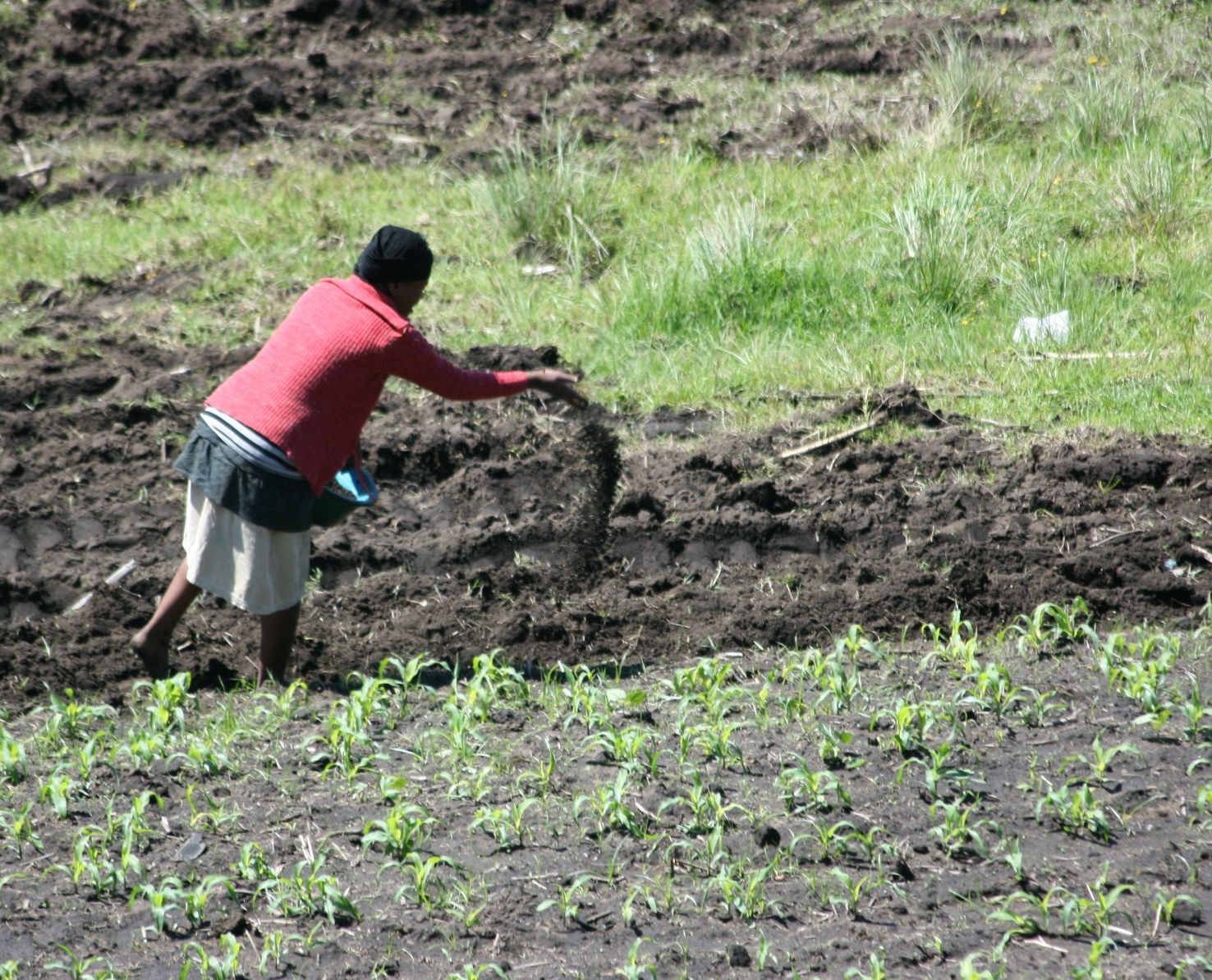

A fertilizer or fertiliser is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply
plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from
liming materials or other non-nutrient
soil amendments. Many sources of fertilizer exist, both natural and
industrially produced.
[ For most modern agricultural practices, fertilization focuses on three main macro nutrients: ]nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
(N), phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol P and atomic number 15. All elemental forms of phosphorus are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive and are therefore never found in nature. They can nevertheless be prepared ar ...
(P), and potassium
Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to ...
(K) with occasional addition of supplements like rock flour
Rock flour, or glacial flour, consists of fine-grained, silt-sized particles of rock, generated by mechanical grinding of bedrock by glacial erosion or by artificial grinding to a similar size. Because the material is very small, it becomes suspe ...
for micronutrients. Farmers apply these fertilizers in a variety of ways: through dry or pelletized or liquid application processes, using large agricultural equipment, or hand-tool methods.
Historically, fertilization came from natural or organic sources: compost
Compost is a mixture of ingredients used as plant fertilizer and to improve soil's physical, chemical, and biological properties. It is commonly prepared by Decomposition, decomposing plant and food waste, recycling organic materials, and man ...
, animal manure, human manure, harvested minerals, crop rotation
Crop rotation is the practice of growing a series of different types of crops in the same area across a sequence of growing seasons. This practice reduces the reliance of crops on one set of nutrients, pest and weed pressure, along with the pro ...
s, and byproducts of human-nature industries (e.g. fish processing waste, or bloodmeal from animal slaughter
Animal slaughter is the killing of animals, usually referring to killing Domestication, domestic livestock. It is estimated that each year, 80 billion land animals are slaughtered for food. Most animals are slaughtered for Human food, food; how ...
). However, starting in the 19th century, after innovations in plant nutrition
Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds necessary for plant growth and reproduction, plant metabolism and their external supply. In its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle, or that the element i ...
, an agricultural industry developed around synthetically created agrochemical fertilizers. This transition was important in transforming the global food system, allowing for larger-scale industrial agriculture
Industrial agriculture is a form of modern farming that refers to the industrialized production of crops and animals and animal products like eggs or milk. The methods of industrial agriculture include innovation in agricultural machinery and ...
with large crop yields.
Nitrogen-fixing
Nitrogen fixation is a chemical process by which molecular dinitrogen () is converted into ammonia (). It occurs both biologically and abiological nitrogen fixation, abiologically in chemical industry, chemical industries. Biological nitrogen ...
chemical processes, such as the Haber process
The Haber process, also called the Haber–Bosch process, is the main industrial procedure for the ammonia production, production of ammonia. It converts atmospheric nitrogen (N2) to ammonia (NH3) by a reaction with hydrogen (H2) using finely di ...
invented at the beginning of the 20th century, and amplified by production capacity created during World War II, led to a boom in using nitrogen fertilizers. In the latter half of the 20th century, increased use of nitrogen fertilizers (800% increase between 1961 and 2019) has been a crucial component of the increased productivity of conventional food systems
The term food system describes the interconnected systems and processes that influence nutrition, Human food, food, health, community development, and agriculture. A food system includes all processes and infrastructure involved in feeding a popul ...
(more than 30% per capita) as part of the so-called "Green Revolution
The Green Revolution, or the Third Agricultural Revolution, was a period during which technology transfer initiatives resulted in a significant increase in crop yields. These changes in agriculture initially emerged in Developed country , devel ...
".
The use of artificial and industrially-applied fertilizers has caused environmental consequences such as water pollution
Water pollution (or aquatic pollution) is the contamination of Body of water, water bodies, with a negative impact on their uses. It is usually a result of human activities. Water bodies include lakes, rivers, oceans, aquifers, reservoirs and ...
and eutrophication
Eutrophication is a general term describing a process in which nutrients accumulate in a body of water, resulting in an increased growth of organisms that may deplete the oxygen in the water; ie. the process of too many plants growing on the s ...
due to nutritional runoff; carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
and other emissions from fertilizer production and mining; and contamination and pollution of soil. Various sustainable agriculture
Sustainable agriculture is agriculture, farming in sustainability, sustainable ways meeting society's present food and textile needs, without compromising the ability for current or future generations to meet their needs. It can be based on an ...
practices can be implemented to reduce the adverse environmental effects of fertilizer and pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are used to control pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others (see table). The most common of these are herbicides, which account for approximately 50% of all p ...
use and environmental damage
Environment most often refers to:
__NOTOC__
* Natural environment, referring respectively to all living and non-living things occurring naturally and the physical and biological factors along with their chemical interactions that affect an organism ...
caused by industrial agriculture
Industrial agriculture is a form of modern farming that refers to the industrialized production of crops and animals and animal products like eggs or milk. The methods of industrial agriculture include innovation in agricultural machinery and ...
.
History

 Management of
Management of soil fertility
Soil fertility refers to the ability of soil to sustain agricultural plant growth, i.e. to provide plant habitat and result in sustained and consistent yields of high quality. has preoccupied farmers since the beginning of agriculture. Middle Eastern, Chinese, Mesoamerican, and Cultures of the Central Andes were all early adopters of agriculture. This is thought to have led to their cultures growing faster in population which allowed an exportation of culture to neighboring hunter-gatherer groups. Fertilizer use along with agriculture allowed some of these early societies a critical advantage over their neighbors, leading them to become dominant cultures in their respective regions (P Bellwood - 2023). Egyptians, Romans, Babylonians, and early Germans are all recorded as using minerals or manure to enhance the productivity of their farms.[ The scientific research of plant nutrition started well before the work of German chemist ]Justus von Liebig
Justus ''Freiherr'' von Liebig (12 May 1803 – 18 April 1873) was a Germans, German scientist who made major contributions to the theory, practice, and pedagogy of chemistry, as well as to agricultural and biology, biological chemistry; he is ...
although his name is most mentioned as the "father of the fertilizer industry". Nicolas Théodore de Saussure
Nicolas-Théodore de Saussure (; 14 October 1767 – 18 April 1845) was a Swiss chemist and student of plant physiology who made seminal advances in phytochemistry. He is one of the major pioneers in the study of photosynthesis.
Biography
Nicolas ...
and scientific colleagues at the time were quick to disprove the simplifications of von Liebig. Prominent scientists whom von Liebig drew were Carl Ludwig Sprenger and Hermann Hellriegel. In this field, a 'knowledge erosion' took place, partly driven by an intermingling of economics and research. John Bennet Lawes, an English entrepreneur
Entrepreneurship is the creation or extraction of economic value in ways that generally entail beyond the minimal amount of risk (assumed by a traditional business), and potentially involving values besides simply economic ones.
An entreprene ...
, began experimenting on the effects of various manures on plants growing in pots in 1837, and a year or two later the experiments were extended to crops in the field. One immediate consequence was that in 1842 he patented a manure formed by treating phosphates with sulfuric acid, and thus was the first to create the artificial manure industry. In the succeeding year, he enlisted the services of Joseph Henry Gilbert; together they performed crop experiments at the Institute of Arable Crops Research.
The Birkeland–Eyde process
The Birkeland–Eyde process was one of the competing industrial processes in the beginning of Nitrogen fertilizer, nitrogen-based fertilizer production. It is a multi-step nitrogen fixation reaction that uses electrical arcs to react atmospheric ...
was one of the competing industrial processes at the beginning of nitrogen-based fertilizer production. This process was used to fix atmospheric nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
(N2) into nitric acid
Nitric acid is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but samples tend to acquire a yellow cast over time due to decomposition into nitrogen oxide, oxides of nitrogen. Most com ...
(HNO3), one of several chemical processes called nitrogen fixation
Nitrogen fixation is a chemical process by which molecular dinitrogen () is converted into ammonia (). It occurs both biologically and abiological nitrogen fixation, abiologically in chemical industry, chemical industries. Biological nitrogen ...
. The resultant nitric acid was then used as a source of nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . salt (chemistry), Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are solubility, soluble in wa ...
(NO3−). A factory based on the process was built in Rjukan
Rjukan () is a List of towns and cities in Norway, town in Tinn Municipality in Telemark county, Norway. The town is also the administrative centre of Tinn Municipality. The town is located in the Vestfjorddalen valley, between the lakes Møsvatn ...
and Notodden
is a municipality in Telemark county, Norway. It is located in the traditional district of Aust-Telemark. The administrative centre of the municipality is the town of Notodden. Other population centres include the villages of Bolkesjø, G ...
in Norway and large hydroelectric power
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies 15% of the world's electricity, almost 4,210 TWh in 2023, which is more than all other Renewable energ ...
facilities were built.
The 1910s and 1920s witnessed the rise of the Haber process
The Haber process, also called the Haber–Bosch process, is the main industrial procedure for the ammonia production, production of ammonia. It converts atmospheric nitrogen (N2) to ammonia (NH3) by a reaction with hydrogen (H2) using finely di ...
and the Ostwald process. The Haber process produces ammonia (NH3) from methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes ...
(CH4) (natural gas
Natural gas (also fossil gas, methane gas, and gas) is a naturally occurring compound of gaseous hydrocarbons, primarily methane (95%), small amounts of higher alkanes, and traces of carbon dioxide and nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide and helium ...
) gas and molecular nitrogen (N2) from the air. The ammonia from the Haber process is then partially converted into nitric acid
Nitric acid is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but samples tend to acquire a yellow cast over time due to decomposition into nitrogen oxide, oxides of nitrogen. Most com ...
(HNO3) in the Ostwald process. It is estimated that a third of annual global food production uses ammonia from the Haber–Bosch process and that this supports nearly half the world's population. After World War II, nitrogen production plants that had ramped up for wartime bomb manufacturing were pivoted towards agricultural uses.tonnes
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1,000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton in the United States to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the s ...
of nitrogen per year.hectare
The hectare (; SI symbol: ha) is a non-SI metric unit of area equal to a square with 100-metre sides (1 hm2), that is, square metres (), and is primarily used in the measurement of land. There are 100 hectares in one square kilometre. ...
() requires of phosphate
Phosphates are the naturally occurring form of the element phosphorus.
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthop ...
fertilizer to be applied; soybean crops require about half, 20–25 kg per hectare. Yara International
Yara International ASA is a Norwegian chemical company. It produces, distributes, and sells nitrogen-based mineral fertilizers and related industrial products. Its product line also includes phosphate and potash-based mineral fertilizers, as we ...
is the world's largest producer of nitrogen-based fertilizers.
Mechanism
Fertilizers enhance the growth of plants. This goal is met in two ways, the traditional one being additives that provide nutrients. The second mode by which some fertilizers act is to enhance the effectiveness of the soil by modifying its water retention and aeration. This article, like many on fertilizers, emphasizes the nutritional aspect.
Fertilizers typically provide, in varying proportions:[
* Three main macronutrients (NPK):
** ]Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
(N): leaf growth and stems
** Phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol P and atomic number 15. All elemental forms of phosphorus are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive and are therefore never found in nature. They can nevertheless be prepared ar ...
(P): development of roots, flowers, seeds and fruit;
** Potassium
Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to ...
(K): strong stem growth, movement of water in plants, promotion of flowering and fruiting;
* three secondary macronutrients: calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to it ...
(Ca), magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 ...
(Mg), and sulfur
Sulfur ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphur ( Commonwealth spelling) is a chemical element; it has symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms ...
(S);
* Micronutrients: copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
(Cu), iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
(Fe), manganese
Manganese is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese was first isolated in the 1770s. It is a transition m ...
(Mn), molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mo (from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'') and atomic number 42. The name derived from Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ores. Molybdenum minerals hav ...
(Mo), zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
(Zn), and boron
Boron is a chemical element; it has symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the boron group it has three ...
(B). Of occasional significance are silicon
Silicon is a chemical element; it has symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic lustre, and is a tetravalent metalloid (sometimes considered a non-metal) and semiconductor. It is a membe ...
(Si), cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. ...
(Co), and vanadium
Vanadium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery-grey, malleable transition metal. The elemental metal is rarely found in nature, but once isolated artificially, the formation of an ...
(V).
The nutrients required for healthy plant life are classified according to the elements, but the elements are not used as fertilizers. Instead, compounds containing these elements are the basis of fertilizers. The macro-nutrients are consumed in larger quantities and are present in plant tissue in quantities from 0.15% to 6.0% on a dry matter
The dry matter or dry weight is a measure of the mass of a completely dried substance.
Analysis of food
The dry matter of plant and animal material consists of all its constituents excluding water. The dry matter of food includes carbohydrate ...
(DM) (0% moisture) basis. Plants are made up of four main elements: hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, and nitrogen. Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen are widely available respectively in carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
and in water. Although nitrogen makes up most of the atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosph ...
, it is in a form that is unavailable to plants. Nitrogen is the most important fertilizer since nitrogen is present in protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s ( amide bonds between amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
s), DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
( puric and pyrimidic bases), and other components (e.g., tetrapyrrolic heme
Heme (American English), or haem (Commonwealth English, both pronounced /Help:IPA/English, hi:m/ ), is a ring-shaped iron-containing molecule that commonly serves as a Ligand (biochemistry), ligand of various proteins, more notably as a Prostheti ...
in chlorophyll
Chlorophyll is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words (, "pale green") and (, "leaf"). Chlorophyll allows plants to absorb energy ...
). To be nutritious to plants, nitrogen must be made available in a "fixed" form. Only some bacteria and their host plants (notably legume
Legumes are plants in the pea family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seeds of such plants. When used as a dry grain for human consumption, the seeds are also called pulses. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consum ...
s) can fix atmospheric nitrogen () by converting it to ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pu ...
(). Phosphate
Phosphates are the naturally occurring form of the element phosphorus.
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthop ...
() is required for the production of DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
(genetic code
Genetic code is a set of rules used by living cell (biology), cells to Translation (biology), translate information encoded within genetic material (DNA or RNA sequences of nucleotide triplets or codons) into proteins. Translation is accomplished ...
) and ATP, the main energy carrier in cells, as well as certain lipid
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing ...
s (phospholipid
Phospholipids are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic "head" containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic "tails" derived from fatty acids, joined by an alcohol residue (usually a glycerol molecule). Marine phospholipids typ ...
s, the main components of the lipidic double layer of the cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extr ...
s).
Microbiological considerations
Two sets of enzymatic reactions are highly relevant to the efficiency of nitrogen-based fertilizers.
;Urease
The first is the hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water ...
(reaction with water) of urea
Urea, also called carbamide (because it is a diamide of carbonic acid), is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two Amine, amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest am ...
(). Many soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, water, and organisms that together support the life of plants and soil organisms. Some scientific definitions distinguish dirt from ''soil'' by re ...
bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
possess the enzyme urease
Ureases (), functionally, belong to the superfamily of amidohydrolases and phosphotriesterases. Ureases are found in numerous Bacteria, Archaea, fungi, algae, plants, and some invertebrates. Ureases are nickel-containing metalloenzymes of high ...
, which catalyzes
Catalysis () is the increase in rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quick ...
the conversion of urea to ammonium
Ammonium is a modified form of ammonia that has an extra hydrogen atom. It is a positively charged (cationic) polyatomic ion, molecular ion with the chemical formula or . It is formed by the protonation, addition of a proton (a hydrogen nucleu ...
ion () and bicarbonate
In inorganic chemistry, bicarbonate (IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogencarbonate) is an intermediate form in the deprotonation of carbonic acid. It is a polyatomic anion with the chemical formula .
Bicarbonate serves a crucial bioche ...
ion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
().
;Ammonia oxidation
Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB), such as species of '' Nitrosomonas'', oxidize
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is ...
ammonia () to nitrite
The nitrite polyatomic ion, ion has the chemical formula . Nitrite (mostly sodium nitrite) is widely used throughout chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The nitrite anion is a pervasive intermediate in the nitrogen cycle in nature. The name ...
(), a process termed nitrification
''Nitrification'' is the biological oxidation of ammonia to nitrate via the intermediary nitrite. Nitrification is an important step in the nitrogen cycle in soil. The process of complete nitrification may occur through separate organisms or ent ...
. Nitrite-oxidizing bacteria, especially '' Nitrobacter'', oxidize nitrite
The nitrite polyatomic ion, ion has the chemical formula . Nitrite (mostly sodium nitrite) is widely used throughout chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The nitrite anion is a pervasive intermediate in the nitrogen cycle in nature. The name ...
() to nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . salt (chemistry), Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are solubility, soluble in wa ...
(), which is extremely soluble
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution.
The extent of the solubi ...
and mobile and is a major cause of eutrophication
Eutrophication is a general term describing a process in which nutrients accumulate in a body of water, resulting in an increased growth of organisms that may deplete the oxygen in the water; ie. the process of too many plants growing on the s ...
and algal bloom
An algal bloom or algae bloom is a rapid increase or accumulation in the population of algae in fresh water or marine water systems. It is often recognized by the discoloration in the water from the algae's pigments. The term ''algae'' encompass ...
.
Classification
Fertilizers are classified in several ways. They are classified according to whether they provide a single nutrient (e.g., K, P, or N), in which case they are classified as "straight fertilizers". "Multinutrient fertilizers" (or "complex fertilizers") provide two or more nutrients, for example, N and P. Fertilizers are also sometimes classified as inorganic (the topic of most of this article) versus organic. Inorganic fertilizers exclude carbon-containing materials except ureas image:Biotin_structure.svg, 220 px, Biotin, a water-soluble B vitamins, B vitamin, is a bicyclic urea.
In chemistry, ureas are a class of organic compounds with the formula (R2N)2CO where R = H, alkyl, aryl, etc. Thus, in addition to describing the ...
. Organic fertilizers are usually (recycled) plant- or animal-derived matter. Inorganic are sometimes called synthetic fertilizers since various chemical treatments are required for their manufacture.
Single nutrient ("straight") fertilizers
The main nitrogen-based straight fertilizer is ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pu ...
(NH3) ammonium
Ammonium is a modified form of ammonia that has an extra hydrogen atom. It is a positively charged (cationic) polyatomic ion, molecular ion with the chemical formula or . It is formed by the protonation, addition of a proton (a hydrogen nucleu ...
(NH4+) or its solutions, including:
* Ammonium nitrate
Ammonium nitrate is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a white crystalline salt consisting of ions of ammonium and nitrate. It is highly soluble in water and hygroscopic as a solid, but does not form hydrates. It is predominantly us ...
(NH4NO3) with 34-35% nitrogen is also widely used.
* Urea
Urea, also called carbamide (because it is a diamide of carbonic acid), is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two Amine, amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest am ...
(CO(NH2)2), with 45-46% nitrogen, another popular source of nitrogen, having the advantage that it is solid and non-explosive, unlike ammonia and ammonium nitrate.
* Calcium ammonium nitrate Is a blend of 20-30% limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
CaCO3 or dolomite (Ca,Mg)CO3 and 70-80% ammonium nitrate
Ammonium nitrate is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a white crystalline salt consisting of ions of ammonium and nitrate. It is highly soluble in water and hygroscopic as a solid, but does not form hydrates. It is predominantly us ...
with 24-28 % nitrogen.
*Calcium nitrate
Calcium nitrate are inorganic compounds with the formula Ca(NO3)2(H2O)x. The anhydrous compound, which is rarely encountered, absorbs moisture from the air to give the tetrahydrate. Both anhydrous and hydrated forms are colourless salts. Hydrated ...
with 15,5% nitrogen and 19% calcium, reportedly holding a small share of the nitrogen fertilizer market (4% in 2007).superphosphate
Superphosphate is a chemical fertiliser first synthesised in the 1840s by reacting bones with sulfuric acid. The process was subsequently improved by reacting phosphate coprolites with sulfuric acid. Subsequently, other phosphate-rich deposits suc ...
s:
* "Single superphosphate" (SSP) consisting of 14–18% P2O5, again in the form of Ca(H2PO4)2, but also phosphogypsum
Phosphogypsum (PG) is the calcium sulfate hydrate formed as a by-product of the production of fertilizer, particularly phosphoric acid, from phosphate rock. It is mainly composed of gypsum (). Although gypsum is a widely used material in the cons ...
().
* Triple superphosphate
Superphosphate is a chemical fertiliser first synthesised in the 1840s by reacting bones with sulfuric acid. The process was subsequently improved by reacting phosphate coprolites with sulfuric acid. Subsequently, other phosphate-rich deposits suc ...
(TSP) typically consists of 44–48% of P2O5 and no gypsum.
A mixture of single superphosphate and triple superphosphate is called double superphosphate. More than 90% of a typical superphosphate fertilizer is water-soluble.
The main potassium-based straight fertilizer is muriate of potash (MOP, 95–99% KCl). It is typically available as 0-0-60 or 0-0-62 fertilizer.
Multinutrient fertilizers
These fertilizers are common. They consist of two or more nutrient components.
;Binary (NP, NK, PK) fertilizers
Major two-component fertilizers provide both nitrogen and phosphorus to the plants. These are called NP fertilizers. The main NP fertilizers are
*monoammonium phosphate
Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (ADP), also known as monoammonium phosphate (MAP) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (NH4)(H2PO4). ADP is a major ingredient of agricultural fertilizers and dry chemical fire extinguishers. It also has ...
(MAP) NH4H2PO4. With 11% nitrogen and 48% P2O5.
*diammonium phosphate
Diammonium phosphate (DAP; IUPAC name diammonium hydrogen phosphate; chemical formula (NH4)2(HPO4)) is one of a series of water- soluble ammonium phosphate salts that can be produced when ammonia reacts with phosphoric acid.
Solid diammonium ph ...
(DAP). (NH4)2HPO4. With 18% nitrogen and 46% P2O5
About 85% of MAP and DAP fertilizers are soluble in water.
;NPK fertilizers
NPK fertilizers are three-component fertilizers providing nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. There exist two types of NPK fertilizers: compound and blends. Compound NPK fertilizers contain chemically bound ingredients, while blended NPK fertilizers are physical mixtures of single nutrient components.
NPK rating is a rating system describing the amount of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in a fertilizer. NPK ratings consist of three numbers separated by dashes (e.g., 10-10-10 or 16-4-8) describing the chemical content of fertilizers. The first number represents the percentage of nitrogen in the product; the second number, P2O5; the third, K2O. Fertilizers do not actually contain P2O5 or K2O, but the system is a conventional shorthand for the amount of the phosphorus (P) or potassium (K) in a fertilizer. A bag of fertilizer labeled 16-4-8 contains of nitrogen (16% of the 50 pounds), an amount of phosphorus equivalent to that in 2 pounds of P2O5 (4% of 50 pounds), and 4 pounds of K2O (8% of 50 pounds). Most fertilizers are labeled according to this N-P-K convention, although Australian convention, following an N-P-K-S system, adds a fourth number for sulfur, and uses elemental values for all values including P and K.
Micronutrients
Micronutrients
Micronutrients are essential chemicals required by organisms in small quantities to perform various biogeochemical processes and regulate physiological functions of cells and organs. By enabling these processes, micronutrients support the heal ...
are consumed in smaller quantities and are present in plant tissue on the order of parts-per-million (ppm), ranging from 0.15 to 400 ppm or less than 0.04% dry matter.boron
Boron is a chemical element; it has symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the boron group it has three ...
, zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
, molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mo (from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'') and atomic number 42. The name derived from Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ores. Molybdenum minerals hav ...
, iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
, and manganese
Manganese is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese was first isolated in the 1770s. It is a transition m ...
.[ These elements are provided as water-soluble salts. Iron presents special problems because it converts to insoluble (bio-unavailable) compounds at moderate soil pH and phosphate concentrations. For this reason, iron is often administered as a chelate complex, e.g., the ]EDTA
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), also called EDTA acid, is an aminopolycarboxylic acid with the formula . This white, slightly water-soluble solid is widely used to bind to iron (Fe2+/Fe3+) and calcium ions (Ca2+), forming water-solubl ...
or EDDHA derivatives. The micronutrient needs depend on the plant and the environment. For example, sugar beet
A sugar beet is a plant whose root contains a high concentration of sucrose and that is grown commercially for sugar production. In plant breeding, it is known as the Altissima cultivar group of the common beet (''Beta vulgaris''). Together with ...
s appear to require boron
Boron is a chemical element; it has symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the boron group it has three ...
, and legume
Legumes are plants in the pea family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seeds of such plants. When used as a dry grain for human consumption, the seeds are also called pulses. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consum ...
s require cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. ...
,
Production
The production of synthetic, or inorganic, fertilizers require prepared chemicals, whereas organic fertilizers are derived from the organic processes of plants and animals in biological process
Biological processes are those processes that are necessary for an organism to live and that shape its capacities for interacting with its environment. Biological processes are made of many chemical reactions or other events that are involved in ...
es using biochemicals.
Nitrogen fertilizers
Nitrogen fertilizers are made from ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pu ...
(NH3) produced by the Haber–Bosch process
The Haber process, also called the Haber–Bosch process, is the main industrial procedure for the production of ammonia. It converts atmospheric nitrogen (N2) to ammonia (NH3) by a reaction with hydrogen (H2) using finely divided iron metal as ...
.natural gas
Natural gas (also fossil gas, methane gas, and gas) is a naturally occurring compound of gaseous hydrocarbons, primarily methane (95%), small amounts of higher alkanes, and traces of carbon dioxide and nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide and helium ...
(CH4) usually supplies the hydrogen, and the nitrogen (N2) is derived from the air. This ammonia is used as a feedstock
A raw material, also known as a feedstock, unprocessed material, or primary commodity, is a basic material that is used to produce goods, finished goods, energy, or intermediate materials/Intermediate goods that are feedstock for future finishe ...
for all other nitrogen fertilizers, such as anhydrous ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3) and urea
Urea, also called carbamide (because it is a diamide of carbonic acid), is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two Amine, amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest am ...
(CO(NH2)2).
Deposits of sodium nitrate
Sodium nitrate is the chemical compound with the chemical formula, formula . This alkali metal nitrate salt (chemistry), salt is also known as Chile saltpeter (large deposits of which were historically mined in Chile) to distinguish it from ordi ...
(NaNO3) ( Chilean saltpeter) are also found in the Atacama Desert
The Atacama Desert () is a desert plateau located on the Pacific Ocean, Pacific coast of South America, in the north of Chile. Stretching over a strip of land west of the Andes Mountains, it covers an area of , which increases to if the barre ...
in Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in western South America. It is the southernmost country in the world and the closest to Antarctica, stretching along a narrow strip of land between the Andes, Andes Mountains and the Paci ...
and was one of the original (1830) nitrogen-rich fertilizers used. It is still mined for fertilizer. Nitrates are also produced from ammonia by the Ostwald process.
Phosphate fertilizers
Phosphate fertilizers are obtained by extraction from phosphate rock
Phosphorite, phosphate rock or rock phosphate is a non- detrital sedimentary rock that contains high amounts of phosphate minerals. The phosphate content of phosphorite (or grade of phosphate rock) varies greatly, from 4% to 20% phosphorus pentox ...
, which contains two principal phosphorus-containing minerals, fluorapatite
Fluorapatite, often with the alternate spelling of fluoroapatite, is a phosphate mineral with the formula Ca5(PO4)3F (calcium fluorophosphate). Fluorapatite is a hard crystalline solid. Although samples can have various color (green, brown, blu ...
Ca5(PO4)3F (CFA) and hydroxyapatite
Hydroxyapatite (International Mineralogical Association, IMA name: hydroxylapatite) (Hap, HAp, or HA) is a naturally occurring mineral form of calcium apatite with the Chemical formula, formula , often written to denote that the Crystal struc ...
Ca5(PO4)3OH. Billions of kg of phosphate rock are mined annually, but the size and quality of the remaining ore is decreasing. These minerals are converted into water-soluble phosphate salts by treatment with acid
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. Hydron, hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis ...
s. The large production of sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen, ...
is primarily motivated by this application. In the nitrophosphate process or Odda process (invented in 1927), phosphate rock with up to a 20% phosphorus (P) content is dissolved with nitric acid
Nitric acid is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but samples tend to acquire a yellow cast over time due to decomposition into nitrogen oxide, oxides of nitrogen. Most com ...
(HNO3) to produce a mixture of phosphoric acid (H3PO4) and calcium nitrate
Calcium nitrate are inorganic compounds with the formula Ca(NO3)2(H2O)x. The anhydrous compound, which is rarely encountered, absorbs moisture from the air to give the tetrahydrate. Both anhydrous and hydrated forms are colourless salts. Hydrated ...
(Ca(NO3)2). This mixture can be combined with a potassium fertilizer to produce a ''compound fertilizer'' with the three macronutrients N, P and K in easily dissolved form.
Potassium fertilizers
Potash
Potash ( ) includes various mined and manufactured salts that contain potassium in water- soluble form. is a mixture of potassium minerals used to make potassium (chemical symbol: K) fertilizers. Potash is soluble in water, so the main effort in producing this nutrient from the ore involves some purification steps, e.g., to remove sodium chloride
Sodium chloride , commonly known as Salt#Edible salt, edible salt, is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. It is transparent or translucent, brittle, hygroscopic, and occurs a ...
(NaCl) (common salt
In common usage, salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl). When used in food, especially in granulated form, it is more formally called table salt. In the form of a natural crystalline mineral, salt is also known as r ...
). Sometimes potash is referred to as K2O, as a matter of convenience to those describing the potassium content. In fact, potash fertilizers are usually potassium chloride
Potassium chloride (KCl, or potassium salt) is a metal halide salt composed of potassium and chlorine. It is odorless and has a white or colorless vitreous crystal appearance. The solid dissolves readily in water, and its solutions have a sa ...
, potassium sulfate
Potassium sulfate (US) or potassium sulphate (UK), also called sulphate of potash (SOP), arcanite, or archaically potash of sulfur, is the inorganic compound with formula K2SO4, a white water-soluble solid. It is commonly used in fertilizers, prov ...
, potassium carbonate
Potassium carbonate is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a white salt, which is soluble in water and forms a strongly alkaline solution. It is deliquescent, often appearing as a damp or wet solid. Potassium carbonate is mainly used ...
, or potassium nitrate
Potassium nitrate is a chemical compound with a sharp, salty, bitter taste and the chemical formula . It is a potassium salt of nitric acid. This salt consists of potassium cations and nitrate anions , and is therefore an alkali metal nit ...
.[Vasant Gowariker, V. N. Krishnamurthy, Sudha Gowariker, Manik Dhanorkar, Kalyani Paranjape "The Fertilizer Encyclopedia" 2009, John Wiley & Sons. . Online . ]
NPK fertilizers
There are three major routes for manufacturing NPK fertilizers (named for their main ingredients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K)):
# bulk blending. The individual fertilizers are combined in the desired nutrient ratio.
# The wet process is based on chemical reactions between liquid raw materials phosphoric acid
Phosphoric acid (orthophosphoric acid, monophosphoric acid or phosphoric(V) acid) is a colorless, odorless phosphorus-containing solid, and inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is commonly encountered as an 85% aqueous solution, ...
, sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen, ...
, ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pu ...
) and solid raw materials (such as potassium chloride
Potassium chloride (KCl, or potassium salt) is a metal halide salt composed of potassium and chlorine. It is odorless and has a white or colorless vitreous crystal appearance. The solid dissolves readily in water, and its solutions have a sa ...
).
*The Nitrophosphate Process. Step 1. Nitrophosphates are made by acidiculating phosphate rock
Phosphorite, phosphate rock or rock phosphate is a non- detrital sedimentary rock that contains high amounts of phosphate minerals. The phosphate content of phosphorite (or grade of phosphate rock) varies greatly, from 4% to 20% phosphorus pentox ...
with nitric acid
Nitric acid is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but samples tend to acquire a yellow cast over time due to decomposition into nitrogen oxide, oxides of nitrogen. Most com ...
.
*Nitric acid + Phosphate rock → Phosphoric acid
Phosphoric acid (orthophosphoric acid, monophosphoric acid or phosphoric(V) acid) is a colorless, odorless phosphorus-containing solid, and inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is commonly encountered as an 85% aqueous solution, ...
+ Calcium sulphate
Calcium sulfate (or calcium sulphate) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic Salt (chemistry), salt with the chemical formula . It occurs in several Hydrate, hydrated forms; the anhydrous state (known as anhydrite) is a white crystalline solid often ...
+ hexafluorosilicic acid.
*Ca5F(PO4)3 + 10 HNO3 →6 H3PO4 + 5 Ca(NO3)2 + HF
*6 HF + SiO2 →H2SiF6 + 2 H2O
Step 2. Removal of Calcium Nitrate. It is important to remove the calcium nitrate
Calcium nitrate are inorganic compounds with the formula Ca(NO3)2(H2O)x. The anhydrous compound, which is rarely encountered, absorbs moisture from the air to give the tetrahydrate. Both anhydrous and hydrated forms are colourless salts. Hydrated ...
because calcium nitrate is extremely hygroscopic
Hygroscopy is the phenomenon of attracting and holding water molecules via either absorption (chemistry), absorption or adsorption from the surrounding Natural environment, environment, which is usually at normal or room temperature. If water mol ...
.
*Method 1.(Odda process) Calcium nitrate crystals are removed by centrifugation.
*Method 2. Sulfonitric Process Ca(NO3)2 + H2SO4 + 2NH3 → CaSO4 + 2NH4NO3
*Method 3.Phosphonitric Process Ca(NO3)2 + H3PO4 + 2NH3 → CaHPO4 + 2NH4NO3
*Method 4.Carbonitric Process Ca(NO3)2 + CO2 + H2O + 2NH3 → CaCO3 + 2NH4NO3
Organic fertilizers

 " Organic fertilizers" can describe those fertilizers with a biologic origin—derived from living or formerly living materials. Organic fertilizers can also describe commercially available and frequently packaged products that strive to follow the expectations and restrictions adopted by "
" Organic fertilizers" can describe those fertilizers with a biologic origin—derived from living or formerly living materials. Organic fertilizers can also describe commercially available and frequently packaged products that strive to follow the expectations and restrictions adopted by "organic agriculture
Organic farming, also known as organic agriculture or ecological farming or biological farming,Labelling, article 30 o''Regulation (EU) 2018/848 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 May 2024 on organic production and labelling of ...
" and "environmentally friendly
Environment friendly processes, or environmental-friendly processes (also referred to as eco-friendly, nature-friendly, and green), are sustainability and marketing terms referring to goods and services, laws, guidelines and policies that c ...
" gardening – related systems of food and plant production that significantly limit or strictly avoid the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides. The "organic fertilizer" ''products'' typically contain both some organic materials as well as acceptable additives such as nutritive rock powders, ground seashells (crab, oyster, etc.), other prepared products such as seed meal or kelp, and cultivated microorganisms and derivatives.
Fertilizers of an organic origin (the first definition) include animal wastes, plant wastes from agriculture, seaweed
Seaweed, or macroalgae, refers to thousands of species of macroscopic, multicellular, marine algae. The term includes some types of ''Rhodophyta'' (red), '' Phaeophyta'' (brown) and ''Chlorophyta'' (green) macroalgae. Seaweed species such as ...
, compost
Compost is a mixture of ingredients used as plant fertilizer and to improve soil's physical, chemical, and biological properties. It is commonly prepared by Decomposition, decomposing plant and food waste, recycling organic materials, and man ...
, and treated sewage sludge
Sewage sludge is the residual, semi-solid material that is produced as a by-product during sewage treatment of industrial or municipal wastewater. The term "septage" also refers to sludge from simple wastewater treatment but is connected to si ...
(biosolid
Biosolids are solid organic matter recovered from a sewage treatment process and used as fertilizer. In the past, it was common for farmers to use animal manure to improve their soil fertility. In the 1920s, the farming community began also to us ...
s). Beyond manures, animal sources can include products from the slaughter of animals – bloodmeal, bone meal, feather meal, hides, hoofs, and horns all are typical components.peat
Peat is an accumulation of partially Decomposition, decayed vegetation or organic matter. It is unique to natural areas called peatlands, bogs, mires, Moorland, moors, or muskegs. ''Sphagnum'' moss, also called peat moss, is one of the most ...
is the most widely used packaged organic soil amendment. It is an immature form of coal and improves the soil by aeration and absorbing water but confers no nutritional value to the plants. It is therefore not a fertilizer as defined in the beginning of the article, but rather an amendment. Coir
Coir (), also called coconut fibre, is a natural fibre extracted from the outer husk of coconut, and used in products such as floor mats, doormats, brushes, and mattresses. Coir is the fibrous material found between the hard, internal shell ...
, (derived from coconut husks), bark, and sawdust when added to soil all act similarly (but not identically) to peat and are also considered organic soil amendments – or texturizers – because of their limited nutritive inputs. Some organic additives can have a reverse effect on nutrients – fresh sawdust can consume soil nutrients as it breaks down and may lower soil pH – but these same organic texturizers (as well as compost, etc.) may increase the availability of nutrients through improved cation exchange, or through increased growth of microorganisms that in turn increase availability of certain plant nutrients. Organic fertilizers such as composts and manures may be distributed locally without going into industry production, making actual consumption more difficult to quantify.
Fertilizer consumption
China has become the largest producer and consumer of nitrogen fertilizers while Africa has little reliance on nitrogen fertilizers. Agricultural and chemical minerals are very important in industrial use of fertilizers, which is valued at approximately $200 billion.arable land
Arable land (from the , "able to be ploughed") is any land capable of being ploughed and used to grow crops.''Oxford English Dictionary'', "arable, ''adj''. and ''n.''" Oxford University Press (Oxford), 2013. Alternatively, for the purposes of a ...
in 2012 are published by The World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purposes of economic development.
The World Bank is the collective name for the Internati ...
. The diagram below shows fertilizer consumption by the European Union (EU) countries as kilograms per hectare (pounds per acre). The total consumption of fertilizer in the EU is 15.9 million tons for 105 million hectare arable land area
Application


 Fertilizers are commonly used for growing all crops, with application rates depending on the soil fertility, usually as measured by a
Fertilizers are commonly used for growing all crops, with application rates depending on the soil fertility, usually as measured by a soil test
A soil test is a laboratory or in-situ analysis to determine the chemical, physical or biological characteristics of a soil. Possibly the most widely conducted soil tests are those performed to estimate the plant-available concentrations of nutri ...
and according to the particular crop. Legumes, for example, fix nitrogen from the atmosphere and generally do not require nitrogen fertilizer.
Liquid vs solid
Fertilizers are applied to crops both as solids and as liquid. About 90% of fertilizers are applied as solids. The most widely used solid inorganic fertilizers are urea
Urea, also called carbamide (because it is a diamide of carbonic acid), is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two Amine, amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest am ...
, diammonium phosphate and potassium chloride.prill
A prill is a small aggregate or globule of a material, most often a dry sphere, formed from a melted liquid through spray crystallization.
Prilled is a term used in mining and manufacturing to refer to a product that has been pelletized. ANFO e ...
s, a solid globule. Liquid fertilizers comprise anhydrous ammonia, aqueous solutions of ammonia, aqueous solutions of ammonium nitrate or urea. These concentrated products may be diluted with water to form a concentrated liquid fertilizer (e.g., UAN). Advantages of liquid fertilizer are its more rapid effect and easier coverage.[ The addition of fertilizer to irrigation water is called " fertigation".][ Granulated fertilizers are more economical to ship and store, not to mention easier to apply.
]
Urea
Urea is highly soluble in water and is therefore also very suitable for use in fertilizer solutions (in combination with ammonium nitrate: UAN), e.g., in 'foliar feed' fertilizers. For fertilizer use, granules are preferred over prills because of their narrower particle size distribution, which is an advantage for mechanical application.
Urea is usually spread at rates of between 40 and 300 kg/ha (35 to 270 lbs/acre) but rates vary. Smaller applications incur lower losses due to leaching. During summer, urea is often spread just before or during rain to minimize losses from volatilization
Pesticide drift, also known as spray drift, is the unintentional diffusion of pesticides toward nontarget species. It is one of the most negative effects of pesticide application. Drift can damage human health, environment, and crops. Together ...
(a process wherein nitrogen is lost to the atmosphere as ammonia gas).
Because of the high nitrogen concentration in urea, it is very important to achieve an even spread. Drilling must not occur on contact with or close to seed, due to the risk of germination damage. Urea dissolves in water for application as a spray or through irrigation systems.
In grain and cotton crops, urea is often applied at the time of the last cultivation before planting. In high rainfall areas and on sandy soils (where nitrogen can be lost through leaching) and where good in-season rainfall is expected, urea can be side- or top-dressed during the growing season. Top-dressing is also popular on pasture and forage crops. In cultivating sugarcane, urea is side dressed after planting and applied to each ratoon crop.
Because it absorbs moisture from the atmosphere, urea is often stored in closed containers.
Overdose or placing urea near seed is harmful.
Slow- and controlled-release fertilizers
Foliar application
Foliar fertilizers are applied directly to leaves. This method is almost invariably used to apply water-soluble straight nitrogen fertilizers and used especially for high-value crops such as fruits. Urea is the most common foliar fertilizer.[
]
Chemicals that affect nitrogen uptake
 Various chemicals are used to enhance the efficiency of nitrogen-based fertilizers. In this way farmers can limit the polluting effects of nitrogen run-off.
Various chemicals are used to enhance the efficiency of nitrogen-based fertilizers. In this way farmers can limit the polluting effects of nitrogen run-off. Nitrification
''Nitrification'' is the biological oxidation of ammonia to nitrate via the intermediary nitrite. Nitrification is an important step in the nitrogen cycle in soil. The process of complete nitrification may occur through separate organisms or ent ...
inhibitors (also known as nitrogen stabilizers) suppress the conversion of ammonia into nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . salt (chemistry), Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are solubility, soluble in wa ...
, an anion that is more prone to leaching. 1-Carbamoyl-3-methylpyrazole (CMP), dicyandiamide, nitrapyrin (2-chloro-6-trichloromethylpyridine) and 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP) are popular.urease
Ureases (), functionally, belong to the superfamily of amidohydrolases and phosphotriesterases. Ureases are found in numerous Bacteria, Archaea, fungi, algae, plants, and some invertebrates. Ureases are nickel-containing metalloenzymes of high ...
s. A popular inhibitor of ureases is ''N''-(''n''-butyl)thiophosphoric triamide ( NBPT).
Overfertilization
Careful use of fertilization technologies is important because excess nutrients can be detrimental. Fertilizer burn can occur when too much fertilizer is applied, resulting in damage or even death of the plant. Fertilizers vary in their tendency to burn roughly in accordance with their salt index.
Environmental effects
Synthetic fertilizer used in agriculture has wide-reaching environmental consequences.
According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Special Report on Climate Change and Land
The United Nations' Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change's (IPCC) Special Report on Climate Change and Land (SRCCL), also known as the "Special Report on climate change, desertification, land degradation, sustainable land management, food se ...
, production of these fertilizers and associated land use
Land use is an umbrella term to describe what happens on a parcel of land. It concerns the benefits derived from using the land, and also the land management actions that humans carry out there. The following categories are used for land use: fo ...
practices are drivers of global warming
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes ...
. The use of fertilizer has also led to a number of direct environmental consequences: agricultural runoff which leads to downstream effects like ocean dead zones and waterway contamination, soil microbiome degradation, and accumulation of toxins in ecosystems. Indirect environmental impacts include: the environmental impacts of fracking for natural gas
Natural gas (also fossil gas, methane gas, and gas) is a naturally occurring compound of gaseous hydrocarbons, primarily methane (95%), small amounts of higher alkanes, and traces of carbon dioxide and nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide and helium ...
used in the Haber process
The Haber process, also called the Haber–Bosch process, is the main industrial procedure for the ammonia production, production of ammonia. It converts atmospheric nitrogen (N2) to ammonia (NH3) by a reaction with hydrogen (H2) using finely di ...
, the agricultural boom is partially responsible for the rapid growth in human population and large-scale industrial agricultural practices are associated with habitat destruction
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss or habitat reduction) occurs when a natural habitat is no longer able to support its native species. The organisms once living there have either moved elsewhere, or are dead, leading to a decrease ...
, pressure on biodiversity and agricultural soil loss.
In order to mitigate environmental and food security
Food security is the state of having reliable access to a sufficient quantity of affordable, healthy Human food, food. The availability of food for people of any class, gender, ethnicity, or religion is another element of food protection. Simila ...
concerns, the international community has included food systems in Sustainable Development Goal 2
Sustainable Development Goal 2 (SDG 2 or Global Goal 2) aims to achieve "zero hunger". It is one of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals established by the United Nations in 2015. The official wording is: "End hunger, achieve food security and im ...
which focuses on creating a climate-friendly and sustainable food production system.[United Nations (2017) Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 6 July 2017, Work of the Statistical Commission pertaining to the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development]
A/RES/71/313
Most policy and regulatory approaches to address these issues focus on pivoting agricultural practices towards sustainable
Sustainability is a social goal for people to co-exist on Earth over a long period of time. Definitions of this term are disputed and have varied with literature, context, and time. Sustainability usually has three dimensions (or pillars): env ...
or regenerative agricultural practices: these use less synthetic fertilizers, better soil management
Soil management is the application of operations, practices, and treatments to protect soil and enhance its performance (such as soil fertility or soil mechanics). It includes soil conservation, soil amendment, and optimal soil health. In agricult ...
(for example no-till agriculture) and more organic fertilizers.
 For each ton of phosphoric acid produced by the processing of phosphate rock, five tons of waste are generated. This waste takes the form of impure, useless, radioactive solid called
For each ton of phosphoric acid produced by the processing of phosphate rock, five tons of waste are generated. This waste takes the form of impure, useless, radioactive solid called phosphogypsum
Phosphogypsum (PG) is the calcium sulfate hydrate formed as a by-product of the production of fertilizer, particularly phosphoric acid, from phosphate rock. It is mainly composed of gypsum (). Although gypsum is a widely used material in the cons ...
. Estimates range from 100,000,000 and 280,000,000 tons of phosphogypsum waste produced annually worldwide.
Water
 Phosphorus and nitrogen fertilizers can affect soil, surface water, and groundwater due to the dispersion of minerals
Phosphorus and nitrogen fertilizers can affect soil, surface water, and groundwater due to the dispersion of minerals[ Cyanobacteria blooms (']algal blooms
Algae ( , ; : alga ) is an informal term for any organisms of a large and diverse group of photosynthetic organisms that are not plants, and includes species from multiple distinct clades. Such organisms range from unicellular microalgae, suc ...
') can also produce harmful toxins
A toxin is a naturally occurring poison produced by metabolic activities of living cells or organisms. They occur especially as proteins, often conjugated. The term was first used by organic chemist Ludwig Brieger (1849–1919), derived ...
that can accumulate in the food chain, and can be harmful to humans.ocean
The ocean is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of Earth. The ocean is conventionally divided into large bodies of water, which are also referred to as ''oceans'' (the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian Ocean, Indian, Southern Ocean ...
s, especially in coastal zones, lake
A lake is often a naturally occurring, relatively large and fixed body of water on or near the Earth's surface. It is localized in a basin or interconnected basins surrounded by dry land. Lakes lie completely on land and are separate from ...
s and river
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside Subterranean river, caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of ...
s. The resulting lack of dissolved oxygen greatly reduces the ability of these areas to sustain oceanic fauna
Fauna (: faunae or faunas) is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding terms for plants and fungi are ''flora'' and '' funga'', respectively. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively ...
. The number of oceanic dead zones near inhabited coastlines is increasing.
As of 2006, the application of nitrogen fertilizer is being increasingly controlled in northwestern Europegroundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and Pore space in soil, soil pore spaces and in the fractures of stratum, rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available fresh water in the world is groundwater. A unit ...
can be broken down by natural processes.
Nitrate pollution
Only a fraction of the nitrogen-based fertilizers is converted to plant matter. The remainder accumulates in the soil or is lost as run-off.surface water
Surface water is water located on top of land, forming terrestrial (surrounding by land on all sides) waterbodies, and may also be referred to as ''blue water'', opposed to the seawater and waterbodies like the ocean.
The vast majority of surfac ...
as well as leaching into groundwater, thereby causing groundwater pollution
Groundwater pollution (also called groundwater contamination) occurs when pollutants are released to the ground and make their way into groundwater. This type of water pollution can also occur naturally due to the presence of a minor and unwant ...
. The excessive use of nitrogen-containing fertilizers (be they synthetic or natural) is particularly damaging, as much of the nitrogen that is not taken up by plants is transformed into nitrate which is easily leached.
Nitrate levels above 10 mg/L (10 ppm) in groundwater can cause ' blue baby syndrome' (acquired methemoglobinemia
Methemoglobinemia, or methaemoglobinaemia, is a condition of elevated methemoglobin in the blood. Symptoms may include headache, dizziness, shortness of breath, nausea, poor muscle coordination, and blue-colored skin (cyanosis). Complications ma ...
). The nutrients, especially nitrates, in fertilizers can cause problems for natural habitats and for human health if they are washed off soil into watercourses or leached through soil into groundwater. Run-off can lead to fertilizing blooms of algae that use up all the oxygen and leave huge "dead zones" behind where other fish and aquatic life can not live.
Soil
Acidification
Soil acidification refers to the process by which the pH level of soil becomes more acidic over time. Soil pH is a measure of the soil's acidity or alkalinity and is determined on a scale from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. A pH value below 7 indicates acidic soil, while a pH value above 7 indicates alkaline or basic soil.
Soil acidification is a significant concern in agriculture and horticulture. It refers to the process of the soil becoming more acidic over time.
Nitrogen-containing fertilizers can cause soil acidification
Soil acidification is the buildup of hydrogen cations, which reduces the soil pH. Chemically, this happens when a proton donor gets added to the soil. The donor can be an acid, such as nitric acid, sulfuric acid, or carbonic acid. It can also be a ...
when added. This may lead to decrease in nutrient availability which may be offset by liming. These fertilizers release ammonium or nitrate ions, which can acidify the soil as they undergo chemical reactions.
When these nitrogen-containing fertilizers are added to the soil, they increase the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in the soil solution, which lowers the pH of the soil.
Accumulation of toxic elements
=Cadmium
=
The concentration of cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, silvery-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12 element, group 12, zinc and mercury (element), mercury. Like z ...
in phosphorus-containing fertilizers varies considerably and can be problematic. For example, mono-ammonium phosphate fertilizer may have a cadmium content of as low as 0.14 mg/kg or as high as 50.9 mg/kg.Nauru
Nauru, officially the Republic of Nauru, formerly known as Pleasant Island, is an island country and microstate in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies within the Micronesia subregion of Oceania, with its nearest neighbour being Banaba (part of ...
and the Christmas Island
Christmas Island, officially the Territory of Christmas Island, is an States and territories of Australia#External territories, Australian external territory in the Indian Ocean comprising the island of the same name. It is about south o ...
s). Continuous use of high-cadmium fertilizer can contaminate soil (as shown in New Zealand)plants
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with cyanobacteria to produce sugars f ...
.European Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the primary Executive (government), executive arm of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with a number of European Commissioner, members of the Commission (directorial system, informall ...
.[Wilfried Werner "Fertilizers, 6. Environmental Aspects" ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim.]
=Fluoride
=
Phosphate rocks contain high levels of fluoride. Consequently, the widespread use of phosphate fertilizers has increased soil fluoride concentrations.
=Radioactive elements
=
The radioactive content of the fertilizers varies considerably and depends both on their concentrations in the parent mineral and on the fertilizer production process.
=Other metals
=
Steel industry wastes, recycled into fertilizers for their high levels of zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
(essential to plant growth), wastes can include the following toxic metals: lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol As and atomic number 33. It is a metalloid and one of the pnictogens, and therefore shares many properties with its group 15 neighbors phosphorus and antimony. Arsenic is not ...
, cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, silvery-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12 element, group 12, zinc and mercury (element), mercury. Like z ...
,
Trace mineral depletion
Attention has been addressed to the decreasing concentrations of elements such as iron, zinc, copper and magnesium in many foods over the last 50–60 years.Intensive farming
Intensive agriculture, also known as intensive farming (as opposed to extensive farming), conventional, or industrial agriculture, is a type of agriculture, both of arable farming, crop plants and of Animal husbandry, animals, with higher levels ...
practices, including the use of synthetic fertilizers are frequently suggested as reasons for these declines and organic farming is often suggested as a solution.zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
, copper, manganese
Manganese is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese was first isolated in the 1770s. It is a transition m ...
, iron and molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mo (from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'') and atomic number 42. The name derived from Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ores. Molybdenum minerals hav ...
were identified as limiting the growth of broad-acre crops and pastures in the 1940s and 1950s.
Changes in soil biology
High levels of fertilizer may cause the breakdown of the symbiotic
Symbiosis (Ancient Greek : living with, companionship < : together; and ''bíōsis'': living) is any type of a close and long-term biolo ...
relationships between plant roots and mycorrhiza
A mycorrhiza (; , mycorrhiza, or mycorrhizas) is a symbiotic association between a fungus and a plant. The term mycorrhiza refers to the role of the fungus in the plant's rhizosphere, the plant root system and its surroundings. Mycorrhizae play ...
l fungi.
Organic agriculture
Two types of agricultural management practices include organic agriculture and conventional agriculture. The former encourages soil fertility using local resources to maximize efficiency. Organic agriculture avoids synthetic agrochemicals. Conventional agriculture uses all the components that organic agriculture does not use.
Hydrogen consumption and sustainability
Most fertilizer is made from dirty hydrogen. Ammonia is produced from natural gas
Natural gas (also fossil gas, methane gas, and gas) is a naturally occurring compound of gaseous hydrocarbons, primarily methane (95%), small amounts of higher alkanes, and traces of carbon dioxide and nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide and helium ...
and air.
Contribution to climate change
The amount of greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth. Unlike other gases, greenhouse gases absorb the radiations that a planet emits, resulting in the greenhouse effect. T ...
es carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
, methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes ...
and nitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide (dinitrogen oxide or dinitrogen monoxide), commonly known as laughing gas, nitrous, or factitious air, among others, is a chemical compound, an Nitrogen oxide, oxide of nitrogen with the Chemical formula, formula . At room te ...
produced during the manufacture
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of the
secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer to a r ...
and use of nitrogen fertilizer is estimated as around 5% of anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions. One third is produced during the production and two thirds during the use of fertilizers. Nitrogen fertilizer can be converted by soil bacteria to nitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide (dinitrogen oxide or dinitrogen monoxide), commonly known as laughing gas, nitrous, or factitious air, among others, is a chemical compound, an Nitrogen oxide, oxide of nitrogen with the Chemical formula, formula . At room te ...
, a greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth. Unlike other gases, greenhouse gases absorb the radiations that a planet emits, resulting in the greenhouse effect. T ...
. Nitrous oxide emissions by humans, most of which are from fertilizer, between 2007 and 2016 have been estimated at 7 million tonnes per year, which is incompatible with limiting global warming to below 2 °C.
Atmosphere
 Through the increasing use of nitrogen fertilizer, which was used at a rate of about 110 million tons (of N) per year in 2012,
Through the increasing use of nitrogen fertilizer, which was used at a rate of about 110 million tons (of N) per year in 2012,nitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide (dinitrogen oxide or dinitrogen monoxide), commonly known as laughing gas, nitrous, or factitious air, among others, is a chemical compound, an Nitrogen oxide, oxide of nitrogen with the Chemical formula, formula . At room te ...
(N2O) has become the third most important greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth. Unlike other gases, greenhouse gases absorb the radiations that a planet emits, resulting in the greenhouse effect. T ...
after carbon dioxide and methane. It has a global warming potential
Global warming potential (GWP) is a measure of how much heat a greenhouse gas traps in the atmosphere over a specific time period, relative to carbon dioxide (). It is expressed as a multiple of warming caused by the same mass of carbon dioxide ( ...
296 times larger than an equal mass of carbon dioxide and it also contributes to stratospheric ozone depletion.
By changing processes and procedures, it is possible to mitigate some, but not all, of these effects on anthropogenic climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
.Methane emissions
Increasing methane emissions are a major contributor to the rising concentration of greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere, and are responsible for up to one-third of near-term global heating. During 2019, about 60% (360 million tons) of methane r ...
from crop fields (notably rice paddy fields) are increased by the application of ammonium-based fertilizers. These emissions contribute to global climate change as methane is a potent greenhouse gas.
Policy
Regulation
In Europe, problems with high nitrate concentrations in runoff are being addressed by the European Union's Nitrates Directive. Within Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* Great Britain, a large island comprising the countries of England, Scotland and Wales
* The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, a sovereign state in Europe comprising Great Britain and the north-eas ...
, farmers are encouraged to manage their land more sustainably in 'catchment-sensitive farming'. In the US, high concentrations of nitrate and phosphorus in runoff and drainage water are classified as nonpoint source pollutants due to their diffuse origin; this pollution is regulated at the state level. Oregon
Oregon ( , ) is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is a part of the Western U.S., with the Columbia River delineating much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while t ...
and Washington, both in the United States, have fertilizer registration programs with on-line databases listing chemical analyses of fertilizers. Carbon emission trading
Carbon emission trading (also called carbon market, emission trading scheme (ETS) or cap and trade) is a type of emissions trading scheme designed for carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases (GHGs). A form of carbon pricing, its purpose ...
and eco-tariffs affect the production and price of fertilizer.
Subsidies
In China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
, regulations have been implemented to control the use of N fertilizers in farming. In 2008, Chinese governments began to partially withdraw fertilizer subsidies
A subsidy, subvention or government incentive is a type of government expenditure for individuals and households, as well as businesses with the aim of stabilizing the economy. It ensures that individuals and households are viable by having acce ...
, including subsidies to fertilizer transportation and to electricity and natural gas use in the industry. In consequence, the price of fertilizer has gone up and large-scale farms have begun to use less fertilizer. If large-scale farms keep reducing their use of fertilizer subsidies, they have no choice but to optimize the fertilizer they have which would therefore gain an increase in both grain yield and profit.
In March 2022, the United States Department of Agriculture announced a new $250M grant to promote American fertilizer production. Part of the Commodity Credit Corporation, the grant program will support fertilizer production that is independent of dominant fertilizer suppliers, made in America, and utilizing innovative production techniques to jumpstart future competition.
See also
* Agroecology
Agroecology is an academic discipline that studies ecological processes applied to agricultural production systems. Bringing ecological principles to bear can suggest new management approaches in agroecosystems. The term can refer to a science, ...
* Circulus (theory)
* Fertigation
* Food and Agriculture Organization
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; . (FAO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger and improve nutrition and food security. Its Latin motto, , translates ...
* History of organic farming
* Milorganite
* Leaf Color Chart
* Phosphogypsum
Phosphogypsum (PG) is the calcium sulfate hydrate formed as a by-product of the production of fertilizer, particularly phosphoric acid, from phosphate rock. It is mainly composed of gypsum (). Although gypsum is a widely used material in the cons ...
* Peak phosphorus
* Soil defertilisation
* Seaweed fertilizer
References
*Gilbeart H. Collings, Commercial Fertilizers, 1938
*Malcolm Vickar, Fertilizer technology and usage, Wisconsin, 1963
*McKetta & Cunningham, Encyclopedia of Chemical Processing and Design,1984
*Ullman´s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 1987, volume A10, page 323-421.
*Kirk Otmer, Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, 1993, volume 10, page 433-514.
Cited sources
*
*
External links
Nitrogen for Feeding Our Food, Its Earthly Origin, Haber Process
International Fertilizer Industry Association (IFA)
Agriculture Guide, Complete Guide to Fertilizers and Fertilization
(archived 6 October 2011)
Nitrogen-Phosphorus-Potassium Values of Organic Fertilizers
.
{{Authority control
Horticulture
Climate change and agriculture
 A fertilizer or fertiliser is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from liming materials or other non-nutrient soil amendments. Many sources of fertilizer exist, both natural and industrially produced. For most modern agricultural practices, fertilization focuses on three main macro nutrients:
A fertilizer or fertiliser is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from liming materials or other non-nutrient soil amendments. Many sources of fertilizer exist, both natural and industrially produced. For most modern agricultural practices, fertilization focuses on three main macro nutrients:  " Organic fertilizers" can describe those fertilizers with a biologic origin—derived from living or formerly living materials. Organic fertilizers can also describe commercially available and frequently packaged products that strive to follow the expectations and restrictions adopted by "
" Organic fertilizers" can describe those fertilizers with a biologic origin—derived from living or formerly living materials. Organic fertilizers can also describe commercially available and frequently packaged products that strive to follow the expectations and restrictions adopted by "

 Fertilizers are commonly used for growing all crops, with application rates depending on the soil fertility, usually as measured by a
Fertilizers are commonly used for growing all crops, with application rates depending on the soil fertility, usually as measured by a 
 Phosphorus and nitrogen fertilizers can affect soil, surface water, and groundwater due to the dispersion of minerals into waterways due to high rainfall, snowmelt and can leaching into groundwater over time. Agricultural run-off is a major contributor to the eutrophication of freshwater bodies. For example, in the US, about half of all the lakes are eutrophic. The main contributor to eutrophication is phosphate, which is normally a limiting nutrient; high concentrations promote the growth of cyanobacteria and algae, the demise of which consumes oxygen. Cyanobacteria blooms ('
Phosphorus and nitrogen fertilizers can affect soil, surface water, and groundwater due to the dispersion of minerals into waterways due to high rainfall, snowmelt and can leaching into groundwater over time. Agricultural run-off is a major contributor to the eutrophication of freshwater bodies. For example, in the US, about half of all the lakes are eutrophic. The main contributor to eutrophication is phosphate, which is normally a limiting nutrient; high concentrations promote the growth of cyanobacteria and algae, the demise of which consumes oxygen. Cyanobacteria blooms (' Through the increasing use of nitrogen fertilizer, which was used at a rate of about 110 million tons (of N) per year in 2012, adding to the already existing amount of reactive nitrogen,
Through the increasing use of nitrogen fertilizer, which was used at a rate of about 110 million tons (of N) per year in 2012, adding to the already existing amount of reactive nitrogen,