
Corrosion is a
natural process that converts a refined
metal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated wit ...
into a more chemically stable
oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound containing at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion (anion bearing a net charge of −2) of oxygen, an O2− ion with oxygen in the oxidation st ...
. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment.
Corrosion engineering
Corrosion engineering is an engineering specialty that applies scientific, technical, engineering skills, and knowledge of natural laws and physical resources to design and implement materials, structures, devices, systems, and procedures to mana ...
is the field dedicated to controlling and preventing corrosion.

In the most common use of the word, this means
electrochemical
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry concerned with the relationship between electrical potential difference and identifiable chemical change. These reactions involve electrons moving via an electronically conducting phase (typi ...
oxidation
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is ...
of metal in reaction with an
oxidant
An oxidizing agent (also known as an oxidant, oxidizer, electron recipient, or electron acceptor) is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or "Electron acceptor, accepts"/"receives" an electron from a (called the , , or ''electr ...
such as
oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
, hydrogen, or hydroxide.
Rusting, the formation of red-orange
iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
oxides, is a well-known example of electrochemical corrosion. This type of corrosion typically produces
oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound containing at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion (anion bearing a net charge of −2) of oxygen, an O2− ion with oxygen in the oxidation st ...
s or
salts
In chemistry, a salt or ionic compound is a chemical compound consisting of an assembly of positively charged ions ( cations) and negatively charged ions (anions), which results in a compound with no net electric charge (electrically neutral). ...
of the original metal and results in a distinctive coloration. Corrosion can also occur in materials other than metals, such as
ceramics
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant, and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porce ...
or
polymers
A polymer () is a substance or material that consists of very large molecules, or macromolecules, that are constituted by many repeating subunits derived from one or more species of monomers. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, b ...
, although in this context, the term "degradation" is more common. Corrosion degrades the useful properties of materials and structures including mechanical strength, appearance, and permeability to liquids and gases. Corrosive is distinguished from caustic: the former implies mechanical degradation, the latter chemical.
Many structural
alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which in most cases at least one is a metal, metallic element, although it is also sometimes used for mixtures of elements; herein only metallic alloys are described. Metallic alloys often have prop ...
s corrode merely from exposure to moisture in air, but the process can be strongly affected by exposure to certain substances. Corrosion can be concentrated locally to form a
pit or crack, or it can extend across a wide area, more or less uniformly corroding the surface. Because corrosion is a
diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical p ...
-controlled process, it occurs on exposed surfaces. As a result, methods to reduce the activity of the exposed surface, such as
passivation and
chromate conversion, can increase a material's corrosion resistance. However, some corrosion mechanisms are less visible and less predictable.
The chemistry of corrosion is complex; it can be considered an electrochemical phenomenon. During corrosion at a particular spot on the surface of an object made of iron, oxidation takes place and that spot behaves as an
anode
An anode usually is an electrode of a polarized electrical device through which conventional current enters the device. This contrasts with a cathode, which is usually an electrode of the device through which conventional current leaves the devic ...
. The
electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
s released at this anodic spot move through the metal to another spot on the object, and
reduce oxygen at that spot in presence of H
+ (which is believed to be available from
carbonic acid
Carbonic acid is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . The molecule rapidly converts to water and carbon dioxide in the presence of water. However, in the absence of water, it is quite stable at room temperature. The interconversion ...
() formed due to dissolution of
carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
from air into water in moist air condition of atmosphere.
Hydrogen ion
A hydrogen ion is created when a hydrogen atom loses or gains an electron. A positively charged hydrogen ion (or proton) can readily combine with other particles and therefore is only seen isolated when it is in a gaseous state or a nearly particl ...
in water may also be available due to dissolution of other acidic oxides from the atmosphere). This spot behaves as a
cathode
A cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device such as a lead-acid battery. This definition can be recalled by using the mnemonic ''CCD'' for ''Cathode Current Departs''. Conventional curren ...
.
Galvanic corrosion

Galvanic corrosion occurs when two different metals have physical or electrical contact with each other and are immersed in a common
electrolyte
An electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity through the movement of ions, but not through the movement of electrons. This includes most soluble Salt (chemistry), salts, acids, and Base (chemistry), bases, dissolved in a polar solven ...
, or when the same metal is exposed to electrolyte with different concentrations. In a
galvanic couple, the more active metal (the anode) corrodes at an accelerated rate and the more
noble metal
A noble metal is ordinarily regarded as a metallic chemical element, element that is generally resistant to corrosion and is usually found in nature in its native element, raw form. Gold, platinum, and the other platinum group metals (ruthenium ...
(the cathode) corrodes at a slower rate. When immersed separately, each metal corrodes at its own rate. What type of metal(s) to use is readily determined by following the
galvanic series
The galvanic series (or electropotential series) determines the nobility of metals and semi-metals. When two metals are submerged in an electrolyte, while also electrically connected by some external conductor, the less noble (base) will experien ...
. For example,
zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
is often used as a sacrificial anode for steel structures. Galvanic corrosion is of major interest to the marine industry and also anywhere water (containing salts) contacts pipes or metal structures.
Factors such as relative size of
anode
An anode usually is an electrode of a polarized electrical device through which conventional current enters the device. This contrasts with a cathode, which is usually an electrode of the device through which conventional current leaves the devic ...
, types of metal, and operating conditions (
temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making ...
,
humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation (meteorology), precipitation, dew, or fog t ...
,
salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt (chemistry), salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensio ...
, etc.) affect galvanic corrosion. The surface area ratio of the anode and
cathode
A cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device such as a lead-acid battery. This definition can be recalled by using the mnemonic ''CCD'' for ''Cathode Current Departs''. Conventional curren ...
directly affects the corrosion rates of the materials. Galvanic corrosion is often prevented by the use of
sacrificial anodes.
Galvanic series
In any given environment (one standard medium is aerated, room-temperature
seawater
Seawater, or sea water, is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% (35 g/L, 35 ppt, 600 mM). This means that every kilogram (roughly one liter by volume) of seawater has approximat ...
), one metal will be either more ''noble'' or more ''active'' than others, based on how strongly its ions are bound to the surface. Two metals in electrical contact share the same electrons, so that the "tug-of-war" at each surface is analogous to competition for free electrons between the two materials. Using the electrolyte as a host for the flow of ions in the same direction, the noble metal will take electrons from the active one. The resulting mass flow or electric current can be measured to establish a hierarchy of materials in the medium of interest. This hierarchy is called a ''galvanic series'' and is useful in predicting and understanding corrosion.
Corrosion removal
Often, it is possible to chemically remove the products of corrosion. For example,
phosphoric acid
Phosphoric acid (orthophosphoric acid, monophosphoric acid or phosphoric(V) acid) is a colorless, odorless phosphorus-containing solid, and inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is commonly encountered as an 85% aqueous solution, ...
in the form of ''naval jelly'' is often applied to ferrous tools or surfaces to remove rust. Corrosion removal should not be confused with
electropolishing
Electropolishing principle: 1. Electrolyte 2. Cathode 3. Workpiece to polish (Anode) 4. Particle moving from the work-piece to the cathode 5. Surface before polishing 6. Surface after polishing
Electropolishing, also known as electrochemical poli ...
, which removes some layers of the underlying metal to make a smooth surface. For example, phosphoric acid may also be used to electropolish copper but it does this by removing copper, not the products of copper corrosion.
Resistance to corrosion
Some metals are more intrinsically resistant to corrosion than others (for some examples, see
galvanic series
The galvanic series (or electropotential series) determines the nobility of metals and semi-metals. When two metals are submerged in an electrolyte, while also electrically connected by some external conductor, the less noble (base) will experien ...
). There are various ways of
protecting metals from corrosion (oxidation) including painting,
hot-dip galvanization
Hot-dip galvanization is a form of galvanization. It is the process of coating iron and steel with zinc, which alloys with the surface of the base metal when immersing the metal in a bath of molten zinc at a temperature of around . When expo ...
,
cathodic protection
Cathodic protection (CP; ) is a technique used to control the corrosion of a metal surface by making it the cathode of an electrochemical cell. A simple method of protection connects the metal to be protected to a more easily corroded " sacrifi ...
, and combinations of these.
Intrinsic chemistry

The materials most resistant to corrosion are those for which corrosion is
thermodynamically unfavorable. Any corrosion products of
gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
or
platinum
Platinum is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Pt and atomic number 78. It is a density, dense, malleable, ductility, ductile, highly unreactive, precious metal, precious, silverish-white transition metal. Its name origina ...
tend to decompose spontaneously into pure metal, which is why these elements can be found in metallic form on Earth and have long been valued. More common "base" metals can only be protected by more temporary means.
Some metals have naturally slow
reaction kinetics, even though their corrosion is thermodynamically favorable. These include such metals as
zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
,
magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 ...
, and
cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, silvery-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12 element, group 12, zinc and mercury (element), mercury. Like z ...
. While corrosion of these metals is continuous and ongoing, it happens at an acceptably slow rate. An extreme example is
graphite
Graphite () is a Crystallinity, crystalline allotrope (form) of the element carbon. It consists of many stacked Layered materials, layers of graphene, typically in excess of hundreds of layers. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable ...
, which releases large amounts of energy upon
oxidation
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is ...
, but has such slow kinetics that it is effectively immune to electrochemical corrosion under normal conditions.
Passivation
Passivation refers to the spontaneous formation of an ultrathin film of corrosion products, known as a passive film, on the metal's surface that act as a barrier to further oxidation. The chemical composition and microstructure of a passive film are different from the underlying metal. Typical passive film thickness on aluminium, stainless steels, and alloys is within 10 nanometers. The passive film is different from oxide layers that are formed upon heating and are in the micrometer thickness range – the passive film recovers if removed or damaged whereas the oxide layer does not. Passivation in natural environments such as air, water and soil at moderate
pH is seen in such materials as
aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
,
stainless steel
Stainless steel, also known as inox, corrosion-resistant steel (CRES), or rustless steel, is an iron-based alloy that contains chromium, making it resistant to rust and corrosion. Stainless steel's resistance to corrosion comes from its chromi ...
,
titanium
Titanium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in ...
, and
silicon
Silicon is a chemical element; it has symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic lustre, and is a tetravalent metalloid (sometimes considered a non-metal) and semiconductor. It is a membe ...
.
Passivation is primarily determined by metallurgical and environmental factors. The effect of pH is summarized using
Pourbaix diagrams, but many other factors are influential. Some conditions that inhibit passivation include high pH for aluminium and zinc, low pH or the presence of
chloride
The term chloride refers to a compound or molecule that contains either a chlorine anion (), which is a negatively charged chlorine atom, or a non-charged chlorine atom covalently bonded to the rest of the molecule by a single bond (). The pr ...
ions for stainless steel, high temperature for titanium (in which case the oxide dissolves into the metal, rather than the electrolyte) and
fluoride
Fluoride (). According to this source, is a possible pronunciation in British English. is an Inorganic chemistry, inorganic, Monatomic ion, monatomic Ion#Anions and cations, anion of fluorine, with the chemical formula (also written ), whose ...
ions for silicon. On the other hand, unusual conditions may result in passivation of materials that are normally unprotected, as the alkaline environment of
concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of aggregate bound together with a fluid cement that cures to a solid over time. It is the second-most-used substance (after water), the most–widely used building material, and the most-manufactur ...
does for
steel
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that demonstrates improved mechanical properties compared to the pure form of iron. Due to steel's high Young's modulus, elastic modulus, Yield (engineering), yield strength, Fracture, fracture strength a ...
rebar
Rebar (short for reinforcement bar or reinforcing bar), known when massed as reinforcing steel or steel reinforcement, is a tension device added to concrete to form ''reinforced concrete'' and reinforced masonry structures to strengthen and aid ...
. Exposure to a liquid metal such as
mercury or hot
solder
Solder (; North American English, NA: ) is a fusible alloy, fusible metal alloy used to create a permanent bond between metal workpieces. Solder is melted in order to wet the parts of the joint, where it adheres to and connects the pieces aft ...
can often circumvent passivation mechanisms.
It has been shown using
electrochemical scanning tunneling microscopy that during iron passivation, an
n-type semiconductor
N-type, N type or Type N may refer to:
* N-type semiconductor is a key material in the manufacture of transistors and integrated circuits
* An N-type connector is a threaded RF connector used to join coaxial cables
* The MG N-type Magnette was p ...
Fe(III) oxide grows at the interface with the metal that leads to the buildup of an electronic barrier opposing electron flow and an electronic
depletion region
In semiconductor physics, the depletion region, also called depletion layer, depletion zone, junction region, space charge region, or space charge layer, is an insulating region within a conductive, doped semiconductor material where the mobil ...
that prevents further oxidation reactions. These results indicate a mechanism of "electronic passivation". The electronic properties of this semiconducting oxide film also provide a mechanistic explanation of corrosion mediated by
chloride
The term chloride refers to a compound or molecule that contains either a chlorine anion (), which is a negatively charged chlorine atom, or a non-charged chlorine atom covalently bonded to the rest of the molecule by a single bond (). The pr ...
, which creates
surface states
Surface states are electronic states found at the Surface (topology), surface of materials. They are formed due to the sharp transition from solid material that ends with a surface and are found only at the atom layers closest to the surface. The t ...
at the oxide surface that lead to electronic breakthrough, restoration of anodic currents, and disruption of the electronic passivation mechanism.
Corrosion in passivated materials
Passivation is extremely useful in mitigating corrosion damage, however even a high-quality alloy will corrode if its ability to form a passivating film is hindered. Proper selection of the right grade of material for the specific environment is important for the long-lasting performance of this group of materials. If breakdown occurs in the passive film due to chemical or mechanical factors, the resulting major modes of corrosion may include
pitting corrosion
Pitting corrosion, or pitting, is a form of extremely localized corrosion that leads to the random creation of small holes in metal. The driving power for pitting corrosion is the depassivation of a small area, which becomes anodic (oxidation re ...
,
crevice corrosion
Crevice corrosion refers to corrosion occurring in occluded spaces such as interstices in which a stagnant solution is trapped and not renewed. These spaces are generally called crevices. Examples of crevices are gaps and contact areas between pa ...
, and
stress corrosion cracking
Stress corrosion cracking (SCC) is the growth of crack formation in a corrosive environment. It can lead to unexpected and sudden failure of normally ductile metal alloys subjected to a tensile stress, especially at elevated temperature. SC ...
.
Pitting corrosion

Certain conditions, such as low concentrations of oxygen or high concentrations of species such as chloride which compete as
anion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conven ...
s, can interfere with a given alloy's ability to re-form a passivating film. In the worst case, almost all of the surface will remain protected, but tiny local fluctuations will degrade the oxide film in a few critical points. Corrosion at these points will be greatly amplified, and can cause ''corrosion pits'' of several types, depending upon conditions. While the corrosion pits only
nucleate under fairly extreme circumstances, they can continue to grow even when conditions return to normal, since the interior of a pit is naturally deprived of oxygen and locally the pH decreases to very low values and the corrosion rate increases due to an autocatalytic process. In extreme cases, the sharp tips of extremely long and narrow corrosion pits can cause
stress concentration
In solid mechanics, a stress concentration (also called a stress raiser or a stress riser or notch sensitivity) is a location in an object where the stress (mechanics), stress is significantly greater than the surrounding region. Stress concentra ...
to the point that otherwise tough alloys can shatter; a thin film pierced by an invisibly small hole can hide a thumb sized pit from view. These problems are especially dangerous because they are difficult to detect before a part or structure
fails. Pitting remains among the most common and damaging forms of corrosion in passivated alloys, but it can be prevented by control of the alloy's environment.
Pitting results when a small hole, or cavity, forms in the metal, usually as a result of de-passivation of a small area. This area becomes anodic, while part of the remaining metal becomes cathodic, producing a localized galvanic reaction. The deterioration of this small area penetrates the metal and can lead to failure. This form of corrosion is often difficult to detect because it is usually relatively small and may be covered and hidden by corrosion-produced compounds.
Weld decay and knifeline attack


Stainless steel can pose special corrosion challenges, since its passivating behavior relies on the presence of a major alloying component (
chromium
Chromium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6 element, group 6. It is a steely-grey, Luster (mineralogy), lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium ...
, at least 11.5%). Because of the elevated temperatures of
welding
Welding is a fabrication (metal), fabrication process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, primarily by using high temperature to melting, melt the parts together and allow them to cool, causing Fusion welding, fusion. Co ...
and heat treatment,
chromium carbides can form in the
grain boundaries
In materials science, a grain boundary is the interface between two grains, or crystallites, in a polycrystalline material. Grain boundaries are two-dimensional crystallographic defect, defects in the crystal structure, and tend to decrease the ...
of stainless alloys. This chemical reaction robs the material of chromium in the zone near the grain boundary, making those areas much less resistant to corrosion. This creates a
galvanic couple with the well-protected alloy nearby, which leads to "weld decay" (corrosion of the grain boundaries in the heat affected zones) in highly corrosive environments. This process can seriously reduce the mechanical strength of welded joints over time.
A stainless steel is said to be "sensitized" if chromium carbides are formed in the microstructure. A typical microstructure of a normalized
type 304 stainless steel shows no signs of sensitization, while a heavily sensitized steel shows the presence of grain boundary precipitates. The dark lines in the sensitized microstructure are networks of chromium carbides formed along the grain boundaries.
Special alloys, either with low carbon content or with added carbon "
getter
A getter is a deposit of reactive material that is placed inside a vacuum system to complete and maintain the vacuum. When gas molecules strike the getter material, they combine with it chemically or by adsorption. Thus the getter removes small ...
s" such as titanium and
niobium
Niobium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Nb (formerly columbium, Cb) and atomic number 41. It is a light grey, crystalline, and Ductility, ductile transition metal. Pure niobium has a Mohs scale of mineral hardness, Mohs h ...
(in types 321 and 347, respectively), can prevent this effect, but the latter require special heat treatment after welding to prevent the similar phenomenon of "knifeline attack". As its name implies, corrosion is limited to a very narrow zone adjacent to the weld, often only a few micrometers across, making it even less noticeable.
Crevice corrosion

Crevice corrosion
Crevice corrosion refers to corrosion occurring in occluded spaces such as interstices in which a stagnant solution is trapped and not renewed. These spaces are generally called crevices. Examples of crevices are gaps and contact areas between pa ...
is a localized form of corrosion occurring in confined spaces (crevices), to which the access of the working fluid from the environment is limited. Formation of a differential aeration cell leads to corrosion inside the crevices. Examples of crevices are gaps and contact areas between parts, under gaskets or seals, inside cracks and seams, spaces filled with deposits, and under sludge piles.
Crevice corrosion is influenced by the crevice type (metal-metal, metal-non-metal), crevice geometry (size, surface finish), and metallurgical and environmental factors. The susceptibility to crevice corrosion can be evaluated with ASTM standard procedures. A critical crevice corrosion temperature is commonly used to rank a material's resistance to crevice corrosion.
Hydrogen grooving
In the
chemical industry
The chemical industry comprises the companies and other organizations that develop and produce industrial, specialty and other chemicals. Central to the modern world economy, the chemical industry converts raw materials ( oil, natural gas, air, ...
, hydrogen grooving is the corrosion of piping at grooves created by the interaction of a corrosive agent, corroded pipe constituents, and
hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
gas
bubble
Bubble, Bubbles or The Bubble may refer to:
Common uses
* Bubble (physics), a globule of one substance in another, usually gas in a liquid
** Soap bubble
* Economic bubble, a situation where asset prices are much higher than underlying fundame ...
s. For example, when
sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen, ...
() flows through steel pipes, the
iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
in the steel reacts with the acid to form a
passivation coating of
iron sulfate () and hydrogen gas (). The iron sulfate coating will protect the steel from further reaction; however, if hydrogen bubbles contact this coating, it will be removed. Thus, a groove can be formed by a travelling bubble, exposing more steel to the acid, causing a
vicious cycle
A vicious circle (or cycle) is a complex chain of events that reinforces itself through a feedback loop, with detrimental results. It is a system with no tendency toward equilibrium (social, economic, ecological, etc.), at least in the short ...
. The grooving is exacerbated by the tendency of subsequent bubbles to follow the same path.
High-temperature corrosion
High-temperature corrosion is chemical deterioration of a material (typically a metal) as a result of heating. This non-galvanic form of corrosion can occur when a metal is subjected to a hot atmosphere containing oxygen, sulfur ("
sulfidation
Sulfidation (British spelling also sulphidation) is a process of installing sulfide ions in a material or molecule. The process is widely used to convert oxides to sulfides but is also related to corrosion and surface modification.
Inorganic, mate ...
"), or other compounds capable of oxidizing (or assisting the oxidation of) the material concerned. For example, materials used in aerospace, power generation, and even in car engines must resist sustained periods at high temperature, during which they may be exposed to an atmosphere containing the potentially highly-corrosive products of combustion.
Some products of high-temperature corrosion can potentially be turned to the advantage of the engineer. The formation of oxides on stainless steels, for example, can provide a protective layer preventing further atmospheric attack, allowing for a material to be used for sustained periods at both room and high temperatures in hostile conditions. Such high-temperature corrosion products, in the form of
compacted oxide layer glazes, prevent or reduce wear during high-temperature sliding contact of metallic (or metallic and ceramic) surfaces.
Thermal oxidation
In microfabrication, thermal oxidation is a way to produce a thin layer of oxide (usually silicon dioxide) on the surface of a wafer. The technique forces an oxidizing agent to diffuse into the wafer at high temperature and react with it. The ra ...
is also commonly used to produce controlled oxide nanostructures, including
nanowires
upright=1.2, Crystalline 2×2-atom tin selenide nanowire grown inside a single-wall carbon nanotube (tube diameter ≈1 nm).
A nanowire is a nanostructure in the form of a wire with the diameter of the order of a nanometre (10−9 m). Mor ...
and thin films.
Microbial corrosion
Microbial corrosion, or commonly known as microbiologically influenced corrosion (MIC), is a corrosion caused or promoted by
microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic scale, microscopic size, which may exist in its unicellular organism, single-celled form or as a Colony (biology)#Microbial colonies, colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen ...
s, usually
chemoautotroph
A chemotroph is an organism that obtains energy by the oxidation of electron donors in their environments. These molecules can be organic (chemoorganotrophs) or inorganic (chemolithotrophs). The chemotroph designation is in contrast to phototroph ...
s. It can apply to both metallic and non-metallic materials, in the presence or absence of oxygen.
Sulfate-reducing bacteria
Sulfate-reducing microorganisms (SRM) or sulfate-reducing prokaryotes (SRP) are a group composed of sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) and sulfate-reducing archaea (SRA), both of which can perform anaerobic respiration utilizing sulfate () as termina ...
are active in the absence of oxygen (anaerobic); they produce
hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is toxic, corrosive, and flammable. Trace amounts in ambient atmosphere have a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. Swedish chemist ...
, causing
sulfide stress cracking
Sulfide stress cracking (SSC) is a form of hydrogen embrittlement which is a cathodic cracking mechanism. It should not be confused with the term stress corrosion cracking which is an anodic cracking mechanism. Susceptible alloys, especially ste ...
. In the presence of oxygen (aerobic), some bacteria may directly oxidize iron to iron oxides and hydroxides, other bacteria oxidize sulfur and produce sulfuric acid causing
biogenic sulfide corrosion.
Concentration cells can form in the deposits of corrosion products, leading to localized corrosion.
Accelerated low-water corrosion (ALWC) is a particularly aggressive form of MIC that affects steel piles in seawater near the low water tide mark. It is characterized by an orange sludge, which smells of hydrogen sulfide when treated with acid. Corrosion rates can be very high and design corrosion allowances can soon be exceeded leading to premature failure of the steel pile. Piles that have been coated and have cathodic protection installed at the time of construction are not susceptible to ALWC. For unprotected piles, sacrificial anodes can be installed locally to the affected areas to inhibit the corrosion or a complete retrofitted sacrificial anode system can be installed. Affected areas can also be treated using cathodic protection, using either sacrificial anodes or applying current to an inert anode to produce a calcareous deposit, which will help shield the metal from further attack.
Metal dusting
Metal dusting is a catastrophic form of corrosion that occurs when susceptible materials are exposed to environments with high carbon activities, such as synthesis gas and other high-CO environments. The corrosion manifests itself as a break-up of bulk metal to metal powder. The suspected mechanism is firstly the deposition of a graphite layer on the surface of the metal, usually from
carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a poisonous, flammable gas that is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the si ...
(CO) in the vapor phase. This graphite layer is then thought to form metastable M
3C species (where M is the metal), which migrate away from the metal surface. However, in some regimes, no M
3C species is observed indicating a direct transfer of metal atoms into the graphite layer.
Protection from corrosion
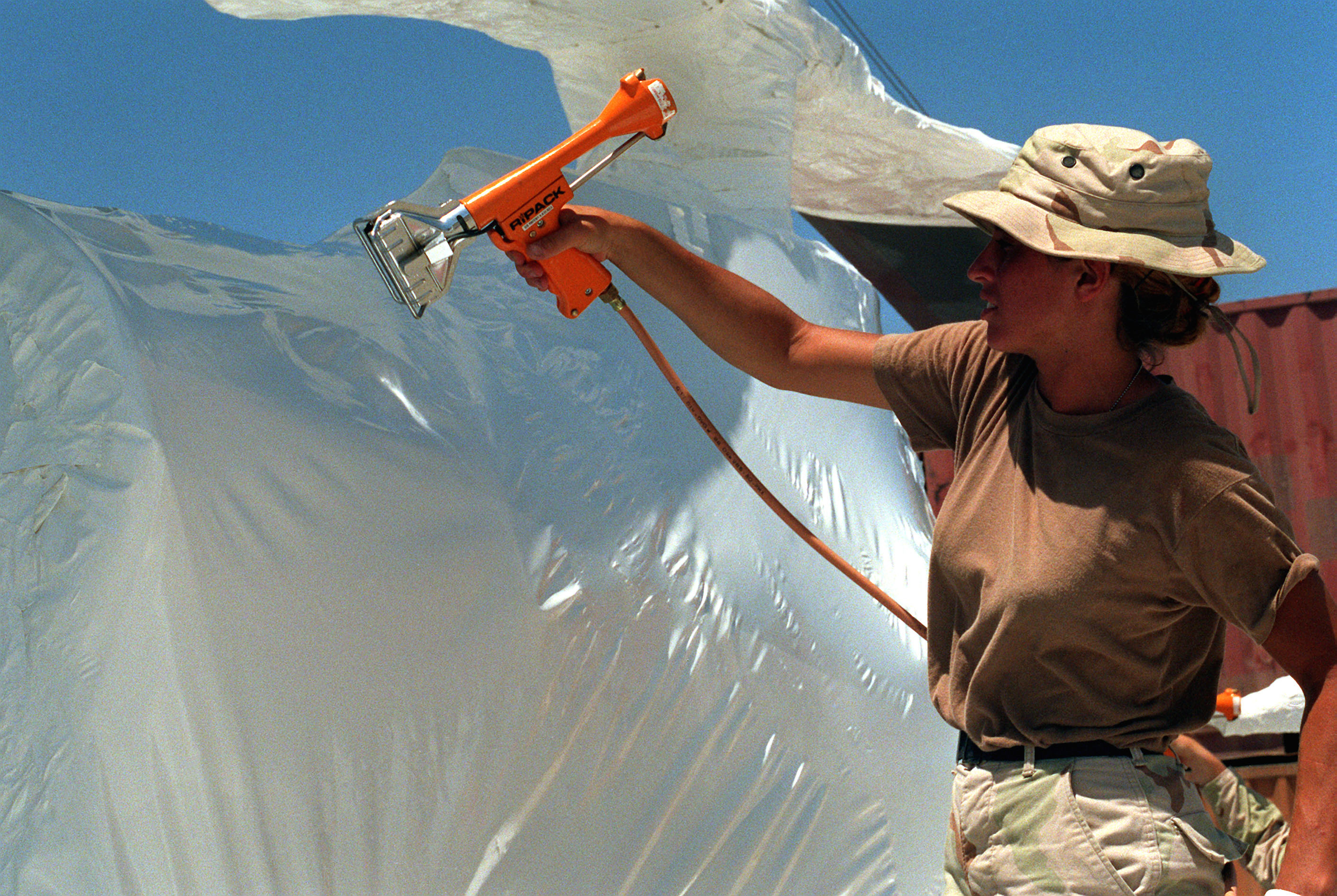

Various treatments are used to slow corrosion damage to metallic objects which are exposed to the weather, salt water, acids, or other hostile environments. Some unprotected metallic alloys are extremely vulnerable to corrosion, such as those used in
neodymium magnet
A nickel-plated neodymium magnet on a bracket from a hard disk drive
file:Nd-magnet.jpg">Nickel-plated neodymium magnet cubes
Left: high-resolution transmission electron microscopy image of Nd2Fe14B; right: crystal structure with unit cell mar ...
s, which can
spall
Spall are fragments of a material that are broken off a larger solid body. It can be produced by a variety of mechanisms, including as a result of projectile impact, corrosion, weathering, cavitation, or excessive rolling pressure (as in a ba ...
or crumble into powder even in dry, temperature-stable indoor environments unless properly treated.
Surface treatments
When surface treatments are used to reduce corrosion, great care must be taken to ensure complete coverage, without gaps, cracks, or pinhole defects. Small defects can act as an "
Achilles' heel
An Achilles' heel (or Achilles heel) is a weakness despite overall strength, which can lead to downfall. While the mythological origin refers to a physical vulnerability, idiomatic references to other attributes or qualities that can lead to do ...
", allowing corrosion to penetrate the interior and causing extensive damage even while the outer protective layer remains apparently intact for a period of time.
Applied coatings


Plating
Plating is a finishing process in which a metal is deposited on a surface. Plating has been done for hundreds of years; it is also critical for modern technology. Plating is used to decorate objects, for corrosion inhibition, to improve solderab ...
,
paint
Paint is a material or mixture that, when applied to a solid material and allowed to dry, adds a film-like layer. As art, this is used to create an image or images known as a painting. Paint can be made in many colors and types. Most paints are ...
ing, and the application of
enamel are the most common
anti-corrosion treatments. They work by providing a barrier of corrosion-resistant material between the damaging environment and the structural material. Aside from cosmetic and manufacturing issues, there may be tradeoffs in mechanical flexibility versus resistance to abrasion and high temperature. Platings usually fail only in small sections, but if the plating is more noble than the substrate (for example, chromium on steel), a
galvanic couple will cause any exposed area to corrode much more rapidly than an unplated surface would. For this reason, it is often wise to plate with active metal such as
zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
or
cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, silvery-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12 element, group 12, zinc and mercury (element), mercury. Like z ...
. If the zinc coating is not thick enough the surface soon becomes unsightly with rusting obvious. The design life is directly related to the metal coating thickness.
Painting either by roller or brush is more desirable for tight spaces; spray would be better for larger coating areas such as steel decks and waterfront applications. Flexible
polyurethane
Polyurethane (; often abbreviated PUR and PU) is a class of polymers composed of organic chemistry, organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links. In contrast to other common polymers such as polyethylene and polystyrene, polyurethane term ...
coatings, like Durabak-M26 for example, can provide an anti-corrosive seal with a highly durable slip resistant membrane. Painted coatings are relatively easy to apply and have fast drying times although temperature and humidity may cause dry times to vary.
Reactive coatings
If the environment is controlled (especially in recirculating systems),
corrosion inhibitor
A corrosion inhibitor or anti-corrosive is a chemical compound added to a liquid or gas to decrease the corrosion rate of a metal that comes into contact with the fluid. The effectiveness of a corrosion inhibitor depends on fluid composition and ...
s can often be added to it. These chemicals form an electrically insulating or chemically impermeable coating on exposed metal surfaces, to suppress electrochemical reactions. Such methods make the system less sensitive to scratches or defects in the coating, since extra inhibitors can be made available wherever metal becomes exposed. Chemicals that inhibit corrosion include some of the salts in
hard water (Roman water systems are known for their
mineral deposits),
chromates
Chromate salts contain the chromate anion, . Dichromate salts contain the dichromate anion, . They are oxyanions of chromium in the +6 oxidation state and are moderately strong oxidizing agents. In an aqueous solution, chromate and dichromate ...
,
phosphate
Phosphates are the naturally occurring form of the element phosphorus.
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthop ...
s,
polyaniline, other
conducting polymers, and a wide range of specially designed chemicals that resemble
surfactant
Surfactants are chemical compounds that decrease the surface tension or interfacial tension between two liquids, a liquid and a gas, or a liquid and a solid. The word ''surfactant'' is a Blend word, blend of "surface-active agent",
coined in ...
s (i.e., long-chain organic molecules with ionic end groups).
Anodization

Aluminium alloy
An aluminium alloy ( UK/IUPAC) or aluminum alloy ( NA; see spelling differences) is an alloy in which aluminium (Al) is the predominant metal. The typical alloying elements are copper, magnesium, manganese, silicon, tin, nickel and zinc. There ...
s often undergo a surface treatment. Electrochemical conditions in the bath are carefully adjusted so that uniform pores, several
nanometer
330px, Different lengths as in respect to the Molecule">molecular scale.
The nanometre (international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: nm), or nanometer (American spelling
Despite the va ...
s wide, appear in the metal's oxide film. These pores allow the oxide to grow much thicker than passivating conditions would allow. At the end of the treatment, the pores are allowed to seal, forming a harder-than-usual surface layer. If this coating is scratched, normal passivation processes take over to protect the damaged area.
Anodizing is very resilient to weathering and corrosion, so it is commonly used for building facades and other areas where the surface will come into regular contact with the elements. While being resilient, it must be cleaned frequently. If left without cleaning,
panel edge staining will naturally occur. Anodization is the process of converting an anode into cathode by bringing a more active anode in contact with it.
Biofilm coatings
A new form of protection has been developed by applying certain species of bacterial films to the surface of metals in highly corrosive environments. This process increases the corrosion resistance substantially. Alternatively, antimicrobial-producing
biofilms
A biofilm is a syntrophic community of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular polymer ...
can be used to inhibit mild steel corrosion from
sulfate-reducing bacteria
Sulfate-reducing microorganisms (SRM) or sulfate-reducing prokaryotes (SRP) are a group composed of sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) and sulfate-reducing archaea (SRA), both of which can perform anaerobic respiration utilizing sulfate () as termina ...
.
Controlled permeability formwork
Controlled permeability formwork (CPF) is a method of preventing the corrosion of
reinforcement
In Behaviorism, behavioral psychology, reinforcement refers to consequences that increase the likelihood of an organism's future behavior, typically in the presence of a particular ''Antecedent (behavioral psychology), antecedent stimulus''. Fo ...
by naturally enhancing the durability of the
cover during concrete placement. CPF has been used in environments to combat the effects of
carbonation
Carbonation is the chemical reaction of carbon dioxide to give carbonates, bicarbonates, and carbonic acid. In chemistry, the term is sometimes used in place of carboxylation, which refers to the formation of carboxylic acids.
In inorganic che ...
, chlorides,
frost
Frost is a thin layer of ice on a solid surface, which forms from water vapor that deposits onto a freezing surface. Frost forms when the air contains more water vapor than it can normally hold at a specific temperature. The process is simila ...
, and abrasion.
Cathodic protection
Cathodic protection (CP) is a technique to control the corrosion of a metal surface by making it the cathode of an
electrochemical cell
An electrochemical cell is a device that either generates electrical energy from chemical reactions in a so called galvanic cell, galvanic or voltaic cell, or induces chemical reactions (electrolysis) by applying external electrical energy in an ...
. Cathodic protection systems are most commonly used to protect steel
pipelines
A pipeline is a system of pipes for long-distance transportation of a liquid or gas, typically to a market area for consumption. The latest data from 2014 gives a total of slightly less than of pipeline in 120 countries around the world. The Un ...
and tanks; steel pier
piles, ships, and offshore
oil platform
An oil platform (also called an oil rig, offshore platform, oil production platform, etc.) is a large structure with facilities to extract and process petroleum and natural gas that lie in rock formations beneath the seabed. Many oil platforms w ...
s.
Sacrificial anode protection
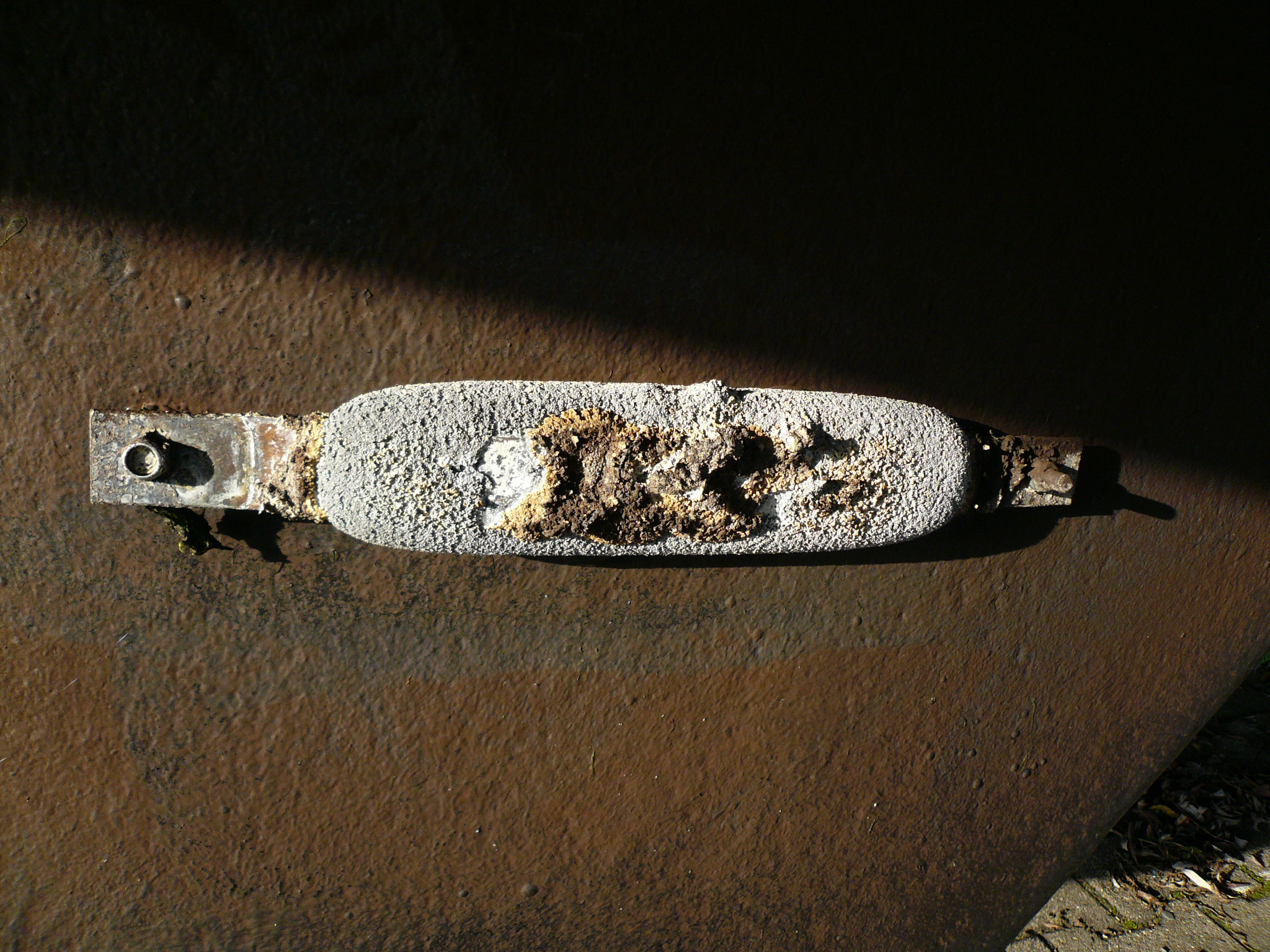

For effective CP, the potential of the steel surface is polarized (pushed) more negative until the metal surface has a uniform potential. With a uniform potential, the driving force for the corrosion reaction is halted. For galvanic CP systems, the anode material corrodes under the influence of the steel, and eventually it must be replaced. The
polarization is caused by the current flow from the anode to the cathode, driven by the difference in
electrode potential
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a Electronic circuit, circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or a gas). In electrochemical cells, electrodes are essential parts that can c ...
between the anode and the cathode. The most common sacrificial anode materials are aluminum, zinc, magnesium and related alloys. Aluminum has the highest capacity, and magnesium has the highest driving voltage and is thus used where resistance is higher. Zinc is general purpose and the basis for galvanizing.
A number of problems are associated with sacrificial anodes. Among these, from an environmental perspective, is the release of zinc, magnesium, aluminum and heavy metals such as
cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, silvery-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12 element, group 12, zinc and mercury (element), mercury. Like z ...
into the environment including seawater. From a working perspective, sacrificial anodes systems are considered to be less precise than modern cathodic protection systems such as Impressed Current Cathodic Protection (ICCP) systems. Their ability to provide requisite protection has to be checked regularly by means of underwater inspection by divers. Furthermore, as they have a finite lifespan, sacrificial anodes need to be replaced regularly over time.
Impressed current cathodic protection
For larger structures, galvanic anodes cannot economically deliver enough current to provide complete protection.
Impressed current cathodic protection (ICCP) systems use anodes connected to a
DC power source (such as a
cathodic protection rectifier). Anodes for ICCP systems are tubular and solid rod shapes of various specialized materials. These include high silicon
cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content of more than 2% and silicon content around 1–3%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloying elements determine the form in which its car ...
, graphite, mixed metal oxide or platinum coated titanium or niobium coated rod and wires.
Anodic protection
Anodic protection impresses anodic current on the structure to be protected (opposite to the cathodic protection). It is appropriate for metals that exhibit passivity (e.g. stainless steel) and suitably small passive current over a wide range of potentials. It is used in aggressive environments, such as solutions of sulfuric acid. Anodic protection is an electrochemical method of corrosion protection by keeping metal in passive state
Rate of corrosion

The formation of an oxide layer is described by the
Deal–Grove model, which is used to predict and control oxide layer formation in diverse situations. A simple test for measuring corrosion is the weight loss method. The method involves exposing a clean weighed piece of the metal or alloy to the corrosive environment for a specified time followed by cleaning to remove corrosion products and weighing the piece to determine the loss of weight. The rate of corrosion () is calculated as
:
where is a constant, is the weight loss of the metal in time , is the surface area of the metal exposed, and is the density of the metal (in g/cm
3).
Other common expressions for the corrosion rate is penetration depth and change of mechanical properties.
Economic impact
In 2002, the US
Federal Highway Administration
The Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) is a division of the United States Department of Transportation that specializes in highway transportation. The agency's major activities are grouped into two programs, the Federal-aid Highway Program a ...
released a study titled "Corrosion Costs and Preventive Strategies in the United States" on the direct costs associated with metallic corrosion in the US industry. In 1998, the total annual direct cost of corrosion in the US roughly $276 billion (or 3.2% of the US
gross domestic product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the total market value of all the final goods and services produced and rendered in a specific time period by a country or countries. GDP is often used to measure the economic performanc ...
at the time). Broken down into five specific industries, the economic losses are $22.6 billion in infrastructure, $17.6 billion in production and manufacturing, $29.7 billion in transportation, $20.1 billion in government, and $47.9 billion in utilities.
Rust is one of the most common causes of bridge accidents. As rust displaces a much higher volume than the originating mass of iron, its build-up can also cause failure by forcing apart adjacent components. It was the cause of the collapse of the
Mianus River Bridge in 1983, when support bearings rusted internally and pushed one corner of the road slab off its support. Three drivers on the roadway at the time died as the slab fell into the river below. The following
NTSB investigation showed that a drain in the road had been blocked for road re-surfacing, and had not been unblocked; as a result, runoff water penetrated the support hangers. Rust was also an important factor in the
Silver Bridge disaster of 1967 in
West Virginia
West Virginia is a mountainous U.S. state, state in the Southern United States, Southern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States.The United States Census Bureau, Census Bureau and the Association of American ...
, when a steel
suspension bridge
A suspension bridge is a type of bridge in which the deck (bridge), deck is hung below suspension wire rope, cables on vertical suspenders. The first modern examples of this type of bridge were built in the early 1800s. Simple suspension bridg ...
collapsed within a minute, killing 46 drivers and passengers who were on the bridge at the time.
Similarly, corrosion of concrete-covered steel and iron can cause the concrete to
spall
Spall are fragments of a material that are broken off a larger solid body. It can be produced by a variety of mechanisms, including as a result of projectile impact, corrosion, weathering, cavitation, or excessive rolling pressure (as in a ba ...
, creating severe structural problems. It is one of the most common failure modes of
reinforced concrete
Reinforced concrete, also called ferroconcrete or ferro-concrete, is a composite material in which concrete's relatively low tensile strength and ductility are compensated for by the inclusion of reinforcement having higher tensile strength or ...
bridge
A bridge is a structure built to Span (engineering), span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or railway) without blocking the path underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, whi ...
s. Measuring instruments based on the half-cell potential can detect the potential corrosion spots before total failure of the concrete structure is reached.
Until 20–30 years ago, galvanized steel pipe was used extensively in the potable water systems for single and multi-family residents as well as commercial and public construction. Today, these systems have long ago consumed the protective zinc and are corroding internally, resulting in poor water quality and pipe failures. The economic impact on homeowners, condo dwellers, and the public infrastructure is estimated at $22 billion as the insurance industry braces for a wave of claims due to pipe failures.
Corrosion in nonmetals
Most
ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant, and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcela ...
materials are almost entirely immune to corrosion. The strong
chemical bond
A chemical bond is the association of atoms or ions to form molecules, crystals, and other structures. The bond may result from the electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions as in ionic bonds or through the sharing of electrons a ...
s that hold them together leave very little free chemical energy in the structure; they can be thought of as already corroded. When corrosion does occur, it is almost always a simple dissolution of the material or chemical reaction, rather than an electrochemical process. A common example of corrosion protection in ceramics is the
lime added to
soda–lime glass
Soda–lime glass, also called soda–lime–silica glass, is the transparent glass used for windowpanes and glass containers (bottles and jars) for beverages, food, and some commodity items. It is the most prevalent type of glass made. Some gl ...
to reduce its solubility in water; though it is not nearly as soluble as pure
sodium silicate
Sodium silicate is a generic name for chemical compounds with the formula or ·, such as sodium metasilicate (), sodium orthosilicate (), and sodium pyrosilicate (). The anions are often polymeric. These compounds are generally colorless tra ...
, normal glass does form sub-microscopic flaws when exposed to moisture. Due to its
brittle
A material is brittle if, when subjected to stress, it fractures with little elastic deformation and without significant plastic deformation. Brittle materials absorb relatively little energy prior to fracture, even those of high strength. ...
ness, such flaws cause a dramatic reduction in the strength of a glass object during its first few hours at room temperature.
Corrosion of polymers
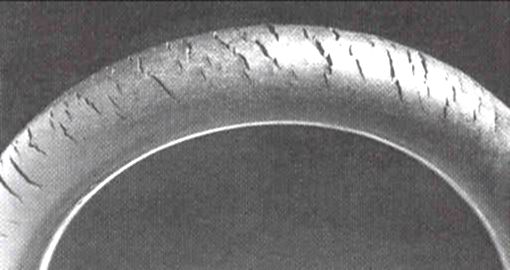 Polymer degradation
Polymer degradation involves several complex and often poorly understood physiochemical processes. These are strikingly different from the other processes discussed here, and so the term "corrosion" is only applied to them in a loose sense of the word. Because of their large molecular weight, very little
entropy
Entropy is a scientific concept, most commonly associated with states of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynamics, where it was first recognized, to the micros ...
can be gained by mixing a given mass of polymer with another substance, making them generally quite difficult to dissolve. While dissolution is a problem in some polymer applications, it is relatively simple to design against.
A more common and related problem is "swelling", where small molecules infiltrate the structure, reducing strength and stiffness and causing a volume change. Conversely, many polymers (notably flexible
vinyl
Vinyl may refer to:
Chemistry
* Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), a particular vinyl polymer
* Vinyl cation, a type of carbocation
* Vinyl group, a broad class of organic molecules in chemistry
* Vinyl polymer, a group of polymers derived from vinyl ...
) are intentionally swelled with
plasticizer
A plasticizer ( UK: plasticiser) is a substance that is added to a material to make it softer and more flexible, to increase its plasticity, to decrease its viscosity, and/or to decrease friction during its handling in manufacture.
Plasticizer ...
s, which can be leached out of the structure, causing brittleness or other undesirable changes.
The most common form of degradation, however, is a decrease in polymer chain length. Mechanisms which break polymer chains are familiar to biologists because of their effect on
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
:
ionizing radiation
Ionizing (ionising) radiation, including Radioactive decay, nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have enough energy per individual photon or particle to ionization, ionize atoms or molecules by detaching ...
(most commonly
ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
light),
free radical
A daughter category of ''Ageing'', this category deals only with the biological aspects of ageing.
Ageing
Biogerontology
Biological processes
Causes of death
Cellular processes
Gerontology
Life extension
Metabolic disorders
Metabolism
...
s, and
oxidizer
An oxidizing agent (also known as an oxidant, oxidizer, electron recipient, or electron acceptor) is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or " accepts"/"receives" an electron from a (called the , , or ''electron donor''). In ot ...
s such as oxygen,
ozone
Ozone () (or trioxygen) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , break ...
, and
chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between ...
.
Ozone cracking is a well-known problem affecting
natural rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds.
Types of polyisoprene ...
for example.
Plastic additives can slow these process very effectively, and can be as simple as a UV-absorbing
pigment
A pigment is a powder used to add or alter color or change visual appearance. Pigments are completely or nearly solubility, insoluble and reactivity (chemistry), chemically unreactive in water or another medium; in contrast, dyes are colored sub ...
(e.g.,
titanium dioxide
Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium(IV) oxide or titania , is the inorganic compound derived from titanium with the chemical formula . When used as a pigment, it is called titanium white, Pigment White 6 (PW6), or Colour Index Internationa ...
or
carbon black
Carbon black (with subtypes acetylene black, channel black, furnace black, lamp black and thermal black) is a material produced by the incomplete combustion of coal tar, vegetable matter, or petroleum products, including fuel oil, fluid cataly ...
).
Plastic shopping bag
In use by consumers worldwide since the 1960s, shopping bags made from various kinds of plastic, are variously called plastic shopping bags, carrier bags, or plastic grocery bags. They are sometimes referred to as single-use bags—referring to c ...
s often do not include these additives so that they break down more easily as ultrafine particles of
litter
Litter consists of waste products that have been discarded incorrectly, without consent, at an unsuitable location. The waste is objects, often man-made, such as aluminum cans, paper cups, food wrappers, cardboard boxes or plastic bottles, but ...
.
Corrosion of glass

Glass is characterized by a high degree of corrosion resistance. Because of its high water resistance, it is often used as primary packaging material in the pharmaceutical industry since most medicines are preserved in a watery solution. Besides its water resistance, glass is also robust when exposed to certain chemically-aggressive liquids or gases.
Glass disease is the corrosion of silicate glasses in
aqueous solution
An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is mostly shown in chemical equations by appending (aq) to the relevant chemical formula. For example, a solution of table salt, also known as sodium chloride (NaCl), in water ...
s. It is governed by two mechanisms:
diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical p ...
-
controlled leaching (ion exchange) and hydrolytic dissolution of the glass network. Both mechanisms strongly depend on the pH of contacting solution: the rate of ion exchange decreases with pH as 10
−0.5pH, whereas the rate of hydrolytic dissolution increases with pH as 10
0.5pH.
Mathematically, corrosion rates of glasses are characterized by normalized corrosion rates of elements (g/cm
2·d) which are determined as the ratio of total amount of released species into the water (g) to the water-contacting surface area (cm
2), time of contact (days), and weight fraction content of the element in the glass :
:
.
The overall corrosion rate is a sum of contributions from both mechanisms (leaching + dissolution): . Diffusion-controlled leaching (ion exchange) is characteristic of the initial phase of corrosion and involves replacement of alkali ions in the glass by a hydronium (H
3O
+) ion from the solution. It causes an ion-selective depletion of near surface layers of glasses and gives an inverse-square-root dependence of corrosion rate with exposure time. The diffusion-controlled normalized leaching rate of cations from glasses (g/cm
2·d) is given by:
:
,
where is time, is the th cation effective diffusion coefficient (cm
2/d), which depends on pH of contacting water as , and is the density of the glass (g/cm
3).
Glass network dissolution is characteristic of the later phases of corrosion and causes a congruent release of ions into the water solution at a time-independent rate in dilute solutions (g/cm
2·d):
:
,
where is the stationary
hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water ...
(dissolution) rate of the glass (cm/d). In closed systems, the consumption of protons from the aqueous phase increases the pH and causes a fast transition to hydrolysis. However, a further saturation of solution with silica impedes hydrolysis and causes the glass to return to an ion-exchange; e.g., diffusion-controlled regime of corrosion.
In typical natural conditions, normalized corrosion rates of silicate glasses are very low and are of the order of 10
−7 to 10
−5 g/(cm
2·d). The very high durability of silicate glasses in water makes them suitable for hazardous and nuclear waste immobilisation.
Glass corrosion tests
There exist numerous standardized procedures for measuring the corrosion (also called chemical durability) of glasses in neutral, basic, and acidic environments, under simulated environmental conditions, in simulated body fluid, at high temperature and pressure, and under other conditions.
The standard procedure ISO 719
describes a test of the extraction of water-soluble basic compounds under neutral conditions: 2 g of glass, particle size 300–500 μm, is kept for 60 min in 50 mL de-ionized water of grade 2 at 98 °C; 25 mL of the obtained solution is titrated against 0.01 mol/L
HCl solution. The volume of HCl required for neutralization is classified according to the table below.
The standardized test ISO 719 is not suitable for glasses with poor or not extractable alkaline components, but which are still attacked by water; e.g., quartz glass, B
2O
3 glass or P
2O
5 glass.
Usual glasses are differentiated into the following classes:
* Hydrolytic class 1 (Type I): This class, which is also called neutral glass, includes
borosilicate glass
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass with silica and boron trioxide as the main glass-forming constituents. Borosilicate glasses are known for having very low coefficients of thermal expansion (≈3 × 10−6 K−1 at 20 °C), ma ...
es (e.g.,
Duran,
Pyrex, Fiolax). Glass of this class contains essential quantities of
boron oxide Boron oxide may refer to one of several oxides of boron:
*Boron trioxide (B2O3, diboron trioxide), the most common form
*Boron monoxide (BO)
*Boron suboxide
Boron suboxide (chemical formula B6O) is a solid compound with a structure built of eight ...
s,
aluminium oxide
Aluminium oxide (or aluminium(III) oxide) is a chemical compound of aluminium and oxygen with the chemical formula . It is the most commonly occurring of several Aluminium oxide (compounds), aluminium oxides, and specifically identified as alum ...
s and
alkaline earth oxides. Through its composition neutral glass has a high resistance against temperature shocks and the highest hydrolytic resistance. Against acid and neutral solutions it shows high chemical resistance, because of its poor alkali content against alkaline solutions.
* Hydrolytic class 2 (Type II): This class usually contains sodium silicate glasses with a high hydrolytic resistance through surface finishing. Sodium silicate glass is a silicate glass, which contains alkali- and
alkaline earth oxide and primarily
sodium oxide and
calcium oxide
Calcium oxide (formula: Ca O), commonly known as quicklime or burnt lime, is a widely used chemical compound. It is a white, caustic, alkaline, crystalline solid at room temperature. The broadly used term '' lime'' connotes calcium-containing ...
.
* Hydrolytic class 3 (Type III): Glass of the 3rd hydrolytic class usually contains sodium silicate glasses and has a mean hydrolytic resistance, which is two times poorer than of type 1 glasses. Acid class DIN 12116 and alkali class DIN 52322 (ISO 695) are to be distinguished from the hydrolytic class DIN 12111 (ISO 719).
See also
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
References
Further reading
*
{{Authority control
Glass chemistry
Metallurgy
 In the most common use of the word, this means
In the most common use of the word, this means  Galvanic corrosion occurs when two different metals have physical or electrical contact with each other and are immersed in a common
Galvanic corrosion occurs when two different metals have physical or electrical contact with each other and are immersed in a common  The materials most resistant to corrosion are those for which corrosion is thermodynamically unfavorable. Any corrosion products of
The materials most resistant to corrosion are those for which corrosion is thermodynamically unfavorable. Any corrosion products of  Certain conditions, such as low concentrations of oxygen or high concentrations of species such as chloride which compete as
Certain conditions, such as low concentrations of oxygen or high concentrations of species such as chloride which compete as 
 Stainless steel can pose special corrosion challenges, since its passivating behavior relies on the presence of a major alloying component (
Stainless steel can pose special corrosion challenges, since its passivating behavior relies on the presence of a major alloying component (
 Various treatments are used to slow corrosion damage to metallic objects which are exposed to the weather, salt water, acids, or other hostile environments. Some unprotected metallic alloys are extremely vulnerable to corrosion, such as those used in
Various treatments are used to slow corrosion damage to metallic objects which are exposed to the weather, salt water, acids, or other hostile environments. Some unprotected metallic alloys are extremely vulnerable to corrosion, such as those used in 


 For effective CP, the potential of the steel surface is polarized (pushed) more negative until the metal surface has a uniform potential. With a uniform potential, the driving force for the corrosion reaction is halted. For galvanic CP systems, the anode material corrodes under the influence of the steel, and eventually it must be replaced. The polarization is caused by the current flow from the anode to the cathode, driven by the difference in
For effective CP, the potential of the steel surface is polarized (pushed) more negative until the metal surface has a uniform potential. With a uniform potential, the driving force for the corrosion reaction is halted. For galvanic CP systems, the anode material corrodes under the influence of the steel, and eventually it must be replaced. The polarization is caused by the current flow from the anode to the cathode, driven by the difference in  The formation of an oxide layer is described by the Deal–Grove model, which is used to predict and control oxide layer formation in diverse situations. A simple test for measuring corrosion is the weight loss method. The method involves exposing a clean weighed piece of the metal or alloy to the corrosive environment for a specified time followed by cleaning to remove corrosion products and weighing the piece to determine the loss of weight. The rate of corrosion () is calculated as
:
where is a constant, is the weight loss of the metal in time , is the surface area of the metal exposed, and is the density of the metal (in g/cm3).
Other common expressions for the corrosion rate is penetration depth and change of mechanical properties.
The formation of an oxide layer is described by the Deal–Grove model, which is used to predict and control oxide layer formation in diverse situations. A simple test for measuring corrosion is the weight loss method. The method involves exposing a clean weighed piece of the metal or alloy to the corrosive environment for a specified time followed by cleaning to remove corrosion products and weighing the piece to determine the loss of weight. The rate of corrosion () is calculated as
:
where is a constant, is the weight loss of the metal in time , is the surface area of the metal exposed, and is the density of the metal (in g/cm3).
Other common expressions for the corrosion rate is penetration depth and change of mechanical properties.
 Polymer degradation involves several complex and often poorly understood physiochemical processes. These are strikingly different from the other processes discussed here, and so the term "corrosion" is only applied to them in a loose sense of the word. Because of their large molecular weight, very little
Polymer degradation involves several complex and often poorly understood physiochemical processes. These are strikingly different from the other processes discussed here, and so the term "corrosion" is only applied to them in a loose sense of the word. Because of their large molecular weight, very little  Glass is characterized by a high degree of corrosion resistance. Because of its high water resistance, it is often used as primary packaging material in the pharmaceutical industry since most medicines are preserved in a watery solution. Besides its water resistance, glass is also robust when exposed to certain chemically-aggressive liquids or gases.
Glass disease is the corrosion of silicate glasses in
Glass is characterized by a high degree of corrosion resistance. Because of its high water resistance, it is often used as primary packaging material in the pharmaceutical industry since most medicines are preserved in a watery solution. Besides its water resistance, glass is also robust when exposed to certain chemically-aggressive liquids or gases.
Glass disease is the corrosion of silicate glasses in