Energy Conservation In India on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The


 India ranks third in oil consumption with 4.669 million barrels/day in 2020 after USA and China. During the calendar year 2019, India imported 221.7 million tons of crude oil and 44.4 million tons of refined petroleum products and exported 60.7 million tons of refined petroleum products. India is the second biggest net importer of crude oil and its products after China. India has built surplus world-class refining capacity using imported crude oil for exporting refined petroleum products. The net imports of crude oil is lesser by one fourth after accounting exports and imports of refined petroleum products. Natural gas production was 26.9 billion cubic meters and consumption 59.7 billion cubic meters during the calendar year 2019.
During the financial year 2012–13, the production of crude oil was 37.86 million tons and 40,679 million standard cubic meters (nearly 26.85 million tons)
India ranks third in oil consumption with 4.669 million barrels/day in 2020 after USA and China. During the calendar year 2019, India imported 221.7 million tons of crude oil and 44.4 million tons of refined petroleum products and exported 60.7 million tons of refined petroleum products. India is the second biggest net importer of crude oil and its products after China. India has built surplus world-class refining capacity using imported crude oil for exporting refined petroleum products. The net imports of crude oil is lesser by one fourth after accounting exports and imports of refined petroleum products. Natural gas production was 26.9 billion cubic meters and consumption 59.7 billion cubic meters during the calendar year 2019.
During the financial year 2012–13, the production of crude oil was 37.86 million tons and 40,679 million standard cubic meters (nearly 26.85 million tons)

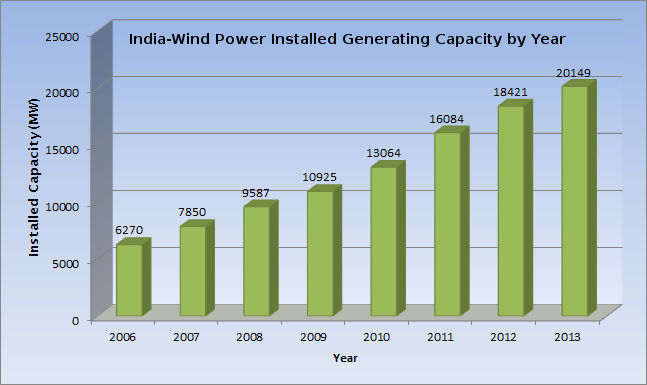 India has the fourth largest installed wind power capacity in the world. As of 31 December 2017, the installed capacity of wind power was 32,848 MW an increase of 4148 MW over the previous year Wind power accounts for nearly 10% of India's total installed power generation capacity and generated 52.666 billion kWh in the fiscal year 2017-18 which is nearly 3% of total electricity generation. The capacity utilisation factor is nearly 16% in the fiscal year 2017-18. The
India has the fourth largest installed wind power capacity in the world. As of 31 December 2017, the installed capacity of wind power was 32,848 MW an increase of 4148 MW over the previous year Wind power accounts for nearly 10% of India's total installed power generation capacity and generated 52.666 billion kWh in the fiscal year 2017-18 which is nearly 3% of total electricity generation. The capacity utilisation factor is nearly 16% in the fiscal year 2017-18. The
 India's
India's
 The installed capacity of commercial solar thermal power plants in India is 227.5 MW with 50 MW in Andhra Pradesh and 177.5 MW in Rajasthan. Solar thermal plants are emerging as cheaper (6 Euro ¢/kWh) and clean
The installed capacity of commercial solar thermal power plants in India is 227.5 MW with 50 MW in Andhra Pradesh and 177.5 MW in Rajasthan. Solar thermal plants are emerging as cheaper (6 Euro ¢/kWh) and clean
 The major disadvantage of solar power (PV type only) is that it can not produce electricity during the nighttime and cloudy daytime also. In India, this disadvantage can be overcome by installing
The major disadvantage of solar power (PV type only) is that it can not produce electricity during the nighttime and cloudy daytime also. In India, this disadvantage can be overcome by installing
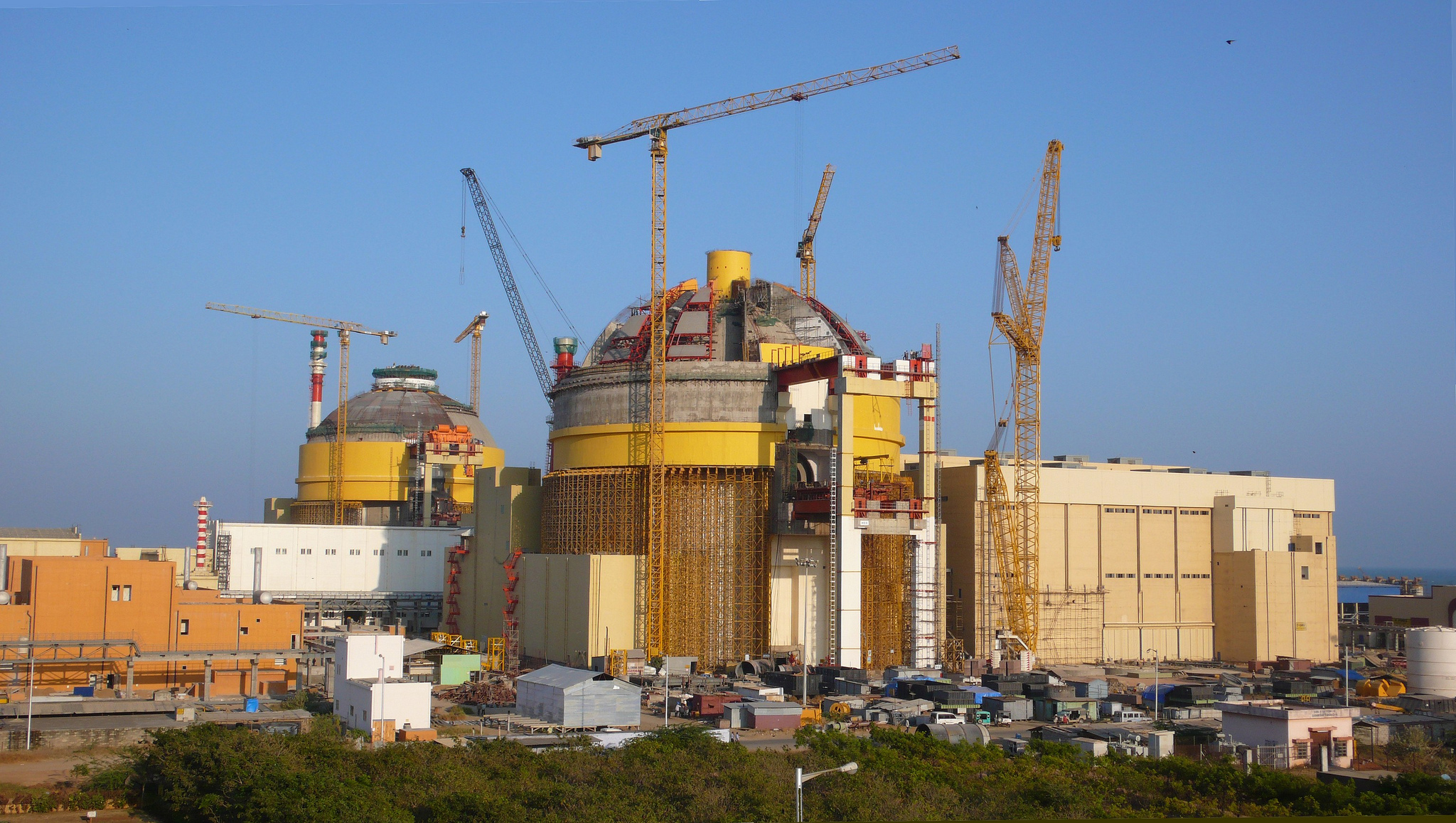 India boasts a quickly advancing and active nuclear power program. It is expected to have 20 GW of nuclear capacity by 2020, though it currently stands as 9th in the world in terms of nuclear capacity.
An Achilles' heel of the Indian nuclear power program, is the fact that India is not a signatory of the
India boasts a quickly advancing and active nuclear power program. It is expected to have 20 GW of nuclear capacity by 2020, though it currently stands as 9th in the world in terms of nuclear capacity.
An Achilles' heel of the Indian nuclear power program, is the fact that India is not a signatory of the
 Total installed Power generation Capacity (end of April 2017)
The total installed utility power generation capacity as on 30 April 2017 with sector wise & type wise break up is as given below.
Notes: Coal includes lignite; Misc: includes contributions from emergency diesel generator sets; *Hydro includes pumped storage generation; na = data not available.
In 2019-20, the total generation from all renewable energy sources is nearly 20% of the total electricity generation (utility and captive) in India.
Total installed Power generation Capacity (end of April 2017)
The total installed utility power generation capacity as on 30 April 2017 with sector wise & type wise break up is as given below.
Notes: Coal includes lignite; Misc: includes contributions from emergency diesel generator sets; *Hydro includes pumped storage generation; na = data not available.
In 2019-20, the total generation from all renewable energy sources is nearly 20% of the total electricity generation (utility and captive) in India.
Ready Reference Policy Handbook about India at one placeThe Carbon Brief Profile: India Latest news about Indian Power Sector at one place
Map of oil and gas infrastructure (incomplete)India's River-Linking Scheme: A case of troubled waters
{{World topic, Energy policy of, noredlinks=yes
energy policy
Energy policies are the government's strategies and decisions regarding the Energy production, production, Energy distribution, distribution, and World energy supply and consumption, consumption of energy within a specific jurisdiction. Energy ...
of India is to increase the locally produced energy in India and reduce energy poverty
In developing countries and some areas of more developed countries, energy poverty is lack of access to modern energy services in the home. In 2022, 759 million people lacked access to consistent electricity and 2.6 billion people used dangerous a ...
, with more focus on developing alternative sources of energy, particularly nuclear
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
*Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
* Nuclear space
*Nuclear ...
, solar
Solar may refer to:
Astronomy
* Of or relating to the Sun
** Solar telescope, a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun
** A device that utilizes solar energy (e.g. "solar panels")
** Solar calendar, a calendar whose dates indicate t ...
and wind
Wind is the natural movement of atmosphere of Earth, air or other gases relative to a planetary surface, planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heatin ...
energy. Net energy import dependency was 40.9% in 2021-22. The primary energy
Primary energy (PE) is the energy found in nature that has not been subjected to any human engineered conversion process. It encompasses energy contained in raw fuels and other forms of energy, including waste, received as input to a system. Pri ...
consumption in India grew by 13.3% in FY2022-23 and is the third biggest with 6% global share after China and USA. The total primary energy consumption from coal (452.2 Mtoe; 45.88%), crude oil (239.1 Mtoe; 29.55%), natural gas (49.9 Mtoe; 6.17%), nuclear energy (8.8 Mtoe; 1.09%), hydroelectricity (31.6 Mtoe; 3.91%) and renewable power (27.5 Mtoe; 3.40%) is 809.2 Mtoe (excluding traditional biomass use) in the calendar year 2018. In 2018, India's net imports are nearly 205.3 million tons of crude oil and its products, 26.3 Mtoe of LNG and 141.7 Mtoe coal totaling to 373.3 Mtoe of primary energy which is equal to 46.13% of total primary energy consumption. India is largely dependent on fossil fuel imports to meet its energy demands – by 2030, India's dependence on energy imports is expected to exceed 53% of the country's total energy consumption.
About 80% of India's electricity generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric power from sources of primary energy. For electric utility, utilities in the electric power industry, it is the stage prior to its Electricity delivery, delivery (Electric power transm ...
is from fossil fuel
A fossil fuel is a flammable carbon compound- or hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the buried remains of prehistoric organisms (animals, plants or microplanktons), a process that occurs within geolog ...
s. India is surplus in electricity generation and also a marginal exporter of electricity in 2017. Since the end of the calendar year 2015, huge power generation capacity has been idling for want of electricity demand. India ranks second after China in renewables production with 208.7 Mtoe in 2016. The carbon intensity
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 electrons. It belongs to grou ...
in India was 0.29 kg of CO2 per kWhe in 2016 which is more than that of USA, China and EU. The total manmade CO2 emissions from energy, process emissions, methane, and flaring is 2797.2 million tons of CO2 in CY2021 which is 7.2% of global emissions. The energy intensity of agriculture sector is seven times less than industrial sector in 2022-23 (see Table 8.9)
In 2020-21, the per-capita energy consumption is 0.6557 Mtoe excluding traditional biomass use and the energy intensity
Energy intensity is a Measurement, measure of the efficient energy use, energy inefficiency of an Economic system, economy. It is calculated as units of energy per unit of GDP (Gross Domestic Product) or some other measure of economic output. Hi ...
of the Indian economy is 0.2233 Mega Joule
The joule ( , or ; symbol: J) is the unit of energy in the International System of Units (SI). In terms of SI base units, one joule corresponds to one kilogram- metre squared per second squared One joule is equal to the amount of work d ...
s per INR (53.4 kcal/INR). India attained 63% overall energy self-sufficiency in 2017. Due to rapid economic expansion, India has one of the world's fastest growing energy markets and is expected to be the second-largest contributor to the increase in global energy demand by 2035, accounting for 18% of the rise in global energy consumption
World energy supply and consumption refers to the global supply of World energy resources, energy resources and its Energy consumption, consumption. The system of global energy supply consists of the energy development, Refineries, refinement, a ...
. Given India's growing energy demands and limited domestic oil and gas reserves, the country has ambitious plans to expand its renewable and most worked out nuclear power programme. India has the world's fourth largest wind power market and also plans to add about 100,000 MW of solar power capacity by 2022. India also envisages to increase the contribution of nuclear power to overall electricity generation capacity from 4.2% to 9% within 25 years. The country has five nuclear reactors under construction (third highest in the world) and plans to construct 18 additional nuclear reactors (second highest in the world) by 2025. During the year 2018, the total investment in energy sector by India was 4.1% (US$75 billion) of US$1.85 trillion global investment.
The energy policy of India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
is characterized by trade-offs between four major drivers: A rapidly growing economy, with a need for dependable and reliable supply of electricity, gas, and petroleum products; Increasing household incomes, with a need for an affordable and adequate supply of electricity, and clean cooking
One aspect of energy poverty is lack of access to clean, modern fuels and technologies for cooking. As of 2020, more than 2.6 billion people in developing countries routinely cook with fuels such as wood, animal dung, coal, or kerosene. Burning ...
fuels; limited domestic reserves of fossil fuels
A fossil fuel is a flammable carbon compound- or hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the buried remains of prehistoric organisms (animals, plants or microplanktons), a process that occurs within geologica ...
, and the need to import a vast fraction of the natural gas, and crude oil, and recently the need to import coal as well; and indoor, urban and regional environmental impacts, necessitating the need for the adoption of cleaner fuels and cleaner technologies. In recent years, these challenges have led to a major set of continuing reforms, restructuring, and a focus on energy conservation
Energy conservation is the effort to reduce wasteful energy consumption by using fewer energy services. This can be done by using energy more effectively (using less and better sources of energy for continuous service) or changing one's behavi ...
.
A report by The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI) outlines a roadmap for India's energy transition in the transport sector, emphasizing electric mobility, alternative fuels, and policy-driven decarbonization efforts.
Fossil fuels
Oil and gas

natural gas
Natural gas (also fossil gas, methane gas, and gas) is a naturally occurring compound of gaseous hydrocarbons, primarily methane (95%), small amounts of higher alkanes, and traces of carbon dioxide and nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide and helium ...
. The net import of crude oil & petroleum products is 146.70 million tons worth of Rs 5611.40 billion. This includes 9.534 million tons of LNG
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas (predominantly methane, CH4, with some mixture of ethane, C2H6) that has been cooled to liquid form for ease and safety of non-pressurized storage or transport. It takes up about 1/600th the volume o ...
imports worth of Rs. 282.15 billion. Internationally, LNG price (One million Btu
The British thermal unit (Btu) is a measure of heat, which is a form of energy. It was originally defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit. It is also part of the United Stat ...
of LNG = 0.1724 barrels of crude oil (boe) = 29.52 cubic meters of natural gas = 21 kg of natural gas = 29.2 liters diesel = 21.3 kg LPG = 0.293 MWh) is fixed below crude oil price in terms of heating value. LNG is slowly gaining its role as direct use fuel in the road and marine transport without regasification
Regasification is a process of converting liquefied natural gas (LNG) at −162 °C (−260 °F) temperature back to natural gas at atmospheric temperature. LNG gasification plants can be located on land as well as on floating barges, i.e. a Float ...
. By the end of June 2016, LNG price has fallen by nearly 50% below its oil parity price making it more economical fuel than diesel/gas oil in transport sector. In 2012-13, India consumed 15.744 million tons petrol and 69.179 million tons diesel which are mainly produced from imported crude oil at huge foreign exchange out go. Using natural gas for heating, cooking and electricity generation is not economical as more and more locally produced natural gas will be converted into LNG for use in the transport sector to reduce crude oil imports. Conversion of old diesel fueled heavy duty vehicles into LNG vehicles would restore original performance economically. In addition to the conventional natural gas production, coal gasification
In industrial chemistry, coal gasification is the process of producing syngas—a mixture consisting primarily of carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (), carbon dioxide (), methane (), and water vapour ()—from coal and water, air and/or oxygen.
H ...
, coal bed methane, coal mine methane and Biogas digesters / Renewable natural gas will also become a source of LNG forming decentralised base for the production of LNG to cater to the widely distributed demand. There is possibility to convert most of the heavy duty vehicles (including diesel driven rail engines) into LNG fuelled vehicles to reduce diesel consumption drastically with operational cost and least pollution benefits. Also, the break even price at user end for switching from imported coal to LNG in electricity generation is estimated near US. The advent of cheaper marine CNG transport will restrict LNG use in high end transport sector to replace costly liquid fuels leaving imported CNG use for other needs. As the marine CNG transport is economical for medium distance transport and has fast unloading flexibility at many ports without costly unloading facilities, they have become alternate solution to submarine gas pipelines. Natural gas/methane can also be converted cheaply into hydrogen gas and carbon black
Carbon black (with subtypes acetylene black, channel black, furnace black, lamp black and thermal black) is a material produced by the incomplete combustion of coal tar, vegetable matter, or petroleum products, including fuel oil, fluid cataly ...
without emitting any greenhouse gas for use in the transport sector with fuel cell vehicle
A fuel cell vehicle (FCV) or fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV) is an electric vehicle that uses a fuel cell, sometimes in combination with a small battery or supercapacitor, to power its onboard electric motor. Fuel cells in vehicles generate el ...
technology.
The state-owned Oil and Natural Gas Corporation (ONGC) acquired shares in oil fields in countries like Sudan, Syria, Iran, and Nigeria – investments that have led to diplomatic tensions with the United States. Because of political instability in the Middle East and increasing domestic demand for energy, India is keen on decreasing its dependency on OPEC
The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC ) is an organization enabling the co-operation of leading oil-producing and oil-dependent countries in order to collectively influence the global oil market and maximize Profit (eco ...
to meet its oil demand, and increasing its energy security
Energy security is the association between national security and the availability of natural resources for energy consumption (as opposed to household energy insecurity). Access to cheaper energy has become essential to the functioning of modern ...
. Several Indian oil companies, primarily led by ONGC and Reliance Industries
Reliance Industries Limited is an Indian multinational conglomerate headquartered in Mumbai. Its businesses include energy, petrochemicals, natural gas, retail, entertainment, telecommunications, mass media, and textiles. Reliance is the ...
, have started a massive hunt for oil in several regions in India, including Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; Literal translation, lit. 'Land of Kings') is a States and union territories of India, state in northwestern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the List of states and union territories of ...
, Krishna Godavari Basin and north-eastern Himalayas.
India has nearly 63 tcf technically recoverable resources of shale gas
Shale gas is an unconventional natural gas that is found trapped within shale formations. Since the 1990s, a combination of horizontal drilling and hydraulic fracturing has made large volumes of shale gas more economical to produce, and ...
which can meet all its needs for twenty years if exploited. India is developing an offshore gas field in Mozambique
Mozambique, officially the Republic of Mozambique, is a country located in Southeast Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi and Zambia to the northwest, Zimbabwe to the west, and Eswatini and South Afr ...
. The proposed Iran-Pakistan-India pipeline is a part of India's plan to meet its increasing energy demand.
Coal
India has the world's 3rd largest provencoal reserves
The reserve list specifies different types of coal and includes countries with at least 0.1% share of the estimated world's proven reserves of coal. All data are taken from the German Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (BGR ...
with nearly 177 billion metric tons as on 1 April 2021. In India, coal is the bulk primary energy contributor with 56.90% share equivalent to 452.2 Mtoe in 2018.
India is the second largest producer of coal in 2023. India is also the second-largest importer of coal 141.7 Mtoe in 2018 and the second-largest consumer of coal with 452.2 Mtoe in 2018. India is also home to the world’s largest coal company, Coal India Ltd, which controls 85% of the country’s coal production with 7.8% production share of coal (including lignite) in the world. Top five hard and brown coal
Lignite (derived from Latin ''lignum'' meaning 'wood'), often referred to as brown coal, is a soft, brown, Combustion, combustible sedimentary rock formed from naturally compressed peat. It has a carbon content around 25–35% and is considered ...
producing countries in 2013 (2012) are (million tons): China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
3,680 (3,645), United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
893 (922), India 605 (607), Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
478 (453) and Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
421 (386). However, India ranks fifth in global coal production at 228 Mtoe (5.9%) in 2013 when its inferior quality coal tonnage is converted into tons of oil equivalent. Coal-fired power plants account for 59% of India's installed electricity capacity. After electricity production, coal is also used for cement production in substantial quantity. Pet coke availability, at a cheaper price than local coal, is replacing coal in cement plants. In financial year 2021-22, India imported nearly 209 million tons of steam coal and coking coal which is 20% of total consumption to meet the demand in electricity, cement, and steel production. In the FY2021-22, India imported nearly 57.16 million tons (90%) of coking coal against the consumption of 63.74 MT.
Gasification
Gasification is a process that converts biomass- or fossil fuel-based carbonaceous materials into gases, including as the largest fractions: nitrogen (N2), carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H2), and carbon dioxide (). This is achieved by reacting ...
of coal or lignite or pet coke produces syngas
Syngas, or synthesis gas, is a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide in various ratios. The gas often contains some carbon dioxide and methane. It is principally used for producing ammonia or methanol. Syngas is combustible and can be used as ...
or coal gas
Coal gas is a flammable gaseous fuel made from coal and supplied to the user via a piped distribution system. It is produced when coal is heated strongly in the absence of air. Town gas is a more general term referring to manufactured gaseous ...
or coke oven gas which is a mixture of hydrogen, carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide gases. Coal gas can be converted into synthetic natural gas (SNG) by using Fischer–Tropsch process
The Fischer–Tropsch process (FT) is a collection of chemical reactions that converts a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen, known as syngas, into liquid hydrocarbons. These reactions occur in the presence of metal catalysts, typically at te ...
at high pressure and medium temperature. Coal gas can also be produced by underground coal gasification
In industrial chemistry, coal gasification is the process of producing syngas—a mixture consisting primarily of carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (), carbon dioxide (), methane (), and water vapour ()—from coal and water, air and/or oxygen.
H ...
where the coal deposits are located deep in the ground or uneconomical to mine the coal. CNG and LNG
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas (predominantly methane, CH4, with some mixture of ethane, C2H6) that has been cooled to liquid form for ease and safety of non-pressurized storage or transport. It takes up about 1/600th the volume o ...
are emerging as economical alternatives to diesel oil with the escalation in international crude oil prices. Synthetic natural gas production technologies have tremendous scope to meet the transport sector requirements fully using the locally available coal in India. Dankuni coal complex is producing syngas which is piped to the industrial users in Calcutta. Many coal based fertiliser plants which are shut down can also be retrofitted economically to produce SNG as LNG and CNG fetch good price by substituting imports. Recently, Indian government fixed the natural gas price at producer end as US on net calorific value (NCV) basis, which is at par with the estimated SNG price from coal. The abundantly available coal in India is low rank coal which is not suitable for coal gasification without blending with pet coke. However, low rank coal/lignite can be converted to SNG by using hydrogen. Talcher coal based fertilizer plant is under final stages of execution to produce 1.21 million tonnes of urea. This plant is designed to use local coal mixed with pet coke available from crude oil refineries. India is planning to use 100 million tonnes of coal for gasification by 2030.
India has recently approved the construction of new coal-fired power stations to address its increasing electricity needs, which are driven by the nation's rapid economic growth. Despite facing criticism for environmental pollution and contributing to global greenhouse emissions, these actions reflect India's practical approach to ensure a stable energy supply. Additionally, the government has extended the operational life of older coal plants, such as the Tuticorin facility, highlighting coal's continued importance in India's energy strategy, even as the country works toward incorporating more renewable energy sources.
India has pledged to decrease its dependence on coal, but the demands of its rapidly growing economy and increasing energy requirements tell a different story. The Tuticorin
Thoothukudi (formerly called Tuticorin) is a port industrial city in Thoothukudi district in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It lies on the Coromandel Coast of the Bay of Bengal. The city is capital and headquarters of the district. ...
power plant in southern India
South India, also known as Southern India or Peninsular India, is the southern part of the Deccan Peninsula in India encompassing the states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Telangana as well as the union territories of ...
, which was scheduled to be shut down because it could not meet pollution standards, continues to operate at high capacity. This scenario is indicative of a wider national trend where the need for consistent and reliable electricity often takes precedence over environmental concerns. Consequently, many older coal-fired power stations
A coal-fired power station or coal power plant is a thermal power station which burns coal to generate electricity. Worldwide there are about 2,500 coal-fired power stations, on average Nameplate capacity, capable of generating a gigawatts, ...
throughout India remain operational and are even undergoing expansions. Faced with the challenge of ensuring a steady power supply, the Indian government has often prioritized meeting its immediate energy needs over fulfilling its environmental promises, leading to a renewed reliance on coal. This situation has important ramifications for India's environmental targets and its contribution to global efforts aimed at reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
Renewable energy
Indian solar power PV tariff has fallen to per kWh in May 2017 which is lower than any other type of power generation in India. In the year 2020, the levelized tariff in US dollars for solar PV electricity has fallen to 1.35 cents/kWh. Also the international tariff of solar thermal storage power plants has fallen to US$0.063/kWh, which is cheaper than fossil fuel plants. The cheaper hybrid solar power (mix of solar PV, wind power, and solar thermal storage power) need not depend on costly and polluting coal/gas fired power generation for ensuring stable grid operation. Solar electricity price is going to become the benchmark price for deciding the other fuel prices (petroleum products, natural gas/biogas
Biogas is a gaseous renewable energy source produced from raw materials such as agricultural waste, manure, municipal waste, plant material, sewage, green waste, Wastewater treatment, wastewater, and food waste. Biogas is produced by anaerobic ...
/LNG, CNG, LPG, coal, lignite, biomass, etc.) based on their ultimate use and advantages.
Biofuels
Gasification
Gasification is a process that converts biomass- or fossil fuel-based carbonaceous materials into gases, including as the largest fractions: nitrogen (N2), carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H2), and carbon dioxide (). This is achieved by reacting ...
of biomass
Biomass is a term used in several contexts: in the context of ecology it means living organisms, and in the context of bioenergy it means matter from recently living (but now dead) organisms. In the latter context, there are variations in how ...
yields wood gas
Wood gas is a fuel gas that can be used for furnaces, stoves, and vehicles. During the production process, biomass or related carbon-containing materials are gasified within the oxygen-limited environment of a wood gas generator to produce a c ...
or syngas
Syngas, or synthesis gas, is a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide in various ratios. The gas often contains some carbon dioxide and methane. It is principally used for producing ammonia or methanol. Syngas is combustible and can be used as ...
which can be converted into carbon neutral
Global net-zero emissions is reached when greenhouse gas emissions and Greenhouse gas removal, removals due to human activities are in balance. It is often called simply net zero. ''Emissions'' can refer to all greenhouse gases or only carbon diox ...
methanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical compound and the simplest aliphatic Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with the chemical formula (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often ab ...
. Nearly 750 million tons of nonedible (by cattle) biomass is available annually in India which can be put to higher value addition use and substitute imported crude oil, coal, LNG, urea fertilizer, nuclear fuels, etc. It is estimated that the renewable and carbon-neutral biomass resources of India can replace the present consumption of all fossil fuels when used productively. Biomass is going to play a crucial role to make India self-sufficient in the energy sector and carbon neutral
Global net-zero emissions is reached when greenhouse gas emissions and Greenhouse gas removal, removals due to human activities are in balance. It is often called simply net zero. ''Emissions'' can refer to all greenhouse gases or only carbon diox ...
.
A huge quantity of imported coal is being used in pulverized coal-fired power stations. Raw biomass can not be used in pulverized coal mills as they are difficult to grind into fine powder due to caking property of raw biomass. However, biomass can be used after torrefaction
Torrefaction of biomass, e.g., wood or grain, is a mild form of pyrolysis at temperatures typically between 200 and 320 °C. Torrefaction changes biomass properties to provide a better fuel quality for combustion and gasification application ...
in the pulverized coal mills to replace imported coal. North west and southern regions can replace imported coal use with torrefied biomass where surplus agriculture/crop residual biomass is available. Biomass power plants can also get extra income by selling the Renewable Purchase Certificates (RPC). Central Government has made cofiring (minimum 5%) of biomass mandatary from October 2022 in all coal fired plants.
In cement production, carbon-neutral biomass is being used to replace coal for reducing carbon footprint drastically.
Biogas
Biogas is a gaseous renewable energy source produced from raw materials such as agricultural waste, manure, municipal waste, plant material, sewage, green waste, Wastewater treatment, wastewater, and food waste. Biogas is produced by anaerobic ...
or natural gas or methane produced from farm/agro/crop/domestic waste can also be used for producing protein rich feed for cattle/fish/poultry/pet animals economically by cultivating '' Methylococcus capsulatus'' bacteria culture in a decentralised manner near to the rural / consumption areas with tiny land and water foot print. With the availability of CO2 gas as by product from these units, cheaper production cost of algae oil
Seaweed oil, also called algae oil or algal oil, is used for making food, with the purified product almost colorless and odorless. It is also under development as a possible alternative fuel and manufacturing agent.
Seaweed oil is also used as a ...
from algae
Algae ( , ; : alga ) is an informal term for any organisms of a large and diverse group of photosynthesis, photosynthetic organisms that are not plants, and includes species from multiple distinct clades. Such organisms range from unicellular ...
or spirulina particularly in tropical countries like India would displace the prime position of crude oil in near future.
Reliance Industries
Reliance Industries Limited is an Indian multinational conglomerate headquartered in Mumbai. Its businesses include energy, petrochemicals, natural gas, retail, entertainment, telecommunications, mass media, and textiles. Reliance is the ...
is already producing hydrogen from Torrefied Biomass from its pet coke/coal gasifiers and planning to install a blue hydrogen pilot plant of 50 tonnes per day plant using a catalytic gasification process. India's three Oil Marketing Companies (OMCs) are currently setting up 12 second-generation ethanol plants across the country which will collect agriculture waste from farmers and convert it into bio-ethanol. In 2018, India has set a target to produce 15 million tons of biogas/bio-CNG by installing 5,000 large scale commercial type biogas plants which can produce daily 12.5 tons of bio-CNG by each plant. As of May 2022, nearly 35 such plants are in operation.
Biopropane is also produced from non-edible vegetable oil
Vegetable oils, or vegetable fats, are oils extracted from seeds or from other parts of edible plants. Like animal fats, vegetable fats are ''mixtures'' of triglycerides. Soybean oil, grape seed oil, and cocoa butter are examples of seed ...
s, used cooking oil, waste animal fat
Animal fats are lipids derived from animals which are used by the animal for a multitude of functions, or can be used by humans for dietary, sanitary, and cosmetic purposes. Depending on the temperature of the fat, it can change between a solid s ...
s, etc.
Hydro power
India is endowed with economically exploitable and viable hydro potential assessed to be about 125,570 MW at 60%capacity factor
The net capacity factor is the unitless ratio of actual electrical energy output over a given period of time to the theoretical maximum electrical energy output over that period. The theoretical maximum energy output of a given installation is def ...
. India ranked fourth globally by underutilized hydropower potential. In addition, 6,780 MW in terms of installed capacity from Small, Mini, and Micro Hydel schemes have been assessed. Also, 56 sites for pumped storage
Pumping may refer to:
* The operation of a pump, for moving a liquid from one location to another
**The use of a breast pump A breast pump is a mechanical device that Lactation, lactating women use to milking, extract milk from their breasts. They ...
schemes (PSS) with an aggregate installed capacity of 94,000 MW have been identified for catering to peak electricity demand and water pumping for irrigation needs. It is the most widely used form of renewable energy
Renewable energy (also called green energy) is energy made from renewable resource, renewable natural resources that are replenished on a human lifetime, human timescale. The most widely used renewable energy types are solar energy, wind pow ...
but the economically exploitable hydropower potential keeps on varying due to technological developments and the comparable cost of electricity generation from other sources. The hydro-electric potential of India ranks 5th in terms of exploitable hydro-potential on the global scenario.
The installed capacity of hydropower is 45,315 MW as of 31 May 2018. India ranks sixth in hydro electricity generation globally after China, Canada, Brazil, USA, and Russia. During the year 2017-18, the total hydroelectricity generation in India is 126.123 billion kWh which works out to 24,000 MW at a 60% capacity factor. Till now, the hydroelectricity sector is dominated by the state and central government-owned companies but this sector is going to grow faster with the participation of the private sector in developing the hydro potential located in the Himalaya
The Himalayas, or Himalaya ( ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. More than 100 pea ...
mountain ranges including northeast of India. However the hydropower potential in central India forming part of Godavari
The Godavari (, �od̪aːʋəɾiː is India's second longest river after the Ganga River and drains the third largest basin in India, covering about 10% of India's total geographical area. Its source is in Trimbakeshwar, Nashik, Maharash ...
, Mahanadi
The Mahanadi River is a major river in East Central India. It drains an area of around and has a total length of . Mahanadi is also known for the Hirakud Dam which was the first major multipurpose river valley project after India's independenc ...
and Narmada
The Narmada River, previously also known as ''Narbada'' or anglicised as ''Nerbudda'', is the 5th longest river in India and overall the longest west-flowing river in the country. It is also the largest flowing river in the state of Madhya Prade ...
river basins has not yet been developed on a major scale due to potential opposition from the tribal population.
Pumped storage
Pumping may refer to:
* The operation of a pump, for moving a liquid from one location to another
**The use of a breast pump A breast pump is a mechanical device that Lactation, lactating women use to milking, extract milk from their breasts. They ...
including off-the-river pumped storage power schemes are perfect centralized peaking power stations for load management in the electricity grid dominated by variable renewable energy
Variable renewable energy (VRE) or intermittent renewable energy sources (IRES) are renewable energy sources that are not dispatchable due to their fluctuating nature, such as wind power and solar power, as opposed to controllable renewable ener ...
generation such as solar and wind power. PSS would be in high demand for meeting peak load demand and storing the surplus electricity as India graduates from an electricity deficit to an electricity surplus. They also produce secondary /seasonal power at no additional cost when rivers are flooding with excess water. Storing electricity by other alternative systems such as batteries, compressed air storage systems, etc is costlier than electricity production by standby generator
Standby generators
A standby generator is a back-up electrical system that operates automatically.Robert B. Hickey ''Electrical Construction Databook'', McGraw Hill, 2002 , Chapter 14 Within seconds of a utility outage an automatic transfer s ...
. India has already established nearly 4785 MW pumped storage capacity which is part of its installed hydro power plants.
Wind power

 India has the fourth largest installed wind power capacity in the world. As of 31 December 2017, the installed capacity of wind power was 32,848 MW an increase of 4148 MW over the previous year Wind power accounts for nearly 10% of India's total installed power generation capacity and generated 52.666 billion kWh in the fiscal year 2017-18 which is nearly 3% of total electricity generation. The capacity utilisation factor is nearly 16% in the fiscal year 2017-18. The
India has the fourth largest installed wind power capacity in the world. As of 31 December 2017, the installed capacity of wind power was 32,848 MW an increase of 4148 MW over the previous year Wind power accounts for nearly 10% of India's total installed power generation capacity and generated 52.666 billion kWh in the fiscal year 2017-18 which is nearly 3% of total electricity generation. The capacity utilisation factor is nearly 16% in the fiscal year 2017-18. The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy
The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) is a ministry of the Government of India, headed by current cabinet (government), Union Cabinet Minister Pralhad Joshi, that is mainly responsible for research and development, intellectual prope ...
(MNRE) of India has announced a revised estimation of the potential wind power resource (excluding offshore wind power
Offshore wind power or offshore wind energy is the generation of electricity through wind farms in bodies of water, usually at sea. There are higher wind speeds offshore than on land, so offshore farms generate more electricity per amount of ca ...
potential) from 49,130 MW assessed at 50m Hub heights to 102,788 MW assessed at 80m Hub height at 15% capacity factor
The net capacity factor is the unitless ratio of actual electrical energy output over a given period of time to the theoretical maximum electrical energy output over that period. The theoretical maximum energy output of a given installation is def ...
.
Solar energy
 India's
India's solar energy
Solar energy is the radiant energy from the Sun's sunlight, light and heat, which can be harnessed using a range of technologies such as solar electricity, solar thermal energy (including solar water heating) and solar architecture. It is a ...
insolation is about 5,000 T kWh per year (i.e. ~ 600 TW), far more than its current total primary energy consumption. India's long-term solar potential could be unparalleled in the world because it has the ideal combination of both high solar insolation
Solar irradiance is the power per unit area ( surface power density) received from the Sun in the form of electromagnetic radiation in the wavelength range of the measuring instrument.
Solar irradiance is measured in watts per square metre ...
and a big potential consumer base
The customer base is a group of customers who repeatedly purchase the goods or services of a business. These customers are a main source of revenue for a company. The customer base may be considered a business's target market, where customer behav ...
density. Also a major factor influencing a region's energy intensity
Energy intensity is a Measurement, measure of the efficient energy use, energy inefficiency of an Economic system, economy. It is calculated as units of energy per unit of GDP (Gross Domestic Product) or some other measure of economic output. Hi ...
is the cost of energy consumed for temperature control. Since cooling load requirements are roughly in phase with the sun's intensity, cooling
Cooling is removal of heat, usually resulting in a lower temperature and/or Phase transition, phase change. Temperature lowering achieved by any other means may also be called cooling.
The Heat transfer, transfer of Internal energy, thermal energ ...
from intense solar radiation could make perfect energy-economic sense in the subcontinent located mostly in the tropics
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the equator, where the sun may shine directly overhead. This contrasts with the temperate or polar regions of Earth, where the Sun can never be directly overhead. This is because of Earth's ax ...
.
Installation of solar power
Solar power, also known as solar electricity, is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Solar panels use the photovoltaic effect to c ...
PV plants requires nearly 2.0 hectares (5 acres) of land per MW capacity which is similar to coal-fired power plants when life cycle coal mining, consumptive water storage & ash disposal areas are also accounted for, and hydropower plants when submergence area of the water reservoir is also accounted. 1.6 million MW capacity solar plants can be installed in India on its 1% land (32,000 square km). There are vast tracts of land suitable for solar power in all parts of India exceeding 8% of its total area which are unproductive barren and devoid of vegetation. Part of wastelands (32,000 square km) when installed with solar power plants can produce 2400 billion kWh of electricity (two times the total generation in 2013-14) with land productivity/yield of 0.9 million Rs per acre (3 Rs/kWh price) which is at par with many industrial areas and many times more than the best productive irrigated agriculture lands. Moreover, these solar power units are not dependent on the supply of any raw material and are self productive. There is unlimited scope for solar electricity to replace all fossil fuel energy requirements (natural gas, coal, lignite, and crude oil) if all the marginally productive lands are occupied by solar power plants in the future. The solar power potential of India can meet perennially to cater to per capita energy consumption at par with USA/Japan for the peak population in its demographic transition
In demography, demographic transition is a phenomenon and theory in the Social science, social sciences referring to the historical shift from high birth rates and high Mortality rate, death rates to low birth rates and low death rates as societi ...
.
Solar thermal power
load following power plant
A load-following power plant, regarded as producing mid-merit or mid-priced electricity, is a power plant that adjusts its power output as demand for electricity fluctuates throughout the day. Load-following plants are typically in between base l ...
s compared to fossil fuel power plants. They can cater the load/ demand perfectly and work as base load power plants when the extracted solar energy is found excess in a day. Proper mix of solar thermal and solar PV can fully match the load fluctuations without the need of costly battery storage.
Synergy with irrigation water pumping and hydropower stations
pumped-storage hydroelectricity
Pumped-storage hydroelectricity (PSH), or pumped hydroelectric energy storage (PHES), is a type of hydroelectric energy storage used by electric power systems for load balancing (electrical power), load balancing.
A PSH system stores energy i ...
stations to store the surplus electricity generated during the daytime for meeting the demand during the night hours. In addition to harnessing most of the water resources, the embankment canals originating from the coastal reservoirs would also be envisaged with pumped-storage hydroelectricity features to store the surplus electricity available during the daytime and reconvert to electricity during the nighttime. This is achieved by utilizing all the usable river waters by interlinking Indian rivers and envisaging coastal reservoir
A Coastal reservoir is a type of reservoir to store fresh water in a dammed area of a coastal sea near a river delta. Saemangeum Seawall, Saemanguem in South Korea, Marina Barrage in Singapore, Qingcaosha in China, Plover Cove Reservoir, Plover C ...
s. Also, all existing and future hydropower stations can be expanded with additional pumped-storage hydroelectricity units to cater nighttime electricity consumption. Most of the groundwater pumping power can be met directly by solar power during the daytime. To achieve food security
Food security is the state of having reliable access to a sufficient quantity of affordable, healthy Human food, food. The availability of food for people of any class, gender, ethnicity, or religion is another element of food protection. Simila ...
, India needs to achieve water security
The aim of water security is to maximize the benefits of water for humans and ecosystems. The second aim is to limit the risks of destructive impacts of water to an acceptable level. These risks include too much water (flood), too little water (d ...
which is possible only by energy security
Energy security is the association between national security and the availability of natural resources for energy consumption (as opposed to household energy insecurity). Access to cheaper energy has become essential to the functioning of modern ...
for harnessing its water resources
Water resources are natural resources of water that are potentially useful for humans, for example as a source of drinking water supply or irrigation water. These resources can be either Fresh water, freshwater from natural sources, or water produ ...
.
Electric vehicles
The retail prices ofpetrol
Gasoline (North American English) or petrol ( Commonwealth English) is a petrochemical product characterized as a transparent, yellowish, and flammable liquid normally used as a fuel for spark-ignited internal combustion engines. When formul ...
and diesel are high in India to make electricity driven vehicles more economical as more and more electricity is generated from solar energy in near future without appreciable environmental effects. During the year 2018, many IPPs offered to sell solar power below 3.00 Rs/kWh to feed into the high voltage grid. This price is far below the affordable retail electricity tariff for the solar power to replace petrol and diesel use in transport sector.
The retail price of diesel is 101.00 Rs/liter in 2021–22, and the retail price of petrol was 110.00 ₹/liter. The affordable electricity retail price (860 kcal/kWh at 75% input electricity to shaft power conversion efficiency) to replace diesel (lower heating value 8572 kcal/liter at 40% fuel energy to crankshaft conversion efficiency) is up to 19 ₹/Kwh. The affordable electricity retail price (860 kcal/kWh at 75% input electricity to shaft power conversion efficiency) to replace petrol (lower heating value 7693 kcal/liter at 33% fuel energy to crankshaft conversion efficiency) is up to 28 ₹/Kwh. In 2021-22, India consumed 30.849 million tons of petrol and 76.687 million tons of diesel which are mainly produced from imported crude oil at huge foreign exchange outgo.
V2G is also feasible with electricity-driven vehicles for catering to the peak load in the electricity grid. Electricity-driven vehicles would become popular in the future when the energy storage / battery technology becomes more compact, lesser density, longer lasting, and maintenance-free.
Others
Nuclear power
 India boasts a quickly advancing and active nuclear power program. It is expected to have 20 GW of nuclear capacity by 2020, though it currently stands as 9th in the world in terms of nuclear capacity.
An Achilles' heel of the Indian nuclear power program, is the fact that India is not a signatory of the
India boasts a quickly advancing and active nuclear power program. It is expected to have 20 GW of nuclear capacity by 2020, though it currently stands as 9th in the world in terms of nuclear capacity.
An Achilles' heel of the Indian nuclear power program, is the fact that India is not a signatory of the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty
The Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons, commonly known as the Non-Proliferation Treaty or NPT, is an international treaty whose objective is to prevent the spread of nuclear weapons and weapons technology, to promote cooperatio ...
. This has many times in its history prevented it from obtaining nuclear technology vital to expanding its nuclear industry. Another consequence of this is that much of its program has been domestically developed much like its nuclear weapons program. The United States-India Peaceful Atomic Energy Cooperation Act seems to be a way to get access to advanced nuclear technologies for India.
India has been using imported enriched uranium and is under International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) safeguards, but it has developed various aspects of the nuclear fuel cycle to support its reactors. The development of select technologies has been strongly affected by limited imports. The use of heavy-water reactors has been particularly attractive for the nation because it allows uranium to be burnt with little to no enrichment. India has also done a great amount of work in the development of a thorium-centered fuel cycle. While uranium deposits in the nation are extremely limited, there are much greater reserves of thorium, and it could provide hundreds of times the energy with the same mass of fuel. The fact that thorium can theoretically be utilized in heavy water reactors has tied the development of the two. A prototype reactor that would burn uranium-plutonium fuel while irradiating a thorium blanket is under construction at the Madras/Kalpakkam Atomic Power Station.
Uranium used for the weapons program has been separate from the power program using uranium from scant indigenous reserves.
Hydrogen energy
The national hydrogen energy road map is constantly evolving in India by consolidating various capabilities at institutional and research centers. The Hydrogen Energy program started in India after joining the IPHE (International Partnership for Hydrogen Economy) in the year 2003. There are nineteen other countries including Australia, United States, UK, Japan, etc. This global partnership helps India to set up commercial use of Hydrogen gas as an energy source. India is already producing blue hydrogen from biomass using the petcoke gasifiers. Nearly 412,000 metric tons/year capacity green hydrogen projects are awarded to produce green hydrogen by the end of 2026. Hydrogen is a carbon neutral fuel. Solar electricity prices in India have already fallen below the affordable price (≈ INR 5.00 per kWh to generate 0.041 lb/kWh hydrogen which is equivalent to 0.071 litres of petrol in terms of lower heating value) to make hydrogen economical fuel by sourcing fromelectrolysis of water
Electrolysis of water is using electricity to Water splitting, split water into oxygen () and hydrogen () gas by electrolysis. Hydrogen gas released in this way can be used as hydrogen fuel, but must be kept apart from the oxygen as the mixture ...
to replace petrol/gasoline as transport fuel. Vehicles with fuel cell
A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel (often hydrogen fuel, hydrogen) and an oxidizing agent (often oxygen) into electricity through a pair of redox reactions. Fuel cells are different from most bat ...
technology based on hydrogen gas are nearly twice more efficient compared to diesel/petrol-fueled engines. Hydrogen can be generated cheaply by splitting methane using electricity without emitting any greenhouse gas and also extracted from wood gas
Wood gas is a fuel gas that can be used for furnaces, stoves, and vehicles. During the production process, biomass or related carbon-containing materials are gasified within the oxygen-limited environment of a wood gas generator to produce a c ...
produced from carbon-neutral biomass. A luxury FCEV car generates one liter of bottled quality drinking water for every 10 km ride which is a significant byproduct. Also FCEV does not emit any particulate matter but removes particulate matter up to PM2.5 from the ambient air. Any medium or heavy duty vehicle can be retrofitted in to fuel cell vehicle as its system power density
Power density, defined as the amount of power (the time rate of energy transfer) per unit volume, is a critical parameter used across a spectrum of scientific and engineering disciplines. This metric, typically denoted in watts per cubic meter ...
(watts/litre) and system specific power
Power-to-weight ratio (PWR, also called specific power, or power-to-mass ratio) is a calculation commonly applied to engines and mobile power sources to enable the comparison of one unit or design to another. Power-to-weight ratio is a measurement ...
(watts/kg) are comparable with that of internal combustion engine. The cost and durability of fuel cell engines with economies of scale
In microeconomics, economies of scale are the cost advantages that enterprises obtain due to their scale of operation, and are typically measured by the amount of Productivity, output produced per unit of cost (production cost). A decrease in ...
production line are comparable with the petrol/diesel engines.
The excess power generation capacity available in India is nearly 500 billion units/year presently and another 75,000 MW conventional power generating capacity is in pipeline excluding the targeted 175,000 MW renewable power by 2022. The hydrogen fuel generated by 500 billion units of electricity can replace all diesel and petrol consumed by heavy and medium duty vehicles in India completely obviating the need of crude oil imports for internal consumption. Use of hydrogen as fuel to replace jet fuel by aircraft is also a promising proposition. Converting petrol/diesel driven road vehicles in to fuel cell electric vehicles on priority would save the huge import cost of crude oil and transform the stranded electricity infrastructure into productive assets with major boost to the overall economic growth. Hydrogen spiked CNG is made available in Delhi to reduce pollution emissions from BS-IV compliant old buses. Low rank coal/lignite can be converted to SNG by using hydrogen.
Electricity as a substitute for imported LPG and PNG
The net import of LPG was 16.607 million tons and the total consumption was 28.33 million tons and the domestic consumption was 25.502 million tons which is 90% of total consumption in 2021–22. The LPG import content is nearly 57% of total consumption in India in 2021-22. The affordable electricity retail price (860 kcal/kWh at 74% heating efficiency) to replace LPG (lower heating value 11,000 kcal/kg at 40% heating efficiency) in domestic cooking is up to 10.2 Rs/kWh when the retail price of an LPG cylinder is Rs 1000 (without subsidy) with 14.2 kg LPG content. Replacing LPG consumption with electricity reduces its imports substantially. India's piped natural gas (PNG) for domestic cooking needs was 12,175 million standard cubic meters (mmscm) which is nearly 19% of total natural gas consumption in 2021–22. Natural gas/ LNG import content is nearly 56% of total consumption in 2021-22. The affordable electricity retail tariff (860 Kcal/kWh at 74% heating efficiency) to replace PNG (net calorific value 8,500 Kcal/scm at 40% heating efficiency) in domestic cooking is up to 9 ₹/kWh when the retail price of PNG is ₹47.59 per scm. Replacing PNG consumption with electricity would reduce costly LNG imports substantially. The domestic consumption ofkerosene
Kerosene, or paraffin, is a combustibility, combustible hydrocarbon liquid which is derived from petroleum. It is widely used as a fuel in Aviation fuel, aviation as well as households. Its name derives from the Greek (''kērós'') meaning " ...
was 1.291 million tons out of 1.493 million tons total consumption in 2021–22. The subsidized retail price of kerosene is 15 ₹/liter whereas the export/import price is 79 ₹/liter. The affordable electricity retail tariff (860 Kcal/Kwh at 74% heating efficiency) to replace kerosene (net calorific value
The heating value (or energy value or calorific value) of a substance, usually a fuel or food (see food energy), is the amount of heat released during the combustion of a specified amount of it.
The ''calorific value'' is the total energy release ...
8240 Kcal/liter at 40% heating efficiency) in domestic cooking is up to 15.22 ₹/kWh when the kerosene retail price is 79 ₹/liter.
During the year 2021-22, The plant load factor (PLF) of coal-fired thermal power stations (nearly 210 GW) was 58.86% only whereas these stations can run above 85% PLF comfortably provided there is adequate electricity demand in the country. The possible additional net electricity generation at 85% PLF is nearly 450 billion kWh, enough to replace all the LPG, PNG and kerosene consumption in domestic sector The incremental cost of generating additional electricity is only their coal fuel cost which is less than 4 Rs/kWh. Enhancing the PLF of coal-fired stations and encouraging domestic electricity consumers to substitute electricity in place of LPG and Kerosene in household cooking, would reduce the government subsidies, and the idle capacity of thermal power stations can be put to use economically. Domestic consumers who are willing to surrender the subsidized LPG / Kerosene permits or are eligible for subsidized LPG / Kerosene permits may be given free electricity connection and a subsidized electricity tariff. To avoid the possibility of fatal electric shocks, power is supplied to the electric cook stove through a residual-current circuit breaker.
Since December 2018, IPPs have been offering to sell solar power below 2.90 Rs/kWh to feed into the high-voltage grid. This price is below the affordable electricity tariff for the solar power to replace LPG, PNG, and Kerosene use at a subsidized price of LPG or Kerosene in the domestic sector. Two wheelers and three wheelers consume 62% and 6% of petrol respectively in India. The saved LPG/Autogas
Autogas is liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) used as a fuel in internal combustion engines of vehicles as well as in stationary applications such as generators. It is a mixture of propane and butane.
Autogas is widely used as a "green" fuel, ...
replaced by electricity in the domestic sector can be used by two and three wheelers with operational cost and least pollution benefits. LPG is also used in heavy-duty vehicles/boats / trains / off-road construction or mining or farming or other equipment to replace diesel or petrol with economy and environmental advantages. It is also possible to convert the existing heavy-duty diesel engines to dual fuel with LPG for reducing the PM10 particulate emissions. Existing petrol engines can be converted at low cost into 100% LPG or dual fuel with LPG for achieving enhanced fuel efficiency and economy with drastically reduced emissions. Non-subsidy LPG prices are below the diesel or petrol prices in India in terms of heat content (heat content-wise one kg of LPG is equal to 1.85 liters of LPG or 1.37 liters of diesel oil or 1.48 liters of petrol
Gasoline (North American English) or petrol ( Commonwealth English) is a petrochemical product characterized as a transparent, yellowish, and flammable liquid normally used as a fuel for spark-ignited internal combustion engines. When formul ...
). Cheaper butane, a constituent of LPG (propane
Propane () is a three-carbon chain alkane with the molecular formula . It is a gas at standard temperature and pressure, but becomes liquid when compressed for transportation and storage. A by-product of natural gas processing and petroleum ref ...
and butane
Butane () is an alkane with the formula C4H10. Butane exists as two isomers, ''n''-butane with connectivity and iso-butane with the formula . Both isomers are highly flammable, colorless, easily liquefied gases that quickly vaporize at ro ...
mixture), can be directly mixed with petrol/gasoline for better use in vehicles. Instead of using LPG as a heating fuel in the domestic sector, for higher-end usage, propane can also be converted into alkylate which is a premium gasoline
Gasoline ( North American English) or petrol ( Commonwealth English) is a petrochemical product characterized as a transparent, yellowish, and flammable liquid normally used as a fuel for spark-ignited internal combustion engines. When for ...
blending stock because it has exceptional antiknock properties and gives clean burning. Propane can be used in hydrogen/Ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pu ...
production with advantages compared to natural gas and also can be transported much cheaper than LNG or natural gas.
Energy trading with neighboring countries
The per capita electricity consumption is low compared to many countries despite cheaperelectricity tariff
Electricity pricing (also referred to as electricity tariffs or the price of electricity) can vary widely by country or by locality within a country. Electricity prices are dependent on many factors, such as the price of power generation, gover ...
in India. Despite low electricity per capita consumption in India, the country is going to achieve surplus electricity generation during the 12th plan (2012 to 2017) period provided its coal production and transport infrastructure is developed adequately. India has been exporting electricity to Bangladesh
Bangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world and among the List of countries and dependencies by ...
and Nepal and importing excess electricity in Bhutan. Surplus electricity can be exported to the neighbouring countries in return for natural gas supplies from Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
, Bangladesh and Myanmar
Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar; and also referred to as Burma (the official English name until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and has ...
.
Bangladesh, Myanmar, and Pakistan are producing substantial natural gas and using for electricity generation purposes. Bangladesh, Myanmar
Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar; and also referred to as Burma (the official English name until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and has ...
and Pakistan produce 55 million cubic metres per day (mcmd), 9 mcmd and 118 mcmd out of which 20 mcmd, 1.4 mcmd and 34 mcmd are consumed for electricity generation respectively. Whereas the natural gas production in India is not even adequate to meet its non-electricity requirements.
Bangladesh, Myanmar, and Pakistan have proven reserves of 200 billion cubic meters (bcm), 1200 bcm, and 500 bcm respectively. There is ample opportunity for mutually beneficial trading in energy resources with these countries. India can supply its surplus electricity to Pakistan and Bangladesh in return for the natural gas imports by gas pipelines. Similarly India can develop on BOOT
A boot is a type of footwear. Most boots mainly cover the foot and the ankle, while some also cover some part of the lower calf. Some boots extend up the leg, sometimes as far as the knee or even the hip. Most boots have a heel that is clearl ...
basis hydro power projects in Bhutan, Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
and Myanmar. India might also be able to enter into long-term power purchase agreements with China for developing the hydropower potential of the Yarlung Tsangpo Grand Canyon
The Yarlung Tsangpo Grand Canyon, also known as the Yarlung Zangbo Grand Canyon, the Tsangpo Canyon, the Brahmaputra Canyon or the Tsangpo Gorge (), is a canyon along the Yarlung Tsangpo River in Tibet Autonomous Region, China. It is the deepes ...
in the Brahmaputra River
The Brahmaputra is a trans-boundary river which flows through Southwestern China, Northeastern India, and Bangladesh. It is known as Brahmaputra or Luit in Assamese language, Assamese, Yarlung Tsangpo in Lhasa Tibetan, Tibetan, the Siang/Dihan ...
basin of Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ), or Greater Tibet, is a region in the western part of East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are other ethnic groups s ...
. There is ample trading synergy for India with its neighboring countries in securing its energy requirements.
India's National Grid is synchronously interconnected to Bhutan, and asynchronously linked with Bangladesh
Bangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world and among the List of countries and dependencies by ...
, Myanmar
Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar; and also referred to as Burma (the official English name until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and has ...
and Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
. An undersea interconnection to Sri Lanka ( India–Sri Lanka HVDC Interconnection) have been proposed. Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
can also export its surplus renewable energy (solar, onshore wind, offshore wind, etc) to india in future.
In 2015, Nepal imported 224.21 MW of electric power from India, and Bangladesh imported 500 MW. In 2018, Bangladesh proposed importing 10,000 MW power from India. To encourage the carbon neutral solar power generation, plans are made to transform the Indian national grid into a transnational grid expanding up to Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
towards east and Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in West Asia. Located in the centre of the Middle East, it covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries ...
towards west spanning nearly 7,000 km wide. Being at the central location of the widened grid, India will be able to import the excess solar power available outside its territory at cheaper prices to meet the morning and evening peak load power demands without much costly energy storage.
Policy framework
In general, India's strategy is to encourage the development of renewable sources of energy by offering financial incentives from the federal and state governments. With the abundant solar energy resource combined with adequate high head pumped hydroelectric energy storage potential, India is capable to meet the ultimate energy requirements of its peak population from its renewable energy sources alone. In 2021, the government has upped India’s target to 500GW of renewable energy by 2030. Increasing energy consumption associated primarily with activities in transport, mining, and manufacturing in India needs rethinking on India's energy production. In India where most of the crude oil and natural gas are imported, the negative effects (externalities or liability to the society) is up to five times of the revenue from fossil fuels in the year 2021. The following trends are manifested in theenergy policy
Energy policies are the government's strategies and decisions regarding the Energy production, production, Energy distribution, distribution, and World energy supply and consumption, consumption of energy within a specific jurisdiction. Energy ...
to achieve energy self-sufficiency, least pollution, climate change mitigation
Climate change mitigation (or decarbonisation) is action to limit the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere that cause climate change. Climate change mitigation actions include energy conservation, conserving energy and Fossil fuel phase-out, repl ...
, and long-term sustainability.
Energy conservation and carbon trading
The greenest energy is the energy we do not use.Energy conservation
Energy conservation is the effort to reduce wasteful energy consumption by using fewer energy services. This can be done by using energy more effectively (using less and better sources of energy for continuous service) or changing one's behavi ...
has emerged as a major policy objective, and the Energy Conservation Act 2001, was passed by the Indian Parliament in September 2001. This Act requires large energy consumers to adhere to energy consumption norms; new buildings to follow the Energy Conservation Building Code
The Bureau of Energy Efficiency is an agency of the Government of India, under the Ministry of Power (India), Ministry of Power, created in March 2002 under the provisions of the nation's 2001 Energy Conservation Act. The agency's function is ...
, and appliances to meet energy performance standards and to display energy consumption labels. The Act also created the Bureau of Energy Efficiency to implement the provisions of the Act. In 2015, Prime Minister Mr. Modi launched a scheme called
Prakash Path urging people to use LED lamps
An LED lamp or LED light is an electric light that produces light using light-emitting diodes (LEDs). LED lamps are significantly more Electrical efficiency, energy-efficient than equivalent Incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamps and f ...
in place of other lamps to drastically cut down lighting power requirements and the evening peak electricity load. Energy efficient brushless DC fans at subsidized prices are offered to the electricity consumers by the electricity distribution companies (DisComs) to decrease peak electricity load.
Energy saving certificates (PAT), various renewable purchase obligations (RPO), and renewable energy certificates (REC) are also traded on the power exchanges regularly. Recent amendment to Energy Conservation Act in December 2022 included carbon trading provisions, green fuels mandatory use, etc. As of May 2023, carbon emission trading system or carbon trading market is not started in India. Enhancing soil carbon
Soil carbon is the solid carbon stored in global Soil, soils. This includes both soil organic matter and Inorganic compound, inorganic carbon as carbonate minerals. It is vital to the soil capacity in our ecosystem. Soil carbon is a carbon sink in ...
or sequestration of carbon in topsoil
Topsoil is the upper layer of soil. It has the highest concentration of organic matter and microorganisms and is where most of the Earth's biological soil activity occurs.
Description
Topsoil is composed of mineral particles and organic mat ...
is feasible by converting desert and semi-desert lands into a lush green farm or forest lands using the available water resources fully.
Electricity generation
The installed capacity of utility power plants is 314.64 GW as on 31 January 2017 and the gross electricity generated by utilities during the year 2015-16 is 1168.359 billion kWh which includes auxiliary power consumption of power generating stations. The installed capacity of captive power plants in industries (1 MW and above) is 50,289 MW as on 31 March 2017 and generated 197 billion kWh in the financial year 2016-17. In addition, there are nearly 75,000 MW aggregate capacity diesel generator sets with units sizes between 100 KVA and 1000 KVA. All India per capita consumption of Electricity is nearly 1,122 kWh during the financial year 2016-17. Total installed Power generation Capacity (end of April 2017)
The total installed utility power generation capacity as on 30 April 2017 with sector wise & type wise break up is as given below.
Notes: Coal includes lignite; Misc: includes contributions from emergency diesel generator sets; *Hydro includes pumped storage generation; na = data not available.
In 2019-20, the total generation from all renewable energy sources is nearly 20% of the total electricity generation (utility and captive) in India.
Total installed Power generation Capacity (end of April 2017)
The total installed utility power generation capacity as on 30 April 2017 with sector wise & type wise break up is as given below.
Notes: Coal includes lignite; Misc: includes contributions from emergency diesel generator sets; *Hydro includes pumped storage generation; na = data not available.
In 2019-20, the total generation from all renewable energy sources is nearly 20% of the total electricity generation (utility and captive) in India.
Rural electrification
As on 28 April 2018, all Indian villages were electrified. India has achieved 100% electrification of all rural and urban households. As of 4 January 2019, 211.88 million rural households are provided with electricity, which is nearly 100% of the 212.65 million total rural households. Up to 4 January 2019, 42.937 million urban households are provided with electricity, which is almost 100% of the 42.941 million total urban households. In urban areas, 88.6% of the households use LPG drastically reducing the use of traditional fuels –fuelwood
Firewood is any wooden material that is gathered and used for fuel. Generally, firewood is not heavily processed, and is in some sort of recognizable log or branch form, compared to other forms of wood fuel like pellets. Firewood can be se ...
, agricultural waste and biomass cakes – for cooking and general heating needs.
See also
* Climate change in India *Electricity sector in India
India is the third largest electricity producer globally.
During the fiscal year (FY) 2023–24, the total electricity generation in the country was 1,949 TWh, of which 1,734 TWh was generated by utilities.
The gross electricity generation p ...
* Energy in India
*Economics of new nuclear power plants
Nuclear power construction costs have varied significantly across the world and over time. Large and rapid increases in costs occurred during the 1970s, especially in the United States. Recent cost trends in countries such as Japan and Korea ha ...
* Levelised energy cost
*Cost of electricity by source
Different methods of electricity generation can incur a variety of different costs, which can be divided into three general categories: 1) wholesale costs, or all costs paid by utilities associated with acquiring and distributing electricity to ...
*Energy returned on energy invested
In energy economics and ecological energetics, energy return on investment (EROI), also sometimes called energy returned on energy invested (ERoEI), is the ratio of the amount of usable energy (the '' exergy'') delivered from a particular energy ...
* Reliance east to west India gas pipeline
* Coal slurry pipeline
* 40,000 MW Yarlung Tsangpo Hydroelectric Project
* Negawatt power
* Water Resources in India
* Indian Rivers Inter-link
* Bioeconomy
* Biomass to liquid
* Gas to liquid
* Coal to liquid
*Torrefaction
Torrefaction of biomass, e.g., wood or grain, is a mild form of pyrolysis at temperatures typically between 200 and 320 °C. Torrefaction changes biomass properties to provide a better fuel quality for combustion and gasification application ...
*Low-carbon economy
A low-carbon economy (LCE) is an economy which absorbs as much greenhouse gas as it emits. Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions due to human activity are the dominant cause of observed climate change since the mid-20th century. There are many proven ...
* Energy cannibalism
* Fossil fuel phase-out
* Renewable natural gas
*Algae fuel
Algae fuel, algal biofuel, or algal oil is an alternative to liquid fossil fuels that use algae as the source of energy-rich oils. Also, algae fuels are an alternative to commonly known biofuel sources, such as corn and sugarcane. When made fro ...
*Solar power in India
Solar power in India is an essential source of renewable energy and electricity generation in India. Since the early 2000s, India has increased its solar power significantly with the help of various government initiatives and rapid awareness ...
* Wind power in India
*Renewable energy in India
India is the world's 3rd largest consumer of electricity
and the world's 3rd largest renewable energy producer with 46.3% of energy capacity installed as of October 2024 (203.18 GW of 452.69 GW) coming from renewable sources. Ernst & Young's ...
*Index of energy articles
This is an index of energy articles.
A
Activation energy
- Alternative energy
- Anisotropy energy
- Atomic energy
B
Binding energy
- Bioenergy
- Black hole
- Breeder reactor
- Brown energy
C
Characteristic energy
- Chemical energy
- C ...
* Index of solar energy articles
* List of energy abbreviations
References
External links
Ready Reference Policy Handbook about India at one place
{{World topic, Energy policy of, noredlinks=yes
Policy
Policy is a deliberate system of guidelines to guide decisions and achieve rational outcomes. A policy is a statement of intent and is implemented as a procedure or protocol. Policies are generally adopted by a governance body within an or ...
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
Policies of India