|
Neostigmine
Neostigmine, sold under the brand name Bloxiverz, among others, is a medication used to treat myasthenia gravis, Ogilvie syndrome, and urinary retention without the presence of a blockage. It is also used in anaesthesia to end the effects of non-depolarising neuromuscular blocking medication. It is given by injection either into a vein, muscle, or under the skin. After injection effects are generally greatest within 30 minutes and last up to 4 hours. Common side effects include nausea, increased saliva, crampy abdominal pain, and slow heart rate. More severe side effects include low blood pressure, weakness, and allergic reactions. It is unclear if use in pregnancy is safe for the baby. Neostigmine is in the cholinergic family of medications. It works by blocking the action of acetylcholinesterase and therefore increases the levels of acetylcholine. Neostigmine was patented in 1931. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. The term is from G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Neuromuscular Blocking Medication
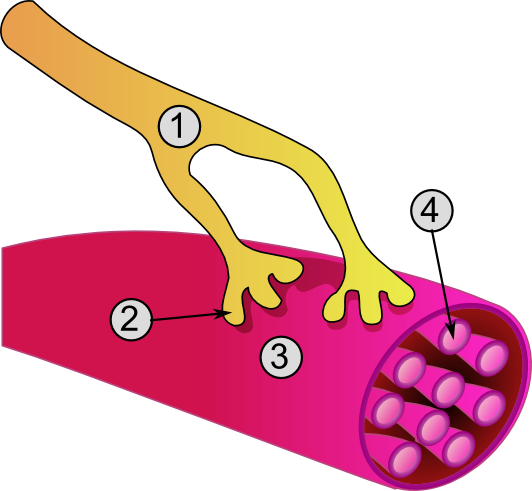
Neuromuscular-blocking drugs, or Neuromuscular blocking agents (NMBAs), block transmission at the neuromuscular junction, causing paralysis of the affected skeletal muscles. This is accomplished via their action on the post-synaptic acetylcholine (Nm) receptors. In clinical use, neuromuscular block is used adjunctively to anesthesia to produce paralysis, firstly to paralyze the vocal cords, and permit endotracheal intubation, and secondly to optimize the surgical field by inhibiting spontaneous ventilation, and causing relaxation of skeletal muscles. Because the appropriate dose of neuromuscular-blocking drug may paralyze muscles required for breathing (i.e., the diaphragm), mechanical ventilation should be available to maintain adequate respiration. This class of medications helps to reduce patient movement, breathing, or ventilator dyssynchrony and allows lower insufflation pressures during laparoscopy. It has several indications for use in the intense c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vecuronium
Vecuronium bromide, sold under the brand name Norcuron among others, is a medication used as part of general anesthesia to provide skeletal muscle relaxation during surgery or mechanical ventilation. It is also used to help with endotracheal intubation; however, agents such as suxamethonium (succinylcholine) or rocuronium are generally preferred if this needs to be done quickly. It is given by injection into a vein. Effects are greatest at about 4 minutes and last for up to an hour. Side effects may include low blood pressure and prolonged paralysis. Allergic reactions are rare. It is unclear if use in pregnancy is safe for the baby. Vecuronium is in the aminosteroid neuromuscular-blocker family of medications and is of the non-depolarizing type. It works by competitively blocking the action of acetylcholine on skeletal muscles. The effects may be reversed with sugammadex or a combination of neostigmine and glycopyrrolate. To minimize residual blockade, reversal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis (MG) is a long-term neuromuscular junction disease that leads to varying degrees of skeletal muscle weakness. The most commonly affected muscles are those of the eyes, face, and swallowing. It can result in double vision, drooping eyelids, and difficulties in talking and walking. Onset can be sudden. Those affected often have a large thymus or develop a thymoma. Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease of the neuromuscular junction which results from antibodies that block or destroy nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (AChR) at the junction between the nerve and muscle. This prevents nerve impulses from triggering muscle contractions. Most cases are due to immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) and IgG3 antibodies that attack AChR in the postsynaptic membrane, causing complement-mediated damage and muscle weakness. Rarely, an inherited genetic defect in the neuromuscular junction results in a similar condition known as congenital myasthenia. Babies of mothers wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rocuronium
Rocuronium bromide (brand names Zemuron, Esmeron) is an aminosteroid non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocker or muscle relaxant used in modern anaesthesia to facilitate tracheal intubation by providing skeletal muscle relaxation for surgery or mechanical ventilation. It is used for standard endotracheal intubation, as well as for rapid sequence induction (RSI). Pharmacology Mechanism of action Rocuronium bromide is a competitive antagonist for the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors at the neuromuscular junction. Of the neuromuscular-blocking drugs it is considered to be a non-depolarizing neuromuscular junction blocker, because it acts by dampening the receptor action causing muscle relaxation, instead of continual depolarisation which is the mechanism of action of the depolarizing neuromuscular junction blockers, like succinylcholine. It was designed to be a weaker antagonist at the neuromuscular junction than pancuronium; hence its monoquaternary structure and its hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ogilvie Syndrome
Ogilvie syndrome, or acute colonic pseudo-obstruction, is the acute dilatation of the colon in the absence of any mechanical obstruction in severely ill patients. Acute colonic pseudo-obstruction is characterized by massive dilatation of the cecum (diameter > 10 cm) and right colon on abdominal X-ray. It is a type of megacolon, sometimes referred to as "acute megacolon," to distinguish it from toxic megacolon. The condition carries the name of the British surgeon Sir William Heneage Ogilvie (1887–1971), who first reported it in 1948. Ogilvie syndrome is an acute illness, which means it occurs suddenly and temporarily, and it only affects the colon. " Intestinal pseudo-obstruction" is a broad term that refers to any paralysis of the intestines that is not caused by a mechanical obstruction. Some individuals develop chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction as a result of a chronic disease or a congenital condition. Signs and symptoms Usually the patient has abdominal dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Acetylcholine
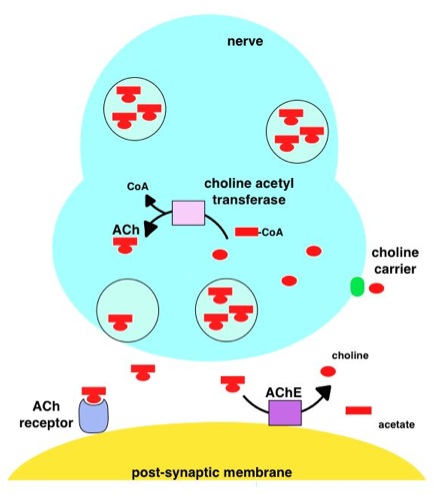
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic compound that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals (including humans) as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Parts in the body that use or are affected by acetylcholine are referred to as cholinergic. Acetylcholine is the neurotransmitter used at the neuromuscular junction. In other words, it is the chemical that motor neurons of the nervous system release in order to activate muscles. This property means that drugs that affect cholinergic systems can have very dangerous effects ranging from paralysis to convulsions. Acetylcholine is also a neurotransmitter in the autonomic nervous system, both as an internal transmitter for both the sympathetic nervous system, sympathetic and the parasympathetic nervous system, and as the final product released by the parasympathetic nervous system. Acetylcholine is the primary neurotransmitter of the parasympathet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Conservative Management
Conservative treatment is a type of medical treatment defined by the avoidance of invasive measures such as surgery or other invasive procedures, usually with the intent to preserve function or body parts. For example, in appendicitis, conservative management may include watchful waiting Watchful waiting (also watch and wait or WAW) is an approach to a medical problem in which time is allowed to pass before medical intervention or therapy is used. During this time, repeated testing may be performed. Related terms include ''expe ... and treatment with antibiotics, as opposed to surgical removal of the appendix. References Medical terminology {{treatment-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Envenomation
Envenomation is the process by which venom is injected by the bite or sting of a venomous animal. Many kinds of animals, including mammals (e.g., the northern short-tailed shrew, ''Blarina brevicauda''), reptiles (e.g., many snakes), spiders, insects (e.g., wasps) and other arthropods, and fish (e.g., stone fish) employ venom for hunting and for self-defense. In particular, snakebite is considered to be a neglected tropical disease causing over 100,000 deaths and maiming over 400,000 people per year. Mechanisms Some venoms are applied externally, especially to sensitive tissues such as the eyes, but most venoms are administered by piercing the skin of the victim. Venom in the saliva of the Gila monster and some other reptiles enters prey through bites of grooved teeth. More commonly animals have specialized organs such as hollow teeth (fangs) and tubular stingers that penetrate the prey's skin, whereupon muscles attached to the attacker's venom reservoir squirt venom deep wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Acetylcholinesterase
Acetylcholinesterase (HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee, HGNC symbol ACHE; EC 3.1.1.7; systematic name acetylcholine acetylhydrolase), also known as AChE, AChase or acetylhydrolase, is the primary cholinesterase in the body. It is an enzyme that catalysis, catalyzes the breakdown of acetylcholine and some other choline esters that function as neurotransmitters: : acetylcholine + H2O = choline + acetate It is found at mainly neuromuscular junctions and in chemical synapses of the cholinergic type, where its activity serves to terminate cholinergic neurotransmission, synaptic transmission. It belongs to the carboxylesterase family of enzymes. It is the primary target of inhibition by organophosphorus compounds such as nerve agents and pesticides. Enzyme structure and mechanism AChE is a hydrolase that hydrolyzes choline esters. It has a very high catalytic activity—each molecule of AChE degrades about 5,000 molecules of acetylcholine (ACh) per second, approaching the limit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Snakebite
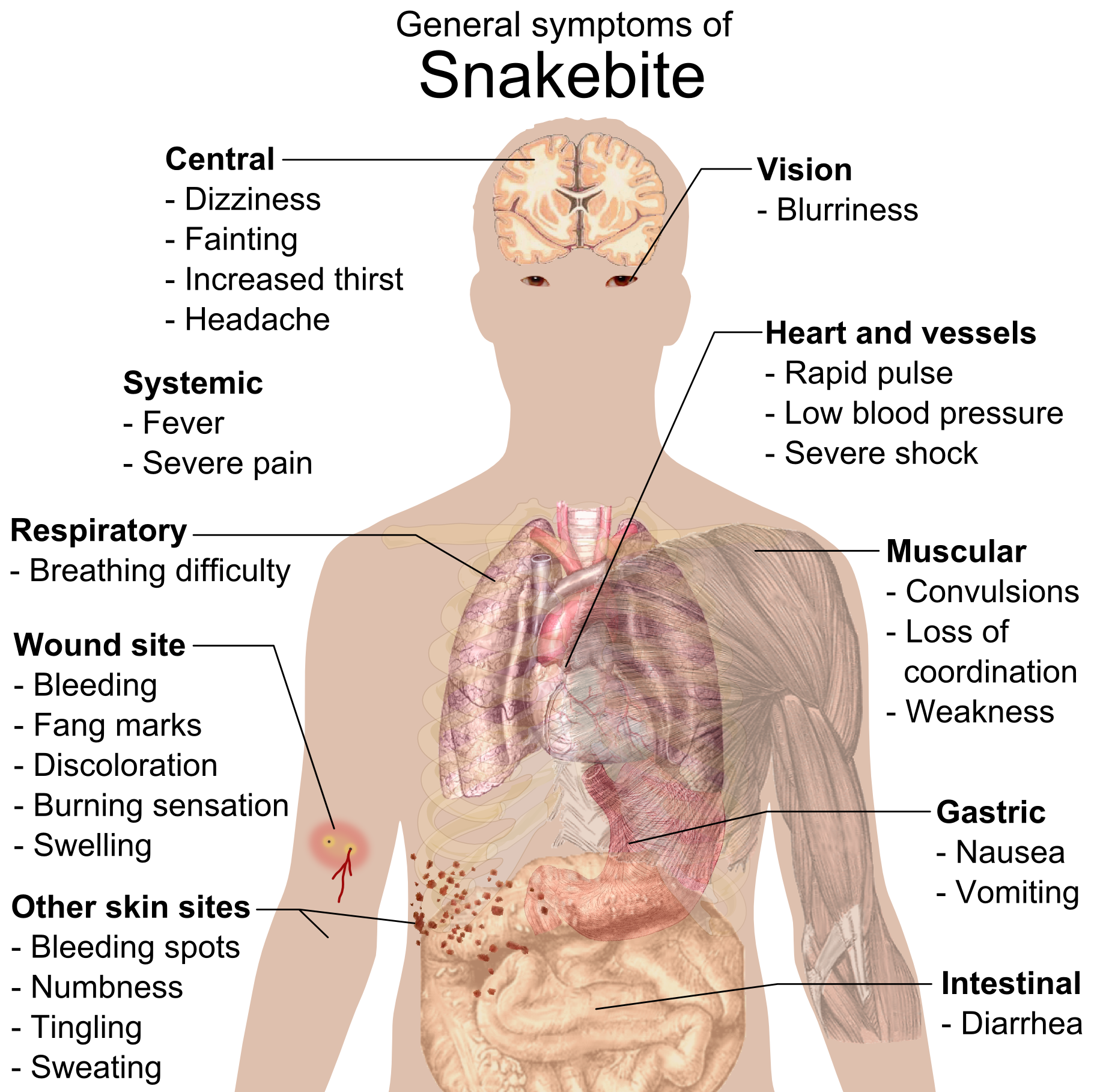
A snakebite is an injury caused by the bite of a snake, especially a venomous snake. A common sign of a bite from a venomous snake is the presence of two puncture wounds from the animal's fangs. Sometimes venom injection from the bite may occur. This may result in redness, swelling, and severe pain at the area, which may take up to an hour to appear. Vomiting, blurred vision, tingling of the limbs, and sweating may result. Most bites are on the hands, arms, or legs. Fear following a bite is common with symptoms of a racing heart and feeling faint. The venom may cause bleeding, kidney failure, a severe allergic reaction, tissue death around the bite, or breathing problems. Bites may result in the loss of a limb or other chronic problems or even death. The outcome depends on the type of snake, the area of the body bitten, the amount of snake venom injected, the general health of the person bitten, and whether or not anti-venom serum has been administered by a doctor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Muscle Relaxant
A muscle relaxant is a drug that affects skeletal muscle function and decreases the muscle tone. It may be used to alleviate symptoms such as muscle spasms, pain, and hyperreflexia. The term "muscle relaxant" is used to refer to two major therapeutic groups: Neuromuscular-blocking drugs, neuromuscular blockers and Antispasmodic, spasmolytics. Neuromuscular blockers act by interfering with transmission at the neuromuscular end plate and have no central nervous system (CNS) activity. They are often used during surgical procedures and in intensive care and emergency medicine to cause temporary paralysis. Spasmolytics, also known as "centrally acting" muscle relaxant, are used to alleviate musculoskeletal pain and spasms and to reduce spasticity in a variety of neurological conditions. While both neuromuscular blockers and spasmolytics are often grouped together as muscle relaxant, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Depolarization
In biology, depolarization or hypopolarization is a change within a cell (biology), cell, during which the cell undergoes a shift in electric charge distribution, resulting in less negative charge inside the cell compared to the outside. Depolarization is essential to the function of many cells, communication between cells, and the overall physiology of an organism. Most cells in higher organisms maintain an internal environment that is negatively charged relative to the cell's exterior. This difference in charge is called the cell's membrane potential. In the process of depolarization, the negative internal charge of the cell temporarily becomes more positive (less negative). This shift from a negative to a more positive membrane potential occurs during several processes, including an action potential. During an action potential, the depolarization is so large that the potential difference across the cell membrane briefly reverses polarity, with the inside of the cell becoming p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |