|
Genetic Code
Genetic code is a set of rules used by living cell (biology), cells to Translation (biology), translate information encoded within genetic material (DNA or RNA sequences of nucleotide triplets or codons) into proteins. Translation is accomplished by the ribosome, which links proteinogenic amino acids in an order specified by messenger RNA (mRNA), using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries. The codons specify which amino acid will be added next during protein biosynthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. The vast majority of genes are encoded with a single scheme (see the Codon tables, RNA codon table). That scheme is often called the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply ''the'' genetic code, though #Variations, variant codes (suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Francis Crick
Francis Harry Compton Crick (8 June 1916 – 28 July 2004) was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist. He, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and Maurice Wilkins played crucial roles in deciphering the Nucleic acid double helix, helical structure of the DNA molecule. Crick and Watson's paper in ''Nature (journal), Nature'' in 1953 laid the groundwork for understanding DNA structure and functions. Together with Maurice Wilkins, they were jointly awarded the 1962 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine "for their discoveries concerning the molecular geometry, molecular structure of nucleic acids and its significance for information transfer in living material". Crick was an important theoretical molecular biologist and played a crucial role in research related to revealing the helical structure of DNA. He is widely known for the use of the term "central dogma" to summarise the idea that once information is transferred from nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) to prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
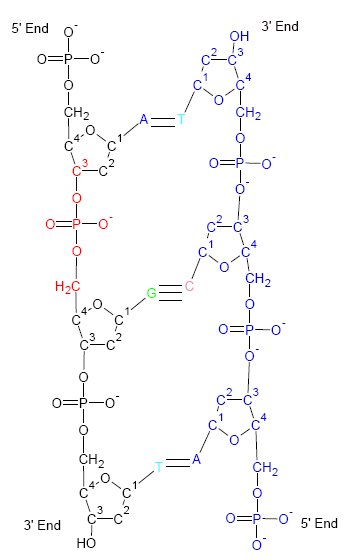
Adenine
Adenine (, ) (nucleoside#List of nucleosides and corresponding nucleobases, symbol A or Ade) is a purine nucleotide base that is found in DNA, RNA, and Adenosine triphosphate, ATP. Usually a white crystalline subtance. The shape of adenine is complementary and pairs to either thymine in DNA or uracil in RNA. In cells adenine, as an independent molecule, is rare. It is almost always covalent bond, covalently bound to become a part of a larger biomolecule. Adenine has a central role in cellular respiration. It is part of adenosine triphosphate which provides the energy that drives and supports most activities in living cell (biology), cells, such as Protein biosynthesis, protein synthesis, chemical synthesis, muscle contraction, and nerve impulse propagation. In respiration it also participates as part of the cofactor (biochemistry), cofactors nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, flavin adenine dinucleotide, and Coenzyme A. It is also part of adenosine, adenosine monophosphate, cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Severo Ochoa
Severo Ochoa de Albornoz (; 24 September 1905 – 1 November 1993) was a Spanish physician and biochemist, and winner of the 1959 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine together with Arthur Kornberg for their discovery of "the mechanisms in the biological synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)". Education and early life Ochoa was born in Luarca (Asturias), Spain. His father was Severo Manuel Ochoa (who he was named after), a lawyer and businessman, and his mother was Carmen de Albornoz. Ochoa was the nephew of Álvaro de Albornoz (President of the Second Spanish Republic in exile and former Foreign Minister), and a cousin of the poet and critic Aurora de Albornoz. His father died when Ochoa was seven, and he and his mother moved to Málaga, where he attended elementary school through high school. His interest in biology was stimulated by the publications of the Spanish neurologist and Nobel laureate Santiago Ramón y Cajal. In 1923, he went to the University of Madrid Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Phenylalanine
Phenylalanine (symbol Phe or F) is an essential α-amino acid with the chemical formula, formula . It can be viewed as a benzyl group substituent, substituted for the methyl group of alanine, or a phenyl group in place of a terminal hydrogen of alanine. This essential amino acid is classified as neutral, and chemical polarity, nonpolar because of the inert and hydrophobic nature of the benzyl side chain. The chirality (chemistry)#Naming conventions, L-isomer is used to biochemically form proteins coded for by DNA. Phenylalanine is a precursor for tyrosine, the monoamine neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and epinephrine (adrenaline), and the biological pigment melanin. It is Genetic code, encoded by the messenger RNA codons UUU and UUC. Phenylalanine is found naturally in the milk of mammals. It is used in the manufacture of food and drink products and sold as a nutritional supplement as it is a direct precursor to the neuromodulation, neuromodulator phe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Polypeptide
Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Polypeptides that have a molecular mass of 10,000 Da or more are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. Peptides fall under the broad chemical classes of biological polymers and oligomers, alongside nucleic acids, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, and others. Proteins consist of one or more polypeptides arranged in a biologically functional way, often bound to ligands such as coenzymes and cofactors, to another protein or other macromolecule such as DNA or RNA, or to complex macromolecular assemblies. Amino acids that have been incorporated into peptides are termed residues. A water molecule is released during formation of each amide bond.. All peptides except cyclic peptides have an N-terminal (amine group) and C-terminal (ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Uracil
Uracil () (nucleoside#List of nucleosides and corresponding nucleobases, symbol U or Ura) is one of the four nucleotide bases in the nucleic acid RNA. The others are adenine (A), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). In RNA, uracil binds to adenine via two hydrogen bonds. In DNA, the uracil nucleobase is replaced by thymine (T). Uracil is a demethylated form of thymine. Uracil is a common and naturally occurring pyrimidine derivative. The name "uracil" was coined in 1885 by the German chemist Robert Behrend, who was attempting to synthesize derivatives of uric acid. Originally discovered in 1900 by Alberto Ascoli, it was isolated by hydrolysis of yeast nuclein; it was also found in bovine thymus and spleen, herring sperm, and wheat Cereal germ, germ. It is a planar, unsaturated compound that has the ability to absorb light. Uracil that was formed extraterrestrially has been detected in the Murchison meteorite, in near-Earth asteroid 162173 Ryugu, Ryugu, and possibly on the surface of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Translation (biology)
In biology, translation is the process in living Cell (biology), cells in which proteins are produced using RNA molecules as templates. The generated protein is a sequence of amino acids. This sequence is determined by the sequence of nucleotides in the RNA. The nucleotides are considered three at a time. Each such triple results in the addition of one specific amino acid to the protein being generated. The matching from nucleotide triple to amino acid is called the genetic code. The translation is performed by a large complex of functional RNA and proteins called ribosomes. The entire process is called gene expression. In translation, messenger RNA (mRNA) is decoded in a ribosome, outside the nucleus, to produce a specific amino acid chain, or polypeptide. The polypeptide later protein folding, folds into an Activation energy, active protein and performs its functions in the cell. The polypeptide can also start folding during protein synthesis. The ribosome facilitates decoding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cell-free System
A cell-free system is an ''in vitro'' tool widely used to study biological reactions that happen within cells apart from a full cell system, thus reducing the complex interactions typically found when working in a whole cell. Subcellular fractions can be isolated by ultracentrifugation to provide molecular machinery that can be used in reactions in the absence of many of the other cellular components. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell internals have been used for creation of these simplified environments. These systems have enabled cell-free synthetic biology to emerge, providing control over what reaction is being examined, as well as its yield, and lessening the considerations otherwise invoked when working with more sensitive live cells. Types Cell-free systems may be divided into two primary classifications: cell extract-based, which remove components from within a whole cell for external use, and purified enzyme-based, which use purified components of the molecules known to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Marshall Nirenberg
Marshall Warren Nirenberg (April 10, 1927 – January 15, 2010) was an American biochemist and geneticist. He shared a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1968 with Har Gobind Khorana and Robert W. Holley for "breaking the genetic code" and describing how it operates in protein synthesis. In the same year, together with Har Gobind Khorana, he was awarded the Louisa Gross Horwitz Prize from Columbia University. Biography Nirenberg was born in New York City to a Jewish family, the son of Minerva (Bykowsky) and Harry Edward Nirenberg, a shirtmaker. He developed rheumatic fever as a boy, so the family moved to Orlando, Florida to take advantage of the subtropical climate. He developed an early interest in biology. In 1948 he received his BS degree, and in 1952, a master's degree in zoology from the University of Florida at Gainesville where he was also a member of the Pi Lambda Phi Fraternity.Membership Directory, 2010, Pi Lambda Phi Inc. His dissertation for the Master's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
RNA Tie Club
The RNA Tie Club was an informal scientific club, meant partly to be humorous, of select scientists who were interested in how proteins were synthesised from genes, specifically the genetic code. It was created by George Gamow upon a suggestion by James Watson in 1954 when the relationship between nucleic acids and amino acids in genetic information was unknown. The club consisted of 20 full members, each representing an amino acid, and four honorary members, representing the four nucleotides. The function of the club members was to think up possible solutions and share with the other members. The first important document of the RNA Tie Club was Francis Crick's adaptor hypothesis in 1955. Experimental work on the hypothesis led to the discovery of transfer RNA, a molecule that carries the key to genetic code. Most of the theoretical groundwork and preliminary experiments on the genetic code were done by the club members within a decade. However, the specific code was discovered by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |