cataplexy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cataplexy is a sudden and transient episode of muscle weakness accompanied by full conscious awareness, typically triggered by emotions such as laughing, crying, or terror. Cataplexy is the first symptom to appear in about 10% of cases of narcolepsy, caused by an autoimmune destruction of hypothalamic
/ref> Cataplectic attacks may occasionally occur spontaneously, with no identifiable emotional trigger.
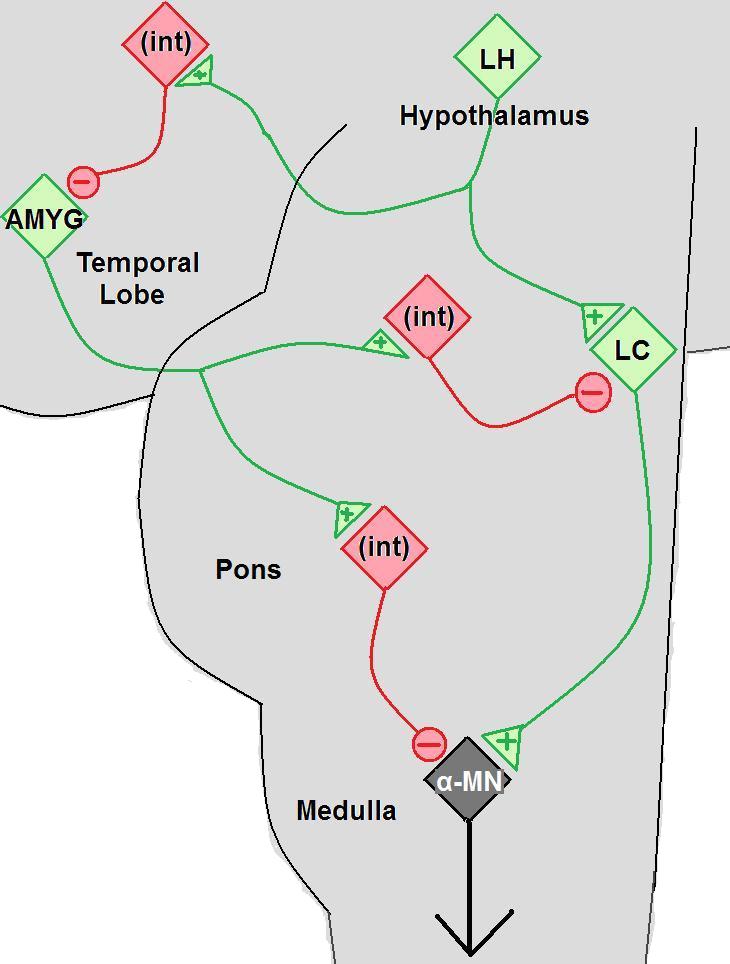 Cataplexy is considered secondary when it is due to specific lesions in the brain that cause a depletion of the hypocretin neurotransmitter. Secondary cataplexy is associated with specific lesions located primarily in the lateral and posterior hypothalamus. Cataplexy due to
Cataplexy is considered secondary when it is due to specific lesions in the brain that cause a depletion of the hypocretin neurotransmitter. Secondary cataplexy is associated with specific lesions located primarily in the lateral and posterior hypothalamus. Cataplexy due to
neurons
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural net ...
that produce the neuropeptide
Neuropeptides are chemical messengers made up of small chains of amino acids that are synthesized and released by neurons. Neuropeptides typically bind to G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) to modulate neural activity and other tissues like the ...
hypocretin (also called orexin), which regulates arousal and has a role in stabilization of the transition between wake and sleep states. Cataplexy without narcolepsy is rare and the cause is unknown.
The term cataplexy originates from the Greek κατά (''kata'', meaning "down"), and πλῆξις (''plēxis'', meaning "strike") and it was first used around 1880 in German physiology literature to describe the phenomenon of tonic immobility also known as " playing possum" (in reference to the opossum
Opossums () are members of the marsupial order Didelphimorphia () endemic to the Americas. The largest order of marsupials in the Western Hemisphere, it comprises 126 species in 18 genera. Opossums originated in South America and entered North A ...
's behavior of feigning death when threatened). In the same year the French neuropsychiatrist Jean-Baptiste Gélineau coined the term 'narcolepsy' and published some clinical reports that contained details about two patients who had similar conditions to those of current narcoleptic cases. Nevertheless, the onset that he reported was in adulthood, as compared to current cases reported in childhood and adolescence. Even if he preferred the term 'astasia' instead of 'cataplexy', the case that he described remains iconic for the diagnosis of full narcoleptic syndrome
A syndrome is a set of medical signs and symptoms which are correlated with each other and often associated with a particular disease or disorder. The word derives from the Greek language, Greek σύνδρομον, meaning "concurrence". When a sy ...
.
Signs and symptoms
Cataplexy manifests itself as muscular weakness which may range from a barely perceptible slackening of the facialmuscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contra ...
s to complete muscle paralysis
Paralysis (: paralyses; also known as plegia) is a loss of Motor skill, motor function in one or more Skeletal muscle, muscles. Paralysis can also be accompanied by a loss of feeling (sensory loss) in the affected area if there is sensory d ...
with postural collapse. Attacks are brief, most lasting from a few seconds to a couple of minutes, and typically involve dropping of the jaw, neck weakness, and/or buckling of the knees. Even in a full-blown collapse, people are usually able to avoid injury because they learn to notice the feeling of the cataplectic attack approaching and the fall is usually slow and progressive. Speech may be slurred and vision
Vision, Visions, or The Vision may refer to:
Perception Optical perception
* Visual perception, the sense of sight
* Visual system, the physical mechanism of eyesight
* Computer vision, a field dealing with how computers can be made to gain und ...
may be impaired (double vision, inability to focus), but hearing and awareness
In philosophy and psychology, awareness is the perception or knowledge of something. The concept is often synonymous with consciousness. However, one can be aware of something without being explicitly conscious of it, such as in the case of bli ...
remain normal.
Cataplexy attacks are self-limiting and resolve without the need for medical intervention. If the person is reclining comfortably, they may transition into sleepiness, hypnagogic hallucinations, or a period of REM sleep. While cataplexy worsens with fatigue, it is different from narcoleptic sleep attacks and is usually, but not always, triggered by strong emotional reactions such as laughter
Laughter is a pleasant physical reaction and emotion consisting usually of rhythmical, usually audible contractions of the diaphragm and other parts of the respiratory system. It is a response to certain external or internal stimuli. Laug ...
, anger
Anger, also known as wrath ( ; ) or rage (emotion), rage, is an intense emotional state involving a strong, uncomfortable and non-cooperative response to a perceived provocation, hurt, or threat.
A person experiencing anger will often experie ...
, surprise, awe, and embarrassment
Embarrassment or awkwardness is an emotional state that is associated with mild to severe levels of discomfort, and which is usually experienced when someone commits (or thinks of) a socially unacceptable or frowned-upon act that is witnessed ...
, or by sudden physical effort, especially if the person is caught off guard. One well-known example of this was the reaction of 1968 Olympic long jump
The long jump is a track and field event in which athletes combine speed, strength and agility in an attempt to leap as far as possible from a takeoff point. Along with the triple jump, the two events that measure jumping for distance as a gr ...
medalist Bob Beamon on learning that he had broken the previous world record by over 0.5 meters (almost 2 feet).Great Olympic Moments - Sir Steve Redgrave, 2011/ref> Cataplectic attacks may occasionally occur spontaneously, with no identifiable emotional trigger.
Mechanism
 Cataplexy is considered secondary when it is due to specific lesions in the brain that cause a depletion of the hypocretin neurotransmitter. Secondary cataplexy is associated with specific lesions located primarily in the lateral and posterior hypothalamus. Cataplexy due to
Cataplexy is considered secondary when it is due to specific lesions in the brain that cause a depletion of the hypocretin neurotransmitter. Secondary cataplexy is associated with specific lesions located primarily in the lateral and posterior hypothalamus. Cataplexy due to brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is conti ...
lesions is uncommon particularly when seen in isolation. The lesions include tumors of the brain or brainstem and arterio-venous malformations. Some of the tumors include astrocytoma, glioblastoma, glioma, and subependymoma. These lesions can be visualized with brain imaging, however in their early stages they can be missed. Other conditions in which cataplexy can be seen include ischemic events, multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease resulting in damage to myelinthe insulating covers of nerve cellsin the brain and spinal cord. As a demyelinating disease, MS disrupts the nervous system's ability to Action potential, transmit ...
, head injury, paraneoplastic syndromes, infections such as encephalitis
Encephalitis is inflammation of the Human brain, brain. The severity can be variable with symptoms including reduction or alteration in consciousness, aphasia, headache, fever, confusion, a stiff neck, and vomiting. Complications may include se ...
, and more rarely Niemann Pick disease. Cataplexy may also occur transiently or permanently due to lesions of the hypothalamus that were caused by surgery, especially in difficult tumor resections. These lesions or generalized processes disrupt the hypocretin neurons and their pathways. The neurological process behind the lesion impairs pathways controlling the normal inhibition of muscle tone drop, consequently resulting in muscle atonia.
Theories for episodes
A phenomenon of REM sleep, muscular paralysis, occurs at an inappropriate time. This loss of tonus is caused by massive inhibition ofmotor neuron
A motor neuron (or motoneuron), also known as efferent neuron is a neuron whose cell body is located in the motor cortex, brainstem or the spinal cord, and whose axon (fiber) projects to the spinal cord or outside of the spinal cord to directly o ...
s in the spinal cord. When this happens during waking, the patient who had a cataplectic attack loses muscular control. As in REM sleep, the person continues to breathe and is able to control eye movements.
Hypocretin
The hypothalamus region of the brain regulates basic functions of hormone release, emotional expression and sleep. One study concluded that the neurochemical hypocretin, also known as orexin, which is regulated by the hypothalamus, was significantly reduced in study participants with symptoms of cataplexy. Hypocretin regulates sleep and states of arousal. Hypocretin deficiency is further associated with decreased levels ofhistamine
Histamine is an organic nitrogenous compound involved in local immune responses communication, as well as regulating physiological functions in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter for the brain, spinal cord, and uterus. Discovered in 19 ...
and epinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands a ...
, chemicals important in promoting wakefulness, arousal and alertness.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of narcolepsy and cataplexy is usually made by symptom presentation. Presenting with the tetrad of symptoms (excessive daytime sleepiness, sleep-onset paralysis, hypnagogic hallucinations, and cataplexy symptoms) is strong evidence of the diagnosis of narcolepsy. A multiple sleep latency test is often conducted to quantify daytime sleepiness. Cataplexy can sometimes be misdiagnosed as a seizure disorder, and people with narcolepsy are often misdiagnosed with other conditions such aspsychiatric disorders
A mental disorder, also referred to as a mental illness, a mental health condition, or a psychiatric disability, is a behavioral or mental pattern that causes significant distress or impairment of personal functioning. A mental disorder is ...
or emotional problems, it can take years for someone to get the proper diagnosis.
Treatment
Cataplexy is treated with medications. Treatment for narcolepsy and cataplexy can be divided to those that act on the excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS) and those that improve cataplexy. Most patients require lifelong use of medications. Most treatments in humans will act only symptomatically and do not target the loss of the orexin-producing neurons. When treating cataplexy, all three systems— adrenergic, cholinergic anddopaminergic
Dopaminergic means "related to dopamine" (literally, "working on dopamine"), a common neurotransmitter. Dopaminergic substances or actions increase dopamine-related activity in the brain.
Dopaminergic pathways, Dopaminergic brain pathways facil ...
—must be considered. The adrenergic system can be inhibited by antidepressants. In mouse models, cataplexy is regulated by the dopaminergic system via the D2-like receptor, which when blocked decreases cataplectic attacks. The role of the cholinergic system has been observed in canine models, where stimulation of this system may lead to severe cataplexy episodes.
There are no behavioral treatments. People with narcolepsy will often try to avoid thoughts and situations that they know are likely to evoke strong emotions and thereby trigger cataplectic attacks.
Gamma-hydroxybutyrate
Gamma-hydroxybutyrate, also known as sodium oxybate, has been found to be effective at reducing the number of cataplexy episodes. Sodium oxybate is generally safe and is typically the recommended treatment. Sodium oxybate is a natural metabolite of GABA. Its main target is the dopaminergic system because at pharmacological concentrations it acts as an agonist and modulates the dopamine neurotransmitters and dopaminergic signalling. It is the only drug authorised by the EMA to treat the whole disease in adults, and by the FDA to treat patients who have cataplexy with the indication to be used for combating excessive daytime sleepiness. This drug helps to normalise sleep architecture and inhibits the intrusion REM sleep elements like paralysis during the day.Antidepressants
If the above treatment is not possible, venlafaxine is recommended. Evidence supporting its effectiveness is primarily based on clinical experience rather than extensive clinical trials. Previous treatments include tricyclic antidepressants such as imipramine, clomipramine or protriptyline. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors may be used to manage both cataplexy and the REM sleep-onset symptoms of sleep paralysis and hypnagogic hallucinations. In clinical practice, venlafaxine and clomipramine are the most common antidepressants used to treat cataplexy. If the patient wishes to have a sedative effect, then clomipramine is prescribed. The effect of these drugs is to suppress the REM component and to increase the brainstem monoaminergic levels. Improvement can be seen within 48 hours after the drug is administered and at doses smaller than the ones used in depression. Nonetheless, antidepressants are not approved by the FDA for the treatment of cataplexy; some jurisdictions have approved clomipramine for this use, however. Frequently, tolerance is developed by the patients and typically the risk of cataplexy rebound or "status cataplecticus" appears when their intake is abruptly interrupted.Future treatments
Immune-based therapies
Narcolepsy with cataplexy is considered an autoimmune-mediated disorder, so some therapies based on this hypothesis have been developed. Immunological therapies developed include: *Corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
s: after testing in 1 human and 1 canine case it proved to be ineffective so is less likely to be further used.
* Intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIgs): it may decrease the symptoms but its effectiveness is still subjective and unconfirmed by the placebo-controlled trials. It was suggested that sometimes it might have life-threatening side effects. Nevertheless, after giving this treatment to a patient with undetectable orexin levels in the cerebrospinal fluid after only 15 days after the disease onset, the cataplexy was improved and the orexin levels started to normalise.
* Plasmapheresis: should be similar with IVIgs but it is more invasive and for it even less data is available.
* Immunoadsorption
* Alemtuzumab
Histaminergic H3 receptor inverse agonist
The histaminergic neurons have a very important role in preserving consciousness and in helping maintain wakefulness and remain active during cataplexy. In narcolepsy, there seems to be an increase in these neurons, possibly to compensate for hypocretin loss. A promising therapy would be to increase the activation of histaminergic neurons by an inverse agonist of the histamine H3 receptor, which enhances histamine release in hypothalamus. An inverse agonist of the histamine H3 is Pitolisant. Results after testing on animals have indicated increased wakefulness in normal animals, decreased sleepiness and blocked the abnormal transitions from REM sleep to awake state in the hypocretin knock-out mice. Also placebo-controlled studies suggest some positive effects of Pitolisant on cataplexy symptoms increasing the levels of alertness and wakefulness.Protective devices
There are several protective devices used that can help to manage the dangers as a results of falls due to cataplexies: *Orthopedic helmets: A protective orthopedic helmet can help prevent severe head injuries in case of falls. *Wheelchair
A wheelchair is a mobilized form of chair using two or more wheels, a footrest, and an armrest usually cushioned. It is used when walking is difficult or impossible to do due to illnesses, injury, disabilities, or age-related health conditio ...
: People with cataplexies may experience falls or other dangerous situations outside their home. A wheelchair can provide a safe and comfortable way for them to move around and should be used as part of standard therapy in those with more than two to three cataplectic attacks per week.
* Crutches: These devices can help them maintain balance and slow down possible falls.
* Orthoses: Orthoses are devices that are worn on the body to support or correct the alignment of the joints. They can be used to help people with narcolepsy maintain their balance and prevent falls.
*Alarm devices: Alarm devices, such as a bed alarm or a wearable alarm, can be used to alert caregivers or family members if the person with narcolepsy is about to fall asleep unexpectedly.
It is important for people with narcolepsy and cataplexy to work with their healthcare team to determine the best protective devices for their specific needs and to ensure their safety and well-being.
Research
Research is being conducted on hypocretin gene therapy and hypocretin cell transplantation for narcolepsy-cataplexy.See also
* Narcolepsy *Neurodegenerative disease
A neurodegenerative disease is caused by the progressive loss of neurons, in the process known as neurodegeneration. Neuronal damage may also ultimately result in their death. Neurodegenerative diseases include amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, mul ...
* Niemann Pick disease
References
{{Disorders of consciousness Muscular disorders Sleep disorders Symptoms and signs: Nervous system