|
Hypocretin
Orexin (), also known as hypocretin, is a neuropeptide that regulates arousal, wakefulness, and appetite. It exists in the forms of orexin-A and orexin-B. The most common form of narcolepsy, type 1, in which the individual experiences brief losses of muscle tone ("drop attacks" or cataplexy), is caused by a lack of orexin in the brain due to destruction of the cells that produce it.Stanford Center for NarcolepsFAQ(retrieved 27-Mar-2012) There are 50,000–80,000 orexin-producing neurons in the human brain, located predominantly in the perifornical area and lateral hypothalamus. They project widely throughout the central nervous system, regulating wakefulness, feeding, and other behaviours. There are two types of orexin peptide and two types of orexin receptor. Orexin was discovered in 1998 almost simultaneously by two independent groups of researchers working on the rat brain. One group named it orexin, from ''orexis,'' meaning "appetite" in Greek; the other group named it hypocr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narcolepsy
Narcolepsy is a chronic neurological disorder that impairs the ability to regulate sleep–wake cycles, and specifically impacts REM (rapid eye movement) sleep. The symptoms of narcolepsy include excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS), sleep-related hallucinations, sleep paralysis, disturbed nocturnal sleep (DNS), and cataplexy. People with narcolepsy typically have poor quality of sleep. There are two recognized forms of narcolepsy, narcolepsy type 1 and type 2. Narcolepsy type 1 (NT1) can be clinically characterized by symptoms of EDS and cataplexy, and/or will have cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) orexin levels of less than 110 pg/ml. Cataplexy are transient episodes of aberrant tone, most typically loss of tone, that can be associated with strong emotion. In pediatric-onset narcolepsy, active motor phenomena are not uncommon. Cataplexy may be mistaken for syncope, tics, or seizures. Narcolepsy type 2 (NT2) does not have features of cataplexy, and CSF orexin levels are normal. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
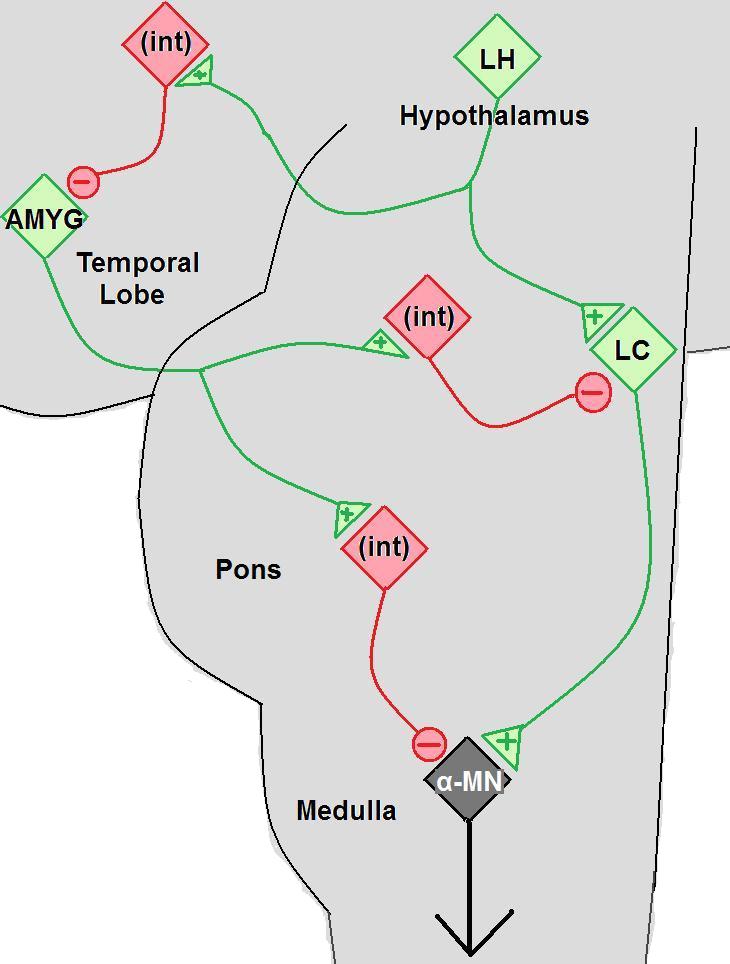
Cataplexy
Cataplexy is a sudden and transient episode of muscle weakness accompanied by full conscious awareness, typically triggered by emotions such as laughing, crying, or terror. Cataplexy is the first symptom to appear in about 10% of cases of narcolepsy, caused by an autoimmune destruction of hypothalamic neurons that produce the neuropeptide hypocretin (also called orexin), which regulates arousal and has a role in stabilization of the transition between wake and sleep states. Cataplexy without narcolepsy is rare and the cause is unknown. The term cataplexy originates from the Greek κατά (''kata'', meaning "down"), and πλῆξις (''plēxis'', meaning "strike") and it was first used around 1880 in German physiology literature to describe the phenomenon of tonic immobility also known as " playing possum" (in reference to the opossum's behavior of feigning death when threatened). In the same year the French neuropsychiatrist Jean-Baptiste Gélineau coined the term 'narcol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Hypothalamus
The lateral hypothalamus (LH), also called the lateral hypothalamic area (LHA), contains the primary orexinergic nucleus within the hypothalamus that widely projects throughout the nervous system; this system of neurons mediates an array of cognitive and physical processes, such as promoting feeding behavior and arousal, reducing pain perception, and regulating body temperature, digestive functions, and blood pressure, among many others. Clinically significant disorders that involve dysfunctions of the orexinergic projection system include narcolepsy, motility disorders or functional gastrointestinal disorders involving visceral hypersensitivity (e.g., irritable bowel syndrome), and eating disorders. The neurotransmitter glutamate and the endocannabinoids (e.g., anandamide) and the orexin neuropeptides orexin-A and orexin-B are the primary signaling neurochemicals in orexin neurons; pathway-specific neurochemicals include GABA, melanin-concentrating hormone, nociceptin, gluc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Kilduff
Thomas S. Kilduff is an American neuroscientist and the director of SRI International's Center for Neuroscience. He specializes in neurobiology related to sleep and wakefulness, and was involved in the discovery of hypocretin (also known as orexin), a neuropeptide system that is highly involved in wakefulness regulation. His group at SRI International also discovered an unusual neuronal population in the cerebral cortex that is activated during sleep. He is also a consulting professor at the Stanford University School of Medicine's Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences. Education Kilduff obtained a B.S. from the University of Florida and earned an M.S. and a Ph.D. in biological sciences from Stanford University, where he was also awarded fellowships from the Danforth Foundation, the Grass Foundation, and the National Science Foundation. Career Kilduff was a senior research scientist at Stanford University's Center for Sleep and Circadian Neurobiology. He was also a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orexin Receptor Type 1
Orexin receptor type 1 (Ox1R or OX1), also known as hypocretin receptor type 1 (HcrtR1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HCRTR1 gene. Function The orexin 1 receptor (OX1), is a G-protein coupled receptor that is heavily expressed in projections from the lateral hypothalamus and is involved in the regulation of feeding behaviour. OX1 selectively binds the orexin-A neuropeptide. It shares 64% identity with OX2. Ligands Agonists * Orexin-A Antagonists * RTIOX-276 - Selective OX1 antagonist * ACT-335827 - Selective OX1 antagonist * Almorexant - Dual OX1 and OX2 antagonist * Lemborexant - Dual OX1 and OX2 antagonist * Nemorexant - Dual OX1 and OX2 antagonist * SB-334,867 - Selective OX1 antagonist * SB-408,124 - Selective OX1 antagonist * SB-649,868 - Dual OX1 and OX2 antagonist * Suvorexant - Dual OX1 and OX2 antagonist An antagonist is a character in a story who is presented as the main enemy or rival of the protagonist and is often depicted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orexin Receptor Type 2
Orexin receptor type 2 (Ox2R or OX2), also known as hypocretin receptor type 2 (HcrtR2), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HCRTR2 gene. It should not be confused for the protein CD200R1 which shares the alias OX2R but is a distinct, unrelated gene located on the human chromosome 3. Structure The structure of the receptor has been solved to 2.5 Å resolution as a fusion protein bound to suvorexant using lipid-mediated crystallization. Function OX2 is a G-protein coupled receptor expressed exclusively in the brain. It has 64% identity with Hypocretin (orexin) receptor 1, OX1. OX2 binds both orexin A and orexin B neuropeptides. OX2 is involved in the central feedback mechanism that regulates feeding behaviour. Mice with enhanced OX2 signaling are resistant to high-fat diet-induced obesity. This receptor is activated by Hipocretin, which is a wake-promoting hypothalamic neuropeptide that acts as a critical regulator of sleep in animals as Zebrafish or Mammal, M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masashi Yanagisawa
is a Japanese-American molecular biologist and physician, famous for his discovery of the hormone endothelin and the neuropeptide orexin, the absence of which is the cause of narcolepsy. He is currently the Director of the International Institute for Integrative Sleep Medicine, University of Tsukuba, and an adjunct professor at the Department of Molecular Genetics, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center. Early life and education Yanagisawa was born in Tokyo in 1960. His father was a surgeon and, thanks to his background in electrical and electronic engineering, an electrophysiology researcher. He graduated from Musashi Junior and Senior High School in 1979, and entered the University of Tsukuba to study medicine. After obtaining an MD in 1985, he pursued a PhD at the same institute, completing it 3 years later. Career Immediately after obtaining his PhD, Yanagisawa started his career as a postdoctoral fellow at the Department of Pharmacology of the University of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wakefulness
Wakefulness is a daily recurring brain state and state of consciousness in which an individual is conscious and engages in coherent cognition, cognitive and behavioral responses to the external world. Being awake is the opposite of being asleep, in which most external inputs to the brain are excluded from neural processing. Effects upon the brain The longer the brain has been awake, the greater the synchronous firing rates of cerebral cortex neurons. After sustained periods of sleep, both the speed and synchronicity of the neurons firing are shown to decrease. Another effect of wakefulness is the reduction of glycogen held in the astrocytes, which supply energy to the neurons. Studies have shown that one of sleep's underlying functions is to replenish this glycogen energy source. Maintenance by the brain Wakefulness is produced by a complex interaction between multiple neurotransmitter systems arising in the brainstem and ascending through the midbrain, hypothalamus, thalamus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orexin-A
Orexin-A, also known as hypocretin-1, is a naturally occurring neuropeptide and orexin isoform. The orexinergic nucleus in the lateral hypothalamus is the primary orexin projection system in the brain. Structure Orexin-A is a peptide composed of 33 amino acids including an N-terminal pyroglutamyl residue and two intramolecular disulfide bridges between cysteine residues in 6 and 12 and 7 and 14 positions. The amino acid sequence is: Pyroglu-Pro-Leu-Pro-Asp-Cys-Cys-Arg-Gln-Lys-Thr-Cys-Ser-Cys-Arg-Leu-Tyr-Glu-Leu-Leu-His-Gly-Ala-Gly-Asn-His-Ala-Ala-Gly-Ile-Leu-Thr-Leu. Mechanism Orexins are highly excitatory neuropeptides that were first discovered in the brains of rats. It is a peptide that is produced by a very small population of cells in the lateral and posterior hypothalamus. Orexins strongly excite various brain nuclei (neurons) to affect an organism's wakefulness by affecting their dopamine, norepinephrine, histamine and acetylcholine systems. These systems work together ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Union Of Basic And Clinical Pharmacology
The International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology (IUPHAR) is a voluntary, non-profit association representing the interests of scientists in pharmacology-related fields to facilitate ''Better Medicines through Global Education and Research'' around the world. History Established in 1959 as a section of the International Union of Physiological Sciences, IUPHAR became an independent organization in 1966 and is a member of the International Council for Science (ICSU). The first World Congress of Pharmacology was held in Stockholm, Sweden in 1961 and subsequently held every three years. After 1990 the World Congresses were moved to a four-year interval. These meetings present the latest pharmacological research, technology, and methodology, and provide a forum for international collaboration and exchange of ideas. A General Assembly, consisting of delegates from all the member societies, is convened during the congresses so member societies have an opportunity to elect t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GenBank
The GenBank sequence database is an open access, annotated collection of all publicly available nucleotide sequences and their protein translations. It is produced and maintained by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI; a part of the National Institutes of Health in the United States) as part of the International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration (INSDC). In October 2024, GenBank contained 34 trillion base pairs from over 4.7 billion nucleotide sequences and more than 580,000 formally described species. The database started in 1982 by Walter Goad and Los Alamos National Laboratory. GenBank has become an important database for research in biological fields and has grown in recent years at an exponential rate by doubling roughly every 18 months. GenBank is built by direct submissions from individual laboratories, as well as from bulk submissions from large-scale sequencing centers. Submissions Only original sequences can be submitted to GenBank. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |