|
Duran (glass)
DURAN is a brand name for the internationally defined borosilicate glass 3.3 (DIN ISO 3585) produced by the German companDURAN Group GmbHsince 2005 under license from the Schott AG, which was the first to develop it, and which sold it from 1893 until the equity carve-out of the DURAN Group in 2005. Because of its high resistance to heat and temperature changes, as well as its high mechanical strength and low coefficient of thermal expansion, DURAN, which Pyrex from Corning is similar to, is not only used for laboratory devices (e.g. components of chemical devices, beakers, Erlenmeyer flasks, etc.) but also in cathode ray tubes, transmitting tubes, and speculums. This glass was developed by Otto Schott in 1887. In 1938 the brand ''DURAN'' was subscribed at the Reichspatentamt and registered in 1943. Milestones 1887: Otto Schott invented the glass 1943: The brand was registered for patent under the trade name DURAN 1950: DURAN borosilicate glass tubing became and has remaine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
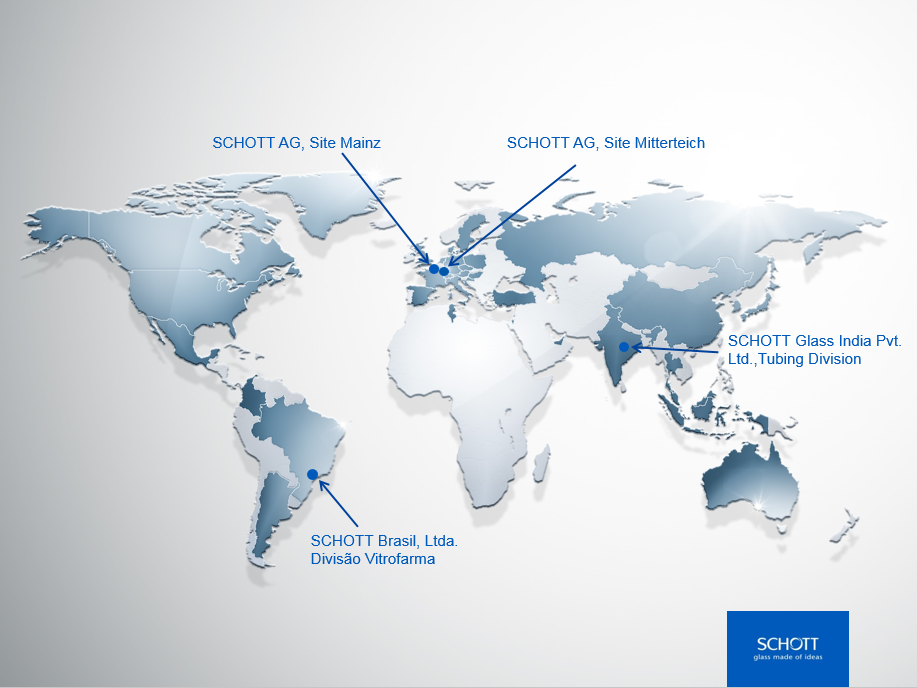
SCHOTT-Rohrglas GmbH
SCHOTT AG Site Mitterteich (formerly SCHOTT-Rohrglas GmbH) in Mitterteich, Germany is one of the leading manufacturers of glass tubing. With more than 1000 employees, it is one of the largest employers in the Tirschenreuth district as well as in the whole Northern Upper Palatine. The Mitterteich site is the largest location of the Business Segment Tubing of Schott AG. Other locations are in Mainz, Germany, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, and Vadodara, India. Company history The history of glass production in Mitterteich dates back to 1883. In 1930 the glass factory in Mitterteich was affiliated to the Grünenplan factory of SCHOTT AG. In 1885 Otto Schott invented the chemically resistant borosilicate glass which was also produced in tubing form. In 1911: a tubing glass was developed which was especially well suited for the production of ampoules. The glass was registered in 1911 under the trade name FIOLAX and is still today one of SCHOTT AG most important products. After the Second Wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glass Tube
Glass tubes are mainly cylindrical hollow-wares. Their special shape combined with the huge variety of glass types (like borosilicate, flint, aluminosilicate, soda lime, lead or quartz glass), allows the use of glass tubing in many applications. For example, laboratory glassware, lighting applications, solar thermal systems and pharmaceutical packaging to name the largest. In the past, scientists constructed their own laboratory apparatus prior to the ubiquity of interchangeable ground glass joints. Today, commercially available parts connected by ground glass joints are preferred; where specialized glassware are required, they are made to measure using commercially available glass tubes by specialist glassblowers. For example, a Schlenk line is made of two large glass tubes, connected by stopcocks and smaller glass tubes, which are further connected to plastic hoses. Industrial Relevance Compared to other materials like plastics the importance of cylindrical half-finished ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glass Production
Glass production involves two main methods – the float glass process that produces sheet glass, and glassblowing that produces bottles and other containers. It has been done in a variety of ways during the history of glass. Glass container production Broadly, modern glass container factories are three-part operations: the "batch house", the "hot end", and the "cold end". The batch house handles the raw materials; the hot end handles the manufacture proper—the forehearth, forming machines, and annealing ovens; and the cold end handles the product-inspection and packaging equipment. Batch processing system (batch house) Batch processing is one of the initial steps of the glass-making process. The batch house simply houses the raw materials in large silos (fed by truck or railcar), and holds anywhere from 1–5 days of material. Some batch systems include material processing such as raw material screening/sieve, drying, or pre-heating (i.e. cullet). Whether automated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Exchanger
A heat exchanger is a system used to transfer heat between a source and a working fluid. Heat exchangers are used in both cooling and heating processes. The fluids may be separated by a solid wall to prevent mixing or they may be in direct contact. They are widely used in space heating, refrigeration, air conditioning, power stations, chemical plants, petrochemical plants, petroleum refineries, natural-gas processing, and sewage treatment. The classic example of a heat exchanger is found in an internal combustion engine in which a circulating fluid known as engine coolant flows through radiator coils and air flows past the coils, which cools the coolant and heats the incoming air. Another example is the heat sink, which is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device to a fluid medium, often air or a liquid coolant. Flow arrangement Image:Heat_exc_1-1.svg, Fig. 1: Shell and tube heat exchanger, single pass (1–1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photobioreactor
Moss photobioreactor to cultivate mosses like ''Physcomitrella patens'' at the laboratory scale A photobioreactor (PBR) refers to any cultivation system designed for growing Photoautotrophism">photoautotrophic organisms using artificial light sources or solar light to facilitate photosynthesis. PBRs are typically used to cultivate microalgae, cyanobacteria, macroalgae, and some mosses. PBRs can be open systems, such as raceway ponds, which rely upon natural sources of light and carbon dioxide. Closed PBRs are flexible systems that can be controlled to the physiological requirements of the cultured organism, resulting in optimal growth rates and purity levels. PBRs are typically used for the cultivation of bioactive compounds for biofuels, pharmaceuticals, and other industrial uses. Open systems Open raceway pond The first approach for the controlled production of phototrophic organisms was a natural open pond or artificial raceway pond. Therein, the culture suspension, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transparency And Translucency
In the field of optics, transparency (also called pellucidity or diaphaneity) is the physical property of allowing light to pass through the material without appreciable scattering of light. On a macroscopic scale (one in which the dimensions are much larger than the wavelengths of the photons in question), the photons can be said to follow Snell's law. Translucency (also called translucence or translucidity) allows light to pass through, but does not necessarily (again, on the macroscopic scale) follow Snell's law; the photons can be scattered at either of the two interfaces, or internally, where there is a change in index of refraction. In other words, a translucent material is made up of components with different indices of refraction. A transparent material is made up of components with a uniform index of refraction. Transparent materials appear clear, with the overall appearance of one color, or any combination leading up to a brilliant spectrum of every color. The opposi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Insulator
An electrical insulator is a material in which electric current does not flow freely. The atoms of the insulator have tightly bound electrons which cannot readily move. Other materials—semiconductors and conductors—conduct electric current more easily. The property that distinguishes an insulator is its resistivity; insulators have higher resistivity than semiconductors or conductors. The most common examples are non-metals. A perfect insulator does not exist because even insulators contain small numbers of mobile charges (charge carriers) which can carry current. In addition, all insulators become electrically conductive when a sufficiently large voltage is applied that the electric field tears electrons away from the atoms. This is known as the breakdown voltage of an insulator. Some materials such as glass, paper and PTFE, which have high resistivity, are very good electrical insulators. A much larger class of materials, even though they may have lower bulk resistivit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Schott
Friedrich Otto Schott (1851–1935) was a German chemist, glass technologist, and the inventor of borosilicate glass. Schott systematically investigated the relationship between the chemical composition of the glass and its properties. In this way, he solved fundamental problems in glass properties, identifying compositions with optical properties that approach the theoretical limit. Schott's findings were a major advance in the optics for microscopy and optical astronomy. His work has been described as "a watershed in the history of glass composition". Early life and education Schott was the son of a window glass maker, Simon Schott. His mother was Karoline Schott. From 1870 to 1873 Schott studied chemical technology at the technical college in Aachen and at the University of Würzburg and at the University of Leipzig. He earned a doctorate in chemistry at Friedrich Schiller University of Jena, specializing in glass science. His doctoral thesis was entitled “Contributions to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borosilicate Glass
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass with silica and boron trioxide as the main glass-forming constituents. Borosilicate glasses are known for having very low coefficients of thermal expansion (≈3 × 10−6 K−1 at 20 °C), making them more resistant to thermal shock than any other common glass. Such glass is subjected to less thermal stress and can withstand temperature differentials without fracturing of about . It is commonly used for the construction of reagent bottles and flasks as well as lighting, electronics, and cookware. Borosilicate glass is sold under various trade names, including Borosil, Duran, Pyrex, Glassco, Supertek, Suprax, Simax, Bellco, Marinex (Brazil), BSA 60, BSC 51 (by NIPRO), Heatex, Endural, Schott, Refmex, Kimax, Gemstone Well, and MG (India). Single ended self-starting lamps are insulated with a mica disc and contained in a borosilicate glass gas discharge tube (arc tube) and a metal cap. They include the sodium-vapor la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
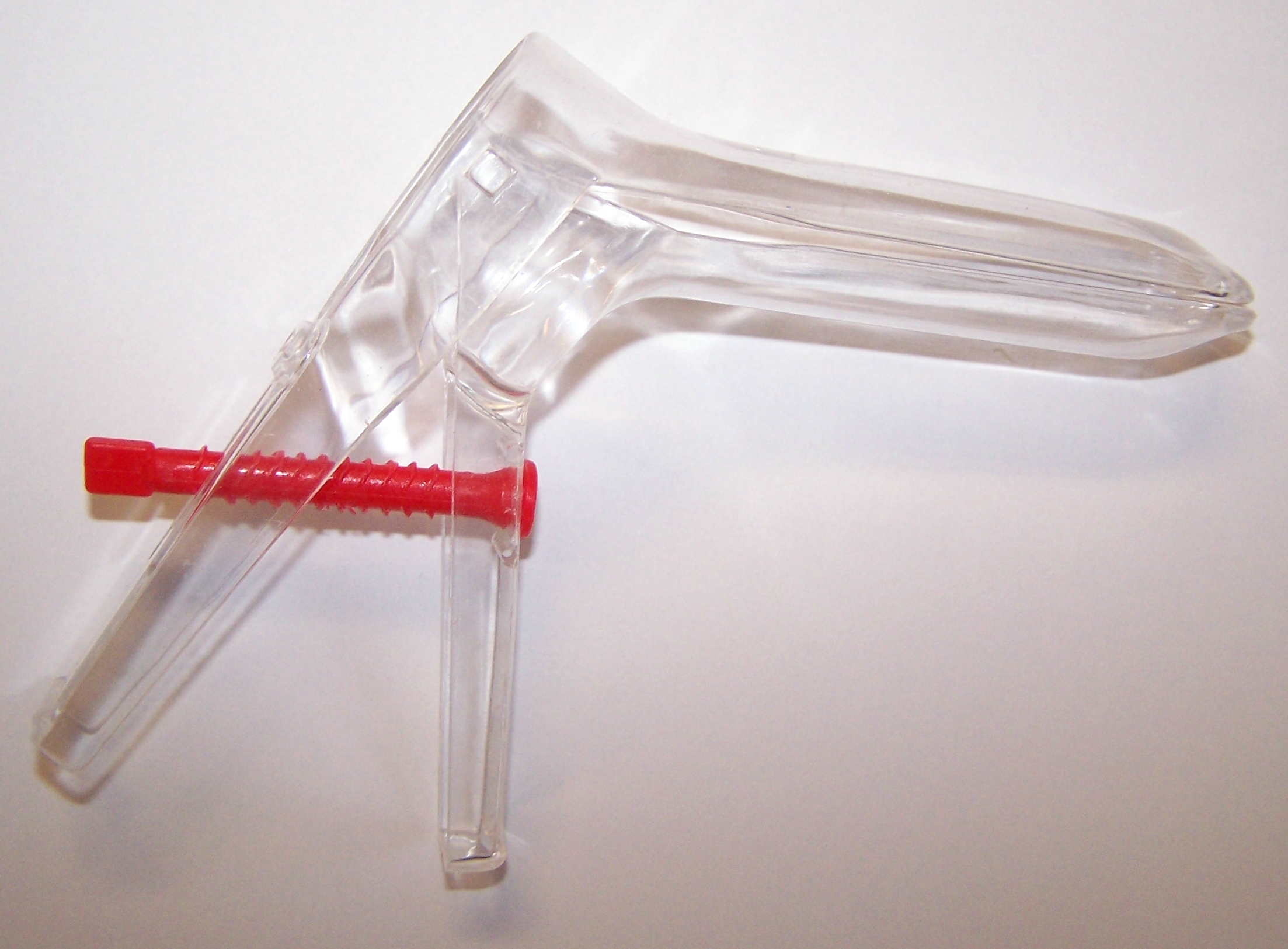
Speculum (medical)
A speculum (Latin for 'mirror'; plural specula or speculums) is a medical tool for investigating body orifices, with a form dependent on the orifice for which it is designed. In old texts, the speculum may also be referred to as a diopter or dioptra. Like an endoscope, a speculum allows a view inside the body; endoscopes, however, tend to have optics while a speculum is intended for direct vision. History Vaginal and anal specula were used by the ancient Greeks and Romans, and speculum artifacts have been found in Pompeii. A vaginal speculum, developed by J. Marion Sims, consists of a hollow cylinder with a rounded end that is divided into two hinged parts, somewhat like the beak of a duck. This speculum is inserted into the vagina to dilate it for examination of the vagina and cervix. The modern vaginal speculum was developed by J. Marion Sims, a plantation doctor in Lancaster County, South Carolina. Between 1845 and 1849, Sims performed dozens of surgeries, without ane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathode Ray Tubes
A cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube containing one or more electron guns, which emit electron beams that are manipulated to display images on a phosphorescent screen. The images may represent electrical waveforms (oscilloscope), pictures ( television set, computer monitor), radar targets, or other phenomena. A CRT on a television set is commonly called a picture tube. CRTs have also been used as memory devices, in which case the screen is not intended to be visible to an observer. The term '' cathode ray'' was used to describe electron beams when they were first discovered, before it was understood that what was emitted from the cathode was a beam of electrons. In CRT television sets and computer monitors, the entire front area of the tube is scanned repeatedly and systematically in a fixed pattern called a raster. In color devices, an image is produced by controlling the intensity of each of three electron beams, one for each additive primary color (red, green, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |