Caribbean Current on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
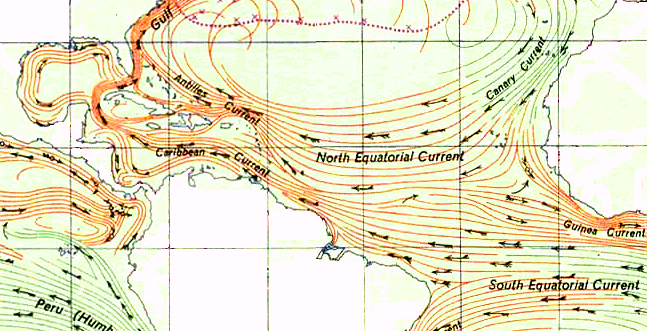
 The Caribbean Current is a warm
The Caribbean Current is a warm

 The Caribbean Current is a warm
The Caribbean Current is a warm ocean current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of seawater generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, sh ...
that transports significant amounts of water and flows northwestward through the Caribbean from the east along the coast of South America and into the Gulf of Mexico. The current results from the flow of the Atlantic South Equatorial Current
The South Equatorial Current are ocean currents in the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Ocean that flow east-to-west between the equator and about 20 degrees south. In the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans, it extends across the equator to about 5 degre ...
as it flows north along the coast of Brazil. As the current turns north through the Yucatán Channel, it is renamed the Yucatán Current. The Caribbean Current water comes from the Atlantic Ocean via the North Equatorial, North Brazil, and Guiana Currents. The circulation of the Columbia-Panama Gyre flows counter-clockwise to the Caribbean Current.
See also
*Ocean current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of seawater generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, sh ...
* Oceanic gyres
In oceanography, a gyre () is any large system of ocean current, ocean surface currents moving in a circular fashion driven by wind movements. Gyres are caused by the Coriolis effect; planetary vorticity, horizontal friction and vertical friction ...
References
Currents of the Atlantic Ocean Caribbean Sea {{Marine-current-stub