The Continuation War, also known as the Second Soviet–Finnish War, was a conflict fought by
Finland
Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, ...
and
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
against the
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
during
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. It began with a Finnish declaration of war on 25 June 1941 and ended on 19 September 1944 with the
Moscow Armistice
The Moscow Armistice was signed between Finland on one side and the Soviet Union and United Kingdom on the other side on 19 September 1944, ending the Continuation War. The Armistice restored the Moscow Peace Treaty of 1940, with a number of modi ...
. The Soviet Union and Finland had previously fought the
Winter War
The Winter War was a war between the Soviet Union and Finland. It began with a Soviet invasion of Finland on 30 November 1939, three months after the outbreak of World War II, and ended three and a half months later with the Moscow Peac ...
from 1939 to 1940, which ended with the Soviet failure to conquer Finland and the
Moscow Peace Treaty
The Moscow Peace Treaty was signed by Finland and the Soviet Union on 12 March 1940, and the ratifications were exchanged on 21 March. It marked the end of the 105-day Winter War, upon which Finland ceded border areas to the Soviet Union. The ...
. Numerous reasons have been proposed for the Finnish decision to invade, with regaining territory lost during the Winter War regarded as the most common. Other justifications for the conflict include Finnish President
Risto Ryti
Risto Heikki Ryti (; 3 February 1889 – 25 October 1956) was a Finnish people, Finnish politician who served as the fifth president of Finland from 1940 to 1944. Ryti started his career as a politician in the field of economics and as a politica ...
's vision of a
Greater Finland and Commander-in-Chief
Carl Gustaf Emil Mannerheim
Baron Carl Gustaf Emil Mannerheim (, 4 June 1867 – 27 January 1951) was a Finnish military commander, aristocrat, and statesman. He served as the military leader of the White Guard (Finland), Whites in the Finnish Civil War (1918), as List of ...
's desire to annex
East Karelia.
The following paragraph contains a bundle of cites for the Finnish participation in the siege of Leningrad, which is a commonly debated complex issue in the article (see talk).-->
On 22 June 1941, the
Axis invaded the Soviet Union. Three days later, the Soviet Union conducted an air raid on Finnish cities which prompted Finland to declare war and allow German troops in Finland to begin offensive warfare. By September 1941, Finland had regained its post–Winter War concessions to the Soviet Union in
Karelia
Karelia (; Karelian language, Karelian and ; , historically Коре́ла, ''Korela'' []; ) is an area in Northern Europe of historical significance for Russia (including the Soviet Union, Soviet era), Finland, and Sweden. It is currentl ...
. The Finnish Army continued its offensive past the 1939 border during the
invasion of East Karelia and halted it only around from the centre of
Leningrad
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the Neva, River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland ...
. It participated in
besieging the city by cutting the northern supply routes and by digging in until 1944. In
Lapland,
joint German–Finnish forces failed to capture
Murmansk
Murmansk () is a port city and the administrative center of Murmansk Oblast in the far Far North (Russia), northwest part of Russia. It is the world's largest city north of the Arctic Circle and sits on both slopes and banks of a modest fjord, Ko ...
or cut the Kirov (Murmansk) Railway. The Soviet
Vyborg–Petrozavodsk offensive in June and August 1944 drove the Finns from most of the territories that they had gained during the war, but the Finnish Army halted the offensive in August 1944.
Hostilities between Finland and the USSR ceased in September 1944 with the signing of the Moscow Armistice in which Finland restored its borders per the 1940 Moscow Peace Treaty and additionally ceded
Petsamo and leased the
Porkkala Peninsula to the Soviets. Furthermore, Finland was required to pay
war reparations to the Soviet Union, accept partial responsibility for the war, and acknowledge that it had been a German ally. Finland was also required by the agreement to expel German troops from Finnish territory, which led to the
Lapland War
During World War II, the Lapland War (; ; ) saw fighting between Finland and Nazi Germany – effectively from September to November 1944 – in Finland's northernmost region, Lapland. Though the Finns and the Germans had been fighting together ...
between Finland and Germany.
Background
Winter War

On 23 August 1939, the Soviet Union and Germany signed the
Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact
The Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, officially the Treaty of Non-Aggression between Germany and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, and also known as the Hitler–Stalin Pact and the Nazi–Soviet Pact, was a non-aggression pact between Nazi Ge ...
in which both parties agreed to divide the independent countries of Finland,
Estonia
Estonia, officially the Republic of Estonia, is a country in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Ru ...
,
Latvia
Latvia, officially the Republic of Latvia, is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is one of the three Baltic states, along with Estonia to the north and Lithuania to the south. It borders Russia to the east and Belarus to t ...
,
Lithuania
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, P ...
,
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
, and
Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
into
spheres of interest, with Finland falling within the Soviet sphere. One week later, Germany
invaded Poland, leading to the United Kingdom and
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
declaring war on Germany. The Soviet Union
invaded eastern Poland on 17 September. The Soviet government turned its attention to the
Baltic states
The Baltic states or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term encompassing Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, and the OECD. The three sovereign states on the eastern co ...
of Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania, demanding that they allow Soviet military bases to be established and troops stationed on their soil. The Baltic governments
acquiesced to these demands and signed agreements in September and October.
In October 1939, the Soviet Union attempted to negotiate with Finland to cede Finnish territory on the
Karelian Isthmus
The Karelian Isthmus (; ; ) is the approximately stretch of land situated between the Gulf of Finland and Lake Ladoga in northwestern Russia, to the north of the River Neva. Its northwestern boundary is a line from the Bay of Vyborg to the we ...
and the islands of the
Gulf of Finland
The Gulf of Finland (; ; ; ) is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland to the north and Estonia to the south, to Saint Petersburg—the second largest city of Russia—to the east, where the river Neva drains into it. ...
, and to establish a Soviet military base near the Finnish capital of
Helsinki
Helsinki () is the Capital city, capital and most populous List of cities and towns in Finland, city in Finland. It is on the shore of the Gulf of Finland and is the seat of southern Finland's Uusimaa region. About people live in the municipali ...
. The
Finnish government
The Finnish Government (; ; ) is the executive branch and cabinet of Finland, which directs the politics of Finland and is the main source of legislation proposed to the Parliament. The Government has collective ministerial responsibility an ...
refused, and the
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People ...
invaded Finland on 30 November 1939. The same day,
Field Marshal C. G. E. Mannerheim, who was chairman of Finland's Defence Council at the time, assumed the position of
Commander-in-Chief of the
Finnish Defence Forces
The Finnish Defence Forces (FDF) (; ) are the military of Finland. The Finnish Defence Forces consist of the Finnish Army, the Finnish Navy, and the Finnish Air Force. In wartime, the Finnish Border Guard becomes part of the Finnish Defence For ...
. The USSR was expelled from the
League of Nations
The League of Nations (LN or LoN; , SdN) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920), Paris Peace ...
and was condemned by the international community for the illegal attack.
Foreign support for Finland was promised, but very little actual help materialised, except from Sweden. The
Moscow Peace Treaty
The Moscow Peace Treaty was signed by Finland and the Soviet Union on 12 March 1940, and the ratifications were exchanged on 21 March. It marked the end of the 105-day Winter War, upon which Finland ceded border areas to the Soviet Union. The ...
concluded the 105-day Winter War on 13 March 1940 and started the
Interim Peace
The Interim Peace (, ) was a short period in the history of Finland during the Second World War. The term is used for the time between the Winter War and the Continuation War, lasting a little over 15 months, from 13 March 1940 to 24 June 1941. ...
. By the terms of the treaty, Finland ceded 9% of its national territory and 13% of its economic capacity to the Soviet Union. Some 420,000 evacuees were resettled from the ceded territories. Finland avoided total conquest of the country by the Soviet Union and retained its sovereignty.
Prior to the war, Finnish foreign policy had been based on
multilateral guarantees of support from the League of Nations and
Nordic countries
The Nordic countries (also known as the Nordics or ''Norden''; ) are a geographical and cultural region in Northern Europe, as well as the Arctic Ocean, Arctic and Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic oceans. It includes the sovereign states of Denm ...
, but this policy was considered a failure. After the war, Finnish public opinion favored the reconquest of
Finnish Karelia. The government declared national defence to be its first priority, and military expenditure rose to nearly half of public spending. Finland both received donations and purchased war materiel during and immediately after the Winter War. Likewise, the Finnish leadership wanted to preserve the
spirit of unanimity that was felt throughout the country during the Winter War. The divisive
White Guard tradition of the
Finnish Civil War
The Finnish Civil War was a civil war in Finland in 1918 fought for the leadership and control of the country between Whites (Finland), White Finland and the Finnish Socialist Workers' Republic (Red Finland) during the country's transition fr ...
's 16 May victory-day celebration was therefore discontinued.
The Soviet Union had received the
Hanko Naval Base
Hanko Naval Base was a short-lived Soviet naval base on the southern coast of Finland, operational for less than two years in the early 1940s. The base was located in the town of Hanko on the Hanko Peninsula, which is located 100 kilometers ...
, on Finland's southern coast near the capital Helsinki, where it deployed over 30,000 Soviet military personnel. Relations between Finland and the Soviet Union remained strained after the signing of the one-sided peace treaty, and there were disputes regarding the implementation of the treaty. Finland sought security against further territorial depredations by the USSR and proposed
mutual defence agreements with
Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of ...
and
Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
, but these initiatives were quashed by Moscow.
German and Soviet expansion in Europe

After the Winter War, Germany was viewed with distrust by the Finnish, as it was considered an ally of the Soviet Union. Nonetheless, the Finnish government sought to restore diplomatic relations with Germany, but also continued its Western-orientated policy and negotiated a war trade agreement with the United Kingdom. The agreement was renounced after the
German invasion of Denmark and Norway on 9 April 1940 resulted in the UK cutting all trade and traffic communications with the Nordic countries. With the
fall of France
The Battle of France (; 10 May – 25 June 1940), also known as the Western Campaign (), the French Campaign (, ) and the Fall of France, during the Second World War was the German invasion of the Low Countries (Belgium, Luxembourg and the Net ...
, a Western orientation was no longer considered a viable option in Finnish foreign policy. On 15 and 16 June, the Soviet Union
occupied the Baltic states almost without any resistance and Soviet
puppet regimes were installed. Within two months Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania were incorporated into the USSR and by mid–1940, the two remaining northern democracies, Finland and Sweden, were encircled by the hostile states of Germany and the Soviet Union.
On 23 June, shortly after the Soviet occupation of the Baltic states began, Soviet Foreign Minister
Vyacheslav Molotov
Vyacheslav Mikhaylovich Molotov (; – 8 November 1986) was a Soviet politician, diplomat, and revolutionary who was a leading figure in the government of the Soviet Union from the 1920s to the 1950s, as one of Joseph Stalin's closest allies. ...
contacted the Finnish government to demand that a mining licence be issued to the Soviet Union for the
nickel
Nickel is a chemical element; it has symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive, but large pieces are slo ...
mines in
Petsamo or, alternatively, permission for the establishment of a joint Soviet-Finnish company to operate there. A licence to mine the deposit had already been granted to a British-Canadian company and so the demand was rejected by Finland. The following month, the Soviets demanded that Finland destroy the fortifications on the
Åland Islands
Åland ( , ; ) is an Federacy, autonomous and Demilitarized zone, demilitarised region of Finland. Receiving its autonomy by a 1920 decision of the League of Nations, it is the smallest region of Finland by both area () and population (30,54 ...
and to grant the Soviets the right to use Finnish railways to transport Soviet troops to the newly acquired Soviet base at Hanko. The Finns very reluctantly agreed to those demands. On 24 July, Molotov accused the Finnish government of persecuting the communist
Finland–Soviet Union Peace and Friendship Society and soon afterward publicly declared support for the group. The society organised demonstrations in Finland, some of which turned into riots.
Russian-language sources from the post-Soviet era, such as the study ''
Stalin's Missed Chance'', maintain that Soviet policies leading up to the Continuation War were best explained as defensive measures by offensive means. The Soviet division of occupied Poland with Germany, the Soviet occupation of the Baltic states and the Soviet invasion of Finland during the Winter War are described as elements in the Soviet construction of a security zone or buffer region from the perceived threat from the
capitalist
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their use for the purpose of obtaining profit. This socioeconomic system has developed historically through several stages and is defined by ...
powers of Western Europe. Other post-Soviet Russian-language sources consider establishment of Soviet
satellite state
A satellite state or dependent state is a country that is formally independent but under heavy political, economic, and military influence or control from another country. The term was coined by analogy to planetary objects orbiting a larger ob ...
s in the
Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Pact (WP), formally the Treaty of Friendship, Co-operation and Mutual Assistance (TFCMA), was a Collective security#Collective defense, collective defense treaty signed in Warsaw, Polish People's Republic, Poland, between the Sovi ...
countries and the
Finno-Soviet Treaty of 1948 as the culmination of the Soviet defence plan. Western historians, such as
Norman Davies
Ivor Norman Richard Davies (born 8 June 1939) is a British and Polish historian, known for his publications on the history of Europe, Poland and the United Kingdom. He has a special interest in Central and Eastern Europe and is UNESCO Profes ...
and
John Lukacs
John Adalbert Lukacs (; Hungarian: ''Lukács János Albert''; January 31, 1924 – May 6, 2019) was a Hungarian-born American historian and author of more than thirty books. Lukacs described himself as a reactionary
In politics, a reactionar ...
, dispute this view and describe pre-war Soviet policy as an attempt to stay out of the war and regain the land lost due to the
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Soviet Russia and the Central Powers (Germany, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and Bulgaria), by which Russia withdrew from World War I. The treaty, whi ...
after the fall of the
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
.
Relations between Finland, Germany and Soviet Union
On 31 July 1940,
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (20 April 1889 – 30 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his suicide in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the lea ...
gave the order to plan an assault on the Soviet Union, meaning Germany had to reassess its position regarding both Finland and Romania. Until then, Germany had rejected Finnish requests to purchase arms, but with the prospect of an invasion of Russia, that policy was reversed, and in August, the secret sale of weapons to Finland was permitted. Military authorities signed an agreement on 12 September, and an official exchange of diplomatic notes was sent on 22 September. Meanwhile, German troops were
allowed to transit through Sweden and Finland. This change in policy meant Germany had effectively redrawn the border of the German and Soviet spheres of influence, in violation of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact.
In response to that new situation, Molotov visited Berlin on 12–13 November 1940. He requested for Germany to withdraw its troops from Finland and to stop enabling Finnish anti-Soviet sentiments. He also reminded the Germans of the 1939 pact. Hitler inquired how the Soviets planned to settle the "Finnish question" to which Molotov responded that it would mirror the events in
Bessarabia
Bessarabia () is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds of Bessarabia lies within modern-day Moldova, with the Budjak region covering the southern coa ...
and the Baltic states. Hitler rejected that course of action. During the
Finnish presidential election in December 1940,
Risto Ryti
Risto Heikki Ryti (; 3 February 1889 – 25 October 1956) was a Finnish people, Finnish politician who served as the fifth president of Finland from 1940 to 1944. Ryti started his career as a politician in the field of economics and as a politica ...
was elected to be president largely due to interference by Molotov in Ryti's favour since he had signed the Moscow Peace Treaty as prime minister.
On 18 December 1940, Hitler officially approved Operation Barbarossa, paving the way for the German invasion of the Soviet Union, in which he expected both Finland and Romania to participate. Meanwhile, Finnish Major General
Paavo Talvela met with German Colonel General
Franz Halder
Franz Halder (30 June 1884 – 2 April 1972) was a German general and the chief of staff of the Oberkommando des Heeres, Army High Command (OKH) in Nazi Germany from 1938 until September 1942. During World War II, he directed the planning and i ...
and Reich Marshal
Hermann Göring
Hermann Wilhelm Göring (or Goering; ; 12 January 1893 – 15 October 1946) was a German Nazism, Nazi politician, aviator, military leader, and convicted war criminal. He was one of the most powerful figures in the Nazi Party, which gov ...
in Berlin, the first time that the Germans had advised the Finnish government, in carefully-couched diplomatic terms, that they were preparing for war with the Soviet Union. Outlines of the actual plan were revealed in January 1941 and regular contact between Finnish and German military leaders began in February. Additionally in January 1941, Moscow again demanded Finland relinquish control of the Petsamo mining area to the Soviets, but Finland, emboldened by a rebuilt defence force and German support, rejected the proposition.
In the late spring of 1941, the USSR made a number of goodwill gestures to prevent Finland from completely falling under German influence. Ambassador was replaced with the more conciliatory and passive . Furthermore, the Soviet government announced that it no longer opposed a
rapprochement
In international relations, a rapprochement, which comes from the French word ''rapprocher'' ("to bring together"), is a re-establishment of cordial relations between two countries. This may be done due to a mutual antagonist, as the German Empire ...
between Finland and Sweden. Those conciliatory measures, however, did not have any effect on Finnish policy. Finland wished to re-enter the war mainly because of the Soviet invasion of Finland during the Winter War, which the League of Nations and Nordic neutrality had failed to prevent due to lack of outside support. Finland primarily aimed to reverse its territorial losses from the 1940 Moscow Peace Treaty and, depending on the success of the German invasion of the Soviet Union, to possibly expand its borders, especially into
East Karelia. Some right-wing groups, such as the
Academic Karelia Society, supported a
Greater Finland ideology. This ideology of a Greater Finland mostly composed of Soviet territories was augmented by anti-Russian sentiments.
German and Finnish war plans
The details of the Finnish preparations for war are still somewhat opaque. Historian
William R. Trotter stated that "it has so far proven impossible to pinpoint the exact date on which Finland was taken into confidence about Operation Barbarossa" and that "neither the Finns nor the Germans were entirely candid with one another as to their national aims and methods. In any case, the step from contingency planning to actual operations, when it came, was little more than a formality".
The inner circle of Finnish leadership, led by Ryti and Mannerheim, actively planned joint operations with Germany under a veil of ambiguous neutrality and without formal agreements after an alliance with Sweden had proved fruitless, according to a meta-analysis by Finnish historian . He likewise refuted the so-called "driftwood theory" that Finland had been merely a piece of driftwood that was swept uncontrollably in the rapids of great power politics. Even then, most historians conclude that Finland had no realistic alternative to co-operating with Germany. On 20 May, the Germans invited a number of Finnish officers to discuss the coordination of Operation Barbarossa. The participants met on 25–28 May in
Salzburg
Salzburg is the List of cities and towns in Austria, fourth-largest city in Austria. In 2020 its population was 156,852. The city lies on the Salzach, Salzach River, near the border with Germany and at the foot of the Austrian Alps, Alps moun ...
and Berlin and continued their meeting in Helsinki from 3 to 6 June. They agreed upon Finnish
mobilisation
Mobilization (alternatively spelled as mobilisation) is the act of assembling and readying military troops and supplies for war. The word ''mobilization'' was first used in a military context in the 1850s to describe the preparation of the ...
and a general division of operations. They also agreed that the Finnish Army would start mobilisation on 15 June, but the Germans did not reveal the actual date of the assault. The Finnish decisions were made by the inner circle of political and military leaders, without the knowledge of the rest of the government. Due to tensions between Germany and the Soviet Union, the government was not informed until 9 June that mobilisation of
reservists would be required.
Finland's relationship with Germany
Finland never signed the
Tripartite Pact
The Tripartite Pact, also known as the Berlin Pact, was an agreement between Germany, Italy, and Japan signed in Berlin on 27 September 1940 by, respectively, Joachim von Ribbentrop, Galeazzo Ciano, and Saburō Kurusu (in that order) and in the ...
. The Finnish leadership stated they would fight against the Soviets only to the extent needed to redress the balance of the 1940 treaty, though some historians consider that it had wider territorial goals under the slogan "shorter borders, longer peace" (). During the war, the Finnish leadership generally referred to the Germans as "brothers-in-arms" but also denied that they were allies of Germany – instead claiming to be "co-belligerents". For Hitler, the distinction was irrelevant since he saw Finland as an ally. The 1947 Paris Peace Treaty signed by Finland described Finland as having been "an ally of Hitlerite Germany" during the Continuation War. In a 2008 poll of 28 Finnish historians carried out by ''
Helsingin Sanomat
, abbreviated ''HS'' and colloquially known as , is the largest subscription newspaper in Finland and the Nordic countries, owned by Sanoma. Except after certain holidays, it is published daily. Its name derives from that of the Finnish capital ...
'', 16 said that Finland had been an ally of Nazi Germany, six said it had not been and six did not take a position.
Order of battle and operational planning
Soviet

The
Northern Front () of the
Leningrad Military District was commanded by Lieutenant General
Markian Popov
Markian Mikhaylovich Popov (; 15 November 1902 – 22 April 1969) was a Soviet military commander, Army general (Soviet Union), Army General (26 August 1943), and Hero of the Soviet Union (1965).
Early life
Markian Popov was born in 1902 in U ...
and numbered around 450,000 soldiers in 18 divisions and 40 independent battalions in the Finnish region. During the Interim Peace, the Soviet Military had relaid operational plans to conquer Finland, but with the German attack, Operation Barbarossa, begun on 22 June 1941, the Soviets required its best units and latest materiel to be deployed against the Germans and so abandoned plans for a renewed offensive against Finland. The
23rd Army was deployed in the Karelian Isthmus, the
7th Army to Ladoga Karelia and the
14th Army to the
Murmansk
Murmansk () is a port city and the administrative center of Murmansk Oblast in the far Far North (Russia), northwest part of Russia. It is the world's largest city north of the Arctic Circle and sits on both slopes and banks of a modest fjord, Ko ...
–
Salla
Salla, known as Kuolajärvi until 1936, is a municipality of Finland, located in Lapland. The municipality has a population of
() and covers an area of of
which
is water. The population density is
.
The nearby settlement of Sallatunturi is ...
area of Lapland. The Northern Front also commanded eight
aviation divisions. As the initial German strike against the
Soviet Air Forces
The Soviet Air Forces (, VVS SSSR; literally "Military Air Forces of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics"; initialism VVS, sometimes referred to as the "Red Air Force") were one of the air forces of the Soviet Union. The other was the Sovie ...
had not affected air units located near Finland, the Soviets could deploy around 700 aircraft supported by a number of
Soviet Navy
The Soviet Navy was the naval warfare Military, uniform service branch of the Soviet Armed Forces. Often referred to as the Red Fleet, the Soviet Navy made up a large part of the Soviet Union's strategic planning in the event of a conflict with t ...
wings. The
Red Banner Baltic Fleet, which outnumbered the
navy of Germany (), comprised 2 battleships, 2 light cruisers, 47 destroyers or large torpedo boats, 75 submarines, over 200 smaller crafts, and 682 aircraft (of which 595 were operational).
Finnish and German
The Finnish Army () mobilised between 475,000 and 500,000 soldiers in 14 divisions and 3 brigades for the invasion, commanded by Field Marshal () Mannerheim. The army was organised as follows:
*
II Corps and
IV Corps: deployed to the Karelian Isthmus and comprised seven infantry divisions and one brigade.
*
Army of Karelia: deployed north of Lake Ladoga and commanded by General
Erik Heinrichs. It comprised the
VI Corps,
VII Corps, and Group Oinonen; a total of seven divisions, including the German 163rd Infantry Division, and three brigades.
* 14th Division: deployed in the
Kainuu
Kainuu (), also historically known as Cajania (), is one of the 19 regions of Finland (''maakunta'' / ''landskap''). Kainuu borders the regions of North Ostrobothnia, North Savo and North Karelia. In the east, it also borders Russia (Republic o ...
region, commanded directly by
Finnish Headquarters ().
Although initially deployed for a static defence, the Finnish Army was to later launch an attack to the south, on both sides of Lake Ladoga, putting pressure on Leningrad and thus supporting the advance of the German
Army Group North
Army Group North () was the name of three separate army groups of the Wehrmacht during World War II. Its rear area operations were organized by the Army Group North Rear Area.
The first Army Group North was deployed during the invasion of Pol ...
through the Baltic states towards Leningrad. Finnish intelligence had overestimated the strength of the Red Army, when in fact it was numerically inferior to Finnish forces at various points along the border. The army, especially its artillery, was stronger than it had been during the Winter War but included only one armoured battalion and had a general lack of motorised transportation; the army possessed 1,829 artillery pieces at the beginning of the invasion. The
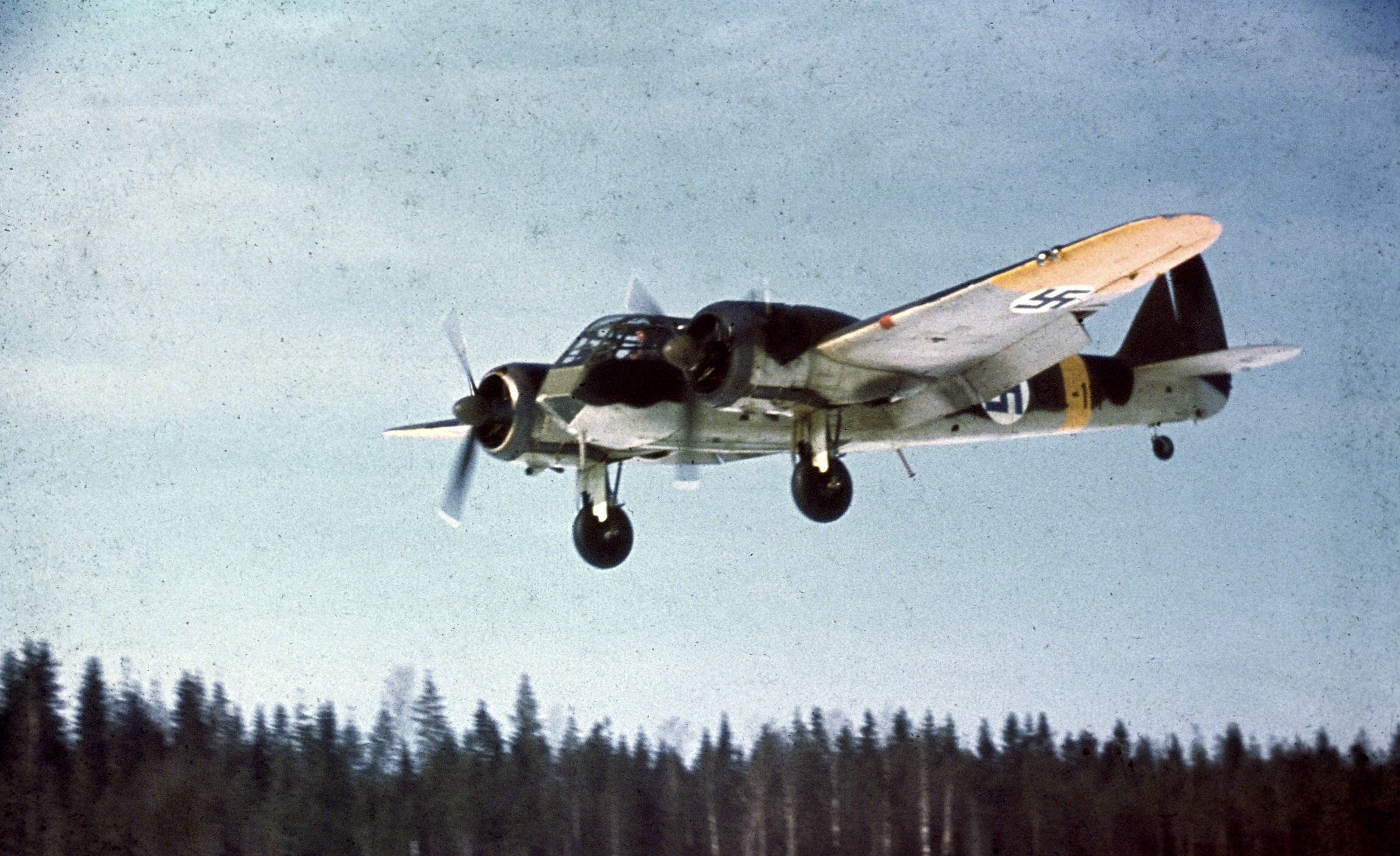
Finnish Air Force
The Finnish Air Force (FAF or FiAF; ; ) is one of the branches of the Finnish Defence Forces. Its peacetime tasks are airspace surveillance, identification flights, and production of readiness formations for wartime conditions. The Finnish Air ...
() had received large donations from Germany prior to the Continuation War including
Curtiss Hawk 75s,
Fokker D.XXI
The Fokker D.XXI Fighter aircraft, fighter was designed in 1935 by Dutch aircraft manufacturer Fokker in response to requirements laid out by the Royal Netherlands East Indies Army Air Force (''Militaire Luchtvaart van het Koninklijk Nederlands-In ...
s,
Dornier Do 22 flying boats,
Morane M.S. 406 bombers, and
Focke-Wulf Fw 44 Stieglitz trainers; in total the Finnish Air Force had 550 aircraft by June 1941, approximately half being combat. By September 1944, despite considerable German supply of aircraft, the Finns only had 384 planes. Even with the increase in supplied aircraft, the air force was constantly outnumbered by the Soviets.

The
Army of Norway, or , comprising four divisions totaling 67,000 German soldiers, held the arctic front, which stretched approximately through Finnish Lapland. This army would also be tasked with striking Murmansk and the
Kirov (Murmansk) Railway during
Operation Silver Fox
Operation Silver Fox (; ) or Murmansk operation () from 29 June to 17 November 1941, was a joint Nazi Germany, German–Finland, Finnish military operation during the Continuation War on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front of World Wa ...
. The Army of Norway was under the direct command of the
German Army High Command () and was organised into
Mountain Corps Norway and
XXXVI Mountain Corps with the
Finnish III Corps and 14th Division attached to it. The
German Air Force High Command () assigned 60 aircraft from ''
Luftflotte 5
Luftflotte 5 (Air Fleet 5) was one of the primary divisions of the German Luftwaffe in World War II. It was formed 12 April 1940 in Hamburg for the invasion of Norway.
It transferred to Oslo, Norway on 24 April 1940 and was the organization respo ...
'' (Air Fleet 5) to provide air support to the Army of Norway and the Finnish Army, in addition to its main responsibility of defending Norwegian air space. In contrast to the front in Finland, a total of 149 divisions and 3,050,000 soldiers were deployed for the rest of Operation Barbarossa.
Finnish offensive phase in 1941
Initial operations
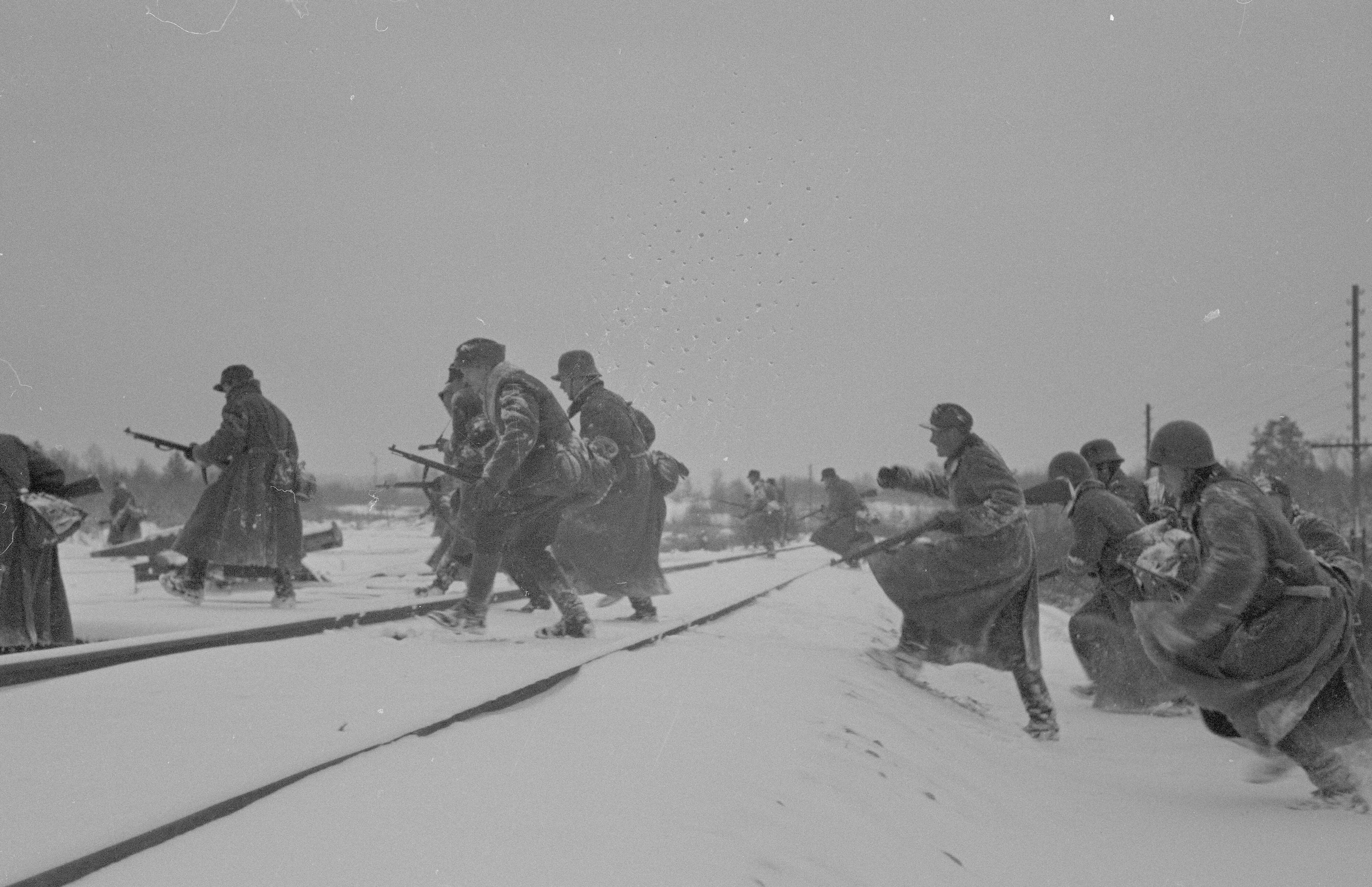

In the evening of 21 June 1941, German mine-layers hiding in the
Archipelago Sea
The Archipelago Sea (, ) is a part of the Baltic Sea between the Gulf of Bothnia, the Gulf of Finland and the Sea of Åland, within Finnish territorial waters. By some definitions it contains the List of archipelagos by number of islands, larges ...
deployed two large minefields across the Gulf of Finland. Later that night, German bombers flew along the gulf to Leningrad, mining the harbour and the river
Neva
The Neva ( , ; , ) is a river in northwestern Russia flowing from Lake Ladoga through the western part of Leningrad Oblast (historical region of Ingria) to the Neva Bay of the Gulf of Finland. Despite its modest length of , it is the fourth- ...
, making a refueling stop at
Utti, Finland, on the return leg. In the early hours of 22 June, Finnish forces launched
Operation Kilpapurjehdus ("Regatta"), deploying troops in the demilitarised Åland Islands. Although the 1921
Åland convention
Åland ( , ; ) is an Federacy, autonomous and Demilitarized zone, demilitarised region of Finland. Receiving its autonomy by a 1920 decision of the League of Nations, it is the smallest region of Finland by both area () and population (30,54 ...
had clauses allowing Finland to defend the islands in the event of an attack, the coordination of this operation with the German invasion and the arrest of the Soviet consulate staff stationed on the islands meant that the deployment was a deliberate violation of the treaty, according to Finnish historian
Mauno Jokipii.
On the morning of 22 June, Hitler's proclamation read: "Together with their Finnish comrades in arms the
heroes from Narvik stand at the edge of the Arctic Ocean. German troops under command of the
conqueror of Norway, and the Finnish freedom fighters under their Marshal's command, are protecting Finnish territory."
Following the launch of
Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and several of its European Axis allies starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during World War II. More than 3.8 million Axis troops invaded the western Soviet Union along ...
at around 3:15 a.m. on 22 June 1941, the Soviet Union sent seven bombers on a retaliatory airstrike into Finland, hitting targets at 6:06 a.m. Helsinki time as reported by the
Finnish coastal defence ship ''Väinämöinen''. On the morning of 25 June, the Soviet Union launched another air offensive, with 460 fighters and bombers targeting 19 airfields in Finland; however, inaccurate intelligence and poor bombing accuracy resulted in several raids hitting Finnish cities, or municipalities, causing considerable damage. 23 Soviet bombers were lost in this strike while the Finnish forces lost no aircraft. Although the USSR claimed that the airstrikes were directed against German targets, particularly airfields in Finland,
the
Finnish Parliament used the attacks as justification for the approval of a "defensive war". According to historian David Kirby, the message was intended more for public opinion in Finland than abroad, where the country was viewed as an ally of the Axis powers.
Finnish advance in Karelia
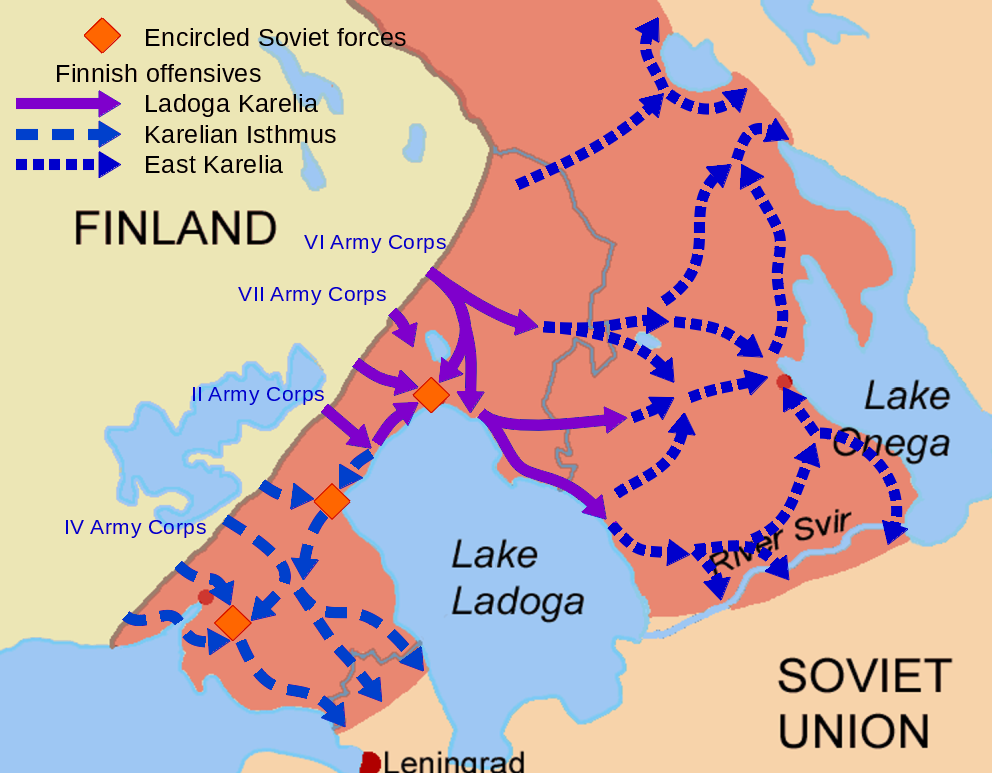
The Finnish plans for the offensive in Ladoga Karelia were finalised on 28 June 1941, and the first stages of the operation began on 10 July. By 16 July, the
VI Corps had reached the northern shore of
Lake Ladoga
Lake Ladoga is a freshwater lake located in the Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Oblast in northwestern Russia, in the vicinity of Saint Petersburg.
It is the largest lake located entirely in Europe, the second largest lake in Russia after Lake ...
, dividing the Soviet 7th Army, which had been tasked with defending the area. The USSR struggled to contain the German assault, and soon the Soviet high command, ''
Stavka
The ''Stavka'' ( Russian and Ukrainian: Ставка, ) is a name of the high command of the armed forces used formerly in the Russian Empire and Soviet Union and currently in Ukraine.
In Imperial Russia ''Stavka'' referred to the administrat ...
'' (), pulled all available units stationed along the Finnish border into the beleaguered front line. Additional reinforcements were drawn from the
237th Rifle Division and the Soviet
10th Mechanised Corps, excluding the , both of which were stationed in Ladoga Karelia, but this stripped much of the reserve strength of the Soviet units defending that area.
The Finnish
II Corps started its offensive in the north of the Karelian Isthmus on 31 July. Other Finnish forces reached the shores of Lake Ladoga on 9 August, encircling most of the three defending Soviet divisions on the northwestern coast of the lake in a
pocket
A pocket is a bag- or envelope-like receptacle either fastened to or inserted in an article of clothing to hold small items. Pockets are also attached to luggage, backpacks, and similar items. In older usage, a pocket was a separate small bag o ...
(); these divisions were later evacuated across the lake. On 22 August, the Finnish
IV Corps began its offensive south of II Corps and advanced towards
Vyborg
Vyborg (; , ; , ; , ) is a town and the administrative center of Vyborgsky District in Leningrad Oblast, Russia. It lies on the Karelian Isthmus near the head of Vyborg Bay, northwest of St. Petersburg, east of the Finnish capital H ...
(). By 23 August, II Corps had reached the
Vuoksi River
The Vuoksi (, historically: "Uzerva"; ; ; ) is a river running through the northernmost part of the Karelian Isthmus from Lake Saimaa in southeastern Finland to Lake Ladoga in northwestern Russia. The river enters Lake Ladoga in three branches ...
to the east and encircled the Soviet forces defending Vyborg. Finnish forces captured Vyborg on 29 August.

The Soviet order to withdraw from Vyborg came too late, resulting in significant losses in materiel, although most of the troops were later evacuated via the
Koivisto Islands. After suffering severe losses, the Soviet 23rd Army was unable to halt the offensive, and by 2 September the Finnish Army had reached the old
1939 border. The advance by Finnish and German forces split the Soviet Northern Front into the
Leningrad Front
The Leningrad Front () was formed during the 1941 German approach on Leningrad (now Saint Petersburg) by dividing the Northern Front into the Leningrad Front and Karelian Front on August 27, 1941.
History
The Leningrad Front was immediately ...
and the
Karelian Front on 23 August. On 31 August, Finnish Headquarters ordered II and IV Corps, which had advanced the furthest, to halt their advance along a line that ran from the Gulf of Finland via
Beloostrov–
Sestra–
Okhta–
Lembolovo to Lake Ladoga. The line ran past the former 1939 border, and approximately from Leningrad; a defensive position was established along this line. On 30 August, the IV Corps fought the Soviet 23rd Army in the
Battle of Porlampi and defeated them on 1 September. Sporadic fighting continued around Beloostrov until the Soviets evicted the Finns on 5 September. The front on the Isthmus stabilised and the
siege of Leningrad
The siege of Leningrad was a Siege, military blockade undertaken by the Axis powers against the city of Leningrad (present-day Saint Petersburg) in the Soviet Union on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front of World War II from 1941 t ...
began on 8 September.
The Finnish Army of Karelia started its attack in East Karelia towards
Petrozavodsk
Petrozavodsk (, ; Karelian language, Karelian, Veps language, Vepsian and ) is the capital city of the Republic of Karelia, Russia, which stretches along the western shore of Lake Onega for some . The population of the city is 280,890 as of 2022.
...
,
Lake Onega
Lake Onega (; also known as Onego; , ; ; Livvi-Karelian language, Livvi: ''Oniegujärvi''; ) is a lake in northwestern Russia, on the territory of the Republic of Karelia, Leningrad Oblast and Vologda Oblast. It belongs to the basin of the Baltic ...
and the
Svir River on 9 September. German Army Group North advanced from the south of Leningrad towards the Svir River and captured
Tikhvin
Tikhvin (; Veps: ) is a town and the administrative center of Tikhvinsky District in Leningrad Oblast, Russia, located on both banks of the Tikhvinka River in the east of the oblast, east of St. Petersburg. Tikhvin is also an industrial ...
but were forced to retreat to the
Volkhov River
The Volkhov ( ; ; ) is a river in Novgorodsky District, Novgorodsky and Chudovsky Districts of Novgorod Oblast and Kirishsky District, Kirishsky and Volkhovsky Districts of Leningrad Oblast in northwestern Russia. The Volkhov River, Volkhov, whi ...
by Soviet counterattacks. Soviet forces repeatedly attempted to expel the Finns from their
bridgehead
In military strategy, a bridgehead (or bridge-head) is the strategically important area of ground around the end of a bridge or other place of possible crossing over a body of water which at time of conflict is sought to be defended or taken over ...
south of the Svir during October and December but were repulsed; Soviet units attacked the German
163rd Infantry Division in October 1941, which was operating under Finnish command across the Svir, but failed to dislodge it. Despite these failed attacks, the Finnish attack in East Karelia had been blunted and their advance had halted by 6 December. During the five-month campaign, the Finns suffered 75,000 casualties, of whom 26,355 had died, while the Soviets had 230,000 casualties, of whom 50,000 became prisoners of war.
Operation Silver Fox in Lapland and Lend-Lease to Murmansk

The German objective in Finnish Lapland was to take Murmansk and cut the Kirov (Murmansk) Railway running from Murmansk to Leningrad by capturing Salla and
Kandalaksha
Kandalaksha () is a town in Kandalakshsky District of Murmansk Oblast, Russia, located at the head of Kandalaksha Gulf on the White Sea, north of the Arctic Circle. Population: 40,564 ( 2002 Census);
Etymology
According to the most common ...
. Murmansk was the only year-round
ice-free port in the north and a threat to the nickel mine at Petsamo. The joint Finnish–German Operation Silver Fox (; ) was started on 29 June 1941 by the German Army of Norway, which had the
Finnish 3rd and
6th Divisions under its command, against the defending Soviet 14th Army and
54th Rifle Division
The 54th Rifle Division was an infantry division of the Soviet Union's Red Army and Soviet Army, formed twice. The division was formed in 1936 and fought in the Winter War. The division spent most of World War II in Karelia fighting with Finnish t ...
. By November, the operation had stalled from the Kirov Railway due to unacclimatised German troops, heavy Soviet resistance, poor terrain, arctic weather and diplomatic pressure by the United States on the Finns regarding the lend-lease deliveries to Murmansk. The offensive and its three sub-operations failed to achieve their objectives. Both sides dug in and the arctic theatre remained stable, excluding minor skirmishes, until the Soviet
Petsamo–Kirkenes Offensive in October 1944.
The crucial
arctic lend-lease convoys from the US and the UK via Murmansk and Kirov Railway to the bulk of the Soviet forces continued throughout World War II. The US supplied almost
$11 billion in materials: 400,000 jeeps and trucks; 12,000 armored vehicles (including 7,000 tanks, which could equip some 20 US armoured divisions); 11,400 aircraft; and of food. As a similar example, British shipments of Matilda, Valentine and Tetrarch tanks accounted for only 6% of total Soviet tank production, but over 25% of medium and heavy tanks produced for the Red Army.
Aspirations, war effort and international relations

The ''Wehrmacht'' rapidly advanced deep into Soviet territory early in the Operation Barbarossa campaign, leading the Finnish government to believe that Germany would defeat the Soviet Union quickly. President Ryti envisioned a Greater Finland, where Finns and other
Finnic peoples
The Finnic peoples, or simply Finns, are the nations who speak languages traditionally classified in the Finno-Permic languages, Finnic language family, and which are thought to have originated in the region of the Volga River. Currently, the l ...
would live inside a "natural defence borderline" by incorporating the
Kola Peninsula
The Kola Peninsula (; ) is a peninsula in the extreme northwest of Russia, and one of the largest peninsulas of Europe. Constituting the bulk of the territory of Murmansk Oblast, it lies almost completely inside the Arctic Circle and is border ...
, East Karelia and perhaps even northern
Ingria
Ingria (; ; ; ) is a historical region including, and adjacent to, what is now the city of Saint Petersburg in northwestern Russia. The region lies along the southeastern shore of the Gulf of Finland, bordered by Lake Ladoga on the Karelian ...
. In public, the proposed frontier was introduced with the slogan "short border, long peace". Some members of the Finnish Parliament, such as members of the
Social Democratic Party
The name Social Democratic Party or Social Democrats has been used by many political parties in various countries around the world. Such parties are most commonly aligned to social democracy as their political ideology.
Active parties
Form ...
and the
Swedish People's Party, opposed the idea, arguing that maintaining the 1939 frontier would be enough. Mannerheim often called the war an anti-Communist crusade, hoping to defeat "
Bolshevism
Bolshevism (derived from Bolshevik) is a revolutionary socialist current of Soviet Leninist and later Marxist–Leninist political thought and political regime associated with the formation of a rigidly centralized, cohesive and disciplined p ...
once and for all". On 10 July, Mannerheim drafted his order of the day, the
Sword Scabbard Declaration, in which he pledged to liberate Karelia; in December 1941 in private letters, he made known his doubts of the need to push beyond the previous borders. The Finnish government assured the United States that it was unaware of the order.
According to Vehviläinen, most Finns thought that the scope of the new offensive was only to regain what had been taken in the Winter War. He further stated that the term 'Continuation War' was created at the start of the conflict by the Finnish government to justify the invasion to the population as a continuation of the defensive Winter War. The government also wished to emphasise that it was not an official ally of Germany, but a 'co-belligerent' fighting against a common enemy and with purely Finnish aims. Vehviläinen wrote that the authenticity of the government's claim changed when the Finnish Army crossed the old frontier of 1939 and began to annex Soviet territory. British author
Jonathan Clements asserted that by December 1941, Finnish soldiers had started questioning whether they were fighting a war of national defence or foreign conquest.
By the autumn of 1941, the Finnish military leadership started to doubt Germany's capability to finish the war quickly. The Finnish Defence Forces suffered relatively severe losses during their advance and, overall, German victory became uncertain as German troops were
halted near Moscow. German troops in northern Finland faced circumstances they were unprepared for and failed to reach their targets. As the front lines stabilised, Finland attempted to start peace negotiations with the USSR. Mannerheim refused to assault Leningrad, which would inextricably tie Finland to Germany; he regarded his objectives for the war to be achieved, a decision that angered the Germans.
Due to the war effort, the Finnish economy suffered from a lack of labour, as well as food shortages and increased prices. To combat this, the Finnish government demobilised part of the army to prevent industrial and agricultural production from collapsing. In October, Finland informed Germany that it would need of grain to manage until next year's harvest. The German authorities would have rejected the request, but Hitler himself agreed. Annual grain deliveries of equaled almost half of the Finnish domestic crop. On 25 November 1941, Finland signed the
Anti-Comintern Pact
The Anti-Comintern Pact, officially the Agreement against the Communist International was an anti-communist pact concluded between Nazi Germany and the Empire of Japan on 25 November 1936 and was directed against the Communist International (Com ...
, a less formal alliance, which the German leadership saw as a "litmus test of loyalty".
Finland maintained good relations with a number of other Western powers. Foreign volunteers from Sweden and Estonia were among the foreigners who joined Finnish ranks.
Infantry Regiment 200, called ("Finnish boys"), mostly Estonians, and the Swedes mustered the
Swedish Volunteer Battalion. The Finnish government stressed that Finland was fighting as a
co-belligerent with Germany against the USSR only to protect itself and that it was still the same democratic country as it had been in the Winter War. For example, Finland maintained diplomatic relations with the exiled Norwegian government and more than once criticised German occupation policy in Norway. Relations between Finland and the United States were more complex since the American public was sympathetic to the "brave little democracy" and had anticommunist sentiments. At first, the United States sympathised with the Finnish cause, but the situation became problematic after the Finnish Army had crossed the 1939 border. Finnish and German troops were a threat to the Kirov Railway and the northern supply line between the Western Allies and the Soviet Union. On 25 October 1941, the US demanded that Finland cease all hostilities against the USSR and to withdraw behind the 1939 border. In public, President Ryti rejected the demands, but in private, he wrote to Mannerheim on 5 November and asked him to halt the offensive. Mannerheim agreed and secretly instructed General
Hjalmar Siilasvuo
Hjalmar Fridolf Siilasvuo (born Hjalmar Fridolf Strömberg, 18 March 1892 – 11 January 1947) was a Finnish lieutenant general (), a knight of the Mannerheim Cross and a member of the Jäger Movement. He participated in the Eastern Front (World ...
and his III Corps to end the assault on the Kirov Railway. Nevertheless, the United States never declared war on Finland during the entire conflict.
British declaration of war and action in the Arctic Ocean
On 12 July 1941, the United Kingdom signed an agreement of joint action with the Soviet Union. Under German pressure, Finland closed the British
legation
A legation was a diplomatic representative office of lower rank than an embassy. Where an embassy was headed by an ambassador, a legation was headed by a minister. Ambassadors outranked ministers and had precedence at official events. Legation ...
in Helsinki and cut diplomatic relations with Britain on 1 August. On 2 August 1941, Britain declared that Finland was under enemy occupation, which ended all economic transactions between Britain and Finland and led to a blockade of Finnish trade. The most sizable British action on Finnish soil was the
Raid on Kirkenes and Petsamo
Operation EF (1941) (Raid on Kirkenes and Petsamo) took place on 30 July 1941, during the Second World War. After the beginning of Operation Barbarossa, the German invasion of the Soviet Union on 22 June 1941, Fleet Air Arm aircraft flew from th ...
, an aircraft-carrier strike on German and Finnish ships on 31 July 1941. The attack accomplished little except the loss of one Norwegian ship and three British aircraft, but it was intended to demonstrate British support for its Soviet ally. From September to October in 1941, a total of 39
Hawker Hurricane
The Hawker Hurricane is a British single-seat fighter aircraft of the 1930s–40s which was designed and predominantly built by Hawker Aircraft Ltd. for service with the Royal Air Force (RAF). It was overshadowed in the public consciousness by ...
s of
No. 151 Wing RAF, based at Murmansk, reinforced and provided pilot-training to the Soviet Air Forces during
Operation Benedict to protect arctic convoys.
On 28 November, the British government presented Finland with an ultimatum demanding for the Finns to cease military operations by 3 December. Unofficially, Finland informed the Allies that Finnish troops would halt their advance in the next few days. The reply did not satisfy London, which declared war on Finland on 6 December. The
Commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the 15th century. Originally a phrase (the common-wealth ...
nations of Canada, Australia,
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
and
New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
soon followed suit. In private, British Prime Minister
Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 1874 – 24 January 1965) was a British statesman, military officer, and writer who was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1940 to 1945 (Winston Churchill in the Second World War, ...
had sent a letter to Mannerheim on 29 November in which Churchill was "deeply grieved" that the British would have to declare war on Finland because of the British alliance with the Soviets. Mannerheim repatriated British volunteers under his command to the United Kingdom via Sweden. According to Clements, the declaration of war was mostly for appearance's sake.
Trench warfare from 1942 to 1944

Unconventional warfare and military operations
Unconventional warfare was fought in both the Finnish and Soviet wildernesses. Finnish
long-range reconnaissance patrol
A long-range reconnaissance patrol, or LRRP, is a small, well-armed reconnaissance team that patrolling, patrols deep into enemy-held territory.Ankony, Robert C., ''Lurps: A Ranger's Diary of Tet, Khe Sanh, A Shau, and Quang Tri,'' revised ed., ...
s, organised both by the
Intelligence Division's
Detached Battalion 4 and by local units, patrolled behind Soviet lines.
Soviet partisans
Soviet partisans were members of Resistance during World War II, resistance movements that fought a Guerrilla warfare, guerrilla war against Axis powers, Axis forces during World War II in the Soviet Union, the previously Territories of Poland an ...
, both resistance fighters and regular long-range patrol detachments, conducted a number of operations in Finland and in
Eastern Karelia from 1941 to 1944. In summer 1942, the USSR formed the 1st Partisan Brigade. The unit was 'partisan' in name only, as it was essentially 600 men and women on long-range patrol intended to disrupt Finnish operations. The 1st Partisan Brigade was able to infiltrate beyond Finnish patrol lines, but was intercepted, and rendered ineffective, in August 1942 at
Lake Segozero.
Irregular partisans distributed propaganda newspapers, such as Finnish translations of the official
Communist Party paper ''
Pravda
''Pravda'' ( rus, Правда, p=ˈpravdə, a=Ru-правда.ogg, 'Truth') is a Russian broadsheet newspaper, and was the official newspaper of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, when it was one of the most in ...
'' (). Notable Soviet politician
Yuri Andropov
Yuri Vladimirovich Andropov ( – 9 February 1984) was a Soviet politician who served as the General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from late 1982 until his death in 1984. He previously served as the List of Chairmen of t ...
took part in these partisan guerrilla actions. Finnish sources state that, although Soviet partisan activity in East Karelia disrupted Finnish military supply and communication assets, almost two thirds of the attacks targeted civilians, killing 200 and injuring 50, including children and elderly.
[.]
Between 1942 and 1943, military operations were limited, although the front did see some action. In January 1942, the Soviet Karelian Front attempted to retake
Medvezhyegorsk (), which had been lost to the Finns in late 1941. With the arrival of spring in April, Soviet forces went on the offensive on the Svir River front, in the
Kestenga () region further north in Lapland as well as in the far north at Petsamo with the
14th Rifle Division's amphibious landings supported by the
Northern Fleet. All Soviet offensives started promisingly, but due either to the Soviets overextending their lines or stubborn defensive resistance, the offensives were repulsed. After Finnish and German counterattacks in Kestenga, the front lines were generally stalemated. In September 1942, the USSR attacked again at Medvezhyegorsk, but despite five days of fighting, the Soviets only managed to push the Finnish lines back on a roughly long stretch of the front. Later that month, a Soviet landing with two battalions in Petsamo was defeated by a German counterattack. In November 1941, Hitler decided to separate the German forces fighting in Lapland from the Army of Norway and create the Army of Lapland, commanded by Colonel General Eduard Dietl. In June 1942, the Army of Lapland was redesignated the
20th Mountain Army.
Siege of Leningrad and naval warfare

In the early stages of the war, the Finnish Army overran the former 1939 border, but ceased their advance from the center of Leningrad. Multiple authors have stated that Finland participated in the siege of Leningrad (), but the full extent and nature of their participation is debated and a clear consensus has yet to emerge. American historian
David Glantz
David M. Glantz (born January 11, 1942) is an American military historian known for his books on the Red Army during World War II and as the chief editor of '' The Journal of Slavic Military Studies''.
Born in Port Chester, New York, Glantz ...
writes that the Finnish Army generally maintained their lines and contributed little to the siege from 1941 to 1944, whereas Russian historian stated in 2002 that Finland tacitly supported Hitler's starvation policy for the city. However, in 2009 British historian
Michael Jones disputed Baryshnikov's claim and asserted that the Finnish Army cut off the city's northern supply routes but did not take further military action. In 2006, American author
Lisa Kirschenbaum wrote that the siege started "when German and Finnish troops severed all land routes in and out of Leningrad."
According to Clements, Mannerheim personally refused Hitler's request of assaulting Leningrad during
their meeting on 4 June 1942. Mannerheim explained to Hitler that "Finland had every reason to wish to stay out of any further provocation of the Soviet Union." In 2014, author
Jeff Rutherford described the city as being "ensnared" between the German and Finnish armies. British historian
John Barber described it as a "siege by the German and Finnish armies from 8 September 1941 to 27 January 1944
.. in his foreword in 2017. Likewise, in 2017,
Alexis Peri wrote that the city was "completely cut off, save a heavily patrolled water passage over Lake Ladoga" by "Hitler's Army Group North and his Finnish allies."
The 150 speedboats, two minelayers and four steamships of the
Finnish Ladoga Naval Detachment, as well as numerous shore batteries, had been stationed on Lake Ladoga since August 1941. Finnish Lieutenant General Paavo Talvela proposed on 17 May 1942 to create a joint Finnish–German–Italian unit on the lake to disrupt Soviet supply convoys to Leningrad. The unit was named
Naval Detachment K and comprised four Italian
MAS torpedo motorboats of the
XII Squadriglia MAS, four German KM-type minelayers and the Finnish
torpedo-motorboat ''Sisu''. The detachment began operations in August 1942 and sank numerous smaller Soviet watercraft and flatboats and assaulted enemy bases and beach fronts until it was dissolved in the winter of 1942–43. Twenty-three
Siebel ferries and nine infantry transports of the German ''
Einsatzstab Fähre Ost'' were also deployed to Lake Ladoga and unsuccessfully
assaulted the island of Sukho, which protected the main supply route to Leningrad, in October 1942.
Despite the siege of the city, the Soviet Baltic Fleet was still able to operate from Leningrad. The Finnish Navy's flagship had been sunk in September 1941 in the gulf by mines during the failed diversionary
Operation North Wind in 1941. In early 1942, Soviet forces recaptured the island of
Gogland, but lost it and the
Bolshoy Tyuters islands to Finnish forces later in spring 1942. During the winter between 1941 and 1942, the Soviet Baltic Fleet decided to use their large submarine fleet in offensive operations. Though initial submarine operations in the summer of 1942 were successful, the and
Finnish Navy
The Finnish Navy ( , ) is one of the branches of the Finnish Defence Forces. The navy employs 2,300 people and about 4,300 conscripts are trained each year. Finnish Navy vessels are given the ship prefix "FNS", short for "Finnish Navy ship", but ...
soon intensified their anti-submarine efforts, making Soviet submarine operations later in 1942 costly. The underwater offensive carried out by the Soviets convinced the Germans to lay
anti-submarine nets as well as supporting minefields between Porkkala Peninsula and
Naissaar, which proved to be an insurmountable obstacle for Soviet submarines. On the
Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five oceanic divisions. It spans an area of approximately and is the coldest of the world's oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, ...
,
Finnish radio intelligence intercepted Allied messages on supply convoys to Murmansk, such as
PQ 17 and
PQ 18, and relayed the information to the ''
Abwehr
The (German language, German for ''resistance'' or ''defence'', though the word usually means ''counterintelligence'' in a military context) ) was the German military intelligence , military-intelligence service for the ''Reichswehr'' and the ...
'', German intelligence.
Finnish military administration and concentration camps

On 19 July 1941, the Finns created a military administration in occupied East Karelia with the goal of preparing the region for eventual incorporation into Finland. The Finns aimed to
expel the Russian portion of the local population (constituting to about a half), who were deemed "non-national", from the area once the war was over, and replace them with
Finno-Ugric
Finno-Ugric () is a traditional linguistic grouping of all languages in the Uralic languages, Uralic language family except for the Samoyedic languages. Its once commonly accepted status as a subfamily of Uralic is based on criteria formulated in ...
peoples. Most of the East Karelian population had already been evacuated before the Finnish forces arrived, but about 85,000 people — mostly elderly, women and children — were left behind, less than half of whom were Karelians. A significant number of civilians, almost 30% of the remaining Russians, were interned in concentration camps.
The winter between 1941 and 1942 was particularly harsh for the Finnish urban population due to poor harvests and a shortage of agricultural labourers. However, conditions were much worse for Russians in Finnish concentration camps. More than 3,500 people died, mostly from
starvation
Starvation is a severe deficiency in caloric energy intake, below the level needed to maintain an organism's life. It is the most extreme form of malnutrition. In humans, prolonged starvation can cause permanent organ damage and eventually, de ...
, amounting to 13.8% of those detained, while the corresponding figure for the free population of the occupied territories was 2.6%, and 1.4% for Finland. Conditions gradually improved, ethnic discrimination in wage levels and food rations was terminated, and new schools were established for the Russian-speaking population the following year, after Commander-in-Chief Mannerheim called for the
International Committee of the Red Cross
The International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) is a humanitarian organization based in Geneva, Switzerland, and is a three-time Nobel Prize laureate. The organization has played an instrumental role in the development of rules of war and ...
from Geneva to inspect the camps. By the end of the occupation, mortality rates had dropped to the same levels as in Finland.
Jews in Finland
In 1939, Finland had a small
Jewish
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
population of approximately 2,000 people, of whom 300 were refugees from Germany, Austria, and Czechoslovakia.
They had full civil rights and fought with other Finns in the ranks of the Finnish Army. The field synagogue in East Karelia was one of the very few functioning synagogues on the Axis side during the war. There were several cases of Jewish officers of the Finnish Army being awarded the German
Iron Cross
The Iron Cross (, , abbreviated EK) was a military decoration in the Kingdom of Prussia, the German Empire (1871–1918), and Nazi Germany (1933–1945). The design, a black cross pattée with a white or silver outline, was derived from the in ...
, which they declined. German soldiers were treated by Jewish medical officers—who sometimes saved the soldiers' lives.
German command mentioned Finnish Jews at the
Wannsee Conference in January 1942, wishing to transport them to the
Majdanek concentration camp in
occupied Poland
' (Norwegian language, Norwegian: ') is a Norwegian political thriller TV series that premiered on TV 2 (Norway), TV2 on 5 October 2015. Based on an original idea by Jo Nesbø, the series is co-created with Karianne Lund and Erik Skjoldbjærg. ...
.
''SS'' leader
Heinrich Himmler
Heinrich Luitpold Himmler (; 7 October 1900 – 23 May 1945) was a German Nazism, Nazi politician and military leader who was the 4th of the (Protection Squadron; SS), a leading member of the Nazi Party, and one of the most powerful p ...
also raised the topic of Finnish Jews during his visit in Finland in the summer of 1942; Finnish Prime Minister
Jukka Rangell replied that Finland did not have a
Jewish question. In November 1942, the Minister of the Interior
Toivo Horelli
Toivo Johannes Horelli (11 October 1888 – 28 June 1975) was a Finnish politician of the National Coalition Party (Finland), National Coalition Party. He was a member of the Parliament of Finland in 1933–1945, and the Minister of the Interior ...
and the head of
State Police
State police, provincial police or regional police are a type of sub-national territorial police force found in nations organized as federations, typically in North America, South Asia, and Oceania. These forces typically have jurisdiction o ...
Arno Anthoni secretly deported eight Jewish refugees to the ''
Gestapo
The (, ), Syllabic abbreviation, abbreviated Gestapo (), was the official secret police of Nazi Germany and in German-occupied Europe.
The force was created by Hermann Göring in 1933 by combining the various political police agencies of F ...
'', raising protests among Finnish Social Democrat Party ministers. Only one of the deportees survived. After the incident, the Finnish government refused to transfer any more Jews to German detainment.
Soviet offensive in 1944
Air raids and the Leningrad–Novgorod Offensive

Finland began to seek an exit from the war after the German defeat at the
Battle of Stalingrad
The Battle of Stalingrad ; see . rus, links=on, Сталинградская битва, r=Stalingradskaya bitva, p=stəlʲɪnˈɡratskəjə ˈbʲitvə. (17 July 19422 February 1943) was a major battle on the Eastern Front of World War II, ...
in February 1943. Finnish Prime Minister
Edwin Linkomies formed a new cabinet in March 1943 with peace as the top priority. Similarly, the Finns were distressed by the Allied
invasion of Sicily in July and the German defeat in the
Battle of Kursk
The Battle of Kursk, also called the Battle of the Kursk Salient, was a major World War II Eastern Front battle between the forces of Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union near Kursk in southwestern Russia during the summer of 1943, resulting in ...
in August. Negotiations were conducted intermittently in 1943 and 1944 between Finland, the Western Allies and the Soviets, but no agreement was reached. Stalin decided to force Finland to surrender with a
bombing campaign on Helsinki. Starting in February 1944, it included three major air attacks totaling over 6,000
sortie
A sortie (from the French word meaning ''exit'' or from Latin root ''surgere'' meaning to "rise up") is a deployment or dispatch of one military unit, be it an aircraft, ship, or troops, from a strongpoint. The term originated in siege warf ...
s. Finnish
anti-aircraft defence repelled the raids, and only 5% of the dropped
bombs
A bomb is an explosive weapon that uses the Exothermic process, exothermic reaction of an explosive material to provide an extremely sudden and violent release of energy. Detonations inflict damage principally through ground- and atmosphere-tra ...
hit their planned targets. In Helsinki, decoy searchlights and fires were placed outside the city to deceive Soviet bombers into dropping their payloads on unpopulated areas. Major air attacks also hit
Oulu
Oulu ( , ; ) is a city in Finland and the regional capital of North Ostrobothnia. It is located on the northwestern coast of the country at the mouth of the Oulujoki, River Oulu. The population of Oulu is approximately , while the Oulu sub-regio ...
and
Kotka
Kotka (; ) is a town in Finland, located on the southeastern coast of the country at the mouth of the Kymi River. The population of Kotka is approximately , while the Kotka-Hamina sub-region, sub-region has a population of approximately . It is th ...
, but pre-emptive radio intelligence and effective defence kept the number of casualties low.
The Soviet
Leningrad–Novgorod Offensive finally lifted the siege of Leningrad on 27 January 1944. The Army Group North was pushed to
Ida-Viru County
Ida-Viru County ( or ; ) is one of the 15 counties of Estonia. It is the most northeastern part of the country. The county contains large deposits of oil shale the main mineral mined in Estonia. Oil shale is used in the production of shale oil ...
on the Estonian border. Stiff
German and Estonian defence in Narva from February to August prevented the use of occupied Estonia as a favourable base for Soviet amphibious and air assaults against Helsinki and other Finnish coastal cities in support of a land offensive.
Field Marshal Mannerheim had reminded the German command on numerous occasions that if the German troops withdrew from Estonia, Finland would be forced to make peace, even on extremely unfavourable terms. Finland abandoned peace negotiations in April 1944 because of the unfavourable terms the USSR demanded.
Vyborg–Petrozavodsk Offensive and breakthrough

On 9 June 1944, the Soviet Leningrad Front launched an offensive against Finnish positions on the Karelian Isthmus and in the area of Lake Ladoga, timed to coincide with
Operation Overlord
Operation Overlord was the codename for the Battle of Normandy, the Allies of World War II, Allied operation that launched the successful liberation of German-occupied Western Front (World War II), Western Europe during World War II. The ope ...
in Normandy as agreed during the
Tehran Conference
The Tehran Conference (codenamed Eureka) was a strategy meeting of the Allies of World War II, held between Joseph Stalin, Franklin D. Roosevelt, and Winston Churchill from 28 November to 1 December 1943. It was the first of the Allied World Wa ...
. Along the -wide breakthrough, the Red Army concentrated 3,000 guns and mortars. In some places, the concentration of artillery pieces exceeded 200 guns for every kilometre of front or one for every . Soviet artillery fired over 80,000 rounds along the front on the Karelian Isthmus. On the second day of the offensive, the artillery barrages and superior number of Soviet forces crushed the main Finnish defence line. The Red Army penetrated the second line of defence, the
Vammelsuu–Taipale line (VT line), at
Kuuterselkä by the sixth day and recaptured Viipuri with insignificant resistance on 20 June. The Soviet breakthrough on the Karelian Isthmus forced the Finns to reinforce the area, thus allowing the concurrent Soviet offensive in East Karelia to meet less resistance and to recapture Petrozavodsk by 28 June 1944.
On 25 June, the Red Army reached the third line of defence, the
Viipuri–Kuparsaari–Taipale line (VKT line), and the decisive
Battle of Tali-Ihantala began, which has been described as the largest battle in Nordic military history. By then, the Finnish Army had retreated around to approximately the same line of defence they had held at the end of the Winter War. Finland especially lacked modern anti-tank weaponry that could stop Soviet heavy armour, such as the
KV-1 or
IS-2. Thus, German Foreign Minister Joachim von Ribbentrop offered German hand-held ''
Panzerfaust'' and ''
Panzerschreck'' antitank weapons in exchange for a guarantee that Finland would not seek a separate peace with the Soviets. On 26 June, President Risto Ryti gave the
guarantee as a personal undertaking that he, Field Marshal Mannerheim and Prime Minister Edwin Linkomies intended to last legally only for the remainder of Ryti's presidency. In addition to delivering thousands of anti-tank weapons, Hitler sent the
122nd Infantry Division and the half-strength 303rd Assault Gun Brigade armed with
Sturmgeschütz III
The ''Sturmgeschütz'' III (StuG III) was an assault gun produced by Nazi Germany during World War II. It was the most-produced German Continuous track, fully tracked armoured fighting vehicle, and second-most produced German armored combat ve ...
tank destroyers as well as the Luftwaffe's
Detachment Kuhlmey to provide temporary support in the most vulnerable sectors. With the new supplies and assistance from Germany, the Finnish Army halted the numerically and materially superior Soviet advance at Tali-Ihantala on 9 July 1944 and stabilised the front.
More battles were fought toward the end of the war, the last of which was the
Battle of Ilomantsi, fought between 26 July and 13 August 1944 and resulting in a Finnish victory with the destruction of two Soviet divisions. Resisting the Soviet offensive had exhausted Finnish resources. Despite German support under the Ryti–Ribbentrop Agreement, Finland asserted that it was unable to blunt another major offensive. Soviet victories against German
Army Groups Center and North during
Operation Bagration
Operation Bagration () was the codename for the 1944 Soviet Byelorussian strategic offensive operation (), a military campaign fought between 22 June and 19 August 1944 in Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, Soviet Byelorussia in the Eastern ...
made the situation even more dire for Finland. With no imminent further Soviet offensives, Finland sought to leave the war. On 1 August, Ryti resigned, and on 4 August, Field Marshal Mannerheim was sworn in as the new president. He annulled the agreement between Ryti and Ribbentrop on 17 August to allow Finland to sue for peace with the Soviets again, and peace terms from Moscow arrived on 29 August.
Ceasefire and peace
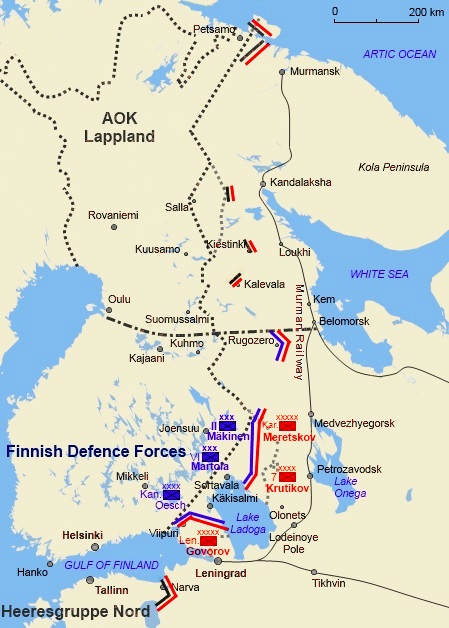
Finland was required to return to the borders agreed to in the 1940 Moscow Peace Treaty, demobilise its armed forces, fulfill war reparations and cede the municipality of Petsamo. The Finns were also required to end any diplomatic relations with Germany immediately and to expel the from Finnish territory by 15 September 1944; any troops remaining were to be disarmed, arrested and turned over to the Allies. The Finnish Parliament accepted those terms in a secret meeting on 2 September and requested for official negotiations for an armistice to begin. The Finnish Army implemented a ceasefire at 8:00 a.m. Helsinki time on 4 September. The Red Army followed suit a day later. On 14 September, a delegation led by Finnish Prime Minister
Antti Hackzell and Foreign Minister
Carl Enckell began negotiating, with the Soviet Union and the United Kingdom, the final terms of the Moscow Armistice, which eventually included additional stipulations from the Soviets. They were presented by Molotov on 18 September and accepted by the Finnish Parliament a day later.

The motivations for the Soviet peace agreement with Finland are debated. Several Western historians stated that the original Soviet designs for Finland were no different from those for the Baltic countries. American political scientist
Dan Reiter
Dan Reiter (born 29 September 1967, in Ann Arbor, Michigan) is an American political scientist. He is currently the Samuel Candler Dobbs Professor at the Department of Political Science at Emory University.
Education
Reiter received his B.A. wit ...
asserted that for Moscow, the control of Finland was necessary. Reiter and the British historian
Victor Rothwell quoted Molotov as telling his Lithuanian counterpart in 1940, when the
Soviets effectively annexed Lithuania, that minor states such as Finland, "will be included within the honourable family of Soviet peoples". Reiter stated that concern over severe losses pushed Stalin into accepting a limited outcome in the war rather than pursuing annexation, although some Soviet documents called for military occupation of Finland. He also wrote that Stalin had described territorial concessions, reparations and military bases as his objective with Finland to representatives from the UK, in December 1941, and the US, in March 1943, as well as the Tehran Conference. He believed that in the end, "Stalin's desire to crush Hitler quickly and decisively without distraction from the Finnish sideshow" concluded the war. Red Army officers captured as prisoners of war during the Battle of Tali-Ihantala revealed that their intention was to reach Helsinki, and that they were to be strengthened with reinforcements for this task. This was confirmed by intercepted Soviet radio messages.
Russian historian Nikolai Baryshnikov disputed the view that the Soviet Union sought to deprive Finland of its independence. He argued that there was no documentary evidence for such claims and that the Soviet government was always open for negotiations. Baryshnikov cited sources like the public information chief of Finnish Headquarters, Major , to show that Finnish leadership had learned of the limited Soviet plans for Finland by at least July 1944 after intelligence revealed that some Soviet divisions were to be transferred to reserve in Leningrad. Finnish historian stated similar findings in 2009. According to him, the Soviets refocused their efforts in the summer of 1944 from the Finnish Front to defeating Germany, and Mannerheim received intelligence from Colonel
Aladár Paasonen in June 1944 that the Soviet Union was aiming for peace, not occupation.
Evidence of the Soviet leadership's intentions for the occupation of Finland has later been uncovered. In 2018, it was revealed that the Soviets' designed and printed (in
Goznak) new banknotes for Finland during the closing phases of the war, which were to be put into use after the planned occupation of the country.
Aftermath and casualties
Finland and Germany

According to Finnish historians, the casualties of the Finnish Defence Forces amounted to 63,204 dead or missing and around 158,000 wounded. Officially, the Soviets captured 2,377
Finnish prisoners-of-war, but Finnish researchers estimated the number to be around 3,500 prisoners. A total of 939 Finnish civilians died in air raids and 190 civilians were killed by Soviet partisans.
Germany suffered approximately 84,000 casualties in the Finnish front: 16,400 killed, 60,400 wounded and 6,800 missing. In addition to the original peace terms of restoring the 1940 border, Finland was required to
pay war reparations to the USSR, conduct
domestic war-responsibility trials, cede the municipality of Petsamo and lease the
Porkkala Peninsula to the Soviets, as well as ban
fascist
Fascism ( ) is a far-right, authoritarian, and ultranationalist political ideology and movement. It is characterized by a dictatorial leader, centralized autocracy, militarism, forcible suppression of opposition, belief in a natural soci ...
elements and allow left-wing groups, such as the
Communist Party of Finland. A Soviet-led
Allied Control Commission
Following the termination of hostilities in World War II, the Allies were in control of the defeated Axis countries. Anticipating the defeat of Germany, Italy and Japan, they had already set up the European Advisory Commission and a proposed Far ...
was installed to enforce and monitor the peace agreement in Finland. The requirement to disarm or expel any German troops left on Finnish soil by 15 September 1944 eventually escalated into the
Lapland War
During World War II, the Lapland War (; ; ) saw fighting between Finland and Nazi Germany – effectively from September to November 1944 – in Finland's northernmost region, Lapland. Though the Finns and the Germans had been fighting together ...
between Finland and Germany and the evacuation of the 200,000-strong 20th Mountain Army to Norway.
The Soviet demand for $600 million in war indemnities was reduced to $300 million (equivalent to $ billion in ), most likely because of pressure from the US and the UK. After the ceasefire, the Soviets insisted for the payments to be based on 1938 prices, which doubled the de facto amount. The temporary Moscow Armistice was finalised without changes later in the
1947 Paris Peace Treaties. Henrik Lunde noted that Finland survived the war without losing its independence, unlike many of Germany's allies. Likewise, Helsinki, along with Moscow, was the only capital of a combatant nation that was not occupied in Continental Europe. In the longer term, Peter Provis analysed that by following self-censorship and limited appeasement policies as well as by fulfilling the Soviet demands, Finland avoided the fate of other nations that were annexed by the Soviets.
Because of Soviet pressure, Finland decided not to accept economic aid from the
Marshall Plan
The Marshall Plan (officially the European Recovery Program, ERP) was an American initiative enacted in 1948 to provide foreign aid to Western Europe. The United States transferred $13.3 billion (equivalent to $ in ) in economic recovery pr ...
. On 6 April 1948, Finland and the Soviet Union agreed to sign the Finno-Soviet Treaty of 1948, which was introduced since Finland wanted more political independence from the USSR and the Soviets sought to prevent Finland from being used by Western powers to invade the USSR. On 19 September 1955, Finland and the Soviet Union agreed to extend the Finno-Soviet Treaty of 1948 and the Soviets also agreed to return the Porkkala Peninsula to Finland. In January 1956, twelve years after the beginning of the lease in 1944, the Soviets withdrew from
their naval base on Porkkala and the peninsula was returned to Finnish sovereignty.
Many civilians who had been displaced after the Winter War had moved back into Karelia during the Continuation War and so had to be
evacuated from Karelia again. Of the 260,000 civilians who had returned to Karelia, only 19 chose to remain and become Soviet citizens. Most of the Ingrian Finns, together with
Votes and
Izhorians living in German-occupied Ingria, had been evacuated to Finland in 1943–1944. After the armistice, Finland was forced to return the evacuees. Soviet authorities did not allow the 55,733 returnees to resettle in Ingria and
deported the Ingrian Finns to central regions of the Soviet Union.
Soviet Union
The war is considered a Soviet victory. According to Finnish historians, Soviet casualties in the Continuation War were not accurately recorded and various approximations have arisen. Russian historian
Grigori Krivosheev estimated in 1997 that around 250,000 were killed or missing in action while 575,000 were medical casualties (385,000 wounded and 190,000 sick). Finnish author Nenye and others stated in 2016 that at least 305,000 were confirmed dead, or missing, according to the latest research and the number of wounded certainly exceeded 500,000. Of material losses, authors Jowett and Snodgrass state that 697 Soviet tanks were destroyed, 842 field artillery pieces captured, and 1,600 airplanes destroyed by Finnish fighter planes (1,030 by anti-aircraft fire and 75 by the Navy).
The number of
Soviet prisoners of war in Finland
Soviet prisoners of war in Finland during World War II were captured in two Soviet Union, Soviet-Finland, Finnish conflicts of that period: the Winter War and the Continuation War. The Finns took about 5,700 Prisoner of war, POWs during the Wint ...
was estimated by Finnish historians to be around 64,000, 56,000 of whom were captured in 1941. Around 2,600 to 2,800 Soviet prisoners of war were rendered to Germany in exchange for roughly 2,200 Finnish prisoners of war. Of the Soviet prisoners, at least 18,318 were documented to have died in Finnish
prisoner of war camp
A prisoner-of-war camp (often abbreviated as POW camp) is a site for the containment of enemy fighters captured as prisoners of war by a belligerent power in time of war.
There are significant differences among POW camps, internment camps, ...
s. Finnish archival sources indicate that the highest mortality rates were observed in the largest prisoner of war camps, with mortality rates as high as 41%. For small camps, the comparable mortality rate was under 5%. Nearly 85% of the deaths happened between November 1941 and September 1942 with the highest monthly number of deaths, 2,665, recorded in February 1942. For comparison, the amount of deaths in February 1943 was 92. Historian attributes the amount of Soviet deaths to several factors, which include Finnish unpreparedness to handle unexpectedly large amounts of prisoners resulting in overcrowding, a lack of warm clothing among prisoners captured predominantly during the summer offensive, limited supplies of food (often made worse by camp personnel stealing food for themselves), and disease as a result of the previous factors. According to historian Antti Kujala, approximately 1,200 prisoners were shot, "most" of whom illegally.
The extent of Finland's participation in the siege of Leningrad, and whether Soviet civilian casualties during the siege should be attributed to the Continuation War, is debated and lacks a consensus (estimates of civilian deaths during the siege range from 632,253 to 1,042,000).
In film and literature
Several literary and cinematic arrangements have been made on the basis of the Continuation War. The best-known story about the Continuation War is
Väinö Linna's novel ''
The Unknown Soldier'' (), which was the basis for three films in
1955,
1985
The year 1985 was designated as the International Youth Year by the United Nations.
Events January
* January 1
** The Internet's Domain Name System is created.
** Greenland withdraws from the European Economic Community as a result of a n ...
, and
2017
2017 was designated as the International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development by the United Nations General Assembly.
Events January
* January 1 – Istanbul nightclub shooting: A gunman dressed as Santa Claus opens fire at the ...
. There is also a 1999 film ''
Ambush
An ambush is a surprise attack carried out by people lying in wait in a concealed position. The concealed position itself or the concealed person(s) may also be called an "". Ambushes as a basic military tactics, fighting tactic of soldi ...
'', based on a novel by
Antti Tuuri on the events in
Rukajärvi, Karelia, and a 2007 film ''
1944: The Final Defence'', based on the Battle of Tali-Ihantala. The final stages of the Continuation War were the primary focus of Soviet director
Yuli Raizman
Yuli Yakovlevich Raizman (; December 15, 1903 – December 11, 1994) was a Soviet and Russian film director, screenwriter and Pedagogy, pedagogue. People's Artist of the USSR (1964) and Hero of Socialist Labour (1973).
Career
In 1924 he became a ...
's 1945 documentary entitled ''A Propos of the Truce with Finland'' (). The documentary illustrates the strategic operations that led to the breakthrough on the Karelian Isthmus by the Soviets as well as how Soviet propaganda presented the war overall. The film is titled ''Läpimurto Kannaksella ja rauhanneuvottelut'' in Finnish.
See also
*
Brezhnev Doctrine
*
Cold-weather warfare
Cold-weather warfare, also known as cold-region warfare, arctic warfare or winter warfare, encompasses military operations affected by snow, ice, thawing conditions, or cold, both on land and at sea, as well as the strategies and tactics used ...
* ''
Einsatzkommando Finnland''
*
Lotta Svärd
*
List of wars between democracies
*
List of wars involving Finland
*
Finland–Russia relations
*
Finnish war children
*
Salpa Line
*
Stalin Line
*
Volkhov Front
Notes
References
Citations
Bibliography
English
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* .
*
*
*
*
*
*
Finnish and Russian
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
Finna (search service for information from Finnish archives, libraries and museums)
Finnish Wartime Photograph Archive(under
CC BY 4.0)
{{Authority control
Eastern European theatre of World War II
Finland in World War II
Continuation
In computer science, a continuation is an abstract representation of the control state of a computer program. A continuation implements ( reifies) the program control state, i.e. the continuation is a data structure that represents the computat ...
Soviet Union–United Kingdom military relations
Finland–Russia relations
Invasions of Russia
1941 in Finland
1942 in Finland
1943 in Finland
1944 in Finland
1941 in the Soviet Union
1942 in the Soviet Union
1943 in the Soviet Union
1944 in the Soviet Union
Conflicts in 1941
Conflicts in 1942
Conflicts in 1943
Conflicts in 1944
Battles and operations of World War II involving Norway
Norwegian Campaign
Axis powers
Karelo-Finnish Soviet Socialist Republic
 On 23 August 1939, the Soviet Union and Germany signed the
On 23 August 1939, the Soviet Union and Germany signed the  After the Winter War, Germany was viewed with distrust by the Finnish, as it was considered an ally of the Soviet Union. Nonetheless, the Finnish government sought to restore diplomatic relations with Germany, but also continued its Western-orientated policy and negotiated a war trade agreement with the United Kingdom. The agreement was renounced after the German invasion of Denmark and Norway on 9 April 1940 resulted in the UK cutting all trade and traffic communications with the Nordic countries. With the
After the Winter War, Germany was viewed with distrust by the Finnish, as it was considered an ally of the Soviet Union. Nonetheless, the Finnish government sought to restore diplomatic relations with Germany, but also continued its Western-orientated policy and negotiated a war trade agreement with the United Kingdom. The agreement was renounced after the German invasion of Denmark and Norway on 9 April 1940 resulted in the UK cutting all trade and traffic communications with the Nordic countries. With the  The Northern Front () of the Leningrad Military District was commanded by Lieutenant General
The Northern Front () of the Leningrad Military District was commanded by Lieutenant General  The Army of Norway, or , comprising four divisions totaling 67,000 German soldiers, held the arctic front, which stretched approximately through Finnish Lapland. This army would also be tasked with striking Murmansk and the Kirov (Murmansk) Railway during
The Army of Norway, or , comprising four divisions totaling 67,000 German soldiers, held the arctic front, which stretched approximately through Finnish Lapland. This army would also be tasked with striking Murmansk and the Kirov (Murmansk) Railway during  In the evening of 21 June 1941, German mine-layers hiding in the
In the evening of 21 June 1941, German mine-layers hiding in the  The Finnish plans for the offensive in Ladoga Karelia were finalised on 28 June 1941, and the first stages of the operation began on 10 July. By 16 July, the VI Corps had reached the northern shore of
The Finnish plans for the offensive in Ladoga Karelia were finalised on 28 June 1941, and the first stages of the operation began on 10 July. By 16 July, the VI Corps had reached the northern shore of  The Soviet order to withdraw from Vyborg came too late, resulting in significant losses in materiel, although most of the troops were later evacuated via the Koivisto Islands. After suffering severe losses, the Soviet 23rd Army was unable to halt the offensive, and by 2 September the Finnish Army had reached the old 1939 border. The advance by Finnish and German forces split the Soviet Northern Front into the
The Soviet order to withdraw from Vyborg came too late, resulting in significant losses in materiel, although most of the troops were later evacuated via the Koivisto Islands. After suffering severe losses, the Soviet 23rd Army was unable to halt the offensive, and by 2 September the Finnish Army had reached the old 1939 border. The advance by Finnish and German forces split the Soviet Northern Front into the  The German objective in Finnish Lapland was to take Murmansk and cut the Kirov (Murmansk) Railway running from Murmansk to Leningrad by capturing Salla and
The German objective in Finnish Lapland was to take Murmansk and cut the Kirov (Murmansk) Railway running from Murmansk to Leningrad by capturing Salla and  The ''Wehrmacht'' rapidly advanced deep into Soviet territory early in the Operation Barbarossa campaign, leading the Finnish government to believe that Germany would defeat the Soviet Union quickly. President Ryti envisioned a Greater Finland, where Finns and other
The ''Wehrmacht'' rapidly advanced deep into Soviet territory early in the Operation Barbarossa campaign, leading the Finnish government to believe that Germany would defeat the Soviet Union quickly. President Ryti envisioned a Greater Finland, where Finns and other 
 In the early stages of the war, the Finnish Army overran the former 1939 border, but ceased their advance from the center of Leningrad. Multiple authors have stated that Finland participated in the siege of Leningrad (), but the full extent and nature of their participation is debated and a clear consensus has yet to emerge. American historian
In the early stages of the war, the Finnish Army overran the former 1939 border, but ceased their advance from the center of Leningrad. Multiple authors have stated that Finland participated in the siege of Leningrad (), but the full extent and nature of their participation is debated and a clear consensus has yet to emerge. American historian  On 19 July 1941, the Finns created a military administration in occupied East Karelia with the goal of preparing the region for eventual incorporation into Finland. The Finns aimed to expel the Russian portion of the local population (constituting to about a half), who were deemed "non-national", from the area once the war was over, and replace them with
On 19 July 1941, the Finns created a military administration in occupied East Karelia with the goal of preparing the region for eventual incorporation into Finland. The Finns aimed to expel the Russian portion of the local population (constituting to about a half), who were deemed "non-national", from the area once the war was over, and replace them with  Finland began to seek an exit from the war after the German defeat at the
Finland began to seek an exit from the war after the German defeat at the  On 9 June 1944, the Soviet Leningrad Front launched an offensive against Finnish positions on the Karelian Isthmus and in the area of Lake Ladoga, timed to coincide with
On 9 June 1944, the Soviet Leningrad Front launched an offensive against Finnish positions on the Karelian Isthmus and in the area of Lake Ladoga, timed to coincide with  Finland was required to return to the borders agreed to in the 1940 Moscow Peace Treaty, demobilise its armed forces, fulfill war reparations and cede the municipality of Petsamo. The Finns were also required to end any diplomatic relations with Germany immediately and to expel the from Finnish territory by 15 September 1944; any troops remaining were to be disarmed, arrested and turned over to the Allies. The Finnish Parliament accepted those terms in a secret meeting on 2 September and requested for official negotiations for an armistice to begin. The Finnish Army implemented a ceasefire at 8:00 a.m. Helsinki time on 4 September. The Red Army followed suit a day later. On 14 September, a delegation led by Finnish Prime Minister Antti Hackzell and Foreign Minister Carl Enckell began negotiating, with the Soviet Union and the United Kingdom, the final terms of the Moscow Armistice, which eventually included additional stipulations from the Soviets. They were presented by Molotov on 18 September and accepted by the Finnish Parliament a day later.
Finland was required to return to the borders agreed to in the 1940 Moscow Peace Treaty, demobilise its armed forces, fulfill war reparations and cede the municipality of Petsamo. The Finns were also required to end any diplomatic relations with Germany immediately and to expel the from Finnish territory by 15 September 1944; any troops remaining were to be disarmed, arrested and turned over to the Allies. The Finnish Parliament accepted those terms in a secret meeting on 2 September and requested for official negotiations for an armistice to begin. The Finnish Army implemented a ceasefire at 8:00 a.m. Helsinki time on 4 September. The Red Army followed suit a day later. On 14 September, a delegation led by Finnish Prime Minister Antti Hackzell and Foreign Minister Carl Enckell began negotiating, with the Soviet Union and the United Kingdom, the final terms of the Moscow Armistice, which eventually included additional stipulations from the Soviets. They were presented by Molotov on 18 September and accepted by the Finnish Parliament a day later.
 The motivations for the Soviet peace agreement with Finland are debated. Several Western historians stated that the original Soviet designs for Finland were no different from those for the Baltic countries. American political scientist
The motivations for the Soviet peace agreement with Finland are debated. Several Western historians stated that the original Soviet designs for Finland were no different from those for the Baltic countries. American political scientist  According to Finnish historians, the casualties of the Finnish Defence Forces amounted to 63,204 dead or missing and around 158,000 wounded. Officially, the Soviets captured 2,377 Finnish prisoners-of-war, but Finnish researchers estimated the number to be around 3,500 prisoners. A total of 939 Finnish civilians died in air raids and 190 civilians were killed by Soviet partisans. Germany suffered approximately 84,000 casualties in the Finnish front: 16,400 killed, 60,400 wounded and 6,800 missing. In addition to the original peace terms of restoring the 1940 border, Finland was required to pay war reparations to the USSR, conduct domestic war-responsibility trials, cede the municipality of Petsamo and lease the Porkkala Peninsula to the Soviets, as well as ban
According to Finnish historians, the casualties of the Finnish Defence Forces amounted to 63,204 dead or missing and around 158,000 wounded. Officially, the Soviets captured 2,377 Finnish prisoners-of-war, but Finnish researchers estimated the number to be around 3,500 prisoners. A total of 939 Finnish civilians died in air raids and 190 civilians were killed by Soviet partisans. Germany suffered approximately 84,000 casualties in the Finnish front: 16,400 killed, 60,400 wounded and 6,800 missing. In addition to the original peace terms of restoring the 1940 border, Finland was required to pay war reparations to the USSR, conduct domestic war-responsibility trials, cede the municipality of Petsamo and lease the Porkkala Peninsula to the Soviets, as well as ban