Congenital Myasthenia Gravis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Myasthenia gravis (MG) is a long-term
File:Synapse diag4.png, Neuromuscular junction: 1.
 Muscle fibers of people with MG are easily fatigued, which the repetitive nerve stimulation test can help diagnose. In single-fiber
Muscle fibers of people with MG are easily fatigued, which the repetitive nerve stimulation test can help diagnose. In single-fiber

 About 10% of people with generalized MG are considered treatment-refractory. Autologous
About 10% of people with generalized MG are considered treatment-refractory. Autologous
neuromuscular junction disease
Neuromuscular junction disease is a medical condition where the normal conduction through the neuromuscular junction fails to function correctly.
Autoimmune
In diseases such as myasthenia gravis, the end plate potential (EPP) fails to effectively ...
that leads to varying degrees of skeletal muscle weakness
Muscle weakness is a lack of muscle strength. Its causes are many and can be divided into conditions that have either true or perceived muscle weakness. True muscle weakness is a primary symptom of a variety of skeletal muscle diseases, includ ...
. The most commonly affected muscles are those of the eye
An eye is a sensory organ that allows an organism to perceive visual information. It detects light and converts it into electro-chemical impulses in neurons (neurones). It is part of an organism's visual system.
In higher organisms, the ey ...
s, face
The face is the front of the head that features the eyes, nose and mouth, and through which animals express many of their emotions. The face is crucial for human identity, and damage such as scarring or developmental deformities may affect th ...
, and swallowing. It can result in double vision
Diplopia is the simultaneous perception of two images of a single object that may be displaced in relation to each other. Also called double vision, it is a loss of visual focus under regular conditions, and is often voluntary. However, when occ ...
, drooping eyelid
Ptosis, also known as blepharoptosis, is a drooping or falling of the upper eyelid. This condition is sometimes called "lazy eye", but that term normally refers to the condition amblyopia. If severe enough and left untreated, the drooping eyeli ...
s, and difficulties in talking and walking. Onset can be sudden. Those affected often have a large thymus
The thymus (: thymuses or thymi) is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, T cells mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. The thymus ...
or develop a thymoma
A thymoma is a tumor originating from the epithelial cells of the thymus that is considered a rare neoplasm. Thymomas are frequently associated with neuromuscular disorders such as myasthenia gravis; thymoma is found in 20% of patients with myast ...
.
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease
An autoimmune disease is a condition that results from an anomalous response of the adaptive immune system, wherein it mistakenly targets and attacks healthy, functioning parts of the body as if they were foreign organisms. It is estimated tha ...
of the neuromuscular junction which results from antibodies
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as bacteria and viruses, including those that caus ...
that block or destroy nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, or nAChRs, are Receptor (biochemistry), receptor polypeptides that respond to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Nicotinic receptors also respond to drugs such as the agonist nicotine. They are found in the c ...
s (AChR) at the junction between the nerve and muscle. This prevents nerve impulse
An action potential (also known as a nerve impulse or "spike" when in a neuron) is a series of quick changes in voltage across a cell membrane. An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific Cell (biology), cell rapidly ri ...
s from triggering muscle contractions. Most cases are due to immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) and IgG3 antibodies that attack AChR in the postsynaptic membrane, causing complement-mediated damage and muscle weakness. Rarely, an inherited genetic defect
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosome abnormality. Although polygenic disorders are ...
in the neuromuscular junction
A neuromuscular junction (or myoneural junction) is a chemical synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber.
It allows the motor neuron to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction.
Muscles require innervation to ...
results in a similar condition known as congenital myasthenia. Babies of mothers with myasthenia may have symptoms during their first few months of life, known as neonatal myasthenia or more specifically transient neonatal myasthenia gravis
Transient neonatal myasthenia gravis, i.e., TNMG (also termed neonatal myasthenia gravis), and its more severe form, fetal acetylcholine receptor inactivation syndrome (i.e., FARIS), is one of the various types of myasthenia gravis (i.e., MG). MG ...
. Diagnosis can be supported by blood tests for specific antibodies, the edrophonium test, electromyography
Electromyography (EMG) is a technique for evaluating and recording the electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles. EMG is performed using an instrument called an electromyograph to produce a record called an electromyogram. An electromyo ...
(EMG), or a nerve conduction study
A nerve conduction study (NCS) is a medical test, medical diagnostic test commonly used to evaluate the function, especially the ability of action potential, electrical conduction, of the motor nerve, motor and sensory nerves of the human body. Th ...
.
Mild forms of Myasthenia gravis may be treated with medications known as acetylcholinesterase inhibitor
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) also often called cholinesterase inhibitors, inhibit the enzyme acetylcholinesterase from breaking down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine into choline and acetate, thereby increasing both the level an ...
s, such as neostigmine
Neostigmine, sold under the brand name Bloxiverz, among others, is a medication used to treat myasthenia gravis, Ogilvie syndrome, and urinary retention without the presence of a blockage. It is also used in anaesthesia to end the effects of n ...
and pyridostigmine
Pyridostigmine is a medication used to treat myasthenia gravis and underactive bladder. It is also used together with atropine to end the effects of neuromuscular blocking medication of the non-depolarizing type. It is also used off-label to t ...
. Immunosuppressants
Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent the activity of the immune system.
Classification
Immunosuppressive drugs can be classified ...
, such as prednisone
Prednisone is a glucocorticoid medication mostly used to immunosuppressive drug, suppress the immune system and decrease inflammation in conditions such as asthma, COPD, and rheumatologic diseases. It is also used to treat high blood calcium ...
or azathioprine
Azathioprine, sold under the brand name Imuran, among others, is an immunosuppressive medication. It is used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, and systemic lupus er ...
, may also be required for more severe symptoms that acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are insufficient to treat. The surgical removal of the thymus may improve symptoms in certain cases. Plasmapheresis
Plasmapheresis (from the Greek language, Greek ŽĆ╬╗╬¼Žā╬╝╬▒, ''plasma'', something molded, and ß╝ĆŽå╬▒╬»Žü╬ĄŽā╬╣Žé ''aphairesis'', taking away) is the removal, treatment, and return or exchange of blood plasma or components thereof from and to the ...
and high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin
Immunoglobulin therapy is the use of a mixture of antibodies (normal human immunoglobulin) to treat several health conditions. These conditions include primary immunodeficiency, immune thrombocytopenic purpura, chronic inflammatory demyelinat ...
may be used when oral medications are insufficient to treat severe symptoms, including during sudden flares of the condition. If the breathing muscles become significantly weak, mechanical ventilation
Mechanical ventilation or assisted ventilation is the Medicine, medical term for using a ventilator, ventilator machine to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move air into and out of the lungs, wit ...
may be required. Once intubated
Intubation (sometimes entubation) is a medical procedure involving the insertion of a tube into the body. Most commonly, intubation refers to tracheal intubation, a procedure during which an endotracheal tube is inserted into the trachea to supp ...
acetylcholinesterase inhibitors may be temporarily held to reduce airway secretions.
Myasthenia gravis affects 50 to 200 people per million. It is newly diagnosed in 3 to 30 people per million each year. Diagnosis has become more common due to increased awareness. Myasthenia gravis most commonly occurs in women under the age of 40 and in men over the age of 60. It is uncommon in children. With treatment, most live to an average life expectancy
Human life expectancy is a statistical measure of the estimate of the average remaining years of life at a given age. The most commonly used measure is ''life expectancy at birth'' (LEB, or in demographic notation ''e''0, where '' ...
. The word is from the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
''mys'', "muscle" and ''asthenia'' "weakness", and the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
''gravis'', "serious".
Signs and symptoms
The initial, main symptom in MG is painlessweakness
Weakness is a symptom of many different medical conditions. The causes are many and can be divided into conditions that have true or perceived muscle weakness. True muscle weakness is a primary symptom of a variety of skeletal muscle diseases, ...
of specific muscles, not fatigue. The muscle weakness becomes progressively worse (fatigue
Fatigue is a state of tiredness (which is not sleepiness), exhaustion or loss of energy. It is a signs and symptoms, symptom of any of various diseases; it is not a disease in itself.
Fatigue (in the medical sense) is sometimes associated wit ...
) during periods of physical activity and improves after periods of rest. Typically, the weakness and fatigue are worse toward the end of the day. Myasthenia gravis generally starts with ocular (eye) weakness; it might then progress to a more severe generalized form, characterized by weakness in the extremities or in muscles that govern basic life functions.
Eyes
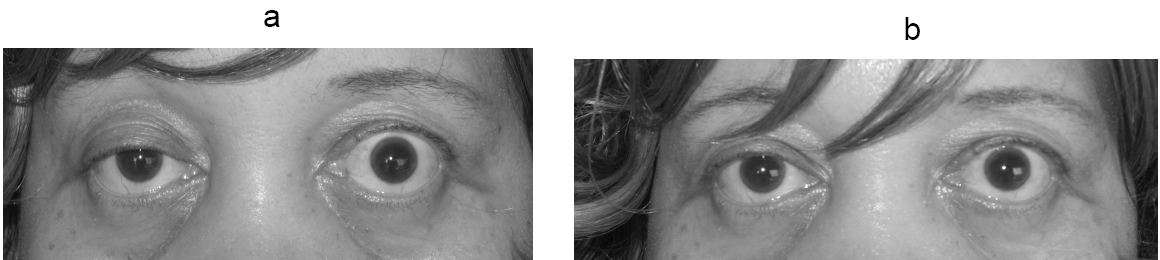
In about two-thirds of individuals, the initial symptom of MG is related to the muscles around the eye. Eyelid drooping ( ptosis may occur due to weakness of m.levator palpebrae superioris
The levator palpebrae superioris () is the muscle in the orbit that elevates the upper eyelid.
Structure
The levator palpebrae superioris originates from inferior surface of the lesser wing of the sphenoid bone, just above the optic foramen. It ...
) and double vision (diplopia
Diplopia is the simultaneous perception of two images of a single object that may be displaced in relation to each other. Also called double vision, it is a loss of visual focus under regular conditions, and is often voluntary. However, when occ ...
, due to weakness of the extraocular muscles
The extraocular muscles, or extrinsic ocular muscles, are the seven extrinsic muscles of the eye in human eye, humans and other animals. Six of the extraocular muscles, the four recti muscles, and the superior oblique muscle, superior and inferior ...
). Eye symptoms tend to get worse when watching television, reading, or driving, particularly in bright conditions. Consequently, some affected individuals choose to wear sunglasses. The term "ocular myasthenia gravis" describes a subtype of MG where muscle weakness is confined to the eyes, i.e. extraocular muscles, m. levator palpebrae superioris, and m. orbicularis oculi
The orbicularis oculi is a sphincter-like muscle in the face that closes the eyelids. It arises from the nasal part of the frontal bone, from the frontal process of the maxilla in front of the lacrimal groove, and from the anterior surface and b ...
. This subtype may evolve into generalized MG, usually after a few years. If a patient with ocular myasthenia gravis does not generalize for 3 or more years after the onset of symptoms, then generalized MG is unlikely to occur.
Eating
The weakness of the muscles involved in swallowing may lead to swallowing difficulty (dysphagia
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under " symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right.
It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or l ...
). Typically, this means that some food may be left in the mouth after an attempt to swallow, or food and liquids may regurgitate into the nose rather than go down the throat (velopharyngeal insufficiency
Velopharyngeal insufficiency is a disorder of structure that causes a failure of the velum (soft palate) to close against the posterior Pharynx, pharyngeal wall (back wall of the throat) during speech in order to close off the nasal cavity durin ...
). Weakness of the muscles that move the jaw (muscles of mastication
The four classical muscles of mastication elevate the mandible (closing the jaw) and move it forward/backward and laterally, facilitating biting and chewing. Other muscles are responsible for opening the jaw, namely the geniohyoid, mylohyoid, an ...
) may cause difficulty chewing. In individuals with MG, chewing tends to become more tiring when chewing tough, fibrous foods. Difficulty in swallowing, chewing, and speaking is the first symptom in about one-sixth of individuals.
Speaking
Weakness of the muscles involved in speaking may lead todysarthria
Dysarthria is a speech sound disorder resulting from neurological injury of the motor component of the motorŌĆōspeech system and is characterized by poor articulation of phonemes. It is a condition in which problems effectively occur with the ...
and hypophonia
Hypophonia is soft speech, especially resulting from a lack of coordination in the vocal musculature. This condition is a common presentation in Parkinson's disease. This condition is generally treated with voice training programs, use of shorter s ...
. Speech may be slow and slurred, or have a nasal quality. In some cases, a singing hobby or profession must be abandoned.
Head and neck
Due to weakness of themuscles of facial expression
The facial muscles are a group of striated skeletal muscles supplied by the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII) that, among other things, control facial expression. These muscles are also called mimetic muscles. They are only found in mammals, alth ...
and muscles of mastication, facial weakness may manifest as the inability to hold the mouth closed (the "hanging jaw sign") and as a snarling expression when attempting to smile. With drooping eyelids, facial weakness may make the individual appear sleepy or sad. Difficulty in holding the head upright may occur.
Other
The muscles that control breathing and limb movements can also be affected; rarely do these present as the first symptoms of MG, but develop over months to years. In a myasthenic crisis, aparalysis
Paralysis (: paralyses; also known as plegia) is a loss of Motor skill, motor function in one or more Skeletal muscle, muscles. Paralysis can also be accompanied by a loss of feeling (sensory loss) in the affected area if there is sensory d ...
of the respiratory muscles occurs, necessitating assisted ventilation
Mechanical ventilation or assisted ventilation is the medical term for using a ventilator machine to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move air into and out of the lungs, with the main goal of he ...
to sustain life. Crises may be triggered by various biological stressors such as infection, fever, an adverse reaction to medication, or emotional stress.
Causes
Medications that cause or worsen myasthenia gravis
Antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
: In the macrolide
Macrolides are a class of mostly natural products with a large macrocyclic lactone ring to which one or more deoxy sugars, usually cladinose and desosamine, may be attached. Macrolides belong to the polyketide class of natural products. ...
family of antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
, azithromycin
Azithromycin, sold under the brand names Zithromax (in oral form) and Azasite (as an eye drop), is an antibiotic medication used for the treatment of several bacterial infections. This includes otitis media, middle ear infections, strep throa ...
, telithromycin
Telithromycin is the first ketolide antibiotic to enter clinical use and is sold under the brand name of Ketek. It is used to treat community acquired pneumonia of mild to moderate severity. After significant safety concerns, the US Food and Dru ...
(which is no longer available in the U.S. market), and erythromycin
Erythromycin is an antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes respiratory tract infections, skin infections, chlamydia infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, and syphilis. It may also be used ...
are reported to exacerbate MG. In the fluoroquinolone
Quinolone antibiotics constitute a large group of broad-spectrum bacteriocidals that share a bicyclic core structure related to the substance 4-quinolone. They are used in human and veterinary medicine to treat bacterial infections, as well ...
antibiotic family, ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic used to treat a number of bacterial infections. This includes bone and joint infections, intra-abdominal infections, certain types of infectious diarrhea, respiratory tract infections, skin ...
, norfloxacin
Norfloxacin, sold under the brand name Noroxin among others, is an antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteri ...
, ofloxacin
Ofloxacin is a quinolone antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. When taken Oral administration, by mouth or intravenous, injection into a vein, these include pneumonia, cellulitis, urinary tract infections, prost ...
, and moxifloxacin
Moxifloxacin is an antibiotic, used to treat bacterial infections, including pneumonia, conjunctivitis, endocarditis, tuberculosis, and sinusitis. It can be given by mouth, by injection into a vein, and as an eye drop.
Common side effec ...
are reported to exacerbate MG. And, In the aminoglycoside
Aminoglycoside is a medicinal and bacteriologic category of traditional Gram-negative antibacterial medications that inhibit protein synthesis and contain as a portion of the molecule an amino-modified glycoside (sugar). The term can also refer ...
family of antibiotics, gentamicin
Gentamicin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic used to treat several types of bacterial infections. This may include bone infections, endocarditis, pelvic inflammatory disease, meningitis, pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and sepsis amo ...
, streptomycin
Streptomycin is an antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections, including tuberculosis, Mycobacterium avium complex, ''Mycobacterium avium'' complex, endocarditis, brucellosis, Burkholderia infection, ''Burkholderia'' i ...
, and neomycin
Neomycin, also known as framycetin, is an aminoglycoside antibiotic that displays bactericidal activity against Gram-negative aerobic bacilli and some anaerobic bacilli where resistance has not yet arisen. It is generally not effective against ...
are reported to exacerbate MG. The aminoglycoside tobramycin
Tobramycin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic derived from '' Streptomyces tenebrarius'' that is used to treat various types of bacterial infections, particularly Gram-negative infections. It is especially effective against species of ''Pseudomo ...
has not been reported to exacerbate MG and may be used in people that require aminoglycoside treatment. Because of the rarity or absent reports on their exacerbation of MG, the following antibiotics are considered safe to use in people with myasthenia gravis: the cephalosporin
The cephalosporins (sg. ) are a class of ╬▓-lactam antibiotics originally derived from the fungus '' Acremonium'', which was previously known as ''Cephalosporium''.
Together with cephamycins, they constitute a subgroup of ╬▓-lactam antibio ...
class of drugs, sulfa drug
Sulfonamide is a functional group (a part of a molecule) that is the basis of several groups of drugs, which are called sulphonamides, sulfa drugs or sulpha drugs. The original antibacterial sulfonamides are synthetic antimicrobial agents th ...
s, the tetracycline group of drugs, clindamycin
Clindamycin is a lincosamide antibiotic medication used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections, including osteomyelitis (bone) or joint infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, strep throat, pneumonia, acute otitis media (mi ...
, polymyxin B
Polymyxin B, sold under the brand name Poly-Rx among others, is an antibiotic used to treat meningitis, pneumonia, sepsis, and urinary tract infections. While it is useful for many Gram negative infections, it is not useful for Gram positive infe ...
, and nitrofurantoin
Nitrofurantoin, sold under the brand name Macrobid among others, is an antibacterial medication of the nitrofuran class used to treat urinary tract infections (UTIs), although it is not as effective for kidney infections. It is taken by mouth ...
.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors: Immune checkpoint inhibitors promote certain types of autoimmune responses by blocking checkpoint pathways that inhibit these responses. They are used to treat cancers that promote their own growth and spread by stimulating checkpoint pathways. These checkpoint inhibitors include pembrolizumab
Pembrolizumab, sold under the brand name Keytruda, is a humanized antibody, more specifically a PD-1 inhibitor, used in cancer immunotherapy that treats melanoma, lung cancer, head and neck cancer, Hodgkin lymphoma, stomach cancer, cerv ...
, nivolumab
Nivolumab, sold under the brand name Opdivo, is an anti-cancer medication in the class of immune checkpoint inhibitors. It selectively binds and blocks the programmed death-1 (PD-1) receptor on T cells, thereby facilitating their activation ...
, ipilimumab
Ipilimumab, sold under the brand name Yervoy, is a monoclonal antibody medication that works to activate the immune system by targeting CTLA-4, a protein receptor that downregulates the immune system.
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) can recogniz ...
, avelumab, atezolizumab
Atezolizumab, sold under the brand name Tecentriq among others, is a monoclonal antibody medication used to treat urothelial carcinoma, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), small cell lung cancer (SCLC), hepatocellular carcinoma and alveolar so ...
, and durvalumab
Durvalumab, sold under the brand name Imfinzi, is an anti-cancer medication used for treatment of various types of cancer. It was Drug development, developed by MedImmune, Medimmune/AstraZeneca. It is a human immunoglobulin G1 kappa (IgG1╬║) mo ...
. From a total 5,898 patients who received these drugs, 52 developed new onset MG and 11 had a flare of their preexisting MG. The symptoms of MG developed within 6 days to 16 weeks (median time 4ŌĆēweeks). Their medicine-induced MG symptoms were often severe with 29 patients developing respiratory failure
Respiratory failure results from inadequate gas exchange by the respiratory system, meaning that the arterial oxygen, carbon dioxide, or both cannot be kept at normal levels. A drop in the oxygen carried in the blood is known as hypoxemia; a r ...
that required mechanical ventilation
Mechanical ventilation or assisted ventilation is the Medicine, medical term for using a ventilator, ventilator machine to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move air into and out of the lungs, wit ...
. Other studies have reported that these checkpoint inhibitors cause respiratory failure in 45% and death in 25ŌĆō40% of patients with MG.
Statin
Statins (or HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors) are a class of medications that lower cholesterol. They are prescribed typically to people who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease.
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) carriers of cholesterol play ...
s: Statins are drugs that lower blood cholesterol
Cholesterol is the principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body Tissue (biology), tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in Animal fat, animal fats and oils.
Cholesterol is biosynthesis, biosynthesized by all anima ...
levels in order to reduce the risk of developing a cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina, heart attack), heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumati ...
due to atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a pattern of the disease arteriosclerosis, characterized by development of abnormalities called lesions in walls of arteries. This is a chronic inflammatory disease involving many different cell types and is driven by eleva ...
In a 2019 review of 169 patients who were reported to develop myasthenia gravis or had worsened myasthenia gravis symptoms while taking a statin (i.e., simvastatin
Simvastatin, sold under the brand name Zocor among others, is a statin, a type of lipid-lowering medication. It is used along with exercise, diet, and weight loss to decrease hyperlipidemia, elevated lipid levels. It is also used to decrease t ...
, atorvastatin
Atorvastatin, sold under the brand name Lipitor among others, is a statin medication used to prevent cardiovascular disease in those at high risk and to treat abnormal lipid levels. For the prevention of cardiovascular disease, statins are a ...
, rosuvastatin
Rosuvastatin, sold under the brand name Crestor among others, is a statin medication, used to prevent cardiovascular disease in those at high risk and treat dyslipidemia, abnormal lipids. It is recommended to be used with dietary changes, exer ...
, pravastatin
Pravastatin, sold under the brand name Pravachol among others, is a statin medication, used for preventing cardiovascular disease in those at high risk and treating abnormal lipids. It is suggested to be used together with diet changes, exerc ...
, lovastatin
Lovastatin, sold under the brand name Mevacor among others, is a statin medication, to treat high blood cholesterol and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Its use is recommended together with lifestyle changes. It is taken by mouth.
...
, or fluvastatin
Fluvastatin is a member of the statin drug class, used to treat hypercholesterolemia and to prevent cardiovascular disease.
It was patented in 1982 and approved for medical use in 1994. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essentia ...
), 138 had developed generalized myasthenia gravis, 13 had developed ocular myasthenia gravis, and 18 had worsening of their myasthenia gravis. Following discontinuance of the statin and treatment of their myasthenia gravis, 63 patients fully recovered, 27 patients were recovering, 19 patients had not yet recovered, 5 patients recovered but had ongoing symptoms, 1 patient had died, and there was no follow-up data for 54 patients. Among these cases, 56% were considered to be serious. A 2024 study evaluated 593 individuals who had myasthenia gravis and 790,399 individuals who did not have myasthenia gravis after being treated with one of the previously cited statins or with pitavastatin
Pitavastatin (usually as a calcium salt) is a member of the blood cholesterol lowering medication class of statins.
Pitavastatin is an inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase, the enzyme that catalyses the first step of cholesterol synthesis.
It was ...
or pravastatin
Pravastatin, sold under the brand name Pravachol among others, is a statin medication, used for preventing cardiovascular disease in those at high risk and treating abnormal lipids. It is suggested to be used together with diet changes, exerc ...
. The statin-treatment caused small but statistically significant increases in numbers of exacerbations of myasthenia gravis as well as new onsets of myasthenia gravis in individuals without the disorder. The development of myasthenia gravis in individuals without myasthenia gravis appeared to be more likely in individuals over 60 years of age. Six non-statin cholesterol-lowering drugs, nicotinic acid
Nicotinic acid, or niacin, is an organic compound and a vitamer of vitamin B3, an essential human nutrient. It is produced by plants and animals from the amino acid tryptophan.
Nicotinic acid is also a prescription medication. Amounts f ...
, cholestyramine
Colestyramine ( INN) or cholestyramine ( USAN) (trade names Questran, Questran Light, Cholybar, Olestyr, Quantalan, Vasosan) is a bile acid sequestrant, which binds bile in the gastrointestinal tract to prevent its reabsorption. It is a strong i ...
, colestipol
Colestipol (trade names Colestid, Cholestabyl) is a bile acid sequestrant used to lower blood cholesterol, specifically low-density lipoprotein (LDL). It is also used to reduce stool volume and frequency, and in the treatment of chronic diarrhea. ...
, colesevelam
Colesevelam is a bile acid sequestrant administered orally. It was developed by GelTex Pharmaceuticals and later acquired by Genzyme. It is marketed in the US by Daiichi Sankyo under the brand name Welchol and elsewhere by Genzyme as Cholesta ...
, alirocumab
Alirocumab, sold under the brand name Praluent, is a medication used as a second-line treatment for high cholesterol for adults whose cholesterol is not controlled by diet and statin treatment. It is a human monoclonal antibody that belongs to ...
, and evolocumab
Evolocumab, sold under the brand name Repatha, is a monoclonal antibody that is an immunotherapy medication for the treatment of hyperlipidemia.
Evolocumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody that inhibits proprotein convertase subtilisin/ke ...
, have been used in patients without causing or worsening myasthenia gravis.
Beta blockers
Beta blockers, also spelled ╬▓-blockers, are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmia), and to protect the heart from a second heart attack after a first heart attack (secondary prevention). ...
: Beta blockers (i.e., ╬▓-blockers) are drugs that block the binding of two stress hormones
Stress hormones are secreted by endocrine glands to modify one's internal environment during times of stress. By performing various functions such as mobilizing energy sources, increasing heart rate, and downregulating metabolic processes which ...
, epinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands a ...
and norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic compound, organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and human body, body as a hormone, neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. The ...
, to their target beta receptors. They are used to decrease the heart rate, reduce the force of heart contractions, and relax blood vessels in order to lower blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of Circulatory system, circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term ...
and reduce the workload on the heart. In one study the odds of an MG exacerbation after taking a beta blocker was increased 2.7-fold compared with MG patients not taking a beta blocker. These exacerbations generally did not occur immediately after their usage and therefore may have reflected other comorbidities in MG patients being treated with beta blockers. In a study of 20 MG patients treated with a beta blocker, 3 who received oral metoprolol
Metoprolol, sold under the brand name Lopressor among others, is a medication used to treat angina, high blood pressure and a number of conditions involving an abnormally fast heart rate. It is also used to prevent further heart problems afte ...
, 9 who received intravenous metoprolol, 1 who received oral labetalol
Labetalol is a medication used to treat hypertension, high blood pressure and in long term management of angina. This includes essential hypertension, hypertensive emergencies, and hypertension of pregnancy. In essential hypertension it is gene ...
, and 9 who received intravenous labetalol, only one (i.e., 5%) of these 20 patients (who received intravenous labetalol) reacted with an exacerbation of myasthenia gravis symptoms. It is suggested that ╬▓-blockers should be avoided in MG patients but may be used when they are carefully monitored.
Ia antiarrhythmic agents: A type Ia antiarrhythmic agent (see Vaughan Williams classification
Antiarrhythmic agents, also known as cardiac dysrhythmia medications, are a class of drugs that are used to suppress abnormally fast rhythms (tachycardias), such as atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia and ventricular tachycardia.
M ...
), i.e., procainamide
Procainamide (PCA) is a medication of the antiarrhythmic class used for the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias. It is a sodium channel blocker of cardiomyocytes; thus it is classified by the Vaughan Williams classification system as class Ia. ...
, which is used to treat cardiac arrhythmia
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. Essentially, this is anything but normal sinus rhythm. A resting heart rate that is too fast ŌĆō above 100 beat ...
s, has caused respiratory failure
Respiratory failure results from inadequate gas exchange by the respiratory system, meaning that the arterial oxygen, carbon dioxide, or both cannot be kept at normal levels. A drop in the oxygen carried in the blood is known as hypoxemia; a r ...
in people with myasthenia gravis who, prior to being treated with it, did not have respiratory symptoms. Furthermore, this drug has caused MG-like symptoms in patients who have kidney failure but do not have MG. And, procainamide worsened muscle dysfunction in a rat model of human MG.
Depolarizing neuromuscular blockers: Depolarizing neuromuscular blockers suppress the neurons' signaling at neuromuscular junctions thereby reducing the affected skeletal muscles contractibility. These blockers are used as muscle relaxants in patients undergoing surgery. Succinylcholine
Suxamethonium chloride (brand names Scoline and Sucostrin, among others), also known as suxamethonium or succinylcholine, or simply sux in medical abbreviation, is a medication used to cause short-term paralysis as part of general anesthesia. T ...
is the only depolarizing neuromuscular blocker available in the U.S. market. Succinylcholine's ability to induce or worsen MG is unclear. It has been suggested to cause life-threatening side effects such as rhabdomyolysis
Rhabdomyolysis (shortened as rhabdo) is a condition in which damaged skeletal muscle breaks down rapidly. Symptoms may include muscle pains, weakness, vomiting, and confusion. There may be tea-colored urine or an irregular heartbeat. Some o ...
, myotonia
Myotonia is a symptom of a small handful of certain neuromuscular disorders characterized by delayed relaxation (prolonged contraction) of the skeletal muscles after voluntary contraction or electrical stimulation, and the muscle shows an abnor ...
, and hyperkalemia
Hyperkalemia is an elevated level of potassium (K+) in the blood. Normal potassium levels are between 3.5 and 5.0 mmol/L (3.5 and 5.0 mEq/L) with levels above 5.5mmol/L defined as hyperkalemia. Typically hyperkalemia does not cause symptoms. Oc ...
in patients with muscle disease although the role of succinylcholine in causing these side effects also remains unclear. Until more evidence on these issues becomes available and since there are other neuromuscular blocking agents without these deleterious side effects, the use of succinylcholine in MG (and other neuromuscular disorders) should probably be avoided where feasible.
Inhalation anesthetics: Inhalation anesthetics are general anesthetic
General anaesthetics (or anesthetics) are often defined as compounds that induce a loss of consciousness in humans or loss of righting reflex in animals. Clinical definitions are also extended to include an induced coma that causes lack of aware ...
s that are delivered by inhalation generally for patients undergoing surgery. People with myasthenia gravis undergoing surgery with inhaled anesthetics (i.e., halothane
Halothane, sold under the brand name Fluothane among others, is a general anaesthetic. It can be used to induce or maintain anaesthesia. One of its benefits is that it does not increase the production of saliva, which can be particularly useful ...
, isoflurane
Isoflurane, sold under the brand name Forane among others, is a halogenated ether used as a general anesthetic. It can be used to start or maintain anesthesia; however, other medications are often used to start anesthesia, due to airway irritat ...
, enflurane
Enflurane (2-chloro-1,1,2-trifluoroethyl difluoromethyl ether) is a halogenated ether. Developed by Ross Terrell in 1963, it was first used clinically in 1966. It was increasingly used for inhalational anesthesia during the 1970s and 1980s but ...
, and sevoflurane
Sevoflurane, sold under the brand name Sevorane, among others, is a sweet-smelling, nonflammable, highly fluorinated methyl isopropyl ether used as an inhalational anaesthetic for induction and maintenance of general anesthesia. After desflu ...
) may develop neuromuscular blockage and have an increased incidence of developing a life-threatening myasthenia crisis which must be treated by prolonged mechanical ventilation. In a study of 795 people with myasthenia gravis undergoing surgical removal of their thymus under general anesthesia, sugammadex
Sugammadex, sold under the brand name Bridion, is a medication for the reversal of neuromuscular blockade induced by rocuronium and vecuronium in general anaesthesia. It is the first selective relaxant binding agent (SRBA). It is marketed by ...
, a neuromuscular-blocking drug
Neuromuscular-blocking drugs, or Neuromuscular blocking agents (NMBAs), block transmission at the neuromuscular junction, causing paralysis of the affected skeletal muscles. This is accomplished via their action on the post-synaptic acetylcho ...
(i.e., a drug that reverses neuromuscular blockade) significantly reduced the development of this crisis.
Glucocorticoids
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebra ...
: Glucocorticoids are anti-inflammatory agents that in initial studies were used at high dosages and found to worsen MG in 25-75% of cases. However, further studies found that glucocorticoids do have favorable effects on MG when taken long-term. Two glucocorticoids, oral prednisone
Prednisone is a glucocorticoid medication mostly used to immunosuppressive drug, suppress the immune system and decrease inflammation in conditions such as asthma, COPD, and rheumatologic diseases. It is also used to treat high blood calcium ...
and prednisolone
Prednisolone is a corticosteroid, a steroid hormone used to treat certain types of allergies, inflammation, inflammatory conditions, autoimmune disorders, and cancers, Electrolyte imbalance, electrolyte imbalances and skin conditions. Some of ...
, are now the first line immunosuppressive
Immunosuppression is a reduction of the activation or efficacy of the immune system. Some portions of the immune system itself have immunosuppressive effects on other parts of the immune system, and immunosuppression may occur as an adverse react ...
treatment for MG. To avoid exacerbation of MG, it is recommended that the corticosteroids should be started at a low dose and gradually increased to the dose achieving maximal responses. To achieve a faster therapeutic responses in cases with severe MG symptoms, it has been recommended to start with high doses of oral or intravenous glucocorticoids after first treating patients with plasmapheresis or intravenous immunoglobulin therapy, each of which reduces the chance of having a severe reaction to the corticosteroids.
Calcium channel blocker
Calcium channel blockers (CCB), calcium channel antagonists or calcium antagonists are a group of medications that disrupt the movement of calcium () through calcium channels. Calcium channel blockers are used as antihypertensive drugs, i.e., as ...
s: Calcium channel blockers (e.g., felodipine
Felodipine is a medication of the calcium channel blocker type that is used to treat high blood pressure.
It was patented in 1978, and approved for medical use in 1988.
Medical uses
Felodipine is used to treat high blood pressure and stable ...
, nifedipine
Nifedipine ( ), sold under the brand name Procardia among others, is a calcium channel blocker medication used to manage angina, high blood pressure, Raynaud's phenomenon, and premature labor. It is one of the treatments of choice for Prinzme ...
, and verapamil
Verapamil, sold under various trade names, is a calcium channel blocker medication used for the treatment of high blood pressure, angina (chest pain from not enough blood flow to the heart), and supraventricular tachycardia. It may also be use ...
) are drugs that lower blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of Circulatory system, circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term ...
in patients with hypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms i ...
. Felodipine and nifedipine are reported to worsen MG and nifedipine and verapamil are reported to cause respiratory failure in patients with severe generalized MG.
Penicillamine
Penicillamine, sold under the brand name of Cuprimine among others, is a medication primarily used for the treatment of Wilson's disease. It is also used for people with kidney stones who have high urine cystine levels, rheumatoid arthritis, ...
: Penicillamine is a chelation therapy
Chelation therapy is a medical procedure that involves the administration of chelating agents to remove heavy metals from the body. Chelation therapy has a long history of use in clinical toxicology and remains in use for some very specific medic ...
drug used to treat various diseases (e.g., Wilson's disease
Wilson's disease (also called hepatolenticular degeneration) is a genetic disorder characterized by the excess build-up of copper in the body. Symptoms are typically related to the brain and liver. Liver-related symptoms include vomiting, wea ...
). About 1-2% of individuals treated long term with penicillamine develop MG and/or develop low concentrations of antibodies to AChR. Their MG is often mild and predominantly ocular MG, becomes evident usually 6ŌĆō7 months (range one month to 8 years) after starting the drug, and goes into complete remission in 70% of the cases within 6ŌĆō10 months after discontinuing the drug. It is recommended that penicillamine be discontinued and thereafter avoided in patients who develop MG symptoms when treated with it.
Botulinum toxin A: Botulinum toxin A (sold under the brand name Botox, Jeuveau, and Xeomin) blocks transmission at neuromuscular junction
A neuromuscular junction (or myoneural junction) is a chemical synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber.
It allows the motor neuron to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction.
Muscles require innervation to ...
s to paralyze the muscles into which it is injected. Local botulinum toxin A injections for cosmetic purposes have on occasion caused weaknesses in distant muscles, symptoms resembling ocular or generalized MG in individuals with subclinical MG, and exacerbations of previously controlled MG. Botulinum toxin A has also been used to treat spasmodic torticollis
Spasmodic torticollis is an extremely painful chronic neurological movement disorder causing the neck to involuntarily turn to the left, right, upwards, and/or downwards. The condition is also referred to as "cervical dystonia". Both Anatomical_te ...
(i.e., involuntarily neck turning), blepharospasm
Blepharospasm is a neurological disorder characterized by intermittent, involuntary spasms and contractions of the orbicularis oculi muscle, orbicularis oculi (eyelid) muscles around both eyes. These result in abnormal twitching or blinking, an ...
(involuntary contraction of the eye lids), and other uncontrolled facial muscle spasms in people with myasthenia gravis without side effects or with only short-lived dysphagia
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under " symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right.
It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or l ...
or diplopia
Diplopia is the simultaneous perception of two images of a single object that may be displaced in relation to each other. Also called double vision, it is a loss of visual focus under regular conditions, and is often voluntary. However, when occ ...
. Botulinum toxin A treatment, it is suggested, is best avoided in people with myasthenia gravis but may be offered with caution to patients with mild or stable MG using gradual increases in its dosages and close monitoring.
Magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 ...
: Magnesium is a chemical element
A chemical element is a chemical substance whose atoms all have the same number of protons. The number of protons is called the atomic number of that element. For example, oxygen has an atomic number of 8: each oxygen atom has 8 protons in its ...
that blocks skeletal muscle contraction by inhibiting the release or acetylcholine
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic compound that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals (including humans) as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Par ...
at the neuromuscular junction and also by lowering the sensitivity of these muscles to acetylcholine. Respiratory failure has occurred after systemic use of magnesium (mainly in the form of intravenous magnesium sulfate
Magnesium sulfate or magnesium sulphate is a chemical compound, a salt with the formula , consisting of magnesium cations (20.19% by mass) and sulfate anions . It is a white crystalline solid, soluble in water but not in ethanol.
Magnesi ...
injections) for pre-eclampsia
Pre-eclampsia is a multi-system disorder specific to pregnancy, characterized by the new onset of hypertension, high blood pressure and often a significant amount of proteinuria, protein in the urine or by the new onset of high blood pressure a ...
and after magnesium replacement during the course of a hospitalization in patients with underlying MG. It is suggested that magnesium when given intravenously or when given orally at high doses should be used with extreme caution in people with myasthenia gravis.
Local anesthetics
A local anesthetic (LA) is a medication that causes absence of all sense, sensation (including pain) in a specific body part without loss of consciousness, providing local anesthesia, as opposed to a general anesthetic, which eliminates all sen ...
: Local anesthetics cause absence of pain and all other sensations in a specific body part without loss of consciousness. There are two broad classes of these anesthetics: esters (i.e., procaine
Procaine is a local anesthetic drug of the amino ester group. It is most commonly used in dental procedures to numb the area around a tooth and is also used to reduce the pain of intramuscular injection of penicillin. Owing to the ubiquity of ...
, cocaine
Cocaine is a tropane alkaloid and central nervous system stimulant, derived primarily from the leaves of two South American coca plants, ''Erythroxylum coca'' and ''Erythroxylum novogranatense, E. novogranatense'', which are cultivated a ...
, tetracaine
Tetracaine, also known as amethocaine, is an ester local anesthetic used to numb the eyes, nose, or throat. It may also be applied to the skin before starting intravenous therapy to decrease pain from the procedure. Typically it is applied as a l ...
benzocaine
Benzocaine, sold under the brand name Orajel amongst others, is a local anesthetic, belonging to the amino ester drug class, commonly used as a topical painkiller or in cough drops. It is the active ingredient in many over-the-counter ...
, and chloroprocaine) and amides (i.e. lidocaine
Lidocaine, also known as lignocaine and sold under the brand name Xylocaine among others, is a local anesthetic of the amino amide type. It is also used to treat ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation. When used for local anae ...
, bupivacaine
Bupivacaine, marketed under the brand name Marcaine among others, is a medication used to decrease sensation in a specific small area. In nerve blocks, it is injected around a nerve that supplies the area, or into the spinal canal's epidural ...
, etidocaine
Etidocaine, marketed under the trade name Duranest, is an amide-type local anesthetic given by Injection (medicine), injection during surgery, surgical procedures and childbirth, labor and delivery. Etidocaine has a long duration of activity, and ...
, levobupivacaine
Levobupivacaine (International nonproprietary name, rINN) is a Local anesthetic, local anaesthetic drug indicated for minor and major General anaesthesia, surgical anaesthesia and pain management. It is a long-acting amide-type local anaesthetic ...
, mepivacaine
Mepivacaine is a local anesthetic of the amide type. Mepivacaine has a reasonably rapid onset (less rapid than that of procaine) and medium duration of action (longer than that of procaine) and is marketed under various trade names including Ca ...
, prilocaine
Prilocaine () is a local anesthetic of the amino amide type first prepared by Claes Tegner and Nils L├Čfgren. In its injectable form (trade name Citanest), it is often used in dentistry. It is also often combined with lidocaine as a topical ...
, and ropivacaine
Ropivacaine (International Nonproprietary Name, rINN) is a local anaesthetic drug belonging to the amino amide group. The name ropivacaine refers to both the racemate and the marketed ''S''-enantiomer. Ropivacaine hydrochloride is commonly mark ...
). Ester local anesthetics are metabolized by pseudocholinesterases which in people with myasthenia gravis taking anticholinesterase drugs may lead to excessive levels of these ester anesthetics. Amide local anesthetics are not metabolized by psuedocholineesterases. Based on these considerations, amide local anesthetics are strongly preferred over ester local anesthetics in patients with MG.
Other Drugs: Rare cases of MG exacerbations have been reported in patients treated with: 1) penicillins
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of ╬▓-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' moulds, principally '' P. chrysogenum'' and '' P. rubens''. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by '' P. chrysogenum'' ...
, i.e., ampicillin
Ampicillin is an antibiotic belonging to the aminopenicillin class of the penicillin family. The drug is used to prevent and treat several bacterial infections, such as respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, meningitis, s ...
and amoxicillin
Amoxicillin is an antibiotic medication belonging to the aminopenicillin class of the penicillin family. The drug is used to treat bacterial infections such as middle ear infection, strep throat, pneumonia, skin infections, odontogenic inf ...
; 2) anti-cancer medications, i.e., lorlatinib
Lorlatinib, sold under the brand name Lorbrena in the United States, Canada, and Japan, and Lorviqua in the European Union, is an anti-cancer medication used for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. It is an orally administered inhibito ...
, nilotinib
Nilotinib, sold under the brand name Tasigna among others, is an anti-cancer medication used to treat chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) which has the Philadelphia chromosome. It may be used both in initial cases of chronic phase CML as well a ...
, imatinib
Imatinib, sold under the brand names Gleevec and Glivec (both marketed worldwide by Novartis) among others, is an oral targeted therapy medication used to treat cancer. Imatinib is a small molecule inhibitor targeting multiple tyrosine kinases ...
(these three drugs are tyrosine kinase inhibitor
A tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) is a pharmaceutical drug that inhibits tyrosine kinases. Tyrosine kinases are enzymes responsible for the activation of many proteins by signal transduction cascades. The proteins are activated by adding a phosph ...
s that may also cause MG), dabrafenib
Dabrafenib, sold under the brand name Tafinlar among others, is an anti-cancer medication used for the treatment of cancers associated with a mutated version of the gene BRAF (gene), BRAF. Dabrafenib acts as an enzyme inhibitor, inhibitor of th ...
, and trametinib
Trametinib, sold under the brand name Mekinist among others, is an anticancer medication used for the treatment of melanoma and glioma. It is a MEK inhibitor drug with anti-cancer activity. It inhibits MEK1 and MEK2. It is taken by mouth.
The ...
; 3) antipsychotic
Antipsychotics, previously known as neuroleptics and major tranquilizers, are a class of Psychiatric medication, psychotropic medication primarily used to manage psychosis (including delusions, hallucinations, paranoia or disordered thought), p ...
drugs, i.e., chlorpromazine
Chlorpromazine (CPZ), marketed under the brand names Thorazine and Largactil among others, is an antipsychotic medication. It is primarily used to treat psychotic disorders such as schizophrenia. Other uses include the treatment of bipolar d ...
, pimozide
Pimozide (sold under the brand name Orap) is a neuroleptic medication, drug of the diphenylbutylpiperidine class. It was discovered at Janssen Pharmaceutica in 1963. It has a high potency compared to chlorpromazine (ratio 50-70:1). On a weigh ...
, thioridazine
Thioridazine (Mellaril or Melleril) is a first generation antipsychotic drug belonging to the phenothiazine drug group and was previously widely used in the treatment of schizophrenia and psychosis. The branded product was withdrawn worldwid ...
, clozapine
Clozapine, sold under the brand name Clozaril among others, is a psychiatric medication and was the first atypical antipsychotic to be discovered. It is used primarily to treat people with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder who have ...
, olanzapine
Olanzapine, sold under the brand name Zyprexa among others, is an atypical antipsychotic primarily used to treat schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. It is also sometimes used off-label for treatment of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomitin ...
, haloperidol
Haloperidol, sold under the brand name Haldol among others, is a typical antipsychotic medication. Haloperidol is used in the treatment of schizophrenia, tics in Tourette syndrome, mania in bipolar disorder, delirium, agitation, acute psychos ...
, quetiapine
Quetiapine ( ), sold under the brand name Seroquel among others, is an atypical antipsychotic medication used in the treatment of schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, bipolar depression, and major depressive disorder. Despite being widely prescri ...
, risperidone
Risperidone, sold under the brand name Risperdal among others, is an atypical antipsychotic used to treat schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, as well as aggressive and self-injurious behaviors associated with autism spectrum disorder. It is t ...
, and olanzapine
Olanzapine, sold under the brand name Zyprexa among others, is an atypical antipsychotic primarily used to treat schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. It is also sometimes used off-label for treatment of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomitin ...
; 4) IFN-╬▒
The type-I interferons (IFN) are cytokines which play essential roles in inflammation, immunoregulation, tumor cells recognition, and T-cell responses. In the human genome, a cluster of thirteen functional IFN genes is located at the 9p21.3 cyt ...
(may also cause MG); and 5) the chemical element, lithium
Lithium (from , , ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the ...
. These agents can be used in people with myasthenia gravis because reports on their exacerbation (or induction) of MG are rare.
Pathophysiology
Myasthenia gravis is anautoimmune
In immunology, autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells, tissues and other normal body constituents. Any disease resulting from this type of immune response is termed an " autoimmune disease" ...
synaptopathy. The disorder occurs when the immune system malfunctions and generates antibodies that attack the body's tissues. The antibodies in MG attack a normal human protein, the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, or a related protein called MuSK
Musk is a class of aromatic substances commonly used as base notes in perfumery. They include glandular secretions from animals such as the musk deer, numerous plants emitting similar fragrances, and artificial substances with similar odors. ' ...
, a muscle-specific kinase. Other, less frequent antibodies are found against LRP4, agrin
Agrin is a large proteoglycan whose best-characterised role is in the development of the neuromuscular junction during embryogenesis. Agrin is named based on its involvement in the aggregation of acetylcholine receptors during synaptogenesi ...
, and titin
Titin (; also called connectin) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TTN'' gene. The protein, which is over 1 ╬╝m in length, functions as a molecular spring that is responsible for the passive elasticity of muscle. It comprises 2 ...
proteins.
Human leukocyte antigen
The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system is a complex of genes on chromosome 6 in humans that encode cell-surface proteins responsible for regulation of the immune system. The HLA system is also known as the human version of the major histo ...
haplotypes are associated with increased susceptibility to myasthenia gravis and other autoimmune disorders. Relatives of people with myasthenia gravis have a higher percentage of other immune disorders.
The thymus gland cells form part of the body's immune system. In those with myasthenia gravis, the thymus gland is large and abnormal. It sometimes contains clusters of immune cells that indicate lymphoid hyperplasia, and the thymus gland may give wrong instructions to immune cells.
Axon
An axon (from Greek ß╝ä╬ŠŽē╬Į ''├Īx┼Źn'', axis) or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see American and British English spelling differences#-re, -er, spelling differences) is a long, slender cellular extensions, projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, ...
2. Muscle cell membrane 3. Synaptic vesicle
In a neuron, synaptic vesicles (or neurotransmitter vesicles) store various neurotransmitters that are exocytosis, released at the chemical synapse, synapse. The release is regulated by a voltage-dependent calcium channel. Vesicle (biology), Ves ...
4. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, or nAChRs, are Receptor (biochemistry), receptor polypeptides that respond to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Nicotinic receptors also respond to drugs such as the agonist nicotine. They are found in the c ...
5. Mitochondrion
A mitochondrion () is an organelle found in the cell (biology), cells of most eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double lipid bilayer, membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine tri ...
File:Gray1178.png, A juvenile thymus shrinks with age.
File:Nicotinic Acetylcholine receptor.png, The nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, or nAChRs, are Receptor (biochemistry), receptor polypeptides that respond to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Nicotinic receptors also respond to drugs such as the agonist nicotine. They are found in the c ...
In pregnancy
For women who are pregnant and already have MG, in a third of cases, they have been known to experience an exacerbation of their symptoms, and in those cases, it usually occurs in thefirst trimester
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception usually occurs following vaginal intercourse, but can also ...
of pregnancy. Signs and symptoms in pregnant mothers tend to improve during the second
The second (symbol: s) is a unit of time derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes, and finally to 60 seconds each (24 ├Ś 60 ├Ś 60 = 86400). The current and formal definition in the International System of U ...
and third trimester
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception usually occurs following vaginal intercourse, but can also o ...
s. Complete remission can occur in some mothers. Immunosuppressive therapy should be maintained throughout pregnancy, as this reduces the chance of neonatal muscle weakness, and controls the mother's myasthenia.
About 10ŌĆō20% of infants with mothers affected by the condition are born with transient neonatal myasthenia gravis (TNMG), which generally produces feeding and respiratory
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies gr ...
difficulties that develop about 12 hours to several days after birth. A child with TNMG typically responds very well to acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, and the condition generally resolves over a period of three weeks, as the antibodies diminish, and generally does not result in any complications. However, a small percentage of fetuses and newborns with TNMG, particularly those who have antibodies directed against the fetal form of the AChR (their disorder is a subtype of TNMG termed the "acetylcholine receptor inactivation syndrome") have a more severe form of TNMG which includes weakness in skeletal muscles regulating breathing, respiratory failure, and various deformities such as arthrogryposis multiplex congenita Arthrogryposis (AMC) describes congenital joint contracture in two or more areas of the body. It derives its name from Greek, literally meaning 'curving of joints' (', 'joint'; ', late Latin form of late Greek ', 'hooking').
Children born with one ...
. In some of these cases, the mother remains asymptomatic
Asymptomatic (or clinically silent) is an adjective categorising the medical conditions (i.e., injuries or diseases) that patients carry but without experiencing their symptoms, despite an explicit diagnosis (e.g., a positive medical test).
P ...
.
Diagnosis
Myasthenia gravis can be difficult to diagnose, as the symptoms can be subtle and hard to distinguish from both normal variants and other neurological disorders. Three types of myasthenic symptoms in children can be distinguished: # Transient neonatal myasthenia gravis occurs in 10 to 15% of babies born to mothers afflicted with the disorder, and disappears after a few weeks. # Congenital myasthenia, the rarest form, occurs when genes are present from both parents. # Juvenile myasthenia gravis is most common in females. Congenital myasthenias cause muscle weakness and fatigability similar to those of MG. The signs of congenital myasthenia usually are present in the first years of childhood, although they may not be recognized until adulthood.Subgroup classification
When diagnosed with MG, patient can be stratified into distinct subgroups based on the clinical features and serological status, e.g. affected muscle group, age of onset, thymic abnormalities, and profile of serum autoantibodies. Based on the affected muscle group, patients can be sub-grouped into ocular MG or generalized MG. Ocular MG is characterized by exclusively ocular symptoms, droopy eyelids, or double vision. Generalized MG has muscle weakness with a variable combination of the bulbar, axial, or limb and respiratory muscles. Patients can also be sub-grouped by the age of onset: juvenile-onset MG (onset age Ōēż 18 years of age), early-onset MG (EOMG; 19ŌĆō50 years of age), late-onset MG (LOMG; onset > 50 years of age), and very late-onset (VLOMG; onset age Ōēź 65 years of age). The subgroup of the autoantibody profile includes AChR seropositive, MuSK seropositive, LRP4 seropositive, and agrin seropositive.Physical examination
During a physical examination to check for MG, a doctor might ask the person to perform repetitive movements. For instance, the doctor may ask one to look at a fixed point for 30 seconds and to relax the muscles of the forehead, because a person with MG and ptosis of the eyes might be involuntarily using the forehead muscles to compensate for the weakness in the eyelids. The clinical examiner might also try to elicit the "curtain sign" in a person by holding one of the person's eyes open, which in the case of MG will lead the other eye to close.Blood tests
If the diagnosis is suspected,serology
Serology is the scientific study of Serum (blood), serum and other body fluids. In practice, the term usually refers to the medical diagnosis, diagnostic identification of Antibody, antibodies in the serum. Such antibodies are typically formed in r ...
can be performed:
* One test is for antibodies against the acetylcholine receptor; the test has a reasonable sensitivity of 80ŌĆō96%, but in ocular myasthenia, the sensitivity falls to 50%.
* A proportion of the people without antibodies against the acetylcholine receptor have antibodies against the MuSK protein.
* In specific situations, testing is performed for Lambert-Eaton syndrome.
Electrodiagnostics
 Muscle fibers of people with MG are easily fatigued, which the repetitive nerve stimulation test can help diagnose. In single-fiber
Muscle fibers of people with MG are easily fatigued, which the repetitive nerve stimulation test can help diagnose. In single-fiber electromyography
Electromyography (EMG) is a technique for evaluating and recording the electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles. EMG is performed using an instrument called an electromyograph to produce a record called an electromyogram. An electromyo ...
, which is considered to be the most sensitive (although not the most specific) test for MG, a thin needle electrode is inserted into different areas of a particular muscle to record the action potentials from several samplings of different individual muscle fibers. Two muscle fibers belonging to the same motor unit are identified, and the temporal variability in their firing patterns is measured. Frequency and proportion of particular abnormal action potential patterns, called "jitter" and "blocking", are diagnostic. Jitter refers to the abnormal variation in the time interval between action potentials of adjacent muscle fibers in the same motor unit. Blocking refers to the failure of nerve impulses to elicit action potentials in adjacent muscle fibers of the same motor unit.
Ice test
Applying ice for 2ŌĆō5 minutes to the muscles reportedly has asensitivity and specificity
In medicine and statistics, sensitivity and specificity mathematically describe the accuracy of a test that reports the presence or absence of a medical condition. If individuals who have the condition are considered "positive" and those who do ...
of 76.9% and 98.3%, respectively, for the identification of MG. Acetylcholinesterase
Acetylcholinesterase (HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee, HGNC symbol ACHE; EC 3.1.1.7; systematic name acetylcholine acetylhydrolase), also known as AChE, AChase or acetylhydrolase, is the primary cholinesterase in the body. It is an enzyme th ...
is thought to be inhibited at the lower temperature, which is the basis for this diagnostic test. This generally is performed on the eyelids when ptosis is present and is deemed positive if a Ōēź2-mm rise in the eyelid occurs after the ice is removed.
Edrophonium test
This test requires theintravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutr ...
administration of edrophonium chloride or neostigmine, drugs that block the breakdown of acetylcholine by cholinesterase
The enzyme cholinesterase (EC 3.1.1.8, choline esterase; systematic name acylcholine acylhydrolase) catalyses the hydrolysis of choline-based esters:
: an acylcholine + H2O = choline + a carboxylate
Several of these serve as neurotransmitte ...
(acetylcholinesterase inhibitors). This test is no longer typically performed, as its use can lead to life-threatening bradycardia
Bradycardia, also called bradyarrhythmia, is a resting heart rate under 60 beats per minute (BPM). While bradycardia can result from various pathological processes, it is commonly a physiological response to cardiovascular conditioning or due ...
(slow heart rate) which requires immediate emergency attention. Production of edrophonium was discontinued in 2008.
Imaging
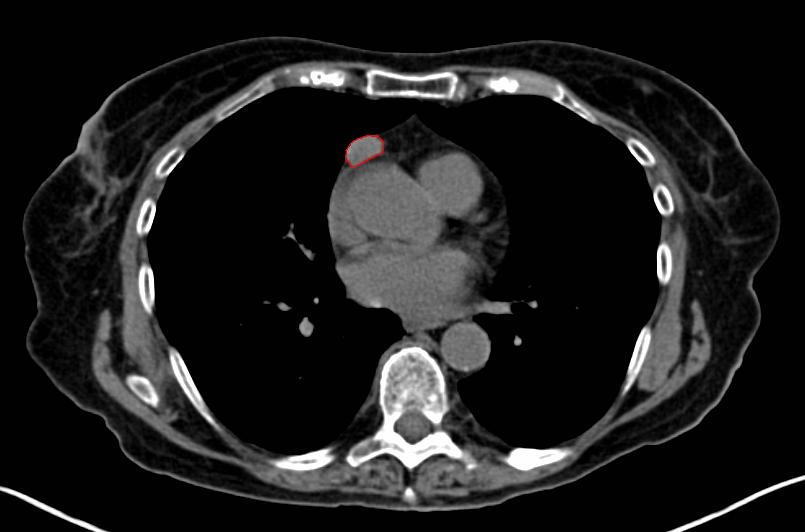
Achest X-ray
A chest radiograph, chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film is a Projectional radiography, projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common fi ...
may identify widening of the mediastinum
The mediastinum (from ;: mediastina) is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is a region that contains vital organs and structures within the thorax, mainly the heart and its vessels, the eso ...
suggestive of thymoma, but computed tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
or magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and ...
(MRI) are more sensitive ways to identify thymomas and are generally done for this reason. MRI of the cranium and orbits may also be performed to exclude compressive and inflammatory lesions of the cranial nerves and ocular muscles.
Pulmonary function test
The forcedvital capacity
Vital capacity (VC) is the maximum amount of air a person can expel from the lungs after a maximum inhalation. It is equal to the sum of inspiratory reserve volume, tidal volume, and expiratory reserve volume. It is approximately equal to Force ...
may be monitored at intervals to detect increasing muscular weakness. Acutely, negative inspiratory force may be used to determine adequacy of ventilation; it is performed on those individuals with MG.
Differential diagnoses
The muscle weakness that worsens with activity (abnormalmuscle fatigue
Muscle fatigue is when muscles that were initially generating a normal amount of force, then experience a declining ability to generate force. It can be a result of vigorous exercise, but abnormal fatigue may be caused by barriers to or interfer ...
) in myasthenia gravis is a symptom shared by other neuromuscular diseases. Most of the metabolic myopathies, such as McArdle disease (GSD-V), have abnormal muscle fatigue rather than fixed muscle weakness. Also, like myasthenia gravis, exercise intolerance in McArdle disease improves with regular physical activity (performed safely using activity adaptations such as getting into second wind
Second wind is a phenomenon in endurance sports, such as marathons or road running (as well as other sports), whereby an athlete who is out of breath and too tired to continue (known as " hitting the wall"), finds the strength to press on at top p ...
, the "30 for 80 rule," and "six second rule"). A small minority of patients with McArdle disease also have the comorbidity of ptosis (drooping upper eyelid). Late-onset GSD-II ( Pompe disease) and GSD-XV also have muscle weakness or fatigue with comorbidities of ptosis and ophthalmoplegia; as do many of the mitochondrial myopathies.
Other diseases that involve abnormal muscle fatigue (which may be described as exercise-induced muscle weakness, reversible muscle weakness, or muscle weakness that improves with rest) include: endocrine myopathies (such as Hoffman syndrome), Tubular aggregate myopathy (TAM), ischemia
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems ...
(such as intermittent claudication
Intermittent claudication, also known as vascular claudication, is a symptom that describes muscle pain on mild exertion (ache, cramp, numbness or sense of fatigue), classically in the calf muscle, which occurs during exercise, such as walking, ...
, popliteal artery entrapment syndrome
The popliteal artery entrapment syndrome (PAES) is an uncommon pathology that occurs when the popliteal artery is compressed by the surrounding popliteal fossa myofascial structures. This results in claudication and chronic leg ischemia. This con ...
, and chronic venous insufficiency
Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) is a medical condition characterized by blood pooling in the veins, leading to increased pressure and strain on the vein walls. The most common cause of CVI is superficial venous reflux, which often results in ...
), and poor diet or malabsorption diseases that lead to vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency or hypovitaminosis D is a vitamin D level that is below normal. It most commonly occurs in people when they have inadequate exposure to sunlight, particularly sunlight with adequate ultraviolet B rays (UVB). Vitamin D def ...
(osteomalic myopathy). Although limb-girdle muscular dystrophies (LGMDs) involve fixed muscle weakness, LGMDR8 also involves muscle fatigue; as do some limb-girdle muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathies such as MDDGC3 (a.k.a. LGMDR15 and LGMD2O). Myofibrillar myopathy 10, dimethylglycine dehydrogenase deficiency, erythrocyte lactate transporter defect, and myopathy with myalgia, increased serum creatine kinase, with or without episodic rhabdomyolysis (MMCKR) also include muscle fatigue.
X-linked episodic muscle weakness (EMWX) includes general muscle weakness, ptosis, and fluctuations in strength. In some individuals, fatiguability was demonstrable, the phenotype having features comparable to congenital myasthenic syndromes and channelopathies
Channelopathies are a group of diseases caused by the dysfunction of ion channel subunits or their interacting proteins. These diseases can be inherited or acquired by other disorders, drugs, or toxins. Mutations in genes encoding ion channels, wh ...
.
Signs and symptoms of myasthenia presenting from infancy or childhood may be one of the congenital myasthenic syndrome
Congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) is an inherited neuromuscular disorder caused by defects of several types at the neuromuscular junction. The effects of the disease are similar to Lambert-Eaton Syndrome and myasthenia gravis, the difference ...
s, which can be inherited in either an autosomal dominant or recessive manner. There are currently over two dozen types of congenital myasthenic syndromes.
LimbŌĆōgirdle myasthenia gravis is a distinct condition from myasthenia gravis. It is an adult-onset, autoimmune condition affecting the neuromuscular junction. However, it lacks eye abnormalities and is associated with autoimmune conditions such as systemic lupus erythematosus, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, and thymoma.
LambertŌĆōEaton myasthenic syndrome
LambertŌĆōEaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS) is a rare autoimmune disorder characterized by muscle weakness of the limbs. It is also known as myasthenic syndrome, EatonŌĆōLambert syndrome, and when related to cancer, carcinomatous myopathy.
...
(LEMS) is an autoimmune condition that attacks the neuromuscular junction, either as a paraneoplastic syndrome (typically older patients) or associated with a non-cancerous primary autoimmune condition (typically younger patients). It usually involves lower limb weakness and exercise-induced fatiguability, although the upper limbs and eyes may also be involved. Lambert's sign is the unusual improvement of grip strength that follows after squeezing the hand at maximum intensity for 2ŌĆō3 seconds.
Management
Treatment is by medication and/or surgery. Medication consists mainly of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors to directly improve muscle function and immunosuppressant drugs to reduce the autoimmune process.Thymectomy
A thymectomy is an operation to remove the thymus. It usually results in remission of myasthenia gravis with the help of medication including steroids. However, this remission may not be permanent. Thymectomy is indicated when thymoma are present ...
is a surgical method to treat MG.
Medication
hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood, in order to replicate inside a patient and produce ...
(HSCT) is sometimes used in severe, treatment-refractory MG. Available data provide preliminary evidence that HSCT can be an effective therapeutic option in carefully selected cases.
Efgartigimod alfa (Vyvgart) was approved for medical use in the United States in December 2021.
Efgartigimod alfa/hyaluronidase (Vyvgart Hytrulo) was approved for medical use in the United States in June 2023.
Rozanolixizumab (Rystiggo) was approved for medical use in the United States in June 2023.
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors can provide symptomatic benefit and may not fully remove a person's weakness from MG. While they might not fully remove all symptoms of MG, they still may allow a person the ability to perform normal daily activities. Usually, acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are started at a low dose and increased until the desired result is achieved. If taken 30 minutes before a meal, symptoms will be mild during eating, which is helpful for those who have difficulty swallowing due to their illness. Another medication used for MG,atropine
Atropine is a tropane alkaloid and anticholinergic medication used to treat certain types of nerve agent and pesticide poisonings as well as some types of slow heart rate, and to decrease saliva production during surgery. It is typically give ...
, can reduce the muscarinic side effects of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Pyridostigmine
Pyridostigmine is a medication used to treat myasthenia gravis and underactive bladder. It is also used together with atropine to end the effects of neuromuscular blocking medication of the non-depolarizing type. It is also used off-label to t ...
is a relatively long-acting drug (when compared to other cholinergic agonists), with a half-life around four hours with relatively few side effects. Generally, it is discontinued in those who are being mechanically ventilated, as it is known to increase the amount of salivary secretions. A few high-quality studies have directly compared cholinesterase inhibitors with other treatments (or placebo); their practical benefit may be so significant that conducting studies in which they would be withheld from some people would be difficult.
Immune suppressants
The steroidprednisone
Prednisone is a glucocorticoid medication mostly used to immunosuppressive drug, suppress the immune system and decrease inflammation in conditions such as asthma, COPD, and rheumatologic diseases. It is also used to treat high blood calcium ...
might also be used to achieve a better result, but it can lead to the worsening of symptoms and takes weeks to achieve its maximal effectiveness. Research suggests that up to 15% of patients do not positively respond to immune suppressants. Due to the myriad symptoms that steroid treatments can cause, it is not the preferred method of treatment. Other immune suppressing medications may also be used including rituximab
Rituximab, sold under the brand name Rituxan among others, is a monoclonal antibody medication used to treat certain autoimmune diseases and types of cancer. It is used for non-Hodgkin lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (in children and ad ...
or azathioprine
Azathioprine, sold under the brand name Imuran, among others, is an immunosuppressive medication. It is used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, and systemic lupus er ...
.
Nipocalimab (Imaavy) was approved for medical use in the United States in April 2025.
Plasmapheresis and IVIG
If the myasthenia is serious (myasthenic crisis),plasmapheresis
Plasmapheresis (from the Greek language, Greek ŽĆ╬╗╬¼Žā╬╝╬▒, ''plasma'', something molded, and ß╝ĆŽå╬▒╬»Žü╬ĄŽā╬╣Žé ''aphairesis'', taking away) is the removal, treatment, and return or exchange of blood plasma or components thereof from and to the ...
can be used to remove the putative antibodies from the circulation. Also, intravenous immunoglobulin
Immunoglobulin therapy is the use of a mixture of antibodies (normal human immunoglobulin) to treat several health conditions. These conditions include primary immunodeficiency, immune thrombocytopenic purpura, chronic inflammatory demyelinat ...
s (IVIGs) can be used to bind the circulating antibodies. Both of these treatments have relatively short-lived benefits, typically measured in weeks, and often are associated with high costs, which make them prohibitive; they are generally reserved for when MG requires hospitalization.
Surgery
Asthymoma
A thymoma is a tumor originating from the epithelial cells of the thymus that is considered a rare neoplasm. Thymomas are frequently associated with neuromuscular disorders such as myasthenia gravis; thymoma is found in 20% of patients with myast ...
s are seen in 10% of all people with the MG, they are often given a chest X-ray and CT scan to evaluate their need for surgical removal of their thymus glands and any cancerous tissue that may be present. Even if surgery is performed to remove a thymoma, it generally does not lead to the remission of MG. Surgery in the case of MG involves the removal of the thymus, although in 2013, no clear benefit was indicated except in the presence of a thymoma. A 2016 randomized, controlled trial, however, found some benefits.
Physical measures
People with MG should be educated regarding the fluctuating nature of their symptoms, including weakness and exercise-induced fatigue. Exercise participation should be encouraged with frequent rest. In people with generalized MG, some evidence indicates a partial home program including training indiaphragmatic breathing
Diaphragmatic breathing, abdominal breathing, belly breathing, or deep breathing, is a breathing technique that is done by contracting the Thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm, a muscle located horizontally between the thoracic cavity and abdominal cav ...
, pursed-lip breathing, and interval-based muscle therapy may improve respiratory muscle strength, chest wall mobility, respiratory pattern, and respiratory endurance.
Medical imaging
In people with myasthenia gravis, older forms ofiodinated contrast
Iodinated contrast is a form of water-soluble, intravenous radiocontrast agent containing iodine, which enhances the visibility of vascular structures and organs during radiography, radiographic procedures. Some pathologies, such as cancer, have p ...
used for medical imaging have caused an increased risk of exacerbation of the disease, but modern forms have no immediate increased risk.
Prognosis
The prognosis of people with MG is generally good, as is quality of life, when given very good treatment. Monitoring of a person with MG is very important, as at least 20% of people diagnosed with it will experience a myasthenic crisis within two years of their diagnosis, requiring rapid medical intervention. Generally, the most disabling period of MG might be years after the initial diagnosis. Assistive devices may be needed to assist with mobility. In the early 1900s, 70% of detected cases died from lung problems; now, that number is estimated to be around 3ŌĆō5%, an improvement attributed to increased awareness and medications to manage symptoms.Epidemiology
MG occurs in all ethnic groups and both sexes. It most commonly affects women under 40 and people from 50 to 70 years old of either sex, but it has been known to occur at any age. Younger people rarely have thymoma.Prevalence
In epidemiology, prevalence is the proportion of a particular population found to be affected by a medical condition (typically a disease or a risk factor such as smoking or seatbelt use) at a specific time. It is derived by comparing the number o ...
in the United States is estimated at between 0.5 and 20.4 cases per 100,000, with an estimated 60,000 Americans affected. In the United Kingdom, an estimated 15 cases of MG occur per 100,000 people. The mortality rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular Statistical population, population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically ...
of MG is around 5-9%.
History
The first to write about MG wereThomas Willis
Thomas Willis Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS (27 January 1621 ŌĆō 11 November 1675) was an English physician who played an important part in the history of anatomy, neurology, and psychiatry, and was a founding member of the Royal Society.
L ...
, Samuel Wilks, Erb, and Goldflam. The term "myasthenia gravis pseudo-paralytica" was proposed in 1895 by Jolly, a German physician. Mary Walker treated a person with MG with physostigmine
Physostigmine (also known as eserine from ''├®s├®r├®'', the West African name for the Calabar bean) is a highly toxic parasympathomimetic alkaloid, specifically, a reversible cholinesterase inhibitor. It occurs naturally in the Calabar bean and ...
in 1934. Simpson and Nastuck detailed the autoimmune nature of the condition. In 1973, Patrick and Lindstrom used rabbits to show that immunization with purified muscle-like acetylcholine receptors caused the development of MG-like symptoms.
Research
Immunomodulating substances, such as drugs that prevent acetylcholine receptor modulation by the immune system, are currently being researched. Some research recently has been on anti-c5 inhibitors for treatment research as they are safe and used in the treatment of other diseases.Ephedrine
Ephedrine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant and sympathomimetic agent that is often used to prevent hypotension, low blood pressure during anesthesia. It has also been used for asthma, narcolepsy, and obesity but is not the preferred ...
seems to benefit some people more than other medications, but it has not been properly studied as of 2014.
In the laboratory, MG is mostly studied in model organisms, such as rodents. In addition, in 2015, scientists developed an ''in vitro'' functional, all-human, neuromuscular junction
A neuromuscular junction (or myoneural junction) is a chemical synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber.
It allows the motor neuron to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction.
Muscles require innervation to ...
assay from human embryonic stem cell
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are Cell potency#Pluripotency, pluripotent stem cells derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, an early-stage pre-Implantation (human embryo), implantation embryo. Human embryos reach the blastocyst stage 4ŌĆ ...
s and somatic-muscle stem cells. After the addition of pathogenic antibodies against the acetylcholine receptor and activation of the complement system
The complement system, also known as complement cascade, is a part of the humoral, innate immune system and enhances (complements) the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear microbes and damaged cells from an organism, promote inf ...
, the neuromuscular co-culture shows symptoms such as weaker muscle contractions. Recent years, scientists have been working on finding the reliable biomarker
In biomedical contexts, a biomarker, or biological marker, is a measurable indicator of some biological state or condition. Biomarkers are often measured and evaluated using blood, urine, or soft tissues to examine normal biological processes, ...
s for MG to monitor the disease development and assess the severity.
References
Further reading
* *External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Myasthenia Gravis Autoimmune diseases Myoneural junction and neuromuscular diseases Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia neurology articles ready to translate