Catalytic Domain on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In biology and biochemistry, the active site is the region of an enzyme where
In biology and biochemistry, the active site is the region of an enzyme where
 Once the substrate is bound and oriented to the active site, catalysis can begin. The residues of the catalytic site are typically very close to the binding site, and some residues can have dual-roles in both binding and catalysis.
Catalytic residues of the site interact with the substrate to lower the activation energy of a reaction and thereby make it proceed faster. They do this by a number of different mechanisms including the approximation of the reactants, nucleophilic/electrophilic catalysis and acid/base catalysis. These mechanisms will be explained below.
Once the substrate is bound and oriented to the active site, catalysis can begin. The residues of the catalytic site are typically very close to the binding site, and some residues can have dual-roles in both binding and catalysis.
Catalytic residues of the site interact with the substrate to lower the activation energy of a reaction and thereby make it proceed faster. They do this by a number of different mechanisms including the approximation of the reactants, nucleophilic/electrophilic catalysis and acid/base catalysis. These mechanisms will be explained below.
 The role of glutathione(GSH) is to remove accumulated reactive oxygen species which may damage cells. During this process, its thiol side chain is oxidised and two glutathione molecules are connected by a
The role of glutathione(GSH) is to remove accumulated reactive oxygen species which may damage cells. During this process, its thiol side chain is oxidised and two glutathione molecules are connected by a

 Enzymes can use
Enzymes can use
 HIV protease inhibitors are used to treat patients having
HIV protease inhibitors are used to treat patients having
 Diisopropyl fluorophosphate (DIFP) is an irreversible inhibitor that blocks the action of serine protease. When it binds to the enzyme a nucleophilic substitution reaction occurs and releases one
Diisopropyl fluorophosphate (DIFP) is an irreversible inhibitor that blocks the action of serine protease. When it binds to the enzyme a nucleophilic substitution reaction occurs and releases one
 An allosteric site is a site on an enzyme, unrelated to its active site, which can bind an effector molecule. This interaction is another mechanism of enzyme regulation. Allosteric modification usually happens in proteins with more than one subunit. Allosteric interactions are often present in metabolic pathways and are beneficial in that they allow one step of a reaction to regulate another step. They allow an enzyme to have a range of molecular interactions, other than the highly specific active site.
An allosteric site is a site on an enzyme, unrelated to its active site, which can bind an effector molecule. This interaction is another mechanism of enzyme regulation. Allosteric modification usually happens in proteins with more than one subunit. Allosteric interactions are often present in metabolic pathways and are beneficial in that they allow one step of a reaction to regulate another step. They allow an enzyme to have a range of molecular interactions, other than the highly specific active site.
substrate
Substrate may refer to:
Physical layers
*Substrate (biology), the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the surface or medium on which an organism grows or is attached
** Substrate (locomotion), the surface over which an organism lo ...
molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The active site consists of amino acid residues that form temporary bonds with the substrate ( binding site) and residues that catalyse a reaction of that substrate (catalytic site). Although the active site occupies only ~10–20% of the volume of an enzyme, it is the most important part as it directly catalyzes the chemical reaction. It usually consists of three to four amino acids, while other amino acids within the protein are required to maintain the tertiary structure of the enzymes.
Each active site is evolved to be optimised to bind a particular substrate and catalyse a particular reaction, resulting in high specificity. This specificity is determined by the arrangement of amino acids within the active site and the structure of the substrates. Sometimes enzymes also need to bind with some cofactors to fulfil their function. The active site is usually a groove or pocket of the enzyme which can be located in a deep tunnel within the enzyme, or between the interfaces of multimeric enzymes. An active site can catalyse a reaction repeatedly as residues are not altered at the end of the reaction (they may change during the reaction, but are regenerated by the end). This process is achieved by lowering the activation energy of the reaction, so more substrates have enough energy to undergo reaction.
Binding site
Usually, an enzyme molecule has only two active sites, and the active sites fit with one specific type of substrate. An active site contains a binding site that binds the substrate and orients it for catalysis. The orientation of the substrate and the close proximity between it and the active site is so important that in some cases the enzyme can still function properly even though all other parts are mutated and lose function. Initially, the interaction between the active site and the substrate is non-covalent and transient. There are four important types of interaction that hold the substrate in a defined orientation and form an enzyme-substrate complex (ES complex):hydrogen bond
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (or H-bond) is a primarily electrostatic force of attraction between a hydrogen (H) atom which is covalently bound to a more electronegative "donor" atom or group (Dn), and another electronegative atom bearing a ...
s, van der Waals interactions
A van is a type of road vehicle used for transporting goods or people. Depending on the type of van, it can be bigger or smaller than a pickup truck and SUV, and bigger than a common car. There is some varying in the scope of the word across th ...
, hydrophobic interactions and electrostatic force interactions. The charge distribution on the substrate and active site must be complementary, which means all positive and negative charges must be cancelled out. Otherwise, there will be a repulsive force pushing them apart. The active site usually contains non-polar amino acids, although sometimes polar amino acids may also occur. The binding of substrate to the binding site requires at least three contact points in order to achieve stereo-, regio-, and enantioselectivity. For example, alcohol dehydrogenase which catalyses the transfer of a hydride ion from ethanol to NAD+ interacts with the substrate methyl group, hydroxyl group
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy g ...
and the pro-''(R)'' hydrogen that will be abstracted during the reaction.
In order to exert their function, enzymes need to assume their correct protein fold (''native fold'') and tertiary structure. To maintain this defined three-dimensional structure, proteins rely on various types of interactions between their amino acid residues. If these interactions are interfered with, for example by extreme pH values, high temperature or high ion concentrations, this will cause the enzyme to denature and lose its catalytic activity.
A tighter fit between an active site and the substrate molecule is believed to increase the efficiency of a reaction. If the tightness between the active site of DNA polymerase and its substrate is increased, the fidelity, which means the correct rate of DNA replication will also increase. Most enzymes have deeply buried active sites, which can be accessed by a substrate via access channels.
There are three proposed models of how enzymes fit their specific substrate: the lock and key model
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...
, the induced fit model, and the conformational selection model. The latter two are not mutually exclusive: conformational selection can be followed by a change in the enzyme's shape. Additionally, a protein may not wholly follow either model. Amino acids at the binding site of ubiquitin generally follow the induced fit model, whereas the rest of the protein generally adheres to conformational selection. Factors such as temperature likely influences the pathway taken during binding, with higher temperatures predicted to increase the importance of conformational selection and decrease that of induced fit.
Lock and key hypothesis
This concept was suggested by the 19th-century chemist Emil Fischer. He proposed that the active site and substrate are two stable structures that fit perfectly without any further modification, just like a key fits into a lock. If one substrate perfectly binds to its active site, the interactions between them will be strongest, resulting in high catalytic efficiency. As time went by, limitations of this model started to appear. For example, the competitive enzyme inhibitor methylglucoside can bind tightly to the active site of4-alpha-glucanotransferase
In enzymology, a 4-alpha-glucanotransferase () is an enzyme that catalyzes a chemical reaction that transfers a segment of a 1,4-alpha-D-glucan to a new position in an acceptor carbohydrate, which may be glucose or a 1,4-alpha-D-glucan.
This enzym ...
and perfectly fits into it. However, 4-alpha-glucanotransferase is not active on methylglucoside and no glycosyl transfer occurs. The Lock and Key hypothesis cannot explain this, as it would predict a high efficiency of methylglucoside glycosyl transfer due to its tight binding. Apart from competitive inhibition, this theory cannot explain the mechanism of action of non-competitive inhibitors either, as they do not bind to the active site but nevertheless influence catalytic activity.
Induced fit hypothesis
Daniel Koshland's theory of enzyme-substrate binding is that the active site and the binding portion of the substrate are not exactly complementary. The induced fit model is a development of the lock-and-key model and assumes that an active site is flexible and changes shape until the substrate is completely bound. This model is similar to a person wearing a glove: the glove changes shape to fit the hand. The enzyme initially has a conformation that attracts its substrate. Enzyme surface is flexible and only the correct catalyst can induce interaction leading to catalysis. Conformational changes may then occur as the substrate is bound. After the reaction products will move away from the enzyme and the active site returns to its initial shape. This hypothesis is supported by the observation that the entire protein domain could move several nanometers during catalysis. This movement of protein surface can create microenvironments that favour the catalysis.Conformational selection hypothesis
This model suggests that enzymes exist in a variety of conformations, only some of which are capable of binding to a substrate. When a substrate is bound to the protein, the equilibrium in the conformational ensemble shifts towards those able to bind ligands (as enzymes with bound substrates are removed from the equilibrium between the free conformations).Types of non-covalent interactions
Electrostatic interaction: In an aqueous environment, the oppositely charged groups in amino acid side chains within the active site and substrates attract each other, which is termed electrostatic interaction. For example, when acarboxylic acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is or , with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxylic ...
(R-COOH) dissociates into RCOO− and H+ ions, COO− will attract positively charged groups such as protonated guanidine side chain of arginine
Arginine is the amino acid with the formula (H2N)(HN)CN(H)(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. The molecule features a guanidino group appended to a standard amino acid framework. At physiological pH, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated (−CO2−) and both the am ...
.
Hydrogen bond: A hydrogen bond is a specific type of dipole-dipole interaction between a partially positive hydrogen atom and a partially negative electron donor that contain a pair of electrons such as oxygen, fluorine
Fluorine is a chemical element with the symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists at standard conditions as a highly toxic, pale yellow diatomic gas. As the most electronegative reactive element, it is extremely reacti ...
and nitrogen. The strength of hydrogen bond depends on the chemical nature and geometric arrangement of each group.
Van der Waals force: Van der Waals force is formed between oppositely charged groups due to transient uneven electron distribution in each group. If all electrons are concentrated at one pole of the group this end will be negative, while the other end will be positive. Although the individual force is weak, as the total number of interactions between the active site and substrate is massive the sum of them will be significant.
Hydrophobic interaction: Non-polar hydrophobic groups tend to aggregate together in the aqueous environment and try to leave from polar solvent. These hydrophobic groups usually have long carbon chain and do not react with water molecules. When dissolving in water a protein molecule will curl up into a ball-like shape, leaving hydrophilic groups in outside while hydrophobic groups are deeply buried within the centre.
Catalytic site
 Once the substrate is bound and oriented to the active site, catalysis can begin. The residues of the catalytic site are typically very close to the binding site, and some residues can have dual-roles in both binding and catalysis.
Catalytic residues of the site interact with the substrate to lower the activation energy of a reaction and thereby make it proceed faster. They do this by a number of different mechanisms including the approximation of the reactants, nucleophilic/electrophilic catalysis and acid/base catalysis. These mechanisms will be explained below.
Once the substrate is bound and oriented to the active site, catalysis can begin. The residues of the catalytic site are typically very close to the binding site, and some residues can have dual-roles in both binding and catalysis.
Catalytic residues of the site interact with the substrate to lower the activation energy of a reaction and thereby make it proceed faster. They do this by a number of different mechanisms including the approximation of the reactants, nucleophilic/electrophilic catalysis and acid/base catalysis. These mechanisms will be explained below.
Mechanisms involved in Catalytic process
Approximation of the reactant
During enzyme catalytic reaction, the substrate and active site are brought together in a close proximity. This approach has various purposes. Firstly, when substrates bind within the active site the effective concentration of it significantly increases than in solution. This means the number of substrate molecules involved in the reaction is also increased. This process also reduces the desolvation energy required for the reaction to occur. In solution substrate molecules are surrounded by solvent molecules and energy is required for enzyme molecules to replace them and contact with the substrate. Since bulk molecules can be excluded from the active site this energy output can be minimised. Next, the active site is designed to reorient the substrate to reduce the activation energy for the reaction to occur. The alignment of the substrate, after binding, is locked in a high energy state and can proceed to the next step. In addition, this binding is favoured by entropy as the energy cost associated with solution reaction is largely eliminated since solvent cannot enter active site. In the end, the active site may manipulate the Molecular orbital of the substrate into a suitable orientation to reduce activation energy. The electrostatic states of substrate and active site must be complementary to each other. A polarized negatively charged amino acid side chain will repel uncharged substrate. But if the transition state involves the formation of an ion centre then the side chain will now produce a favourable interaction.Covalent catalysis
Many enzymes including serine protease, cysteine protease, protein kinase andphosphatase
In biochemistry, a phosphatase is an enzyme that uses water to cleave a phosphoric acid Ester, monoester into a phosphate ion and an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol. Because a phosphatase enzyme catalysis, catalyzes the hydrolysis of its Substrate ...
evolved to form transient covalent bonds between them and their substrates to lower the activation energy and allow the reaction to occur. This process can be divided into 2 steps: formation and breakdown. The former step is rate-limit step while the later step is needed to regenerate intact enzyme.
Nucleophilic catalysis: This process involves the donation of electrons from the enzyme's nucleophile
In chemistry, a nucleophile is a chemical species that forms bonds by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are ...
to a substrate to form a covalent bond between them during the transition state. The strength of this interaction depends on two aspects.: the ability of the nucleophilic group to donate electrons and the electrophile to accept them. The former one is mainly affected by the basicity(the ability to donate electron pairs) of the species while the later one is in regard to its p''K''a. Both groups are also affected by their chemical properties such as polarizability, electronegativity and ionization potential. Amino acids that can form nucleophile including serine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − form un ...
, cysteine
Cysteine (symbol Cys or C; ) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile.
When present as a deprotonated catalytic residue, sometime ...
, aspartate
Aspartic acid (symbol Asp or D; the ionic form is known as aspartate), is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Like all other amino acids, it contains an amino group and a carboxylic acid. Its α-amino group is in the pro ...
and glutamine.
Electrophilic catalysis: The mechanism behind this process is exactly same as nucleophilic catalysis except that now amino acids in active site act as electrophile while substrates are nucleophiles. This reaction usually requires cofactors as the amino acid side chains are not strong enough in attracting electrons.
Metal ions
Metal ions have multiple roles during the reaction. Firstly it can bind to negatively charged substrate groups so they will not repel electron pairs from active site's nucleophilic groups. It can attract negatively charged electrons to increase electrophilicity. It can also bridge between active site and substrate. At last, they may change the conformational structure of the substrate to favour reaction.Acid/base catalysis
In some reactions, protons and hydroxide may directly act as acid and base in term of specific acid and specific base catalysis. But more often groups in substrate and active site act as Brønsted–Lowry acid and base. This is called general acid and general base theory. The easiest way to distinguish between them is to check whether thereaction rate
The reaction rate or rate of reaction is the speed at which a chemical reaction takes place, defined as proportional to the increase in the concentration of a product per unit time and to the decrease in the concentration of a reactant per unit ...
is determined by the concentrations of the general acid and base. If the answer is yes then the reaction is the general type. Since most enzymes have an optimum pH of 6 to 7, the amino acids in the side chain usually have a p''K''a of 4~10. Candidate include aspartate
Aspartic acid (symbol Asp or D; the ionic form is known as aspartate), is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Like all other amino acids, it contains an amino group and a carboxylic acid. Its α-amino group is in the pro ...
, glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; the ionic form is known as glutamate) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can syn ...
, histidine, cysteine
Cysteine (symbol Cys or C; ) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile.
When present as a deprotonated catalytic residue, sometime ...
. These acids and bases can stabilise the nucleophile or electrophile formed during the catalysis by providing positive and negative charges.
Conformational distortion
Quantitative studies of enzymatic reactions often found that the acceleration of chemical reaction speed cannot be fully explained by existing theories like the approximation, acid/base catalysis and electrophile/nucleophile catalysis. And there is an obvious paradox: in reversible enzymatic reaction if the active site perfectly fits the substrates then the backward reaction will be slowed since products cannot fit perfectly into the active site. So conformational distortion was introduced and argues that both active site and substrate can undergo conformational changes to fit with each other all the time.Preorganised active site complementarity to the transition state
This theory is a little similar to the Lock and Key Theory, but at this time the active site is preprogrammed to bind perfectly to substrate in transition state rather than in ground state. The formation of transition state within the solution requires a large amount of energy to relocate solvent molecules and the reaction is slowed. So the active site can substitute solvent molecules and surround the substrates to minimize the counterproductive effect imposed by the solution. The presence of charged groups with the active site will attract substrates and ensure electrostatic complementarity.Examples of enzyme catalysis mechanisms
In reality, most enzyme mechanisms involve a combination of several different types of catalysis.disulphide bond
In biochemistry, a disulfide (or disulphide in British English) refers to a functional group with the structure . The linkage is also called an SS-bond or sometimes a disulfide bridge and is usually derived by the coupling of two thiol groups. In ...
to form a dimer(GSSG). In order to regenerate glutathione the disulphide bond has to be broken, In human cells, this is done by glutathione reductase(GR).
Glutathione reductase is a dimer that contains two identical subunits. It requires one NADP and one FAD as the cofactors. The active site is located in the linkage between two subunits. The NADPH is involved in the generation of FADH-. In the active site, there are two cysteine
Cysteine (symbol Cys or C; ) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile.
When present as a deprotonated catalytic residue, sometime ...
residues besides the FAD cofactor and are used to break the disulphide bond during the catalytic reaction. NADPH is bound by three positively charged residues: Arg-218, His-219 and Arg-224.
The catalytic process starts when the FAD is reduced by NADPH to accept one electron and from FADH−. It then attacks the disulphide bond formed between 2 cysteine residues, forming one SH bond and a single S− group. This S− group will act as a nucleophile to attack the disulphide bond in the oxidised glutathione(GSSG), breaking it and forming a cysteine-SG complex. The first SG− anion is released and then receives one proton from adjacent SH group and from the first glutathione monomer. Next the adjacent S− group attack disulphide bond in cysteine-SG complex and release the second SG− anion. It receives one proton in solution and forms the second glutathione monomer.
Chymotrypsin
Chymotrypsin
Chymotrypsin (, chymotrypsins A and B, alpha-chymar ophth, avazyme, chymar, chymotest, enzeon, quimar, quimotrase, alpha-chymar, alpha-chymotrypsin A, alpha-chymotrypsin) is a digestive enzyme component of pancreatic juice acting in the duodenu ...
is a serine endopeptidase that is present in pancreatic juice and helps the hydrolysis of proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
and peptide. It catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptide bonds in L-isomers of tyrosine, phenylalanine
Phenylalanine (symbol Phe or F) is an essential α-amino acid with the formula . It can be viewed as a benzyl group substituted for the methyl group of alanine, or a phenyl group in place of a terminal hydrogen of alanine. This essential amino a ...
, and tryptophan. In the active site of this enzyme, three amino acid residues work together to form a catalytic triad which makes up the catalytic site. In chymotrypsin, these residues are Ser-195, His-57 and Asp-102.
The mechanism of chymotrypsin can be divided into two phases. First, Ser-195 nucleophilically attacks the peptide bond
In organic chemistry, a peptide bond is an amide type of covalent chemical bond linking two consecutive alpha-amino acids from C1 (carbon number one) of one alpha-amino acid and N2 (nitrogen number two) of another, along a peptide or protein cha ...
carbon in the substrate to form a tetrahedral intermediate. The nucleophilicity of Ser-195 is enhanced by His-57, which abstracts a proton from Ser-195 and is in turn stabilised by the negatively charged carboxylate group (RCOO−) in Asp-102. Furthermore, the tetrahedral oxyanion intermediate generated in this step is stabilised by hydrogen bonds
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (or H-bond) is a primarily electrostatic force of attraction between a hydrogen (H) atom which is covalently bound to a more electronegative "donor" atom or group (Dn), and another electronegative atom bearing a ...
from Ser-195 and Gly-193.
In the second stage, the R'NH group is protonated by His-57 to form R'NH2 and leaves the intermediate, leaving behind the acylated
In chemistry, acylation (or alkanoylation) is the chemical reaction in which an acyl group () is added to a compound. The compound providing the acyl group is called the acylating agent.
Because they form a strong electrophile when treated with ...
Ser-195. His-57 then acts as a base again to abstract one proton from a water molecule. The resulting hydroxide anion nucleophilically attacks the acyl-enzyme complex to form a second tetrahedral oxyanion intermediate, which is once again stabilised by H bonds. In the end, Ser-195 leaves the tetrahedral intermediate, breaking the CO bond that connected the enzyme to the peptide substrate. A proton is transferred to Ser-195 through His-57, so that all three amino acid return to their initial state.
Unbinding
Substrate unbinding is influenced by various factors. Larger ligands generally stay in the active site longer, as do those with more rotatable bonds (although this may be a side effect of size). When the solvent is excluded from the active site, less flexible proteins result in longer residence times. More hydrogen bonds shielded from the solvent also decrease unbinding.Cofactors
 Enzymes can use
Enzymes can use cofactors
Cofactor may also refer to:
* Cofactor (biochemistry), a substance that needs to be present in addition to an enzyme for a certain reaction to be catalysed
* A domain parameter in elliptic curve cryptography, defined as the ratio between the order ...
as ‘helper molecules’. Coenzymes are referred to those non-protein molecules that bind with enzymes to help them fulfill their jobs. Mostly they are connected to the active site by non-covalent bonds such as hydrogen bond
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (or H-bond) is a primarily electrostatic force of attraction between a hydrogen (H) atom which is covalently bound to a more electronegative "donor" atom or group (Dn), and another electronegative atom bearing a ...
or hydrophobic interaction. But sometimes a covalent bond can also form between them. For example, the heme in cytochrome C
The cytochrome complex, or cyt ''c'', is a small hemeprotein found loosely associated with the inner membrane of the mitochondrion. It belongs to the cytochrome c family of proteins and plays a major role in cell apoptosis. Cytochrome c is hig ...
is bound to the protein through thioester bond. In some occasions, coenzymes can leave enzymes after the reaction is finished. Otherwise, they permanently bind to the enzyme. Coenzyme is a broad concept which includes metal ions, various vitamins and ATP
ATP may refer to:
Companies and organizations
* Association of Tennis Professionals, men's professional tennis governing body
* American Technical Publishers, employee-owned publishing company
* ', a Danish pension
* Armenia Tree Project, non ...
. If an enzyme needs coenzyme to work itself, it is called an apoenzyme. In fact, it alone cannot catalyze reactions properly. Only when its cofactor comes in and binds to the active site to form holoenzyme does it work properly.
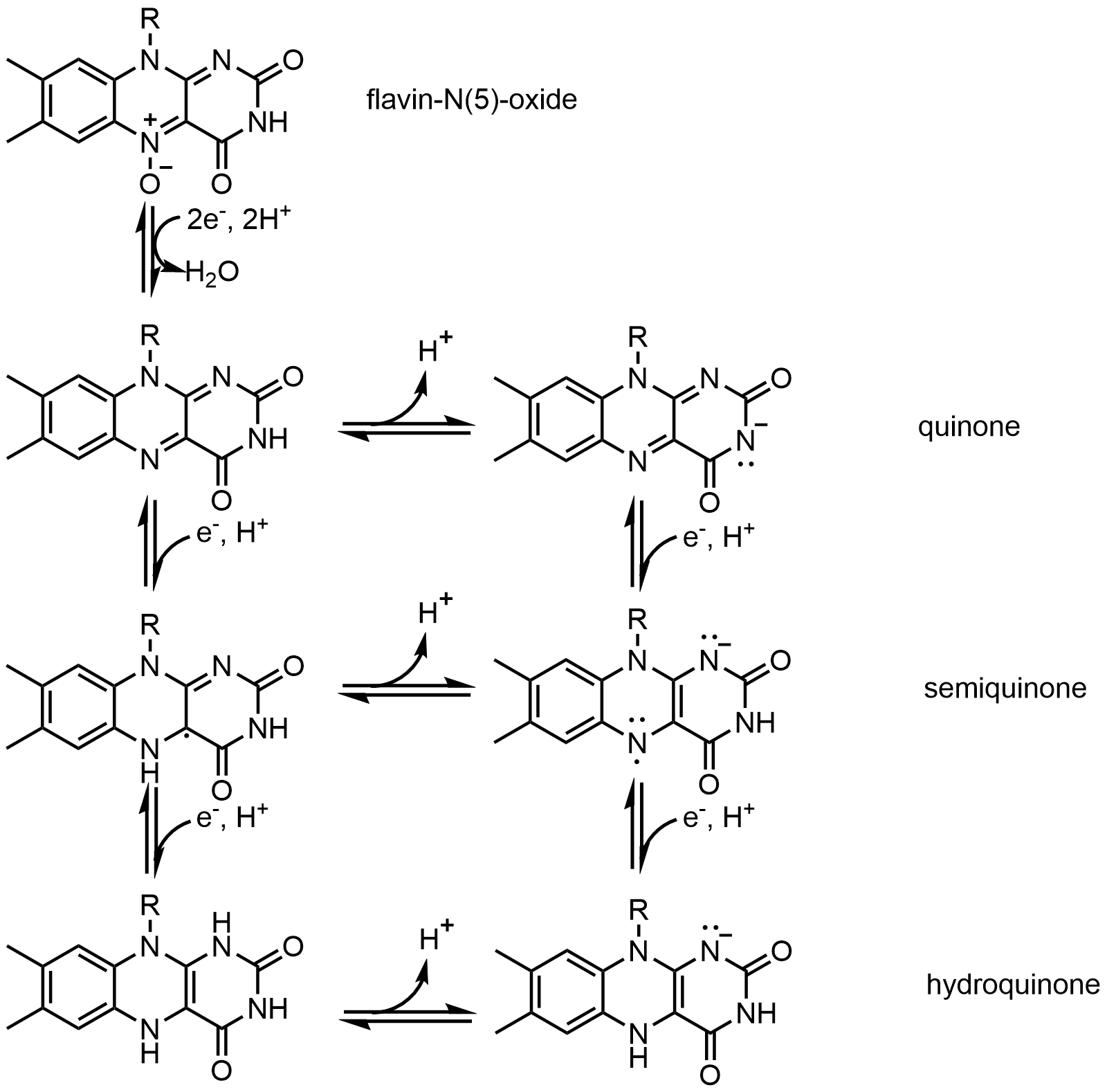
One example of the coenzyme is Flavin. It contains a distinct conjugated isoalloxazine ring system. Flavin has multiple redox states and can be used in processes that involve the transfer of one or two electrons. It can act as an electron acceptor
An electron acceptor is a chemical entity that accepts electrons transferred to it from another compound. It is an oxidizing agent that, by virtue of its accepting electrons, is itself reduced in the process. Electron acceptors are sometimes mista ...
in reaction, like the oxidation of NAD to NADH, to accept two electrons and form 1,5-dihydroflavin. On the other hand, it can form semiquinone( free radical) by accepting one electron, and then converts to fully reduced form by the addition of an extra electron. This property allows it to be used in one electron oxidation process.
Inhibitors
Inhibitors disrupt the interaction between enzyme and substrate, slowing down the rate of a reaction. There are different types of inhibitor, including both reversible and irreversible forms. Competitive inhibitors are inhibitors that only target free enzyme molecules. They compete with substrates for free enzyme acceptor and can be overcome by increasing the substrate concentration. They have two mechanisms. Competitive inhibitors usually have structural similarities to the substrates and or ES complex. As a result, they can fit into the active site and trigger favourable interactions to fill in the space and block substrates from entry. They can also induce transient conformational changes in the active site so substrates cannot fit perfectly with it. After a short period of time, competitive inhibitors will drop off and leave the enzyme intact. Inhibitors are classified as non-competitive inhibitors when they bind both free enzyme and ES complex. Since they do not compete with substrates for the active site, they cannot be overcome by simply increasing the substrate concentration. They usually bind to a different site on the enzyme and alter the 3-dimensional structure of the active site to block substrates from entry or leaving the enzyme. Irreversible inhibitors are similar to competitive inhibitors as they both bind to the active site. However, irreversible inhibitors form irreversible covalent bonds with the amino acid residues in the active site and never leave. Therefore, the active site is occupied and the substrate cannot enter. Occasionally the inhibitor will leave but the catalytic site is permanently altered in shape. These inhibitors usually contain electrophilic groups likehalogen
The halogens () are a group in the periodic table consisting of five or six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), astatine (At), and tennessine (Ts). In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, this group is ...
substitutes and epoxides. As time goes by more and more enzymes are bound by irreversible inhibitors and cannot function anymore.
Examples of competitive and irreversible enzyme inhibitors
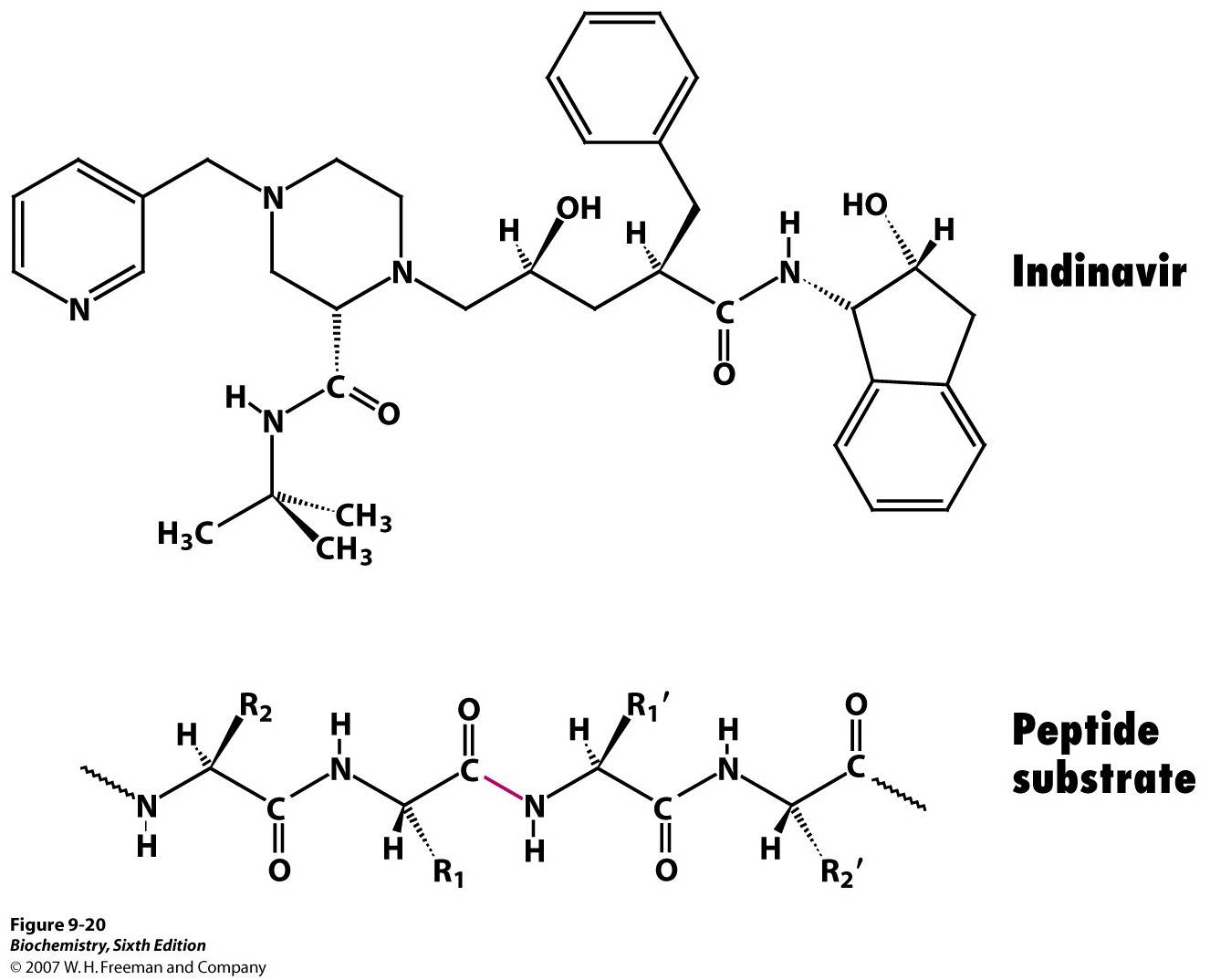
Competitive inhibitor: HIV protease inhibitor
 HIV protease inhibitors are used to treat patients having
HIV protease inhibitors are used to treat patients having AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual m ...
virus by preventing its DNA replication. HIV protease is used by the virus to cleave Gag-Pol polyprotein into 3 smaller proteins that are responsible for virion assembly, package and maturation. This enzyme targets the specific phenylalanine
Phenylalanine (symbol Phe or F) is an essential α-amino acid with the formula . It can be viewed as a benzyl group substituted for the methyl group of alanine, or a phenyl group in place of a terminal hydrogen of alanine. This essential amino a ...
-proline
Proline (symbol Pro or P) is an organic acid classed as a proteinogenic amino acid (used in the biosynthesis of proteins), although it does not contain the amino group but is rather a secondary amine. The secondary amine nitrogen is in the prot ...
cleave site within the target protein. If HIV protease is switched off the virion particle will lose function and cannot infect patients. Since it is essential in viral replication and is absent in healthy human, it is an ideal target for drug development.
HIV protease belongs to aspartic protease family and has a similar mechanism. Firstly the aspartate
Aspartic acid (symbol Asp or D; the ionic form is known as aspartate), is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Like all other amino acids, it contains an amino group and a carboxylic acid. Its α-amino group is in the pro ...
residue activates a water molecule and turns it into a nucleophile
In chemistry, a nucleophile is a chemical species that forms bonds by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are ...
. Then it attacks the carbonyl group within the peptide bond
In organic chemistry, a peptide bond is an amide type of covalent chemical bond linking two consecutive alpha-amino acids from C1 (carbon number one) of one alpha-amino acid and N2 (nitrogen number two) of another, along a peptide or protein cha ...
(NH-CO) to form a tetrahedral intermediate. The nitrogen atom within the intermediate receives a proton, forming an amide group
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent organic groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it is p ...
and subsequent rearrangement leads to the break down of the bond between it and the intermediate and forms two products.
Inhibitors usually contain a nonhydrolyzable hydroxyethylene or hydroxyethylamine groups that mimic the tetrahedral intermediate. Since they share a similar structure and electrostatic arrangement to the transition state of substrates they can still fit into the active site but cannot be broken down, so hydrolysis cannot occur.
Non-competitive inhibitor: Strychnine
Strychnine is aneurotoxin
Neurotoxins are toxins that are destructive to nerve tissue (causing neurotoxicity). Neurotoxins are an extensive class of exogenous chemical neurological insultsSpencer 2000 that can adversely affect function in both developing and mature ner ...
that causes death by affecting nerves that control muscular contraction and cause respiration difficulty. The impulse is transmitted between the synapse through a neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neuro ...
called acetylcholine
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic chemical that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals (including humans) as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Part ...
. It is released into the synapse
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target effector cell.
Synapses are essential to the transmission of nervous impulses from ...
between nerve cells and binds to receptors in the postsynaptic cell. Then an action potential is generated and transmitted through the postsynaptic cell to start a new cycle.
Glycine can inhibit the activity of neurotransmitter receptors, thus a larger amount of acetylcholinesterase is required to trigger an action potential. This makes sure that the generation of nerve impulses is tightly controlled. However, this control is broken down when strychnine is added. It inhibits glycine receptors(a chloride channel) and a much lower level of neurotransmitter concentration can trigger an action potential. Nerves now constantly transmit signals and cause excessive muscular contraction, leading to asphyxiation and death.
Irreversible inhibitor:Diisopropyl fluorophosphate
hydrogen fluoride
Hydrogen fluoride (fluorane) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . This colorless gas or liquid is the principal industrial source of fluorine, often as an aqueous solution called hydrofluoric acid. It is an important feedstock i ...
molecule. The OH group in the active site acts as a nucleophile to attack the phosphorus in DIFP and form a tetrahedral intermediate and release a proton. Then the P-F bond is broken, one electron is transferred to the F atom and it leaves the intermediate as F− anion. It combines with a proton in solution to form one HF molecule. A covalent bond formed between the active site and DIFP, so the serine side chain is no longer available to the substrate.
In drug discovery
Identification of active sites is crucial in the process ofdrug discovery
In the fields of medicine, biotechnology and pharmacology, drug discovery is the process by which new candidate medications are discovered.
Historically, drugs were discovered by identifying the active ingredient from traditional remedies or by ...
. The 3-D structure of the enzyme is analysed to identify active site residues and design drugs which can fit into them. Proteolytic enzymes are targets for some drugs, such as protease inhibitors, which include drugs against AIDS and hypertension.
These protease inhibitors bind to an enzyme's active site and block interaction with natural substrates.
An important factor in drug design is the strength of binding between the active site and an enzyme inhibitor. If the enzyme found in bacteria is significantly different from the human enzyme then an inhibitor can be designed against that particular bacterium without harming the human enzyme. If one kind of enzyme is only present in one kind of organism, its inhibitor can be used to specifically wipe them out.
Active sites can be mapped to aid the design of new drugs such as enzyme inhibitors. This involves the description of the size of an active site and the number and properties of sub-sites, such as details of the binding interaction. Modern database technology called CPASS (Comparison of Protein Active Site Structures) however allows the comparison of active sites in more detail and the finding of structural similarity using software.
Application of enzyme inhibitors
Allosteric sites
See also
* Hugh Stott Taylor * SitExReferences
Further reading
* Alan Fersht, ''Structure and Mechanism in Protein Science: A Guide to Enzyme Catalysis and Protein Folding.'' W. H. Freeman, 1998. * Bugg, T. Introduction to Enzyme and Coenzyme Chemistry. (2nd edition), Blackwell Publishing Limited, 2004. . {{DEFAULTSORT:Active Site Enzymes Catalysis