Chiari Malformations on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
 The most common pathophysiological mechanism by which Chiari type I malformations occurs is due to a congenitally small posterior fossa. Other pathophysiological mechanisms involve increased intracranial pressure above the foramen magnum which causes a downward pressure against the cerebellum, thus causing the cerebellar tonsils to displace below the foramen magnum. Such causes include
The most common pathophysiological mechanism by which Chiari type I malformations occurs is due to a congenitally small posterior fossa. Other pathophysiological mechanisms involve increased intracranial pressure above the foramen magnum which causes a downward pressure against the cerebellum, thus causing the cerebellar tonsils to displace below the foramen magnum. Such causes include
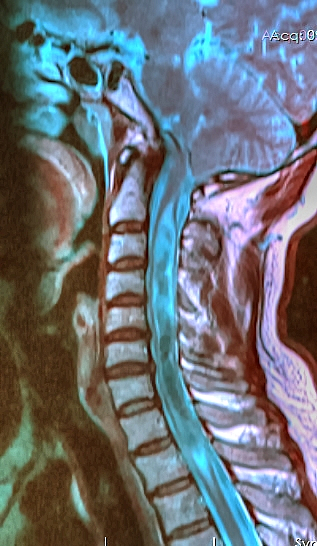 Other conditions sometimes causally associated with Chiari malformation include hydrocephalus,
Other conditions sometimes causally associated with Chiari malformation include hydrocephalus,
dural graft
may be applied to cover the expanded posterior fossa. In those with type I Chiari malformations (especially those with a syrinx), a bone resection with duraplasty (compared to a bone resection without duraplasty) is associated with greater symptom relief and has a higher rate of symptomatic remission, and a lower need for re-operation. However, a bone resection with duraplasty was also associated with a higher rate of surgical complications. Re-operation may be needed in up to 6.8% of patients, and possible causes of re-operation include incomplete decompression and dural scarring. Other complications that are possible in surgical repair of type I Chiari malformations include an
neurology
Neurology (from , "string, nerve" and the suffix wikt:-logia, -logia, "study of") is the branch of specialty (medicine) , medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the nervous syst ...
, the Chiari malformation ( ; CM) is a structural defect in the cerebellum
The cerebellum (: cerebella or cerebellums; Latin for 'little brain') is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as it or eve ...
, characterized by a downward displacement of one or both cerebellar tonsils through the foramen magnum
The foramen magnum () is a large, oval-shaped opening in the occipital bone of the skull. It is one of the several oval or circular openings (foramina) in the base of the skull. The spinal cord, an extension of the medulla oblongata, passes thro ...
(the opening at the base of the skull
The base of skull, also known as the cranial base or the cranial floor, is the most inferior area of the skull. It is composed of the endocranium and the lower parts of the calvaria.
Structure
Structures found at the base of the skull are for ...
).
CMs can cause headaches
A headache, also known as cephalalgia, is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of depression in those with severe headaches.
Head ...
, difficulty swallowing
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under " symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right.
It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or li ...
, vomiting, dizziness
Dizziness is an imprecise term that can refer to a sense of disorientation in space, vertigo, or lightheadedness. It can also refer to Balance disorder, disequilibrium or a non-specific feeling, such as giddiness or foolishness.
Dizziness is a ...
, neck pain, unsteady gait, poor hand coordination, numbness
Hypoesthesia or numbness is a common side effect of various medical conditions that manifests as a reduced sense of touch or sensation, or a partial loss of sensitivity to Sensory receptor, sensory stimuli. In everyday speech this is generally r ...
and tingling of the hands and feet, and speech problems. Less often, people may experience ringing or buzzing in the ears, weakness, slow heart rhythm, fast heart rhythm, curvature of the spine (scoliosis
Scoliosis (: scolioses) is a condition in which a person's Vertebral column, spine has an irregular curve in the coronal plane. The curve is usually S- or C-shaped over three dimensions. In some, the degree of curve is stable, while in others ...
) related to spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
impairment, abnormal breathing such as in central sleep apnea
Central sleep apnea (CSA) or central sleep apnea syndrome (CSAS) is a sleep-related Disorder (medicine)#Disorder, disorder in which the effort to Breathing, breathe is diminished or absent, typically for 10 to 30 seconds either intermittently o ...
, and, in severe cases, paralysis
Paralysis (: paralyses; also known as plegia) is a loss of Motor skill, motor function in one or more Skeletal muscle, muscles. Paralysis can also be accompanied by a loss of feeling (sensory loss) in the affected area if there is sensory d ...
. CM can sometimes lead to non-communicating hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a condition in which cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) builds up within the brain, which can cause pressure to increase in the skull. Symptoms may vary according to age. Headaches and double vision are common. Elderly adults with n ...
as a result of obstruction of cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless Extracellular fluid#Transcellular fluid, transcellular body fluid found within the meninges, meningeal tissue that surrounds the vertebrate brain and spinal cord, and in the ventricular system, ven ...
(CSF) outflow. The CSF outflow is caused by phase difference in outflow and influx of blood in the vasculature
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart an ...
of the brain.
The malformation is named after the Austrian pathologist Hans Chiari
Hans Chiari ( , ; 4 September 1851 − 6 May 1916) was a pathologist from Vienna, Austria-Hungary. He was the son of gynecologist Johann Baptist Chiari (1817–1854) and the brother of otorhinolaryngologist Ottokar Chiari (1853–1918).
Biograp ...
. A type II CM is also known as an Arnold–Chiari malformation after Chiari and German pathologist Julius Arnold
Julius Arnold (19 August 1835 – 3 February 1915) was a German pathologist born in Zurich. He was the son of anatomist Friedrich Arnold (1803–1890).
He studied medicine at the Universities of Heidelberg, Prague, Vienna and Berlin, where he wa ...
.
Signs and symptoms
Findings are due tobrainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is conti ...
and lower cranial nerve dysfunction. Onset of symptoms are less likely to be present during adulthood in most patients. Younger children generally have a substantially different presentation of clinical symptoms from older children. Younger children are more likely to have a more rapid neurological degeneration with profound brainstem dysfunction over several days.
Headache is the most common symptom in those with Chiari malformation type 1 (in which only the cerebellar tonsils descend below the foramen magnum). This headache is usually occipital or sub-occipital in location (but may also present in other cranial areas), is usually dull or throbbing in character and is characteristically associated with Valsalva
The Valsalva maneuver is performed by a forceful attempt of exhalation against a closed airway, usually done by closing one's mouth and pinching one's nose shut while expelling air, as if blowing up a balloon. Variations of the maneuver can be ...
maneuvers (such as bearing down, coughing, sneezing, bending over or forcefully exhaling against a closed airway).Considering a headache is one of the most common symptoms, it is important to note that a tension headache is also a common repetative sign before diagnosis.
Symptoms that may be due to Chiari malformations include:
* Neurogenic dysphagia
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under " symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right.
It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or l ...
: Difficulty swallowing.
* Cyanosis
Cyanosis is the change of Tissue (biology), tissue color to a bluish-purple hue, as a result of decrease in the amount of oxygen bound to the hemoglobin in the red blood cells of the capillary bed. Cyanosis is apparent usually in the Tissue (bi ...
: Bluish discoloration of skin while feeding.
* Weak crying
* Facial weakness
* Aspiration
* Headaches aggravated by Valsalva maneuver
The Valsalva maneuver is performed by a forceful attempt of exhalation against a closed airway, usually done by closing one's mouth and pinching one's nose shut while expelling air, as if blowing up a balloon. Variations of the maneuver can be ...
s
* Tinnitus
Tinnitus is a condition when a person hears a ringing sound or a different variety of sound when no corresponding external sound is present and other people cannot hear it. Nearly everyone experiences faint "normal tinnitus" in a completely ...
(ringing in the ears)
* Lhermitte's sign
In neurology, Lhermitte phenomenon, also called the barber chair phenomenon, is an uncomfortable "electrical" sensation that runs down the back and into the limbs. The sensation can feel like it goes up or down the spine. It is painful for some, ...
(electrical sensation that runs down the back and into the limbs)
* Vertigo
Vertigo is a condition in which a person has the sensation that they are moving, or that objects around them are moving, when they are not. Often it feels like a spinning or swaying movement. It may be associated with nausea, vomiting, perspira ...
(dizziness)
* Nausea
* Schmahmann's syndrome
* Nystagmus
Nystagmus is a condition of involuntary (or voluntary, in some cases) Eye movement (sensory), eye movement. People can be born with it but more commonly acquire it in infancy or later in life. In many cases it may result in visual impairment, re ...
(irregular eye movements; typically, so-called "downbeat nystagmus")
* Facial pain
* Muscle weakness
* Impaired gag reflex
* Dysphagia
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under " symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right.
It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or l ...
(difficulty swallowing)
* Restless leg syndrome
Restless legs syndrome (RLS), also known as Willis–Ekbom disease (WED), is a neurological disorder, usually chronic, that causes an overwhelming urge to move one's legs. There is often an unpleasant feeling in the legs that improves temporaril ...
* Sleep apnea
Sleep apnea (sleep apnoea or sleep apnœa in British English) is a sleep-related breathing disorder in which repetitive Apnea, pauses in breathing, periods of shallow breathing, or collapse of the upper airway during sleep results in poor vent ...
* Sleep disorders
* Impaired coordination
* Severe cases may develop all the symptoms and signs of a bulbar palsy
The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (invol ...
* Paralysis
Paralysis (: paralyses; also known as plegia) is a loss of Motor skill, motor function in one or more Skeletal muscle, muscles. Paralysis can also be accompanied by a loss of feeling (sensory loss) in the affected area if there is sensory d ...
due to pressure at the cervico-medullary junction may progress in a so-called "clockwise" fashion, affecting the right arm, then the right leg, then the left leg, and finally the left arm; or the opposite way around.
* Papilledema on fundoscopic exam due to increased intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the pressure exerted by fluids such as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inside the skull and on the brain tissue. ICP is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and at rest, is normally 7–15 mmHg for a supine adult. ...
* Pupillary dilation
Pupillary response is a physiological response that varies the size of the pupil between 1.5 mm and 8 mm, via the optic and oculomotor cranial nerve.
A constriction response (miosis), is the narrowing of the pupil, which may be caused by scler ...
* Dysautonomia
Dysautonomia, autonomic failure, or autonomic dysfunction is a condition in which the autonomic nervous system (ANS) does not work properly. This condition may affect the functioning of the heart, bladder, intestines, sweat glands, pupils, and ...
: tachycardia
Tachycardia, also called tachyarrhythmia, is a heart rate that exceeds the normal resting rate. In general, a resting heart rate over 100 beats per minute is accepted as tachycardia in adults. Heart rates above the resting rate may be normal ...
(rapid heart), syncope (fainting), polydipsia
Polydipsia is excessive thirst or excess drinking.Porth, C. M. (1990). ''Pathophysiology: Concepts of altered health states''. Philadelphia: J.B. Lippincott Company. The word derives , which is derived . Polydipsia is a nonspecific symptom in v ...
(extreme thirst), chronic fatigue
* Apnea
Apnea (also spelled apnoea in British English) is the temporary cessation of breathing. During apnea, there is no movement of the muscles of inhalation, and the volume of the lungs initially remains unchanged. Depending on how blocked the ...
: Sudden pause of breathing, usually during sleep.
* Opisthotonos
Opisthotonus or opisthotonos (from and ) is a state of severe hyperextension and spasticity in which an individual's head, neck and spinal column enter into a complete "bridging" or "arching" position.
This extreme arched pose is an extrapyram ...
: Spasm of the head which causes head to arch backwards. More common in infants than adults.
* Stridor
Stridor () is an extra-thoracic high-pitched breath sound resulting from turbulent air flow in the larynx or lower in the bronchial tree. It is different from a stertor, which is a noise originating in the pharynx.
Stridor is a physical sig ...
The blockage of cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless Extracellular fluid#Transcellular fluid, transcellular body fluid found within the meninges, meningeal tissue that surrounds the vertebrate brain and spinal cord, and in the ventricular system, ven ...
(CSF) flow may also cause a syrinx
In classical Greek mythology, Syrinx () was an Arcadian nymph and a follower of Artemis, known for her chastity. Being pursued by Pan, she fled into the river Ladon, and at her own request was metamorphosed into a reed from which Pan then mad ...
to form, eventually leading to syringomyelia
Syringomyelia is a generic term referring to a disorder in which a cyst or cavity forms within the spinal cord. Often, syringomyelia is used as a generic term before an etiology is determined. This cyst, called a syrinx, can expand and elongate ...
. Central cord symptoms such as hand weakness, dissociated sensory loss, and, in severe cases, paralysis may occur.
Syringomyelia
Syringomyelia is most often chronic progressive degenerative disorder characterized by a fluid-filledcyst
A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct envelope and division compared with the nearby tissue. Hence, it is a cluster of cells that have grouped together to form a sac (like the manner in which water molecules group together to form a bubb ...
located in the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
. However, there can be also cases where the syrinx in terms of size and extent of symptoms actually stays stable throughout a lifetime. Syringomyelia symptoms include pain, weakness, numbness, and stiffness in the back, shoulders, arms or legs. Other symptoms include headaches, the inability to feel changes in the temperature, sweating, sexual dysfunction, and loss of bowel and bladder control. It is usually seen in the cervical region but can extend into the medulla oblongata
The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involun ...
and pons
The pons (from Latin , "bridge") is part of the brainstem that in humans and other mammals, lies inferior to the midbrain, superior to the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum.
The pons is also called the pons Varolii ("bridge of ...
or it can reach downward into the thoracic
The thorax (: thoraces or thoraxes) or chest is a part of the anatomy of mammals and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen.
In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main ...
or lumbar
In tetrapod anatomy, lumbar is an adjective that means of or pertaining to the abdominal segment of the torso, between the diaphragm (anatomy), diaphragm and the sacrum.
Naming and location
The lumbar region is sometimes referred to as the lowe ...
segments. Syringomyelia is often associated with type I Chiari malformation and is commonly seen between the C-4 and C-6 levels. The exact development of syringomyelia is unknown but many theories suggest that the herniated tonsils in type I Chiari malformations cause a "plug" to form, which does not allow an outlet of CSF from the brain to the spinal canal. Syringomyelia is present in 25% of patients with type I Chiari malformations.
Pathophysiology
 The most common pathophysiological mechanism by which Chiari type I malformations occurs is due to a congenitally small posterior fossa. Other pathophysiological mechanisms involve increased intracranial pressure above the foramen magnum which causes a downward pressure against the cerebellum, thus causing the cerebellar tonsils to displace below the foramen magnum. Such causes include
The most common pathophysiological mechanism by which Chiari type I malformations occurs is due to a congenitally small posterior fossa. Other pathophysiological mechanisms involve increased intracranial pressure above the foramen magnum which causes a downward pressure against the cerebellum, thus causing the cerebellar tonsils to displace below the foramen magnum. Such causes include hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a condition in which cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) builds up within the brain, which can cause pressure to increase in the skull. Symptoms may vary according to age. Headaches and double vision are common. Elderly adults with n ...
(an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid SFaround the brain), space occupying lesions in the brain such as tumors, subdural hematomas
A subdural hematoma (SDH) is a type of bleeding in which a collection of blood—usually but not always associated with a traumatic brain injury—gathers between the inner layer of the dura mater and the arachnoid mater of the meninges surroun ...
or other subdural fluid collections, arachnoid cysts, craniosynostosis
Craniosynostosis is a condition in which one or more of the fibrous sutures in a young infant's skull prematurely fuses by turning into bone (ossification), thereby changing the growth pattern of the skull. Because the skull cannot expand perpe ...
(early closure of the cranial sutures)(especially of the lambdoid suture), hyperostosis
Hyperostosis is an excessive growth of bone. It may lead to exostosis. It occurs in many musculoskeletal disorders and from use of drugs like Isotretinoin.
Disorders featuring hyperostosis include:
* Camurati-Engelmann disease, type 2
* Hyper ...
(an excessive growth of bone) (such as craniometaphyseal dysplasia, osteopetrosis
Osteopetrosis, literally , also known as marble bone disease or Albers-Schönberg disease, is an extremely rare inherited disorder whereby the bones harden, becoming denser, in contrast to more prevalent conditions like osteoporosis, in which ...
). Another pathophysiological mechanism by which Chiari malformations form is by negative pressure or a pulling force from below the foramen magnum which pulls against the brain, causing the cerebellar tonsils to herniate past the foramen magnum. Causes of this negative or pulling pressure include a tethered cord
Tethered cord syndrome (TCS) refers to a group of neurological disorders that relate to malformations of the spinal cord.cerebrospinal fluid leak
A cerebrospinal fluid leak (CSF leak or CSFL) is a medical condition where the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that surrounds the brain and spinal cord leaks out of one or more holes or tears in the dura mater. A CSF leak is classed as either spontane ...
creating a negative pressure around the spinal cord as the fluid surrounding the cord leaks out, or a CSF-venous fistula, in which the CSF leaks into a nearby vein.
Traumatic brain injury may cause delayed acquired Chiari malformation, but the pathophysiology of this is unknown. This is due to the fact that the condition can go asymptomatic for years and a diagnosis is often led through testing for a variety of symptoms. Additionally, ectopia may be present but asymptomatic until a whiplash injury causes it to become symptomatic. Other conditions linked to Chiari malformations include X-linked vitamin D-resistant rickets, and neurofibromatosis type I
Neurofibromatosis type I (NF-1), or von Recklinghausen syndrome, is a complex multi-system neurocutaneous disorder caused by a subset of genetic mutations at the neurofibromin 1 (''NF1'') locus. Other conditions associated with mutation of the ...
.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made through a combination of patient history, neurological examination, and medical imaging.Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and ...
(MRI) is considered the preferred imaging modality for Chiari malformation. The MRI visualizes neural tissue such as the cerebellar tonsils and spinal cord as well as bone and other soft tissues. CT and CT myelography are other options and were used prior to the advent of MRI, unfortunately the resolution of CT based modalities do not characterize syringomyelia and other neural abnormalities as well.
By convention, the cerebellar tonsil position is measured relative to the basion-opisthion line, using sagittal T1 MRI images or sagittal CT images. The selected cutoff distance for abnormal tonsil position is somewhat arbitrary, as not every person will be symptomatic at a certain amount of tonsil displacement, and the probability of symptoms and syrinx increases with greater displacement; however, greater than 5 mm is the most frequently cited cutoff number, though some consider 3–5 mm to be "borderline"; pathological signs and syrinx may occur beyond that distance. One study showed little difference in cerebellar tonsil position between standard recumbent MRI and upright MRI for patients without a history of whiplash injury. Neuroradiological investigation is used to first rule out any intracranial condition that could be responsible for tonsillar herniation. Neuroradiological diagnostics evaluate the severity of crowding of the neural structures within the posterior cranial fossa and their pressure against the foramen magnum. Chiari 1.5 is a term used when both brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is conti ...
and tonsillar herniation through the foramen magnum are present.
The diagnosis of a Chiari II malformation can be made prenatally, through ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound with frequency, frequencies greater than 20 Hertz, kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible hearing range, limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply ...
.
Classification
In the late 19th century, Austrian pathologistHans Chiari
Hans Chiari ( , ; 4 September 1851 − 6 May 1916) was a pathologist from Vienna, Austria-Hungary. He was the son of gynecologist Johann Baptist Chiari (1817–1854) and the brother of otorhinolaryngologist Ottokar Chiari (1853–1918).
Biograp ...
described seemingly related anomalies of the hindbrain, the so-called Chiari malformations I, II and III. Later, other investigators added a fourth (Chiari IV) malformation. The scale of severity is rated I – IV, with IV being the most severe. Types III and IV are very rare. Since Dr. Chiari's original descriptions Chiari 0, 1.5, 3.5, and 5 have been described in the medical literature.
Types of Chiari malformation
 Other conditions sometimes causally associated with Chiari malformation include hydrocephalus,
Other conditions sometimes causally associated with Chiari malformation include hydrocephalus, syringomyelia
Syringomyelia is a generic term referring to a disorder in which a cyst or cavity forms within the spinal cord. Often, syringomyelia is used as a generic term before an etiology is determined. This cyst, called a syrinx, can expand and elongate ...
, spinal curvature
The spinal column, also known as the vertebral column, spine or backbone, is the core part of the axial skeleton in vertebrates. The vertebral column is the defining and eponymous characteristic of the vertebrate. The spinal column is a segmente ...
, tethered spinal cord syndrome
Tethered cord syndrome (TCS) refers to a group of neurological disorders that relate to malformations of the spinal cord.connective tissue disorder
Connective tissue diseases (also termed connective tissue disorders, or collagen vascular diseases), are medical conditions that affect connective tissue.
Connective tissues protect, support, and provide structure for the body's other tissues a ...
s such as Ehlers–Danlos syndrome
Ehlers–Danlos syndromes (EDS) is a group of 14 genetic connective-tissue disorders. Symptoms often include loose joints, joint pain, stretchy velvety skin, and abnormal scar formation. These may be noticed at birth or in early childhood. Co ...
and Marfan syndrome
Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a multi-systemic genetic disorder that affects the connective tissue. Those with the condition tend to be tall and thin, with dolichostenomelia, long arms, legs, Arachnodactyly, fingers, and toes. They also typically ha ...
.
Chiari malformation is the most frequently used term for this set of conditions. The use of the term "Arnold–Chiari malformation" has fallen somewhat out of favor over time, although it is used to refer to the type II malformation. Current sources use "Chiari malformation" to describe its four specific types, reserving the term "Arnold–Chiari" for type II only. Some sources still use "Arnold–Chiari" for all four types.
Chiari malformation type 1 emerges during skull and brain development, often without symptoms until late childhood or adulthood. In contrast, the pediatric forms include type 2 and type 3, which are present from birth, making them congenital conditions.
Chiari malformation or Arnold–Chiari malformation should not be confused with Budd–Chiari syndrome
Budd–Chiari syndrome is a condition when an occlusion or obstruction in the hepatic veins prevent normal outflow of blood from the liver.
The symptoms are non-specific and vary widely, but it may present with the classical triad of abdomin ...
, a hepatic condition also named for Hans Chiari
Hans Chiari ( , ; 4 September 1851 − 6 May 1916) was a pathologist from Vienna, Austria-Hungary. He was the son of gynecologist Johann Baptist Chiari (1817–1854) and the brother of otorhinolaryngologist Ottokar Chiari (1853–1918).
Biograp ...
.
In Pseudo-Chiari Malformation, leaking of CSF may cause displacement of the cerebellar tonsils and similar symptoms sufficient to be mistaken for a Chiari I malformation.
Treatment
While there is no current cure, the treatments for Chiari malformation are surgery and management of symptoms. Treatment is directed on the occurrence of clinical symptoms rather than the radiological findings. The presence of a syrinx is known to give specific signs and symptoms that vary from dysesthetic sensations to algothermal dissociation tospasticity
Spasticity () is a feature of altered skeletal muscle performance with a combination of paralysis, increased tendon reflex activity, and hypertonia. It is also colloquially referred to as an unusual "tightness", stiffness, or "pull" of muscles. ...
and paresis
In medicine, paresis (), compound word from Greek , (πᾰρᾰ- “beside” + ἵημι “let go, release”), is a condition typified by a weakness of voluntary movement, or by partial loss of voluntary movement or by impaired movement. Whe ...
. These are important indications that decompressive surgery is needed for patients with Chiari Malformation Type II. Type II patients have severe brainstem damage and rapidly diminishing neurological response.
Decompressive surgery involves removing the lamina
Lamina may refer to:
People
* Saa Emerson Lamina, Sierra Leonean politician
* Tamba Lamina, Sierra Leonean politician and diplomat
Science and technology
* Planar lamina, a two-dimensional planar closed surface with mass and density, in mathem ...
of the first and sometimes the second or third cervical vertebrae
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In saurop ...
and part of the occipital bone
The occipital bone () is a neurocranium, cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput (back and lower part of the skull). It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish. The occipital bone lies over the occipital lob ...
of the skull
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
to relieve pressure. The flow of spinal fluid may be augmented by a shunt. The surgery may involve the opening of the dura mater to allow decompression of the brain. dural graft
may be applied to cover the expanded posterior fossa. In those with type I Chiari malformations (especially those with a syrinx), a bone resection with duraplasty (compared to a bone resection without duraplasty) is associated with greater symptom relief and has a higher rate of symptomatic remission, and a lower need for re-operation. However, a bone resection with duraplasty was also associated with a higher rate of surgical complications. Re-operation may be needed in up to 6.8% of patients, and possible causes of re-operation include incomplete decompression and dural scarring. Other complications that are possible in surgical repair of type I Chiari malformations include an
aseptic meningitis
Aseptic meningitis is the inflammation of the meninges, a membrane covering the brain and spinal cord, in patients whose cerebral spinal fluid test result is negative with routine bacterial cultures. Aseptic meningitis is caused by viruses, mycob ...
due to irritation from the dural grafts which is seen in 32% of cases. Rates of aseptic meningitis are lower with dural allografts or autografts as compared to bovine or synthetic grafts. Another complication includes a CSF leak, which may occur in up to 21% of people post-operatively.
A small number of neurological surgeons believe that detethering the spinal cord as an alternate approach relieves the compression of the brain against the skull opening (foramen magnum), obviating the need for decompression surgery and associated trauma. However, this approach is significantly less documented in the medical literature, with reports on only a handful of patients. The alternative spinal surgery is also not without risk.
Complications of decompression surgery can arise. They include bleeding, damage to structures in the brain and spinal canal, meningitis
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, intense headache, vomiting and neck stiffness and occasion ...
, CSF fistulas, occipito-cervical instability, and pseudomeningocele. Rare post-operative complications include hydrocephalus and brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is conti ...
compression by retroflexion of odontoid. Also, an extended CVD created by a wide opening and big duroplasty can cause a cerebellar "slump". This complication needs to be corrected by cranioplasty.
In certain cases, irreducible compression of the brainstem occurs from in front (anteriorly or ventral) resulting in a smaller posterior fossa and associated Chiari malformation. In these cases, an anterior decompression is required. The most commonly used approach is to operate through the mouth (transoral) to remove the bone compressing the brainstem, typically the odontoid. This results in decompressing the brainstem and therefore gives more room for the cerebellum, thus decompressing the Chiari malformation. Arnold Menzes, MD, is the neurosurgeon who pioneered this approach in the 1970s at the University of Iowa. Between 1984 and 2008 (the MR imaging era), 298 patients with irreducible ventral compression of the brainstem and Chiari type I malformation underwent a transoral approach for ventral cervicomedullary decompression at the University of Iowa. The results have been excellent resulting in improved brainstem function and resolution of the Chiari malformation in the majority of patients.
Epidemiology
The incidence of congenital Chiari I malformation was previously believed to be in the range of one per 1000 births, but is likely much higher. Women are three times more likely than men to have a congenital Chiari malformation. Type II malformations are more prevalent in people of Celtic descent. A study using upright MRI found cerebellar tonsillar ectopia in 23% of adults with headache from motor-vehicle-accident head trauma. Upright MRI was more than twice as sensitive as standard MRI, likely because gravity affects cerebellar position. Cases of congenital Chiari malformation may be explained by evolutionary and genetic factors. Typically, an infant's brain weighs around 400g at birth and triples to 1100-1400g by age 11. At the same time the cranium triples in volume from 500 cm3 to 1500 cm3 to accommodate the growing brain. During human evolution, the skull underwent numerous changes to accommodate the growing brain. The evolutionary changes included increased size and shape of the skull, decreased basal angle and basicranial length. These modifications resulted in significant reduction of the size of the posterior fossa in modern humans. In normal adults, the posterior fossa comprises 27% of the total intracranial space, while in adults with Chiari Type I, it is only 21%. H. neanderthalensis had platycephalic (flattened) skulls. Some cases of Chiari are associated with platybasia (flattening of the skull base).History
The history of Chiari malformation: * 1883: Cleland was the first to describe Chiari II or Arnold–Chiari malformation on his report of a child with spina bifida, hydrocephalus, and anatomical alterations of the cerebellum and brainstem. * 1891:Hans Chiari
Hans Chiari ( , ; 4 September 1851 − 6 May 1916) was a pathologist from Vienna, Austria-Hungary. He was the son of gynecologist Johann Baptist Chiari (1817–1854) and the brother of otorhinolaryngologist Ottokar Chiari (1853–1918).
Biograp ...
, a Viennese pathologist, described the case of a 17-year-old female with elongation of the tonsils into cone shaped projections which accompany the medulla and are crammed into the spinal canal.
* 1907: Schwalbe and Gredig, pupils of German pathologist Julius Arnold
Julius Arnold (19 August 1835 – 3 February 1915) was a German pathologist born in Zurich. He was the son of anatomist Friedrich Arnold (1803–1890).
He studied medicine at the Universities of Heidelberg, Prague, Vienna and Berlin, where he wa ...
, described four cases of meningomyelocele and alterations in the brainstem and cerebellum, and gave the name "Arnold–Chiari" to these malformations.
* 1932: Van Houweninge Graftdijk was the first to report the surgical treatment of Chiari malformations. All patients died from surgery or postoperative complications.
* 1935: Russell and Donald suggested that decompression of the spinal cord at the foramen magnum might facilitate the CSF circulation.
* 1940: Gustafson and Oldberg diagnosed Chiari malformation with syringomyelia.
* 1974: Bloch ''et al.'' described the tonsils position to be classified between 7 mm and 8 mm below cerebellum.
* 1985: Aboulezz used MRI for discovery of extension
Society and culture
The condition was brought to the mainstream on the series '' CSI: Crime Scene Investigation'' in the tenth-season episode "Internal Combustion" on February 4, 2010.Notable people
*Rosanne Cash
Rosanne Cash (born May 24, 1955) is an American singer-songwriter and author. She is the eldest daughter of country musician Johnny Cash and his first wife, Vivian Cash.
Although Cash is often classified as a country artist, her music draws f ...
– U.S. singer-songwriter; daughter of Johnny Cash
* Julia Clukey
Julia Clukey (born April 29, 1985, in Augusta, Maine) is an American luger who started competing in 2002. Her best List of Luge World Cup champions, Luge World Cup season finish was 12th in women's singles in 2007–08 Luge World Cup, 2007–08 ...
– U.S. luge competitor for Team USA in 2010 Vancouver Winter Olympics
* Joanna David
Joanna David (born Joanna Elizabeth Hacking; 17 January 1947) is an English people, English actress, best known for her television work.
Early life and education
David was born in Lancaster, Lancashire, Lancaster, England, daughter of Major Jo ...
– British television and stage actress
* J. B. Holmes – U.S. professional golfer
* Marissa Irwin – U.S. fashion model with Chiari secondary to Ehlers–Danlos syndrome
Ehlers–Danlos syndromes (EDS) is a group of 14 genetic connective-tissue disorders. Symptoms often include loose joints, joint pain, stretchy velvety skin, and abnormal scar formation. These may be noticed at birth or in early childhood. Co ...
* Bobby Jones – U.S. World Golf Hall of Fame golfer and founder of the Augusta National Golf Club
* Allysa Seely
Allysa Seely (born January 4, 1989) is an American paratriathlete and gold medalist at the 2016 and 2020 Summer Paralympics.
Background
Seely was born on January 4, 1989. She grew up in Glendale, Arizona and graduated from Mountain Ridge High ...
– U.S. Gold Medalist at the 2016 Summer Paralympics in the paratriathlon
* Leah Shapiro – U.S. drummer for the band Black Rebel Motorcycle Club
* Michelle Stilwell
Michelle Stilwell (''nee'' Bauknecht; born July 4, 1974) is a Canadian athlete and politician. She represented Canada at four Summer Paralympic Games (2000, 2008, 2012 and 2016), as well as the 2015 Parapan American Games. She competed in wheel ...
– Canadian wheelchair racer and politician
* Rachid Taha
Rachid Taha (, Latn, ar, Rashīd Ṭāhā, ; 18 September 1958 – 12 September 2018) was an Algerian people, Algerian singer and activist based in France described as "sonically adventurous". His music was influenced by many different styles in ...
– Algerian singer
* Sabre Norris – Australian skateboarder and surfer
See also
*Hypermobility spectrum disorder
Hypermobility spectrum disorder (HSD), related to earlier diagnoses such as hypermobility syndrome (HMS), and joint hypermobility syndrome (JHS) is a heritable connective tissue disorder that affects joints and ligaments. Different forms and s ...
Notes
References
{{Congenital malformations and deformations of nervous system Congenital disorders of nervous system Diseases named after discoverers