Canadian history on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The history of Canada covers the period from the arrival of the
 Archeological and Indigenous genetic evidence indicates that North and South America were the last continents into which humans migrated. During the
Archeological and Indigenous genetic evidence indicates that North and South America were the last continents into which humans migrated. During the
 Under
Under
 French interest in the
French interest in the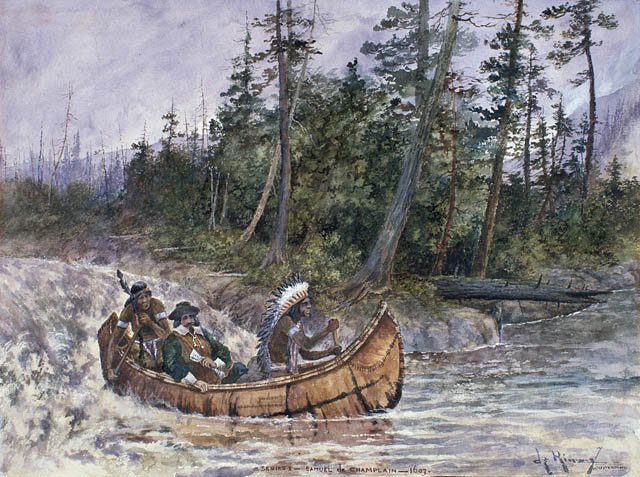  In 1604, a North American fur trade monopoly was granted to Pierre Du Gua, Sieur de Mons. The fur trade became one of the main economic ventures in North America. Du Gua led his first colonization expedition to an island located near the mouth of the St. Croix River. Among his lieutenants was a geographer named
In 1604, a North American fur trade monopoly was granted to Pierre Du Gua, Sieur de Mons. The fur trade became one of the main economic ventures in North America. Du Gua led his first colonization expedition to an island located near the mouth of the St. Croix River. Among his lieutenants was a geographer named  In 1608 Champlain founded what is now
In 1608 Champlain founded what is now  After Champlain's death in 1635, the
After Champlain's death in 1635, the
 The British ordered the Acadians expelled from their lands in 1755 during the
The British ordered the Acadians expelled from their lands in 1755 during the
 As part of the terms of the
As part of the terms of the
 During the
During the  The signing of the Treaty of Paris in 1783 formally ended the war. Great Britain made several concessions to the US at the expense of the North American colonies. Notably, the borders between Canada and the United States were officially demarcated; all land south and west of the Great Lakes, which was formerly a part of the Province of Quebec and included modern-day Michigan, Wisconsin, Illinois, Indiana and Ohio, was ceded to the Americans. Fishing rights were also granted to the United States in the Gulf of St. Lawrence and on the coast of Newfoundland and the Grand Banks. The British ignored part of the treaty and maintained their military outposts in the Great Lakes areas it had ceded to the U.S., and they continued to supply their native allies with munitions. The British evacuated the outposts with the
The signing of the Treaty of Paris in 1783 formally ended the war. Great Britain made several concessions to the US at the expense of the North American colonies. Notably, the borders between Canada and the United States were officially demarcated; all land south and west of the Great Lakes, which was formerly a part of the Province of Quebec and included modern-day Michigan, Wisconsin, Illinois, Indiana and Ohio, was ceded to the Americans. Fishing rights were also granted to the United States in the Gulf of St. Lawrence and on the coast of Newfoundland and the Grand Banks. The British ignored part of the treaty and maintained their military outposts in the Great Lakes areas it had ceded to the U.S., and they continued to supply their native allies with munitions. The British evacuated the outposts with the
 The British government then sent Lord Durham to examine the situation; he stayed in Canada for five months before returning to Britain, bringing with him his Durham Report, which strongly recommended
The British government then sent Lord Durham to examine the situation; he stayed in Canada for five months before returning to Britain, bringing with him his Durham Report, which strongly recommended
 Spanish explorers had taken the lead in the Pacific Northwest coast, with the voyages of Juan José Pérez Hernández in 1774 and 1775. By the time the Spanish determined to build a fort on
Spanish explorers had taken the lead in the Pacific Northwest coast, with the voyages of Juan José Pérez Hernández in 1774 and 1775. By the time the Spanish determined to build a fort on
 The Seventy-Two Resolutions from the 1864 Quebec Conference and Charlottetown Conference laid out the framework for uniting British colonies in North America into a federation. The Resolutions became the basis for the London Conference of 1866, which led to the formation of the Dominion of Canada on July 1, 1867. The term ''dominion'' was chosen to indicate Canada's status as a self-governing
The Seventy-Two Resolutions from the 1864 Quebec Conference and Charlottetown Conference laid out the framework for uniting British colonies in North America into a federation. The Resolutions became the basis for the London Conference of 1866, which led to the formation of the Dominion of Canada on July 1, 1867. The term ''dominion'' was chosen to indicate Canada's status as a self-governing
 In 1873, John A. Macdonald ( First Prime Minister of Canada) created the
In 1873, John A. Macdonald ( First Prime Minister of Canada) created the  As Canada expanded, the Canadian government rather than the British Crown negotiated treaties with the resident First Nations' peoples, beginning with '' Treaty 1'' in 1871. The treaties extinguished
As Canada expanded, the Canadian government rather than the British Crown negotiated treaties with the resident First Nations' peoples, beginning with '' Treaty 1'' in 1871. The treaties extinguished
 The
The
 The '' Military Voters Act'' of 1917 gave the vote to British women who were war widows or had sons or husbands serving overseas. Unionist Prime Minister Borden pledged himself during the 1917 campaign to equal suffrage for women. After his landslide victory, he introduced a bill in 1918 for extending the franchise to women. This passed without division but did not apply to Quebec provincial and municipal elections. The women of Quebec gained full suffrage in 1940. The first woman elected to Parliament was Agnes Macphail of Ontario in 1921.
The '' Military Voters Act'' of 1917 gave the vote to British women who were war widows or had sons or husbands serving overseas. Unionist Prime Minister Borden pledged himself during the 1917 campaign to equal suffrage for women. After his landslide victory, he introduced a bill in 1918 for extending the franchise to women. This passed without division but did not apply to Quebec provincial and municipal elections. The women of Quebec gained full suffrage in 1940. The first woman elected to Parliament was Agnes Macphail of Ontario in 1921.
 In 1926 Prime Minister Mackenzie King advised the Governor General, Lord Byng, to dissolve Parliament and call another election, but Byng refused, the only time that the Governor General has exercised such a power. Instead, Byng called upon Meighen, the Conservative Party leader, to form a government. Meighen attempted to do so but was unable to obtain a majority in the Commons and he, too, advised dissolution, which this time was accepted. The episode, the King–Byng affair, marks a constitutional crisis that was resolved by a new tradition of complete non-interference in Canadian political affairs on the part of the British government.
In 1926 Prime Minister Mackenzie King advised the Governor General, Lord Byng, to dissolve Parliament and call another election, but Byng refused, the only time that the Governor General has exercised such a power. Instead, Byng called upon Meighen, the Conservative Party leader, to form a government. Meighen attempted to do so but was unable to obtain a majority in the Commons and he, too, advised dissolution, which this time was accepted. The episode, the King–Byng affair, marks a constitutional crisis that was resolved by a new tradition of complete non-interference in Canadian political affairs on the part of the British government.
 Canada was hit hard by the worldwide
Canada was hit hard by the worldwide  Urban unemployment nationwide was 19 per cent; Toronto's rate was 17 per cent, according to the census of 1931. Farmers who stayed on their farms were not considered unemployed. By 1933, 30 per cent of the labour force was out of work, and one-fifth of the population became dependent on government assistance. Wages fell as did prices. The worst hit were areas dependent on primary industries such as farming,
Urban unemployment nationwide was 19 per cent; Toronto's rate was 17 per cent, according to the census of 1931. Farmers who stayed on their farms were not considered unemployed. By 1933, 30 per cent of the labour force was out of work, and one-fifth of the population became dependent on government assistance. Wages fell as did prices. The worst hit were areas dependent on primary industries such as farming,  Times were especially hard in western Canada, where a full recovery did not occur until the Second World War began in 1939. One response was the creation of new political parties such as the Social Credit movement and the
Times were especially hard in western Canada, where a full recovery did not occur until the Second World War began in 1939. One response was the creation of new political parties such as the Social Credit movement and the
 Canada's involvement in the Second World War began when Canada declared war on
Canada's involvement in the Second World War began when Canada declared war on  On the political side, Mackenzie King rejected any notion of a government of national unity. The 1940 federal election was held as normally scheduled, producing another majority for the Liberals. The Conscription Crisis of 1944 greatly affected unity between French and English-speaking Canadians, though was not as politically intrusive as that of the First World War.
During the war, Canada became more closely linked to the U.S. The Americans took virtual control of Yukon in order to build the Alaska Highway, and were a major presence in the British colony of Newfoundland with major airbases. After the start of the war with Japan in December 1941, the government, in cooperation with the U.S., began the Japanese-Canadian internment, which sent British Columbia residents of Japanese descent to relocation camps far from the coast. The reason was intense public demand for removal and fears of espionage or sabotage. The government ignored reports from the RCMP and Canadian military that most of the Japanese were law-abiding and not a threat.
On the political side, Mackenzie King rejected any notion of a government of national unity. The 1940 federal election was held as normally scheduled, producing another majority for the Liberals. The Conscription Crisis of 1944 greatly affected unity between French and English-speaking Canadians, though was not as politically intrusive as that of the First World War.
During the war, Canada became more closely linked to the U.S. The Americans took virtual control of Yukon in order to build the Alaska Highway, and were a major presence in the British colony of Newfoundland with major airbases. After the start of the war with Japan in December 1941, the government, in cooperation with the U.S., began the Japanese-Canadian internment, which sent British Columbia residents of Japanese descent to relocation camps far from the coast. The reason was intense public demand for removal and fears of espionage or sabotage. The government ignored reports from the RCMP and Canadian military that most of the Japanese were law-abiding and not a threat.
 Prosperity returned to Canada during the Second World War and continued in the following years, with the development of
Prosperity returned to Canada during the Second World War and continued in the following years, with the development of  Throughout the mid-1950s, prime ministers Louis St. Laurent and his successor
Throughout the mid-1950s, prime ministers Louis St. Laurent and his successor
 In 1981, the Canadian House of Commons and Senate passed a resolution requesting that the British Parliament enact a package of constitutional amendments which would end the last powers of the British Parliament to legislate for Canada and would create an entirely Canadian process for constitutional amendments. The resolution set out the text of the proposed Canada Act, which also included the text of the '' Constitution Act, 1982''. The British Parliament duly passed the Canada Act 1982, the Queen granting
In 1981, the Canadian House of Commons and Senate passed a resolution requesting that the British Parliament enact a package of constitutional amendments which would end the last powers of the British Parliament to legislate for Canada and would create an entirely Canadian process for constitutional amendments. The resolution set out the text of the proposed Canada Act, which also included the text of the '' Constitution Act, 1982''. The British Parliament duly passed the Canada Act 1982, the Queen granting  On June 23, 1985, Air India Flight 182 was destroyed above the Atlantic Ocean by a bomb on board exploding; all 329 on board were killed, of whom 280 were Canadian citizens. The Air India attack is the largest mass murder in Canadian history.
The Progressive Conservative (PC) government of
On June 23, 1985, Air India Flight 182 was destroyed above the Atlantic Ocean by a bomb on board exploding; all 329 on board were killed, of whom 280 were Canadian citizens. The Air India attack is the largest mass murder in Canadian history.
The Progressive Conservative (PC) government of
 Canada became the fourth country in the world and the first country in the Americas to legalize same-sex marriage nationwide with the enactment of the '' Civil Marriage Act'' in 2005. Court decisions, starting in 2003, had already legalized
Canada became the fourth country in the world and the first country in the Americas to legalize same-sex marriage nationwide with the enactment of the '' Civil Marriage Act'' in 2005. Court decisions, starting in 2003, had already legalized
online
, 91pp. * Argyle, Ray, ''Turning Points: The campaigns that changed Canada, 2004 and before.'' (2004) Scholarly analysis of 15 major national and provincial elections from 1866 to 2004
online
* Black, Conrad. ''Rise to Greatness: The History of Canada From the Vikings to the Present'' (2014), 1120p
excerpt
* Brown, Craig, ed. ''Illustrated History of Canada'' (McGill-Queen's Press-MQUP, 2012), Chapters by experts * Bumsted, J.M. ''The Peoples of Canada: A Pre-Confederation History''; ''The Peoples of Canada: A Post-Confederation History'' (2 vol. 2014), University textbook * ''Chronicles of Canada Series'' (32 vol. 1915–1916) edited by G. M. Wrong and H. H. Langto
online detailed popular history
* Conrad, Margaret, Alvin Finkel and Donald Fyson. ''Canada: A History'' (Toronto: Pearson, 2012) * * * Granatstein, J. L. ''Prime ministers: Ranking Canada's leaders'' (1999
online
evaluates all 20 prime ministers from 1867 to 1999. * Granatstein, J. L., and Dean F. Oliver, eds. ''The Oxford Companion to Canadian Military History,'' (2011
online review
* * * McNaught, Kenneth. ''The Penguin History of Canada'' (Penguin books, 1988) * * * Norrie, Kenneth, Douglas Owram and J.C. Herbert Emery. (2002) ''A History of the Canadian Economy'' (4th ed. 2007) * * Stacey, C. P. ''Arms, Men and Governments: The War Policies of Canada 1939–1945'' (1970), the standard scholarly history of WWII policies
online free
online free
* Crowe, Harry S. et al. eds ''A Source-Book of Canadian History: Selected Documents and Personal Papers'' (1964) 508pp
online
* ; 707pp * Leacy, F.H. ed. ''Historical statistics of Canada'' (2nd ed. Ottawa: Statistics Canada, 1983). 800 p.
online
* Stewart Reid, J.H. ; et al., eds. (1964). ''A Source-book of Canadian History: Selected Documents and Personal Papers'' (Longmans Canada
online
484pp; primary sources on more than 200 topics * Talman, James J. and Louis L. Snyder, eds. ''Basic Documents in Canadian History'' (1959
online
192 pp * Thorner, Thomas ed. '' "A few acres of snow" : documents in pre-confederation Canadian history'' (2nd ed. 2003)
online free to borrow
** Thorner, Thomas ed. ''A country nourished on self-doubt : documents in post-confederation Canadian history'' (2nd ed 2003)
online free
online
* McKercher, Asa, and Philip Van Huizen, eds. ''Undiplomatic History: The New Study of Canada and the World'' (2019
excerpt
* Muise D. A. ed. '' A Reader's Guide to Canadian History: 1, Beginnings to Confederation (1982); '' (1982) Topical articles by leading scholars ** Granatstein J.L. and Paul Stevens, ed. ''A Reader's Guide to Canadian History: vol 2: Confederation to the present'' (1982), Topical articles by leading scholars * ; essays by experts evaluate the scholarly literature ** ; essays by experts evaluate the scholarly literature * Rich, E. E. "Canadian History." ''Historical Journal'' 14#4 (1971): 827–52
online
''The Canadian Encyclopedia''
National Historic Sites of Canada
(archived June 5, 2011)
– Guide to the Sources (archived August 21, 2014)
The Quebec History encyclopedia
by Marianopolis College
The Historica-Dominion Institute
includes Heritage Minutes (archived January 1, 2012)
H-CANADA, daily academic discussion email list
Canadian History & Knowledge
– Association for Canadian Studies
Baldwin Collection of Canadiana
at Toronto Public Library {{DEFAULTSORT:History of Canada
Paleo-Indians
Paleo-Indians were the first peoples who entered and subsequently inhabited the Americas towards the end of the Late Pleistocene period. The prefix ''paleo-'' comes from . The term ''Paleo-Indians'' applies specifically to the lithic period in ...
to North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
thousands of years ago to the present day. The lands encompassing present-day Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
have been inhabited for millennia by Indigenous peoples
There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territ ...
, with distinct trade networks, spiritual beliefs, and styles of social organization. Some of these older civilizations had long faded by the time of the first European arrivals and have been discovered through archeological investigations.
From the late 15th century, French and British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
expeditions explored, colonized, and fought over various places within North America in what constitutes present-day Canada. The colony of New France
New France (, ) was the territory colonized by Kingdom of France, France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Kingdom of Great Br ...
was claimed in 1534 by Jacques Cartier
Jacques Cartier (; 31 December 14911 September 1557) was a French maritime explorer from Brittany. Jacques Cartier was the first Europeans, European to describe and map the Gulf of Saint Lawrence and the shores of the Saint Lawrence River, wh ...
, with permanent settlements beginning in 1608. France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
ceded nearly all its North American possessions to Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-west coast of continental Europe, consisting of the countries England, Scotland, and Wales. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the List of European ...
in 1763 at the Treaty of Paris after the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War, 1756 to 1763, was a Great Power conflict fought primarily in Europe, with significant subsidiary campaigns in North America and South Asia. The protagonists were Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of Prus ...
. The now British Province of Quebec was divided into Upper and Lower Canada in 1791. The two provinces were united as the Province of Canada
The Province of Canada (or the United Province of Canada or the United Canadas) was a British colony in British North America from 1841 to 1867. Its formation reflected recommendations made by John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham, in the Report ...
by the Act of Union 1840
The ''British North America Act, 1840'' ( 3 & 4 Vict. c. 35), also known as the ''Act of Union 1840'', () was approved by Parliament in July 1840 and proclaimed February 10, 1841, in Montreal. It abolished the legislatures of Lower Canada and ...
, which came into force in 1841. In 1867, the Province of Canada was joined with two other British colonies of New Brunswick
New Brunswick is a Provinces and Territories of Canada, province of Canada, bordering Quebec to the north, Nova Scotia to the east, the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to the northeast, the Bay of Fundy to the southeast, and the U.S. state of Maine to ...
and Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, located on its east coast. It is one of the three Maritime Canada, Maritime provinces and Population of Canada by province and territory, most populous province in Atlan ...
through Confederation
A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a political union of sovereign states united for purposes of common action. Usually created by a treaty, confederations of states tend to be established for dealing with critical issu ...
, forming a self-governing entity. "Canada" was adopted as the legal name of the new country and the word "Dominion
A dominion was any of several largely self-governance, self-governing countries of the British Empire, once known collectively as the ''British Commonwealth of Nations''. Progressing from colonies, their degrees of self-governing colony, colon ...
" was conferred as the country's title. Over the next eighty-two years, Canada expanded by incorporating other parts of British North America, finishing with Newfoundland and Labrador
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of . As of 2025 the populatio ...
in 1949.
Although responsible government
Responsible government is a conception of a system of government that embodies the principle of parliamentary accountability, the foundation of the Westminster system of parliamentary democracy. Governments (the equivalent of the executive br ...
had existed in British North America since 1848, Britain continued to set its foreign and defence policies until the end of World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
. The Balfour Declaration of 1926
The Balfour Declaration of 1926 was issued by the 1926 Imperial Conference of British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent t ...
, the 1930 Imperial Conference and the passing of the Statute of Westminster in 1931 recognized that Canada had become co-equal with the United Kingdom. The Patriation of the Constitution in 1982 marked the removal of legal dependence on the British parliament. Canada currently consists of ten provinces and three territories and is a parliamentary democracy and a constitutional monarchy
Constitutional monarchy, also known as limited monarchy, parliamentary monarchy or democratic monarchy, is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in making decisions. ...
.
Over centuries, elements of Indigenous, French, British and more recent immigrant customs have combined to form a Canadian culture that has also been strongly influenced by its linguistic, geographic and economic neighbour, the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
. Since the conclusion of the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, Canada's strong support for multilateralism
In international relations, multilateralism refers to an alliance of multiple countries pursuing a common goal. Multilateralism is based on the principles of inclusivity, equality, and cooperation, and aims to foster a more peaceful, prosperous, an ...
and internationalism has been closely related to its peacekeeping efforts.
Indigenous peoples
Indigenous societies
 Archeological and Indigenous genetic evidence indicates that North and South America were the last continents into which humans migrated. During the
Archeological and Indigenous genetic evidence indicates that North and South America were the last continents into which humans migrated. During the Wisconsin glaciation
The Wisconsin glaciation, also called the Wisconsin glacial episode, was the most recent glacial period of the North American ice sheet complex, peaking more than 20,000 years ago. This advance included the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, which nucleated ...
, which began 100,000–75,000 years ago and ended about 11,00 years ago, falling sea levels allowed people to move gradually across the Bering land bridge (Beringia
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 70th parallel north, 72° north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south ...
), from Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states ...
into northwest North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
. At that point, they were blocked by the Laurentide ice sheet, then covering most of Canada, confining them to Alaska and the Yukon for thousands of years. The exact dates and routes of the peopling of the Americas are the subject of an ongoing debate.
About 16,000 years ago, the glacial melt allowed people to move by land south and east out of Beringia, and into Canada. The Haida Gwaii
Haida Gwaii (; / , literally "Islands of the Haida people"), previously known as the Queen Charlotte Islands, is an archipelago located between off the British Columbia Coast, northern Pacific coast in the Canadian province of British Columbia ...
islands, Old Crow Flats, and the Bluefish Caves contain some of the earliest Paleo-Indian archeological sites in Canada. Ice Age hunter-gatherer
A hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living in a community, or according to an ancestrally derived Lifestyle, lifestyle, in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local naturally occurring sources, esp ...
s of this period left lithic flake
In archaeology, a lithic flake is a "portion of rock (geology), rock removed from an objective piece by percussion or pressure,"Andrefsky, W. (2005) ''Lithics: Macroscopic Approaches to Analysis''. 2d Ed. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press and ...
fluted stone tools and the remains of large butchered mammals.
The North American climate stabilized around 8000 BCE (10,000 years ago). Climatic conditions were similar to modern patterns; however, the receding glacial ice sheets still covered large portions of the land, creating lakes of meltwater. Most population groups during the Archaic periods were still highly mobile hunter-gatherers. However, individual groups started to focus on resources available to them locally; thus with the passage of time, there is a pattern of increasing regional generalization (i.e.: Paleo-Arctic, Plano and Maritime Archaic traditions).
The Woodland cultural period dates from about 2000 BCE to 1000 CE and is applied to the Ontario
Ontario is the southernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Located in Central Canada, Ontario is the Population of Canada by province and territory, country's most populous province. As of the 2021 Canadian census, it ...
, Quebec, and Maritime regions. The introduction of pottery distinguishes the Woodland culture from the previous Archaic-stage inhabitants. The Laurentian-related people of Ontario manufactured the oldest pottery excavated to date in Canada.
The Hopewell tradition is an Indigenous culture that flourished along American rivers from 300 BCE to 500 CE. At its greatest extent, the Hopewell Exchange System connected cultures and societies to the peoples on the Canadian shores of Lake Ontario
Lake Ontario is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is bounded on the north, west, and southwest by the Canadian province of Ontario, and on the south and east by the U.S. state of New York (state), New York. The Canada–United Sta ...
. Canadian expression of the Hopewellian peoples encompasses the Point Peninsula, Saugeen, and Laurel complexes.
The eastern woodland areas of what became Canada were home to the Algonquian and Iroquoian peoples. The Algonquian language is believed to have originated in the western plateau of Idaho or the plains of Montana and moved with migrants eastward, eventually extending in various manifestations all the way from Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay, sometimes called Hudson's Bay (usually historically), is a large body of Saline water, saltwater in northeastern Canada with a surface area of . It is located north of Ontario, west of Quebec, northeast of Manitoba, and southeast o ...
to what is today Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, located on its east coast. It is one of the three Maritime Canada, Maritime provinces and Population of Canada by province and territory, most populous province in Atlan ...
in the east and as far south as the Tidewater region of Virginia.
Speakers of eastern Algonquian languages included the Mi'kmaq and Abenaki
The Abenaki ( Abenaki: ''Wαpánahki'') are Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands of Canada and the United States. They are an Algonquian-speaking people and part of the Wabanaki Confederacy. The Eastern Abenaki language was pred ...
of the Maritime region of Canada and likely the extinct Beothuk of Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of . As of 2025 the population ...
. The Ojibwa and other Anishinaabe speakers of the central Algonquian languages retain an oral tradition of having moved to their lands around the western and central Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes spanning the Canada–United States border. The five lakes are Lake Superior, Superior, Lake Michigan, Michigan, Lake Huron, H ...
from the sea, likely the Atlantic coast. According to oral tradition, the Ojibwe formed the Council of Three Fires in 796 CE with the Odawa and the Potawatomi.
The Five Nations of the Iroquois (Haudenosaunee) were centred from at least 1000 CE in northern New York, but their influence extended into what is now southern Ontario and the Montreal area of modern Quebec. They spoke varieties of Iroquoian languages. The Iroquois Confederacy, according to oral tradition, was formed in 1142 CE. In addition, there were other Iroquoian-speaking peoples in the area, including the St. Lawrence Iroquoians, the Erie, and others.
On the Great Plains
The Great Plains is a broad expanse of plain, flatland in North America. The region stretches east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, and grassland. They are the western part of the Interior Plains, which include th ...
, the Cree
The Cree, or nehinaw (, ), are a Indigenous peoples of the Americas, North American Indigenous people, numbering more than 350,000 in Canada, where they form one of the country's largest First Nations in Canada, First Nations. They live prim ...
or ''Nēhilawē'' (who spoke a closely related Central Algonquian language, the plains Cree language
Plains Cree (endonym: ; alternatively: "language of the prairie people") is a dialect of the Algonquian languages, Algonquian language, Cree language, Cree, which is the most populous Indigenous languages of Canada, Canadian indigenous lan ...
) depended on the vast herds of bison to supply food and many of their other needs. To the northwest were the peoples of the Na-Dene languages, which include the Athapaskan-speaking peoples and the Tlingit, who lived on the islands of southern Alaska and northern British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Situated in the Pacific Northwest between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that ...
. The Na-Dene language group is believed to be linked to the Yeniseian languages of Siberia. The Dene
The Dene people () are an Indigenous group of First Nations who inhabit the northern boreal, subarctic and Arctic regions of Canada. The Dene speak Northern Athabaskan languages and it is the common Athabaskan word for "people". The term ...
of the western Arctic may represent a distinct wave of migration from Asia to North America.
The Interior of British Columbia was home to the Salishan language groups such as the Shuswap (Secwepemc), Okanagan and southern Athabaskan language groups, primarily the Dakelh (Carrier) and the Tsilhqot'in. The inlets and valleys of the British Columbia Coast
The British Columbia Coast, popularly referred to as the BC Coast or simply the Coast, is a geographic region of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of British Columbia. As the entire western continental coastline of Canada ...
sheltered large, distinctive populations, such as the Haida, Kwakwaka'wakw and Nuu-chah-nulth
The Nuu-chah-nulth ( ; ), also formerly referred to as the Nootka, Nutka, Aht, Nuuchahnulth or Tahkaht, are one of the Indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast in Canada. The term Nuu-chah-nulth is used to describe fifteen related tri ...
, sustained by the region's abundant salmon and shellfish. These peoples developed complex cultures dependent on the western red cedar that included wooden houses, both seagoing whaling and war canoes, elaborately carved potlatch
A potlatch is a gift-giving feast practiced by Indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast of Canada and the United States,Harkin, Michael E., 2001, Potlatch in Anthropology, International Encyclopedia of the Social and Behavioral Scienc ...
items, and totem poles.
In the Arctic Archipelago, the distinctive Paleo-Eskimos known as Dorset peoples, whose culture has been traced back to around 500 BCE, were replaced by the ancestors of today's Inuit
Inuit (singular: Inuk) are a group of culturally and historically similar Indigenous peoples traditionally inhabiting the Arctic and Subarctic regions of North America and Russia, including Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwe ...
by 1500 CE. This transition is supported by archeological records and Inuit mythology that tells of having driven off the ''Tuniit'' or 'first inhabitants'. Inuit traditional laws are anthropologically different from Western law. ''Customary law
A legal custom is the established pattern of behavior within a particular social setting. A claim can be carried out in defense of "what has always been done and accepted by law".
Customary law (also, consuetudinary or unofficial law) exists wher ...
'' was non-existent in Inuit society before the introduction of the Canadian legal system.
European contact
The Norse, who had settledGreenland
Greenland is an autonomous territory in the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark. It is by far the largest geographically of three constituent parts of the kingdom; the other two are metropolitan Denmark and the Faroe Islands. Citizens of Greenlan ...
and Iceland
Iceland is a Nordic countries, Nordic island country between the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between North America and Europe. It is culturally and politically linked with Europe and is the regi ...
, arrived around 1000 CE and built a small settlement at L'Anse aux Meadows
L'Anse aux Meadows () is an archaeological site, first excavated in the 1960s, of a Norse colonization of North America, Norse settlement dating to approximately 1,000 years ago. The site is located on the northernmost tip of the island of Newf ...
at the northernmost tip of Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of . As of 2025 the population ...
(carbon dating estimate 990 – 1050 CE). L'Anse aux Meadows, the only confirmed Norse site in North America outside of Greenland, is also notable for its connection with the attempted settlement of Vinland
Vinland, Vineland, or Winland () was an area of coastal North America explored by Vikings. Leif Erikson landed there around 1000 AD, nearly five centuries before the voyages of Christopher Columbus and John Cabot. The name appears in the V ...
by Leif Erikson
Leif Erikson, also known as Leif the Lucky (), was a Norsemen, Norse explorer who is thought to have been the first European to set foot on continental Americas, America, approximately half a millennium before Christopher Columbus. According ...
around the same period or, more broadly, with Norse exploration of the Americas.
 Under
Under letters patent
Letters patent (plurale tantum, plural form for singular and plural) are a type of legal instrument in the form of a published written order issued by a monarch, President (government title), president or other head of state, generally granti ...
from King Henry VII of England
Henry VII (28 January 1457 – 21 April 1509), also known as Henry Tudor, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from his seizure of the crown on 22 August 1485 until his death in 1509. He was the first monarch of the House of Tudor.
Henr ...
, the Italian John Cabot
John Cabot ( ; 1450 – 1499) was an Italians, Italian navigator and exploration, explorer. His 1497 voyage to the coast of North America under the commission of Henry VII of England, Henry VII, King of England is the earliest known Europe ...
became the first European known to have landed in Canada after the Viking Age
The Viking Age (about ) was the period during the Middle Ages when Norsemen known as Vikings undertook large-scale raiding, colonising, conquest, and trading throughout Europe and reached North America. The Viking Age applies not only to their ...
. Records indicate that on June 24, 1497, he sighted land at a northern location believed to be somewhere in the Atlantic provinces. Official tradition deemed the first landing site to be at Cape Bonavista, Newfoundland, although other locations are possible. After 1497 Cabot and his son Sebastian Cabot continued to make other voyages to find the Northwest Passage, and other explorers continued to sail out of England to the New World, although the details of these voyages are not well recorded.
Based on the Treaty of Tordesillas, the Spanish Crown claimed it had territorial rights in the area visited by John Cabot in 1497 and 1498 CE. However, Portuguese explorers like João Fernandes Lavrador
João Fernandes Lavrador (1453–1501) () was a Portuguese explorer of the late 15th century. He was one of the first modern explorers of the Northeast coasts of North America, including the large Labrador peninsula, which was named after him ...
would continue to visit the north Atlantic coast, which accounts for the appearance of "Labrador
Labrador () is a geographic and cultural region within the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It is the primarily continental portion of the province and constitutes 71% of the province's area but is home to only 6% of its populatio ...
" on maps of the period. In 1501 and 1502 the Corte-Real brothers explored Newfoundland (Terra Nova) and Labrador claiming these lands as part of the Portuguese Empire
The Portuguese Empire was a colonial empire that existed between 1415 and 1999. In conjunction with the Spanish Empire, it ushered in the European Age of Discovery. It achieved a global scale, controlling vast portions of the Americas, Africa ...
. In 1506, King Manuel I of Portugal created taxes for the cod fisheries in Newfoundland waters. João Álvares Fagundes and Pero de Barcelos established fishing outposts in Newfoundland and Nova Scotia around 1521 CE; however, these were later abandoned, with the Portuguese colonizers focusing their efforts on South America. The extent and nature of Portuguese activity on the Canadian mainland during the 16th century remains unclear and controversial.
Canada under French rule
 French interest in the
French interest in the New World
The term "New World" is used to describe the majority of lands of Earth's Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas, and sometimes Oceania."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: ...
began with Francis I of France
Francis I (; ; 12 September 1494 – 31 March 1547) was King of France from 1515 until his death in 1547. He was the son of Charles, Count of Angoulême, and Louise of Savoy. He succeeded his first cousin once removed and father-in-law Louis&nbs ...
, who in 1524 sponsored Giovanni da Verrazzano's navigation of the region between Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
and Newfoundland in hopes of finding a route to the Pacific Ocean. Although the English had laid claims to it in 1497 when John Cabot made landfall somewhere on the North American coast (likely either modern-day Newfoundland or Nova Scotia) and had claimed the land for England on behalf of King Henry VII, these claims were not exercised and England did not attempt to create a permanent colony.
As for the French, however, Jacques Cartier
Jacques Cartier (; 31 December 14911 September 1557) was a French maritime explorer from Brittany. Jacques Cartier was the first Europeans, European to describe and map the Gulf of Saint Lawrence and the shores of the Saint Lawrence River, wh ...
planted a cross in the Gaspé Peninsula in 1534 and claimed the land in the name of Francis I, creating a region called "Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
" the following summer. Cartier had sailed up the St. Lawrence river as far as the Lachine Rapids
The Lachine Rapids () are a series of rapids on the Saint Lawrence River, between the Island of Montreal and the South Shore. They are confusingly located near the borough of Lasalle and not Lachine.
The Lachine Rapids contain large standi ...
, to the spot where Montreal now stands. Permanent settlement attempts by Cartier at Charlesbourg-Royal in 1541, at Sable Island
Sable Island (, literally "island of sand") is a small, remote island off the coast of Nova Scotia, Canada. Sable Island is located in the North Atlantic Ocean, about southeast of Halifax, Nova Scotia, Halifax, and about southeast of the clo ...
in 1598 by Marquis de La Roche-Mesgouez, and at Tadoussac, Quebec in 1600 by François Gravé Du Pont all eventually failed. Despite these initial failures, French fishing fleets visited the Atlantic coast communities and sailed into the St. Lawrence River, trading and making alliances with First Nations
First nations are indigenous settlers or bands.
First Nations, first nations, or first peoples may also refer to:
Indigenous groups
*List of Indigenous peoples
*First Nations in Canada, Indigenous peoples of Canada who are neither Inuit nor Mé ...
, as well as establishing fishing settlements such as in Percé (1603). As a result of France's claim and activities in the colony of Canada, the name ''Canada'' was found on international maps showing the existence of this colony within the St. Lawrence river region.
 In 1604, a North American fur trade monopoly was granted to Pierre Du Gua, Sieur de Mons. The fur trade became one of the main economic ventures in North America. Du Gua led his first colonization expedition to an island located near the mouth of the St. Croix River. Among his lieutenants was a geographer named
In 1604, a North American fur trade monopoly was granted to Pierre Du Gua, Sieur de Mons. The fur trade became one of the main economic ventures in North America. Du Gua led his first colonization expedition to an island located near the mouth of the St. Croix River. Among his lieutenants was a geographer named Samuel de Champlain
Samuel de Champlain (; 13 August 1574#Fichier]For a detailed analysis of his baptismal record, see #Ritch, RitchThe baptism act does not contain information about the age of Samuel, neither his birth date nor his place of birth. – 25 December ...
, who promptly carried out a major exploration of the northeastern coastline of what is now the United States. In the spring of 1605, under Samuel de Champlain, the new Saint Croix Island, Maine#St. Croix Settlement, St. Croix settlement was moved to Port Royal (today's Annapolis Royal, Nova Scotia). Samuel de Champlain also landed at Saint John Harbour on June 24, 1604 (the feast of St. John the Baptist) and is where the city of Saint John, New Brunswick
Saint John () is a port#seaport, seaport city located on the Bay of Fundy in the province of New Brunswick, Canada. It is Canada's oldest Municipal corporation, incorporated city, established by royal charter on May 18, 1785, during the reign ...
, and the Saint John River gets their name.
 In 1608 Champlain founded what is now
In 1608 Champlain founded what is now Quebec City
Quebec City is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Quebec. As of July 2021, the city had a population of 549,459, and the Census Metropolitan Area (including surrounding communities) had a populati ...
, one of the earliest permanent settlements, which would become the capital of New France. He took personal administration over the city and its affairs and sent out expeditions to explore the interior. Champlain became the first known European to encounter Lake Champlain
Lake Champlain ( ; , ) is a natural freshwater lake in North America. It mostly lies between the U.S. states of New York (state), New York and Vermont, but also extends north into the Canadian province of Quebec.
The cities of Burlington, Ve ...
in 1609. By 1615, he had travelled by canoe up the Ottawa River
The Ottawa River (, ) is a river in the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec. It is named after the Algonquin word "to trade", as it was the major trade route of Eastern Canada at the time. For most of its length, it defines the border betw ...
through Lake Nipissing and Georgian Bay to the centre of Huron country near Lake Simcoe
Lake Simcoe is a lake in southern Ontario, Canada, the fourth-largest lake wholly within the province, after Lake Nipigon, Lac Seul, and Lake Nipissing. At the time of the first European contact in the 17th century, the lake was called ''Ouentir ...
. During these voyages, Champlain aided the Wyandot people (aka "Hurons") in their battles against the Iroquois Confederacy. As a result, the Iroquois would become enemies of the French and be involved in multiple conflicts (known as the French and Iroquois Wars) until the signing of the Great Peace of Montreal in 1701.
The English, led by Humphrey Gilbert, had claimed St. John's, Newfoundland, in 1583 as the first North American English colony by royal prerogative of Queen Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was List of English monarchs, Queen of England and List of Irish monarchs, Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. She was the last and longest reigning monarch of the House of Tudo ...
. In the reign of King James I, the English established additional colonies in Cupids and Ferryland, Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of . As of 2025 the population ...
, and soon after established the first successful permanent settlements of Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
to the south. On September 29, 1621, a charter for the foundation of a New World Scottish colony was granted by King James to William Alexander. In 1622, the first settlers left Scotland. They initially failed and permanent Nova Scotian settlements were not firmly established until 1629 during the end of the Anglo-French War. These colonies did not last long except the fisheries in Ferryland under David Kirke. In 1631, under Charles I of England
Charles I (19 November 1600 – 30 January 1649) was King of Kingdom of England, England, Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland, and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland from 27 March 1625 until Execution of Charles I, his execution in 1649.
Charles was born ...
, the Treaty of Suza was signed, ending the war and returning Nova Scotia to the French. New France was not fully restored to French rule until the 1632 Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye. This led to new French immigrants and the founding of Trois-Rivières
Trois-Rivières (, ; ) is a city in the Mauricie administrative region of Quebec, Canada. It is located at the confluence of the Saint-Maurice River, Saint-Maurice and Saint Lawrence River, Saint Lawrence rivers, on the north shore of the Sain ...
in 1634.
Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
and the Jesuit establishment became the most dominant force in New France and hoped to establish a utopia
A utopia ( ) typically describes an imagined community or society that possesses highly desirable or near-perfect qualities for its members. It was coined by Sir Thomas More for his 1516 book ''Utopia (book), Utopia'', which describes a fictiona ...
n European and Aboriginal Christian community. In 1642, the Sulpicians sponsored a group of settlers led by Paul Chomedey de Maisonneuve, who founded Ville-Marie, the precursor to present-day Montreal
Montreal is the List of towns in Quebec, largest city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Quebec, the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-largest in Canada, and the List of North American cit ...
. In 1663 the French crown took direct control of the colonies from the Company of New France.
Although immigration rates to New France remained very low under direct French control, most of the new arrivals were farmers, and the rate of population growth among the settlers themselves had been very high. The women had about 30 per cent more children than comparable women who remained in France. Yves Landry says, "Canadians had an exceptional diet for their time." This was due to the natural abundance of meat, fish, and pure water; the good food conservation conditions during the winter; and an adequate wheat supply in most years. The 1666 census of New France was conducted by France's intendant, Jean Talon, in the winter of 1665–1666. The census showed a population count of 3,215 ''Acadians
The Acadians (; , ) are an ethnic group descended from the French colonial empire, French who settled in the New France colony of Acadia during the 17th and 18th centuries. Today, most descendants of Acadians live in either the Northern Americ ...
'' and '' habitants'' (French-Canadian farmers) in the administrative districts of Acadia
Acadia (; ) was a colony of New France in northeastern North America which included parts of what are now the The Maritimes, Maritime provinces, the Gaspé Peninsula and Maine to the Kennebec River. The population of Acadia included the various ...
and Canada. The census also revealed a great difference in the number of men at 2,034 versus 1,181 women.
Wars during the colonial era
By the early 1700s, the New France settlers were well established along the shores of the St. Lawrence River and parts of Nova Scotia, with a population of around 16,000. However, new arrivals stopped coming from France in the proceeding decades, meaning that the English and Scottish settlers in Newfoundland, Nova Scotia, and the southernThirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies were the British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America which broke away from the British Crown in the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), and joined to form the United States of America.
The Thirteen C ...
outnumbered the French population approximately ten to one by the 1750s.
From 1670, through the Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC), originally the Governor and Company of Adventurers of England Trading Into Hudson’s Bay, is a Canadian holding company of department stores, and the oldest corporation in North America. It was the owner of the ...
, the English also laid claim to Hudson Bay and its drainage basin, known as Rupert's Land
Rupert's Land (), or Prince Rupert's Land (), was a territory in British North America which comprised the Hudson Bay drainage basin. The right to "sole trade and commerce" over Rupert's Land was granted to Hudson's Bay Company (HBC), based a ...
, establishing new trading posts and forts, while continuing to operate fishing settlements in Newfoundland. French expansion along the Canadian canoe routes challenged the Hudson's Bay Company claims, and in 1686, Pierre Troyes led an overland expedition from Montreal to the shore of the bay, where they managed to capture a handful of outposts. La Salle's explorations gave France a claim to the Mississippi River Valley, where fur trappers and a few settlers set up scattered forts and settlements.
There were four French and Indian Wars and two additional wars in Acadia and Nova Scotia between the Thirteen American Colonies and New France from 1688 to 1763. During King William's War (1688 to 1697), military conflicts in Acadia included the Battle of Port Royal (1690); a naval battle in the Bay of Fundy ( Action of July 14, 1696); and the Raid on Chignecto (1696). The Treaty of Ryswick in 1697 ended the war between the two colonial powers of England and France for a brief time. During Queen Anne's War (1702 to 1713), the British Conquest of Acadia occurred in 1710, resulting in Nova Scotia (other than Cape Breton) being officially ceded to the British by the Treaty of Utrecht
The Peace of Utrecht was a series of peace treaty, peace treaties signed by the belligerents in the War of the Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht between April 1713 and February 1715. The war involved three contenders for the vac ...
, including Rupert's Land, which France had conquered in the late 17th century ( Battle of Hudson's Bay). As an immediate result of this setback, France founded the powerful Fortress of Louisbourg
The Fortress of Louisbourg () is a tourist attraction as a National Historic Sites of Canada, National Historic Site and the location of a one-quarter partial reconstruction of an 18th-century Kingdom of France, French fortress at Louisbourg, Nov ...
on Cape Breton Island
Cape Breton Island (, formerly '; or '; ) is a rugged and irregularly shaped island on the Atlantic coast of North America and part of the province of Nova Scotia, Canada.
The island accounts for 18.7% of Nova Scotia's total area. Although ...
.
Louisbourg was intended to serve as a year-round military and naval base for France's remaining North American empire and to protect the entrance to the St. Lawrence River. Father Rale's War resulted in both the fall of New France's influence in present-day Maine
Maine ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the United States, and the northeasternmost state in the Contiguous United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Provinces and ...
and the British recognition that it would have to negotiate with the Mi'kmaq in Nova Scotia. During King George's War (1744 to 1748), an army of New Englanders led by William Pepperrell mounted an expedition of 90 vessels and 4,000 men against Louisbourg in 1745. Within three months the fortress surrendered. The return of Louisbourg to French control by the peace treaty prompted the British to found Halifax in 1749 under Edward Cornwallis. Despite the official cessation of war between the British and French empires with the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle, the conflict in Acadia and Nova Scotia continued as Father Le Loutre's War.
 The British ordered the Acadians expelled from their lands in 1755 during the
The British ordered the Acadians expelled from their lands in 1755 during the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War, 1754 to 1763, was a colonial conflict in North America between Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of France, France, along with their respective Native Americans in the United States, Native American ...
, an event called the Expulsion of the Acadians or . The "expulsion" resulted in approximately 12,000 Acadians being shipped to destinations throughout Britain's North America and to France, Quebec and the French Caribbean colony of Saint-Domingue. The first wave of the expulsion of the Acadians began with the Bay of Fundy Campaign (1755) and the second wave began after the final Siege of Louisbourg (1758). Many of the Acadians settled in southern Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
, creating the Cajun culture there. Some Acadians managed to hide and others eventually returned to Nova Scotia, but they were far outnumbered by a new migration of New England Planters who settled on the former lands of the Acadians and transformed Nova Scotia from a colony of occupation for the British to a settled colony with stronger ties to New England. Britain eventually gained control of Quebec City after the Battle of the Plains of Abraham and the Battle of Fort Niagara in 1759, and finally captured Montreal in 1760.
Canada under British rule
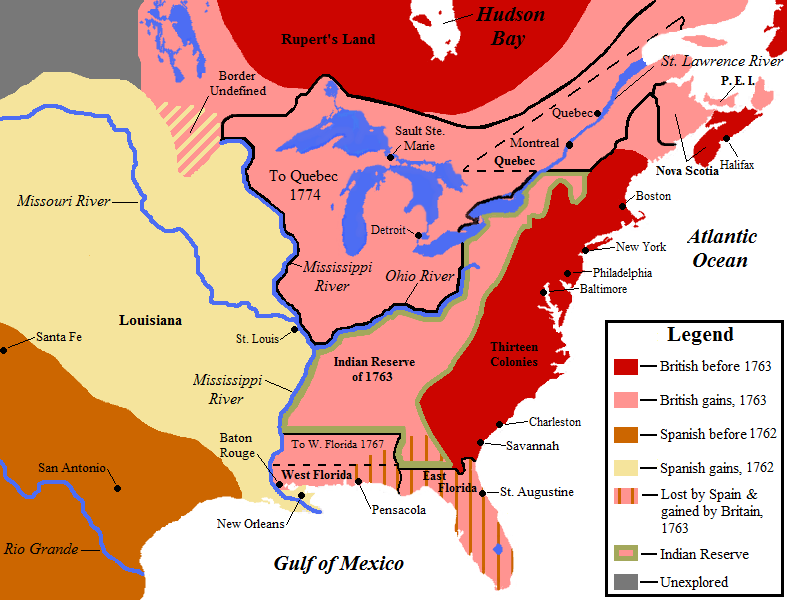
 As part of the terms of the
As part of the terms of the Treaty of Paris (1763)
The Treaty of Paris, also known as the Treaty of 1763, was signed on 10 February 1763 by the kingdoms of Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain, Kingdom of France, France and Spanish Empire, Spain, with Kingdom of Portugal, Portugal in agree ...
, signed after the defeat of New France in the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War, 1756 to 1763, was a Great Power conflict fought primarily in Europe, with significant subsidiary campaigns in North America and South Asia. The protagonists were Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of Prus ...
, France renounced its claims to territory in mainland North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
, except for fishing rights off Newfoundland and the two small islands of Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Pierre and Miquelon ( ), officially the Territorial Collectivity of Saint Pierre and Miquelon (), is a self-governing territorial overseas collectivity of France in the northwestern Atlantic Ocean, located near the Canada, Canadian prov ...
where its fishermen could dry their fish. France had already secretly transferred its vast Louisiana territory to Spain under the Treaty of Fontainebleau (1762) in which King Louis XV
Louis XV (15 February 1710 – 10 May 1774), known as Louis the Beloved (), was King of France from 1 September 1715 until his death in 1774. He succeeded his great-grandfather Louis XIV at the age of five. Until he reached maturity (then defi ...
of France had given his cousin King Charles III of Spain the entire area of the drainage basin
A drainage basin is an area of land in which all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, ...
of the Mississippi River from the Great Lakes to the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico () is an oceanic basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, mostly surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north, and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States; on the southw ...
and from the Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, are a mountain range in eastern to northeastern North America. The term "Appalachian" refers to several different regions associated with the mountain range, and its surrounding terrain ...
to the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in great-circle distance, straight-line distance from the northernmost part of Western Can ...
. France and Spain kept the Treaty of Fontainebleau secret from other countries until 1764. However under the Treaty of Paris, the eastern side of the Mississippi river basin became British territory. Great Britain returned to France its most important sugar-producing colony, Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe is an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France in the Caribbean. It consists of six inhabited islands—Basse-Terre Island, Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, Guadeloupe, Grande-Terre, Marie-Galant ...
, which the French considered more valuable than Canada. (Guadeloupe produced more sugar than all the British islands combined, and Voltaire
François-Marie Arouet (; 21 November 169430 May 1778), known by his ''Pen name, nom de plume'' Voltaire (, ; ), was a French Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment writer, philosopher (''philosophe''), satirist, and historian. Famous for his wit ...
had notoriously dismissed Canada as "", " A few acres of snow").
Following the Treaty of Paris, King George III
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and King of Ireland, Ireland from 25 October 1760 until his death in 1820. The Acts of Union 1800 unified Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and ...
issued the Royal Proclamation of 1763. The proclamation organized Great Britain's new North American empire and stabilized relations between the British Crown and Aboriginal peoples, formally recognizing aboriginal title, regulated trade, settlement, and land purchases on the western frontier. In the former French territory, the new British rulers of Canada first abolished and then later reinstated most of the property, religious, political, and social culture of the French-speaking , guaranteeing the right of the to practice the Catholic faith and to the use of French civil law (now Quebec Civil Code) in the Quebec Act of 1774, passed by the British Parliament.
American Revolution and the Loyalists
 During the
During the American Revolution
The American Revolution (1765–1783) was a colonial rebellion and war of independence in which the Thirteen Colonies broke from British America, British rule to form the United States of America. The revolution culminated in the American ...
, there was some sympathy for the American cause among the Acadians and the New Englanders in Nova Scotia. Neither party joined the rebels, although several hundred individuals joined the revolutionary cause. An invasion of Quebec by the Continental Army
The Continental Army was the army of the United Colonies representing the Thirteen Colonies and later the United States during the American Revolutionary War. It was formed on June 14, 1775, by a resolution passed by the Second Continental Co ...
in 1775, with a goal to take Quebec from British control, was halted at the Battle of Quebec by Guy Carleton, with the assistance of local militias. The defeat of the British army during the Siege of Yorktown in October 1781 signalled the end of Great Britain's struggle to suppress the American Revolution.
When the British evacuated New York City in 1783, they took many Loyalist refugees to Nova Scotia, while other Loyalists went to southwestern Quebec. So many Loyalists arrived on the shores of the St. John River that a separate colony—New Brunswick
New Brunswick is a Provinces and Territories of Canada, province of Canada, bordering Quebec to the north, Nova Scotia to the east, the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to the northeast, the Bay of Fundy to the southeast, and the U.S. state of Maine to ...
—was created in 1784; followed in 1791 by the division of Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
into the largely French-speaking Lower Canada
The Province of Lower Canada () was a British colonization of the Americas, British colony on the lower Saint Lawrence River and the shores of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence established in 1791 and abolished in 1841. It covered the southern portion o ...
( French Canada) along the St. Lawrence River and the Gaspé Peninsula and an anglophone Loyalist Upper Canada
The Province of Upper Canada () was a Province, part of The Canadas, British Canada established in 1791 by the Kingdom of Great Britain, to govern the central third of the lands in British North America, formerly part of the Province of Queb ...
, with its capital settled by 1796 in York
York is a cathedral city in North Yorkshire, England, with Roman Britain, Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers River Ouse, Yorkshire, Ouse and River Foss, Foss. It has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a Yor ...
(present-day Toronto
Toronto ( , locally pronounced or ) is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, most populous city in Canada. It is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Ontario. With a p ...
). After 1790, most of the new settlers were American farmers searching for new lands; although generally favourable to republicanism, they were relatively non-political and stayed neutral in the War of 1812
The War of 1812 was fought by the United States and its allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom and its allies in North America. It began when the United States United States declaration of war on the Uni ...
. In 1785, Saint John, New Brunswick became the first incorporated city in what would later become Canada.
 The signing of the Treaty of Paris in 1783 formally ended the war. Great Britain made several concessions to the US at the expense of the North American colonies. Notably, the borders between Canada and the United States were officially demarcated; all land south and west of the Great Lakes, which was formerly a part of the Province of Quebec and included modern-day Michigan, Wisconsin, Illinois, Indiana and Ohio, was ceded to the Americans. Fishing rights were also granted to the United States in the Gulf of St. Lawrence and on the coast of Newfoundland and the Grand Banks. The British ignored part of the treaty and maintained their military outposts in the Great Lakes areas it had ceded to the U.S., and they continued to supply their native allies with munitions. The British evacuated the outposts with the
The signing of the Treaty of Paris in 1783 formally ended the war. Great Britain made several concessions to the US at the expense of the North American colonies. Notably, the borders between Canada and the United States were officially demarcated; all land south and west of the Great Lakes, which was formerly a part of the Province of Quebec and included modern-day Michigan, Wisconsin, Illinois, Indiana and Ohio, was ceded to the Americans. Fishing rights were also granted to the United States in the Gulf of St. Lawrence and on the coast of Newfoundland and the Grand Banks. The British ignored part of the treaty and maintained their military outposts in the Great Lakes areas it had ceded to the U.S., and they continued to supply their native allies with munitions. The British evacuated the outposts with the Jay Treaty
The Treaty of Amity, Commerce, and Navigation, Between His Britannic Majesty and the United States of America, commonly known as the Jay Treaty, and also as Jay's Treaty, was a 1794 treaty between the United States and Great Britain that averted ...
of 1795, but the continued supply of munitions irritated the Americans in the run-up to the War of 1812.
Canadian historians have had mixed views on the long-term impact of the American Revolution. Arthur Lower in the 1950s provided the long-standard historical interpretation that for English Canada the results were counter-revolutionary:
nglish Canadainherited, not the benefits, but the bitterness of the Revolution…. English Canada started its life with as powerful a nostalgic shove backward into the past as the Conquest had given to French Canada: two little peoples officially devoted to counter-revolution, to lost causes, to the tawdry ideals of a society of men and masters, and not to the self-reliant freedom alongside of them.Recently Michel Ducharme has agreed that Canada did indeed oppose "republican liberty", as exemplified by the United States and France. However, he says it did find a different path forward when it fought against British rulers after 1837 to secure "modern liberty". That form of liberty focused not on the virtues of citizens but on protecting their rights from infringement by the state.
War of 1812
The War of 1812 was fought between the United States and the British, with the British North American colonies being heavily involved. Greatly outgunned by the British Royal Navy, the American war plans focused on an invasion of Canada (especially what is today eastern and western Ontario). The American frontier states voted for war to suppress the First Nations raids that frustrated the settlement of the frontier. The war on the border with the United States was characterized by a series of multiple failed invasions and fiascos on both sides. American forces took control ofLake Erie
Lake Erie ( ) is the fourth-largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and also has the shortest avera ...
in 1813, driving the British out of western Ontario, killing the Shawnee leader Tecumseh, and breaking the military power of his confederacy. The war was overseen by British army officers like Isaac Brock and Charles de Salaberry with the assistance of First Nations and loyalist informants, most notably Laura Secord.
The War ended with no boundary changes thanks to the Treaty of Ghent of 1814, and the Rush–Bagot Treaty of 1817. A demographic result was the shifting of the destination of American migration from Upper Canada to Ohio
Ohio ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Erie to the north, Pennsylvania to the east, West Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, Indiana to the ...
, Indiana
Indiana ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Michigan to the northwest, Michigan to the north and northeast, Ohio to the east, the Ohio River and Kentucky to the s ...
and Michigan
Michigan ( ) is a peninsular U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, Upper Midwestern United States. It shares water and land boundaries with Minnesota to the northwest, Wisconsin to the west, ...
, without fear of Indigenous attacks. After the war, supporters of Britain tried to repress the republicanism
Republicanism is a political ideology that encompasses a range of ideas from civic virtue, political participation, harms of corruption, positives of mixed constitution, rule of law, and others. Historically, it emphasizes the idea of self ...
that was common among American immigrants to Canada. The troubling memory of the war and the American invasions etched itself into the consciousness of Canadians as a distrust of the intentions of the United States towards the British presence in North America.pp. 254–255
Rebellions and the Durham Report
The rebellions of 1837 against the British colonial government took place in both Upper and Lower Canada. In Upper Canada, a band of Reformers under the leadership ofWilliam Lyon Mackenzie
William Lyon Mackenzie (March12, 1795 August28, 1861) was a Scottish-born Canadian-American journalist and politician. He founded newspapers critical of the Family Compact, a term used to identify the establishment of Upper Canada. He represe ...
took up arms in a disorganized and ultimately unsuccessful series of small-scale skirmishes around Toronto, London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
, and Hamilton
Hamilton may refer to:
* Alexander Hamilton (1755/1757–1804), first U.S. Secretary of the Treasury and one of the Founding Fathers of the United States
* ''Hamilton'' (musical), a 2015 Broadway musical by Lin-Manuel Miranda
** ''Hamilton'' (al ...
.
In Lower Canada, a more substantial rebellion occurred against British rule. Both English- and French-Canadian rebels, sometimes using bases in the neutral United States, fought several skirmishes against the authorities. The towns of Chambly and Sorel were taken by the rebels, and Quebec City was isolated from the rest of the colony. Montreal rebel leader Robert Nelson read the " Declaration of Independence of Lower Canada" to a crowd assembled at the town of Napierville in 1838. The rebellion of the '' Patriote movement'' was defeated after battles across Quebec. Hundreds were arrested, and several villages were burnt in reprisal.
 The British government then sent Lord Durham to examine the situation; he stayed in Canada for five months before returning to Britain, bringing with him his Durham Report, which strongly recommended
The British government then sent Lord Durham to examine the situation; he stayed in Canada for five months before returning to Britain, bringing with him his Durham Report, which strongly recommended responsible government
Responsible government is a conception of a system of government that embodies the principle of parliamentary accountability, the foundation of the Westminster system of parliamentary democracy. Governments (the equivalent of the executive br ...
. A less well-received recommendation was the amalgamation of Upper and Lower Canada for the deliberate assimilation of the French-speaking population. The Canadas were merged into a single colony, the United Province of Canada, by the 1840 Act of Union, and responsible government was achieved in 1848, a few months after it was accomplished in Nova Scotia. The parliament of United Canada in Montreal was set on fire by a mob of Tories in 1849 after the passing of an indemnity bill for the people who suffered losses during the rebellion in Lower Canada.
Between the Napoleonic Wars
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Napoleonic Wars
, partof = the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars
, image = Napoleonic Wars (revision).jpg
, caption = Left to right, top to bottom:Battl ...
and 1850, some 800,000 immigrants came to the colonies of British North America, mainly from the British Isles
The British Isles are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner Hebrides, Inner and Outer Hebr ...
, as part of the great migration of Canada. These included Gaelic-speaking Highland Scots displaced by the Highland Clearances
The Highland Clearances ( , the "eviction of the Gaels") were the evictions of a significant number of tenants in the Scottish Highlands and Islands, mostly in two phases from 1750 to 1860.
The first phase resulted from Scottish Agricultural R ...
to Nova Scotia and Scottish and English settlers to the Canadas, particularly Upper Canada. The Irish Famine of the 1840s significantly increased the pace of Irish Catholic immigration to British North America, with over 35,000 distressed Irish landing in Toronto alone in 1847 and 1848.
Pacific colonies
 Spanish explorers had taken the lead in the Pacific Northwest coast, with the voyages of Juan José Pérez Hernández in 1774 and 1775. By the time the Spanish determined to build a fort on
Spanish explorers had taken the lead in the Pacific Northwest coast, with the voyages of Juan José Pérez Hernández in 1774 and 1775. By the time the Spanish determined to build a fort on Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island is an island in the northeastern Pacific Ocean and part of the Canadian province of British Columbia. The island is in length, in width at its widest point, and in total area, while are of land. The island is the largest ...
, the British navigator James Cook
Captain (Royal Navy), Captain James Cook (7 November 1728 – 14 February 1779) was a British Royal Navy officer, explorer, and cartographer famous for his three voyages of exploration to the Pacific and Southern Oceans, conducted between 176 ...
had visited Nootka Sound and charted the coast as far as Alaska, while British and American maritime fur traders had begun a busy era of commerce with the coastal peoples to satisfy the brisk market for sea otter pelts in China, thereby launching what became known as the China Trade.
In 1789 war threatened between Britain and Spain on their respective rights; the Nootka Crisis
The Nootka Crisis, also known as the Spanish Armament, was an international incident and political dispute between Spain and Great Britain triggered by a series of events revolving around sovereignty claims and rights of navigation and trade. It ...
was resolved peacefully largely in favour of Britain, the much stronger naval power at the time. In 1793 Alexander MacKenzie, a Scotsman working for the North West Company, crossed the continent and with his Aboriginal guides and French-Canadian crew, reached the mouth of the Bella Coola River, completing the first continental crossing north of Mexico, missing George Vancouver
Captain (Royal Navy), Captain George Vancouver (; 22 June 1757 – 10 May 1798) was a Royal Navy officer and explorer best known for leading the Vancouver Expedition, which explored and charted North America's northwestern West Coast of the Uni ...
's charting expedition to the region by only a few weeks. In 1821, the North West Company and Hudson's Bay Company merged, with a combined trading territory that was extended by a licence to the North-Western Territory and the Columbia and New Caledonia
New Caledonia ( ; ) is a group of islands in the southwest Pacific Ocean, southwest of Vanuatu and east of Australia. Located from Metropolitan France, it forms a Overseas France#Sui generis collectivity, ''sui generis'' collectivity of t ...
fur districts, which reached the Arctic Ocean on the north and the Pacific Ocean on the west.
The Colony of Vancouver Island was chartered in 1849, with the trading post at Fort Victoria as the capital. This was followed by the Colony of the Queen Charlotte Islands in 1853, and by the creation of the Colony of British Columbia The Colony of British Columbia refers to one of two colonies of British North America, located on the Pacific coast of modern-day Canada:
* Colony of British Columbia (1858–1866)
* Colony of British Columbia (1866–1871)
See also
* History of ...
in 1858 and the Stikine Territory in 1861, with the latter three being founded expressly to keep those regions from being overrun and annexed by American gold miners. The Colony of the Queen Charlotte Islands and most of the Stikine Territory were merged into the Colony of British Columbia in 1863 (the remainder, north of the 60th Parallel, became part of the North-Western Territory).
Confederation
 The Seventy-Two Resolutions from the 1864 Quebec Conference and Charlottetown Conference laid out the framework for uniting British colonies in North America into a federation. The Resolutions became the basis for the London Conference of 1866, which led to the formation of the Dominion of Canada on July 1, 1867. The term ''dominion'' was chosen to indicate Canada's status as a self-governing
The Seventy-Two Resolutions from the 1864 Quebec Conference and Charlottetown Conference laid out the framework for uniting British colonies in North America into a federation. The Resolutions became the basis for the London Conference of 1866, which led to the formation of the Dominion of Canada on July 1, 1867. The term ''dominion'' was chosen to indicate Canada's status as a self-governing polity
A polity is a group of people with a collective identity, who are organized by some form of political Institutionalisation, institutionalized social relations, and have a capacity to mobilize resources.
A polity can be any group of people org ...
of the British Empire, the first time it was used about a country. With the coming into force of the British North America Act, 1867 (enacted by the British Parliament), Canada became a federated country in its own right. (According to James Bowden, writing in The Dorchester Review, "Ottawa turned its back on 'Dominion' in the 1940s and 1950s," impelled by what historian C.P. Champion referred to as "neo-nationalism.")
Federation emerged from multiple impulses: the British wanted Canada to defend itself; the Maritimes needed railroad connections, which were promised in 1867; English-Canadian nationalism
Nationalism is an idea or movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, it presupposes the existence and tends to promote the interests of a particular nation, Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: Theory, I ...
sought to unite the lands into one country, dominated by the English language and loyalist culture; many French-Canadians saw an opportunity to exert political control within a new largely French-speaking Quebecpp. 323–324 and exaggerated fears of possible U.S. expansion northward. On a political level, there was a desire for the expansion of responsible government and elimination of the legislative deadlock between Upper and Lower Canada, and their replacement with provincial legislatures in a federation. This was especially pushed by the liberal Reform movement
Reformism is a type of social movement that aims to bring a social system, social or also a political system closer to the community's ideal. A reform movement is distinguished from more Radicalism (politics), radical social movements such as re ...
of Upper Canada and the French-Canadian ''Parti rouge
The (, "Red Party"; or , "Democratic Party") was a political group that contested elections in the Canada East, Eastern section of the Province of Canada. It was formed around 1847 by radical French-Canadians; the party was inspired by the ideas ...
'' in Lower Canada who favoured a decentralized union in comparison to the Upper Canadian Conservative party and to some degree the French-Canadian '' Parti bleu'', which favoured a centralized union.
Territorial expansion west (1867–1914)
Using the lure of theCanadian Pacific Railway
The Canadian Pacific Railway () , also known simply as CPR or Canadian Pacific and formerly as CP Rail (1968–1996), is a Canadian Class I railway incorporated in 1881. The railway is owned by Canadian Pacific Kansas City, Canadian Pacific Ka ...
, a transcontinental line that would unite the nation, Ottawa attracted support in the Maritimes and in British Columbia.
In 1866, the Colony of British Columbia and the Colony of Vancouver Island merged into a single Colony of British Columbia. After Rupert's Land was transferred to Canada by Britain in 1870, connecting to the eastern provinces, British Columbia joined Canada in 1871. In 1873, Prince Edward Island
Prince Edward Island is an island Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. While it is the smallest province by land area and population, it is the most densely populated. The island has several nicknames: "Garden of the Gulf", ...
joined. Newfoundland—which had no use for a transcontinental railway—voted no in 1869, and did not join Canada until 1949.
 In 1873, John A. Macdonald ( First Prime Minister of Canada) created the
In 1873, John A. Macdonald ( First Prime Minister of Canada) created the North-West Mounted Police
The North-West Mounted Police (NWMP) was a Canadian paramilitary police force, established in 1873, to maintain order in the new Canadian North-West Territories (NWT) following the 1870 transfer of Rupert's Land and North-Western Territory to ...
(now the Royal Canadian Mounted Police
The Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP; , GRC) is the Law enforcement in Canada, national police service of Canada. The RCMP is an agency of the Government of Canada; it also provides police services under contract to 11 Provinces and terri ...
) to help police the Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories is a federal Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Canada. At a land area of approximately and a 2021 census population of 41,070, it is the second-largest and the most populous of Provinces and territorie ...
. Specifically the Mounties were to assert Canadian sovereignty to prevent possible American encroachments into the area. The Mounties' first large-scale mission was to suppress the second independence movement by Manitoba
Manitoba is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada at the Centre of Canada, longitudinal centre of the country. It is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, fifth-most populous province, with a population ...
's Métis
The Métis ( , , , ) are a mixed-race Indigenous people whose historical homelands include Canada's three Prairie Provinces extending into parts of Ontario, British Columbia, the Northwest Territories and the northwest United States. They ha ...
, a mixed-blood people of joint First Nations and European descent, who originated in the mid-17th century. The desire for independence erupted in the Red River Rebellion in 1869 and the later North-West Rebellion in 1885 led by Louis Riel. Suppressing the Rebellion was Canada's first independent military action and demonstrated the need to complete the Canadian Pacific Railway. It guaranteed Anglophone control of the Prairies and demonstrated the national government was capable of decisive action. However, it lost the Conservative Party most of their support in Quebec and led to a permanent distrust of the Anglophone community on the part of the Francophones.
 As Canada expanded, the Canadian government rather than the British Crown negotiated treaties with the resident First Nations' peoples, beginning with '' Treaty 1'' in 1871. The treaties extinguished
As Canada expanded, the Canadian government rather than the British Crown negotiated treaties with the resident First Nations' peoples, beginning with '' Treaty 1'' in 1871. The treaties extinguished aboriginal title
Aboriginal title is a common law doctrine that the Indigenous land rights, land rights of indigenous peoples to customary land, customary tenure persist after the assumption of sovereignty to that land by another Colonization, colonising state. ...
on traditional territories, created reserves for the indigenous peoples' exclusive use, and opened up the rest of the territory for settlement. Indigenous people were induced to move to these new reserves, sometimes forcibly. The government imposed the ''Indian Act
The ''Indian Act'' () is a Canadian Act of Parliament that concerns registered Indians, their bands, and the system of Indian reserves. First passed in 1876 and still in force with amendments, it is the primary document that defines how t ...
'' in 1876 to govern the relations between the federal government and the Indigenous peoples and govern the relations between the new settlers and the Indigenous peoples. Under the ''Indian Act'', the government started the Residential School System to convert the Indigenous peoples to "industrious Christian Canadians" and extinguish native language and culture.
In the 1890s, legal experts codified a framework of criminal law, culminating in '' The Criminal Code, 1892''. This solidified the liberal ideal of "equality before the law" in a way that made an abstract principle into a tangible reality for every adult Canadian. Wilfrid Laurier
Sir Henri Charles Wilfrid Laurier (November 20, 1841 – February 17, 1919) was a Canadian lawyer, statesman, and Liberal politician who served as the seventh prime minister of Canada from 1896 to 1911. The first French Canadians, French ...
who served 1896–1911 as the Seventh Prime Minister of Canada felt Canada was on the verge of becoming a world power, and declared that the 20th century would "belong to Canada"
The Alaska boundary dispute, simmering since the Alaska Purchase of 1867, became critical when gold was discovered in the Yukon
Yukon () is a Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Canada, bordering British Columbia to the south, the Northwest Territories to the east, the Beaufort Sea to the north, and the U.S. state of Alaska to the west. It is Canada’s we ...
during the late 1890s, with the U.S. controlling all the possible ports of entry. Canada argued its boundary included the port of Skagway. The dispute went to arbitration in 1903, but the British delegate sided with the Americans, angering Canadians who felt the British had betrayed Canadian interests to curry favour with the U.S.
In 1905, Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Western Canada. It is bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and to the south by the ...
and Alberta
Alberta is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Canada. It is a part of Western Canada and is one of the three Canadian Prairies, prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to its west, Saskatchewan to its east, t ...
were admitted as provinces. They were growing rapidly thanks to abundant wheat crops that attracted immigration to the plains by Ukrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary eth ...
and Northern and Central Europeans and by settlers from the United States, Britain and eastern Canada.
Laurier signed a reciprocity treaty with the U.S. that would lower tariffs in both directions. Conservatives under Robert Borden
Sir Robert Laird Borden (June 26, 1854 – June 10, 1937) was a Canadian lawyer and Conservative Party of Canada (1867–1942), Conservative politician who served as the eighth prime minister of Canada from 1911 to 1920. He is best known ...
denounced it, saying it would integrate Canada's economy into that of the U.S. and loosen ties with Britain. The Conservative party won the 1911 Canadian federal election.
World Wars and Interwar Years (1914–1945)
First World War
 The
The Canadian Forces
The Canadian Armed Forces (CAF; , FAC) are the unified Military, military forces of Canada, including sea, land, and air commands referred to as the Royal Canadian Navy, Canadian Army and the Royal Canadian Air Force. Under the ''National Defenc ...
and civilian
A civilian is a person who is not a member of an armed force. It is war crime, illegal under the law of armed conflict to target civilians with military attacks, along with numerous other considerations for civilians during times of war. If a civi ...
participation in the First World War helped to foster a sense of British-Canadian nationhood. The highpoints of Canadian military achievement during the First World War came during the Somme, Vimy, Passchendaele battles and what later became known as " Canada's Hundred Days". The reputation Canadian troops earned, along with the success of Canadian flying aces including William George Barker and Billy Bishop, helped to give the nation a new sense of identity. The War Office
The War Office has referred to several British government organisations throughout history, all relating to the army. It was a department of the British Government responsible for the administration of the British Army between 1857 and 1964, at ...
in 1922 reported approximately 67,000 killed and 173,000 wounded during the war. This excludes civilian deaths in war-time incidents like the Halifax Explosion.
Support for Great Britain during the First World War caused a major political crisis over conscription, with Francophones, mainly from Quebec, rejecting national policies. During the crisis, large numbers of enemy aliens (especially Ukrainians and Germans) were put under government controls. The Liberal party
The Liberal Party is any of many political parties around the world.
The meaning of ''liberal'' varies around the world, ranging from liberal conservatism on the right to social liberalism on the left. For example, while the political systems ...
was deeply split, with most of its Anglophone leaders joining the unionist government headed by Prime Minister Borden, the leader of the Conservative party. The Liberals regained their influence after the war under the leadership of William Lyon Mackenzie King, who served as prime minister with three separate terms between 1921 and 1949.
Women's suffrage
When Canada was founded, women could not vote in federal elections. Women did have a local vote in some provinces, as inCanada West
The Province of Canada (or the United Province of Canada or the United Canadas) was a British colony in British North America from 1841 to 1867. Its formation reflected recommendations made by John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham, in the Report ...
from 1850, where women owning land could vote for school trustees. By 1900 other provinces adopted similar provisions, and in 1916 Manitoba took the lead in extending full women's suffrage
Women's suffrage is the women's rights, right of women to Suffrage, vote in elections. Several instances occurred in recent centuries where women were selectively given, then stripped of, the right to vote. In Sweden, conditional women's suffra ...
. Simultaneously suffragists gave strong support to the prohibition movement, especially in Ontario and the Western provinces.
 The '' Military Voters Act'' of 1917 gave the vote to British women who were war widows or had sons or husbands serving overseas. Unionist Prime Minister Borden pledged himself during the 1917 campaign to equal suffrage for women. After his landslide victory, he introduced a bill in 1918 for extending the franchise to women. This passed without division but did not apply to Quebec provincial and municipal elections. The women of Quebec gained full suffrage in 1940. The first woman elected to Parliament was Agnes Macphail of Ontario in 1921.
The '' Military Voters Act'' of 1917 gave the vote to British women who were war widows or had sons or husbands serving overseas. Unionist Prime Minister Borden pledged himself during the 1917 campaign to equal suffrage for women. After his landslide victory, he introduced a bill in 1918 for extending the franchise to women. This passed without division but did not apply to Quebec provincial and municipal elections. The women of Quebec gained full suffrage in 1940. The first woman elected to Parliament was Agnes Macphail of Ontario in 1921.
1920s
On the world stage
Convinced that Canada had proven itself on the battlefields of Europe, Prime Minister Borden demanded that it have a separate seat at the Paris Peace Conference in 1919. This was initially opposed not only by Britain but also by the United States, which saw such a delegation as an extra British vote. Borden responded by pointing out that since Canada had lost nearly 60,000 men, a far larger proportion of its men, its right to equal status as a nation had been consecrated on the battlefield. British Prime Minister David Lloyd George eventually relented, and convinced the reluctant Americans to accept the presence of delegations from Canada,India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
, Australia, Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of . As of 2025 the population ...
, New Zealand, and South Africa. These also received their own seats in the League of Nations. Canada asked for neither reparations nor mandates. It played only a modest role in Paris, but just having a seat was a matter of pride. It was cautiously optimistic about the new League of Nations, in which it played an active and independent role.
In 1922 British Prime Minister David Lloyd George appealed repeatedly for Canadian support in the Chanak crisis, in which a war threatened between Britain and Turkey. Canada refused, leading to the fall of Lloyd George. The Department of External Affairs, which had been founded in 1909, was expanded and promoted Canadian autonomy as Canada reduced its reliance on British diplomats and used its own foreign service. Thus began the careers of such important diplomats as Norman Robertson and Hume Wrong, and future prime minister Lester Pearson.
In the 1920s, Canada set up a successful wheat marketing "pool" to keep prices high. Canada negotiated with the United States, Australia, and the Soviet Union to expand the pool, but the effort failed when the Great Depression caused distrust and low prices.
With prohibition underway in the United States, smugglers bought large quantities of Canadian liquor. Both the Canadian distillers and the U.S. State Department put heavy pressure on the Customs and Excise Department to loosen or tighten border controls. Liquor interests paid off corrupt Canadian border officials until the U.S. finally ended prohibition in 1933.
Domestic affairs
In 1921 to 1926, William Lyon Mackenzie King's Liberal government pursued a conservative domestic policy with the object of lowering wartime taxes and, especially, cooling wartime ethnic tensions, as well as defusing postwar labour conflicts. The Progressives refused to join the government but did help the Liberals defeat non-confidence motions. King faced a delicate balancing act of reducing tariffs enough to please the Prairie-based Progressives, but not too much to alienate his vital support in industrial Ontario and Quebec, which needed tariffs to compete with American imports. King and Conservative leader Arthur Meighen sparred constantly and bitterly in Commons debates. The Progressives gradually weakened. Their effective and passionate leader, Thomas Crerar, resigned to return to his grain business, and was replaced by the more placid Robert Forke. The socialist reformer J. S. Woodsworth gradually gained influence and power among the Progressives, and he reached an accommodation with King on policy matters. In 1926 Prime Minister Mackenzie King advised the Governor General, Lord Byng, to dissolve Parliament and call another election, but Byng refused, the only time that the Governor General has exercised such a power. Instead, Byng called upon Meighen, the Conservative Party leader, to form a government. Meighen attempted to do so but was unable to obtain a majority in the Commons and he, too, advised dissolution, which this time was accepted. The episode, the King–Byng affair, marks a constitutional crisis that was resolved by a new tradition of complete non-interference in Canadian political affairs on the part of the British government.
In 1926 Prime Minister Mackenzie King advised the Governor General, Lord Byng, to dissolve Parliament and call another election, but Byng refused, the only time that the Governor General has exercised such a power. Instead, Byng called upon Meighen, the Conservative Party leader, to form a government. Meighen attempted to do so but was unable to obtain a majority in the Commons and he, too, advised dissolution, which this time was accepted. The episode, the King–Byng affair, marks a constitutional crisis that was resolved by a new tradition of complete non-interference in Canadian political affairs on the part of the British government.
Great Depression
 Canada was hit hard by the worldwide
Canada was hit hard by the worldwide Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and ...
that began in 1929. Between 1929 and 1933, the gross national product dropped 40 per cent (compared to 37 per cent in the US). Unemployment reached 27 per cent at the depth of the Depression in 1933. Many businesses closed, as corporate profits of in 1929 turned into losses of in 1933. Canadian exports shrank by 50% from 1929 to 1933. Construction all but stopped (down 82 per cent, 1929–33), and wholesale prices dropped 30%. Wheat prices plunged from 78c per bushel (1928 crop) to 29c in 1932.
 Urban unemployment nationwide was 19 per cent; Toronto's rate was 17 per cent, according to the census of 1931. Farmers who stayed on their farms were not considered unemployed. By 1933, 30 per cent of the labour force was out of work, and one-fifth of the population became dependent on government assistance. Wages fell as did prices. The worst hit were areas dependent on primary industries such as farming,
Urban unemployment nationwide was 19 per cent; Toronto's rate was 17 per cent, according to the census of 1931. Farmers who stayed on their farms were not considered unemployed. By 1933, 30 per cent of the labour force was out of work, and one-fifth of the population became dependent on government assistance. Wages fell as did prices. The worst hit were areas dependent on primary industries such as farming, mining
Mining is the Resource extraction, extraction of valuable geological materials and minerals from the surface of the Earth. Mining is required to obtain most materials that cannot be grown through agriculture, agricultural processes, or feasib ...
and logging, as prices fell and there were few alternative jobs. Most families had moderate losses and little hardship, though they too became pessimistic and their debts became heavier as prices fell. Some families saw most or all of their assets disappear and suffered severely.
In 1930, in the first stage of the long depression, Prime Minister Mackenzie King believed that the crisis was a temporary swing of the business cycle and that the economy would soon recover without government intervention. He refused to provide unemployment relief or federal aid to the provinces, saying that if Conservative provincial governments demanded federal dollars, he would not give them "a five-cent piece." The main issue was the rapid deterioration in the economy and whether the prime minister was out of touch with the hardships of ordinary people. The winner of the 1930 election was Richard Bedford Bennett and the Conservatives. Bennett had promised high tariffs and large-scale spending, but as deficits increased, he became wary and cut back severely on Federal spending. With falling support and the depression getting only worse, Bennett attempted to introduce policies based on the New Deal
The New Deal was a series of wide-reaching economic, social, and political reforms enacted by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the United States between 1933 and 1938, in response to the Great Depression in the United States, Great Depressi ...
of President Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), also known as FDR, was the 32nd president of the United States, serving from 1933 until his death in 1945. He is the longest-serving U.S. president, and the only one to have served ...
(FDR) in the United States, but he got little passed. Bennett's government became a focus of popular discontent. For example, auto owners saved on gasoline by using horses to pull their cars, dubbing them Bennett Buggies. The Conservative failure to restore prosperity led to the return of Mackenzie King's Liberals in the 1935 election.
In 1935, the Liberals used the slogan "King or Chaos" to win a landslide in the 1935 election. Promising a much-desired trade treaty with the U.S., the Mackenzie King government passed the 1935 Reciprocal Trade Agreement. It marked the turning point in Canadian-American economic relations, reversing the disastrous trade war of 1930–31, lowering tariffs and yielding a dramatic increase in trade.
The worst of the Depression had passed by 1935, as the Government of Canada launched relief programs such as the ''National Housing Act'' and the National Employment Commission. The Canadian Broadcasting Corporation
The Canadian Broadcasting Corporation (), branded as CBC/Radio-Canada, is the Canadian Public broadcasting, public broadcaster for both radio and television. It is a Crown corporation that serves as the national public broadcaster, with its E ...
became a crown corporation
Crown corporation ()
is the term used in Canada for organizations that are structured like private companies, but are directly and wholly owned by the government.
Crown corporations have a long-standing presence in the country, and have a sign ...
in 1936. Trans-Canada Airlines (the precursor to Air Canada
Air Canada is the flag carrier and the largest airline of Canada, by size and passengers carried. Air Canada is headquartered in the borough of Saint-Laurent in the city of Montreal. The airline, founded in 1937, provides scheduled and cha ...
) was formed in 1937, as was the National Film Board of Canada
The National Film Board of Canada (NFB; ) is a Canadian public film and digital media producer and distributor. An agency of the Government of Canada, the NFB produces and distributes documentary films, animation, web documentaries, and altern ...
in 1939. In 1938, Parliament transformed the Bank of Canada
The Bank of Canada (BoC; ) is a Crown corporations of Canada, Crown corporation and Canada's central bank. Chartered in 1934 under the ''Bank of Canada Act'', it is responsible for formulating Canada's monetary policy,OECD. OECD Economic Surve ...
from a private entity to a crown corporation.
One political response was a highly restrictive immigration policy and a rise in nativism.
 Times were especially hard in western Canada, where a full recovery did not occur until the Second World War began in 1939. One response was the creation of new political parties such as the Social Credit movement and the
Times were especially hard in western Canada, where a full recovery did not occur until the Second World War began in 1939. One response was the creation of new political parties such as the Social Credit movement and the Cooperative Commonwealth Federation
The Co-operative Commonwealth Federation (CCF; , FCC) was a federal democratic socialistThe following sources describe the CCF as a democratic socialist political party:
*
*
*
*
*
* and social-democraticThese sources describe the CCF as ...
, as well as popular protest in the form of the On-to-Ottawa Trek.
Statute of Westminster
Following theBalfour Declaration of 1926
The Balfour Declaration of 1926 was issued by the 1926 Imperial Conference of British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent t ...
, the British Parliament passed the Statute of Westminster in 1931 which acknowledged Canada as coequal with the United Kingdom and the other Commonwealth realms
A Commonwealth realm is a sovereign state in the Commonwealth of Nations that has the same constitutional monarch and head of state as the other realms. The current monarch is King Charles III. Except for the United Kingdom, in each of the ...
. It was a crucial step in the development of Canada as a separate state in that it provided for nearly complete legislative autonomy from the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Although the United Kingdom retained formal authority over certain Canadian constitutional changes, it relinquished this authority with the passing of the Canada Act 1982 which was the final step in achieving full sovereignty.
Second World War
 Canada's involvement in the Second World War began when Canada declared war on
Canada's involvement in the Second World War began when Canada declared war on Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
on September 10, 1939, delaying it one week after Britain acted to symbolically demonstrate independence. Canada played a major role in supplying food, raw materials, munitions and money to the hard-pressed British economy, training airmen for the Commonwealth, guarding the western half of the North Atlantic Ocean against German U-boat
U-boats are Submarine#Military, naval submarines operated by Germany, including during the World War I, First and Second World Wars. The term is an Anglicization#Loanwords, anglicized form of the German word , a shortening of (), though the G ...
s, and providing combat troops for the invasions of Italy, France and Germany in 1943–45.
Of a population of approximately 11.5 million, 1.1 million Canadians served in the armed forces in the Second World War. Many thousands more served with the Canadian Merchant Navy. In all, more than died, and another were wounded. Building up the Royal Canadian Air Force
The Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF; ) is the air and space force of Canada. Its role is to "provide the Canadian Forces with relevant, responsive and effective airpower". The RCAF is one of three environmental commands within the unified Can ...
was a high priority; it was kept separate from Britain's Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the Air force, air and space force of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. It was formed towards the end of the World War I, First World War on 1 April 1918, on the merger of t ...
. The British Commonwealth Air Training Plan Agreement, signed in December 1939, bound Canada, Britain, New Zealand, and Australia to a program that eventually trained half the airmen from those four nations in the Second World War.
The Battle of the Atlantic
The Battle of the Atlantic, the longest continuous military campaign in World War II, ran from 1939 to the defeat of Nazi Germany in 1945, covering a major part of the naval history of World War II. At its core was the Allies of World War II, ...
began immediately, and from 1943 to 1945 was led by Leonard W. Murray, from Nova Scotia. German U-boats operated in Canadian and Newfoundland waters throughout the war, sinking many naval and merchant vessels. The Canadian army
The Canadian Army () is the command (military formation), command responsible for the operational readiness of the conventional ground forces of the Canadian Armed Forces. It maintains regular forces units at bases across Canada, and is also re ...
was involved in the failed defence of Hong Kong, the unsuccessful Dieppe Raid in August 1942, the Allied invasion of Italy
The Allied invasion of Italy was the Allies of World War II, Allied Amphibious warfare, amphibious landing on mainland Italy that took place from 3 September 1943, during the Italian campaign (World War II), Italian campaign of World War II. T ...
, and the highly successful invasion of France and the Netherlands in 1944–45.
 On the political side, Mackenzie King rejected any notion of a government of national unity. The 1940 federal election was held as normally scheduled, producing another majority for the Liberals. The Conscription Crisis of 1944 greatly affected unity between French and English-speaking Canadians, though was not as politically intrusive as that of the First World War.
During the war, Canada became more closely linked to the U.S. The Americans took virtual control of Yukon in order to build the Alaska Highway, and were a major presence in the British colony of Newfoundland with major airbases. After the start of the war with Japan in December 1941, the government, in cooperation with the U.S., began the Japanese-Canadian internment, which sent British Columbia residents of Japanese descent to relocation camps far from the coast. The reason was intense public demand for removal and fears of espionage or sabotage. The government ignored reports from the RCMP and Canadian military that most of the Japanese were law-abiding and not a threat.
On the political side, Mackenzie King rejected any notion of a government of national unity. The 1940 federal election was held as normally scheduled, producing another majority for the Liberals. The Conscription Crisis of 1944 greatly affected unity between French and English-speaking Canadians, though was not as politically intrusive as that of the First World War.
During the war, Canada became more closely linked to the U.S. The Americans took virtual control of Yukon in order to build the Alaska Highway, and were a major presence in the British colony of Newfoundland with major airbases. After the start of the war with Japan in December 1941, the government, in cooperation with the U.S., began the Japanese-Canadian internment, which sent British Columbia residents of Japanese descent to relocation camps far from the coast. The reason was intense public demand for removal and fears of espionage or sabotage. The government ignored reports from the RCMP and Canadian military that most of the Japanese were law-abiding and not a threat.
Post-war era (1945–1960)
 Prosperity returned to Canada during the Second World War and continued in the following years, with the development of
Prosperity returned to Canada during the Second World War and continued in the following years, with the development of universal health care
Universal health care (also called universal health coverage, universal coverage, or universal care) is a health care system in which all residents of a particular country or region are assured access to health care. It is generally organized a ...
, old-age pensions, and veterans' pensions. The financial crisis of the Great Depression had led the Dominion of Newfoundland to relinquish responsible government in 1934 and become a crown colony ruled by a British governor. In 1948, the British government gave voters three Newfoundland Referendum choices: remaining a crown colony, returning to Dominion status (that is, independence), or joining Canada. The British and Canadian governments collaborated to ensure that joining the United States was not an option. After bitter debate Newfoundlanders voted to join Canada in 1949 as a province.
The foreign policy of Canada during the Cold War was closely tied to that of the United States. Canada was a founding member of NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO ; , OTAN), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental Transnationalism, transnational military alliance of 32 Member states of NATO, member s ...
(which Canada wanted to be a transatlantic economic and political union as well). In 1950, Canada sent combat troops to Korea during the Korean War
The Korean War (25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953) was an armed conflict on the Korean Peninsula fought between North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea; DPRK) and South Korea (Republic of Korea; ROK) and their allies. North Korea was s ...
as part of the United Nations forces. The federal government's desire to assert its territorial claims in the Arctic during the Cold War manifested with the High Arctic relocation, in which Inuit were moved from Nunavik (the northern third of Quebec) to barren Cornwallis Island; this project was later the subject of a long investigation by the Royal Commission on Aboriginal Peoples.
In 1956, the United Nations responded to the Suez Crisis
The Suez Crisis, also known as the Second Arab–Israeli War, the Tripartite Aggression in the Arab world and the Sinai War in Israel, was a British–French–Israeli invasion of Egypt in 1956. Israel invaded on 29 October, having done so w ...
by convening a United Nations Emergency Force to supervise the withdrawal of invading forces. The peacekeeping force was initially conceptualized by the Secretary of External Affairs and future Prime Minister Lester B. Pearson. Pearson was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize
The Nobel Peace Prize (Swedish language, Swedish and ) is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the Will and testament, will of Sweden, Swedish industrialist, inventor, and armaments manufacturer Alfred Nobel, along with the prizes in Nobe ...
in 1957 for his work in establishing the peacekeeping operation.
 Throughout the mid-1950s, prime ministers Louis St. Laurent and his successor
Throughout the mid-1950s, prime ministers Louis St. Laurent and his successor John Diefenbaker
John George Diefenbaker (September 18, 1895 – August 16, 1979) was the 13th prime minister of Canada, serving from 1957 to 1963. He was the only Progressive Conservative Party of Canada, Progressive Conservative party leader between 1930 an ...
attempted to create a new, highly advanced jet fighter, the Avro Arrow
The Avro Canada CF-105 Arrow was a Delta wing, delta-winged interceptor aircraft designed and built by Avro Canada. The CF-105 held the promise of Mach number, Mach 2 speeds at altitudes exceeding and was intended to serve as the Royal ...
. The controversial aircraft was cancelled by Diefenbaker in 1959. Diefenbaker instead purchased the BOMARC
The Boeing CIM-10 Bomarc ("Boeing Michigan Aeronautical Research Center") (IM-99 Weapon System prior to September 1962) was a supersonic ramjet powered long-range surface-to-air missile (SAM) used during the Cold War for the air defense of Nor ...
missile defence system and American aircraft. In 1958 Canada established (with the United States) the North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD).
There were voices on both left and right that warned against being too close to the United States. Few Canadians listened before 1957. Instead, there was wide consensus on foreign and defence policies from 1948 to 1957. Bothwell, Drummond and English state:
:That support was remarkably uniform geographically and racially, both coast to coast and among French and English. From the CCF on the left to the Social Credit on the right, the political parties agreed that NATO was a good thing, and communism a bad thing, that a close association with Europe was desirable, and that the Commonwealth embodied a glorious past.
However, the consensus did not last. By 1957 the Suez crisis alienated Canada from both Britain and France; politicians distrusted American leadership, businessmen questioned American financial investments; and intellectuals ridiculed the values of American television and Hollywood offerings that all Canadians watched. "Public support for Canada's foreign policy came unstuck. Foreign policy, from being a winning issue for the Liberals, was fast becoming a losing one."
1960–1981
In the 1960s, theQuiet Revolution
The Quiet Revolution () was a period of socio-political and socio-cultural transformation in French Canada, particularly in Quebec, following the 1960 Quebec general election. This period was marked by the secularization of the government, the ...
took place in Quebec, overthrowing the old establishment which centred on the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Quebec
The Archdiocese of Québec (; ) is a Latin Church ecclesiastical jurisdiction or archdiocese of the Catholic Church in Quebec, Canada. It is the oldest episcopal see in the New World north of Mexico and the Primate (bishop), primatial see of Can ...
and led to modernizing of the economy and society. Québécois nationalists demanded independence, and tensions rose until violence erupted during the 1970 October Crisis. John Saywell says, "The two kidnappings and the murder of Pierre Laporte were the biggest domestic news stories in Canada's history." In 1976 the Parti Québécois was elected to power in Quebec, with a nationalist vision that included securing French linguistic rights in the province and the pursuit of some form of sovereignty for Quebec. This culminated in the 1980 referendum in Quebec on the question of sovereignty-association, which was turned down by 59% of the voters.
In 1965, Canada adopted the maple leaf flag, although not without considerable debate and misgivings among large number of English Canadians. The World's Fair
A world's fair, also known as a universal exhibition, is a large global exhibition designed to showcase the achievements of nations. These exhibitions vary in character and are held in different parts of the world at a specific site for a perio ...
titled Expo 67 came to Montreal, coinciding with the Canadian Centennial that year. The fair opened on April 28, 1967, with the theme "Man and His World" and became the best attended of all BIE-sanctioned world expositions until that time.
Legislative restrictions on Canadian immigration that had favoured British and other European immigrants were amended in the 1960s, opening the doors to immigrants from all parts of the world. While the 1950s had seen high levels of immigration from Britain, Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelan ...
, Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, and northern continental Europe, by the 1970s immigrants increasingly came from India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
, Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
, Jamaica
Jamaica is an island country in the Caribbean Sea and the West Indies. At , it is the third-largest island—after Cuba and Hispaniola—of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean. Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, west of Hispaniola (the is ...
and Haiti
Haiti, officially the Republic of Haiti, is a country on the island of Hispaniola in the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and south of the Bahamas. It occupies the western three-eighths of the island, which it shares with the Dominican ...
. Immigrants of all backgrounds tended to settle in the major urban centres, particularly Toronto, Montreal and Vancouver.
During his long tenure in the office (1968–1979, 1980–1984), Prime Minister Pierre Trudeau
Joseph Philippe Pierre Yves Elliott Trudeau (October 18, 1919 – September 28, 2000) was a Canadian politician, statesman, and lawyer who served as the 15th prime minister of Canada from 1968 to 1979 and from 1980 to 1984. Between his no ...
made social and cultural change his political goals, including the pursuit of official bilingualism in Canada
The official languages of Canada are English and French, which "have equality of status and equal rights and privileges as to their use in all institutions of the Parliament and Government of Canada," according to Canada's constitution. "Offici ...
and plans for significant constitutional change. The west, particularly the petroleum-producing provinces like Alberta, opposed many of the policies emanating from central Canada, with the National Energy Program creating considerable antagonism and growing western alienation. Multiculturalism in Canada was adopted as the official policy of the Canadian government during the prime ministership of Pierre Trudeau.
1982–2000
 In 1981, the Canadian House of Commons and Senate passed a resolution requesting that the British Parliament enact a package of constitutional amendments which would end the last powers of the British Parliament to legislate for Canada and would create an entirely Canadian process for constitutional amendments. The resolution set out the text of the proposed Canada Act, which also included the text of the '' Constitution Act, 1982''. The British Parliament duly passed the Canada Act 1982, the Queen granting
In 1981, the Canadian House of Commons and Senate passed a resolution requesting that the British Parliament enact a package of constitutional amendments which would end the last powers of the British Parliament to legislate for Canada and would create an entirely Canadian process for constitutional amendments. The resolution set out the text of the proposed Canada Act, which also included the text of the '' Constitution Act, 1982''. The British Parliament duly passed the Canada Act 1982, the Queen granting Royal Assent
Royal assent is the method by which a monarch formally approves an act of the legislature, either directly or through an official acting on the monarch's behalf. In some jurisdictions, royal assent is equivalent to promulgation, while in othe ...
on March 29, 1982, 115 years to the day since Queen Victoria granted Royal Assent to the ''Constitution Act, 1867''. On April 17, 1982, the Queen signed the Proclamation on the grounds of Parliament Hill in Ottawa bringing the ''Constitution Act, 1982'' into force, thus patriating the Constitution of Canada.
Previously, the main portions of the constitution had existed only as an act passed of the British parliament, though under the constitutional convention recognised in the Balfour Declaration of 1926
The Balfour Declaration of 1926 was issued by the 1926 Imperial Conference of British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent t ...
, it could not be altered without Canadian consent. Canada had established complete sovereignty as an independent country, with the Queen's role as monarch of Canada separate from her role as the British monarch or the monarch of any of the other Commonwealth realms.
In addition to the enactment of a constitutional amending formula, the ''Constitution Act, 1982'' enacted the ''Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms
The ''Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms'' (), often simply referred to as the ''Charter'' in Canada, is a bill of rights entrenched in the Constitution of Canada, forming the first part of the '' Constitution Act, 1982''. The ''Char ...
''. The Charter is a constitutionally entrenched bill of rights which applies to both the federal government and the provincial governments, unlike the earlier '' Canadian Bill of Rights''. The patriation of the constitution was Trudeau's last major act as Prime Minister; he resigned in 1984.
 On June 23, 1985, Air India Flight 182 was destroyed above the Atlantic Ocean by a bomb on board exploding; all 329 on board were killed, of whom 280 were Canadian citizens. The Air India attack is the largest mass murder in Canadian history.
The Progressive Conservative (PC) government of
On June 23, 1985, Air India Flight 182 was destroyed above the Atlantic Ocean by a bomb on board exploding; all 329 on board were killed, of whom 280 were Canadian citizens. The Air India attack is the largest mass murder in Canadian history.
The Progressive Conservative (PC) government of Brian Mulroney
Martin Brian Mulroney (March 20, 1939 – February 29, 2024) was a Canadian lawyer, businessman, and politician who served as the 18th prime minister of Canada from 1984 to 1993.
Born in the eastern Quebec city of Baie-Comeau, Mulroney studi ...
began efforts to gain Quebec's support for the ''Constitution Act, 1982'' and end western alienation. In 1987, the Meech Lake Accord talks began between the provincial and federal governments, seeking constitutional changes favourable to Quebec. The failure of the Meech Lake Accord resulted in the formation of a separatist party, Bloc Québécois. The constitutional reform process under Prime Minister Mulroney culminated in the failure of the Charlottetown Accord which would have recognized Quebec as a " distinct society" but was rejected in 1992 by a narrow margin.
Under Brian Mulroney, relations with the United States began to grow more closely integrated. In 1986, Canada and the U.S. signed the "Acid Rain Treaty" to reduce acid rain. In 1989, the federal government adopted the Canada–United States Free Trade Agreement (Agreement) with the United States despite significant animosity from the Canadian public who were concerned about the economic and cultural impacts of close integration with the United States. The Agreement would later be replaced with the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) and its side agreement, the North American Agreement on Environmental Cooperation in 1994.
On July 11, 1990, the Oka Crisis land dispute began between the Mohawk people of Kanesatake and the adjoining town of Oka, Quebec. The dispute was the first of a number of well-publicized conflicts between First Nations and the Canadian government in the late 20th century. In August 1990, Canada was one of the first nations to condemn Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and ...
's invasion of Kuwait
The Iraqi invasion of Kuwait, codenamed Project 17, began on 2 August 1990 and marked the beginning of the Gulf War. After defeating the Kuwait, State of Kuwait on 4 August 1990, Ba'athist Iraq, Iraq went on to militarily occupy the country fo ...
, and it quickly agreed to join the U.S.-led coalition. Canada deployed destroyers and later a CF-18 Hornet squadron with support personnel, as well as a field hospital to deal with casualties.
Following Mulroney's resignation as prime minister in 1993, Kim Campbell took office and became Canada's first female prime minister. Campbell remained in office for only a few months: the 1993 election saw the collapse of the Progressive Conservative Party from government to two seats, while the Bloc Québécois became the official opposition. Prime Minister Jean Chrétien
Joseph Jacques Jean Chrétien (; born January 11, 1934) is a retired Canadian politician, statesman, and lawyer who served as the 20th prime minister of Canada from 1993 to 2003. He served as Leader of the Liberal Party of Canada, leader of t ...
of the Liberals took office in November 1993 with a majority government
A majority government is a government by one or more governing parties that hold an absolute majority of seats in a legislature. Such a government can consist of one party that holds a majority on its own, or be a coalition government of multi ...
and was re-elected with further majorities during the 1997
Events January
* January 1 – The Emergency Alert System is introduced in the United States.
* January 11 – Turkey threatens Cyprus on account of a deal to buy Russian S-300 missiles, prompting the Cypriot Missile Crisis.
* January 1 ...
and 2000 elections.
In 1995, the government of Quebec held a second referendum on sovereignty that was rejected by a margin of 50.6% to 49.4%. In 1998, the Canadian Supreme Court ruled unilateral secession by a province to be unconstitutional, and Parliament passed the '' Clarity Act'' outlining the terms of a negotiated departure.
2001–present
Environmental issues increased in importance in Canada during the late 90s, resulting in the signing of the Kyoto Accord on climate change by Canada's Liberal government in 2002. The accord was in 2007 nullified by Prime Minister Stephen Harper's Conservative government, which proposed a "made-in-Canada" solution to climate change. Canada became the fourth country in the world and the first country in the Americas to legalize same-sex marriage nationwide with the enactment of the '' Civil Marriage Act'' in 2005. Court decisions, starting in 2003, had already legalized
Canada became the fourth country in the world and the first country in the Americas to legalize same-sex marriage nationwide with the enactment of the '' Civil Marriage Act'' in 2005. Court decisions, starting in 2003, had already legalized same-sex marriage
Same-sex marriage, also known as gay marriage, is the marriage of two people of the same legal Legal sex and gender, sex. marriage between same-sex couples is legally performed and recognized in 38 countries, with a total population of 1.5 ...
in eight out of ten provinces and one of three territories. Before the passage of the act, more than 3,000 same-sex couples had married in these areas.
The Canadian Alliance and PC Party merged into the Conservative Party of Canada
The Conservative Party of Canada (CPC; , ), sometimes referred to as the Tories, is a Government of Canada, federal List of political parties in Canada, political party in Canada. It was formed in 2003 by the merger of the two main Right-wing ...
in 2003, ending a 13-year division of the conservative vote. The party was elected twice as a minority government under the leadership of Stephen Harper in the 2006 federal election and 2008 federal election. Harper's Conservative Party won a majority in the 2011 federal election with the New Democratic Party under Jack Layton forming the Official Opposition for the first time.
Under Harper, Canada and the United States continued to integrate state and provincial agencies to strengthen security along the Canada–United States border through the Western Hemisphere Travel Initiative. From 2002 to 2011, Canada was involved in the Afghanistan War as part of the U.S. stabilization force and the NATO-commanded International Security Assistance Force
The International Security Assistance Force (ISAF) was a multinational military mission in Afghanistan from 2001 to 2014. It was established by United Nations Security Council United Nations Security Council Resolution 1386, Resolution 1386 ac ...
. In July 2010, the largest purchase in Canadian military history, totalling billion for the acquisition of 65 F-35 fighters, was announced by the federal government. Canada is one of several nations that assisted in the development of the F-35 and has invested over in the program.
In 2008, the Government of Canada formally apologized to the indigenous peoples of Canada for the residential school system and the damage it caused. The government set up the Truth and Reconciliation Commission of Canada
The Truth and Reconciliation Commission of Canada (TRC; []) was a truth and reconciliation commission active in Canada from 2008 to 2015, organized by the parties of the Indian Residential Schools Settlement Agreement.
The commission was offi ...
that year to document the damage caused by the residential school system and the reconciliation needed to proceed into the future. It provided a "call to action" report in 2015.
On 19 October 2015, Stephen Harper's Conservatives were defeated by a newly resurgent Liberal party under the leadership of Justin Trudeau and which had been reduced to third-party status in the 2011 elections.
Multiculturalism (cultural and ethnic diversity) has been emphasized in recent decades. Ambrose and Mudde conclude that: "Canada's unique multiculturalism policy ... which is based on a combination of selective immigration, comprehensive integration, and strong state repression of dissent on these policies. This unique blend of policies has led to a relatively low level of opposition to multiculturalism".
In 2013, the consumption of cannabis
''Cannabis'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae that is widely accepted as being indigenous to and originating from the continent of Asia. However, the number of species is disputed, with as many as three species be ...
for medical reasons was legalized. In October 2018, the Canadian government under Justin Trudeau passed the '' Cannabis Act'', legalizing the recreational use and sale of cannabis. Under the new law, Canadians could consume cannabis and cannabis products in public, grow limited numbers of plants themselves, pardons for simple possession convictions were promised, while drivers could not have any traces of THC in their blood.
From January 2020 to May 2022, Canada was greatly impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
, which caused over 40,000 deaths in the country, the third highest mortality toll in North America (behind the United States and Mexico).
On 28 April 2025, Mark Carney's Liberals secured a third consecutive minority government, beating Pierre Poilievre's Conservatives, a Liberal upset largely attributed to a rise in Canadian patriotism following United States President Donald Trump
Donald John Trump (born June 14, 1946) is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who is the 47th president of the United States. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he served as the 45 ...
's threats to annex Canada and announcement of tariffs against the country.
Historiography
The Conquest of New France has always been a central and contested theme of Canadian memory. Cornelius Jaenen argues: :The Conquest has remained a difficult subject for French-Canadian historians because it can be viewed either as economically and ideologically disastrous or as a providential intervention to enable Canadians to maintain their language and religion under British rule. For virtually all Anglophone historians it was a victory for British military, political, and economic superiority which would eventually only benefit the conquered. Historians of the 1950s tried to explain the economic inferiority of the French Canadians by arguing that the Conquest: At the other pole, are those Francophone historians who see the positive benefit of enabling the preservation of language, religion, and traditional customs under British rule. French-Canadian debates have escalated since the 1960s, as the Conquest is seen as a pivotal moment in the history of Quebec's nationalism. Historian Jocelyn Létourneau suggested in the 21st century, "1759 does not belong primarily to a past that we might wish to study and understand, but, rather, to a present and a future that we might wish to shape and control." Anglophone historians, on the other hand, portray the Conquest as a victory for British military, political and economic superiority that was a permanent benefit to the French. Allan Greer argues that Whig history was once the dominant style of scholars. He says the: :interpretive schemes that dominated Canadian historical writing through the middle decades of the twentieth century were built on the assumption that history had a discernible direction and flow. Canada was moving towards a goal in the nineteenth century; whether this endpoint was the construction of a transcontinental, commercial, and political union, the development of parliamentary government, or the preservation and resurrection of French Canada, it was certainly a Good Thing. Thus the rebels of 1837 were quite literally on the wrong track. They lost because they ''had'' to lose; they were not simply overwhelmed by superior force, they were justly chastised by the God of History.See also
* List of Canadian historians * Canadian studies ;National historic significance * Events of National Historic Significance * National Historic Sites of Canada * Persons of National Historic Significance ;History by topic * Constitutional history of Canada * Economic history of Canada * History of Canadian newspapers * History of Canadian sports * History of cities in Canada * History of education in Canada * History of medicine in Canada * History of rail transport in Canada * Social history of Canada * Orange Order in Canada * Anti-Quebec sentiment * Acadian Renaissance ;Academia * Canadian Journal of History * Canadian Historical Review * Journal of Canadian Studies;:Media * Heritage Minutes * History Trek, Canadian History web portal designed for childrenReferences
Further reading
* For an annotated bibliography and evaluation of major books, see ''Canada: A Reader's Guide,'' (2nd ed., 2000) by J. André Senécalonline
, 91pp. * Argyle, Ray, ''Turning Points: The campaigns that changed Canada, 2004 and before.'' (2004) Scholarly analysis of 15 major national and provincial elections from 1866 to 2004
online
* Black, Conrad. ''Rise to Greatness: The History of Canada From the Vikings to the Present'' (2014), 1120p
excerpt
* Brown, Craig, ed. ''Illustrated History of Canada'' (McGill-Queen's Press-MQUP, 2012), Chapters by experts * Bumsted, J.M. ''The Peoples of Canada: A Pre-Confederation History''; ''The Peoples of Canada: A Post-Confederation History'' (2 vol. 2014), University textbook * ''Chronicles of Canada Series'' (32 vol. 1915–1916) edited by G. M. Wrong and H. H. Langto
online detailed popular history
* Conrad, Margaret, Alvin Finkel and Donald Fyson. ''Canada: A History'' (Toronto: Pearson, 2012) * * * Granatstein, J. L. ''Prime ministers: Ranking Canada's leaders'' (1999
online
evaluates all 20 prime ministers from 1867 to 1999. * Granatstein, J. L., and Dean F. Oliver, eds. ''The Oxford Companion to Canadian Military History,'' (2011
online review
* * * McNaught, Kenneth. ''The Penguin History of Canada'' (Penguin books, 1988) * * * Norrie, Kenneth, Douglas Owram and J.C. Herbert Emery. (2002) ''A History of the Canadian Economy'' (4th ed. 2007) * * Stacey, C. P. ''Arms, Men and Governments: The War Policies of Canada 1939–1945'' (1970), the standard scholarly history of WWII policies
online free
Scholarly article collections
* Bumsted, J. M. and Len Keffert, eds. ''Interpreting Canada's Past'' (2 vol. 2011) * Conrad, Margaret and Alvin Finkel, eds. ''Nation and Society: Readings in Pre-Confederation Canadian History''; ''Nation and Society: Readings in Post-Confederation Canadian History'' (2nd ed. 2008) * Francis, R. Douglas and Donald B Smith, eds. ''Readings in Canadian History'' (7th ed. 2006)Primary sources and statistics
* Bliss, J.W.M. ''Canadian history in documents, 1763–1966'' (1966), 390pponline free
* Crowe, Harry S. et al. eds ''A Source-Book of Canadian History: Selected Documents and Personal Papers'' (1964) 508pp
online
* ; 707pp * Leacy, F.H. ed. ''Historical statistics of Canada'' (2nd ed. Ottawa: Statistics Canada, 1983). 800 p.
online
* Stewart Reid, J.H. ; et al., eds. (1964). ''A Source-book of Canadian History: Selected Documents and Personal Papers'' (Longmans Canada
online
484pp; primary sources on more than 200 topics * Talman, James J. and Louis L. Snyder, eds. ''Basic Documents in Canadian History'' (1959
online
192 pp * Thorner, Thomas ed. '' "A few acres of snow" : documents in pre-confederation Canadian history'' (2nd ed. 2003)
online free to borrow
** Thorner, Thomas ed. ''A country nourished on self-doubt : documents in post-confederation Canadian history'' (2nd ed 2003)
online free
Historiography
* Berger, Carl. ''Writing Canadian History: Aspects of English Canadian Historical Writing since 1900'' (2nd ed. 1986), 364pp evaluates the work of most of the leading 20th century historians of Canada. * Careless, J. M. S. "Canadian Nationalism – Immature or Obsolete?" ''Report of the Annual Meeting of the Canadian Historical Association / Rapports annuels de la Société historique du Canada'' (1954) 33#1 pp: 12–19online
* McKercher, Asa, and Philip Van Huizen, eds. ''Undiplomatic History: The New Study of Canada and the World'' (2019
excerpt
* Muise D. A. ed. '' A Reader's Guide to Canadian History: 1, Beginnings to Confederation (1982); '' (1982) Topical articles by leading scholars ** Granatstein J.L. and Paul Stevens, ed. ''A Reader's Guide to Canadian History: vol 2: Confederation to the present'' (1982), Topical articles by leading scholars * ; essays by experts evaluate the scholarly literature ** ; essays by experts evaluate the scholarly literature * Rich, E. E. "Canadian History." ''Historical Journal'' 14#4 (1971): 827–52
online
External links
''The Canadian Encyclopedia''
National Historic Sites of Canada
(archived June 5, 2011)
– Guide to the Sources (archived August 21, 2014)
The Quebec History encyclopedia
by Marianopolis College
The Historica-Dominion Institute
includes Heritage Minutes (archived January 1, 2012)
H-CANADA, daily academic discussion email list
Canadian History & Knowledge
– Association for Canadian Studies
Baldwin Collection of Canadiana
at Toronto Public Library {{DEFAULTSORT:History of Canada