|
Invasion Of Normandy
Operation Overlord was the codename for the Battle of Normandy, the Allied operation that launched the successful liberation of German-occupied Western Europe during World War II. The operation was launched on 6 June 1944 ( D-Day) with the Normandy landings (Operation Neptune). A 1,200-plane airborne assault preceded an amphibious assault involving more than 5,000 vessels. Nearly 160,000 troops crossed the English Channel on 6 June, and more than two million Allied troops were in France by the end of August. The decision to undertake cross-channel landings in 1944 was made at the Trident Conference in Washington in May 1943. American General Dwight D. Eisenhower was appointed commander of Supreme Headquarters Allied Expeditionary Force, and British General Bernard Montgomery was named commander of the 21st Army Group, which comprised all the land forces involved in the operation. The Normandy coast in northwestern France was chosen as the site of the landings, with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Front (World War II)
The Western Front was a European theatre of World War II, military theatre of World War II encompassing Denmark, Norway, Luxembourg, Belgium, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, French Third Republic, France, and Nazi Germany, Germany. The Italian campaign (World War II), Italian front is considered a separate but related theatre. The Western Front's 1944–1945 phase was officially deemed the European Theater of Operations, United States Army, European Theater by the United States, whereas Italy fell under the Mediterranean Theater of Operations, United States Army, Mediterranean Theater along with the North African campaign. The Western Front was marked by two phases of large-scale combat operations. The first phase saw the capitulation of Luxembourg, Netherlands, Belgium, and France during May and June 1940 after their defeat in the Low Countries and the northern half of France, and continued into an air war between Germany and Britain that climaxed with the Battle of Brita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernard Montgomery
Field Marshal Bernard Law Montgomery, 1st Viscount Montgomery of Alamein (; 17 November 1887 – 24 March 1976), nicknamed "Monty", was a senior British Army officer who served in the First World War, the Irish War of Independence and the Second World War. Montgomery first saw action in the First World War as a junior officer of the Royal Warwickshire Regiment. At Méteren, near the Belgian border at Bailleul, he was shot through the right lung by a sniper, during the First Battle of Ypres. On returning to the Western Front as a general staff officer, he took part in the Battle of Arras in AprilMay 1917. He also took part in the Battle of Passchendaele in late 1917 before finishing the war as chief of staff of the 47th (2nd London) Division. In the inter-war years he commanded the 17th (Service) Battalion, Royal Fusiliers and, later, the 1st Battalion, Royal Warwickshire Regiment before becoming commander of the 9th Infantry Brigade and then general officer comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normandy Landings
The Normandy landings were the landing operations and associated airborne operations on 6 June 1944 of the Allies of World War II, Allied invasion of Normandy in Operation Overlord during the Second World War. Codenamed Operation Neptune and often referred to as D-Day (after D-Day (military term), the military term), it is the largest seaborne invasion in history. The operation began the liberation of France, and the rest of Western Europe, and laid the foundations of the Allied victory on the Western Front (World War II), Western Front. Planning for the operation began in 1943. In the months leading up to the invasion, the Allies conducted a substantial military deception, codenamed Operation Bodyguard, to mislead the Germans as to the date and location of the main Allied landings. The weather on the day selected for D-Day was not ideal, and the operation had to be delayed 24 hours; a further postponement would have meant a delay of at least two weeks, as the planners had re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D-Day (military Term)
The Normandy landings were the landing operations and associated airborne operations on 6 June 1944 of the Allied invasion of Normandy in Operation Overlord during the Second World War. Codenamed Operation Neptune and often referred to as D-Day (after the military term), it is the largest seaborne invasion in history. The operation began the liberation of France, and the rest of Western Europe, and laid the foundations of the Allied victory on the Western Front. Planning for the operation began in 1943. In the months leading up to the invasion, the Allies conducted a substantial military deception, codenamed Operation Bodyguard, to mislead the Germans as to the date and location of the main Allied landings. The weather on the day selected for D-Day was not ideal, and the operation had to be delayed 24 hours; a further postponement would have meant a delay of at least two weeks, as the planners had requirements for the phase of the moon, the tides, and time of day, that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Overlord
Operation Overlord was the codename for the Battle of Normandy, the Allies of World War II, Allied operation that launched the successful liberation of German-occupied Western Front (World War II), Western Europe during World War II. The operation was launched on 6 June 1944 (D-Day (military term), D-Day) with the Normandy landings (Operation Neptune). A 1,200-plane Airborne forces, airborne assault preceded an amphibious warfare, amphibious assault involving more than 5,000 vessels. Nearly 160,000 troops crossed the English Channel on 6 June, and more than two million Allied troops were in France by the end of August. The decision to undertake cross-channel landings in 1944 was made at the Washington Conference (1943), Trident Conference in Washington, D.C., Washington in May 1943. American General Dwight D. Eisenhower was appointed commander of Supreme Headquarters Allied Expeditionary Force, and British General Bernard Montgomery was named commander of the 21st Army Group, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Model
Otto Moritz Walter Model (; 24 January 1891 – 21 April 1945) was a German during World War II. Although he was a hard-driving, aggressive panzer commander early in the war, Model became best known as a practitioner of defensive warfare. His relative success as commander of the 9th Army (Wehrmacht), Ninth Army in the battles of 1941–1942 determined his future career path. Model first came to Hitler's, Hitler's attention before World War II, but their relationship did not become especially close until 1942. His tenacious style of fighting and loyalty to the Nazi regime won him plaudits from Hitler, who considered him one of his best field commanders and repeatedly sent him to salvage apparently desperate situations on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front as commander of Army Group North, Army Group North Ukraine and Army Group Centre. In August 1944 Model was sent to the Western Front (World War II), Western Front as commander of OB West and Army Group B. His r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Group B
Army Group B () was the name of four distinct German Army Group, army group commands that saw action during World War II. The first Army Group B was created on 12 October 1939 (from the former Army Group North) and fought in the Battle of France on the northern flank. It was responsible for a part of the German invasion of Belgium (1940), German invasion of Belgium and the majority of the German invasion of the Netherlands. In the later stage of that campaign ("Fall Rot, Case Red"), it again advanced on the German right flank towards the Somme (river), Somme river, the city of Paris and the France–Spain border, Franco-Spanish border. After 16 August 1940, it was deployed to East Prussia and to the General Government in Occupation of Poland (1939–1945), German-occupied Poland. When Operation Barbarossa began on 22 June 1941, Army Group B was renamed on the same day to become "Army Group Center". The second Army Group B came into existence on 9 July 1942, when Army Group South ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
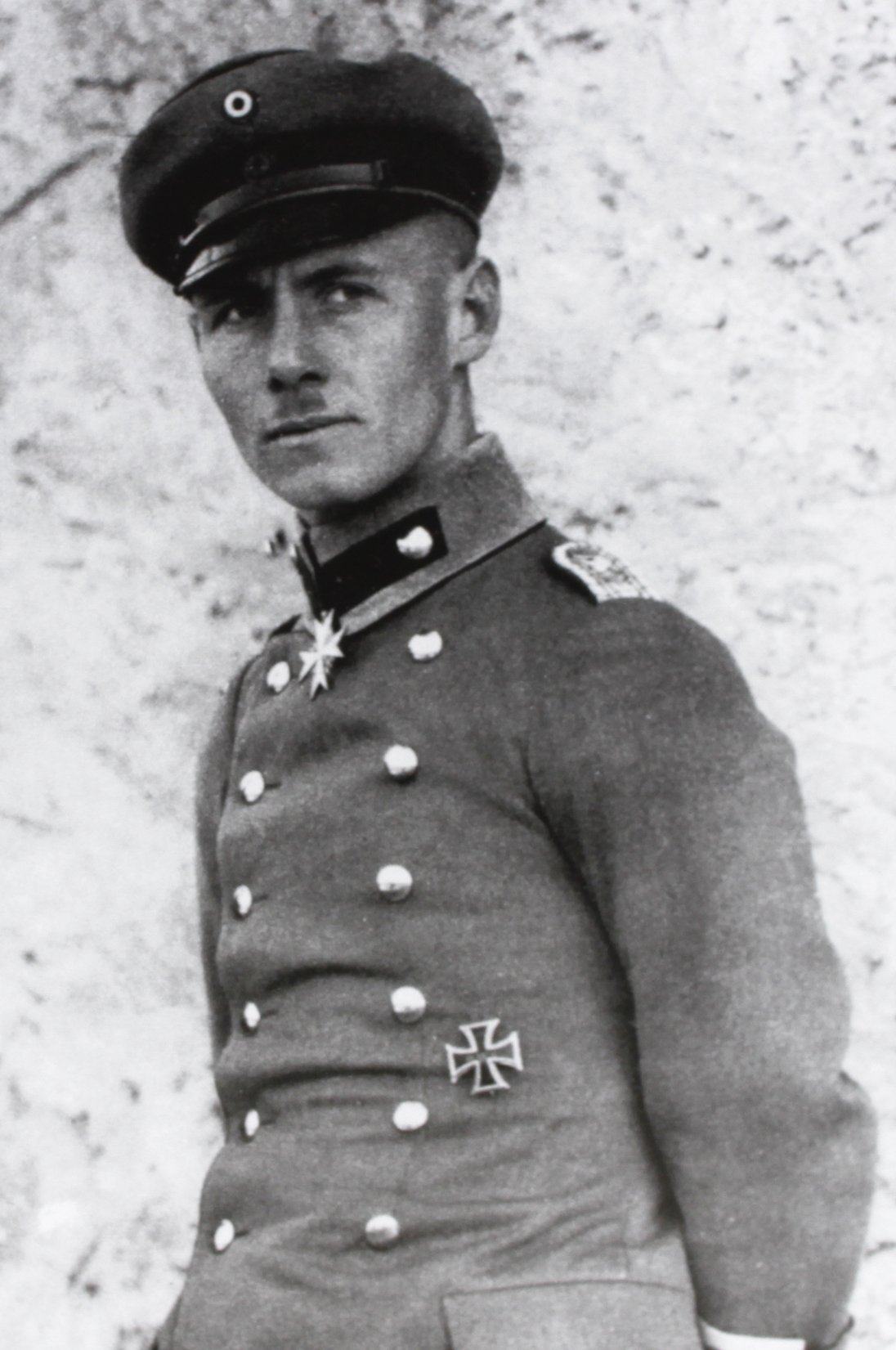
Erwin Rommel
Johannes Erwin Eugen Rommel (; 15 November 1891 – 14 October 1944), popularly known as The Desert Fox (, ), was a German '' Generalfeldmarschall'' (field marshal) during World War II. He served in the ''Wehrmacht'' (armed forces) of Nazi Germany, as well as in the ''Reichswehr'' of the Weimar Republic, and the army of Imperial Germany. Rommel was a highly decorated officer in World War I and was awarded the ''Pour le Mérite'' for his actions on the Italian Front. In 1937, he published his classic book on military tactics, '' Infantry Attacks'', drawing on his experiences in that war. In World War II, he commanded the 7th Panzer Division during the 1940 invasion of France. His leadership of German and Italian forces in the North African campaign established his reputation as one of the ablest tank commanders of the war, and earned him the nickname ''der Wüstenfuchs'', "the Desert Fox". Among his British adversaries he had a reputation for chivalry, and his phrase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Günther Von Kluge
Günther Adolf Ferdinand von Kluge (30 October 1882 – 19 August 1944) was a German '' Generalfeldmarschall'' (Field Marshal) during World War II who held commands on both the Eastern and Western Fronts, until his suicide in connection with the 20 July plot. He commanded the 4th Army of the Wehrmacht during the invasion of Poland in 1939 and the Battle of France in 1940, earning a promotion to Generalfeldmarschall. Kluge went on to command the 4th Army in Operation Barbarossa (the invasion of the Soviet Union) and the Battle for Moscow in 1941. Amid the crisis of the Soviet counter-offensive in December 1941, Kluge was promoted to command Army Group Centre replacing Field Marshal Fedor von Bock. Several members of the German military resistance to Adolf Hitler served on his staff, including Henning von Tresckow. Kluge was aware of the plotters' activities but refused to offer his support unless Hitler was killed. His command on the Eastern Front lasted until October 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OB West
''Oberbefehlshaber West'' ( German: initials ''OB West'') (German: "Commander-in-Chief n theWest") was the overall commander of the '' Westheer'', the German armed forces on the Western Front during World War II. It was directly subordinate to the Oberkommando der Wehrmacht (the German armed forces High Command). The area under the command of the OB West varied as the war progressed. At its furthest extent, it reached the French Atlantic coast. By the end of World War II in Europe, it was reduced to commanding troops in Bavaria Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total l .... Commanders Order of battle from June 1944 to January 1945 Notes References Oberbefehlshaber West, German Army, 06.06.1944{More citations needed, date=April 2021 German High Command during W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerd Von Rundstedt
Karl Rudolf Gerd von Rundstedt (12 December 1875 – 24 February 1953) was a German ''Generalfeldmarschall'' (Field Marshal) in the ''German Army (1935–1945), Heer'' (Army) of Nazi Germany and OB West, ''Oberbefehlshaber West'' (Commander-in-Chief in the West) during World War II. At the end of the war, aged 69, with over 52 years of service, he was the Army's most senior officer. Born into a Prussian family with a long military tradition, Rundstedt entered the Prussian Army in 1892. During World War I, he served mainly as a staff officer. In the interwar period, he continued his military career, reaching the rank of (Colonel General) before retiring in 1938. He was recalled at the beginning of World War II as commander of Army Group South in the invasion of Poland. He commanded Army Group A during the Battle of France, and requested the Halt Order during the Battle of Dunkirk. He was 1940 Field Marshal Ceremony, promoted to the rank of Field Marshal in 1940. In the inva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Führer
( , spelled ''Fuehrer'' when the umlaut is unavailable) is a German word meaning "leader" or " guide". As a political title, it is strongly associated with Adolf Hitler, the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 to 1945. Hitler officially called himself ''der Führer und Reichskanzler'' (the Leader and Chancellor of the Reich) after the death of President Paul von Hindenburg in 1934, as well as the subsequent merging of the offices of ''Reichspräsident'' and '' Reichskanzler''. Nazi Germany cultivated the ("leader principle"), and Hitler was generally known as simply ("the Leader"). In compound words, the use of remains common in German and is used in words such as ( travel guide), ( museum docent), ( mountain guide), or (leader of the opposition). However, because of its strong association with Hitler, the isolated word itself usually has negative connotations when used with the meaning of "leader", especially in political contexts. The word has cognates in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |