Eschatology (; ) concerns expectations of the end of
present age
The present is the period of time that is occurring now. The present is contrasted with the past, the period of time that has already occurred; and the future, the period of time that has yet to occur.
It is sometimes represented as a hyperplane ...
,
human history
Human history or world history is the record of humankind from prehistory to the present. Early modern human, Modern humans evolved in Africa around 300,000 years ago and initially lived as hunter-gatherers. They Early expansions of hominin ...
, or the world itself. The end of the world or end times is predicted by several
world religion
World religions is a Social construction, socially-constructed category used in the Religious studies, study of religion to demarcate religions that are deemed to have been especially large, internationally widespread, or influential in the deve ...
s (both
Abrahamic
The term Abrahamic religions is used to group together monotheistic religions revering the Biblical figure Abraham, namely Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. The religions share doctrinal, historical, and geographic overlap that contrasts them wit ...
and non-Abrahamic), which teach that negative world events will reach a climax. Briefly: the eschaton is the all-inclusive term evoking this predicted climax of a particular theological or political worldview. The scope of expected consequence is global and not local. Eschatology denotes the theory, discussion, techniques, behaviors and orientation toward the eschaton. Theories of afterlife may also be a dimension of eschatology in certain contexts—in these contexts the afterlife of an individual is a kind of hologram or particular microcosm of the overall eschaton. The Eschaton is, furthermore, related to
telos
Telos (; ) is a term used by philosopher Aristotle to refer to the final cause of a natural organ or entity, or of human art. ''Telos'' is the root of the modern term teleology, the study of purposiveness or of objects with a view to their aims, ...
: a Greek word simultaneously denoting purpose, climax and end (ie. death, terminus etc. but also perfection, completion etc.). Eschaton is the ''end'' dimension referred to within ''telos''. What is not
teleological
Teleology (from , and )Partridge, Eric. 1977''Origins: A Short Etymological Dictionary of Modern English'' London: Routledge, p. 4187. or finalityDubray, Charles. 2020 912Teleology. In ''The Catholic Encyclopedia'' 14. New York: Robert Applet ...
is probably not eschatological.
Abrahamic Particularity of Eschatology
Preoccupation with eschatology is classically associated with
Abrahamic
The term Abrahamic religions is used to group together monotheistic religions revering the Biblical figure Abraham, namely Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. The religions share doctrinal, historical, and geographic overlap that contrasts them wit ...
religions:
Judaism
Judaism () is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic, Monotheism, monotheistic, ethnic religion that comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Jews, Jewish people. Religious Jews regard Judaism as their means of o ...
,
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
and
Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
.
A distinction between Abrahamic eschatology ( ἔσχᾰτον re: ''eschatology'' is a Greek word) and the Hindu
Kali-Yuga cycle, for example, is that the Hindu vision of this end is mythological and cosmic in scope whereas the eschaton in Abrahamic religions is understood and expected to be historical and terrestrial according to the terms of the
creed
A creed, also known as a confession of faith, a symbol, or a statement of faith, is a statement of the shared beliefs of a community (often a religious community) which summarizes its core tenets.
Many Christian denominations use three creeds ...
.
Many—or perhaps most—world religions and folk religions have stories about the end of the world. In most of these traditions, apart from the Abrahamic, whether or not the end of the world is something to look forward to or even accelerate towards by application of personal and communal effort is highly questionable.
Apocalypticism
Apocalypticism is the religious belief that the Eschatology, end of the world is imminent, even within one's own lifetime. This belief is usually accompanied by the idea that civilization will soon come to a tumultuous end due to some sort of ...
in the sense of
millenarianism
Millenarianism or millenarism () is the belief by a religious, social, or political group or movement in a coming fundamental transformation of society, after which "all things will be changed". Millenarianism exists in various cultures and re ...
, generally, is the particularly Abrahamic element of eschatology in this sense.
High Medieval & Modern Judaism as an Outlier
Judaism here is an outlier: as early as the twelfth century CE
Maimonides
Moses ben Maimon (1138–1204), commonly known as Maimonides (, ) and also referred to by the Hebrew acronym Rambam (), was a Sephardic rabbi and Jewish philosophy, philosopher who became one of the most prolific and influential Torah schola ...
notes that opinion as to the character of the
messianic age
In Abrahamic religions, the Messianic Age () is the future eternal period of time on Earth in which the messiah will reign and bring universal peace and brotherhood, without any evil (through mankind's own terms). Many believe that there will be s ...
is divided, and speculation—while perhaps not enforceably preventable—is largely a recreational pastime unsuited to the scholar. Even in the
Talmud
The Talmud (; ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law (''halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of Haskalah#Effects, modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the cen ...
strong reservations are expressed about the likelihood or even of the desirability of the Messiah’s arrival. This is not to say that Judaism has no
fundamentalists concerned with eschatology—it does—but the theme is less pronounced and less central to discussion in most centuries on record versus the role of eschatology in Christianity or even in Islam.
Liberal sects of all Abrahamic religions tend in this direction of skepticism or may maintain some remove from these ‘mysteries of the tradition,’ leaving space for awe and unspeakability from a perspective of humility on the basis of human limitations in conception.
Fundamentalisms of all sorts, correspondingly, tend to emphasize eschatology.
Hybrid or Syncretic Origins of Judeo-Christian Eschatology
Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism ( ), also called Mazdayasnā () or Beh-dīn (), is an Iranian religions, Iranian religion centred on the Avesta and the teachings of Zoroaster, Zarathushtra Spitama, who is more commonly referred to by the Greek translation, ...
and
Gnosticism
Gnosticism (from Ancient Greek language, Ancient Greek: , Romanization of Ancient Greek, romanized: ''gnōstikós'', Koine Greek: Help:IPA/Greek, �nostiˈkos 'having knowledge') is a collection of religious ideas and systems that coalesced ...
may seem to be exceptions here--but these are precursor religions to Judaism and Christianity respectively. The Babylonian captivity put Judaens in contact with
Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism ( ), also called Mazdayasnā () or Beh-dīn (), is an Iranian religions, Iranian religion centred on the Avesta and the teachings of Zoroaster, Zarathushtra Spitama, who is more commonly referred to by the Greek translation, ...
, prior to the re-establishment of the cult in
Second Temple Judaism
Second Temple Judaism is the Judaism, Jewish religion as it developed during the Second Temple period, which began with the construction of the Second Temple around 516 BCE and ended with the Siege of Jerusalem (70 CE), destruction of Jerusalem in ...
which is (for the most part) where legible historical records of its practice and beliefs begin. The
Alexandrian and
Roman conquests of Judah put Judaism in contact with gnosticism, prior to the emergence of
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
.
Afterlife as a Dimension of Eschatology
Belief in an afterlife--which is especially inflected in Christian eschatology--and beliefs concerned with what may compose human experience and/or relationship to divinity in the afterlife is more universal to all of the world's great (ie. numerously subscribed) religions with the partial exception of certain trends or tendencies of attitude in substantive sects within Buddhism (wherein a belief in reincarnation may or may not be essential according to communal tendency) and in liberal Judaism (wherein 'belief' in general is subordinate to practice, and belief in a subjectively experienced afterlife may be less common in significant proportions of some communities depending on time and place).
Reincarnation may be seen as substantively distinct in implication and phenomenological description from eschatological (and largely Abrahamic) ideas of resurrection. The reincarnated soul dies into a new terrestrial life. The degree to which Christian ideas of the resurrection resemble this mapping of posthumous continuity of the soul is but slight—they seem in some respects far-removed from one another as conceptions of life after death.
Resurrection
Since all Abrahamic faiths belief have traditions about a resurrection--occurring at a particular and singular time (namely on
the Last Day, the
Day of Judgment
The Last Judgment is a concept found across the Abrahamic religions and the '' Frashokereti'' of Zoroastrianism.
Christianity considers the Second Coming of Jesus Christ to entail the final judgment by God of all people who have ever lived, res ...
, or in other words at the advent of the Eschaton) Abrahamic beliefs about afterlife and eschatology may be considered an overlapping domain and this further underlines the particularity of the eschatological to Abrahamic faiths.
Not all Jews believe in the resurrection and in
second temple Judaism
Second Temple Judaism is the Judaism, Jewish religion as it developed during the Second Temple period, which began with the construction of the Second Temple around 516 BCE and ended with the Siege of Jerusalem (70 CE), destruction of Jerusalem in ...
, the
Sadducees
The Sadducees (; ) were a sect of Jews active in Judea during the Second Temple period, from the second century BCE to the destruction of the Second Temple in 70 CE. The Sadducees are described in contemporary literary sources in contrast to ...
were agnostic as to questions having to do with the Resurrection: perfect unanimity on this subject was never recovered in the faith if, indeed, it ever existed at any point in time.
It may well be the case that the earliest Jewish writings which seem to reference the resurrection (such as Ezekiel's
valley of dry bones) have explanations other than a resurrection at the end of time (re: Ezekiel may have been talking poetically about reviving the community of Judah, not about a universal reconstitution of all human flesh from all times occurring all at once at the end of history et. al).
Millenarianism vs. Eschatology
Millenarianism
Millenarianism or millenarism () is the belief by a religious, social, or political group or movement in a coming fundamental transformation of society, after which "all things will be changed". Millenarianism exists in various cultures and re ...
is not identical to eschatology, but these territories have been and will likely continue to be overlapping domains.
A certain fervor or expectation of the end may be a feature of all
Abrahamic
The term Abrahamic religions is used to group together monotheistic religions revering the Biblical figure Abraham, namely Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. The religions share doctrinal, historical, and geographic overlap that contrasts them wit ...
theologies, historically. In Christianity and Judaism, the fervor of these beliefs are connected to messianic expectation: Either the Messiah will come (in Judaism) or he will return (in Christianity).
The Islamic eschaton often has somewhat more to do with
Jihad
''Jihad'' (; ) is an Arabic word that means "exerting", "striving", or "struggling", particularly with a praiseworthy aim. In an Islamic context, it encompasses almost any effort to make personal and social life conform with God in Islam, God ...
or with
the lesser Jihad, but also retains many dimensions and specifics of Judeo-Christian eschatologies.
The eschatological dimension of faith is not always active in a manner that is heavily foregrounded at all times, in all places, or in all communities belonging to these traditions. Eschatology will generally not be denied, on the occasion of inquiry with a
Priest
A priest is a religious leader authorized to perform the sacred rituals of a religion, especially as a mediatory agent between humans and one or more deity, deities. They also have the authority or power to administer religious rites; in parti ...
,
Cleric
Clergy are formal leaders within established religions. Their roles and functions vary in different religious traditions, but usually involve presiding over specific rituals and teaching their religion's doctrines and practices. Some of the ter ...
,
Pastor
A pastor (abbreviated to "Ps","Pr", "Pstr.", "Ptr." or "Psa" (both singular), or "Ps" (plural)) is the leader of a Christianity, Christian congregation who also gives advice and counsel to people from the community or congregation. In Lutherani ...
,
Rabbi
A rabbi (; ) is a spiritual leader or religious teacher in Judaism. One becomes a rabbi by being ordained by another rabbi—known as ''semikha''—following a course of study of Jewish history and texts such as the Talmud. The basic form of t ...
or
Imam
Imam (; , '; : , ') is an Islamic leadership position. For Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslims, Imam is most commonly used as the title of a prayer leader of a mosque. In this context, imams may lead Salah, Islamic prayers, serve as community leaders, ...
--but it may not always provide the focus of
homily
A homily (from Greek ὁμιλία, ''homilía'') is a commentary that follows a reading of scripture, giving the "public explanation of a sacred doctrine" or text. The works of Origen and John Chrysostom (known as Paschal Homily) are considered ...
,
liturgy
Liturgy is the customary public ritual of worship performed by a religious group. As a religious phenomenon, liturgy represents a communal response to and participation in the sacred through activities reflecting praise, thanksgiving, remembra ...
or communal attention and energy.
A way of articulating the distinction between the eschatological believer and
Millenarian
Millenarianism or millenarism () is the belief by a religious organization, religious, social, or political party, political group or Social movement, movement in a coming fundamental Social transformation, transformation of society, after which ...
might be that ''eschatology'' emphasizes the inevitability and eventuality of the end as an unavoidable dimension of truth but after a certain and widely variable threshold they may not speak further on the matter. Eschatology has importance, but may or may not be the most important aspect of faith on any given day or in every situation. Whereas the ''Millenarian'' looks forward to the ''eschaton'' occurring in their own lifetime, and emphasizes this as the major theme of teaching and praxis.
Ecumenicalism of Millenarianism
Belief that the end of the world is imminent is known as
apocalypticism
Apocalypticism is the religious belief that the Eschatology, end of the world is imminent, even within one's own lifetime. This belief is usually accompanied by the idea that civilization will soon come to a tumultuous end due to some sort of ...
, and over time has been held both by members of mainstream religions and by
doomsday cult
A doomsday cult is a cult that believes in apocalypticism and millenarianism, including both those that predict disaster and those that attempt to destroy the entire universe. Sociologist John Lofland coined the term ''doomsday cult'' in his 19 ...
s. In the context of
mysticism
Mysticism is popularly known as becoming one with God or the Absolute (philosophy), Absolute, but may refer to any kind of Religious ecstasy, ecstasy or altered state of consciousness which is given a religious or Spirituality, spiritual meani ...
, the term refers metaphorically to the end of ordinary reality and to reunion with the
divine
Divinity (from Latin ) refers to the quality, presence, or nature of that which is divine—a term that, before the rise of monotheism, evoked a broad and dynamic field of sacred power. In the ancient world, divinity was not limited to a singl ...
. Many religions treat eschatology as a future event prophesied in sacred texts or in
folklore
Folklore is the body of expressive culture shared by a particular group of people, culture or subculture. This includes oral traditions such as Narrative, tales, myths, legends, proverbs, Poetry, poems, jokes, and other oral traditions. This also ...
, while other religions may have concepts of renewal or transformation after significant events. The explicit description of a new earth is primarily found in Christian teachings (this description can be found in Chapter 21 of the
Book of Revelation
The Book of Revelation, also known as the Book of the Apocalypse or the Apocalypse of John, is the final book of the New Testament, and therefore the final book of the Bible#Christian Bible, Christian Bible. Written in Greek language, Greek, ...
).
The Abrahamic religions maintain a linear
cosmology
Cosmology () is a branch of physics and metaphysics dealing with the nature of the universe, the cosmos. The term ''cosmology'' was first used in English in 1656 in Thomas Blount's ''Glossographia'', with the meaning of "a speaking of the wo ...
, with end-time scenarios containing themes of
transformation and
redemption. In
Judaism
Judaism () is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic, Monotheism, monotheistic, ethnic religion that comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Jews, Jewish people. Religious Jews regard Judaism as their means of o ...
, the term "end of days" makes reference to the
Messianic Age
In Abrahamic religions, the Messianic Age () is the future eternal period of time on Earth in which the messiah will reign and bring universal peace and brotherhood, without any evil (through mankind's own terms). Many believe that there will be s ...
and includes an in-gathering of the exiled
Jewish diaspora
The Jewish diaspora ( ), alternatively the dispersion ( ) or the exile ( ; ), consists of Jews who reside outside of the Land of Israel. Historically, it refers to the expansive scattering of the Israelites out of their homeland in the Southe ...
, the coming of the
Messiah
In Abrahamic religions, a messiah or messias (; ,
; ,
; ) is a saviour or liberator of a group of people. The concepts of '' mashiach'', messianism, and of a Messianic Age originated in Judaism, and in the Hebrew Bible, in which a ''mashiach ...
, the
resurrection of the righteous, and the
world to come
The world to come, age to come, heaven on Earth, and the Kingdom of God are eschatology, eschatological phrases reflecting the belief that the World (theology), current world or Dispensation (period), current age is flawed or cursed and will be r ...
.
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
depicts the end time as a period of
tribulation
In Christian eschatology, the Great Tribulation () is a period mentioned by Jesus in the Olivet Discourse as a sign that would occur in the time of the end.
At , "the Great Tribulation" () is used to indicate the period spoken of by Jesus. u ...
that precedes the
second coming
The Second Coming (sometimes called the Second Advent or the Parousia) is the Christianity, Christian and Islam, Islamic belief that Jesus, Jesus Christ will return to Earth after his Ascension of Jesus, ascension to Heaven (Christianity), Heav ...
of
Christ
Jesus ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the Jesus in Christianity, central figure of Christianity, the M ...
, who will face the rise of the
Antichrist
In Christian eschatology, Antichrist (or in broader eschatology, Anti-Messiah) refers to a kind of entity prophesied by the Bible to oppose Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ and falsely substitute themselves as a savior in Christ's place before ...
along with his power structure and
false prophet
In religion, a false prophet or pseudoprophet is a person who falsely claims the gift of prophecy or divine inspiration, or to speak for God, or who makes such claims for evil ends. Often, someone who is considered a "true prophet" by some peop ...
s, and usher in the
Kingdom of God
The concept of the kingship of God appears in all Abrahamic religions, where in some cases the terms kingdom of God and kingdom of Heaven are also used. The notion of God's kingship goes back to the Hebrew Bible, which refers to "his kingdom" ...
. In later traditions of Islam, separate hadiths detail the
Day of Judgment
The Last Judgment is a concept found across the Abrahamic religions and the '' Frashokereti'' of Zoroastrianism.
Christianity considers the Second Coming of Jesus Christ to entail the final judgment by God of all people who have ever lived, res ...
as preceded by the appearance of the
Masīḥ ad-Dajjāl, and followed by the descending of
ʿĪsā
In Islam, Jesus (), referred to by the Arabic rendering of his name Isa, is believed to be the penultimate Prophets and messengers in Islam, prophet and messenger of God in Islam, God and the Messiah in Islam, Messiah being the last of the mess ...
(
Jesus
Jesus (AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many Names and titles of Jesus in the New Testament, other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the Jesus in Chris ...
), which shall triumph over the false Messiah or Antichrist; his defeat will lead to a sequence of events that will end with the sun rising from the west and the beginning of the
Qiyāmah (Judgment Day).
Dharmic religions
Indian religions, sometimes also termed Dharmic religions or Indic religions, are the religions that originated in the Indian subcontinent. These religions, which include Buddhism, Hinduism, Jainism, and Sikhism,Adams, C. J."Classification o ...
tend to have more cyclical worldviews, with end-time eschatologies characterized by
decay, redemption, and rebirth (though some believe transitions between cycles are relatively uneventful). In
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified ...
, the end time occurs when
Kalki
Kalki (), also called Kalkin, is the prophesied tenth and final incarnation of the Hinduism, Hindu god Vishnu. According to Vaishnavism, Vaishnava cosmology, Kalki is destined to appear at the end of the Kali Yuga, the last of the four ages i ...
, the final incarnation of
Vishnu
Vishnu (; , , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism, and the god of preservation ( ...
, descends atop a
white horse
A white horse is born predominantly white and stays white throughout its life. A white horse has mostly pink skin under its hair coat, and may have brown, blue, or hazel eyes. "True white" horses, especially those that carry one of the dominant w ...
and brings an end to the current ''
Kali Yuga
''Kali Yuga'' (Devanagari: कलियुग), in Hinduism, is the fourth, shortest, and worst of the four '' yugas'' (world ages) in a '' Yuga cycle'', preceded by '' Dvapara Yuga'' and followed by the next cycle's '' Krita (Satya) Yuga''. I ...
'', completing a cycle that starts again with the regeneration of the world. In
Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
, the
Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha (),*
*
*
was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism. According to Buddhist legends, he was ...
predicted his teachings would be forgotten after 5,000 years, followed by turmoil. It says a ''
bodhisattva
In Buddhism, a bodhisattva is a person who has attained, or is striving towards, '' bodhi'' ('awakening', 'enlightenment') or Buddhahood. Often, the term specifically refers to a person who forgoes or delays personal nirvana or ''bodhi'' in ...
'' named
Maitreya
Maitreya (Sanskrit) or Metteyya (Pali), is a bodhisattva who is regarded as the future Buddhahood, Buddha of this world in all schools of Buddhism, prophesied to become Maitreya Buddha or Metteyya Buddha.Williams, Paul. ''Mahayana Buddhism: Th ...
will appear and rediscover the teachings of the ''Buddha Dharma'', and that the ultimate destruction of the world will then come through seven suns.
Eschatology-Adjacent Theories in the History and Philosophy of Science
Since the development of the concept of
deep time
Deep time is the concept of geological time that spans billions of years, far beyond the scale of human experience. It provides the temporal framework for understanding the formation and evolution of Earth, the development of life, and the slo ...
in the 18th century and the calculation of the
estimated age of planet Earth, scientific discourse about end times has considered the
ultimate fate of the universe
The ultimate fate of the universe is a topic in physical cosmology, whose theoretical restrictions allow possible scenarios for the evolution and ultimate fate of the universe to be described and evaluated. Based on available observational evi ...
. Theories have included the
Big Rip
In physical cosmology, the Big Rip is a hypothetical cosmological model concerning the ultimate fate of the universe, in which the matter of the universe, from stars and galaxies to atoms and subatomic particles, and even spacetime itself, is p ...
,
Big Crunch
The Big Crunch is a hypothetical scenario for the ultimate fate of the universe, in which the expansion of the universe eventually reverses and the universe recollapses, ultimately causing the cosmic scale factor to reach absolute zero, an eve ...
,
Big Bounce
The Big Bounce hypothesis is a cosmological model for the origin of the known universe. It was originally suggested as a phase of the ''cyclic model'' or ''oscillatory universe'' interpretation of the Big Bang, where the first cosmological event ...
, and
Big Freeze (
heat death). Social and scientific commentators also worry about
global catastrophic risks and
scenarios
In the performing arts, a scenario (, ; ; from Italian , "that which is pinned to the scenery") is a synoptical collage of an event or series of actions and events. In the ''commedia dell'arte'', it was an outline of entrances, exits, and action ...
that could result in
human extinction
Human extinction or omnicide is the hypothetical end of the human species, either by population decline due to extraneous natural causes, such as an asteroid impact or large-scale volcanism, or via anthropogenic destruction (self-extinction ...
.
The degree to which
cosmology
Cosmology () is a branch of physics and metaphysics dealing with the nature of the universe, the cosmos. The term ''cosmology'' was first used in English in 1656 in Thomas Blount's ''Glossographia'', with the meaning of "a speaking of the wo ...
and
eschatology
Eschatology (; ) concerns expectations of the end of Contemporary era, present age, human history, or the world itself. The end of the world or end times is predicted by several world religions (both Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic and non-Abrah ...
from earlier periods of culture have influenced scientific mappings of
cosmology
Cosmology () is a branch of physics and metaphysics dealing with the nature of the universe, the cosmos. The term ''cosmology'' was first used in English in 1656 in Thomas Blount's ''Glossographia'', with the meaning of "a speaking of the wo ...
and of
extinction
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
or
supernova
A supernova (: supernovae or supernovas) is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. A supernova occurs during the last stellar evolution, evolutionary stages of a massive star, or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion ...
or cosmic heat death etc. is a matter of lively discussion in certain departments of the Anglo-European university community. That there has been ''some'' influence cannot be doubted.
Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton () was an English polymath active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author. Newton was a key figure in the Scientific Revolution and the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment that followed ...
was interested in calculating the date of the Messiah's arrival and in the process of performing such calculations (and many others) he eventually produced
the calculus at which point, apparently, he ceased to investigate the date of 'the End' and went on ultimately, to accept a position as the head of the
Royal Mint
The Royal Mint is the United Kingdom's official maker of British coins. It is currently located in Llantrisant, Wales, where it moved in 1968.
Operating under the legal name The Royal Mint Limited, it is a limited company that is wholly ow ...
. The degree to which eschatological concerns and curiosities provide a background from which scientific exploration takes off is more substantive than this, but the illustration of this element in Isaac Newton's career suffices for our brief description considering the centrality of calculus--at the very least, as a necessary precursor--to effectively all modern scientific cosmological theories.
Science, however, does not assume that the universe has a purpose and if it did, according to the
rules of parsimony, it would not be able to investigate or even attempt to describe that purpose. In this sense, cosmic heat death and extinction--though scientifically proven as phenomena according to our best working theories--are not technically eschatological: because they are not purposive or intentionally directed events as they have been scientifically conceived.
Exceptional Cases at the Boundary of Scientific Concern
The above-paragraph is true, except in the case of
atomic war in relation to extinction--say, for example. There may well be other exceptions. Since the competencies required for examining the potential motivations to unleash atomic war lies outside the domain of
classical and
quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical Scientific theory, theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Addison-Wesley, 1989, It is ...
, those disciplines can't usefully ask questions about it in a manner that is internal to the discipline itself—though the outcomes of their researches may be implicated. ''Physicists'' may ask those questions but not according to their technical
imprimatur
An imprimatur (sometimes abbreviated as ''impr.'', from Latin, "let it be printed") is a declaration authorizing publication of a book. The term is also applied loosely to any mark of approval or endorsement. The imprimatur rule in the Catho ...
as physicists--just as human beings. The study of these sorts of problems, more recently, has gone under the heading
X-Risk. As in:
Existential risk
A global catastrophic risk or a doomsday scenario is a hypothetical event that could damage human well-being on a global scale, endangering or even destroying Modernity, modern civilization. Existential risk is a related term limited to even ...
, or
extinction risk.
"Extinction
omnicide">Human_extinction.html" ;"title="n the sense of Human extinction">omnicideis not the sense of an ending, but the end of sense," writes Thomas Moynihan to distinguish modern from antique from views of the end.
All purposive or directed thought falls apart upon contemplating extinction or the meaning of extinction. The modern end cannot be conceived, because there is no narrative function or perspective beyond that available to scientific conception or according to informed and scientifically literate human conceptions at this stage of awareness and inquiry.
This is a formal problem of some real consequence and concern, since incommunicability of major zones or threats in the field of existential risk does not lower the threshold of danger but (rather) will tend to increase the threat of certain (and now predominantly threatening) types of existential risk: namely the overlapping catastrophes of
global warming
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes ...
, habitat destruction">Mass Extinction">mass-extinction, habitat destruction and the continuity or acceleration of all these phenomena under the epiphenomena of a media regime coordinated by artificial intelligence.
The word "eschatology" arises from the Ancient Greek term (''éschatos''), meaning "last", and ''-logy'', meaning "the study of", and first appeared in English around 1844. The ''
'' defines eschatology as "the part of theology concerned with death, judgment, and the final destiny of the soul and of humankind".
, to lead the Jewish people and the world and to usher in an age of justice and peace, the
.
Judaism usually refers to the end times as the "end of days" (''aḥarit ha-yamim'', אחרית הימים), a phrase that appears several times in the

 Protestants are divided between Millennialists and Amillennialists. Millennialists concentrate on the issue of whether the true believers will see the
Protestants are divided between Millennialists and Amillennialists. Millennialists concentrate on the issue of whether the true believers will see the 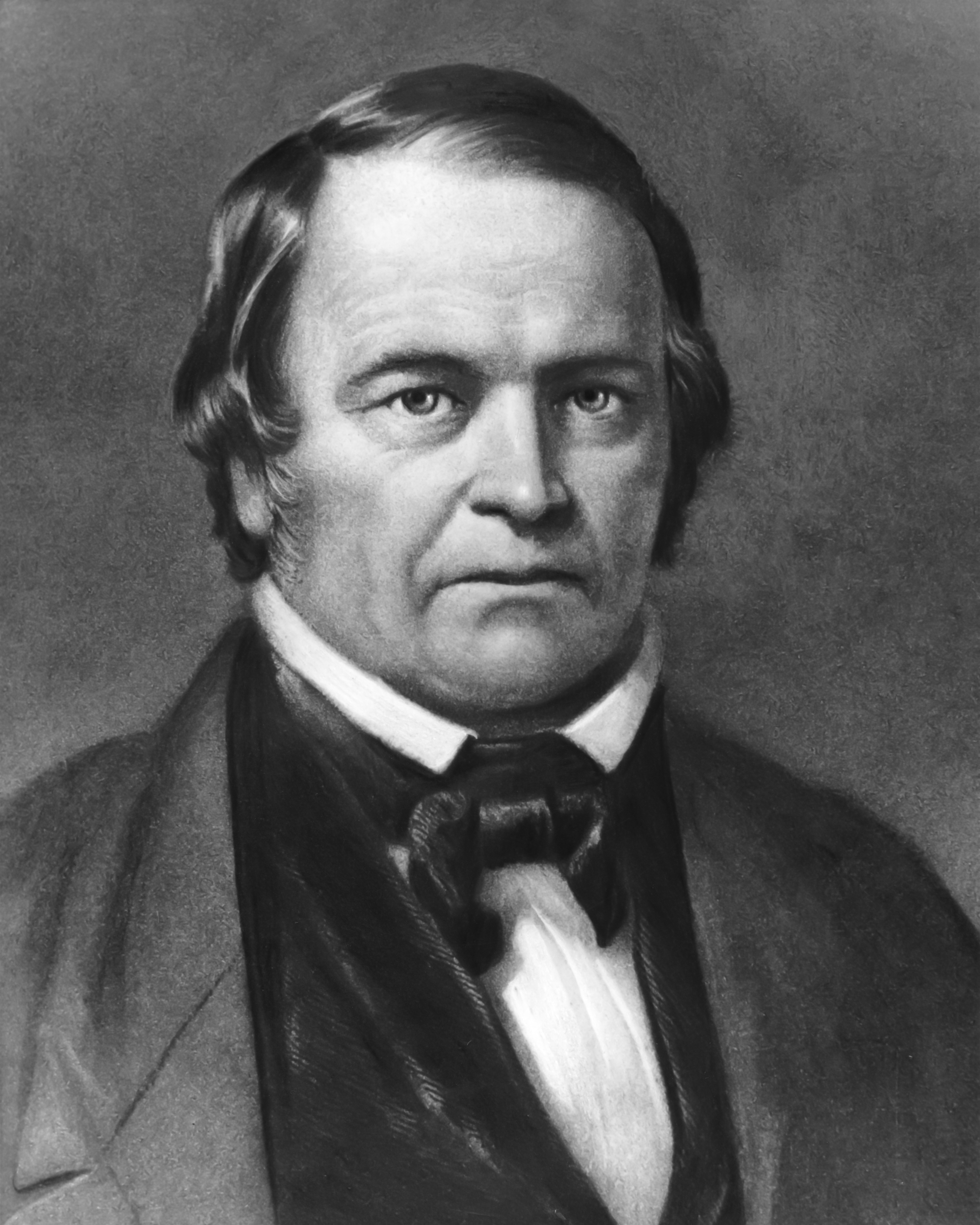 In 1843, William Miller made the first of several predictions that the world would end in only a few months. As his predictions did not come true (referred to as the
In 1843, William Miller made the first of several predictions that the world would end in only a few months. As his predictions did not come true (referred to as the  Rastafari have a unique interpretation of end times, based on the
Rastafari have a unique interpretation of end times, based on the