Canker Sore on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Aphthous stomatitis, or recurrent aphthous stomatitis (RAS), commonly referred to as a canker sore or salt blister, is a common condition characterized by the repeated formation of
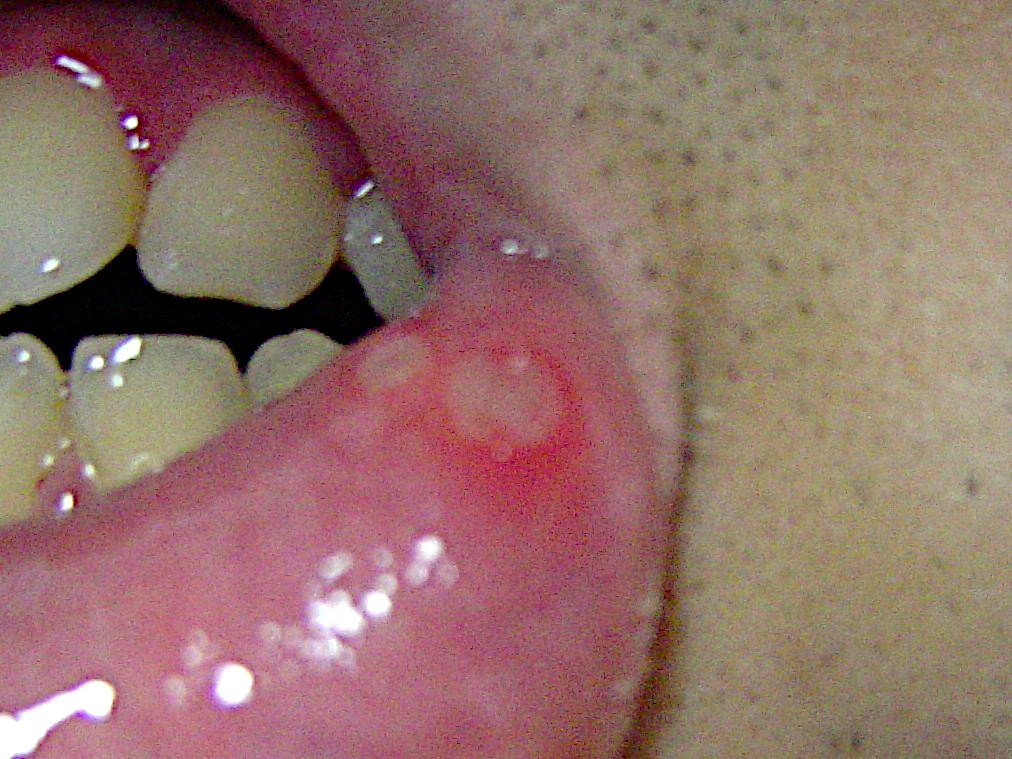
 Persons with aphthous stomatitis have no detectable systemic symptoms or signs (i.e., outside the mouth). Generally, symptoms may include
Persons with aphthous stomatitis have no detectable systemic symptoms or signs (i.e., outside the mouth). Generally, symptoms may include
benign
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse; the term is most familiar as a characterization of cancer.
A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous benign tumor, ''benign'' tumor in that a malig ...
and non- contagious mouth ulcers (aphthae) in otherwise healthy individuals.
The cause is not completely understood but involves a T cell
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell ...
-mediated immune response
An immune response is a physiological reaction which occurs within an organism in the context of inflammation for the purpose of defending against exogenous factors. These include a wide variety of different toxins, viruses, intra- and extracellula ...
triggered by a variety of factors which may include nutritional deficiencies, local trauma, stress, hormonal
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones a ...
influences, allergies
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, are various conditions caused by hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include Allergic rhinitis, hay fever, Food allergy, food al ...
, genetic predisposition
Genetic predisposition refers to a genetic characteristic which influences the possible phenotypic development of an individual organism within a species or population under the influence of environmental conditions. The term genetic susceptibil ...
, certain foods, dehydration
In physiology, dehydration is a lack of total body water that disrupts metabolic processes. It occurs when free water loss exceeds intake, often resulting from excessive sweating, health conditions, or inadequate consumption of water. Mild deh ...
, some food additives, or some hygienic chemical additives like SDS (common in toothpaste).
These ulcers occur periodically and heal completely between attacks. In the majority of cases, the individual ulcers last about 7–10 days, and ulceration episodes occur 3–6 times per year. Most appear on the non-keratinizing epithelial surfaces in the mouth – i.e. anywhere except the attached gingiva, the hard palate
The hard palate is a thin horizontal bony plate made up of two bones of the facial skeleton, located in the roof of the mouth. The bones are the palatine process of the maxilla and the horizontal plate of palatine bone. The hard palate spans ...
, and the dorsum of the tongue
The tongue is a Muscle, muscular organ (anatomy), organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for chewing and swallowing as part of the digestive system, digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper s ...
– although the more severe forms, which are less common, may also involve keratinizing epithelial surfaces. Symptoms range from a minor nuisance to interfering with eating and drinking. The severe forms may be debilitating, even causing weight loss
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health, or physical fitness, refers to a reduction of the total body mass, by a mean loss of fluid, body fat (adipose tissue), or lean mass (namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon, and other conn ...
due to malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
.
The condition is very common, affecting about 20% of the general population to some degree. The onset is often during childhood or adolescence
Adolescence () is a transitional stage of human Developmental biology, physical and psychological Human development (biology), development that generally occurs during the period from puberty to adulthood (typically corresponding to the age o ...
, and the condition usually lasts for several years before gradually disappearing. There is no cure, but treatments such as corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
s aim to manage pain, reduce healing time and reduce the frequency of episodes of ulceration.
Signs and symptoms

 Persons with aphthous stomatitis have no detectable systemic symptoms or signs (i.e., outside the mouth). Generally, symptoms may include
Persons with aphthous stomatitis have no detectable systemic symptoms or signs (i.e., outside the mouth). Generally, symptoms may include prodromal
In medicine, a prodrome is an early Medical sign, sign or symptom (or set of signs and symptoms, referred to as prodromal symptoms) that often indicates the onset of a disease before more diagnostically specific signs and symptoms develop. More spe ...
sensations such as burning, itching, or stinging, which may precede the appearance of any lesion by some hours; and pain, which is often out of proportion to the extent of the ulceration and is worsened by physical contact, especially with certain foods and drinks (e.g., if they are acidic or abrasive). Pain is worst in the days immediately following the initial formation of the ulcer, and then recedes as healing progresses. If there are lesions on the tongue, speaking and chewing can be uncomfortable, and ulcers on the soft palate
The soft palate (also known as the velum, palatal velum, or muscular palate) is, in mammals, the soft biological tissue, tissue constituting the back of the roof of the mouth. The soft palate is part of the palate of the mouth; the other part is ...
, back of the throat, or esophagus
The esophagus (American English), oesophagus (British English), or œsophagus (Œ, archaic spelling) (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, see spelling difference) all ; : ((o)e)(œ)sophagi or ((o)e)(œ)sophaguses), c ...
can cause painful swallowing. Signs are limited to the lesions themselves.
Ulceration episodes usually occur about 3–6 times per year. However, severe disease is characterized by virtually constant ulceration (new lesions developing before old ones have healed) and may cause debilitating chronic pain and interfere with comfortable eating. In severe cases, this prevents adequate nutrient intake leading to malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
and weight loss.
Aphthous ulcers typically begin as erythema
Erythema (, ) is redness of the skin or mucous membranes, caused by hyperemia (increased blood flow) in superficial capillaries. It occurs with any skin injury, infection, or inflammation. Examples of erythema not associated with pathology inc ...
tous macules (reddened, flat area of mucosa
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It ...
) which develop into ulcers that are covered with a yellow-grey fibrin
Fibrin (also called Factor Ia) is a fibrous protein, fibrous, non-globular protein involved in the Coagulation, clotting of blood. It is formed by the action of the protease thrombin on fibrinogen, which causes it to polymerization, polymerize. ...
ous membrane
A membrane is a selective barrier; it allows some things to pass through but stops others. Such things may be molecules, ions, or other small particles. Membranes can be generally classified into synthetic membranes and biological membranes. Bi ...
that can be scraped away. A reddish "halo" surrounds the ulcer. The size, number, location, healing time, and periodicity between episodes of ulcer formation are all dependent upon the subtype of aphthous stomatitis.
Causes
The cause is not entirely clear, but is thought to be multifactorial. It has been suggested that aphthous stomatitis is not a single entity, but rather a group of conditions with different causes. Multiple research studies have attempted to identify a causative organism, but aphthous stomatitis appears to be non-contagious, non-infectious, and not sexually transmissible. The mucosal destruction is thought to be the result of aT cell
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell ...
(T lymphocyte) mediated immune response which involves the generation of interleukin
Interleukins (ILs) are a group of cytokines (secreted proteins and signal molecules) that are expressed and secreted by white blood cells (leukocytes) as well as some other body cells. The human genome encodes more than 50 interleukins and related ...
s and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α). Mast cell
A mast cell (also known as a mastocyte or a labrocyte) is a resident cell of connective tissue that contains many granules rich in histamine and heparin. Specifically, it is a type of granulocyte derived from the myeloid stem cell that is a p ...
s and macrophage
Macrophages (; abbreviated MPhi, φ, MΦ or MP) are a type of white blood cell of the innate immune system that engulf and digest pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that ...
s are also involved, secreting TNF-α along with the T cells. When early aphthous ulcers are biopsied, the histologic appearance shows a dense inflammatory infiltrate, 80% of which is made up of T cells. Persons with aphthous stomatitis also have circulating lymphocytes which react with peptide
Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Polypeptides that have a molecular mass of 10,000 Da or more are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty am ...
s 91–105 of heat shock protein 65–60, and the ratio of CD4+ T cells
The T helper cells (Th cells), also known as CD4+ cells or CD4-positive cells, are a type of T cell that play an important role in the adaptive immune system. They aid the activity of other immune cells by releasing cytokines. They are considere ...
to CD8+ T cells in the peripheral blood of individuals with aphthous stomatitis is decreased.
Aphthous stomatitis has been associated with other autoimmune diseases, namely systemic lupus erythematosus
Lupus, formally called systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Common ...
, Behçet's disease and inflammatory bowel diseases. However, common autoantibodies
An autoantibody is an antibody (a type of protein) produced by the immune system that is directed against one or more of the individual's own proteins. Many autoimmune diseases (notably lupus erythematosus) are associated with such antibodies.
Pr ...
are not detected in most patients, and the condition tends to resolve spontaneously with advancing age rather than worsen.
Evidence for the T cell-mediated mechanism of mucosal destruction is strong, but the exact triggers for this process are unknown and are thought to be multiple and varied from one person to the next. This suggests that there are a number of possible triggers, each of which is capable of producing the disease in different subgroups. In other words, different subgroups appear to have different causes for the condition. These can be considered in three general groups, namely primary immuno-dysregulation, decrease of the mucosal barrier and states of heightened antigenic sensitivity (see below). Risk factors in aphthous stomatitis are also sometimes considered as either host-related or environmental.
Immunity
At least 40% of people with aphthous stomatitis have a positive family history, suggesting that some people are genetically predisposed to developing oral ulceration. HLA-B12, HLA-B51, HLA-Cw7, HLA-A2, HLA-A11, and HLA-DR2 are examples ofhuman leukocyte antigen
The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system is a complex of genes on chromosome 6 in humans that encode cell-surface proteins responsible for regulation of the immune system. The HLA system is also known as the human version of the major histo ...
types associated with aphthous stomatitis. However, these HLA types are inconsistently associated with the condition, and also vary according to ethnicity. People who have a positive family history of aphthous stomatitis tend to develop a more severe form of the condition, and at an earlier age than is typical.
Stress has effects on the immune system, which may explain why some cases directly correlate with stress. It is often stated that in studies of students with the condition, ulceration is exacerbated during examination periods and lessened during periods of vacation. Alternatively, it has been suggested that oral parafunctional activities such as lip or cheek chewing become more pronounced during periods of stress, and hence the mucosa is subjected to more minor trauma.
Aphthous-like ulceration also occurs in conditions involving systemic immuno-dysregulation, e.g. cyclic neutropenia and human immunodeficiency virus
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of ''Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause AIDS, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of th ...
infection. In cyclic neutropenia, more severe oral ulceration occurs during periods of severe immuno-dysregulation, and resolution of the underlying neutropenia is associated with healing of the ulcers. The relative increase in percentage of CD8+ T cells, caused by a reduction in numbers of CD4+ T cells may be implicated in RAS-type ulceration in HIV infection.
Mucosal barrier
The thickness of the mucosa may be an important factor in aphthous stomatitis. Usually, ulcers form on the thinner, non-keratinizing mucosal surfaces in the mouth. Factors which decrease the thickness of the mucosa increase the frequency of occurrence, and factors which increase the thickness of the mucosa correlate with decreased ulceration. The nutritional deficiencies associated with aphthous stomatitis (vitamin B12, folate, and iron) can all cause a decrease in the thickness of the oral mucosa (atrophy
Atrophy is the partial or complete wasting away of a part of the body. Causes of atrophy include mutations (which can destroy the gene to build up the organ), malnutrition, poor nourishment, poor circulatory system, circulation, loss of hormone, ...
).
Local trauma is also associated with aphthous stomatitis, and it is known that trauma can decrease the mucosal barrier. Trauma could occur during injections of local anesthetic in the mouth, or otherwise during dental treatments, frictional trauma from a sharp surface in the mouth such as broken tooth, or from tooth brushing.
Hormonal factors are capable of altering the mucosal barrier. In one study, a small group of females with aphthous stomatitis had fewer occurrences of aphthous ulcers during the luteal phase
The menstrual cycle is on average 28 days in length. It begins with Menstruation, menses (day 1–7) during the follicular phase (day 1–14), followed by ovulation (day 14) and ending with the luteal phase (day 14–28). While historically, medi ...
of the menstrual cycle
The menstrual cycle is a series of natural changes in hormone production and the structures of the uterus and ovaries of the female reproductive system that makes pregnancy possible. The ovarian cycle controls the production and release of eg ...
or with use of the contraceptive pill. This phase is associated with a fall in progestogen levels, mucosal proliferation and keratinization. This subgroup often experiences remission during pregnancy. However, other studies report no correlation between aphthous stomatitis and menstrual period, pregnancy or menopause.
Aphthous stomatitis is less common in people who smoke, and there is also a correlation between habit duration and severity of the condition. Tobacco use is associated with an increase in keratinization of the oral mucosa. In extreme forms, this may manifest as leukoplakia
Oral leukoplakia is a potentially malignant disorder affecting the oral mucosa. It is defined as "essentially an oral mucosal white/gray lesion that cannot be considered as any other definable lesion." Oral leukoplakia is a gray patch or plaque th ...
or stomatitis nicotina (smoker's keratosis). This increased keratinization may mechanically reinforce the mucosa and reduce the tendency of ulcers to form after minor trauma, or present a more substantial barrier to microbes and antigens, but this is unclear. Nicotine is also known to stimulate production of adrenal steroids and reduce production of TNF-α, interleukin-1 and interleukin-6. Smokeless tobacco
Smokeless tobacco is a tobacco product that is used by means other than smoking. Their use involves chewing, sniffing, or placing the product between gum and the cheek or lip. Smokeless tobacco products are produced in various forms, such as ...
products also seem to protect against aphthous stomatitis. Cessation of smoking is known to sometimes precede the onset of aphthous stomatitis in people previously unaffected, or exacerbate the condition in those who were already experiencing aphthous ulceration. Despite this correlation, starting smoking again does not usually lessen the condition.
Antigenic sensitivity
Variousantigenic
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule, moiety, foreign particulate matter, or an allergen, such as pollen, that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response.
Anti ...
triggers have been implicated as a trigger, including L forms of streptococci, herpes simplex virus
Herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2) are two members of the Herpesviridae#Human herpesvirus types, human ''Herpesviridae'' family, a set of viruses that produce Viral disease, viral infections in the majority of humans. Both HSV-1 a ...
, varicella-zoster virus, adenovirus
Adenoviruses (members of the family ''Adenoviridae'') are medium-sized (90–100 nm), nonenveloped (without an outer lipid bilayer) viruses with an icosahedral nucleocapsid containing a double-stranded DNA genome. Their name derives from t ...
, and cytomegalovirus
''Cytomegalovirus'' (CMV) (from ''cyto-'' 'cell' via Greek - 'container' + 'big, megalo-' + -''virus'' via Latin 'poison') is a genus of viruses in the order '' Herpesvirales'', in the family '' Herpesviridae'', in the subfamily '' Betaherp ...
. Some people with aphthous stomatitis may show herpes virus within the epithelium of the mucosa
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It ...
, but without any productive infection. In some persons, attacks of ulceration occur at the same time as asymptomatic viral shedding and elevated viral titres.
In some instances, recurrent mouth ulcers may be a manifestation of an allergic reaction
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, are various conditions caused by hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include Allergic rhinitis, hay fever, Food allergy, food al ...
. Possible allergens include certain foods (e.g., chocolate, coffee, strawberries, eggs, nuts, tomatoes, cheese, citrus fruits, benzoate
Benzoic acid () is a white (or colorless) solid organic compound with the formula , whose structure consists of a benzene ring () with a carboxyl () substituent. The benzoyl group is often abbreviated "Bz" (not to be confused with "Bn," which ...
s, cinnamaldehyde
Cinnamaldehyde is an organic compound with the formula or . Occurring naturally as predominantly the ''trans'' (''E'') isomer, it gives cinnamon its flavor and odor. It is a phenylpropanoid that is naturally synthesized by the shikimate pathway ...
, and highly acidic foods), toothpastes, and mouthwashes. Where dietary allergens are responsible, mouth ulcers usually develop within about 12–24 hours of exposure.
Sodium lauryl sulphate (SLS), a detergent
A detergent is a surfactant or a mixture of surfactants with Cleanliness, cleansing properties when in Concentration, dilute Solution (chemistry), solutions. There are a large variety of detergents. A common family is the alkylbenzene sulfonate ...
present in some brands of toothpaste and other oral healthcare products, may produce oral ulceration in some individuals. It has been shown that aphthous stomatitis is more common in people using toothpastes containing SLS, and that some reduction in ulceration occurs when a SLS-free toothpaste is used.
Systemic disease
Aphthous-like ulceration may occur in association with several systemic disorders (see table). These ulcers are clinically and histopathologically identical to the lesions of aphthous stomatitis, but this type of oral ulceration is not considered to be true aphthous stomatitis by some sources. Some of these conditions may cause ulceration on other mucosal surfaces in addition to the mouth such as theconjunctiva
In the anatomy of the eye, the conjunctiva (: conjunctivae) is a thin mucous membrane that lines the inside of the eyelids and covers the sclera (the white of the eye). It is composed of non-keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium with gobl ...
or the genital mucous membranes. Resolution of the systemic condition often leads to decreased frequency and severity of the oral ulceration.
Behçet's disease is a triad of mouth ulcers, genital ulcers and anterior uveitis
Uveitis () is inflammation of the uvea, the pigmented layer of the eye between the inner retina and the outer fibrous layer composed of the sclera and cornea. The uvea consists of the middle layer of pigmented vascular structures of the eye and ...
. The main feature of Behçet's disease is aphthous-like ulceration, but this is usually more severe than seen in aphthous stomatitis without a systemic cause, and typically resembles major or herpetiforme ulceration or both. Aphthous-like ulceration is the first sign of the disease in 25–75% of cases. Behçet's is more common in individuals whose ethnic origin is from regions along the Silk Road
The Silk Road was a network of Asian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over , it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and religious interactions between the ...
(between the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
and the Far East
The Far East is the geographical region that encompasses the easternmost portion of the Asian continent, including North Asia, North, East Asia, East and Southeast Asia. South Asia is sometimes also included in the definition of the term. In mod ...
). It tends to be rare in other countries such as the United States and the United Kingdom. MAGIC syndrome is a possible variant of Behçet's disease, and is associated with aphthous-like ulceration. The name stands for "mouth and genital ulcers with inflamed cartilage" ( relapsing polychondritis).
PFAPA syndrome is a rare condition that tends to occur in children. The name stands for "periodic fever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, s ...
, aphthae, pharyngitis (sore throat) and cervical adenitis" (inflammation of the lymph node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that includ ...
s in the neck). The fevers occur periodically about every 3–5 weeks. The condition appears to improve with tonsillectomy or immunosuppression, suggesting an immunologic cause.
In cyclic neutropenia, there is a reduction in the level of circulating neutrophil
Neutrophils are a type of phagocytic white blood cell and part of innate immunity. More specifically, they form the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. Their functions vary in differe ...
s in the blood that occurs about every 21 days. Opportunistic infection
An opportunistic infection is an infection that occurs most commonly in individuals with an immunodeficiency disorder and acts more severe on those with a weakened immune system. These types of infections are considered serious and can be caused b ...
s commonly occur and aphthous-like ulceration is worst during this time.
Hematinic deficiencies (vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin involved in metabolism. One of eight B vitamins, it serves as a vital cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor in DNA synthesis and both fatty acid metabolism, fatty acid and amino a ...
, folic acid
Folate, also known as vitamin B9 and folacin, is one of the B vitamins. Manufactured folic acid, which is converted into folate by the body, is used as a dietary supplement and in food fortification as it is more stable during processing and ...
and iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
), occurring singly or in combination, and with or without any underlying gastrointestinal disease, may be twice as common in people with RAS. However, iron and vitamin supplements only infrequently improve the ulceration. The relationship to vitamin B12 deficiency has been the subject of many studies. Although these studies found that 0–42% of those with recurrent ulcers have a vitamin B12 deficiency, an association with deficiency is rare. Even in the absence of deficiency, vitamin B12 supplementation may be helpful due to unclear mechanisms. Hematinic deficiencies can cause anemia
Anemia (also spelt anaemia in British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen. This can be due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin availabl ...
, which is also associated with aphthous-like ulceration.
Gastrointestinal disorders are sometimes associated with aphthous-like stomatitis, e.g. most commonly celiac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine. Patients develop intolerance to gluten, which is present in foods such as wheat, rye, spel ...
, but also inflammatory bowel disease
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of inflammatory conditions of the colon and small intestine, with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis (UC) being the principal types. Crohn's disease affects the small intestine and large intestine ...
such as Crohn's disease
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever, abdominal distension, and weight loss. Complications outside of the ...
or ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is one of the two types of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), with the other type being Crohn's disease. It is a long-term condition that results in inflammation and ulcers of the colon and rectum. The primary sympto ...
. The link between gastrointestinal disorders and aphthous stomatitis is probably related to nutritional deficiencies caused by malabsorption
Malabsorption is a state arising from abnormality in absorption of food nutrients across the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Impairment can be of single or multiple nutrients depending on the abnormality. This may lead to malnutrition and a varie ...
. Less than 5% of people with RAS have celiac disease, which can present with a wide range of non-specific symptoms, especially in adults. Sometimes aphthous-like ulcerations can be the only sign of celiac disease. For persons with celiac disease, following a strict gluten-free diet
A gluten-free diet (GFD) is a nutritional plan that strictly excludes gluten, which is a mixture of prolamin proteins found in wheat (and all of its species and hybrids, such as spelt, kamut, and triticale), as well as barley, rye, and oats ...
can often end the outbreaks of painful mouth ulcers.
Other examples of systemic conditions associated with aphthous-like ulceration include reactive arthritis, and recurrent erythema multiforme.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is mostly based on the clinical appearance and the medical history. The most important diagnostic feature is a history of recurrent, self healing ulcers at fairly regular intervals. Although there are many causes of oral ulceration, ''recurrent'' oral ulceration has relatively few causes, most commonly aphthous stomatitis, but rarely Behçet's disease, erythema multiforme, ulceration associated with gastrointestinal disease, and recurrent intra-oral herpes simplex infection. A systemic cause is more likely in adults who suddenly develop recurrent oral ulceration with no prior history. Special investigations may be indicated to rule out other causes of oral ulceration. These includeblood test
A blood test is a medical laboratory, laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a hypodermic needle, or via fingerprick. Multiple tests for specific blood components, such as a glucose ...
s to exclude anemia, deficiencies of iron, folate or vitamin B12, or celiac disease. However, the nutritional deficiencies may be latent and the peripheral blood picture may appear relatively normal. Some suggest that screening for celiac disease should form part of the routine work up for individuals complaining of recurrent oral ulceration. Many of the systemic diseases cause other symptoms apart from oral ulceration, which is in contrast to aphthous stomatitis where there is isolated oral ulceration. Patch testing may be indicated if allergies are suspected (e.g. a strong relationship between certain foods and episodes of ulceration). Several drugs can cause oral ulceration (e.g. nicorandil), and a trial substitution to an alternative drug may highlight a causal relationship.
Tissue biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, an interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiology, interventional cardiologist. The process involves the extraction of sampling (medicine), sample ...
is not usually required, unless to rule out other suspected conditions such as oral squamous cell carcinoma
Squamous-cell carcinoma (SCC), also known as epidermoid carcinoma, comprises a number of different types of cancer that begin in squamous cells. These cells form on the surface of the skin, on the lining of hollow organs in the body, and on the ...
. The histopathologic
Histopathology (compound of three Greek language, Greek words: 'tissue', 'suffering', and ''-logy, -logia'' 'study of') is the light microscope, microscopic examination of Tissue (biology), tissue in order to study the manifestations of dis ...
appearance is not pathognomonic
Pathognomonic (synonym ''pathognomic'') is a term, often used in medicine, that means "characteristic for a particular disease". A pathognomonic sign is a particular sign whose presence means that a particular disease is present beyond any doubt. ...
(the microscopic appearance is not specific to the condition). Early lesions have a central zone of ulceration covered by a fibrinous membrane. In the connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, a group of cells that are similar in structure, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops mostly from the mesenchyme, derived from the mesod ...
deep to the ulcer there is increased vascularity
Vascularity, in bodybuilding, is the condition of having many highly visible, prominent, and often extensively-ramified superficial veins. The skin appears "thin"—sometimes virtually transparent—due to an extreme reduction of subcutaneous fat ...
and a mixed inflammatory infiltrate composed of lymphocytes, histiocytes and polymorphonuclear leukocytes. The epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
on the margins of the ulcer shows spongiosis and there are many mononuclear cells in the basal third. There are also lymphocytes and histiocytes in the connective tissue surrounding deeper blood vessels near to the ulcer, described histologically as "perivascular cuffing".
Classification
Aphthous stomatitis has been classified as a type of non-infectious stomatitis (inflammation of the mouth). One classification distinguishes "common simple aphthae", accounting for 95% of cases, with 3–6 attacks per year, rapid healing, minimal pain and restriction of ulceration to the mouth; and "complex aphthae", accounting for 5% of cases, where ulcers may be present on the genital mucosa in addition to mouth, healing is slower and pain is more severe. A more common method of classifying aphthous stomatitis is into three variants, distinguished by the size, number and location of the lesions, the healing time of individual ulcers and whether a scar is left after healing (see below).Minor aphthous ulceration
This is the most common type of aphthous stomatitis, accounting for about 80–85% of all cases. This subtype is termed minor aphthous ulceration (MiAU), or minor recurrent aphthous stomatitis (MiRAS). The lesions themselves may be referred to as minor aphthae or minor aphthous ulcers. These lesions are generally less than 10 mm in diameter (usually about 2–3 mm), and affect non- keratinized mucosal surfaces (i.e. the labial and buccal mucosa,lateral
Lateral is a geometric term of location which may also refer to:
Biology and healthcare
* Lateral (anatomy), a term of location meaning "towards the side"
* Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle, an intrinsic muscle of the larynx
* Lateral release ( ...
borders of the tongue and the floor of the mouth). Usually several ulcers appear at the same time, but single ulcers are possible. Healing usually takes seven to ten days and leaves no scar. Between episodes of ulceration, there is usually an ulcer-free period of variable length.
Major aphthous ulceration
This subtype makes up about 10% of all cases of aphthous stomatitis. It is termed major aphthous ulceration (MaAU) or major recurrent aphthous stomatitis (MaRAS). Major aphthous ulcers (major aphthae) are similar to minor aphthous ulcers, but are more than 10 mm in diameter and the ulceration is deeper. Because the lesions are larger, healing takes longer (about twenty to thirty days), and may leave scars. Each episode of ulceration usually produces a greater number of ulcers, and the time between attacks is less than seen in minor aphthous stomatitis. Major aphthous ulceration usually affects non-keratinized mucosal surfaces, but less commonly keratinized mucosa may also be involved, such as the dorsum (top surface) of thetongue
The tongue is a Muscle, muscular organ (anatomy), organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for chewing and swallowing as part of the digestive system, digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper s ...
or the gingiva (gums). The soft palate or the fauces (back of the throat) may also be involved, the latter being part of the oropharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its ...
rather than the oral cavity
A mouth also referred to as the oral is the body orifice through which many animals ingest food and vocalize. The body cavity immediately behind the mouth opening, known as the oral cavity (or in Latin), is also the first part of the alime ...
. Compared to minor aphthous ulceration, major aphthae tend to have an irregular outline.
Herpetiform ulceration
Herpetiform ulcers, (also termed stomatitis herpetiformis, or herpes-like ulcerations) is a subtype of aphthous stomatitis so named because the lesions resemble a primary infection withherpes simplex virus
Herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2) are two members of the Herpesviridae#Human herpesvirus types, human ''Herpesviridae'' family, a set of viruses that produce Viral disease, viral infections in the majority of humans. Both HSV-1 a ...
( primary herpetic gingivostomatitis). However, herpetiform ulceration is not caused by herpes viruses. As with all types of aphthous stomatitis, it is not contagious. Unlike true herpetic ulcers, herpetiforme ulcers are not preceded by vesicles (small, fluid-filled blisters). Herpetiforme ulcers are less than 1 mm in diameter and occur in variably sized crops up to one hundred at a time. Adjacent ulcers may merge to form larger, continuous areas of ulceration. Healing occurs within fifteen days without scarring. The ulceration may affect keratinized mucosal surfaces in addition to non keratinized. Herpetiform ulceration is often extremely painful, and the lesions recur more frequently than minor or major aphthous ulcers. Recurrence may be so frequent that ulceration is virtually continuous. It generally occurs in a slightly older age group than the other subtypes, and females are affected slightly more frequently than males.
RAS type ulceration
Recurrent oral ulceration associated with systemic conditions is termed "RAS-type ulceration", "RAS-like ulceration", or "aphthous-like ulcers". Aphthous stomatitis occurs in individuals with no associated systemic disease. Persons with certain systemic diseases may be prone to oral ulceration, but this is secondary to the underlying medical condition (see thesystemic disease
A systemic disease is one that affects a number of Organ (anatomy), organs and Tissue (biology), tissues, or affects the Human body, body as a whole. It differs from a localized disease, which is a disease affecting only part of the body (e.g., ...
section). This kind of ulceration is considered by some to be separate from true aphthous stomatitis. However, this definition is not strictly applied. For example, many sources refer to oral ulceration caused by anemia and/or nutritional deficiencies as aphthous stomatitis, and some also consider Behçet's disease to be a variant.
Treatment
The vast majority of people with aphthous stomatitis have minor symptoms and do not require any specific therapy. The pain is often tolerable with simple dietary modification during an episode of ulceration such as avoiding spicy and acidic foods and beverages. Many differenttopical
A topical medication is a medication that is applied to a particular place on or in the body. Most often topical medication means application to body surfaces such as the skin or mucous membranes to treat ailments via a large range of classes ...
and systemic medications have been proposed (see table), sometimes showing little or no evidence of usefulness when formally investigated. Some of the results of interventions for RAS may in truth represent a placebo effect
A placebo ( ) can be roughly defined as a sham medical treatment. Common placebos include inert tablets (like sugar pills), inert injections (like saline), sham surgery, and other procedures.
Placebos are used in randomized clinical trials ...
. No therapy is curative, with treatment aiming to relieve pain, promote healing and reduce the frequency of episodes of ulceration.
Medication
The first line of therapy for aphthous stomatitis are topical agents rather than systemic medication, with topical corticosteroids being the mainstay treatment. Systemic treatment is usually reserved for severe disease due to the risk of adverse side effects associated with many of these agents. Asystematic review
A systematic review is a scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from published studies on ...
found that no single systemic intervention was found to be effective. Good oral hygiene
Oral hygiene is the practice of keeping one's oral cavity clean and free of disease and other problems (e.g. bad breath) by regular brushing of the teeth (dental hygiene) and adopting good hygiene habits. It is important that oral hygiene be carr ...
is important to prevent secondary infection of the ulcers.
Occasionally, in females where ulceration is correlated to the menstrual cycle or to birth control pills, progestogen or a change in birth control may be beneficial. Use of nicotine replacement therapy for people who have developed oral ulceration after stopping smoking has also been reported. Starting smoking again does not usually lessen the condition. Trauma can be reduced by avoiding rough or sharp foodstuffs and by brushing teeth with care. If sodium lauryl sulfate is suspected to be the cause, avoidance of products containing this chemical may be useful and prevent recurrence in some individuals. Similarly patch testing may indicate that food allergy is responsible, and the diet modified accordingly. If investigations reveal deficiency states, correction of the deficiency may result in resolution of the ulceration. For example, there is some evidence that vitamin B12 supplementation may prevent recurrence in some individuals.
Other
Surgical excision of aphthous ulcers has been described, but it is an ineffective and inappropriate treatment.Silver nitrate
Silver nitrate is an inorganic compound with chemical formula . It is a versatile precursor to many other silver compounds, such as those used in photography. It is far less sensitive to light than the halides. It was once called ''lunar causti ...
has also been used as a chemical cauterant. Apart from the mainstream approaches detailed above, there are numerous treatments of unproven effectiveness, ranging from herbal remedies to otherwise alternative treatments, including ''Aloe vera
''Aloe vera'' () is a succulent plant species of the genus ''Aloe''. It is widely distributed, and is considered an invasive species in many world regions.
An evergreen perennial plant, perennial, it originates from the Arabian Peninsula, but ...
'', '' Myrtus communis'', '' Rosa damascena'', potassium alum
Potassium alum, potash alum, or potassium aluminium sulfate is a chemical compound defined as the double sulfate of potassium and aluminium, with chemical formula KAl(SO4)2. It is commonly encountered as the dodecahydrate, KAl(SO4)2·12H2O. It ...
, nicotine, polio virus vaccine
A vaccine is a biological Dosage form, preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease, infectious or cancer, malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verifi ...
and prostaglandin E2
Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), also known as dinoprostone, is a naturally occurring prostaglandin with oxytocic properties that is used as a medication. Dinoprostone is used in labor induction, bleeding after delivery, termination of pregnanc ...
.
A 2023 systematic review found that supplementation with vitamin B12, zinc sulfate and omega-3 seem to be beneficial in the management of RAS.
Prognosis
By definition, there is no serious underlying medical condition, and most importantly, the ulcers do not representoral cancer
Oral cancer, also known as oral cavity cancer, tongue cancer or mouth cancer, is a cancer of the lining of the lips, mouth, or upper throat. In the mouth, it most commonly starts as a painless red or white patch, that thickens, gets ulcerated ...
nor are they infectious. However, aphthae are capable of causing significant discomfort. There is a spectrum of severity, with symptoms ranging from a minor nuisance to disabling. Due to pain during eating, weight loss may develop as a result of not eating in severe cases of aphthous stomatitis. Usually, the condition lasts for several years before spontaneously disappearing in later life.
Epidemiology
Aphthous stomatitis affects between 5% and 66% of people, with about 20% of individuals in most populations having the condition to some degree. This makes it the most common disease of the oral mucosa. Aphthous stomatitis occurs worldwide, but is more common in developed countries. Within nations, it is more common in higher socioeconomic groups. Males and females are affected in an equal ratio, and the peak age of onset between 10 and 19 years. About 80% of people with aphthous stomatitis first developed the condition before the age of 30. There have been reports of ethnic variation. For example, in the United States, aphthous stomatitis may be three times more common in white-skinned people than black-skinned people.History, society and culture
"Aphthous affectations" and "aphthous ulcerations" of the mouth are mentioned several times in the treatise "Of the Epidemics" (part of theHippocratic corpus
The Hippocratic Corpus (Latin: ''Corpus Hippocraticum''), or Hippocratic Collection, is a collection of around 60 early Ancient Greek medical works strongly associated with the physician Hippocrates and his teachings. The Hippocratic Corpus cov ...
, in the 4th century BCE), although it seems likely that this was oral ulceration as a manifestation of some infectious disease, since they are described as occurring in epidemic
An epidemic (from Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of hosts in a given population within a short period of time. For example, in meningococcal infection ...
-like patterns, with concurrent symptoms such as fever.
Aphthous stomatitis was once thought to be a form of recurrent herpes simplex virus infection, and some clinicians still refer to the condition as "herpes" despite this cause having been disproven.
The informal term "canker sore" is sometimes used, mainly in North America, either to describe this condition generally, or to refer to the individual ulcers of this condition, or mouth ulcers of any cause unrelated to this condition. The origin of the word "canker" is thought to have been influenced by Latin, Old English, Middle English and Old North French. In Latin, ''cancer'' translates to "malignant tumor" or literally "crab" (related to the likening of sectioned tumors to the limbs of a crab). The closely related word in Middle English and Old North French, '' chancre'', now more usually applied to syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms depend on the stage it presents: primary, secondary, latent syphilis, latent or tertiary. The prim ...
, is also thought to be involved. Despite this etymology, aphthous stomatitis is not a form of cancer but rather entirely benign.
An aphtha (plural ''aphthae'') is a non specific term that refers to an ulcer of the mouth. The word is derived from the Greek word ''aphtha'' meaning "eruption" or "ulcer". The lesions of several other oral conditions are sometimes described as aphthae, including Bednar's aphthae (infected, traumatic ulcers on the hard palate in infants), oral candidiasis, and foot-and-mouth disease
Foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) or hoof-and-mouth disease (HMD) is an infectious disease, infectious and sometimes fatal virus (biology), viral disease that primarily affects even-toed ungulates, including domestic and wild Bovidae, bovids. The vir ...
. When used without qualification, ''aphthae'' commonly refers to lesions of recurrent aphthous stomatitis. Since the word aphtha is often taken to be synonymous with ulcer, it has been suggested that the term "aphthous ulcer" is redundant, but it remains in common use. Stomatitis is also a non-specific term referring to any inflammatory process in the mouth, with or without oral ulceration. It may describe many different conditions apart from aphthous stomatitis such as angular stomatitis.
The current most widely used medical term is "recurrent aphthous stomatitis" or simply "aphthous stomatitis". Historically, many different terms have been used to refer to recurrent aphthous stomatitis or its sub-types, and some are still in use. Mikulicz's aphthae is a synonym of minor RAS, named after Jan Mikulicz-Radecki. Synonyms for major RAS include Sutton's ulcers (named after Richard Lightburn Sutton), Sutton's disease, Sutton's syndrome and periadenitis mucosa necrotica recurrens. Synonyms for aphthous stomatitis as a whole include (recurrent) oral aphthae, (recurrent) aphthous ulceration and (oral) aphthosis.
In traditional Chinese medicine
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is an alternative medicine, alternative medical practice drawn from traditional medicine in China. A large share of its claims are pseudoscientific, with the majority of treatments having no robust evidence ...
, claimed treatments for aphthae focus on clearing heat and nourishing Yin.
Rembrandt Gentle White toothpaste did not contain sodium lauryl sulfate, and was specifically marketed as being for the benefit of "canker sore sufferers". When the manufacturer Johnson & Johnson
Johnson & Johnson (J&J) is an American multinational pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical technologies corporation headquartered in New Brunswick, New Jersey, and publicly traded on the New York Stock Exchange. Its common stock is a c ...
discontinued the product in 2014, it caused a backlash of anger from long-term customers, and the toothpaste began to sell for many times the original price on the auction website eBay
eBay Inc. ( , often stylized as ebay) is an American multinational e-commerce company based in San Jose, California, that allows users to buy or view items via retail sales through online marketplaces and websites in 190 markets worldwide. ...
.
See also
* Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis, also known as "trench mouth"—another painful, non-contagious mouth infection with similar symptoms * CankerMelts (licorice
Liquorice (Commonwealth English) or licorice (American English; see spelling differences; ) is the common name of ''Glycyrrhiza glabra'', a flowering plant of the bean family Fabaceae, from the root of which a sweet, aromatic flavouring is ...
)
* Mouth ulcer
References
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Aphthous Ulcer Laryngology Conditions of the mucous membranes Oral mucosal pathology