|
Clomipramine
Clomipramine, sold under the brand name Anafranil among others, is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA). It is used in the treatment of various conditions, most notably obsessive–compulsive disorder but also many other disorders, including hyperacusis, panic disorder, major depressive disorder, trichotillomania, body dysmorphic disorder and chronic pain. It has also been notably used to treat premature ejaculation and the cataplexy associated with narcolepsy. It may also address certain fundamental features surrounding narcolepsy besides cataplexy (especially hypnagogic and hypnopompic hallucinations). The evidence behind this, however, is less robust. As with other antidepressants (notably including selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors), it may paradoxically increase the risk of suicide in those under the age of 25, at least in the first few weeks of treatment. It is typically taken by mouth, although intravenous preparations are sometimes used. Common side effects includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tricyclic Antidepressant
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are a class of medications that are used primarily as antidepressants. TCAs were discovered in the early 1950s and were marketed later in the decade. They are named after their chemical structure, which contains three rings of atoms. Tetracyclic antidepressants (TeCAs), which contain four rings of atoms, are a closely related group of antidepressant compounds. Although TCAs are sometimes prescribed for depressive disorders, they have been largely replaced in clinical use in most parts of the world by newer antidepressants such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (NRIs). Adverse effects have been found to be of a similar level between TCAs and SSRIs. Medical uses The TCAs are used primarily in the clinical treatment of mood disorders such as major depressive disorder (MDD), dysthymia, and treatment-resistant variants. They are also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obsessive–compulsive Disorder
Obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD) is a mental disorder in which an individual has intrusive thoughts (an ''obsession'') and feels the need to perform certain routines (''Compulsive behavior, compulsions'') repeatedly to relieve the distress caused by the obsession, to the extent where it impairs general function. Obsessions are persistent unwanted thoughts, mental images, or urges that generate feelings of anxiety, disgust, or discomfort. Some common obsessions include fear of contamination, obsession with symmetry, the fear of acting Blasphemy, blasphemously, sexual obsessions, and the fear of possibly harming others or themselves. Compulsions are repeated actions or routines that occur in response to obsessions to achieve a relief from anxiety. Common compulsions include excessive hand washing, cleaning, counting, ordering, repeating, avoiding triggers, hoarding, neutralizing, seeking assurance, praying, and checking things. OCD can also manifest exclusively through m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
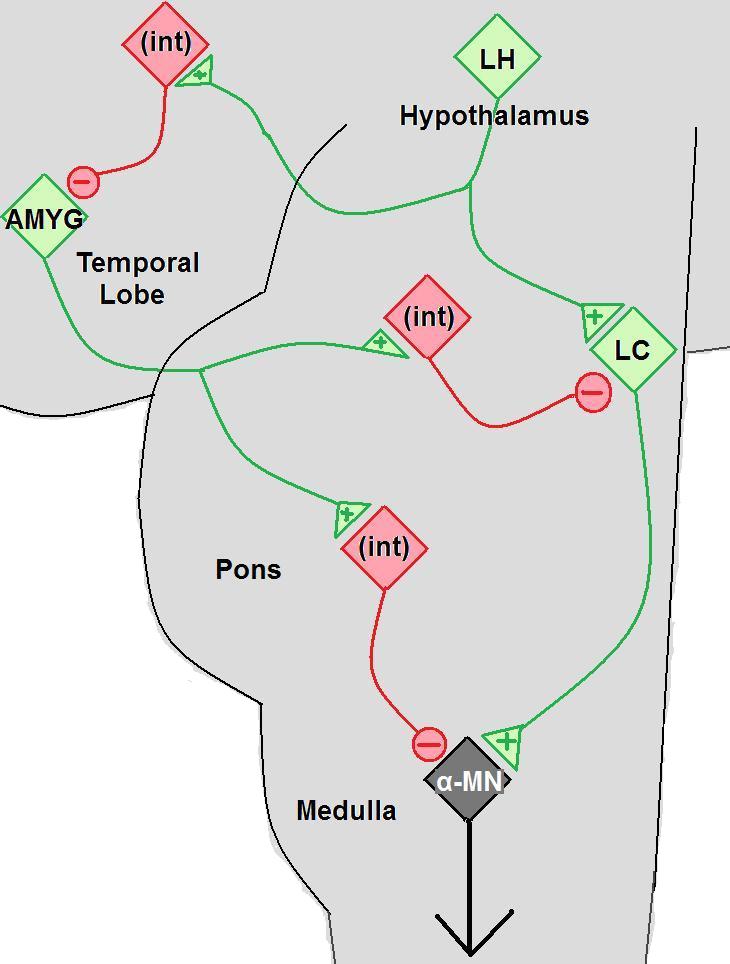
Cataplexy
Cataplexy is a sudden and transient episode of muscle weakness accompanied by full conscious awareness, typically triggered by emotions such as laughing, crying, or terror. Cataplexy is the first symptom to appear in about 10% of cases of narcolepsy, caused by an autoimmune destruction of hypothalamic neurons that produce the neuropeptide hypocretin (also called orexin), which regulates arousal and has a role in stabilization of the transition between wake and sleep states. Cataplexy without narcolepsy is rare and the cause is unknown. The term cataplexy originates from the Greek κατά (''kata'', meaning "down"), and πλῆξις (''plēxis'', meaning "strike") and it was first used around 1880 in German physiology literature to describe the phenomenon of tonic immobility also known as " playing possum" (in reference to the opossum's behavior of feigning death when threatened). In the same year the French neuropsychiatrist Jean-Baptiste Gélineau coined the term 'narcol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichotillomania
Trichotillomania (TTM), also known as hair-pulling disorder or compulsive hair pulling, is a mental disorder characterized by a long-term urge that results in the pulling out of one's own hair. A brief positive feeling may occur as hair is removed. Efforts to stop pulling hair typically fail. Hair removal may occur anywhere; however, the head and around the eyes are most common. The hair pulling is to such a degree that it results in distress and hair loss can be seen. As of 2023, the specific cause or causes of trichotillomania are unclear. Trichotillomania is probably due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The disorder may run in families. It occurs more commonly in those with obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD). Episodes of pulling may be triggered by anxiety. People usually acknowledge that they pull their hair, and broken hairs may be seen on examination. Other conditions that may present similarly include body dysmorphic disorder; however, in that co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desmethylclomipramine
Norclomipramine, also known as ''N''-desmethylclomipramine and chlordesipramine, is the major active metabolite of the tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) clomipramine Clomipramine, sold under the brand name Anafranil among others, is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA). It is used in the treatment of various conditions, most notably obsessive–compulsive disorder but also many other disorders, including hyper ... (Anafranil). References {{Tricyclics Alpha-1 blockers Secondary amines Antihistamines Chloroarenes Dibenzazepines H1 receptor antagonists Human drug metabolites Muscarinic antagonists Serotonin receptor antagonists Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors Tricyclic antidepressants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperacusis
Hyperacusis is an increased Hearing, sensitivity to sound and a low tolerance for environmental noise. Definitions of hyperacusis can vary significantly; it often revolves around damage to or dysfunction of the Stapes, ''stapes'' bone, stapedius muscle or tensor tympani. It is often categorized into four subtypes: loudness, pain (also called noxacusis), annoyance, and fear. It can be a highly debilitating Auditory processing disorder, hearing disorder. There are a variety of causes and risk factors, with the most common being exposure to loud noise. It is often coincident with tinnitus. Proposed mechanisms in the literature involve dysfunction in the brain, inner ear, or middle ear. Little is known about the prevalence of hyperacusis, in part due to the degree of variation in the term's definition. Reported prevalence estimates vary widely, and further research is needed to obtain strong epidemiological data. Signs and symptoms Hyperacusis symptoms can include an increased per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narcolepsy
Narcolepsy is a chronic neurological disorder that impairs the ability to regulate sleep–wake cycles, and specifically impacts REM (rapid eye movement) sleep. The symptoms of narcolepsy include excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS), sleep-related hallucinations, sleep paralysis, disturbed nocturnal sleep (DNS), and cataplexy. People with narcolepsy typically have poor quality of sleep. There are two recognized forms of narcolepsy, narcolepsy type 1 and type 2. Narcolepsy type 1 (NT1) can be clinically characterized by symptoms of EDS and cataplexy, and/or will have cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) orexin levels of less than 110 pg/ml. Cataplexy are transient episodes of aberrant tone, most typically loss of tone, that can be associated with strong emotion. In pediatric-onset narcolepsy, active motor phenomena are not uncommon. Cataplexy may be mistaken for syncope, tics, or seizures. Narcolepsy type 2 (NT2) does not have features of cataplexy, and CSF orexin levels are normal. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciba-Geigy
Novartis AG is a Swiss multinational pharmaceutical corporation based in Basel, Switzerland. Novartis is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in the world and was the eighth largest by revenue in 2024. Novartis manufactures the drugs clozapine (Clozaril), diclofenac (Voltaren; sold to GlaxoSmithKline in 2015 deal), carbamazepine (Tegretol), valsartan (Diovan), imatinib mesylate (Gleevec/Glivec), cyclosporine (Neoral/Sandimmune), letrozole (Femara), methylphenidate (Ritalin; produced by Sandoz since 2023), terbinafine (Lamisil), deferasirox (Exjade), and others. Novartis was formed in 1996 by the merger of Ciba-Geigy and Sandoz. It was considered the largest corporate merger in history during that time. The pharmaceutical and agrochemical divisions of both companies formed Novartis as an independent entity. The name Novartis was based on the Latin terms, ''novae artes'' (new skills). After the merger, other Ciba-Geigy and Sandoz businesses were sold, or, like Ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CYP2D6
Cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''CYP2D6'' gene. ''CYP2D6'' is primarily expressed in the liver. It is also highly expressed in areas of the central nervous system, including the substantia nigra. CYP2D6, a member of the cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidase system, is one of the most important enzymes involved in the metabolism of xenobiotics in the body. In particular, CYP2D6 is responsible for the metabolism and elimination of approximately 25% of clinically used drugs, via the addition or removal of certain functional groups – specifically, hydroxylation, demethylation, and dealkylation. CYP2D6 also activates some prodrugs. This enzyme also metabolizes several endogenous substances, such as N,N-Dimethyltryptamine, hydroxytryptamines, neurosteroids, and both ''m''-tyramine and ''p''-tyramine which CYP2D6 metabolizes into dopamine in the brain and liver. Considerable variation exists in the efficiency and amount of C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premature Ejaculation
Premature ejaculation (PE) is a male sexual dysfunction that occurs when a male Ejaculation, expels semen (and most likely experiences orgasm) soon after beginning sexual activity, and with minimal penile stimulation. It has also been called ''early ejaculation'', ''rapid ejaculation'', ''rapid climax'', ''premature climax'' and (historically) ''ejaculatio praecox.'' There is no uniform cut-off defining "premature", but a consensus of experts at the International Society for Sexual Medicine endorsed a definition of around one minute after penetration. The International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) applies a cut-off of 15 seconds from the beginning of sexual intercourse. Although men with premature ejaculation describe feeling that they have less control over ejaculating, it is not clear if that is true, and many or most average men also report that they wish they could last longer. In males, typical intravaginal ejaculation latency time is approximately 4–8 minutes. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suicidal Behavior
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Risk factors for suicide include mental disorders, physical disorders, and substance abuse. Some suicides are impulsive acts driven by stress (such as from financial or academic difficulties), relationship problems (such as breakups or divorces), or harassment and bullying. Those who have previously attempted suicide are at a higher risk for future attempts. Effective suicide prevention efforts include limiting access to methods of suicide such as firearms, drugs, and poisons; treating mental disorders and substance abuse; careful media reporting about suicide; improving economic conditions; and dialectical behaviour therapy (DBT). Although crisis hotlines, like 988 in North America and 13 11 14 in Australia, are common resources, their effectiveness has not been well studied. Suicide is the 10th leading cause of death worldwide, accounting for approximately 1.5% of total deaths. In a given year, this is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |