|
Deep Time
Deep time is the concept of geological time that spans billions of years, far beyond the scale of human experience. It provides the temporal framework for understanding the formation and evolution of Earth, the development of life, and the slow-moving processes that shape planetary change. First developed as a scientific idea in the 18th century and popularized in the 20th century by writers such as John McPhee, the concept of deep time has influenced fields ranging from geology and evolutionary biology to climate science, philosophy, education, and environmental ethics. Today, deep time is increasingly used in science communication and public engagement, offering a powerful lens for understanding human impact during the Anthropocene. Origins and definition The philosophical concept of geological time was developed in the 18th century by Scottish geologist James Hutton; his "system of the habitable Earth" was a deistic mechanism keeping the world eternally suitable for huma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geologic Time Scale
The geologic time scale or geological time scale (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochronology (a scientific branch of geology that aims to determine the age of rocks). It is used primarily by Earth scientists (including geologists, paleontologists, geophysicists, geochemists, and paleoclimatologists) to describe the timing and relationships of events in geologic history. The time scale has been developed through the study of rock layers and the observation of their relationships and identifying features such as lithologies, paleomagnetic properties, and fossils. The definition of standardised international units of geological time is the responsibility of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), a constituent body of the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), whose primary objective is to preci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Enlightenment
The Scottish Enlightenment (, ) was the period in 18th- and early-19th-century Scotland characterised by an outpouring of intellectual and scientific accomplishments. By the eighteenth century, Scotland had a network of parish schools in the Scottish Lowlands and five universities. The Enlightenment culture was based on close readings of new books, and intense discussions which took place daily at such intellectual gathering places in Edinburgh as The Select Society and, later, The Poker Club, as well as within Scotland's ancient universities (St Andrews, Glasgow, Edinburgh, King's College, and Marischal College). Sharing the humanist and rational outlook of the Western Enlightenment of the same time period, the thinkers of the Scottish Enlightenment asserted the importance of human reason combined with a rejection of any authority that could not be justified by reason. In Scotland, the Enlightenment was characterised by a thoroughgoing empiricism and practicality where t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
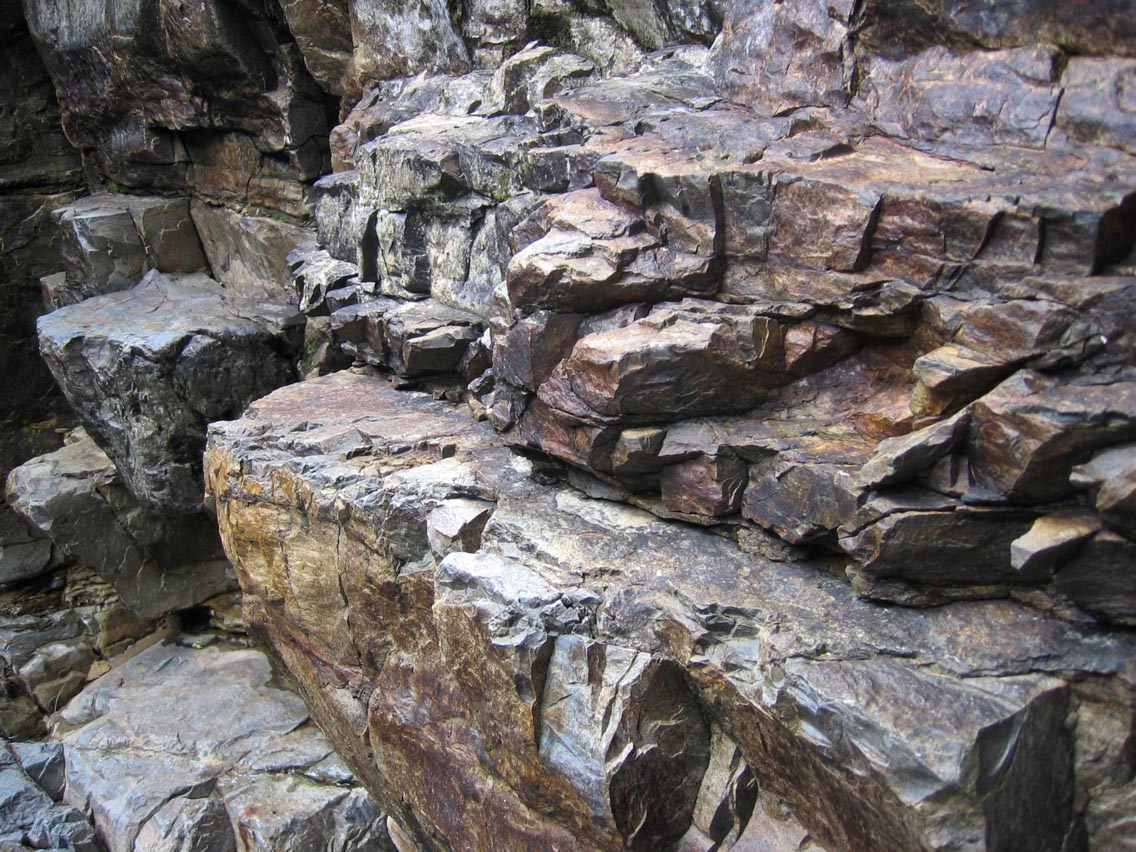
Hutton's Unconformity
Hutton's Unconformity is a name given to various notable geological sites in Scotland identified by the 18th-century Scottish geologist James Hutton as places where the junction between two types of rock formations can be seen. This geological phenomenon marks the location where rock formations created at different times and by different processes adjoin. For Hutton, such an unconformity provided evidence for his Plutonist theories of uniformitarianism and the age of Earth. An unconformity is a break in the normal progression of sedimentary deposits, where newer deposits are laid on top of older. The example Hutton discovered is known as an angular unconformity in which a sharp change in younging direction can be seen in the orientation of bedding planes. The younging direction points ''from'' the oldest bed, to the ''youngest'' bed in the sequence of sedimentary beds. In his search, Hutton and colleagues examined rock outcrops and cliffs, both riverside and sea, and found se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
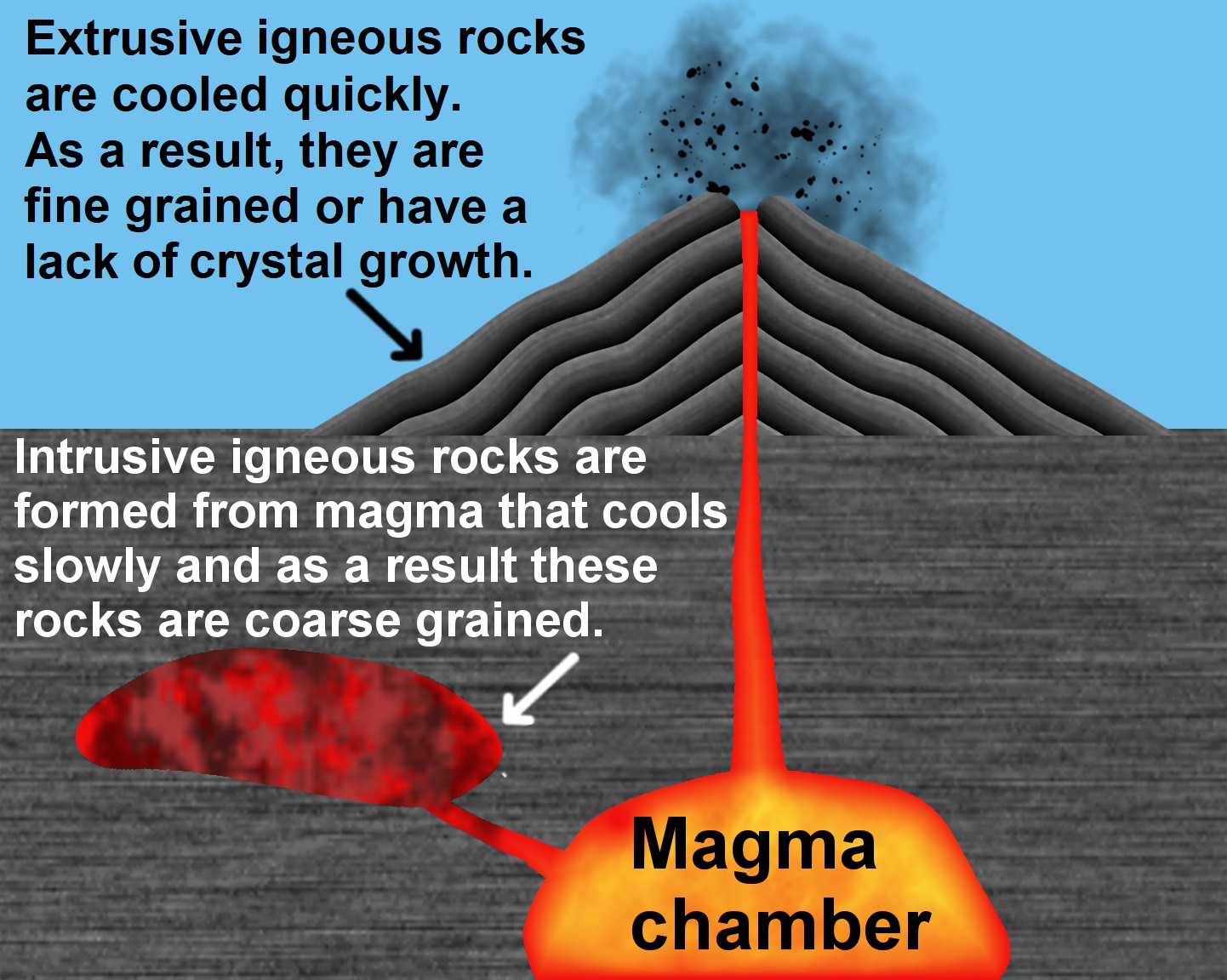
Plutonism
Plutonism is the geology, geologic theory that the igneous rocks forming the Earth originated from intrusive Magma, magmatic activity, with a continuing gradual process of weathering and erosion wearing away rocks, which were then deposited on the sea bed, re-formed into layers of sedimentary rock by heat and pressure, and raised again. It proposes that basalt is solidified molten magma. The theory lead to plutonic (intrinsic) rock classification, which includes intrinsic igneous rocks such as gabbro, diorite, granite and pegmatite. The name ''plutonism'' references Pluto (mythology), Pluto, the classical mythology, classical ruler of the Greek underworld, underworld and the Roman god of wealth. A main reason Pluto was incorporated into the classification was due to the plutonic rocks commonly being present in gold and silver ore deposits (veins). The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' traces use of the word "plutonists" to 1799, and the appearance of the word ''plutonism'' to 1842. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock (geology)
In geology, rock (or stone) is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized by the minerals included, its Chemical compound, chemical composition, and the way in which it is formed. Rocks form the Earth's outer solid layer, the Earth's crust, crust, and most of its interior, except for the liquid Earth's outer core, outer core and pockets of magma in the asthenosphere. The study of rocks involves multiple subdisciplines of geology, including petrology and mineralogy. It may be limited to rocks found on Earth, or it may include planetary geology that studies the rocks of other celestial objects. Rocks are usually grouped into three main groups: igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks and metamorphic rocks. Igneous rocks are formed when magma cools in the Earth's crust, or lava cools on the ground surface or the seabed. Sedimentary rocks are formed by diagenesis and lithification of sediments, which in turn are formed by the weathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neptunism
Neptunism is a superseded scientific theory of geology proposed by Abraham Gottlob Werner (1749–1817) in the late 18th century, who proposed that rocks formed from the crystallisation of minerals in the early Earth's oceans. The theory took its name from Neptune, the ancient Roman god of the sea. There was considerable debate between its proponents (neptunists) and those favouring a rival theory known as plutonism which gave a significant role to volcanic origins, and which in modified form replaced neptunism in the early 19th century as the principle of uniformitarianism was shown to fit better with the geological facts as they became better known. Modern geology acknowledges many different forms of rock formation, and explains the formation of sedimentary rock through processes very similar to those described by neptunism. Historical development In the mid-eighteenth century as the investigation of geology found evidence such as fossils, naturalists developed new ideas w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abraham Gottlob Werner
Abraham Gottlob Werner (; 25 September 174930 June 1817) was a German geologist A geologist is a scientist who studies the structure, composition, and History of Earth, history of Earth. Geologists incorporate techniques from physics, chemistry, biology, mathematics, and geography to perform research in the Field research, ... who set out an early theory about the Stratigraphy, stratification of the Earth's crust and propounded a history of the Earth that came to be known as Neptunism. While most tenets of Neptunism were eventually set aside, Werner is remembered for his demonstration of Succession (geology), chronological succession in rocks; for the zeal with which he infused his pupils; and for the impulse he thereby gave to the study of geology. He has been called the "father of German geology". Life Werner was born in Wehrau (now Osiecznica, Lower Silesian Voivodeship), a village in Prussian Silesia. His family had been involved in the mining industry for many years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horace Bénédict De Saussure
Horace Bénédict de Saussure (; 17 February 1740 – 22 January 1799) was a Genevan geologist, meteorologist, physicist, mountaineer and Alpine explorer, often called the founder of alpinism and modern meteorology, and considered to be the first person to build a successful solar oven. Early life and education Horace Bénédict de Saussure was born 17 February 1740, in Conches, near Geneva (''today in Switzerland but then an independent republic''). Saussure's family were Genevan patricians. His father, Nicolas de Saussure, was an agriculturist, agronomist and author. Because his mother was "sickly", Saussure was brought up by his mother's sister and her husband the Genevan naturalist Charles Bonnet, who sparked Horace-Bénédict's early interest in botany. After attending the "Collège" of his hometown, he completed his studies at the Geneva Academy in 1759 with a dissertation on heat (''Dissertatio physica de igne''). Career In 1760, Saussure made the first of nume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicolas Steno
Niels Steensen (; Latinized to Nicolas Steno or Nicolaus Stenonius; 1 January 1638 – 25 November 1686 ) was a Danish scientist, a pioneer in both anatomy and geology who became a Catholic bishop in his later years. He has been beatified by the Catholic Church. Steensen was trained in the classical texts on science; however, by 1659 he seriously questioned accepted knowledge of the natural world. Importantly he questioned explanations for tear production, the idea that fossils grew in the ground and explanations of rock formation. His investigations and his subsequent conclusions on fossils and rock formation have led scholars to consider him one of the founders of modern stratigraphy and modern geology. The importance of Steensen's foundational contributions to geology may be gauged from the fact that half of the twenty papers in a recent miscellany volume on ''The Revolution in Geology from the Renaissance to the Enlightenment'' focus on Steensen, the "preeminent Baroqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geologists
A geologist is a scientist who studies the structure, composition, and history of Earth. Geologists incorporate techniques from physics, chemistry, biology, mathematics, and geography to perform research in the field and the laboratory. Geologists work in the energy and mining sectors to exploit natural resources. They monitor environmental hazards such as earthquakes, volcanoes, tsunamis and landslides. Geologists are also important contributors to climate change discussions. History James Hutton is often viewed as the first modern geologist. In 1785 he presented a paper entitled ''Theory of the Earth'' to the Royal Society of Edinburgh. In his paper, he explained his theory that the Earth must be much older than had previously been supposed to allow enough time for mountains to be eroded and for sediments to form new rocks at the bottom of the sea, which in turn were raised up to become dry land. Hutton published a two-volume version of his ideas in 1795Vol. 1 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Farrar, Straus And Giroux
Farrar, Straus and Giroux (FSG) is an American book publishing company, founded in 1946 by Roger Williams Straus Jr. and John C. Farrar. FSG is known for publishing literary books, and its authors have won numerous awards, including Pulitzer Prizes, National Book Awards, and Nobel Prizes. As of 1993, the publisher has been a division of Macmillan Publishers, Macmillan, whose parent company is the German publishing conglomerate Holtzbrinck Publishing Group. Founding Farrar, Straus, and Company was founded in 1945 by Roger W. Straus Jr. and John C. Farrar. The first book was ''Yank: The G.I. Story of the War'', a compilation of articles that appeared in ''Yank, the Army Weekly'', then ''There Were Two Pirates'', a novel by James Branch Cabell. The first years of existence were rough until they published the diet book ''Look Younger, Live Longer'' by Gayelord Hauser in 1950. The book went on to sell 500,000 copies and Straus said that the book carried them along for a while. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
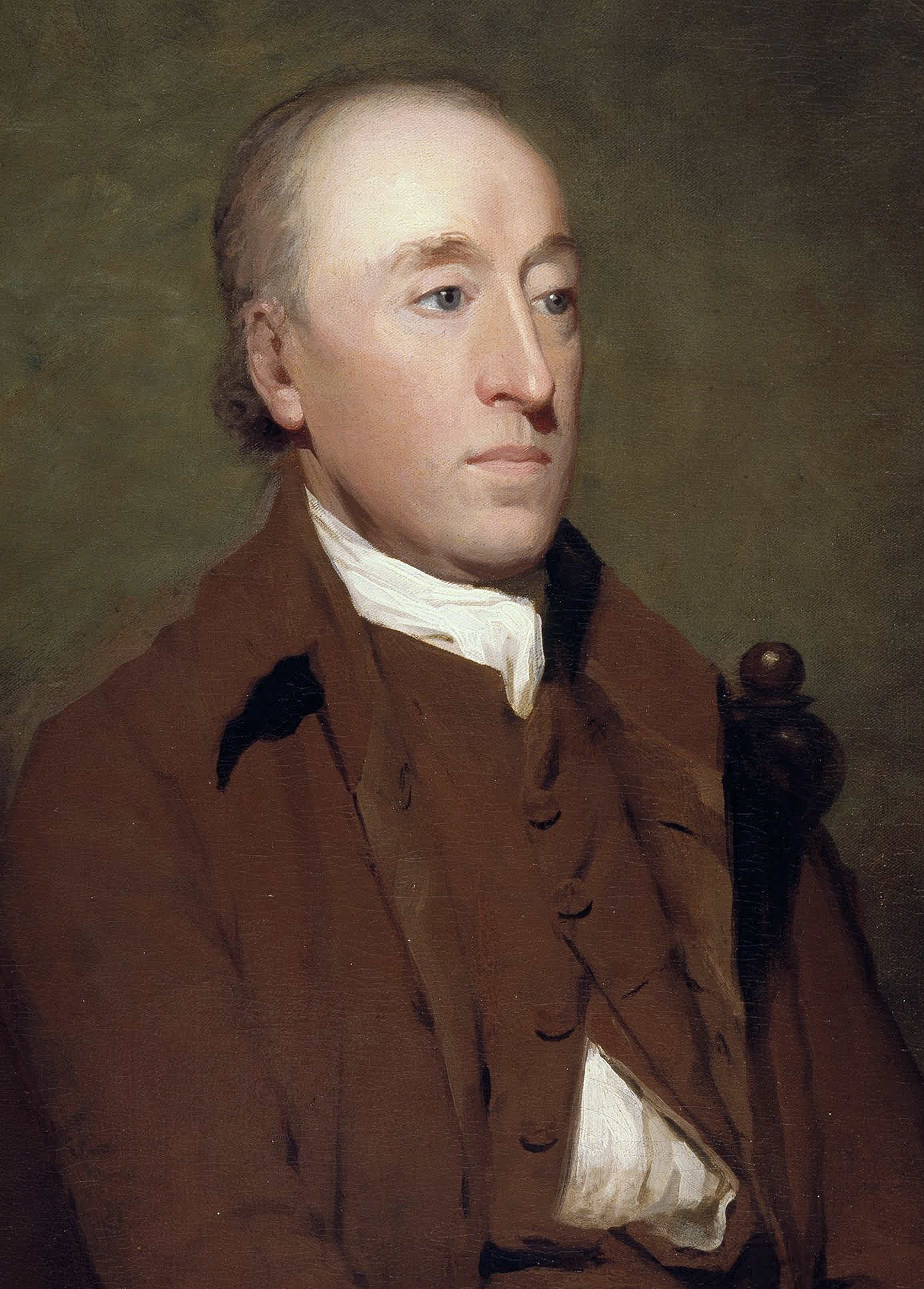
Sir James Hall, 4th Baronet
Sir James Hall of Dunglass, 4th Baronet FRS FRSE (17 January 1761 – 23 June 1832) was a Scottish geologist and geophysicist. He was a Member of Parliament for St. Michael's borough ( Mitchell, Cornwall) 1807–1812. Education Hall was born at Dunglass Castle, East Lothian, to Magdalena, daughter of Sir Robert Pringle, 3rd Baronet, of Tillich, Gloucestershire and Sir John Hall, 3rd Baronet (died 1776). He studied at Christ's College, Cambridge, and the University of Edinburgh. As an Edinburgh student during the early 1780s, Hall studied chemistry under Joseph Black and natural history under John Walker. Though mineralogy was frequent taught in medical courses, Walker was one of the first professors to offer systematic lectures on the new field of geology. While attending Walker's popular course, Hall was taught how to use the chemical composition of minerals to determine relative age of strata. Walker also emphasized the geological relevance of chemists like William Cull ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |