Emirate Of Melitene on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Malatya ( hy, ıäıíı¼ıíı®ı½ıí, translit=Malat'ya;
 Arslantepe has been inhabited since the development of agriculture in the
Arslantepe has been inhabited since the development of agriculture in the

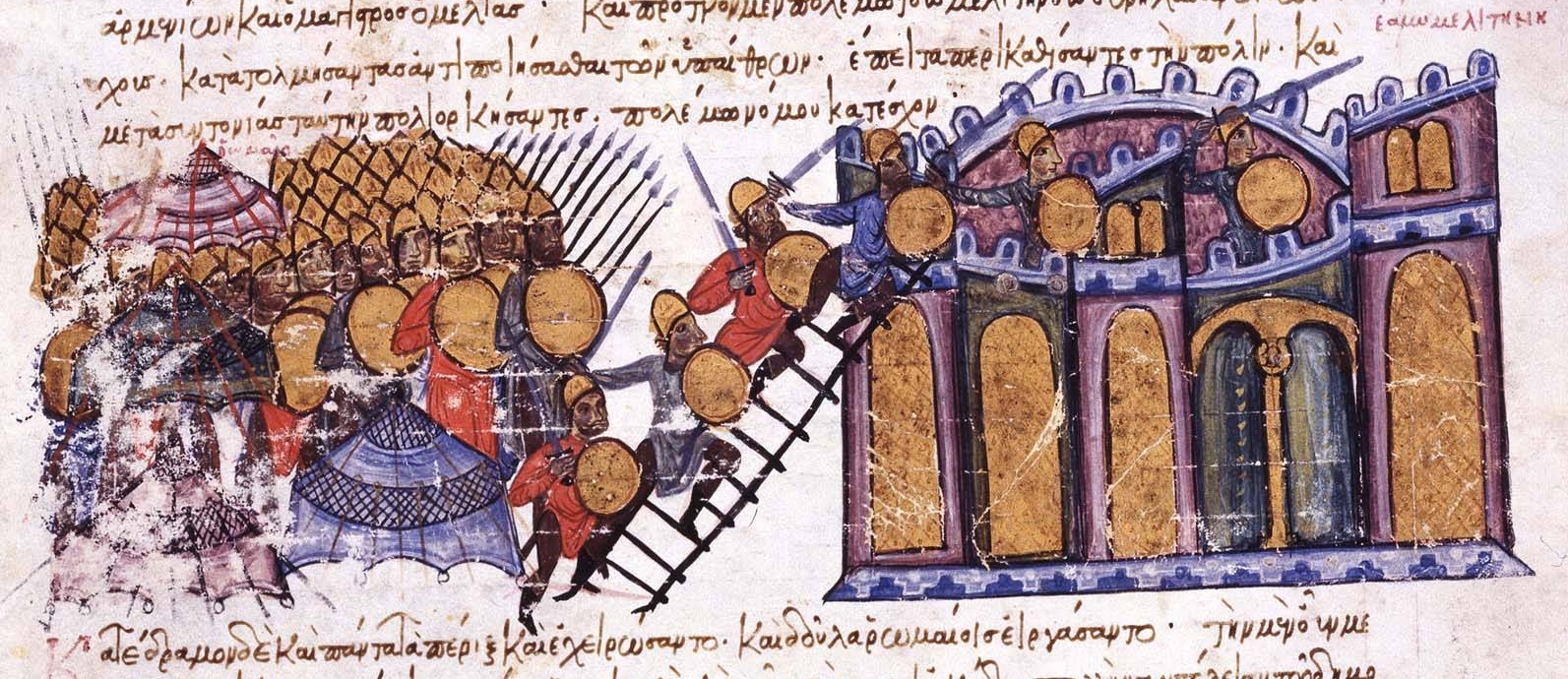
 During the reign of the Emperor
During the reign of the Emperor  In the period that followed the
In the period that followed the


 The current city of Malatya was founded in 1838, with the old site of Mitilene now designated as Old Malatya. The reason behind the displacement of the city center was that the Ottoman army settled and stayed, probably by seizing from its settlers, in the previous city center, in the winter of 1838ÔÇô39, before taking the road for Battle of Nezib in 1849. Because of this, citizens of the Malatya established the new city based on a near town called Aspuzu. The city saw rapid expansion in the 19th century, and by the end of the century it had around 5000 households, 50 mosques, six
The current city of Malatya was founded in 1838, with the old site of Mitilene now designated as Old Malatya. The reason behind the displacement of the city center was that the Ottoman army settled and stayed, probably by seizing from its settlers, in the previous city center, in the winter of 1838ÔÇô39, before taking the road for Battle of Nezib in 1849. Because of this, citizens of the Malatya established the new city based on a near town called Aspuzu. The city saw rapid expansion in the 19th century, and by the end of the century it had around 5000 households, 50 mosques, six
 The economy of the city of Malatya is dominated by
The economy of the city of Malatya is dominated by
 K├Âfte (meatballs) have a special place in the local cuisine as do apricots, which are used in many meals from
K├Âfte (meatballs) have a special place in the local cuisine as do apricots, which are used in many meals from
 Malatya Fair and Apricot Festivities has been held since 1978, every year in July, to promote Malatya and apricots and to convene the producers to meet one another. During the festivities, sports activities, concerts and apricot contests are organized.
Near the Apricot Festivities, there are other annual activities in summer. Cherry Festivities at Yeşilyurt District of Malatya and Grape Festivities at
Malatya Fair and Apricot Festivities has been held since 1978, every year in July, to promote Malatya and apricots and to convene the producers to meet one another. During the festivities, sports activities, concerts and apricot contests are organized.
Near the Apricot Festivities, there are other annual activities in summer. Cherry Festivities at Yeşilyurt District of Malatya and Grape Festivities at
 Malatya is administered by a metropolitan municipality, which covers the whole province. There are two central districts, each with their own municipalities, that make up the city of Malatya: these are Battalgazi and Ye┼ƒilyurt, Malatya, Ye┼ƒilyurt. Battalgazi has a population of around 300,000 and covers 47 central neighbourhoods, three rural former municipalities and 28 villages. Ye┼ƒilyurt contains 36 central neighborhoods, three rural former municipalities and 16 villages, and has a population of around 250,000. The metropolitan municipality was won in 2014 by Ahmet ├çak─▒r of the ruling AK Party with 62.9% of the vote; the candidate of the Republican People's Party, CHP was in the second place with 16.7% of the vote. Battalgazi was won by Selahattin G├╝rkan of the AK Party with 63.1% of the vote and Ye┼ƒilyurt was won Hac─▒ U─ƒur Polat of the AK Party with 62.4% of the vote. The two central districts voted overwhelmingly in favour of the AK Party in the June 2015 Turkish general election, June 2015 election with AK Party winning 66.2% of the vote in Battalgazi and 56.9% in Ye┼ƒilyurt. These percentages further increased in the November 2015 Turkish general election, November 2015 election to 74.7% and 66.2% respectively. In both elections, CHP had the second place in both districts with its votes remaining in the range of 10ÔÇô18%.
Malatya is administered by a metropolitan municipality, which covers the whole province. There are two central districts, each with their own municipalities, that make up the city of Malatya: these are Battalgazi and Ye┼ƒilyurt, Malatya, Ye┼ƒilyurt. Battalgazi has a population of around 300,000 and covers 47 central neighbourhoods, three rural former municipalities and 28 villages. Ye┼ƒilyurt contains 36 central neighborhoods, three rural former municipalities and 16 villages, and has a population of around 250,000. The metropolitan municipality was won in 2014 by Ahmet ├çak─▒r of the ruling AK Party with 62.9% of the vote; the candidate of the Republican People's Party, CHP was in the second place with 16.7% of the vote. Battalgazi was won by Selahattin G├╝rkan of the AK Party with 63.1% of the vote and Ye┼ƒilyurt was won Hac─▒ U─ƒur Polat of the AK Party with 62.4% of the vote. The two central districts voted overwhelmingly in favour of the AK Party in the June 2015 Turkish general election, June 2015 election with AK Party winning 66.2% of the vote in Battalgazi and 56.9% in Ye┼ƒilyurt. These percentages further increased in the November 2015 Turkish general election, November 2015 election to 74.7% and 66.2% respectively. In both elections, CHP had the second place in both districts with its votes remaining in the range of 10ÔÇô18%.
 ─░n├Ân├╝ University, one of the largest universities in eastern Turkey, is in Malatya. It was established on 28 January 1975 and has three institutions and nine faculties, with more than 2,500 faculty and 20,000 students. Its larger campus is in the eastern part of Malatya.
There are 162 high schools and some of the well-known, national high school entrance examination-based high schools in Malatya are; Fethi Gemuhluoglu High School of Science, Private Turgut Özal Anatolian High School, Malatya Science High School and Malatya Anatolian High School.
─░n├Ân├╝ University, one of the largest universities in eastern Turkey, is in Malatya. It was established on 28 January 1975 and has three institutions and nine faculties, with more than 2,500 faculty and 20,000 students. Its larger campus is in the eastern part of Malatya.
There are 162 high schools and some of the well-known, national high school entrance examination-based high schools in Malatya are; Fethi Gemuhluoglu High School of Science, Private Turgut Özal Anatolian High School, Malatya Science High School and Malatya Anatolian High School.
 By its relative advance in Industrialization, industrial growth, Malatya is a pole of attraction for its surrounding regions, in commercial and inward immigration. The city is at a key junction in Turkey's road and rail network. By rail, it serves as the junction for Aleppo through SyriaÔÇôSamsun line. The Bus station, bus terminal is 5 km west of the city center; there are regular intercity services to and from Ankara, Istanbul and Gaziantep. The railway station is 3 km west of the city center, and daily express trains run to Elaz─▒─ƒ, Diyarbak─▒r, Istanbul and Ankara. These stations are easily reached by taxis and dolmu┼ƒ services.
Construction of a trolleybus line was under way in 2013,''Trolleybus Magazine'' No. 314 (MarchÔÇôApril 2014), p. 54. National Trolleybus Association (UK). ISSN 0266-7452. and the line opened in March 2015,''Trolleybus Magazine'' No. 321 (MayÔÇôJune 2015), p. 90. operating under the name Trambus. It serves a route that is around in length and connects Ma┼ƒti bus station (Ma┼ƒti Otogar), in the west, with ─░n├Ân├╝ University (─░n├Ân├╝ ├£niversitesi), in the east.''Trolleybus Magazine'' No. 328 (JulyÔÇôAugust 2016), p. 124.
Malatya's airport, Erhaç Airport, is 26 km west of the city center. There are daily domestic flights from Istanbul, Ankara and İzmir. Since 2007 there have been international flights during the summer months. These flights are especially from German cities to Malatya, and most of the passengers are Turkish citizens or their descendants who are living and working in Germany.
By its relative advance in Industrialization, industrial growth, Malatya is a pole of attraction for its surrounding regions, in commercial and inward immigration. The city is at a key junction in Turkey's road and rail network. By rail, it serves as the junction for Aleppo through SyriaÔÇôSamsun line. The Bus station, bus terminal is 5 km west of the city center; there are regular intercity services to and from Ankara, Istanbul and Gaziantep. The railway station is 3 km west of the city center, and daily express trains run to Elaz─▒─ƒ, Diyarbak─▒r, Istanbul and Ankara. These stations are easily reached by taxis and dolmu┼ƒ services.
Construction of a trolleybus line was under way in 2013,''Trolleybus Magazine'' No. 314 (MarchÔÇôApril 2014), p. 54. National Trolleybus Association (UK). ISSN 0266-7452. and the line opened in March 2015,''Trolleybus Magazine'' No. 321 (MayÔÇôJune 2015), p. 90. operating under the name Trambus. It serves a route that is around in length and connects Ma┼ƒti bus station (Ma┼ƒti Otogar), in the west, with ─░n├Ân├╝ University (─░n├Ân├╝ ├£niversitesi), in the east.''Trolleybus Magazine'' No. 328 (JulyÔÇôAugust 2016), p. 124.
Malatya's airport, Erhaç Airport, is 26 km west of the city center. There are daily domestic flights from Istanbul, Ankara and İzmir. Since 2007 there have been international flights during the summer months. These flights are especially from German cities to Malatya, and most of the passengers are Turkish citizens or their descendants who are living and working in Germany.
Malatya Sivil Toplum Örgütleri Birliği
Malatya Sivil Toplum Örgütleri Birliği
Malatya NetHaber
Malatya NetHABER
Malatya Haber Ajans─▒
Malatya Haberleri
Malatyam.com
Malatya Haber Portal─▒ ÔÇô Malatya'n─▒n G├╝ncel Haberleri
Malatya Sons├Âz gazetesi
Malatya Haberleri
Malatya Oto Kiralama
Malatya Oto Kiralama
Malatya Haber
Malatya Haber {{Authority control Malatya, Populated places established in 1838 1838 establishments in the Ottoman Empire Districts of Malatya Province Roman fortifications in Cappadocia
Syro-Aramaic
The Syriac language (; syc, / '), also known as Syriac Aramaic (''Syrian Aramaic'', ''Syro-Aramaic'') and Classical Syriac ▄á▄½▄ó▄É ▄Ñ▄¼▄Ø▄®▄É (in its literary and liturgical form), is an Aramaic dialect that emerged during the first century ...
▄í▄á▄Ø▄ø▄Ø▄ó▄É Mal─½ß╣¡─½n├í; ku, Melet├«; Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
: ╬£╬Á╬╗╬╣¤ä╬À╬¢╬«) is a large city in the Eastern Anatolia region of Turkey
Turkey ( tr, T├╝rkiye ), officially the Republic of T├╝rkiye ( tr, T├╝rkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
and the capital of Malatya Province. The city has been a human settlement for thousands of years.
In Hittite, ''melid'' or ''milit'' means "honey", offering a possible etymology for the name, which was mentioned in the contemporary sources of the time under several variations (e.g., Hittite: ''Malidiya'' and possibly also ''Midduwa''; Akkadian Akkadian or Accadian may refer to:
* Akkadians, inhabitants of the Akkadian Empire
* Akkadian language, an extinct Eastern Semitic language
* Akkadian literature, literature in this language
* Akkadian cuneiform, early writing system
* Akkadian myt ...
: Meliddu;Hawkins, John D. ''Corpus of Hieroglyphic Luwian Inscriptions. Vol. 1: Inscriptions of the Iron Age.'' Walter de Gruyter, 2000. Urar╠®tian: Meliß╣¡eia).
Strabo says that the city was known "to the ancients"Strabo ''Geographica, Translated from the Greek text by W. Falconer (London, 1903); Book XII, Chapter I'' as Melitene (Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
''╬£╬Á╬╗╬╣¤ä╬À╬¢╬«''), a name adopted by the Romans following Roman expansion into the east. According to Strabo, the inhabitants of Melitene shared with the nearby Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Re ...
ns and Cataonia
Cataonia ( grc, K╬▒¤ä╬▒o╬¢╬»╬▒) was one of the divisions of ancient Cappadocia.
It is described by Strabo, who had visited it, as a level plain surrounded by mountains: on the south by the Amanus, and on the west by the Antitaurus, which bra ...
ns the same language and culture.
The site of ancient Melitene lies a few kilometres from the modern city in what is now the village of Arslantepe and near the district center of Battalgazi (Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
to Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, ð×╬©¤ë╬╝╬▒╬¢╬╣╬║╬« ╬æ¤à¤ä╬┐╬║¤ü╬▒¤ä╬┐¤ü╬»╬▒, Oth┼ìmanik─ô Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
). Present-day Battalgazi was the location of the city of Malatya until the 19th century, when a gradual move of the city to the present third location began. Battalgazi's official name was Eskimalatya (''Old Malatya''); until recently, it was a name used locally. In Turkey the city is renowned for its apricot
An apricot (, ) is a fruit, or the tree that bears the fruit, of several species in the genus '' Prunus''.
Usually, an apricot is from the species '' P. armeniaca'', but the fruits of the other species in ''Prunus'' sect. ''Armeniaca'' are al ...
s, as up to 80% of the Turkish apricot production is provided by Malatya, giving Malatya the name ''kay─▒s─▒ diyar─▒'' ("apricot realm").
History
Arslantepe
 Arslantepe has been inhabited since the development of agriculture in the
Arslantepe has been inhabited since the development of agriculture in the Fertile Crescent
The Fertile Crescent ( ar, Ϻ┘ä┘ç┘äϺ┘ä Ϻ┘äÏ«ÏÁ┘èÏ¿) is a crescent-shaped region in the Middle East, spanning modern-day Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, State of Palestine, Palestine and Jordan, together with the northern region of Kuwait, sou ...
, nearly 6,000 years ago. From the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
, the site became an administrative center of a larger region in the kingdom of Isuwa
Isuwa (transcribed Išuwa and sometimes rendered Ishuwa) was the ancient Hittite name for one of its neighboring Anatolian kingdoms to the east, in an area which later became the Luwian Neo-Hittite state of Kammanu.
The land
The land of Isu ...
. The city was heavily fortified, probably due to the Hittite menace from the west. The Hittites conquered the city in the fourteenth century B.C. In Hittite, ''melid'' or ''milit'' means "honey", offering a possible etymology for the name, which was mentioned in the contemporary sources of the time under several variations (e.g., Hittite: ''Malidiya'' and possibly also ''Midduwa''; Akkadian Akkadian or Accadian may refer to:
* Akkadians, inhabitants of the Akkadian Empire
* Akkadian language, an extinct Eastern Semitic language
* Akkadian literature, literature in this language
* Akkadian cuneiform, early writing system
* Akkadian myt ...
: Meliddu; Urar╠®tian: Meliß╣¡eia).
After the end of the Hittite Empire, the city became the center of the Neo-Hittite
The states that are called Syro-Hittite, Neo-Hittite (in older literature), or Luwian-Aramean (in modern scholarly works), were Luwian and Aramean regional polities of the Iron Age, situated in southeastern parts of modern Turkey and northwester ...
state of Kammanu
Kammanu was a Luwian speaking Neo-Hittite state in a plateau (Malatya Plain) to the north of the Taurus Mountains and to the west of Euphrates river in the late 2nd millennium BC, formed from part of Kizzuwatna
Kizzuwatna (or Kizzuwadna; in An ...
. The city continued old Hittite traditions and styles. Researchers have discovered a palace inside the city walls with statues and reliefs that are examples of the artistic works of that age. The people erected a palace, accompanied by monumental stone sculptures of lions and the ruler. Kammanu was vassal state of Urartu
Urartu (; Assyrian: ',Eberhard Schrader, ''The Cuneiform inscriptions and the Old Testament'' (1885), p. 65. Babylonian: ''Urashtu'', he, ÎÉÍ▓οͩοͩÎÿ ''Ararat'') is a geographical region and Iron Age kingdom also known as the Kingdom of Va ...
between 804 and 743.
According to Igor Diakonoff and John Greppin, there was likely an Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian Diaspora, Armenian communities across the ...
presence in Melid by 1200 BCE.
The Neo-Assyria
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history and the final and greatest phase of Assyria as an independent state. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew t ...
n king Tiglath-Pileser I
Tiglath-Pileser I (; from the Hebraic form of akk, , Tukult─½-apil-E┼íarra, "my trust is in the son of E┼íarra") was a king of Assyria during the Middle Assyrian period (1114ÔÇô1076 BC). According to Georges Roux, Tiglath-Pileser was "one of ...
(1115ÔÇô1077 B.C.) forced the kingdom of Malidiya to pay tribute to Assyria. Malidiya continued to prosper until the Neo-Assyrian king Sargon II
Sargon II (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , meaning "the faithful king" or "the legitimate king") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 722 BC to his death in battle in 705. Probably the son of Tiglath-Pileser III (745ÔÇô727), Sargon is genera ...
(722ÔÇô705) sacked the city in 712 BC. At the same time, the Cimmerians
The Cimmerians (Akkadian: , romanized: ; Hebrew: , romanized: ; Ancient Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic people originating in the Caspian steppe, part of whom subsequently migrated into W ...
and Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Cent ...
invaded Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yar─▒madas─▒), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The r ...
and the city declined. Some occupation continued on the site into the Hellenistic and Roman periodsÔÇöa smithy with four ovens has been excavated from the Roman period. There was a long gap in occupation between the mid-7th century and renewed use of the site in the late 12th or early 13th century.
Archeologists first began to excavate the site of Arslantepe in the 1930s, led by French archaeologist Louis Delaporte. Since 1961, an Italian team of archaeologists, led by Marcella Frangipane
Marcella Frangipane (born 10 October 1948) is a professor of archaeology at the Sapienza University of Rome. She works on the prehistory and protohistory of the Near East and Middle East. She was elected a foreign associate of the National Ac ...
in the early 21st century, has been working at the site.
From the 6th century BC, Melid was ruled by the Armenian Orontid Dynasty
The Orontid dynasty, also known as the Eruandids or Eruandunis, ruled the Satrapy of Armenia until 330 BC and the Kingdom of Armenia from 321 BC to 200 BC. The Orontids ruled first as client kings or satraps of the Achaemenid Empire and after t ...
, who were subjects of the Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, ÉĺÉÅüÉÅé, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest em ...
. After periods of Achaemenid and Macedonian
Macedonian most often refers to someone or something from or related to Macedonia.
Macedonian(s) may specifically refer to:
People Modern
* Macedonians (ethnic group), a nation and a South Slavic ethnic group primarily associated with North M ...
rule, Melid (Malatya) was part of the Kingdom of Lesser Armenia.
Melitene during the Roman Empire

Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus, or Diodorus of Sicily ( grc-gre, ╬ö╬╣¤î╬┤¤ë¤ü╬┐¤é ; 1st century BC), was an ancient Greek historian. He is known for writing the monumental universal history '' Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which ...
wrote that Ptolemaeus of Commagene attacked and captured the Melitene from the Kingdom of Cappadocia
Cappadocia ( el, ╬Ü╬▒¤Ç¤Ç╬▒╬┤╬┐╬║╬»╬▒) was a Hellenistic-era Iranian kingdom centered in the historical region of Cappadocia in Asia Minor (present-day Turkey). It developed from the former Achaemenid satrapy of Cappadocia, and it was founded by ...
, but couldn't keep it for long since Ariarathes V of Cappadocia
Ariarathes V Eusebes Philopator ( grc-gre, ß╝ê¤ü╬╣╬▒¤ü╬¼╬©╬À¤é ╬òߢɤâ╬Á╬▓╬«¤é ╬ª╬╣╬╗╬┐¤Ç╬¼¤ä¤ë¤ü; reigned 163ÔÇô130 BC) was a son of the preceding king Ariarathes IV of Cappadocia and queen Antiochis. He was distinguished by his contemporarie ...
marched against him, with a strong army, and Ptolemaeus withdrew.
The Kingdom of Cappadocia, ruled by the House of Ariobarzanes (95ÔÇô36 BC), became a Roman client in 63 BC. After the Kingdom's annexation by the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, ╬Æ╬▒¤â╬╣╬╗╬Á╬»╬▒ ¤äß┐Â╬¢ ß┐¼¤ë╬╝╬▒╬»¤ë╬¢, Basile├¡a t├┤n Rh┼ìma├¡┼ìn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Medite ...
in 17 AD, the settlement was re-established as Melitene in 72 AD on a different site, as the base camp of Legio XII ''Fulminata''T. A. Sinclair, "Eastern Turkey, an Architectural and Archaeological Survey", volume 3, page 3. (which continued to be based there until at least the early 5th century according to Notitia Dignitatum
The ''Notitia Dignitatum'' (Latin for "The List of Offices") is a document of the late Roman Empire that details the administrative organization of the Western and the Eastern Roman Empire. It is unique as one of very few surviving documents of ...
). The legionary base of Melitene controlled access to southern Armenia and the upper Tigris. It was the end point of the important highway running east from Caesarea (modern Kayseri). The camp attracted a civilian population and was probably granted city status by Trajan in the early 2nd century AD, with the rank of Municipium. It is known for being a prolific source of imperial coins minted from the 3rd to the early 5th centuries.
Procopius
Procopius of Caesarea ( grc-gre, ╬á¤ü╬┐╬║¤î¤Ç╬╣╬┐¤é ߢü ╬Ü╬▒╬╣¤â╬▒¤ü╬Á¤ì¤é ''Prok├│pios ho Kaisare├║s''; la, Procopius Caesariensis; ÔÇô after 565) was a prominent late antique Greek scholar from Caesarea Maritima. Accompanying the Roman ge ...
wrote admiringly of the temples, agoras and theatres of Melitene, but no evidence of them now remains. It was a major center in the province of Armenia Minor ( hy, ıôı©ÍäÍÇ ıÇıíıÁÍä ''Pokr Hayk'',) created by Diocletian from territory separated from the province of Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Re ...
. In 392 A.D., emperor Theodosius I
Theodosius I ( grc-gre, ╬ÿ╬Á╬┐╬┤¤î¤â╬╣╬┐¤é ; 11 January 347 ÔÇô 17 January 395), also called Theodosius the Great, was Roman emperor from 379 to 395. During his reign, he succeeded in a crucial war against the Goths, as well as in two ...
divided Armenia Minor into two new provinces: First Armenia, with its capital at Sebasteia (modern Sivas
Sivas (Latin and Greek: ''Sebastia'', ''Sebastea'', ╬ú╬Á╬▓╬¼¤â¤ä╬Á╬╣╬▒, ╬ú╬Á╬▓╬▒¤â¤ä╬«, ) is a city in central Turkey and the seat of Sivas Province.
The city, which lies at an elevation of in the broad valley of the K─▒z─▒l─▒rmak river, is ...
); and Second Armenia
Roman Armenia refers to the rule of parts of Greater Armenia by the Roman Empire, from the 1st century AD to the end of Late Antiquity. While Armenia Minor had become a client state and incorporated into the Roman Empire proper during the 1s ...
, with its capital at Melitene.
Middle Ages and Ottoman rule

 During the reign of the Emperor
During the reign of the Emperor Justinian I
Justinian I (; la, Iustinianus, ; grc-gre, ß╝©╬┐¤à¤â¤ä╬╣╬¢╬╣╬▒╬¢¤î¤é ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was the Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovat ...
(527ÔÇô565), administrative reforms were carried out in this region: The province of Second Armenia was renamed Third Armenia (''Armenia Tertia''), with its territory unchanged and its capital still at Melitene. Melitene's city walls were constructed in the 6th century by the emperors Anastasius and Justinian. Those that still stand mostly date from the Arab period, perhaps of the 8th century, though retaining the layout of and some remnants from earlier building phases. The city was captured by the Rashidun Caliphate
The Rashidun Caliphate ( ar, Ϻ┘Ä┘ä┘ÆÏ«┘É┘ä┘ÄϺ┘ü┘ÄÏ®┘Å ┘▒┘äÏ▒┘Ä┘æϺÏ┤┘ÉÏ»┘ÄÏ®┘Å, al-Khil─üfah ar-R─ü┼íidah) was the first caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was ruled by the first four successive caliphs of Muhammad after hi ...
in 638. It then became a base for their raids deeper into the Byzantine Empire, a policy continued by the Abbasids
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, Ϻ┘ä┘ÆÏ«┘É┘ä┘ÄϺ┘ü┘ÄÏ®┘ŠϺ┘ä┘ÆÏ╣┘ÄÏ¿┘Ä┘æϺÏ│┘É┘è┘Ä┘æÏ®, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
. In the 9th century, under its semi-independent emir Umar al-Aqta, Malatya rose to become a major opponent of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
until Umar was defeated and killed at the Battle of Lalakaon in 863. The Byzantines attacked the city many times, but did not finally take it until the campaigns of John Kourkouas in 927ÔÇô934. After successively accepting and renouncing vassal status, the city was finally taken in May 934, its Muslim inhabitants driven out or forced to convert, and replaced by Greek and Armenian settlers.
The West Syrian
Syrians ( ar, Ï│┘Å┘êÏ▒┘É┘è┘Å┘æ┘ê┘å, ''S┼½riyy─½n'') are an Eastern Mediterranean ethnic group indigenous to the Levant. They share common Levantine Semitic roots. The cultural and linguistic heritage of the Syrian people is a blend of both indig ...
diocese of Melitene has been established since the sixth century and was as well surrounded by other bishoprics belonging to nearby towns. In the tenth century the Emperor Nikephoros II Phokas
Nikephoros II Phokas (; ÔÇô 11 December 969), Latinized Nicephorus II Phocas, was Byzantine emperor from 963 to 969. His career, not uniformly successful in matters of statecraft or of war, nonetheless included brilliant military exploits whi ...
convinced the Jacobite Patriarch of Antioch
The Syriac Orthodox Patriarch of Antioch ▄ª▄ø▄¬▄Ø▄¬▄ƒ▄É ▄ò▄É▄ó▄ø▄Ø▄ÿ▄ƒ▄Ø▄É is the bishop of Antioch, and head of the Syriac Orthodox Church ( Syriac: ▄Ñ▄║▄ò▄¼▄│▄É ▄ú▄¢▄ÿ╠ú▄¬▄Ø▄│▄Ø▄¼▄│▄É ▄¼▄¬▄║▄Ø▄¿▄░▄¼ ▄½▄¢▄ÿ╠ú▄Æ╠ú▄Ü▄│▄É). He is the Head of the Ho ...
to move the head of the patriarchate into the region of Melitene. The city was attacked and devastated by the Seljuks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, Ï│┘äϼ┘ê┘é█îϺ┘å ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
in 1058.
 In the period that followed the
In the period that followed the Turkish
Turkish may refer to:
*a Turkic language spoken by the Turks
* of or about Turkey
** Turkish language
*** Turkish alphabet
** Turkish people, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
*** Turkish citizen, a citizen of Turkey
*** Turkish communities and mi ...
advance into the Byzantine Empire after the defeat at the Battle of Manzikert
The Battle of Manzikert or Malazgirt was fought between the Byzantine Empire and the Seljuk Empire on 26 August 1071 near Manzikert, theme of Iberia (modern Malazgirt in Muş Province, Turkey). The decisive defeat of the Byzantine army and ...
, Gabriel of Melitene Gabriel of Melitene (died 1102/3) was the ruler of Melitene (modern Malatya). Along with Thoros of Edessa, Gabriel was a former officer of Philaretos Brachamios. Philaretos had installed Gabriel as the ruler of Melitene. Following the death of Phi ...
, a Greek Orthodox
The term Greek Orthodox Church (Greek: ß╝Ö╬╗╬╗╬À╬¢╬┐¤ü╬©¤î╬┤╬┐╬¥╬À ß╝ÿ╬║╬║╬╗╬À¤â╬»╬▒, ''Ellinorth├│doxi Ekklis├¡a'', ) has two meanings. The broader meaning designates "the entire body of Orthodox (Chalcedonian) Christianity, sometimes also call ...
Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian Diaspora, Armenian communities across the ...
who had risen from the ranks of the Byzantine army, governed the city. From 1086 to 1100 he preserved his independence with the aid of the Beylik of the Danishmends
The Danishmendids or Danishmends ( fa, Ï»┘êÏ»┘àϺ┘å ϻϺ┘åÏ┤┘à┘åÏ»; tr, D├óni┼ƒmendliler) was a Turkish beylik that ruled in north-central and eastern Anatolia from 1071/1075 to 1178. The dynasty centered originally around Sivas, Tokat, and ...
. After 1100, he invested heavily on the commanders of the First Crusade
The First Crusade (1096ÔÇô1099) was the first of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land from Islamic ...
, especially Bohemond I of Antioch and Baldwin of Boulogne
Baldwin I, also known as Baldwin of Boulogne (1060s ÔÇô 2April 1118), was the first count of Edessa from 1098 to 1100, and king of Jerusalem from 1100 to his death in 1118. He was the youngest son of Eustace II, Count of Boulogne, and Ida of Lor ...
.
The Danishmends took over Malatya one year later in 1101 (see Battle of Melitene). With the Anatolian Seljuk Sultanate based in Konya
Konya () is a major city in central Turkey, on the southwestern edge of the Central Anatolian Plateau, and is the capital of Konya Province. During antiquity and into Seljuk times it was known as Iconium (), although the Seljuks also called it D ...
taking over the Beylik of Danishmend in the late 12th century, Malatya became part of their realm. Under Danishmend and Seljuk rule, Malatya became a centre of knowledge as many Persian and Arabic scholars took residence in the city. The Seljuk Sultanate also undertook an extensive development of the city. After being ruled by the Ilkhanids
The Ilkhanate, also spelled Il-khanate ( fa, Ϻ█î┘ä ϫϺ┘åϺ┘å, ''Ilx─ün─ün''), known to the Mongols as ''H├╝leg├╝ Ulus'' (, ''Qulug-un Ulus''), was a khanate established from the southwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. The Ilkhanid realm, ...
for around 50 years at the end of the 13th century, the Muslim population of the city invited the Mamluk Sultanate
The Mamluk Sultanate ( ar, Ï│┘äÏÀ┘åÏ® Ϻ┘ä┘à┘àϺ┘ä┘è┘â, translit=Salß╣¡anat al-Mam─ül─½k), also known as Mamluk Egypt or the Mamluk Empire, was a state that ruled Egypt, the Levant and the Hejaz (western Arabia) from the mid-13th to early 16t ...
to Malatya in 1315. On 28 April 1315, the Mamluk army entered the city; this was followed by the looting of the city by the army. The Eretna Dynasty gained sovereignty over the city for some time, but from 1338 onwards the Mamluks secured its control. However, for the latter part of the 14th century, the control of the city fluctuated between the Mamluks and the Dulkadirids. The city was captured by the Ottoman army led by Yavuz Sultan Selim on 28 July 1516 and remained under Ottoman rule until the establishment of the Republic of Turkey. Under the Ottomans, the city lost the quality of being on the frontiers, as well as the allure it held in the Middle Ages. It was plagued between the 16th and 18th centuries by successive rebellions.
Modern period


 The current city of Malatya was founded in 1838, with the old site of Mitilene now designated as Old Malatya. The reason behind the displacement of the city center was that the Ottoman army settled and stayed, probably by seizing from its settlers, in the previous city center, in the winter of 1838ÔÇô39, before taking the road for Battle of Nezib in 1849. Because of this, citizens of the Malatya established the new city based on a near town called Aspuzu. The city saw rapid expansion in the 19th century, and by the end of the century it had around 5000 households, 50 mosques, six
The current city of Malatya was founded in 1838, with the old site of Mitilene now designated as Old Malatya. The reason behind the displacement of the city center was that the Ottoman army settled and stayed, probably by seizing from its settlers, in the previous city center, in the winter of 1838ÔÇô39, before taking the road for Battle of Nezib in 1849. Because of this, citizens of the Malatya established the new city based on a near town called Aspuzu. The city saw rapid expansion in the 19th century, and by the end of the century it had around 5000 households, 50 mosques, six madrasa
Madrasa (, also , ; Arabic: ┘àÏ»Ï▒Ï│Ï® , pl. , ) is the Arabic word for any type of educational institution, secular or religious (of any religion), whether for elementary instruction or higher learning. The word is variously transliterated '' ...
s, nine inns and five Turkish bath
A hammam ( ar, Ï¡┘à┘æϺ┘à, translit=ß©Ñamm─üm, tr, hamam) or Turkish bath is a type of steam bath or a place of public bathing associated with the Islamic world. It is a prominent feature in the culture of the Muslim world and was inherite ...
s. Ottoman sources also recorded ten churches. In 1889 and 1890, Malatya was struck by two large fires that destroyed thousands of shops. The city was then hit by the 1893 Malatya earthquake
The 1893 Malatya earthquake occurred at 02:30 local time on 3 March in Malatya, Eastern Anatolia Region of Turkey. It had a surface wave magnitude of 7.1 and reached maximum felt intensity of X (''Extreme'') on the Mercalli intensity scale. This ...
, which killed 1300, destroying 1200 houses and four mosques. A cholera outbreak that subsequently took place in 1893 killed 896 people. The destroyed buildings were rebuilt in 1894.
Malatya was the scene of anti-Armenian violence during the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. During the Hamidian Massacres of 1895ÔÇô1896, 7,500 Armenian civilians were massacred and Armenian villages in the rural countryside of Malatya were destroyed. In the aftermath, a Red Cross
The International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is a Humanitarianism, humanitarian movement with approximately 97 million Volunteering, volunteers, members and staff worldwide. It was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure re ...
team sent to Malatya and led by Julian B. Hubbell concluded that 1,500 Armenian houses had been pillaged and 375 burned to the ground.
According to the 1913 ''Catholic Encyclopedia'', Malatya city was inhabited by 30,000 people with a clear ethnic Turkish
Turkish may refer to:
*a Turkic language spoken by the Turks
* of or about Turkey
** Turkish language
*** Turkish alphabet
** Turkish people, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
*** Turkish citizen, a citizen of Turkey
*** Turkish communities and mi ...
majority, and an Armenian population of 3,000, of whom 800 were Catholics
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
. Of the five churches in the city, three belonged to the Armenians. In the spring of 1915, the vast majority of the Armenians of the town were rounded up by Ottoman authorities and deported on death marches as part of the Armenian genocide
The Armenian genocide was the systematic destruction of the Armenians in the Ottoman Empire, Armenian people and identity in the Ottoman Empire during World War I. Spearheaded by the ruling Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), it was ...
. According to reports of the governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
of the Malatya district, of the 6,935 registered Armenians in Malatya, 197 were left in the town as artisans. In the early Republican era, Malatya became the centre of Malatya Province and enjoyed a substantial growth in terms of population as well as covered area. This development was further accelerated by the construction of the Adana-Fevzipaşa-Malatya railroad in 1931, and a few years later in 1937, by the construction of the Sivas-Malatya railroad.
Until recently the city was home to departments of the Turkish Aeronautical Association, Turkish Hearths
Turkish Hearths ( tr, T├╝rk Ocaklar─▒) is a non-governmental organization (NGO) in Turkey. It was founded in 1912, during the last years of the Ottoman Empire, in a period when almost all non-Turkish elements had their own national committees, an ...
, and Turkish Red Crescent. In 2014 Malatya became a metropolitan municipality in Turkey, alongside 12 other cities, by a Turkish governmental law that was passed in 2012. Following the 2014 Turkish local elections
Local elections (formal: local authority general elections, Turkish: ''Mahalli İdareler Genel Seçimi'' or simply ''Yerel Seçimleri'') were held in Turkey on 30 March 2014, with some repeated on 1 June 2014. Metropolitan and district mayors as ...
the new municipality officially took office. Today the city is generally considered to be a notable trade and industrial hub, as well as a cultural centre point thanks to the ─░n├Ân├╝ University that was established on 28 January 1975.
Demographics
According to German geographers Georg Hassel and Adam Christian Gaspari, Malatya was composed of 1200 to 1500 houses in early 19th century, inhabited by Ottomans, Turkmens, Armenians, and Greeks.William Harrison Ainsworth
William Harrison Ainsworth (4 February 18053 January 1882) was an English historical novelist born at King Street in Manchester. He trained as a lawyer, but the legal profession held no attraction for him. While completing his legal studies in ...
visited the city of Malatya in 1837, noting a population of 8 thousand Muslims, chiefly Turkomans, and 3 thousand Armenians.
Climate
Malatya has acold semi-arid climate
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-a ...
(K├Âppen climate classification
The K├Âppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir K├Âppen (1846ÔÇô1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by K├Âppen, nota ...
: ''BSk'') or a temperate continental climate (Trewartha climate classification
The Trewartha climate classification (TCC) or the K├ÂppenÔÇôTrewartha climate classification (KTC) is a climate classification system first published by American geographer Glenn Thomas Trewartha in 1966. It is a modified version of the K├Âpp ...
: ''Dca''), with hot, dry summers and cold, snowy winters.
Economy
 The economy of the city of Malatya is dominated by
The economy of the city of Malatya is dominated by agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled peop ...
, textile manufacturing
Textile Manufacturing or Textile Engineering is a major industry. It is largely based on the conversion of fibre into yarn, then yarn into fabric. These are then dyed or printed, fabricated into cloth which is then converted into useful go ...
, and construction. As with the general province, apricot
An apricot (, ) is a fruit, or the tree that bears the fruit, of several species in the genus '' Prunus''.
Usually, an apricot is from the species '' P. armeniaca'', but the fruits of the other species in ''Prunus'' sect. ''Armeniaca'' are al ...
production is important for subsistence in the central district. Malatya is the world leader in apricot production. The city has two organized industrial zones, where the chief industry is textile.
Historically, Malatya produced opium
Opium (or poppy tears, scientific name: ''Lachryma papaveris'') is dried latex obtained from the seed capsules of the opium poppy '' Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid morphine, which ...
. The British, in 1920, described the opium from Malatya as having "the highest percentage of morphia
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies ('' Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a pain medication, and is also commonly used recreationally, or to make other illicit opioids. The ...
".
Culture
Cuisine
kebab
Kebab (, ; ar, ┘âϿϺϿ, link=no, Latn, ar, kab─üb, ; tr, kebap, link=no, ) or kabob (North American) is a type of cooked meat dish (food), dish that originates from Middle Eastern cuisine, cuisines of the Middle East. Many variants of the ...
s (meat broiled or roasted in small pieces) to desserts. There are over 70 kinds of k├Âfte, usually made with wheat and other ingredients. Ka─ƒ─▒t kebab─▒ is one of the most important local specialties ÔÇô a dish made of lamb and vegetables broiled in a wrapper, usually oily paper. Other important dishes are a variety of stuffed specialties, including stuffed mulberry leaves, cabbage, chard, lettuce wraps with olive oil, vine leaves, cherry leaves, bean leaves, grape leaves, beets, onions, and zucchini flowers.
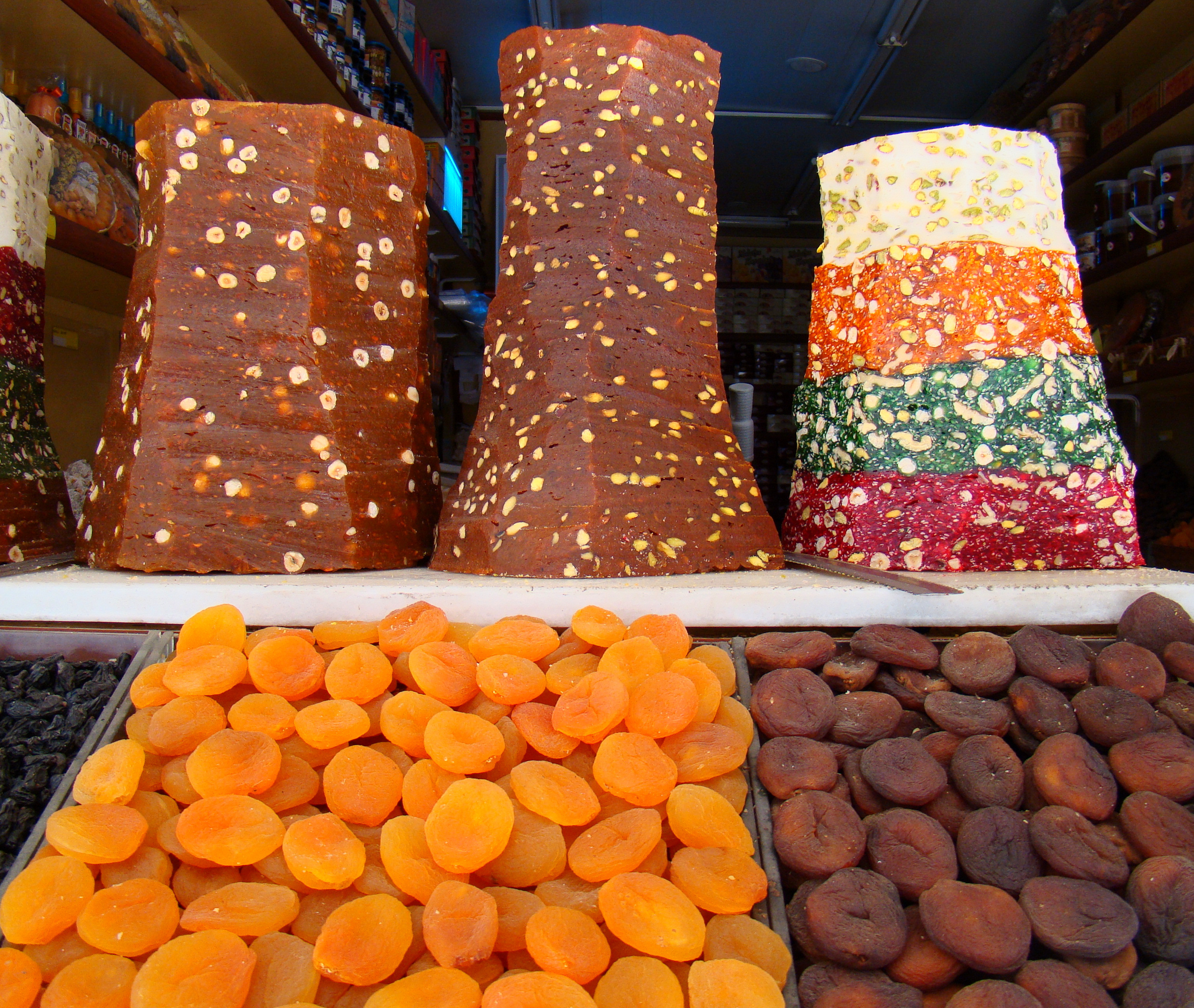
The Malatya region is best known for its apricot
An apricot (, ) is a fruit, or the tree that bears the fruit, of several species in the genus '' Prunus''.
Usually, an apricot is from the species '' P. armeniaca'', but the fruits of the other species in ''Prunus'' sect. ''Armeniaca'' are al ...
orchards. About 50% of the fresh apricot production and 95% of the dried apricot
Dried apricots are a type of traditional dried fruit. When treated with sulfur dioxide ''(SOÔéé)'', the color is vivid orange. Organic fruit not treated with sulfur vapor is darker in color and has a coarser texture. Generally, the lighter the ...
production in Turkey, the world's leading apricot producer, is provided by Malatya and the name of the fruit is synonymous with the city. It reached its most delicious and sophisticated form in the fertile soil of Malatya, nourished from the alluvial soil of the Euphrates. Overall, about 10ÔÇô15% of the worldwide crop of fresh apricots, and about 65ÔÇô80% of the worldwide production of dried apricots comes out of Malatya. Malatya apricots are often sun-dried by family-run orchards using traditional methods, before they are collected and shipped throughout the world.
Festivals
 Malatya Fair and Apricot Festivities has been held since 1978, every year in July, to promote Malatya and apricots and to convene the producers to meet one another. During the festivities, sports activities, concerts and apricot contests are organized.
Near the Apricot Festivities, there are other annual activities in summer. Cherry Festivities at Yeşilyurt District of Malatya and Grape Festivities at
Malatya Fair and Apricot Festivities has been held since 1978, every year in July, to promote Malatya and apricots and to convene the producers to meet one another. During the festivities, sports activities, concerts and apricot contests are organized.
Near the Apricot Festivities, there are other annual activities in summer. Cherry Festivities at Yeşilyurt District of Malatya and Grape Festivities at Arapgir
Arapgir ( hy, È▒ÍÇıíıóı»ı½ÍÇ; ku, Erebgir) is a town and district of Malatya Province, Turkey. As of 2000 it had a population of 17,070 people.
It is situated at the confluence of the eastern and western Euphrates, but some miles from the righ ...
District are organized annually.
Sports
Malatya's initial team is Malatyaspor whose colors are red and yellow. Malatyaspor competes in Malatya First Amateur League. Malatyaspor plays their home games in Malatya ─░n├Ân├╝ Stadium in the city's center. Malatya's other team is Yeni Malatyaspor (formerly Malatya Belediyespor) whose colors are black and yellow (formerly green and orange). They compete inS├╝per Lig
The S├╝per Lig (, ''Super League''), officially known as Spor Toto S├╝per Lig for sponsorship reasons, is a Turkish professional league for association football clubs. It is the top-flight of the Turkish football league system and is run by the ...
.
Administration and politics
 Malatya is administered by a metropolitan municipality, which covers the whole province. There are two central districts, each with their own municipalities, that make up the city of Malatya: these are Battalgazi and Ye┼ƒilyurt, Malatya, Ye┼ƒilyurt. Battalgazi has a population of around 300,000 and covers 47 central neighbourhoods, three rural former municipalities and 28 villages. Ye┼ƒilyurt contains 36 central neighborhoods, three rural former municipalities and 16 villages, and has a population of around 250,000. The metropolitan municipality was won in 2014 by Ahmet ├çak─▒r of the ruling AK Party with 62.9% of the vote; the candidate of the Republican People's Party, CHP was in the second place with 16.7% of the vote. Battalgazi was won by Selahattin G├╝rkan of the AK Party with 63.1% of the vote and Ye┼ƒilyurt was won Hac─▒ U─ƒur Polat of the AK Party with 62.4% of the vote. The two central districts voted overwhelmingly in favour of the AK Party in the June 2015 Turkish general election, June 2015 election with AK Party winning 66.2% of the vote in Battalgazi and 56.9% in Ye┼ƒilyurt. These percentages further increased in the November 2015 Turkish general election, November 2015 election to 74.7% and 66.2% respectively. In both elections, CHP had the second place in both districts with its votes remaining in the range of 10ÔÇô18%.
Malatya is administered by a metropolitan municipality, which covers the whole province. There are two central districts, each with their own municipalities, that make up the city of Malatya: these are Battalgazi and Ye┼ƒilyurt, Malatya, Ye┼ƒilyurt. Battalgazi has a population of around 300,000 and covers 47 central neighbourhoods, three rural former municipalities and 28 villages. Ye┼ƒilyurt contains 36 central neighborhoods, three rural former municipalities and 16 villages, and has a population of around 250,000. The metropolitan municipality was won in 2014 by Ahmet ├çak─▒r of the ruling AK Party with 62.9% of the vote; the candidate of the Republican People's Party, CHP was in the second place with 16.7% of the vote. Battalgazi was won by Selahattin G├╝rkan of the AK Party with 63.1% of the vote and Ye┼ƒilyurt was won Hac─▒ U─ƒur Polat of the AK Party with 62.4% of the vote. The two central districts voted overwhelmingly in favour of the AK Party in the June 2015 Turkish general election, June 2015 election with AK Party winning 66.2% of the vote in Battalgazi and 56.9% in Ye┼ƒilyurt. These percentages further increased in the November 2015 Turkish general election, November 2015 election to 74.7% and 66.2% respectively. In both elections, CHP had the second place in both districts with its votes remaining in the range of 10ÔÇô18%.
Mayors of Malatya
* 1984-1989 Erdem Seyhan Semercioğlu Motherland Party (Turkey), ANAP * 1989-1994 Ahmet Münir Erkal Motherland Party (Turkey), ANAP * 1994-1998 Ahmet Münir Erkal Welfare Party, RP * 1998-1999 Ahmet Münir Erkal Virtue Party, FP * 1999-2004 Mehmet Yaşar Çerçi Nationalist Movement Party, MHP * 2004-2009 Hüseyin Cemal Akın AK Party * 2009-2018 Ahmet Çakır AK Party * 2018-2019 Hacı Uğur Polat AK Party * 2019-current Selahattin Gürkan AK PartyEducation
Transportation
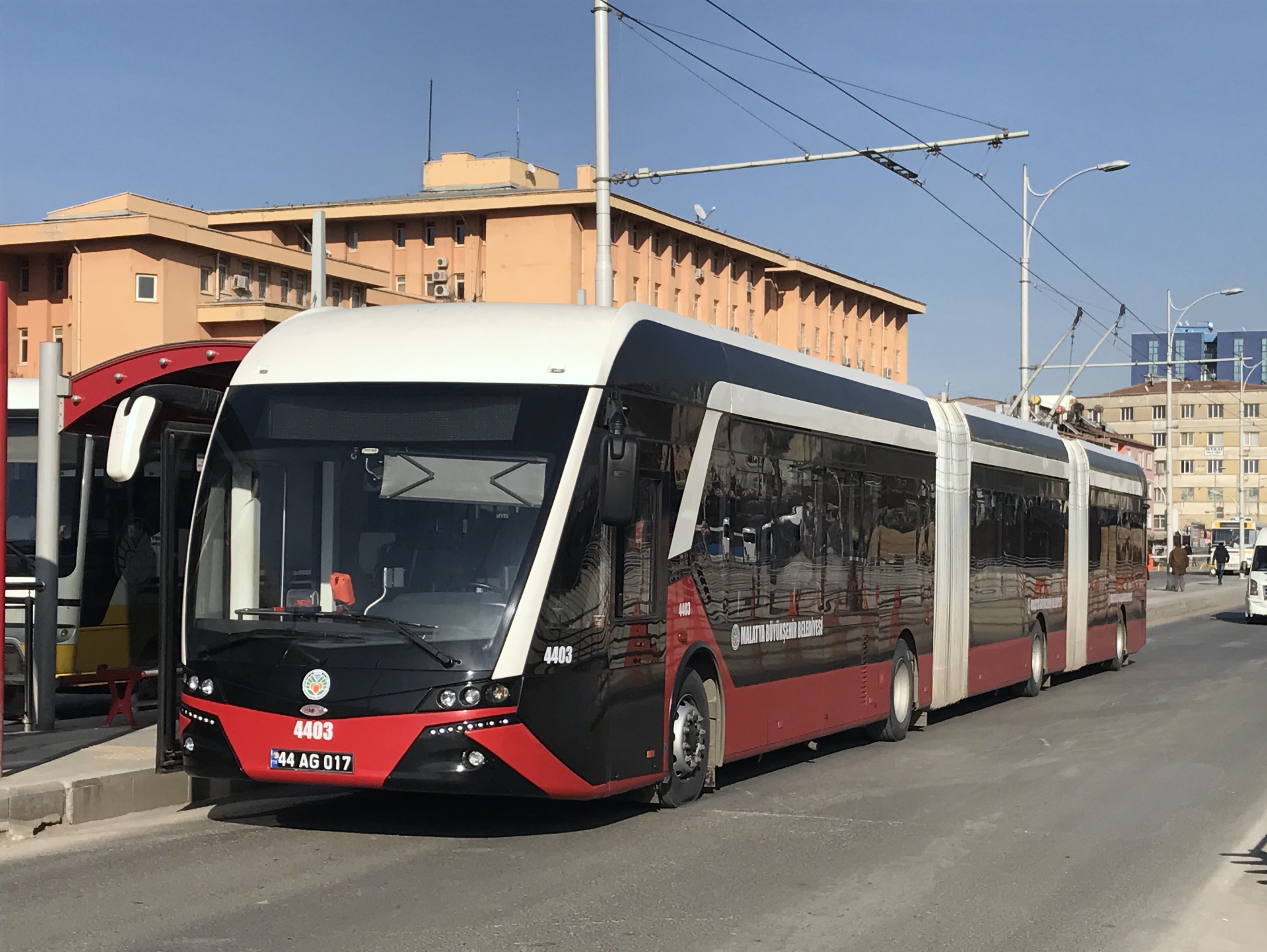
 By its relative advance in Industrialization, industrial growth, Malatya is a pole of attraction for its surrounding regions, in commercial and inward immigration. The city is at a key junction in Turkey's road and rail network. By rail, it serves as the junction for Aleppo through SyriaÔÇôSamsun line. The Bus station, bus terminal is 5 km west of the city center; there are regular intercity services to and from Ankara, Istanbul and Gaziantep. The railway station is 3 km west of the city center, and daily express trains run to Elaz─▒─ƒ, Diyarbak─▒r, Istanbul and Ankara. These stations are easily reached by taxis and dolmu┼ƒ services.
Construction of a trolleybus line was under way in 2013,''Trolleybus Magazine'' No. 314 (MarchÔÇôApril 2014), p. 54. National Trolleybus Association (UK). ISSN 0266-7452. and the line opened in March 2015,''Trolleybus Magazine'' No. 321 (MayÔÇôJune 2015), p. 90. operating under the name Trambus. It serves a route that is around in length and connects Ma┼ƒti bus station (Ma┼ƒti Otogar), in the west, with ─░n├Ân├╝ University (─░n├Ân├╝ ├£niversitesi), in the east.''Trolleybus Magazine'' No. 328 (JulyÔÇôAugust 2016), p. 124.
Malatya's airport, Erhaç Airport, is 26 km west of the city center. There are daily domestic flights from Istanbul, Ankara and İzmir. Since 2007 there have been international flights during the summer months. These flights are especially from German cities to Malatya, and most of the passengers are Turkish citizens or their descendants who are living and working in Germany.
By its relative advance in Industrialization, industrial growth, Malatya is a pole of attraction for its surrounding regions, in commercial and inward immigration. The city is at a key junction in Turkey's road and rail network. By rail, it serves as the junction for Aleppo through SyriaÔÇôSamsun line. The Bus station, bus terminal is 5 km west of the city center; there are regular intercity services to and from Ankara, Istanbul and Gaziantep. The railway station is 3 km west of the city center, and daily express trains run to Elaz─▒─ƒ, Diyarbak─▒r, Istanbul and Ankara. These stations are easily reached by taxis and dolmu┼ƒ services.
Construction of a trolleybus line was under way in 2013,''Trolleybus Magazine'' No. 314 (MarchÔÇôApril 2014), p. 54. National Trolleybus Association (UK). ISSN 0266-7452. and the line opened in March 2015,''Trolleybus Magazine'' No. 321 (MayÔÇôJune 2015), p. 90. operating under the name Trambus. It serves a route that is around in length and connects Ma┼ƒti bus station (Ma┼ƒti Otogar), in the west, with ─░n├Ân├╝ University (─░n├Ân├╝ ├£niversitesi), in the east.''Trolleybus Magazine'' No. 328 (JulyÔÇôAugust 2016), p. 124.
Malatya's airport, Erhaç Airport, is 26 km west of the city center. There are daily domestic flights from Istanbul, Ankara and İzmir. Since 2007 there have been international flights during the summer months. These flights are especially from German cities to Malatya, and most of the passengers are Turkish citizens or their descendants who are living and working in Germany.
Notable people
Sister cities
* Seoul, South KoreaNotes
Further reading
* Ba┼ƒgelen, Nezih. ''Malatya: Bir zamanlar'' (Malatya: Once upon a time). Ankara, 1998. * Alboyajian, Arshag. ''ıèıíı┐ı┤ı©Íéı®ı½Íéı ıäıíı¼ıíı®ı½ı©ıÁ ı░ıíıÁı©Íü'' (''The History of Armenian Malatya''). Beirut, 1961.External links
Malatya Sivil Toplum Örgütleri Birliği
Malatya Sivil Toplum Örgütleri Birliği
Malatya NetHaber
Malatya NetHABER
Malatya Haber Ajans─▒
Malatya Haberleri
Malatyam.com
Malatya Haber Portal─▒ ÔÇô Malatya'n─▒n G├╝ncel Haberleri
Malatya Sons├Âz gazetesi
Malatya Haberleri
Malatya Oto Kiralama
Malatya Oto Kiralama
Malatya Haber
Malatya Haber {{Authority control Malatya, Populated places established in 1838 1838 establishments in the Ottoman Empire Districts of Malatya Province Roman fortifications in Cappadocia