Paradise, is the Bible, biblical paradise described in Book of Genesis, Genes ...
, and point to the Valley of Megiddo as the place where the current world system A world-system is a socioeconomic system, under systems theory, that encompasses part or all of the globe, detailing the aggregate structural result of the sum of the interactions between polities. World-systems are usually larger than single state ...
will terminate, after which the Messiah will rule for 1,000 years.
=Adventists and Millerites
= Religious movements which expect that thesecond coming of Christ
The Second Coming (sometimes called the Second Advent or the Parousia) is a Christian (as well as Islamic and Baha'i) belief that Jesus will return again after his ascension to heaven about two thousand years ago. The idea is based on messia ...
will be a cataclysmic event are generally called adventism
Adventism is a branch of Protestant Christianity that believes in the imminent Second Coming (or the "Second Advent") of Jesus Christ. It originated in the 1830s in the United States during the Second Great Awakening when Baptist preacher Wil ...
. These have arisen throughout the Christian era, but were particularly common after the Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
. Emanuel Swedenborg
Emanuel Swedenborg (, ; born Emanuel Swedberg; 29 March 1772) was a Swedish pluralistic-Christian theologian, scientist, philosopher and mystic. He became best known for his book on the afterlife, ''Heaven and Hell'' (1758).
Swedenborg had ...
considered the second coming to be symbolic, and to have occurred in 1757. Along with others, he developed a religious system around the second coming of Christ, disclosed by new prophecy or special revelation not described in the Bible. The Millerites are diverse religious groups which similarly rely upon a special gift of interpretation for predicting the second coming.
The difference between the 19th-century Millerite and adventist movements and contemporary prophecy is that William Miller and his followers, based on biblical interpretation, predicted the time of the Second Coming to have occurred in 1844. Contemporary writing of end time has suggested the timetable will be triggered by future wars and moral catastrophe, and that this time of tribulation is close at hand.
Seventh-day Adventists believe biblical prophecy to foretell an end time scenario in which the United States works in conjunction with the Catholic Church to mandate worship on a day other than the true Sabbath, Saturday, as prescribed in the Ten Commandments (Exodus 20:8–11). This will bring about a situation where one must choose for or against the Bible as the will of God.
=Preterists
= Another view of the ''end times'' ispreterism
Preterism, a Christian eschatological view, interprets some (partial preterism) or all (full preterism) prophecies of the Bible as events which have already happened. This school of thought interprets the Book of Daniel as referring to events th ...
. It distinguishes ''the time of the end'' from ''the end of time''. Preterists believe the term ''last days'' (or ''Time of the End'') refers to, neither the last days of the Earth, nor the last days of humankind, but the end of the Old Covenant
The Mosaic covenant (named after Moses), also known as the Sinaitic covenant (after the biblical Mount Sinai), refers to a covenant between God and the Israelites, including their proselytes, not limited to the ten commandments, nor the event ...
between God
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
and Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
; which, according to preterism, took place when the Temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called church (building), churches), Hindui ...
in Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
was destroyed in 70 CE.
Preterists believe that prophecies
In religion, a prophecy is a message that has been communicated to a person (typically called a ''prophet'') by a supernatural entity. Prophecies are a feature of many cultures and belief systems and usually contain divine will or law, or pret ...
—such as the Second Coming
The Second Coming (sometimes called the Second Advent or the Parousia) is a Christian (as well as Islamic and Baha'i) belief that Jesus will return again after his ascension to heaven about two thousand years ago. The idea is based on messi ...
, the desecration of the Jewish Temple, the destruction of Jerusalem, the rise of the Antichrist
In Christian eschatology, the Antichrist refers to people prophesied by the Bible to oppose Jesus Christ and substitute themselves in Christ's place before the Second Coming. The term Antichrist (including one plural form)1 John ; . 2 John ...
, the Great Tribulation
In Christian eschatology, the Great Tribulation ( grc, θλῖψις μεγάλη, thlîpsis megálē) is a period mentioned by Jesus in the Olivet Discourse as a sign that would occur in the time of the end.
At Revelation 7:14, "the Great Tri ...
, the advent of The Day of the Lord, and a Final Judgment
The Last Judgment, Final Judgment, Day of Reckoning, Day of Judgment, Judgment Day, Doomsday, Day of Resurrection or The Day of the Lord (; ar, یوم القيامة, translit=Yawm al-Qiyāmah or ar, یوم الدین, translit=Yawm ad-Dīn, ...
—had been fulfilled when the Romans sacked Jerusalem and completely destroyed its Temple.
Proponents of ''full preterism'' do not believe in a coming resurrection of the dead
General resurrection or universal resurrection is the belief in a resurrection of the dead, or resurrection from the dead ( Koine: , ''anastasis onnekron''; literally: "standing up again of the dead") by which most or all people who have died ...
. They place this event (as well as the Second Coming) in the year 70. Advocates of partial preterism
Preterism, a Christian eschatological view, interprets some (partial preterism) or all (full preterism) prophecies of the Bible as events which have already happened. This school of thought interprets the Book of Daniel as referring to events th ...
do believe in a coming resurrection. Full preterists contend that partial preterists are merely ''futurists'', since they believe the Second Coming, the Resurrection, the Rapture
The rapture is an eschatological position held by some Christians, particularly those of American evangelicalism, consisting of an end-time event when all Christian believers who are alive, along with resurrected believers, will rise "in the c ...
, and the Judgment are yet to come.
Many preterists believe first-century Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
experienced the Rapture to rejoin the Christ
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religi ...
.
According with Preterism's interpretation
Interpretation may refer to:
Culture
* Aesthetic interpretation, an explanation of the meaning of a work of art
* Allegorical interpretation, an approach that assumes a text should not be interpreted literally
* Dramatic Interpretation, an event ...
of end times, many "time passages" in the New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Christ ...
foretell a Second Coming
The Second Coming (sometimes called the Second Advent or the Parousia) is a Christian (as well as Islamic and Baha'i) belief that Jesus will return again after his ascension to heaven about two thousand years ago. The idea is based on messi ...
of Christ, with last days to take place within the lifetimes of his disciples: Matt. 10:23, Matt. 16:28, Matt. 24:34, Matt. 26:64, Rom. 13:11–12, 1 Cor. 7:29–31, 1 Cor. 10:11, Phil. 4:5, James 5:8–9, 1 Pet. 4:7, 1 Jn. 2:18.
=Dispensationalists
= Dispensationalism is anevangelical
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide interdenominational movement within Protestant Christianity that affirms the centrality of being " born again", in which an individual exp ...
futurist Biblical interpretation that foresees a series of dispensations, or periods, in which God relates to human beings under different Biblical covenants
The Hebrew Bible makes reference to a number of covenants ( he, בְּרִיתוֹת) with God ( YHWH). These include the Noahic Covenant (in Genesis), which is between God and all living creatures, as well as a number of more specific covenants ...
. The belief system is primarily rooted in the writings of John Nelson Darby
John Nelson Darby (18 November 1800 – 29 April 1882) was an Anglo-Irish Bible teacher, one of the influential figures among the original Plymouth Brethren and the founder of the Exclusive Brethren. He is considered to be the father of moder ...
and is premillennial in content. The reestablishment of Israel in 1948 provided a major impetus to the dispensationalist belief system. The wars of Israel after 1948 with its Arab neighbors provided further support, according to John F. Walvoord. After the Six-Day War
The Six-Day War (, ; ar, النكسة, , or ) or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states (primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, S ...
in 1967, and the Yom Kippur War
The Yom Kippur War, also known as the Ramadan War, the October War, the 1973 Arab–Israeli War, or the Fourth Arab–Israeli War, was an armed conflict fought from October 6 to 25, 1973 between Israel and a coalition of Arab states led by Eg ...
in 1973, it seemed plausible to many Fundamentalist Christians in the 1970s that Middle East turmoil may well be leading up to the fulfillment of various Bible prophecies and to the Battle of Armageddon
According to the Book of Revelation in the New Testament of the Christian Bible, Armageddon (, from grc, Ἁρμαγεδών ''Harmagedōn'', Late Latin: , from Hebrew: ''Har Məgīddō'') is the prophesied location of a gathering of armies ...
.
Members of the dispensationalist movement such as Hal Lindsey, J. Dwight Pentecost, John Walvoord
John F. Walvoord (May 1, 1910 – December 20, 2002) was a Christian theologian, pastor, and president of Dallas Theological Seminary from 1952 to 1986. He was the author of over 30 books, focusing primarily on eschatology and theology including ' ...
, all of whom have Dallas Theological Seminary
Dallas Theological Seminary (DTS) is an evangelical theological seminary in Dallas, Texas. It is known for popularizing the theological system dispensationalism. DTS has campuses in Dallas, Houston, and Washington, D.C., as well as extension ca ...
backgrounds, and some other writers, claimed further that the European Economic Community, which preceded the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been ...
, would become a United States of Europe, which would in turn become a Revived Roman Empire ruled by the Antichrist
In Christian eschatology, the Antichrist refers to people prophesied by the Bible to oppose Jesus Christ and substitute themselves in Christ's place before the Second Coming. The term Antichrist (including one plural form)1 John ; . 2 John ...
. The Revived Roman Empire also figured into the New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Christ ...
writers' vision of the future. The fact that in the early 1970s, there were (erroneously thought to be) seven nations in the European Economic Community was held to be significant; this aligned the Community with a seven-headed beast mentioned in Revelation. This specific prophecy has required revision, but the idea of a Revived Roman Empire remains.
Dispensationalism, in contrast to the Millerite Adventist movement, had its beginning in the 19th century, when John Nelson Darby
John Nelson Darby (18 November 1800 – 29 April 1882) was an Anglo-Irish Bible teacher, one of the influential figures among the original Plymouth Brethren and the founder of the Exclusive Brethren. He is considered to be the father of moder ...
, founder of the Plymouth Brethren
The Plymouth Brethren or Assemblies of Brethren are a low church and non-conformist Christian movement whose history can be traced back to Dublin, Ireland, in the mid to late 1820s, where they originated from Anglicanism. The group emphasize ...
religious denomination
A religious denomination is a subgroup within a religion that operates under a common name and tradition among other activities.
The term refers to the various Christian denominations (for example, Eastern Orthodox, Catholic, and the many var ...
, incorporated into his system of Biblical interpretation a system of organizing Biblical time into a number of discrete dispensations, each of which marks a separate covenant with God. Darby's beliefs were widely publicized in Cyrus I. Scofield's '' Scofield Reference Bible'', an annotated Bible that became popular in the United States.
Since the majority of the Biblical prophets were writing at a time when the Temple in Jerusalem
The Temple in Jerusalem, or alternatively the Holy Temple (; , ), refers to the two now-destroyed religious structures that served as the central places of worship for Israelites and Jews on the modern-day Temple Mount in the Old City of Jeru ...
was still functioning, they wrote as if it would still be standing during the prophesied events. According to preterism, this was a fulfillment of the prophecies. However, according to Futurists, their destruction in AD 70 put the prophetic timetable on hold. Many such believers therefore anticipated the return of Jews to Israel and the reconstruction of the Temple before the Second Coming could occur.
Post-tribulation pre-millennialism
A view of the Second Coming of Christ as held by post-tribulational pre-millennialists holds that the Church of Christ will have to undergo great persecution by being present during the great tribulation.Specific prophetic movements
 In 1843, William Miller made the first of several predictions that the world would end in only a few months. As his predictions did not come true (referred to as the
In 1843, William Miller made the first of several predictions that the world would end in only a few months. As his predictions did not come true (referred to as the Great Disappointment
The Great Disappointment in the Millerite movement was the reaction that followed Baptist preacher William Miller's proclamations that Jesus Christ would return to the Earth by 1844, which he called the Second Advent. His study of the Daniel ...
), followers of Miller went on to found separate groups, the most successful of which is the Seventh-day Adventist Church
The Seventh-day Adventist Church is an Adventism, Adventist Protestantism, Protestant Christian denomination which is distinguished by its observance of Saturday, the Names of the days of the week#Numbered days of the week, seventh day of the ...
.
Members of the Baháʼí Faith
The Baháʼí Faith is a religion founded in the 19th century that teaches the essential worth of all religions and the unity of all people. Established by Baháʼu'lláh in the 19th century, it initially developed in Iran and parts of the ...
believe Miller's interpretation of signs and dates of the coming of Jesus were, for the most part, correct. They believe the fulfillment of biblical prophecies of the coming of Christ came through a forerunner of their own religion, the Báb
The Báb (b. ʿAlí Muḥammad; 20 October 1819 – 9 July 1850), was the messianic founder of Bábism, and one of the central figures of the Baháʼí Faith. He was a merchant from Shiraz in Qajar Iran who, in 1844 at the age of 25, claim ...
. According to the Báb's words, 4 April 1844 was "the first day that the Spirit descended" into his heart. His subsequent declaration to Mullá Husayn-i Bushru'i that he was the "Promised One"—an event now commemorated by Baháʼís as a major holy day—took place on 23 May 1844. It was in October of that year that the Báb embarked on a pilgrimage to Mecca
The Hajj (; ar, حَجّ '; sometimes also spelled Hadj, Hadji or Haj in English) is an annual Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca, Saudi Arabia, the holiest city for Muslims. Hajj is a mandatory religious duty for Muslims that must be carried o ...
, where he openly declared his claims to the Sharif of Mecca
The Sharif of Mecca ( ar, شريف مكة, Sharīf Makkah) or Hejaz ( ar, شريف الحجاز, Sharīf al-Ḥijāz, links=no) was the title of the leader of the Sharifate of Mecca, traditional steward of the holy cities of Mecca and Medina and ...
. The first news coverage of these events in the West was in 1845 by ''The Times
''The Times'' is a British daily national newspaper based in London. It began in 1785 under the title ''The Daily Universal Register'', adopting its current name on 1 January 1788. ''The Times'' and its sister paper '' The Sunday Times'' ...
'', followed by others in 1850 in the United States. The first Baháʼí to come to America was in 1892. Several Baháʼí books and pamphlets make mention of the Millerites, the prophecies used by Miller and the Great Disappointment, most notably William Sears's ''Thief in the Night''.
Restorationism (Christian primitivism)
End times theology is also significant to restorationist Christian religions, which consider themselves distinct from both Catholicism and Protestantism.=Jehovah's Witnesses
= The eschatology of
The eschatology of Jehovah's Witnesses
Jehovah's Witnesses is a millenarian restorationist Christian denomination with nontrinitarian beliefs distinct from mainstream Christianity. The group reports a worldwide membership of approximately 8.7 million adherents involved ...
is central to their religious beliefs. They believe Jesus Christ
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious ...
has been ruling in heaven as king since 1914 (a date they believe was prophesied in the Bible) and that after that time a period of cleansing occurred, resulting in God's selection of the Bible Students associated with Charles Taze Russell as his people in 1919. They also believe that the destruction of those who reject the Bible's message and thus willfully refuse to obey God will shortly take place at Armageddon
According to the Book of Revelation in the New Testament of the Christian Bible, Armageddon (, from grc, Ἁρμαγεδών ''Harmagedōn'', Late Latin: , from Hebrew: ''Har Məgīddō'') is the prophesied location of a gathering of armies ...
, ensuring that the beginning of the new earthly society will be composed of willing subjects of that kingdom.
The religion's doctrines surrounding 1914 are the legacy of a series of emphatic claims regarding the years 1799,''The Watchtower'', 1 March 1922, page 73, "The indisputable facts, therefore, show that the 'time of the end' began in 1799; that the Lord's second presence began in 1874." 1874, 1878, 1914,''The Watchtower''July 15, 1894, p. 1677
: "We see no reason for changing the figures—nor could we change them if we would. They are, we believe, God's dates, not ours. But bear in mind that the end of 1914 is not the date for the beginning, but for the end of the time of trouble." 19181 September 1916 ''The Watchtower'', page
264–265
and 1925''Millions Now Living Will Never Die'', 1920, page 97, "Based upon the argument heretofore set forth, then, that the old order of things, the old world, is ending and is therefore passing away, and that the new order is coming in, and that 1925 shall mark the resurrection of the faithful worthies of old and the beginning of reconstruction, it is reasonable to conclude that millions of people now on the earth will be still on the earth in 1925. Then, based upon the promises set forth in the divine Word, we must reach the positive and indisputable conclusion that millions now living will never die." made in the Watch Tower Society's publications between 1879 and 1924. Claims about the significance of those years, including the presence of Jesus Christ, the beginning of the "last days", the destruction of worldly governments and the earthly resurrection of Jewish patriarchs, were successively abandoned. In 1922 the society's principal magazine, ''
The Watchtower
''The Watchtower Announcing Jehovah's Kingdom'' is an illustrated religious magazine, published by the Watch Tower Bible and Tract Society of Pennsylvania. Jehovah's Witnesses distribute ''The Watchtower—Public Edition'', along with its comp ...
'', described its chronology as "no stronger than its weakest link", but also claimed the chronological relationships to be "of divine origin and divinely corroborated... in a class by itself, absolutely and unqualifiedly correct" and "indisputable facts", and repudiation of Russell's teachings was described as "equivalent to a repudiation of the Lord".
The Watch Tower Society has acknowledged its early leaders promoted "incomplete, even inaccurate concepts". The Governing Body of Jehovah's Witnesses
The Governing Body of Jehovah's Witnesses is the ruling council of Jehovah's Witnesses, based in the denomination's Warwick, New York, headquarters. The body formulates doctrines, oversees the production of written material for publications and ...
says that, unlike Old Testament
The Old Testament (often abbreviated OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew writings by the Israelites. The ...
prophets, its interpretations of the Bible are not inspired
Inspiration, inspire, or inspired often refers to:
* Artistic inspiration, sudden creativity in artistic production
* Biblical inspiration, the doctrine in Judeo-Christian theology concerned with the divine origin of the Bible
* Creative inspir ...
or infallible. It says that Bible prophecies can be fully understood only after their fulfillment, citing examples of biblical figures who did not understand the meaning of prophecies they received. Watch Tower Society literature often cites Proverbs 4:18, "The path of the righteous ones is like the bright light that is getting lighter and lighter until the day is firmly established" ( NWT) to support their view that there would be an increase in knowledge during "the time of the end", and that this increase in knowledge needs adjustments. Watch Tower Society publications also say that unfulfilled expectations are partly due to eagerness for God's Kingdom
The concept of the kingship of God appears in all Abrahamic religions, where in some cases the terms Kingdom of God and Kingdom of Heaven are also used. The notion of God's kingship goes back to the Hebrew Bible, which refers to "his kingdom" b ...
and that they do not call their core beliefs into question.
=The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
= Members ofthe Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a nontrinitarian Christian church that considers itself to be the restoration of the original church founded by Jesus Christ. The ...
(LDS Church) believe there will be a Second Coming of Jesus to the earth at some time in the future. The LDS Church and its leaders do not make any predictions of the date of the Second Coming.
According to church doctrine, the true gospel
Gospel originally meant the Christian message (" the gospel"), but in the 2nd century it came to be used also for the books in which the message was set out. In this sense a gospel can be defined as a loose-knit, episodic narrative of the words a ...
will be taught in all parts of the world prior to the Second Coming.Matthew 24:14KJV They also believe there will be increasing war, earthquakes, hurricanes, and man-made disasters prior to the Second Coming. Disasters of all kind will happen before Christ comes. Upon the return of Jesus Christ, all people will be resurrected, the righteous in a first resurrection and the unrighteous in a second, later resurrection. Christ shall reign for a period of 1000 years, after which the Final Judgement will occur.
Realized eschatology
Realized eschatology is a Christian eschatological theory that holds that the eschatological passages in theNew Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Christ ...
do not refer to the future, but instead refer to the ministry of Jesus
The ministry of Jesus, in the canonical gospels, begins with his baptism in the countryside of Roman Judea and Transjordan, near the River Jordan by John the Baptist, and ends in Jerusalem, following the Last Supper with his disciples.''Chr ...
and his lasting legacy.
Islam
Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abra ...
believe there are three periods before the Day of Judgment
The Last Judgment, Final Judgment, Day of Reckoning, Day of Judgment, Judgment Day, Doomsday, Day of Resurrection or The Day of the Lord (; ar, یوم القيامة, translit=Yawm al-Qiyāmah or ar, یوم الدین, translit=Yawm ad-Dīn, ...
with some debate as to whether the periods could overlap.
Sunni
Sunnis believe the dead will then stand in a grand assembly, awaiting a scroll detailing their righteous deeds, sinful acts and ultimate judgment. Prophet Muhammad will be the first to be resurrected. Punishments will include ''adhab'', or severe pain and embarrassment, and ''khizy'' or shame."Reward and Punishment", ''Encyclopedia of the Qur'an''(2005) There will also be a punishment of the grave between death and the resurrection. Several Sunni scholars explain some of the signs metaphorically. The signs of the coming end time are divided into major and minor signs: Following the second period, the third is said to be marked by the ten major signs known as ''alamatu's-sa'ah al- kubra'' (The major signs of the end).Sahih Muslim, Book 41, Hadith 6931 They are as follows: # A huge black cloud of smoke (dukhan) will cover the earth.Sahih Muslim # Three sinkings of the earth, one in the East. # One sinking of the earth in the West. # One sinking of the earth in Arabia. # The false messiah—anti-Christ, Masih ad-Dajjal—shall appear with great powers as a one-eyed man with his right eye blind and deformed like a grape. Although believers will not be deceived, he will claim to be God, to hold the keys to heaven and hell, and will lead many astray. In reality, his heaven is hell, and his hell is heaven. The Dajjal will be followed by seventy thousand Jews of Isfahan wearing Persian shawls.Muslim, Book 41, Hadith 7034 # Thereturn
Return may refer to:
In business, economics, and finance
* Return on investment (ROI), the financial gain after an expense.
* Rate of return, the financial term for the profit or loss derived from an investment
* Tax return, a blank document o ...
of Isa
Isa or ISA may refer to:
Places
* Isa, Amur Oblast, Russia
* Isa, Kagoshima, Japan
* Isa, Nigeria
* Isa District, Kagoshima, former district in Japan
* Isa Town, middle class town located in Bahrain
* Mount Isa, Queensland, Australia
* Mount Is ...
(Jesus), from the fourth sky, to kill Dajjal.
# ''Ya'jooj'' and ''Ma'jooj'' (Gog and Magog
Gog and Magog (; he, גּוֹג וּמָגוֹג, ''Gōg ū-Māgōg'') appear in the Hebrew Bible and the Quran as individuals, tribes, or lands. In Ezekiel 38, Gog is an individual and Magog is his land; in Genesis 10, Magog is a man and ep ...
), a Japhetic tribe of vicious beings who had been imprisoned by Dhul-Qarnayn, will break out. They will ravage the earth, drink all the water of Lake Tiberias, and kill all believers in their way. Isa, Imam Al-Mahdi
The Mahdi ( ar, ٱلْمَهْدِيّ, al-Mahdī, lit=the Guided) is a messianic figure in Islamic eschatology who is believed to appear at the end of times to rid the world of evil and injustice. He is said to be a descendant of Muhammad who ...
, and the believers with them will go to the top of a mountain and pray for the destruction of Gog and Magog. God eventually will send disease and worms to wipe them out.
# The sun will rise from the West.
# The '' Dabbat al-ard'', or Beast of the Earth
Beast of the Earth (), sometimes called The Dabba/Dabbah in Islamic eschatology, will be one of the signs of the coming of the Last Day or Judgement Day. It will appear before or after the sun rises in the west, where the Beast will be sighted f ...
, will come out of the ground to talk to people.
# The second blow of the trumpet will be sounded, the dead will return to life, and a fire will come out of Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast an ...
that shall gather all to Mahshar Al Qiy'amah (The Gathering for Judgment).
Shia
Many of the signs shown above are shared by both Sunni and Shia beliefs, with some exceptions, e.g.Imam Al-Mahdi
The Mahdi ( ar, ٱلْمَهْدِيّ, al-Mahdī, lit=the Guided) is a messianic figure in Islamic eschatology who is believed to appear at the end of times to rid the world of evil and injustice. He is said to be a descendant of Muhammad who ...
defeating Al-Masih ad-Dajjal.
Concepts and terminology in Shia eschatology
Islamic eschatology ( ar, علم آخر الزمان في الإسلام, ) is a field of study in Islam concerning future events that would happen in the end times. It is primarily based on hypothesis and speculations based on sources from ...
include Mi'ad, the Occultation
An occultation is an event that occurs when one object is hidden from the observer by another object that passes between them. The term is often used in astronomy, but can also refer to any situation in which an object in the foreground blocks ...
, Al-Yamani, and Sufyani. In Twelver Shia
Twelver Shīʿīsm ( ar, ٱثْنَا عَشَرِيَّة; '), also known as Imāmīyyah ( ar, إِمَامِيَّة), is the largest branch of Shīʿa Islam, comprising about 85 percent of all Shīʿa Muslims. The term ''Twelver'' refers t ...
narrations about the last days, the literature largely revolves around Muhammad al-Mahdi, who is considered by many beliefs to be the true twelfth appointed successor to Muhammad. Muhammad al-Mahdi will help mankind against the deception by the ''Dajjal'' who will try to get people in to a new world religion which is called "the great deception".
Ahmadiyya
Ahmadiyya
Ahmadiyya (, ), officially the Ahmadiyya Muslim Community or the Ahmadiyya Muslim Jama'at (AMJ, ar, الجماعة الإسلامية الأحمدية, al-Jamāʿah al-Islāmīyah al-Aḥmadīyah; ur, , translit=Jamā'at Aḥmadiyyah Musl ...
is considered distinct from mainstream Islam. In its writing, the present age has been witness to the evil of man and wrath of God, with war and natural disaster. Ghulam Ahmad is seen as the promised Messiah and the Mahdi
The Mahdi ( ar, ٱلْمَهْدِيّ, al-Mahdī, lit=the Guided) is a messianic figure in Islamic eschatology who is believed to appear at the end of times to rid the world of evil and injustice. He is said to be a descendant of Muhammad w ...
, fulfilling Islamic and Biblical prophecies, as well as scriptures of other religions such as Hinduism. His teaching will establish spiritual reform and establish an age of peace. This will continue for a thousand years, and will unify mankind under one faith.
Ahmadis believe that despite harsh and strong opposition and discrimination they will eventually be triumphant and their message vindicated both by Muslims and non-Muslims alike. Ahmadis also incorporate the eschatological views from other religions into their doctrine and believe Mirza Ghulam Ahmed falls into this sequence.
Baháʼí Faith
In theBaháʼí Faith
The Baháʼí Faith is a religion founded in the 19th century that teaches the essential worth of all religions and the unity of all people. Established by Baháʼu'lláh in the 19th century, it initially developed in Iran and parts of the ...
, creation has neither a beginning nor an end; Baháʼís regard the eschatologies of other religions as symbolic. In Baháʼí belief, human time is marked by a series of progressive revelations in which successive messengers or prophets come from God. The coming of each of these messengers is seen as the day of judgment to the adherents of the previous religion, who may choose to accept the new messenger and enter the "heaven" of belief, or denounce the new messenger and enter the "hell" of denial. In this view, the terms "heaven" and "hell" become symbolic terms for a person's spiritual progress and their nearness to or distance from God. In Baháʼí belief, Bahá'u'lláh (1817-1892), the founder of the Baháʼí Faith, was the Second Coming
The Second Coming (sometimes called the Second Advent or the Parousia) is a Christian (as well as Islamic and Baha'i) belief that Jesus will return again after his ascension to heaven about two thousand years ago. The idea is based on messi ...
of Christ and also the fulfilment of previous eschatological expectations of Islam and other major religions.
The inception of the Baháʼí Faith coincides with Great Disappointment
The Great Disappointment in the Millerite movement was the reaction that followed Baptist preacher William Miller's proclamations that Jesus Christ would return to the Earth by 1844, which he called the Second Advent. His study of the Daniel ...
of the Millerite prophesy in 1844.
ʻAbdu'l-Bahá
ʻAbdu'l-Bahá (; Persian: , 23 May 1844 – 28 November 1921), born ʻAbbás ( fa, عباس), was the eldest son of Baháʼu'lláh and served as head of the Baháʼí Faith from 1892 until 1921. ʻAbdu'l-Bahá was later canonized as the la ...
taught that Armageddon
According to the Book of Revelation in the New Testament of the Christian Bible, Armageddon (, from grc, Ἁρμαγεδών ''Harmagedōn'', Late Latin: , from Hebrew: ''Har Məgīddō'') is the prophesied location of a gathering of armies ...
would begin in 1914, but without a clear indication of its end date. Baháʼís believe that the mass martyrdom anticipated during the ''End Times'' had already passed within the historical context of the Baháʼí Faith. Baháʼís expect their faith to be eventually embraced by the masses of the world, ushering in a golden age
The term Golden Age comes from Greek mythology, particularly the '' Works and Days'' of Hesiod, and is part of the description of temporal decline of the state of peoples through five Ages, Gold being the first and the one during which the Go ...
.
Rastafari
 Rastafari have a unique interpretation of end times, based on the
Rastafari have a unique interpretation of end times, based on the Old Testament
The Old Testament (often abbreviated OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew writings by the Israelites. The ...
and the Book of Revelation
The Book of Revelation is the final book of the New Testament (and consequently the final book of the Christian Bible). Its title is derived from the first word of the Koine Greek text: , meaning "unveiling" or "revelation". The Book o ...
. They believe Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the Er ...
n Emperor Haile Selassie I
Haile Selassie I ( gez, ቀዳማዊ ኀይለ ሥላሴ, Qädamawi Häylä Səllasé, ; born Tafari Makonnen; 23 July 189227 August 1975) was Emperor of Ethiopia from 1930 to 1974. He rose to power as Regent Plenipotentiary of Ethiopia ('' ...
to be God incarnate, the ''King of kings'' and ''Lord of lords'' mentioned in Revelation 5:5. They saw the crowning of Selassie as the second coming
The Second Coming (sometimes called the Second Advent or the Parousia) is a Christian (as well as Islamic and Baha'i) belief that Jesus will return again after his ascension to heaven about two thousand years ago. The idea is based on messi ...
, and the Second Italo-Ethiopian War
The Second Italo-Ethiopian War, also referred to as the Second Italo-Abyssinian War, was a war of aggression which was fought between Fascist Italy (1922–1943), Italy and Ethiopian Empire, Ethiopia from October 1935 to February 1937. In Ethio ...
as fulfillment of Revelation. There is also the expectation that Selassie will return for a day of judgment and bring home the "lost children of Israel", which in Rastafari refers to those taken from Africa through the slave trade
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
. There will then be an era of peace and harmony at Mount Zion
Zion ( he, צִיּוֹן ''Ṣīyyōn'', LXX , also variously transliterated ''Sion'', ''Tzion'', ''Tsion'', ''Tsiyyon'') is a placename in the Hebrew Bible used as a synonym for Jerusalem as well as for the Land of Israel as a whole (see Na ...
in Africa.
Cyclic cosmology
Hinduism
The Vaishnavite tradition links contemporary Hindu eschatology to the figure ofKalki
Kalki ( sa, कल्कि), also called Kalkin or Karki, is the prophesied tenth and final incarnation of the Hindu god Vishnu. He is described to appear in order to end the Kali Yuga, one of the four periods in the endless cycle of exis ...
, the tenth and last avatar
Avatar (, ; ), is a concept within Hinduism that in Sanskrit literally means "descent". It signifies the material appearance or incarnation of a powerful deity, goddess or spirit on Earth. The relative verb to "alight, to make one's appeara ...
of Vishnu
Vishnu ( ; , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism.
Vishnu is known as "The Preserver" within ...
. Many Hindus believe that before the age
''The Age'' is a daily newspaper in Melbourne, Australia, that has been published since 1854. Owned and published by Nine Entertainment, ''The Age'' primarily serves Victoria, but copies also sell in Tasmania, the Australian Capital Territo ...
draws to a close, Kalki will reincarnate as Shiva
Shiva (; sa, शिव, lit=The Auspicious One, Śiva ), also known as Mahadeva (; ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐ, or Hara, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions within Hin ...
and simultaneously dissolve and regenerate the universe. In contrast, Shaivites hold the view that Shiva is incessantly destroying and creating the world.
In Hindu eschatology, time is cyclic and consists of kalpas. Each lasts 4.1–8.2 billion years, which is a period of one full day and night for Brahma
Brahma ( sa, ब्रह्मा, Brahmā) is a Hindu god, referred to as "the Creator" within the Trimurti, the trinity of supreme divinity that includes Vishnu, and Shiva.Jan Gonda (1969)The Hindu Trinity Anthropos, Bd 63/64, H 1/2, pp ...
, who will be alive for 311 trillion, 40 billion years. Within a ''kalpa'' there are periods of creation
Creation may refer to:
Religion
*'' Creatio ex nihilo'', the concept that matter was created by God out of nothing
*Creation myth, a religious story of the origin of the world and how people first came to inhabit it
*Creationism, the belief that ...
, preservation and decline. After this larger cycle, all of creation will contract to a singularity and then again will expand from that single point, as the ages Ages may refer to:
*Advanced glycation end-products, known as AGEs
*Ages, Kentucky, census-designated place, United States
* ''Ages'' (album) by German electronic musician Edgar Froese
*The geologic time scale, a system of chronological measuremen ...
continue in a religious fractal
In mathematics, a fractal is a geometric shape containing detailed structure at arbitrarily small scales, usually having a fractal dimension strictly exceeding the topological dimension. Many fractals appear similar at various scales, as il ...
pattern.
Within the current kalpa, there are four epochs that encompass the cycle. They progress from a beginning of complete purity to a descent into total corruption. The last of the four ages is Kali Yuga
''Kali Yuga'', in Hinduism, is the fourth and worst of the four '' yugas'' (world ages) in a '' Yuga Cycle'', preceded by ''Dvapara Yuga'' and followed by the next cycle's '' Krita (Satya) Yuga''. It is believed to be the present age, which ...
(which most Hindus believe is the current time), characterized by quarrel, hypocrisy, impiety, violence and decay. The four pillars of dharma will be reduced to one, with truth being all that remains. As written in the Gita:
At this time of chaos, the final avatar,''Yadā yadā hi dharmasya glānirbhavati Bhārata'' ''Abhyutthānam adharmasya tadātmānam sṛjāmyaham'' Whenever there is decay of righteousness in Bharata ( Aryavarta) And a rise of unrighteousness then I manifest Myself!
Kalki
Kalki ( sa, कल्कि), also called Kalkin or Karki, is the prophesied tenth and final incarnation of the Hindu god Vishnu. He is described to appear in order to end the Kali Yuga, one of the four periods in the endless cycle of exis ...
, endowed with eight superhuman faculties will appear on a white horse. Kalki will amass an army to "establish righteousness upon the earth" and leave "the minds of the people as pure as crystal."
At the completion of Kali Yuga
''Kali Yuga'', in Hinduism, is the fourth and worst of the four '' yugas'' (world ages) in a '' Yuga Cycle'', preceded by ''Dvapara Yuga'' and followed by the next cycle's '' Krita (Satya) Yuga''. It is believed to be the present age, which ...
, the next Yuga Cycle will begin with a new Satya Yuga, in which all will once again be righteous with the reestablishment of dharma. This, in turn, will be followed by epochs of Treta Yuga, Dvapara Yuga
''Dvapara Yuga'' ( Dwapara Yuga), in Hinduism, is the third and third best of the four '' yugas'' (world ages) in a '' Yuga Cycle'', preceded by '' Treta Yuga'' and followed by '' Kali Yuga''. ''Dvapara Yuga'' lasts for 864,000 years (2,400 divi ...
and again another Kali Yuga. This cycle will then repeat until the larger cycle of existence under Brahma
Brahma ( sa, ब्रह्मा, Brahmā) is a Hindu god, referred to as "the Creator" within the Trimurti, the trinity of supreme divinity that includes Vishnu, and Shiva.Jan Gonda (1969)The Hindu Trinity Anthropos, Bd 63/64, H 1/2, pp ...
returns to the singularity, and a new universe is born.
The cycle of birth
Birth is the act or process of bearing or bringing forth offspring, also referred to in technical contexts as parturition. In mammals, the process is initiated by hormones which cause the muscular walls of the uterus to contract, expelling the ...
, growth, decay, and renewal at the individual level finds its echo in the cosmic order, yet is affected by vagueries of divine intervention in Vaishnavite belief.
Buddhism
There is no classic account of beginning or end in Buddhism; Masao Abe attributes this to the absence of God. History is embedded in the continuing process of samsara or the "beginningless and endless cycles of birth-death-rebirth". Buddhists believe there is an end to things but it is not final because they are bound to be born again. However, the writers ofMahayana
''Mahāyāna'' (; "Great Vehicle") is a term for a broad group of Buddhist traditions, texts, philosophies, and practices. Mahāyāna Buddhism developed in India (c. 1st century BCE onwards) and is considered one of the three main existing bra ...
Buddhist scriptures establish a specific end-time account in Buddhist tradition: this describes the return of Maitreya Buddha
Maitreya (Sanskrit: ) or Metteyya (Pali: ), also Maitreya Buddha or Metteyya Buddha, is regarded as the future Buddha of this world in Buddhist eschatology. As the 5th and final Buddha of the current kalpa, Maitreya's teachings will be aimed ...
, who would bring about an end to the world. This constitutes one of the two major branches of Buddhist eschatology, with the other being the Sermon of the Seven Suns. End time in Buddhism could also involve a cultural eschatology covering "final things", which include the idea that Sakyamuni Buddha's dharma
Dharma (; sa, धर्म, dharma, ; pi, dhamma, italic=yes) is a key concept with multiple meanings in Indian religions, such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, Sikhism and others. Although there is no direct single-word translation for ...
will also come to an end.
Maitreya
The Buddha described his teachings disappearing five thousand years from when he preached them, corresponding approximately to the year 4300 since he was born in 623 BCE. At this time, knowledge of dharma will be lost as well. The last of his relics will be gathered in Bodh Gaya and cremated. There will be a new era in which the next Buddha Maitreya will appear, but it will be preceded by the degeneration of human society. This will be a period of greed, lust, poverty, ill will, violence, murder, impiety, physical weakness, sexual depravity and societal collapse, and even the Buddha himself will be forgotten. This will be followed by the coming of Maitreya when the teachings ofdharma
Dharma (; sa, धर्म, dharma, ; pi, dhamma, italic=yes) is a key concept with multiple meanings in Indian religions, such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, Sikhism and others. Although there is no direct single-word translation for ...
are forgotten. Maitreya was the first Bodhisattva around whom a cult developed, in approximately the third century CE.
The earliest known mention of Maitreya occurs in the Cakavatti, or Sihanada Sutta in Digha Nikaya
Digha is a seaside resort town in the state of West Bengal, India. It lies in Purba Medinipur district and at the northern end of the Bay of Bengal. It has a low gradient with a shallow sand beach. It is a popular sea resort in West Bengal.
...
26 of the Pali Canon
The Pāli Canon is the standard collection of scriptures in the Theravada Buddhist tradition, as preserved in the Pāli language. It is the most complete extant early Buddhist canon. It derives mainly from the Tamrashatiya school.
During ...
. In it, Gautama Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism.
According to Buddhist tradition, he was born in ...
predicted his teachings of dharma would be forgotten after 5,000 years.
The text then foretells the birth of Maitreya Buddha in the city of Ketumatī
Ketumati (Ch'ih-t'ou) is a legendary place in some Buddhist traditions viewed as the earthly paradise of the prophesied figure called Maitreya, who is the future Buddha. Devotees of Maitreya believe that the kingdom is a pure land where Maitreya ...
in present-day Benares
Varanasi (; ; also Banaras or Benares (; ), and Kashi.) is a city on the Ganges river in northern India that has a central place in the traditions of pilgrimage, death, and mourning in the Hindu world.
*
*
*
* The city has a syncretic t ...
, whose king will be the Cakkavattī Sankha. Sankha will live in the former palace of King Mahāpanadā, and will become a renunciate who follows Maitreya.
In Mahayana Buddhism, Maitreya will attain ''bodhi
The English term enlightenment is the Western translation of various Buddhist terms, most notably bodhi and vimutti. The abstract noun ''bodhi'' (; Sanskrit: बोधि; Pali: ''bodhi''), means the knowledge or wisdom, or awakened intellect, ...
'' in seven days, the minimum period, by virtue of his many lifetimes of preparation. Once Buddha, he will rule over the Ketumati Pure Land, an earthly paradise sometimes associated with the Indian city of Varanasi
Varanasi (; ; also Banaras or Benares (; ), and Kashi.) is a city on the Ganges river in northern India that has a central place in the traditions of pilgrimage, death, and mourning in the Hindu world.
*
*
*
* The city has a syncretic t ...
or Benares in present-day Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. With over 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populated state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was established in 1950 ...
. In Mahayana Buddhism, the Buddha presides over a land of purity. For example, Amitabha presides over Sukhavati, more popularly known as the "Western Paradise".
Edward Conze
Edward Conze, born Eberhard Julius Dietrich Conze (1904–1979) was a scholar of Marxism and Buddhism, known primarily for his commentaries and translations of the Prajñāpāramitā literature.
Biography
Conze's parents, Dr. Ernst Conze (1872� ...
in his ''Buddhist Scriptures'' (1959) gives an account of Maitreya:
Maitreya currently resides in Tushita
Tuṣita (Sanskrit) or Tusita (Pāli) is one of the six deva-worlds of the Kāmadhātu, located between the Yāma heaven and the heaven. Like the other heavens, is said to be reachable through meditation. It is the heaven where the Bodhisatt ...
, but will come to Jambudvipa when needed most as successor to the historic Śākyamuni Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism.
According to Buddhist tradition, he was born in ...
. Maitreya will achieve complete enlightenment during his lifetime, and following this reawakening he will bring back the timeless teaching of dharma
Dharma (; sa, धर्म, dharma, ; pi, dhamma, italic=yes) is a key concept with multiple meanings in Indian religions, such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, Sikhism and others. Although there is no direct single-word translation for ...
to this plane and rediscover enlightenment
Enlightenment or enlighten may refer to:
Age of Enlightenment
* Age of Enlightenment, period in Western intellectual history from the late 17th to late 18th century, centered in France but also encompassing (alphabetically by country or culture): ...
. The Arya Maitreya Mandala, founded in 1933 by Lama Anagarika Govinda, is based on the idea of Maitreya.
Maitreya eschatology forms the central canon of the White Lotus Society
The White Lotus () is a syncretic religious and political movement which forecasts the imminent advent of the "King of Light" (), i.e., the future Buddha Maitreya. As White Lotus sects developed, they appealed to many Han Chinese who found sola ...
, a religious and political movement which emerged in Yuan China
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; xng, , , literally "Great Yuan State"), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after its division. It was established by Kublai, the fif ...
. It later branched into the Chinese underground criminal organization
Organized crime (or organised crime) is a category of transnational, national, or local groupings of highly centralized enterprises run by criminals to engage in illegal activity, most commonly for profit. While organized crime is generally tho ...
known as the Triads, which exist today as an international underground criminal network.
Note that no description of Maitreya occurs in any other sutta in the canon, casting doubt as to the authenticity of the scripture. In addition, sermons of the Buddha normally are in response to a question, or in a specific context, but this sutta has a beginning and an ending, and its content is quite different from the others. This has led some to conclude that the whole sutta is apocrypha
Apocrypha are works, usually written, of unknown authorship or of doubtful origin. The word ''apocryphal'' (ἀπόκρυφος) was first applied to writings which were kept secret because they were the vehicles of esoteric knowledge considered ...
l, or tampered with.
Richard Gombrich
Richard Francis Gombrich (; born 17 July 1937) is a British Indologist and scholar of Sanskrit, Pāli, and Buddhist studies. He was the Boden Professor of Sanskrit at the University of Oxford from 1976 to 2004. He is currently Founder-Presi ...
, ''Theravada Buddhism: A Social History from Ancient Benares to Modern Colombo''. Routledge and Kegan Paul, 1988, pages 83–85.
Sermon of the Seven Suns
In his "Sermon of the Seven Suns" in thePali Canon
The Pāli Canon is the standard collection of scriptures in the Theravada Buddhist tradition, as preserved in the Pāli language. It is the most complete extant early Buddhist canon. It derives mainly from the Tamrashatiya school.
During ...
, the Buddha describes the ultimate fate of the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surf ...
in an apocalypse
Apocalypse () is a literary genre in which a supernatural being reveals cosmic mysteries or the future to a human intermediary. The means of mediation include dreams, visions and heavenly journeys, and they typically feature symbolic imager ...
characterized by the consequent appearance of seven suns in the sky, each causing progressive ruin until the planet is destroyed:
The canon goes on to describe the progressive destruction of each sun. The third sun will dry the Ganges River
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
and other rivers, whilst the fourth will cause the lakes to evaporate; the fifth will dry the oceans. Later:
The sermon completes with the Earth immersed into an extensive holocaust. The Pali Canon does not indicate when this will happen relative to Maitreya.
Norse mythology


Norse mythology
Norse, Nordic, or Scandinavian mythology is the body of myths belonging to the North Germanic peoples, stemming from Old Norse religion and continuing after the Christianization of Scandinavia, and into the Nordic folklore of the modern peri ...
depicts the end of days as ''Ragnarök'', an Old Norse
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic languages, North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and t ...
term translatable as "twilight of the gods". It will be heralded by a devastation known as Fimbulvetr
In Norse mythology, (commonly rendered in English as Fimbulwinter), is the immediate prelude to the events of Ragnarök. It means 'great winter'.
Summary
is the harsh winter that precedes the end of the world and puts an end to all life on E ...
which will seize Midgard
In Germanic cosmology, Midgard (an anglicised form of Old Norse language, Old Norse ; Old English , Old Saxon , Old High German , and Gothic language, Gothic ''Midjun-gards''; "middle yard", "middle enclosure") is the name for Earth (equivalent ...
in cold and darkness. The sun and moon will disappear from the sky, and poison will fill the air. The dead will rise from the ground and there will be widespread despair.
There follows a battle between—on the one hand—the Gods with the Æsir
The Æsir (Old Norse: ) are the gods of the principal pantheon in Norse religion. They include Odin, Frigg, Höðr, Thor, and Baldr. The second Norse pantheon is the Vanir. In Norse mythology, the two pantheons wage war against each oth ...
, Vanir
In Norse mythology, the Vanir (; Old Norse: , singular Vanr ) are a group of gods associated with fertility, wisdom, and the ability to see the future. The Vanir are one of two groups of gods (the other being the Æsir) and are the namesake of the ...
and Einherjar, led by Odin, and—on the other hand—forces of Chaos, including the fire giants and jötunn
A (also jotun; in the normalised scholarly spelling of Old Norse, ; ; plural / ) or, in Old English, (plural ) is a type of supernatural being in Germanic mythology. In Norse mythology, they are often contrasted with gods (Æsir and Vanir ...
, led by Loki
Loki is a god in Norse mythology. According to some sources, Loki is the son of Fárbauti (a jötunn) and Laufey (mentioned as a goddess), and the brother of Helblindi and Býleistr. Loki is married to Sigyn and they have two sons, Narfi ...
. In the fighting Odin will be swallowed whole by his old nemesis Fenrir.Larrington (1996:266). The god Freyr
Freyr (Old Norse: 'Lord'), sometimes anglicized as Frey, is a widely attested god in Norse mythology, associated with kingship, fertility, peace, and weather. Freyr, sometimes referred to as Yngvi-Freyr, was especially associated with Sweden an ...
fights Surtr
In Norse mythology, Surtr (Old Norse "black"Orchard (1997:154). "the swarthy one",Simek (2007:303–304) Surtur in modern Icelandic), also sometimes written Surt in English, is a jötunn. Surtr is attested in the ''Poetic Edda'', compiled in the ...
but loses. Víðarr
In Norse mythology, Víðarr (Old Norse: , possibly "wide ruler",Orchard (1997:174—175). sometimes anglicized as Vidar , Vithar, Vidarr, and Vitharr) is a god among the Æsir associated with vengeance. Víðarr is described as the son of Odin ...
, son of Odin, will then avenge his father by ripping Fenrir's jaws apart and stabbing the wolf in the heart with his spear. The serpent Jörmungandr
In Norse mythology, Jörmungandr ( non, Jǫrmungandr, lit=the Vast gand, see Etymology), also known as the Midgard Serpent or World Serpent ( non, Miðgarðsormr), is an unfathomably large sea serpent or worm who dwells in the world sea, encir ...
will open its gaping maw and be met in combat by Thor
Thor (; from non, Þórr ) is a prominent god in Germanic paganism. In Norse mythology, he is a hammer-wielding god associated with lightning, thunder, storms, sacred groves and trees, strength, the protection of humankind, hallowing ...
. Thor, also a son of Odin, will defeat the serpent, only to take nine steps afterwards before collapsing in his own death.
After this people will flee their homes as the sun blackens and the earth sinks into the sea. The stars will vanish, steam will rise, and flames will touch the heavens. This conflict will result in the deaths of most of the major Gods and forces of Chaos. Finally, Surtr
In Norse mythology, Surtr (Old Norse "black"Orchard (1997:154). "the swarthy one",Simek (2007:303–304) Surtur in modern Icelandic), also sometimes written Surt in English, is a jötunn. Surtr is attested in the ''Poetic Edda'', compiled in the ...
will fling fire across the nine worlds. The ocean will then completely submerge Midgard
In Germanic cosmology, Midgard (an anglicised form of Old Norse language, Old Norse ; Old English , Old Saxon , Old High German , and Gothic language, Gothic ''Midjun-gards''; "middle yard", "middle enclosure") is the name for Earth (equivalent ...
.
After the cataclysm
Cataclysm is derived from the Greek (), 'down, against', and (), 'wash over, surge'. It may refer to:
Common meanings
*Generally, any large-scale disaster
*Deluge (mythology)
*Doomsday event, see hypothetical risks to civilization, humans, and p ...
, the world will resurface new and fertile, and the surviving Gods will meet. Baldr, another son of Odin, will be reborn in the new world, according to Völuspá
''Vǫluspá'' (also ''Völuspá'', ''Vǫlospá'' or ''Vǫluspǫ́''; Old Norse: 'Prophecy of the völva, a seeress'; reconstructed Old Norse: ) is the best known poem of the '' Poetic Edda''. It tells the story of the creation of the world an ...
. The two human survivors, Líf and Lífþrasir, will then repopulate this new earth.
No end times
Taoism
The Taoist faith is not concerned with what came before or after life, knowing only their own being in the Tao. The philosophy is that people come and go, just like mountains, trees and stars, but Tao will go on for time immemorial.Analogies in science and philosophy
futures studies
Futures studies, futures research, futurism or futurology is the systematic, interdisciplinary and holistic study of social and technological advancement, and other environmental trends, often for the purpose of exploring how people will l ...
and transhumanists investigate how the accelerating rate of scientific progress may lead to a "technological singularity
The technological singularity—or simply the singularity—is a hypothetical future point in time at which technological growth becomes uncontrollable and irreversible, resulting in unforeseeable changes to human civilization. According to the m ...
" in the future that would profoundly and unpredictably change the course of human history, and result in ''Homo sapiens'' no longer being the dominant life form on Earth. Sandberg, AndersAn overview of models of technological singularity
/ref> Occasionally the term "physical eschatology" is applied to the long-term predictions of astrophysics about the
future of Earth
The biological and geological future of Earth can be extrapolated based on the estimated effects of several long-term influences. These include the chemistry at Earth's surface, the cooling rate of the planet's interior, the gravitational ...
and ultimate fate of the universe
The ultimate fate of the universe is a topic in physical cosmology, whose theoretical restrictions allow possible scenarios for the evolution and ultimate fate of the universe to be described and evaluated. Based on available observational ev ...
.Baum, Seth D. "Is humanity doomed? Insights from astrobiology." Sustainability 2.2 (2010): 591–603. The Sun will turn into a red giant
A red giant is a luminous giant star of low or intermediate mass (roughly 0.3–8 solar masses ()) in a late phase of stellar evolution. The outer atmosphere is inflated and tenuous, making the radius large and the surface temperature around or ...
in approximately 6 billion years. Life on Earth will become impossible due to a rise in temperature long before the planet is actually swallowed up by the Sun. Even later, the Sun will become a white dwarf
A white dwarf is a stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very dense: its mass is comparable to the Sun's, while its volume is comparable to the Earth's. A white dwarf's faint luminosity comes ...
.
See also
Notes
References
Further reading
* * Craig C. Hill, ''In God's Time: The Bible and the Future'', Grand Rapids: Eerdmans 2002. * Dave Hunt, ''A Cup of Trembling'', Harvest House Publishers, Eugene, (Oregon) 1995 . * Jonathan Menn, ''Biblical Eschatology'', Eugene, Oregon, Wipf & Stock 2013. . * Joseph Ratzinger., ''Eschatology: Death and Eternal Life'', Washington D.C.:Catholic University of America Press
The Catholic University of America Press, also known as CUA Press, is the publishing division of The Catholic University of America. Founded on November 14, 1939, and incorporated on July 16, 1941,Roy J. Deferrari ''Memoirs of the Catholic Univer ...
1985. .
* Robert Sungenis, Scott Temple, David Allen Lewis, ''Shock Wave 2000!'' subtitled ''The Harold Camping
Harold Egbert Camping (July 19, 1921December 15, 2013) was an American Christian radio broadcaster and evangelist. Beginning in 1958, he served as president of Family Radio, a California-based radio station group that, at its peak, broadcast t ...
1994 Debacle'', New Leaf Press, Inc. 2004
* Stephen Travis, ''Christ Will Come Again: Hope for the Second Coming of Jesus'', Toronto: Clements Publishing 2004.
* Jerry L. Walls (ed.), ''The Oxford Handbook of Eschatology'', New York: Oxford University Press 2008.
External links
* * {{Authority control Prophecy Mythology Last events Ultimate fate of the universe