Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a
contagious disease
A contagious disease is an infectious disease that can be spread rapidly in several ways, including direct contact, indirect contact, and droplet contact.
These diseases are caused by organisms such as parasites, bacteria, fungi, and viruses. ...
caused by the
coronavirus
Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the comm ...
SARS-CoV-2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19, the respiratory illness responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. The virus previously had the Novel coronavirus, provisional nam ...
. In January 2020, the disease spread worldwide, resulting in the
COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
.
The
symptoms of COVID‑19
The symptoms of COVID-19 are variable depending on the Covid variant, type of variant contracted, ranging from mild symptoms to a potentially fatal illness. Common symptoms include coughing, fever, Anosmia, loss of smell (anosmia) and Ageusia ...
can vary but often include fever, fatigue, cough,
breathing difficulties
Shortness of breath (SOB), known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that ...
,
loss of smell, and
loss of taste
Ageusia (from negative prefix ''a-'' and Ancient Greek ''γεῦσις'' geûsis 'taste') is the loss of taste functions of the tongue, particularly the inability to detect sweetness, sourness, bitterness, saltiness, and umami (meaning 'savory t ...
. Symptoms may begin one to fourteen days
after exposure to the virus. At least a third of people who are infected
do not develop noticeable symptoms. Of those who develop symptoms noticeable enough to be classified as patients, most (81%) develop mild to moderate symptoms (up to mild
pneumonia
Pneumonia is an Inflammation, inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of Cough#Classification, productive or dry cough, ches ...
), while 14% develop severe symptoms (
dyspnea
Shortness of breath (SOB), known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that ...
,
hypoxia, or more than 50% lung involvement on imaging), and 5% develop critical symptoms (
respiratory failure
Respiratory failure results from inadequate gas exchange by the respiratory system, meaning that the arterial oxygen, carbon dioxide, or both cannot be kept at normal levels. A drop in the oxygen carried in the blood is known as hypoxemia; a r ...
,
shock
Shock may refer to:
Common uses
Healthcare
* Acute stress reaction, also known as psychological or mental shock
** Shell shock, soldiers' reaction to battle trauma
* Circulatory shock, a medical emergency
** Cardiogenic shock, resulting from ...
, or
multiorgan dysfunction).
Older people have a higher risk of developing severe symptoms. Some complications result in death. Some people continue to experience a range of effects (
long COVID
Long may refer to:
Measurement
* Long, characteristic of something of great duration
* Long, characteristic of something of great length
* Longitude (abbreviation: long.), a geographic coordinate
* Longa (music), note value in early music mens ...
) for months or years after infection, and damage to organs has been observed.
Multi-year studies on the long-term effects are ongoing.
occurs when infectious particles are breathed in or come into contact with the eyes, nose, or mouth. The risk is highest when people are in close proximity, but small
airborne particles containing the virus can remain suspended in the air and travel over longer distances, particularly indoors. Transmission can also occur when people touch their eyes, nose, or mouth after touching surfaces or objects that have been contaminated by the virus. People remain contagious for up to 20 days and can spread the virus even if they do not develop symptoms.
Testing methods for COVID-19 to detect the virus's
nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are large biomolecules that are crucial in all cells and viruses. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomer components: a pentose, 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main classes of nuclei ...
include real-time
reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is a laboratory technique combining reverse transcription of RNA into DNA (in this context called complementary DNA or cDNA) and amplification of specific DNA targets using polymerase cha ...
(RTPCR),
transcription-mediated amplification
Transcription-mediated amplification (TMA) is an isothermal (performed at constant temperature), single-tube nucleic acid Gene_duplication#As_amplification, amplification system utilizing two enzymes, RNA polymerase and reverse transcriptase.
"Am ...
,
and
(RTLAMP)
from a
nasopharyngeal swab
A nasopharyngeal swab is a device used for collecting a sample of Mucus#Respiratory system, nasal secretions from the back of the nose and throat. The sample is then analyzed for the presence of organisms or other clinical markers for disease. Th ...
.
Several
COVID-19 vaccine
A COVID19 vaccine is a vaccine intended to provide acquired immunity against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 ( COVID19).
Knowledge about the structure and fun ...
s have been approved and distributed in various countries, many of which have initiated
mass vaccination campaigns. Other
preventive measure
In simple terms, risk is the possibility of something bad happening. Risk involves uncertainty about the effects/implications of an activity with respect to something that humans value (such as health, well-being, wealth, property or the environ ...
s include physical or
social distancing
In public health, social distancing, also called physical distancing, (NB. Regula Venske is president of the PEN Centre Germany.) is a set of non-pharmaceutical interventions or measures intended to prevent the spread of a contagious dise ...
,
quarantining
A quarantine is a restriction on the movement of people, animals, and goods which is intended to prevent the spread of disease or pests. It is often used in connection to disease and illness, preventing the movement of those who may have been ...
, ventilation of indoor spaces,
use of face masks or coverings in public, covering coughs and sneezes,
hand washing
Hand washing (or handwashing), also known as hand hygiene, is the act of cleaning one's hands with soap, soap or handwash and water to remove viruses, bacteria, microorganisms, dirt, grease, and other harmful or unwanted substances stuck to th ...
, and keeping unwashed hands away from the face. While
drugs have been developed to inhibit the virus, the primary
treatment is still
symptomatic
Signs and symptoms are diagnostic indications of an illness, injury, or condition.
Signs are objective and externally observable; symptoms are a person's reported subjective experiences.
A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature ...
, managing the disease through
supportive care
Symptomatic treatment, supportive care, supportive therapy, or palliative treatment is any medical therapy of a disease that only affects its symptoms, not the underlying cause. It is usually aimed at reducing the signs and symptoms for the co ...
,
isolation, and
experimental measures.
The first known case was
identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019.
Most scientists believe that the SARS-CoV-2 virus entered into human populations through natural
zoonosis
A zoonosis (; plural zoonoses) or zoonotic disease is an infectious disease of humans caused by a pathogen (an infectious agent, such as a virus, bacterium, parasite, fungi, or prion) that can jump from a non-human vertebrate to a human. When ...
, similar to the
SARS-CoV-1
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 1 (SARS-CoV-1), previously known as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV), is a strain (biology), strain of coronavirus that causes severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), the ...
and
MERS-CoV
Middle East respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus (MERS-CoV, ''Betacoronavirus cameli'') or EMC/2012 ( HCoV-EMC/2012), is the virus that causes Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS). It is a species of coronavirus which infects humans, ba ...
outbreaks, and consistent with other pandemics in human history.
Social and environmental factors including
climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
,
natural ecosystem destruction and
wildlife trade
Wildlife trade refers to the exchange of products derived from non-domesticated animals or plants usually extracted from their natural environment or raised under controlled conditions. It can involve the trade of living or dead individuals, tis ...
increased the likelihood of such
zoonotic spillover.
Nomenclature
During the initial outbreak in
Wuhan
Wuhan; is the capital of Hubei, China. With a population of over eleven million, it is the most populous city in Hubei and the List of cities in China by population, eighth-most-populous city in China. It is also one of the nine National cent ...
, the virus and disease were commonly referred to as "coronavirus" and "Wuhan coronavirus", with the disease sometimes called "Wuhan pneumonia". In the past, many diseases have been named after geographical locations, such as the
Spanish flu
The 1918–1920 flu pandemic, also known as the Great Influenza epidemic or by the common misnomer Spanish flu, was an exceptionally deadly global influenza pandemic caused by the H1N1 subtype of the influenza A virus. The earliest docum ...
,
Middle East respiratory syndrome
Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) is a viral respiratory infection caused by '' Middle East respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus'' (MERS-CoV). Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe depending on age and risk level. Typi ...
, and
Zika virus
Zika virus (ZIKV; pronounced or ) is a member of the virus family ''Flaviviridae''. It is spread by daytime-active ''Aedes'' mosquitoes, such as '' A. aegypti'' and '' A. albopictus''. Its name comes from the Ziika Forest of Uganda, where ...
.
In January 2020, the
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
(WHO) recommended 2019-nCoV and 2019-nCoV acute respiratory disease as interim names for the virus and disease per 2015 guidance and international guidelines against using geographical locations or groups of people in disease and virus names to prevent
social stigma
Stigma, originally referring to the visible marking of people considered inferior, has evolved to mean a negative perception or sense of disapproval that a society places on a group or individual based on certain characteristics such as their ...
.
The official names COVID‑19 and SARS-CoV-2 were issued by the WHO on 11 February 2020 with COVID-19 being shorthand for "coronavirus disease 2019".
The WHO additionally uses "the COVID‑19 virus" and "the virus responsible for COVID‑19" in public communications.
Symptoms and signs
Complications

Complications may include
pneumonia
Pneumonia is an Inflammation, inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of Cough#Classification, productive or dry cough, ches ...
,
acute respiratory distress syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a type of respiratory failure characterized by rapid onset of widespread inflammation in the lungs. Symptoms include shortness of breath (dyspnea), rapid breathing (tachypnea), and bluish skin co ...
(ARDS),
multi-organ failure
Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) is altered organ function in an acutely ill patient requiring immediate medical intervention.
There are different stages of organ dysfunction for certain different organs, both in acute and in chronic o ...
,
septic shock
Septic shock is a potentially fatal medical condition that occurs when sepsis, which is organ injury or damage in response to infection, leads to dangerously low blood pressure and abnormalities in cellular metabolism. The Third International C ...
, and death.
Cardiovascular complications may include heart failure,
arrhythmia
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, are irregularities in the cardiac cycle, heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. Essentially, this is anything but normal sinus rhythm. A resting heart rate that is too fast – ab ...
s (including
atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (AF, AFib or A-fib) is an Heart arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia) characterized by fibrillation, rapid and irregular beating of the Atrium (heart), atrial chambers of the heart. It often begins as short periods ...
),
heart inflammation,
thrombosis
Thrombosis () is the formation of a Thrombus, blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel (a vein or an artery) is injured, the body uses platelets (thrombocytes) and fib ...
, particularly
venous thromboembolism
Venous thrombosis is the blockage of a vein caused by a thrombus (blood clot). A common form of venous thrombosis is deep vein thrombosis (DVT), when a blood clot forms in the deep veins. If a thrombus breaks off ( embolizes) and flows to the lun ...
,
and endothelial cell injury and dysfunction. Approximately 20–30% of people who present with COVID‑19 have
elevated liver enzymes
In medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for patients, managing the Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injur ...
, reflecting liver injury.
Neurologic manifestations include
seizure
A seizure is a sudden, brief disruption of brain activity caused by abnormal, excessive, or synchronous neuronal firing. Depending on the regions of the brain involved, seizures can lead to changes in movement, sensation, behavior, awareness, o ...
, stroke,
encephalitis
Encephalitis is inflammation of the Human brain, brain. The severity can be variable with symptoms including reduction or alteration in consciousness, aphasia, headache, fever, confusion, a stiff neck, and vomiting. Complications may include se ...
, and
Guillain–Barré syndrome
Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS) is a rapid-onset Paralysis, muscle weakness caused by the immune system damaging the peripheral nervous system. Typically, both sides of the body are involved, and the initial symptoms are changes in sensation ...
(which includes
loss of motor functions).
Following the infection, children may develop
paediatric multisystem inflammatory syndrome
Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C), or paediatric inflammatory multisystem syndrome (PIMS / PIMS-TS), or systemic inflammatory syndrome in COVID-19 (SISCoV), is a rare systemic illness involving persistent fever and extreme ...
, which has symptoms similar to
Kawasaki disease
Kawasaki disease (also known as mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome) is a syndrome of unknown cause that results in a fever and mainly affects children under 5 years of age. It is a form of vasculitis, in which medium-sized blood vessels become in ...
, which can be fatal. In very rare cases, acute
encephalopathy
Encephalopathy (; ) means any disorder or disease of the brain, especially chronic degenerative conditions. In modern usage, encephalopathy does not refer to a single disease, but rather to a syndrome of overall brain dysfunction; this syndrome ...
can occur, and it can be considered in those who have been diagnosed with COVID‑19 and have an altered mental status.
According to the US
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the National public health institutes, national public health agency of the United States. It is a Federal agencies of the United States, United States federal agency under the United S ...
, pregnant women are at increased risk of becoming seriously ill from COVID‑19.
This is because pregnant women with COVID‑19 appear to be more likely to develop respiratory and obstetric complications that can lead to
miscarriage
Miscarriage, also known in medical terms as a spontaneous abortion, is an end to pregnancy resulting in the loss and expulsion of an embryo or fetus from the womb before it can fetal viability, survive independently. Miscarriage before 6 weeks ...
,
premature delivery
Preterm birth, also known as premature birth, is the birth of a baby at fewer than 37 weeks gestational age, as opposed to full-term delivery at approximately 40 weeks. Extreme preterm is less than 28 weeks, very early preterm birth is between ...
and
intrauterine growth restriction
Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), or fetal growth restriction, is the poor growth of a fetus while in the womb during pregnancy. IUGR is defined by clinical features of malnutrition and evidence of reduced growth regardless of an infant's ...
.
Fungal infections such as
aspergillosis
Aspergillosis is a fungal infection of usually the lungs, caused by the genus ''Aspergillus'', a common mold that is breathed in frequently from the air, but does not usually affect most people. It generally occurs in people with lung diseases su ...
,
candidiasis
Candidiasis is a fungal infection due to any species of the genus '' Candida'' (a yeast). When it affects the mouth, in some countries it is commonly called thrush. Signs and symptoms include white patches on the tongue or other areas of the ...
,
cryptococcosis
Cryptococcosis is a potentially fatal fungal infection of mainly the lungs, presenting as a pneumonia, and in the brain, where it appears as a meningitis. Coughing, difficulty breathing, chest pain and fever are seen when the lungs are infect ...
and
mucormycosis
Mucormycosis, also known as black fungus, is a severe fungal infection that comes under fulminant fungal sinusitis, usually in people who are immunocompromised. It is curable only when diagnosed early. Symptoms depend on where in the body the ...
have been recorded in people recovering from COVID‑19.
Cause
COVID‑19 is caused by infection with a
strain of
coronavirus
Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the comm ...
known as "severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2" (
SARS-CoV-2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19, the respiratory illness responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. The virus previously had the Novel coronavirus, provisional nam ...
).
Transmission

Virology

Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a
novel
A novel is an extended work of narrative fiction usually written in prose and published as a book. The word derives from the for 'new', 'news', or 'short story (of something new)', itself from the , a singular noun use of the neuter plural of ...
severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. It was first isolated from three people with pneumonia connected to the
cluster
may refer to:
Science and technology Astronomy
* Cluster (spacecraft), constellation of four European Space Agency spacecraft
* Cluster II (spacecraft), a European Space Agency mission to study the magnetosphere
* Asteroid cluster, a small ...
of acute respiratory illness cases in Wuhan.
All structural features of the novel SARS-CoV-2 virus particle occur in related
coronavirus
Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the comm ...
es in nature,
particularly in ''
Rhinolophus sinicus
The Chinese rufous horseshoe bat (''Rhinolophus sinicus'') is a species of bat in the family Rhinolophidae. It is found in Bhutan, China, India, Nepal, and Vietnam.
The species is most easily confused with '' R. affinis'', from which it is bes ...
'' (Chinese horseshoe bats).
Outside the human body, the virus is destroyed by household soap which bursts its
protective bubble.
Hospital disinfectants, alcohols, heat,
povidone-iodine
Povidone-iodine (PVP-I), also known as iodopovidone, is an antiseptic used for skin disinfection before and after surgery. It may be used both to disinfect the hands of healthcare providers and the skin of the person they are caring for. It may ...
, and
ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
-C (UV-C) irradiation are also effective disinfection methods for surfaces.
SARS-CoV-2 is closely related to the original
SARS-CoV
Severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus (SARSr-CoV or SARS-CoV'', Betacoronavirus pandemicum'')The terms ''SARSr-CoV'' and ''SARS-CoV'' are sometimes used interchangeably, especially prior to the discovery of SARS-CoV-2. This m ...
.
It is thought to have an animal (
zoonotic
A zoonosis (; plural zoonoses) or zoonotic disease is an infectious disease of humans caused by a pathogen (an infectious agent, such as a virus, bacterium, parasite, fungi, or prion) that can jump from a non-human vertebrate to a human. When h ...
) origin. Genetic analysis has revealed that the coronavirus genetically clusters with the genus ''
Betacoronavirus
''Betacoronavirus'' (β-CoVs or Beta-CoVs) is one of four genera (''Alphacoronavirus, Alpha''-, ''Beta-'', ''Gammacoronavirus, Gamma-'', and ''Deltacoronavirus (genus), Delta-'') of coronaviruses. Member viruses are Viral envelope, enveloped, p ...
'', in subgenus ''
Sarbecovirus
Severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus (SARSr-CoV or SARS-CoV'', Betacoronavirus pandemicum'')The terms ''SARSr-CoV'' and ''SARS-CoV'' are sometimes used interchangeably, especially prior to the discovery of SARS-CoV-2. This m ...
'' (lineage B) together with two bat-derived strains. It is 96% identical at the whole
genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
level to other bat coronavirus samples (BatCov
RaTG13
Bat coronavirus RaTG13 is a SARS-like betacoronavirus identified in the droppings of the horseshoe bat '' Rhinolophus affinis''. It was discovered in 2013 in bat droppings from a mining cave near the town of Tongguan in Mojiang county in Yunna ...
).
The structural proteins of SARS-CoV-2 include
membrane glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide (sugar) chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as ...
(M),
envelope protein
A viral envelope is the outermost layer of many types of viruses. It protects the genetic material in their life cycle when traveling between host cells. Not all viruses have envelopes. A viral envelope protein or E protein is a protein in the env ...
(E),
nucleocapsid protein
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are found in almost ...
(N), and the
spike protein
In virology, a spike protein or peplomer protein is a protein that forms a large structure known as a spike or peplomer projecting from the surface of an viral envelope, enveloped virus. as cited in The proteins are usually glycoproteins that ...
(S). The M protein of SARS-CoV-2 is about 98% similar to the M protein of bat SARS-CoV, maintains around 98% homology with pangolin SARS-CoV, and has 90% homology with the M protein of SARS-CoV; whereas, the similarity is only around 38% with the M protein of
MERS-CoV
Middle East respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus (MERS-CoV, ''Betacoronavirus cameli'') or EMC/2012 ( HCoV-EMC/2012), is the virus that causes Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS). It is a species of coronavirus which infects humans, ba ...
.
SARS-CoV-2 variants
The many thousands of SARS-CoV-2 variants are grouped into either
clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach t ...
s or
lineages.
The WHO, in collaboration with partners, expert networks, national authorities, institutions and researchers, have established nomenclature systems for naming and tracking SARS-CoV-2 genetic lineages by
GISAID
GISAID (), the Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data, previously the Global Initiative on Sharing Avian Influenza Data, is a global science initiative established in 2008 to provide access to genomic data of influenza viruses. The datab ...
,
Nextstrain
Nextstrain is a collaboration between researchers in Seattle, United States and Basel, Switzerland which provides a collection of open-source tools for visualising the genetics behind the spread of viral outbreaks.
Its aim is to support public h ...
and
Pango
Pango (stylized as Παν語) is a text (i.e. glyph) layout engine library which works with the HarfBuzz shaping engine for displaying multi-language text.
Full-function rendering of text and cross-platform support is achieved when Pango is use ...
. The expert group convened by the WHO recommended the labelling of variants using letters of the
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet has been used to write the Greek language since the late 9th or early 8th century BC. It was derived from the earlier Phoenician alphabet, and is the earliest known alphabetic script to systematically write vowels as wel ...
, for example,
Alpha
Alpha (uppercase , lowercase ) is the first letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of one. Alpha is derived from the Phoenician letter ''aleph'' , whose name comes from the West Semitic word for ' ...
,
Beta
Beta (, ; uppercase , lowercase , or cursive ; or ) is the second letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 2. In Ancient Greek, beta represented the voiced bilabial plosive . In Modern Greek, it represe ...
,
Delta
Delta commonly refers to:
* Delta (letter) (Δ or δ), the fourth letter of the Greek alphabet
* D (NATO phonetic alphabet: "Delta"), the fourth letter in the Latin alphabet
* River delta, at a river mouth
* Delta Air Lines, a major US carrier ...
, and
Gamma
Gamma (; uppercase , lowercase ; ) is the third letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 3. In Ancient Greek, the letter gamma represented a voiced velar stop . In Modern Greek, this letter normally repr ...
, giving the justification that they "will be easier and more practical to discussed by non-scientific audiences".
Nextstrain
Nextstrain is a collaboration between researchers in Seattle, United States and Basel, Switzerland which provides a collection of open-source tools for visualising the genetics behind the spread of viral outbreaks.
Its aim is to support public h ...
divides the variants into five clades (19A, 19B, 20A, 20B, and 20C), while
GISAID
GISAID (), the Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data, previously the Global Initiative on Sharing Avian Influenza Data, is a global science initiative established in 2008 to provide access to genomic data of influenza viruses. The datab ...
divides them into seven (L, O, V, S, G, GH, and GR).
The Pango tool groups variants into
lineages, with many circulating lineages being classed under the B.1 lineage.
Several notable variants of SARS-CoV-2 emerged throughout 2020.
Cluster 5
Cluster 5 is a designation used by the Danish Statens Serum Institut for a virus variant described by the institute in autumn 2020, in connection with investigations of SARS-CoV-2 infection among mink and humans in the north of Jutland, Denmark.
...
emerged among
mink
Mink are dark-colored, semiaquatic, carnivorous mammals of the genera ''Neogale'' and '' Mustela'' and part of the family Mustelidae, which also includes weasels, otters, and ferrets. There are two extant species referred to as "mink": the A ...
s and mink farmers in
Denmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous a ...
. After
strict quarantines and the
slaughter of all the country's mink, the cluster was assessed to no longer be circulating among humans in Denmark as of 1 February 2021.
, there are five dominant variants of SARS-CoV-2 spreading among global populations: the
Alpha variant
The Alpha variant (B.1.1.7) was a SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern. It was estimated to be 40–80% more transmissible than the wild-type SARS-CoV-2 (with most estimates occupying the middle to higher end of this range). Scientists more widel ...
(B.1.1.7, formerly called the UK variant), first found in London and Kent, the
Beta variant (B.1.351, formerly called the South Africa variant), the
Gamma variant (P.1, formerly called the Brazil variant), the
Delta variant
The Delta variant (B.1.617.2) was a variant of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. It was first detected in India on 5 October 2020. The Delta variant was named on 31 May 2021 and had spread to over 179 countries by 22 November 202 ...
(B.1.617.2, formerly called the India variant), and the
Omicron variant
Omicron (B.1.1.529) is a Variants of SARS-CoV-2, variant of SARS-CoV-2 first reported to the World Health Organization (WHO) by the Network for Genomics Surveillance in South Africa on 24 November 2021. It was first detected in Botswana and has ...
(B.1.1.529), which had spread to 57 countries as of 7 December.
On 19 December 2023, the WHO declared that another distinctive variant, JN.1, had emerged as a "variant of interest". Though the WHO expected an increase in cases globally, particularly for countries entering winter, the overall global health risk was considered low.
Pathophysiology

The SARS-CoV-2 virus can infect a wide range of cells and systems of the body. COVID‑19 is most known for affecting the upper respiratory tract (sinuses, nose, and throat) and the lower respiratory tract (windpipe and lungs).
The lungs are the organs most affected by COVID‑19 because the virus accesses host cells via the
receptor
Receptor may refer to:
* Sensory receptor, in physiology, any neurite structure that, on receiving environmental stimuli, produces an informative nerve impulse
*Receptor (biochemistry), in biochemistry, a protein molecule that receives and respond ...
for the enzyme
angiotensin-converting enzyme 2
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is an enzyme that can be found either attached to the membrane of cells (mACE2) in the intestines, kidney, testis, gallbladder, and heart or in a soluble form (sACE2). Both membrane bound and soluble ACE2 ...
(ACE2), which is most abundant on the surface of
type II alveolar cell
A pulmonary alveolus (; ), also called an air sac or air space, is one of millions of hollow, distensible cup-shaped cavities in the lungs where pulmonary gas exchange takes place. Oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide at the blood–air bar ...
s of the lungs. The virus uses a special surface glycoprotein called a "
spike
Spike, spikes, or spiking may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
Books
* ''The Spike'' (novel), a novel by Arnaud de Borchgrave
* ''The Spike'' (Broderick book), a nonfiction book by Damien Broderick
* ''The Spike'', a starship in Peter ...
" to connect to the ACE2 receptor and enter the host cell.
Respiratory tract
Following viral entry, COVID‑19 infects the ciliated epithelium of the nasopharynx and upper airways. Autopsies of people who died of COVID‑19 have found
diffuse alveolar damage
Diffuse alveolar damage (DAD) is a Histology, histologic term used to describe specific changes that occur to the structure of the lungs during injury or Respiratory disease, disease. Most often DAD is described in association with the early stag ...
, and lymphocyte-containing inflammatory infiltrates within the lung.
From the
CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
s of COVID-19 infected lungs, white patches were observed containing fluid known as
ground-glass opacity
Ground-glass opacity (GGO) is a finding seen on chest x-ray (radiograph) or computed tomography (CT) imaging of the lungs. It is typically defined as an area of hazy opacification (x-ray) or increased attenuation (CT) due to air displacement by ...
(GGO) or simply ground glass. This tended to correlate with the clear jelly liquid found in lung autopsies of people who died of COVID-19. One possibility addressed in medical research is that
hyuralonic acid (HA) could be the leading factor for this observation of the clear jelly liquid found in the lungs, in what could be hyuralonic storm, in conjunction with
cytokine storm
A cytokine storm, also called hypercytokinemia, is a pathological reaction in humans and other animals in which the innate immune system causes an uncontrolled and excessive release of pro-inflammatory signaling molecules called cytokines. Cytok ...
.
Nervous system
One common symptom, loss of smell, results from
infection of the support cells of the olfactory epithelium, with subsequent damage to the
olfactory neuron
An olfactory receptor neuron (ORN), also called an olfactory sensory neuron (OSN), is a sensory neuron within the olfactory system.
Structure
Humans have between 10 and 20 million olfactory receptor neurons (ORNs). In vertebrates, ORNs are Bi ...
s.
The involvement of both the central and peripheral nervous system in COVID‑19 has been reported in many medical publications.
It is clear that many people with
COVID-19 exhibit neurological or mental health issues. The virus is not detected in the
central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
(CNS) of the majority of people with COVID-19 who also have
neurological issues. However, SARS-CoV-2 has been detected at low levels in the brains of those who have died from COVID‑19, but these results need to be confirmed.
While virus has been detected in
cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless Extracellular fluid#Transcellular fluid, transcellular body fluid found within the meninges, meningeal tissue that surrounds the vertebrate brain and spinal cord, and in the ventricular system, ven ...
of autopsies, the exact mechanism by which it invades the CNS remains unclear and may first involve invasion of peripheral nerves given the low levels of ACE2 in the brain. The virus may also enter the bloodstream from the lungs and cross the blood–brain barrier to gain access to the CNS, possibly within an infected white blood cell.

Research conducted when Alpha was the dominant variant has suggested COVID-19 may cause brain damage. Later research showed that all variants studied (including Omicron) killed brain cells, but the exact cells killed varied by variant. It is unknown if such damage is temporary or permanent. Observed individuals infected with COVID-19 (most with mild cases) experienced an additional 0.2% to 2% of brain tissue lost in regions of the brain connected to the sense of smell compared with uninfected individuals, and the overall effect on the brain was equivalent on average to at least one extra year of normal ageing; infected individuals also scored lower on several cognitive tests. All effects were more pronounced among older ages.
Gastrointestinal tract
The virus also affects gastrointestinal organs as ACE2 is abundantly expressed in the
gland
A gland is a Cell (biology), cell or an Organ (biology), organ in an animal's body that produces and secretes different substances that the organism needs, either into the bloodstream or into a body cavity or outer surface. A gland may also funct ...
ular cells of
gastric
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The Ancient Greek name for the stomach is ''gaster'' which is used as ''gastric'' in medical terms re ...
,
duodenal
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In mammals, it may be the principal site for iron absorption.
The duodenum precedes the jejunum and ileum and is the shortest p ...
and
rectal
The rectum (: rectums or recta) is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the Gastrointestinal tract, gut in others. Before expulsion through the anus or cloaca, the rectum stores the feces te ...
epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
as well as
endothelial
The endothelium (: endothelia) is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the res ...
cells and
enterocyte
Enterocytes, or intestinal absorptive cells, are simple columnar epithelial cells which line the inner surface of the small and large intestines. A glycocalyx surface coat contains digestive enzymes. Microvilli on the apical surface increase ...
s of the
small intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ (anatomy), organ in the human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract where most of the #Absorption, absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intes ...
.
Cardiovascular system
The virus can cause
acute myocardial injury and chronic damage to the
cardiovascular system
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart a ...
.
An acute cardiac injury was found in 12% of infected people admitted to the hospital in Wuhan, China,
and is more frequent in severe disease. Rates of cardiovascular symptoms are high, owing to the systemic inflammatory response and immune system disorders during disease progression, but acute myocardial injuries may also be related to ACE2 receptors in the heart.
ACE2 receptors are highly expressed in the heart and are involved in heart function.
A high incidence of
thrombosis
Thrombosis () is the formation of a Thrombus, blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel (a vein or an artery) is injured, the body uses platelets (thrombocytes) and fib ...
and
venous thromboembolism
Venous thrombosis is the blockage of a vein caused by a thrombus (blood clot). A common form of venous thrombosis is deep vein thrombosis (DVT), when a blood clot forms in the deep veins. If a thrombus breaks off ( embolizes) and flows to the lun ...
occurs in people transferred to
intensive care unit
An intensive care unit (ICU), also known as an intensive therapy unit or intensive treatment unit (ITU) or critical care unit (CCU), is a special department of a hospital or health care facility that provides intensive care medicine.
An inten ...
s with COVID‑19 infections, and may be related to poor prognosis. Blood vessel dysfunction and clot formation (as suggested by high
D-dimer
D-dimer (or D dimer) is a dimer that is a fibrin degradation product (FDP), a small protein fragment present in the blood after a blood clot is degraded by fibrinolysis. It is so named because it contains two D fragments of the fibrin protein ...
levels caused by blood clots) may have a significant role in mortality, incidents of clots leading to
pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an pulmonary artery, artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include dyspnea, shortness of breath, chest pain ...
s, and
ischaemic events (strokes) within the brain found as complications leading to death in people infected with COVID‑19.
[ Infection may initiate a chain of vasoconstrictive responses within the body, including pulmonary vasoconstriction a possible mechanism in which oxygenation decreases during pneumonia.]arterioles
An arteriole is a small-diameter blood vessel in the microcirculation that extends and branches out from an artery and leads to capillaries.
Arterioles have muscular walls (usually only one to two layers of smooth muscle cells) and are the pr ...
and capillaries
A capillary is a small blood vessel, from 5 to 10 micrometres in diameter, and is part of the microcirculation system. Capillaries are microvessels and the smallest blood vessels in the body. They are composed of only the tunica intima (the in ...
was found in brain tissue samples of people who died from COVID‑19.
COVID19 may also cause substantial structural changes to blood cell
A blood cell (also called a hematopoietic cell, hemocyte, or hematocyte) is a cell produced through hematopoiesis and found mainly in the blood. Major types of blood cells include red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), ...
s, sometimes persisting for months after hospital discharge. A low level of blood lymphocytess may result from the virus acting through ACE2-related entry into lymphocytes.
Kidneys
Another common cause of death is complications related to the kidney
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organ (anatomy), organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and rig ...
s.
Immunopathology
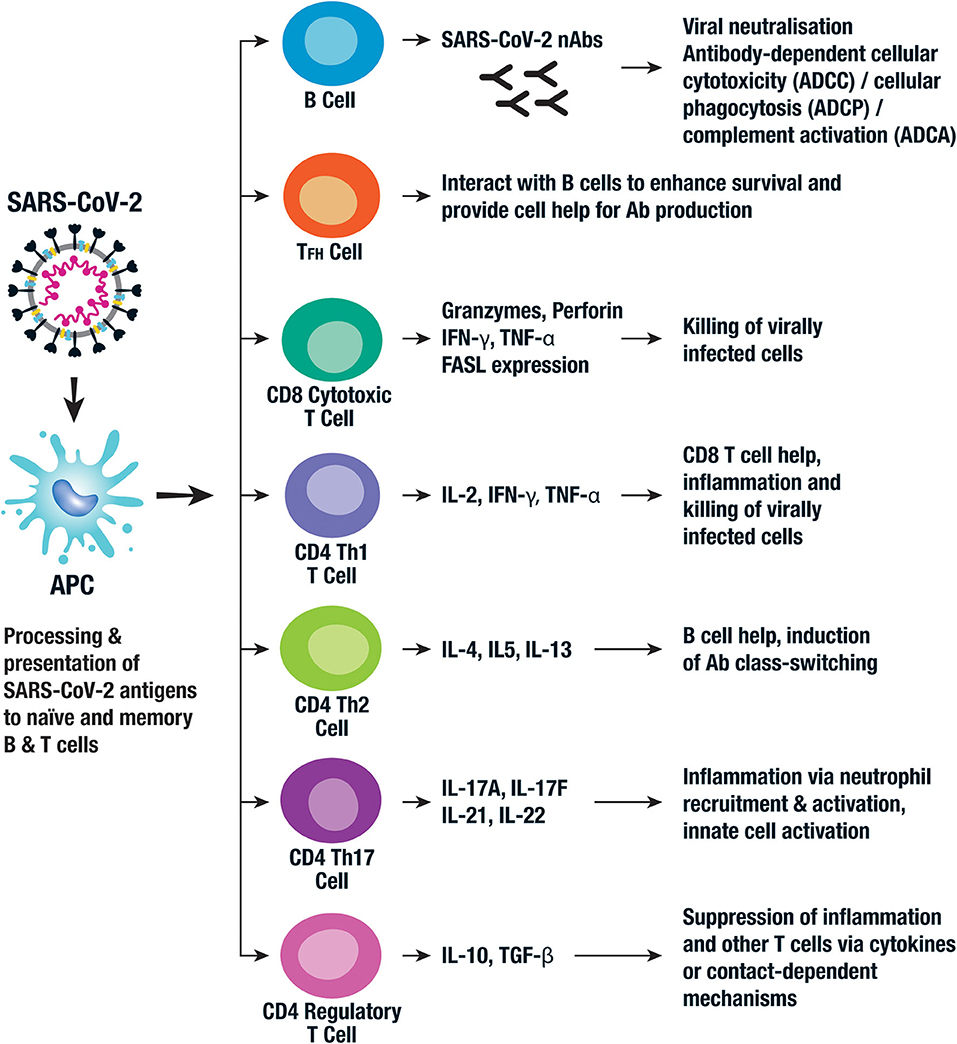 Although SARS-CoV-2 has a tropism for ACE2-expressing epithelial cells of the respiratory tract, people with severe COVID‑19 have symptoms of systemic hyperinflammation. Clinical laboratory findings of elevated IL2, IL6, IL7, as well as the following suggest an underlying immunopathology:
Although SARS-CoV-2 has a tropism for ACE2-expressing epithelial cells of the respiratory tract, people with severe COVID‑19 have symptoms of systemic hyperinflammation. Clinical laboratory findings of elevated IL2, IL6, IL7, as well as the following suggest an underlying immunopathology:Tumour necrosis factor
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF), formerly known as TNF-α, is a chemical messenger produced by the immune system that induces inflammation. TNF is produced primarily by activated macrophages, and induces inflammation by binding to its receptors ...
(TNFα) indicative of cytokine release syndrome
In immunology, cytokine release syndrome (CRS) is a form of systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) that can be triggered by a variety of factors such as infections and certain drugs. It refers to cytokine storm syndromes (CSS) and occur ...
(CRS)
Interferon alpha
The type-I interferons (IFN) are cytokines which play essential roles in inflammation, immunoregulation, tumor cells recognition, and T-cell responses. In the human genome, a cluster of thirteen functional IFN genes is located at the 9p21.3 cyt ...
plays a complex, Janus-faced role in the pathogenesis of COVID-19. Although it promotes the elimination of virus-infected cells, it also upregulates the expression of ACE-2, thereby facilitating the SARS-Cov2 virus to enter cells and to replicate. A competition of negative feedback loops (via protective effects of interferon alpha) and positive feedback loops (via upregulation of ACE-2) is assumed to determine the fate of people with COVID-19.
Additionally, people with COVID‑19 and acute respiratory distress syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a type of respiratory failure characterized by rapid onset of widespread inflammation in the lungs. Symptoms include shortness of breath (dyspnea), rapid breathing (tachypnea), and bluish skin co ...
(ARDS) have classical serum
Serum may refer to:
Biology and pharmacology
*Serum (blood), plasma from which the clotting proteins have been removed
**Antiserum, blood serum with specific antibodies for passive immunity
*Serous fluid, any clear bodily fluid
Places
*Serum, Ind ...
biomarker
In biomedical contexts, a biomarker, or biological marker, is a measurable indicator of some biological state or condition. Biomarkers are often measured and evaluated using blood, urine, or soft tissues to examine normal biological processes, ...
s of CRS, including elevated C-reactive protein
C-reactive protein (CRP) is an annular (ring-shaped) pentameric protein found in blood plasma, whose circulating concentrations rise in response to inflammation. It is an acute-phase protein of hepatic origin that increases following interleukin ...
(CRP), lactate dehydrogenase
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH or LD) is an enzyme found in nearly all living cells. LDH catalyzes the conversion of pyruvic acid, pyruvate to lactic acid, lactate and back, as it converts NAD+ to NADH and back. A dehydrogenase is an enzyme that t ...
(LDH), D-dimer
D-dimer (or D dimer) is a dimer that is a fibrin degradation product (FDP), a small protein fragment present in the blood after a blood clot is degraded by fibrinolysis. It is so named because it contains two D fragments of the fibrin protein ...
, and ferritin
Ferritin is a universal intracellular and extracellular protein that stores iron and releases it in a controlled fashion. The protein is produced by almost all living organisms, including archaea, bacteria, algae, higher plants, and animals. ...
.
Systemic inflammation results in vasodilation
Vasodilation, also known as vasorelaxation, is the widening of blood vessels. It results from relaxation of smooth muscle cells within the vessel walls, in particular in the large veins, large arteries, and smaller arterioles. Blood vessel wa ...
, allowing inflammatory lymphocytic and monocytic infiltration of the lung and the heart. In particular, pathogenic GM-CSF-secreting T cells were shown to correlate with the recruitment of inflammatory IL-6-secreting monocyte
Monocytes are a type of leukocyte or white blood cell. They are the largest type of leukocyte in blood and can differentiate into macrophages and monocyte-derived dendritic cells. As a part of the vertebrate innate immune system monocytes also ...
s and severe lung pathology in people with COVID‑19. Lymphocytic infiltrates have also been reported at autopsy.
Viral and host factors
Virus proteins
 Multiple viral and host factors affect the pathogenesis of the virus. The S-protein, otherwise known as the spike protein, is the viral component that attaches to the host receptor via the
Multiple viral and host factors affect the pathogenesis of the virus. The S-protein, otherwise known as the spike protein, is the viral component that attaches to the host receptor via the ACE2
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is an enzyme that can be found either attached to the membrane of cells (mACE2) in the intestines, kidney, testis, gallbladder, and heart or in a soluble form (sACE2). Both membrane bound and soluble ACE2 ...
receptors. It includes two subunits: S1 and S2.
* S1 determines the virus-host range and cellular tropism via the receptor-binding domain.
* S2 mediates the membrane fusion of the virus to its potential cell host via the H1 and HR2, which are heptad repeat
The heptad repeat is an example of a structural motif that consists of a repeating pattern of seven amino acids:
''a b c d e f g''
H P P H C P C
where H represents hydrophobic residues, C represents, typically, charged residues, and P repre ...
regions.
Studies have shown that S1 domain induced IgG
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is a type of antibody. Representing approximately 75% of serum antibodies in humans, IgG is the most common type of antibody found in blood circulation. IgG molecules are created and released by plasma B cells. Each IgG ant ...
and IgA IGA or IgA may refer to:
Businesses and organizations
* IGA (supermarkets) (initially Independent Grocers Alliance), a name used by many independent supermarkets throughout the world
** IGA (Australian supermarket group), the local Australian v ...
antibody levels at a much higher capacity. It is the focus spike proteins expression that are involved in many effective COVID‑19 vaccines.
Host factors
Human angiotensin converting enzyme 2
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is an enzyme that can be found either attached to the membrane of cells (mACE2) in the intestines, kidney, testis, gallbladder, and heart or in a soluble form (sACE2). Both membrane bound and soluble ACE2 ...
(hACE2) is the host factor that SARS-CoV-2 virus targets causing COVID‑19. Theoretically, the usage of angiotensin receptor blocker
Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), formally angiotensin II receptor type 1 (AT1) antagonists, also known as angiotensin receptor blockers, angiotensin II receptor antagonists, or AT1 receptor antagonists, are a group of pharmaceuticals tha ...
s (ARB) and ACE inhibitor
Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors) are a class of medication used primarily for the treatment of high blood pressure and heart failure. This class of medicine works by causing relaxation of blood vessels as well as a decr ...
s upregulating ACE2 expression might increase morbidity
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that are asso ...
with COVID‑19, though animal data suggest some potential protective effect of ARB; however no clinical studies have proven susceptibility or outcomes. Until further data is available, guidelines and recommendations for people with hypertension remain.
The effect of the virus on ACE2 cell surfaces leads to leukocytic infiltration, increased blood vessel permeability, alveolar wall permeability, as well as decreased secretion of lung surfactants. These effects cause the majority of the respiratory symptoms. However, the aggravation of local inflammation causes a cytokine storm eventually leading to a systemic inflammatory response syndrome
In immunology, systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) is an inflammation, inflammatory state affecting the whole body. It is the body's Immune response, response to an infectious or noninfectious Insult (medical), insult. Although the ...
.
Among healthy adults not exposed to SARS-CoV-2, about 35% have CD4+ T cells that recognise the SARS-CoV-2 S protein
Spike (S) glycoprotein (sometimes also called spike protein, formerly known as E2) is the largest of the four major structural proteins found in coronaviruses. The spike protein assembles into trimers that form large structures, called spikes o ...
(particularly the S2 subunit) and about 50% react to other proteins of the virus, suggesting cross-reactivity
Cross-reactivity, in a general sense, is the reactivity of an observed agent which initiates reactions outside the main reaction expected. This has implications for any kind of test or assay, including diagnostic tests in medicine, and can be a c ...
from previous common cold
The common cold, or the cold, is a virus, viral infectious disease of the upper respiratory tract that primarily affects the Respiratory epithelium, respiratory mucosa of the human nose, nose, throat, Paranasal sinuses, sinuses, and larynx. ...
s caused by other coronaviruses.
It is unknown whether different persons use similar antibody genes in response to COVID‑19.
Host cytokine response
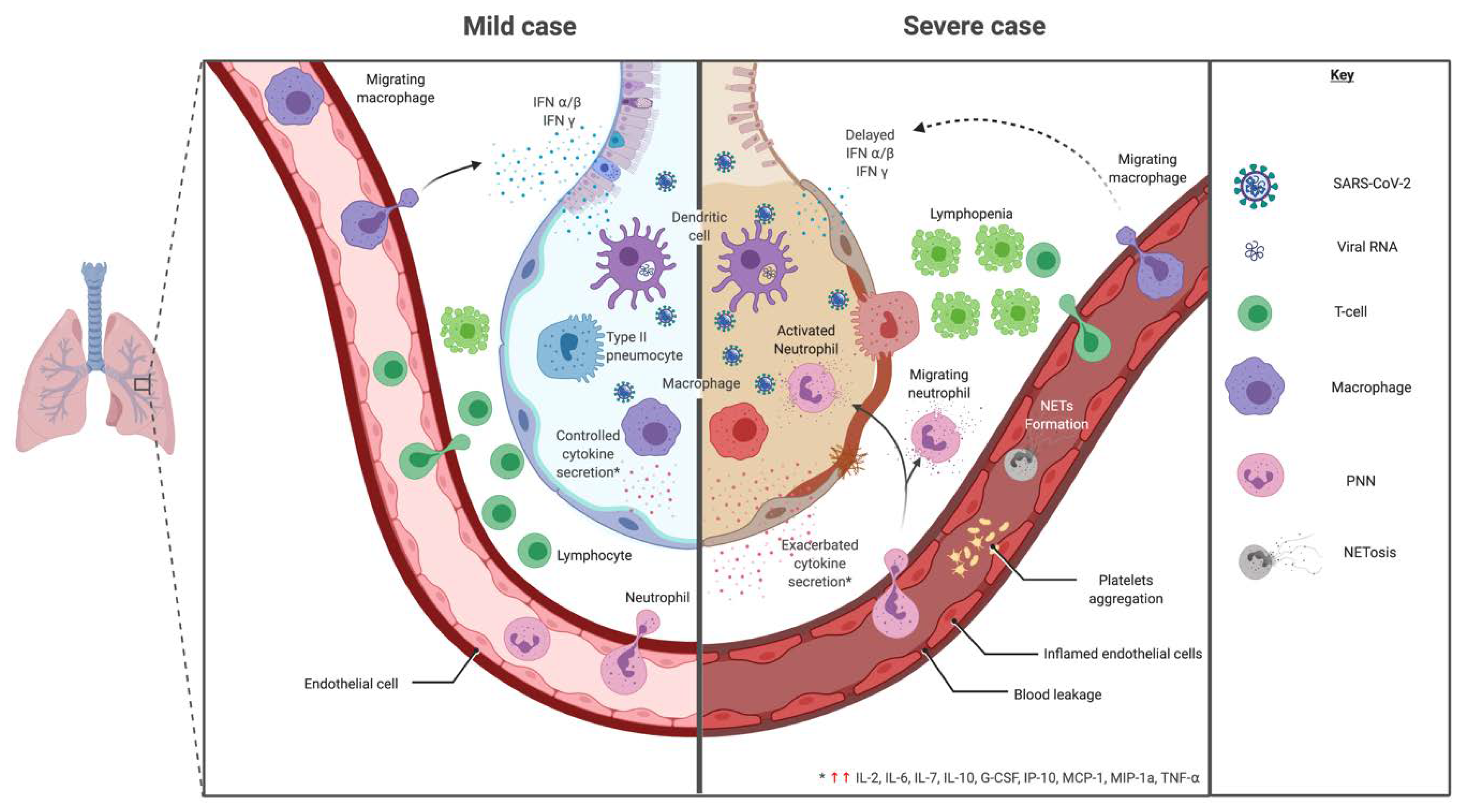 The severity of the inflammation can be attributed to the severity of what is known as the
The severity of the inflammation can be attributed to the severity of what is known as the cytokine storm
A cytokine storm, also called hypercytokinemia, is a pathological reaction in humans and other animals in which the innate immune system causes an uncontrolled and excessive release of pro-inflammatory signaling molecules called cytokines. Cytok ...
.interferon-gamma
Interferon gamma (IFNG or IFN-γ) is a dimerized soluble cytokine that is the only member of the type II class of interferons. The existence of this interferon, which early in its history was known as immune interferon, was described by E. F. ...
, interferon-inducible protein 10, and monocyte chemoattractant protein1 were all associated with COVID‑19 disease severity. Treatment has been proposed to combat the cytokine storm as it remains to be one of the leading causes of morbidity
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that are asso ...
and mortality in COVID‑19 disease.
A cytokine storm is due to an acute hyperinflammatory response that is responsible for clinical illness in an array of diseases but in COVID‑19, it is related to worse prognosis and increased fatality. The storm causes acute respiratory distress syndrome, blood clotting events such as strokes, myocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when Ischemia, blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom ...
, encephalitis
Encephalitis is inflammation of the Human brain, brain. The severity can be variable with symptoms including reduction or alteration in consciousness, aphasia, headache, fever, confusion, a stiff neck, and vomiting. Complications may include se ...
, acute kidney injury
Acute kidney injury (AKI), previously called acute renal failure (ARF), is a sudden decrease in renal function, kidney function that develops within seven days, as shown by an increase in serum creatinine or a decrease in urine output, or both.
...
, and vasculitis
Vasculitis is a group of disorders that destroy blood vessels by inflammation. Both artery, arteries and veins are affected. Lymphangitis (inflammation of lymphatic vessels) is sometimes considered a type of vasculitis. Vasculitis is primarily c ...
. The production of IL-1, IL-2
The Ilyushin Il-2 (Russian language, Russian: Илью́шин Ил-2) is a Ground attack aircraft, ground-attack plane that was produced by the Soviet Union in large numbers during the World War II, Second World War. The word ''shturmovík'' (C ...
, IL-6, TNF-alpha
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF), formerly known as TNF-α, is a chemical messenger produced by the immune system that induces inflammation. TNF is produced primarily by activated macrophages, and induces inflammation by binding to its receptors o ...
, and interferon-gamma
Interferon gamma (IFNG or IFN-γ) is a dimerized soluble cytokine that is the only member of the type II class of interferons. The existence of this interferon, which early in its history was known as immune interferon, was described by E. F. ...
, all crucial components of normal immune responses, inadvertently become the causes of a cytokine storm. The cells of the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
, the microglia
Microglia are a type of glia, glial cell located throughout the brain and spinal cord of the central nervous system (CNS). Microglia account for about around 5–10% of cells found within the brain. As the resident macrophage cells, they act as t ...
, neuron
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural net ...
s, and astrocyte
Astrocytes (from Ancient Greek , , "star" and , , "cavity", "cell"), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. They perform many functions, including biochemical control of en ...
s, are also involved in the release of pro-inflammatory cytokine
An inflammatory cytokine or proinflammatory cytokine is a type of signaling molecule (a cytokine) that is secreted from immune cells like helper T cells (Th) and macrophages, and certain other cell types that promote inflammation. They include int ...
s affecting the nervous system, and effects of cytokine storms toward the CNS are not uncommon.
Pregnancy response
There are many unknowns for pregnant women during the COVID-19 pandemic. Given that they are prone to have complications and severe disease infection with other types of coronaviruses, they have been identified as a vulnerable group and advised to take supplementary preventive measures.vaccinated
A vaccine is a biological Dosage form, preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease, infectious or cancer, malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verifi ...
.
Diagnosis
COVID‑19 can provisionally be diagnosed on the basis of symptoms and confirmed using reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is a laboratory technique combining reverse transcription of RNA into DNA (in this context called complementary DNA or cDNA) and amplification of specific DNA targets using polymerase cha ...
(RT-PCR) or other nucleic acid test
A nucleic acid test (NAT) is a technique used to detect a particular nucleic acid sequence and thus usually to detect and identify a particular species or subspecies of organism, often a virus or bacterium that acts as a pathogen in blood, tissu ...
ing of infected secretions.serological test
Serology is the scientific study of serum and other body fluids. In practice, the term usually refers to the diagnostic identification of antibodies in the serum. Such antibodies are typically formed in response to an infection (against a given mi ...
s, which detect antibodies
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as bacteria and viruses, including those that caus ...
produced by the body in response to the infection.
Viral testing
The standard methods of testing for presence of SARS-CoV-2 are nucleic acid test
A nucleic acid test (NAT) is a technique used to detect a particular nucleic acid sequence and thus usually to detect and identify a particular species or subspecies of organism, often a virus or bacterium that acts as a pathogen in blood, tissu ...
s,nasopharyngeal swab
A nasopharyngeal swab is a device used for collecting a sample of Mucus#Respiratory system, nasal secretions from the back of the nose and throat. The sample is then analyzed for the presence of organisms or other clinical markers for disease. Th ...
; however, a nasal swab or sputum sample may also be used.Public Health England
Public Health England (PHE) was an executive agency of the Department of Health and Social Care in England which began operating on 1 April 2013 to protect and improve health and wellbeing and reduce health inequalities. Its formation came as a ...
and approved for use in the UK.University of Oxford
The University of Oxford is a collegiate university, collegiate research university in Oxford, England. There is evidence of teaching as early as 1096, making it the oldest university in the English-speaking world and the List of oldest un ...
's CEBM has pointed to mounting evidence
Imaging
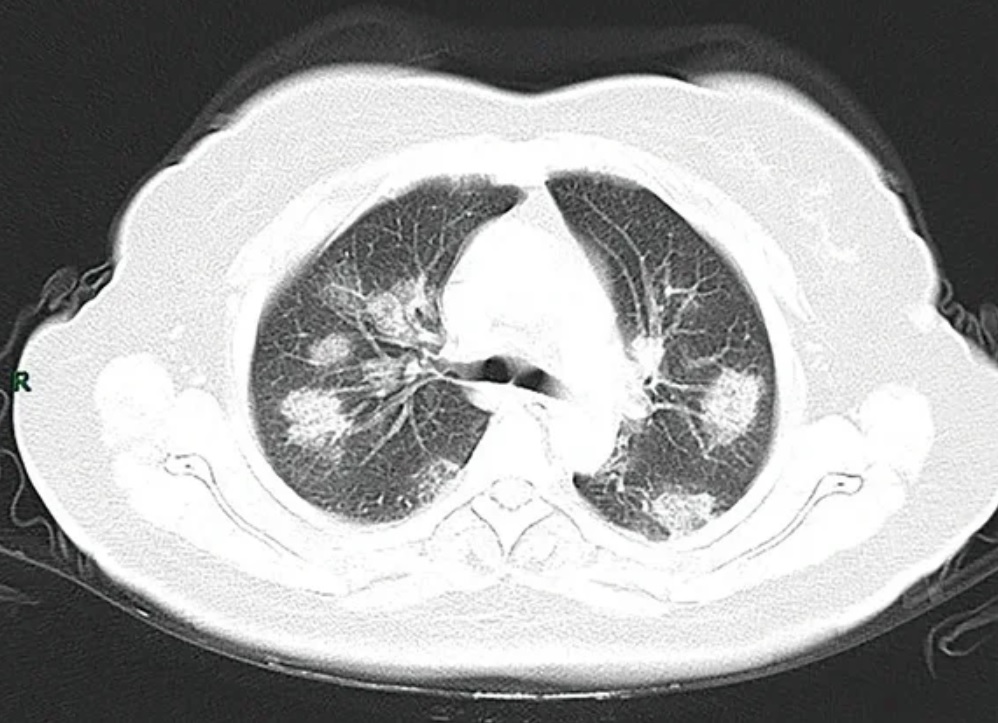

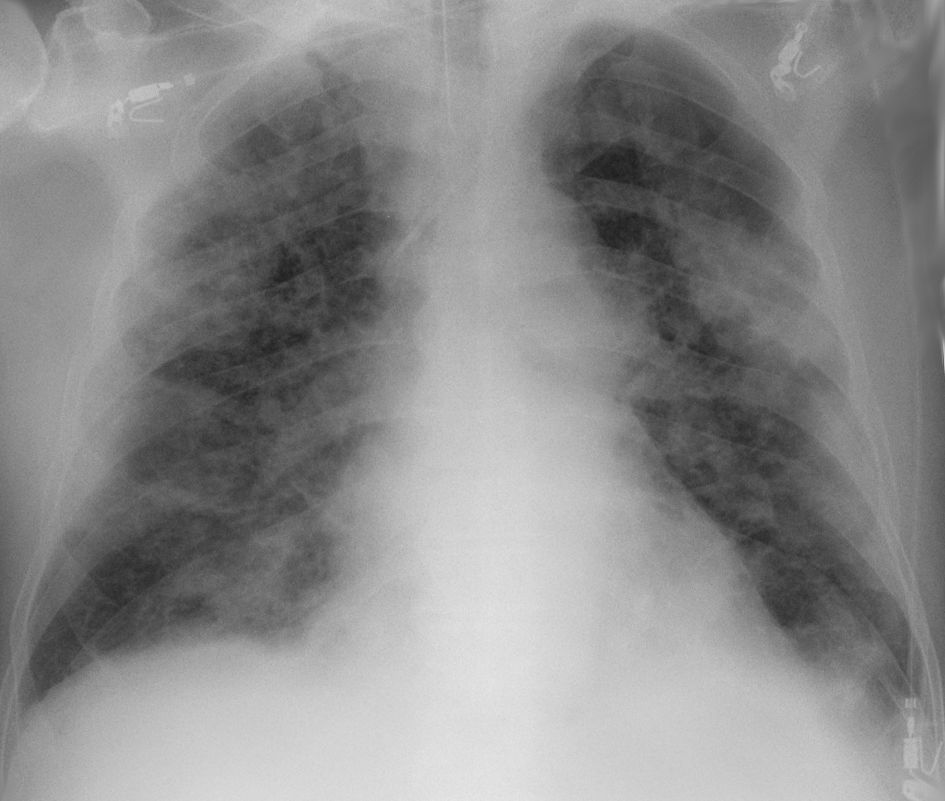 Chest CT scans may be helpful to diagnose COVID‑19 in individuals with a high clinical suspicion of infection but are not recommended for routine screening.
Chest CT scans may be helpful to diagnose COVID‑19 in individuals with a high clinical suspicion of infection but are not recommended for routine screening.crazy paving
Crazy paving is a means of Pavement (material), hard-surfacing used outdoors, most frequently in gardens. Paving stone (flooring), Paving stones of irregular size and shape are laid in a haphazard manner sometimes with Mortar (masonry), mortar f ...
(lobular septal thickening with variable alveolar filling), and consolidation may appear as the disease progresses.radiograph
Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical ("diagnostic" radiography and "therapeu ...
s and computed tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
(CT) of people who are symptomatic include asymmetric peripheral ground-glass opacities without pleural effusion
A pleural effusion is accumulation of excessive fluid in the pleural space, the potential space that surrounds each lung.
Under normal conditions, pleural fluid is secreted by the parietal pleural capillaries at a rate of 0.6 millilitre per kilog ...
s.adenovirus
Adenoviruses (members of the family ''Adenoviridae'') are medium-sized (90–100 nm), nonenveloped (without an outer lipid bilayer) viruses with an icosahedral nucleocapsid containing a double-stranded DNA genome. Their name derives from t ...
, imaging without confirmation by rRT-PCR is of limited specificity in identifying COVID‑19.
Coding
In late 2019, the WHO assigned emergency ICD-10
ICD-10 is the 10th revision of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD), a medical classification list by the World Health Organization (WHO). It contains codes for diseases, signs and symptoms, abnormal findings, complaints, social cir ...
disease codes U07.1 for deaths from lab-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection and U07.2 for deaths from clinically or epidemiologically diagnosed COVID‑19 without lab-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Pathology
The main pathological findings at autopsy are:
* Macroscopy: pericarditis
Pericarditis () is inflammation of the pericardium, the fibrous sac surrounding the heart. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp chest pain, which may also be felt in the shoulders, neck, or back. The pain is typically less severe whe ...
, lung consolidation
A pulmonary consolidation is a region of normally compressible lung tissue that has filled with liquid instead of air. The condition is marked by induration (swelling or hardening of normally soft tissue) of a normally aerated lung. It is consid ...
and pulmonary oedema
Pulmonary edema (British English: oedema), also known as pulmonary congestion, is excessive fluid accumulation in the tissue or air spaces (usually alveoli) of the lungs. This leads to impaired gas exchange, most often leading to shortness ...
exudation
An exudate is a fluid released by an organism through pores or a wound, a process known as exuding or exudation.
''Exudate'' is derived from ''exude'' 'to ooze' from Latin 'to (ooze out) sweat' (' 'out' and ' 'to sweat').
Medicine
An exudate ...
, minor fibrin
Fibrin (also called Factor Ia) is a fibrous protein, fibrous, non-globular protein involved in the Coagulation, clotting of blood. It is formed by the action of the protease thrombin on fibrinogen, which causes it to polymerization, polymerize. ...
exudationpneumocyte
A pulmonary alveolus (; ), also called an air sac or air space, is one of millions of hollow, distensible cup-shaped cavities in the lungs where pulmonary gas exchange takes place. Oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide at the blood–air bar ...
hyperplasia
Hyperplasia (from ancient Greek ὑπέρ ''huper'' 'over' + πλάσις ''plasis'' 'formation'), or hypergenesis, is an enlargement of an organ or tissue caused by an increase in the amount of Tissue (biology), organic tissue that results from ...
, large atypical pneumocyte
A pulmonary alveolus (; ), also called an air sac or air space, is one of millions of hollow, distensible cup-shaped cavities in the lungs where pulmonary gas exchange takes place. Oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide at the blood–air bar ...
s, interstitial inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
with lymphocytic
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include T cells (for cell-mediated and cytotoxic adaptive immunity), B cells (for humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immunity), and inn ...
infiltration and multinucleated giant cell formationDiffuse alveolar damage
Diffuse alveolar damage (DAD) is a Histology, histologic term used to describe specific changes that occur to the structure of the lungs during injury or Respiratory disease, disease. Most often DAD is described in association with the early stag ...
(DAD) with diffuse alveolar
Alveolus (; pl. alveoli, adj. alveolar) is a general anatomical term for a concave cavity or pit.
Uses in anatomy and zoology
* Pulmonary alveolus, an air sac in the lungs
** Alveolar cell or pneumocyte
** Alveolar duct
** Alveolar macrophage
* M ...
exudates
An exudate is a fluid released by an organism through pores or a wound, a process known as exuding or exudation.
''Exudate'' is derived from ''exude'' 'to ooze' from Latin 'to (ooze out) sweat' (' 'out' and ' 'to sweat').
Medicine
An exudate ...
. DAD is the cause of acute respiratory distress syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a type of respiratory failure characterized by rapid onset of widespread inflammation in the lungs. Symptoms include shortness of breath (dyspnea), rapid breathing (tachypnea), and bluish skin co ...
(ARDS) and severe hypoxaemia
Hypoxemia (also spelled hypoxaemia) is an abnormally low level of oxygen in the blood. More specifically, it is oxygen deficiency in arterial blood. Hypoxemia is usually caused by pulmonary disease. Sometimes the concentration of oxygen in the ...
.Organisation
An organization or organisation ( Commonwealth English; see spelling differences) is an entity—such as a company, or corporation or an institution ( formal organization), or an association—comprising one or more people and having a pa ...
of exudate
An exudate is a fluid released by an organism through pores or a wound, a process known as exuding or exudation.
''Exudate'' is derived from ''exude'' 'to ooze' from Latin language, Latin 'to (ooze out) sweat' (' 'out' and ' 'to sweat').
Medi ...
s in alveolar cavities and pulmonary interstitial fibrosisbronchoalveolar lavage
Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL), also known as bronchoalveolar washing, is a diagnostic method of the lower respiratory system in which a bronchoscope is passed through the mouth or nose into an appropriate airway in the lungs, with a measured amou ...
(BAL)
* Blood and vessels: disseminated intravascular coagulation
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a condition in which blood clots form throughout the body, blocking Microvessel, small blood vessels. Symptoms may include chest pain, shortness of breath, leg pain, problems speaking, or problems ...
(DIC); leukoerythroblastic
Anemia (also spelt anaemia in British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen. This can be due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin availabl ...
reaction, endotheliitis Endotheliitis is an immune response within the endothelium in blood vessels, in which they become inflamed. The condition can cause oedema of the surrounding tissue, including the stroma, and can cause irritation and pain. If it is within the corne ...
,hemophagocytosis
Hemophagocytosis is a dangerous form of phagocytosis in which histiocytes engulf red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and their precursors in bone marrow and other tissues.
It is part of the presentation of hemophagocytic lymphohistioc ...
cardiac muscle cell
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle or myocardium) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, the others being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the Heart#Wa ...
necrosissteatosis
Steatosis, also called fatty change, is abnormal retention of fat (lipids) within a cell or organ. Steatosis most often affects the liver – the primary organ of lipid metabolism – where the condition is commonly referred to as fatty liver dis ...
infarction
Infarction is tissue death (necrosis) due to Ischemia, inadequate blood supply to the affected area. It may be caused by Thrombosis, artery blockages, rupture, mechanical compression, or vasoconstriction. The resulting lesion is referred to as a ...
white pulp
White pulp is a histological designation for regions of the spleen (named because it appears whiter than the surrounding red pulp on cross section), that encompasses approximately 25% of splenic tissue. White pulp consists entirely of lymphoid ...
depletion.
Prevention
 Preventive measures to reduce the chances of infection include getting vaccinated, staying at home, wearing a mask in public, avoiding crowded places, keeping distance from others, ventilating indoor spaces, managing potential exposure durations, washing hands with soap and water often and for at least twenty seconds, practising good respiratory hygiene, and avoiding touching the eyes, nose, or mouth with unwashed hands.
Preventive measures to reduce the chances of infection include getting vaccinated, staying at home, wearing a mask in public, avoiding crowded places, keeping distance from others, ventilating indoor spaces, managing potential exposure durations, washing hands with soap and water often and for at least twenty seconds, practising good respiratory hygiene, and avoiding touching the eyes, nose, or mouth with unwashed hands.FDA
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
, and in several other countries.National Institutes of Health
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in 1887 and is part of the United States Department of Health and Human Service ...
guidelines do not recommend any medication for prevention of COVID‑19, before or after exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus, outside the setting of a clinical trial.curve
In mathematics, a curve (also called a curved line in older texts) is an object similar to a line, but that does not have to be straight.
Intuitively, a curve may be thought of as the trace left by a moving point. This is the definition that ...
".
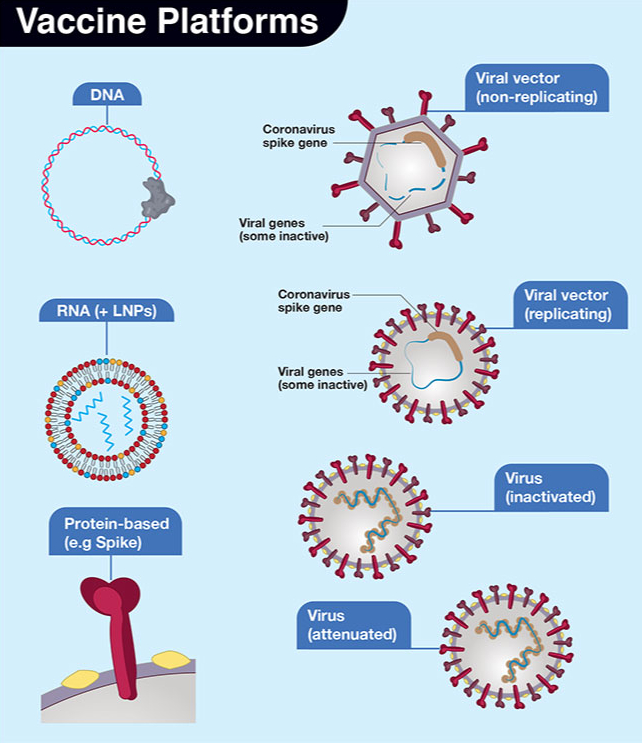
Vaccine

Face masks and respiratory hygiene

Indoor ventilation and avoiding crowded indoor spaces
The CDC states that avoiding crowded indoor spaces reduces the risk of COVID-19 infection.ventilation
Ventilation may refer to:
* Ventilation (physiology), the movement of air between the environment and the lungs via inhalation and exhalation
** Mechanical ventilation, in medicine, using artificial methods to assist breathing
*** Respirator, a ma ...
and air filtration
A particulate air filter is a device composed of fibrous, or porous materials which removes particulates such as smoke, dust, pollen, mold, viruses and bacteria from the air. Filters containing an adsorbent or catalyst such as charcoal (carbo ...
in public spaces to help clear out infectious aerosols.ventilation
Ventilation may refer to:
* Ventilation (physiology), the movement of air between the environment and the lungs via inhalation and exhalation
** Mechanical ventilation, in medicine, using artificial methods to assist breathing
*** Respirator, a ma ...
. The risk of COVID‑19 infection increases especially in spaces where people engage in physical exertion or raise their voice (e.g., exercising, shouting, singing) as this increases exhalation of respiratory droplets. Prolonged exposure to these conditions, typically more than 15 minutes, leads to higher risk of infection.Displacement ventilation Displacement ventilation (DV) is a room air distribution strategy where conditioned outdoor air is supplied at a low velocity from air supply diffusers located near floor level and extracted above the occupied zone, usually at ceiling height.
Sys ...
with large natural inlets can move stale air directly to the exhaust in laminar flow
Laminar flow () is the property of fluid particles in fluid dynamics to follow smooth paths in layers, with each layer moving smoothly past the adjacent layers with little or no mixing. At low velocities, the fluid tends to flow without lateral m ...
while significantly reducing the concentration of droplets and particles. Passive ventilation
Passive ventilation is the process of supplying air to and removing air from an indoor space without using mechanical systems. It refers to the flow of external air to an indoor space as a result of pressure differences arising from natural forc ...
reduces energy consumption and maintenance costs but may lack controllability
Controllability is an important property of a control system and plays a crucial role in many regulation problems, such as the stabilization of unstable systems using feedback, tracking problems, obtaining optimal control strategies, or, simply p ...
and heat recovery
Heat recovery ventilation (HRV), also known as mechanical ventilation heat recovery (MVHR) is a ventilation system that recovers energy by operating between two air sources at different temperatures. It is used to reduce the heating and cooling ...
. Displacement ventilation can also be achieved mechanically with higher energy and maintenance costs. The use of large ducts and openings helps to prevent mixing in closed environments. Recirculation and mixing should be avoided because recirculation prevents dilution of harmful particles and redistributes possibly contaminated air, and mixing increases the concentration and range of infectious particles and keeps larger particles in the air.
Hand-washing and hygiene
 Thorough hand hygiene after any cough or sneeze is required.
Thorough hand hygiene after any cough or sneeze is required.hand sanitiser
Hand sanitizer (also known as hand antiseptic, hand disinfectant, hand rub, or handrub) is a liquid, gel, or foam used to kill viruses, bacteria, and other microorganisms on the hands. It can also come in the form of a cream, spray, or wipe. W ...
with at least 60% alcohol. For areas where commercial hand sanitisers are not readily available, the WHO provides two formulations for local production. In these formulations, the antimicrobial activity arises from ethanol
Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with its formula also written as , or EtOH, where Et is the ps ...
or isopropanol
Isopropyl alcohol (IUPAC name propan-2-ol and also called isopropanol or 2-propanol) is a colorless, flammable, organic compound with a pungent alcoholic odor.
Isopropyl alcohol, an organic polar molecule, is miscible in water, ethanol, an ...
. Hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscosity, viscous than Properties of water, water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usua ...
is used to help eliminate bacterial spore
An endospore is a dormant, tough, and non-reproductive structure produced by some bacteria in the phylum Bacillota. The name "endospore" is suggestive of a spore or seed-like form (''endo'' means 'within'), but it is not a true spore (i.e., not ...
s in the alcohol; it is "not an active substance for hand antisepsis
An antiseptic ( and ) is an antimicrobial substance or compound that is applied to living tissue to reduce the possibility of sepsis, infection, or putrefaction. Antiseptics are generally distinguished from ''antibiotics'' by the latter's abili ...
". Glycerol
Glycerol () is a simple triol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, sweet-tasting, viscous liquid. The glycerol backbone is found in lipids known as glycerides. It is also widely used as a sweetener in the food industry and as a humectant in pha ...
is added as a humectant
A humectant is a hygroscopic (water-absorbing) substance used to keep things moist. They are used in many products, including food, cosmetics, medicines and pesticides. When used as a food additive, a humectant has the effect of keeping moistu ...
.
Social distancing
Social distancing (also known as physical distancing) includes infection control
Infection prevention and control (IPC) is the discipline concerned with preventing healthcare-associated infections; a practical rather than academic sub-discipline of epidemiology. In Northern Europe, infection prevention and control is expande ...
actions intended to slow the spread of the disease by minimising close contact between individuals. Methods include quarantines; travel restrictions; and the closing of schools, workplaces, stadiums, theatres, or shopping centres. Individuals may apply social distancing methods by staying at home, limiting travel, avoiding crowded areas, using no-contact greetings, and physically distancing themselves from others.
In 2020, outbreaks occurred in prisons due to crowding and an inability to enforce adequate social distancing.
Surface cleaning
After being expelled from the body, coronaviruses can survive on surfaces for hours to days. If a person touches the dirty surface, they may deposit the virus at the eyes, nose, or mouth where it can enter the body and cause infection.antimicrobial resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR or AR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from antimicrobials, which are drugs used to treat infections. This resistance affects all classes of microbes, including bacteria (antibiotic resista ...
through the use of inappropriate cleaning products and processes.UV light
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of t ...
in sunlight
Sunlight is the portion of the electromagnetic radiation which is emitted by the Sun (i.e. solar radiation) and received by the Earth, in particular the visible spectrum, visible light perceptible to the human eye as well as invisible infrare ...
.room temperature
Room temperature, colloquially, denotes the range of air temperatures most people find comfortable indoors while dressed in typical clothing. Comfortable temperatures can be extended beyond this range depending on humidity, air circulation, and ...
or lower, and when the relative humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation (meteorology), precipitation, dew, or fog t ...
is low (<50%).ethanol
Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with its formula also written as , or EtOH, where Et is the ps ...
* 50–100% isopropanol
Isopropyl alcohol (IUPAC name propan-2-ol and also called isopropanol or 2-propanol) is a colorless, flammable, organic compound with a pungent alcoholic odor.
Isopropyl alcohol, an organic polar molecule, is miscible in water, ethanol, an ...
* 0.1% sodium hypochlorite
Sodium hypochlorite is an alkaline inorganic chemical compound with the formula (also written as NaClO). It is commonly known in a dilute aqueous solution as bleach or chlorine bleach. It is the sodium salt of hypochlorous acid, consisting of ...
* 0.5% hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscosity, viscous than Properties of water, water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usua ...
* 0.2–7.5% povidone-iodine
Povidone-iodine (PVP-I), also known as iodopovidone, is an antiseptic used for skin disinfection before and after surgery. It may be used both to disinfect the hands of healthcare providers and the skin of the person they are caring for. It may ...
* 50–200 ppm hypochlorous acid
Hypochlorous acid is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula , also written as HClO, HOCl, or ClHO. Its structure is . It is an acid that forms when chlorine dissolves in water, and itself partially dissociates, forming a hypochlorite an ...
Other solutions, such as benzalkonium chloride
Benzalkonium chloride (BZK, BKC, BAK, BAC), also known as alkyldimethylbenzylammonium chloride (ADBAC) is a type of cationic surfactant. It is an organic salt classified as a quaternary ammonium compound. ADBACs have three main categories of use: ...
and chlorhexidine gluconate
Chlorhexidine is a disinfectant and antiseptic which is used for skin disinfection before surgery and to disinfect surgical instruments. It is also used for cleaning wounds, preventing dental plaque, treating yeast infections of the mouth, ...
, are less effective. Ultraviolet germicidal irradiation
Ultraviolet germicidal irradiation (UVGI) is a disinfection technique employing ultraviolet (UV) light, particularly UV-C (180–280 nm), to kill or inactivate microorganisms. UVGI primarily inactivates microbes by damaging their genetic ma ...
may also be used,
Self-isolation
Self-isolation
In health care facilities, isolation represents one of several measures that can be taken to implement in infection control: the prevention of communicable diseases from being transmitted from a patient to other patients, health care workers ...
at home has been recommended for those diagnosed with COVID‑19 and those who suspect they have been infected. Health agencies have issued detailed instructions for proper self-isolation.
International travel-related control measures
A 2021 Cochrane rapid review found that based upon low-certainty evidence, international travel-related control measures such as restricting cross-border travel may help to contain the spread of COVID‑19.
Treatment
Prognosis and risk factors
The severity of COVID‑19 varies. The disease may take a mild course with few or no symptoms, resembling other common upper respiratory diseases such as the common cold
The common cold, or the cold, is a virus, viral infectious disease of the upper respiratory tract that primarily affects the Respiratory epithelium, respiratory mucosa of the human nose, nose, throat, Paranasal sinuses, sinuses, and larynx. ...
. In 3–4% of cases (7.4% for those over age 65) symptoms are severe enough to cause hospitalisation.Istituto Superiore di Sanità
The ''Istituto Superiore di Sanità'' (Italian National Institute of Health, literally 'Higher Health Institute'), also ISS, is an Italian public institution that, as the leading technical-scientific body of the Italian National Health Service ( ...
reported that the median time between the onset of symptoms and death was twelve days, with seven being hospitalised. However, people transferred to an ICU had a median time of ten days between hospitalisation and death.prothrombin
Prothrombin (coagulation factor II) is encoded in the human by the F2-gene. It is proteolytically cleaved during the clotting process by the prothrombinase enzyme complex to form thrombin.
Thrombin (Factor IIa) (, fibrose, thrombase, throm ...
time and elevated C-reactive protein
C-reactive protein (CRP) is an annular (ring-shaped) pentameric protein found in blood plasma, whose circulating concentrations rise in response to inflammation. It is an acute-phase protein of hepatic origin that increases following interleukin ...
levels on admission to the hospital are associated with severe course of COVID‑19 and with a transfer to ICU.
Some early studies suggest 10% to 20% of people with COVID‑19 will experience symptoms lasting longer than a month.Tedros Adhanom
Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus (, sometimes spelled ; born 3 March 1965) is an Ethiopian public health official, researcher, diplomat, and the Director-General of the World Health Organization since 2017. He is the first African to become WHO Dire ...
warned that "to a significant number of people, the COVID virus poses a range of serious long-term effects". He has described the vast spectrum of COVID‑19 symptoms that fluctuate over time as "really concerning". They range from fatigue, a cough and shortness of breath, to inflammation and injury of major organsincluding the lungs and heart, and also neurological and psychologic effects. Symptoms often overlap and can affect any system in the body. Infected people have reported cyclical bouts of fatigue, headaches, months of complete exhaustion, mood swings, and other symptoms. Tedros therefore concluded that a strategy of achieving herd immunity
Herd immunity (also called herd effect, community immunity, population immunity, or mass immunity) is a form of indirect protection that applies only to contagious diseases. It occurs when a sufficient percentage of a population has become i ...
by infection, rather than vaccination, is "morally unconscionable and unfeasible".scientific review
A review article is an article that summarizes the current state of understanding on a topic within a certain discipline. A review article is generally considered a secondary source since it may analyze and discuss the method and conclusions ...
s smokers are more likely to require intensive care or die compared to non-smokers.obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classifi ...
, especially in conjunction with fatty liver disease
Fatty liver disease (FLD), also known as hepatic steatosis and steatotic liver disease (SLD), is a condition where excess fat builds up in the liver. Often there are no or few symptoms. Occasionally there may be tiredness or pain in the upper r ...
, contributes to an increased health risk of COVID‑19.hypogonadism
Hypogonadism means diminished functional activity of the human gonad, gonads—the testicles or the ovary, ovaries—that may result in diminished biosynthesis, production of sex hormones. Low androgen (e.g., testosterone) levels are referred t ...
were 2.4 times more likely than men with eugonadism to be hospitalised if they contracted COVID-19; Hypogonad men treated with testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting se ...
were less likely to be hospitalised for COVID-19 than men who were not treated for hypogonadism.
Genetic risk factors
Genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinians, Augustinian ...
plays an important role in the ability to fight off Covid.type I interferon
The type-I interferons (IFN) are cytokines which play essential roles in inflammation, immunoregulation, tumor cells recognition, and T-cell responses. In the human genome, a cluster of thirteen functional IFN genes is located at the 9p21.3 cyt ...
s or produce auto-antibodies
An autoantibody is an antibody (a type of protein) produced by the immune system that is directed against one or more of the individual's own proteins. Many autoimmune diseases (notably lupus erythematosus) are associated with such antibodies.
Pr ...
against these may get much sicker from COVID‑19. Genetic screening
Genetic testing, also known as DNA testing, is used to identify changes in DNA sequence or chromosome structure. Genetic testing can also include measuring the results of genetic changes, such as RNA analysis as an output of gene expression, or ...
is able to detect interferon
Interferons (IFNs, ) are a group of signaling proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of several viruses. In a typical scenario, a virus-infected cell will release interferons causing nearby cells to heighten ...
effector genes. Some genetic variants are risk factors in specific populations. For instance, an allele
An allele is a variant of the sequence of nucleotides at a particular location, or Locus (genetics), locus, on a DNA molecule.
Alleles can differ at a single position through Single-nucleotide polymorphism, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP), ...
of the DOCK2
Dedicator of cytokinesis protein 2 (Dock2) is a protein encoded in the human by the ''DOCK2'' gene. Dock2 is a large (~180 kDa) protein involved in intracellular signalling networks. It is a member of the DOCK-A subfamily of the DOCK family of g ...
gene (dedicator of cytokinesis 2 gene) is a common risk factor in Asian populations but much less common in Europe. The mutation leads to lower expression of DOCK2 especially in younger people with severe COVID-19 infections. In fact, many other genes and genetic variants have been found that determine the outcome of SARS-CoV-2 infections.
Children
While very young children have experienced lower rates of infection, older children have a rate of infection that is similar to the population as a whole. Children are likely to have milder symptoms and are at lower risk of severe disease than adults.
Long-term effects
Around 10% to 30% of non-hospitalised people with COVID-19 go on to develop long COVID
Long may refer to:
Measurement
* Long, characteristic of something of great duration
* Long, characteristic of something of great length
* Longitude (abbreviation: long.), a geographic coordinate
* Longa (music), note value in early music mens ...
. For those that do need hospitalisation, the incidence of long-term effects is over 50%.pulmonary fibrosis
Pulmonary fibrosis is a condition in which the lungs become scarred over time. Symptoms include shortness of breath, a dry cough, feeling tired, weight loss, and nail clubbing. Complications may include pulmonary hypertension, respiratory ...
or reduced lung function as measured by DLCO
DLCO or TLCO ( diffusing capacity or transfer factor of the lung for carbon monoxide (CO),) is the extent to which oxygen passes from the air sacs of the lungs into the blood. Commonly, it refers to the test used to determine this parameter. It w ...
, even in asymptomatic people, but with the suggestion of continuing improvement with the passing of more time.cognitive deficit
Cognitive impairment is an inclusive term to describe any characteristic that acts as a barrier to the cognition process or different areas of cognition. Cognition, also known as cognitive function, refers to the mental processes of how a person ...
, dementia
Dementia is a syndrome associated with many neurodegenerative diseases, characterized by a general decline in cognitive abilities that affects a person's ability to perform activities of daily living, everyday activities. This typically invo ...
, psychotic disorders, and epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of Non-communicable disease, non-communicable Neurological disorder, neurological disorders characterized by a tendency for recurrent, unprovoked Seizure, seizures. A seizure is a sudden burst of abnormal electrical activit ...
or seizures persists at an increased level two years after infection.
Immunity
 The
The immune response
An immune response is a physiological reaction which occurs within an organism in the context of inflammation for the purpose of defending against exogenous factors. These include a wide variety of different toxins, viruses, intra- and extracellula ...
by humans to SARS-CoV-2 virus occurs as a combination of the cell-mediated immunity and antibody production, just as with most other infections. B cells interact with T cells and begin dividing before selection into the plasma cell, partly on the basis of their affinity for antigen. Since SARS-CoV-2 has been in the human population only since December 2019, it remains unknown if the immunity
Immunity may refer to:
Medicine
* Immunity (medical), resistance of an organism to infection or disease
* ''Immunity'' (journal), a scientific journal published by Cell Press
Biology
* Immune system
Engineering
* Radiofrequence immunity ...
is long-lasting in people who recover from the disease.
Mortality
Several measures are commonly used to quantify mortality. These numbers vary by region and over time and are influenced by the volume of testing, healthcare system quality, treatment options, time since the initial outbreak, and population characteristics such as age, sex, and overall health.mortality rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular Statistical population, population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically ...
reflects the number of deaths within a specific demographic group divided by the population of that demographic group. Consequently, the mortality rate reflects the prevalence as well as the severity of the disease within a given population. Mortality rates are highly correlated to age, with relatively low rates for young people and relatively high rates among the elderly.
Case fatality rate
The case fatality rate
In epidemiology, case fatality rate (CFR) – or sometimes more accurately case-fatality risk – is the proportion of people who have been diagnosed with a certain disease and end up dying of it. Unlike a disease's mortality rate, the CFR does ...
(CFR) reflects the number of deaths divided by the number of diagnosed cases within a given time interval. Based on Johns Hopkins University statistics, the global death-to-case ratio is (/) as of . The number varies by region.
Infection fatality rate
A key metric in gauging the severity of COVID‑19 is the infection fatality rate
In epidemiology, case fatality rate (CFR) – or sometimes more accurately case-fatality risk – is the proportion of people who have been Medical diagnosis, diagnosed with a certain disease and end up Cause of death, dying of it. Unlike a disea ...
(IFR), also referred to as the ''infection fatality ratio'' or ''infection fatality risk''. This metric is calculated by dividing the total number of deaths from the disease by the total number of infected individuals; hence, in contrast to the CFR, the IFR incorporates asymptomatic and undiagnosed infections as well as reported cases.
Estimates
 A December 2020 systematic review and meta-analysis estimated that population IFR during the first wave of the pandemic was about 0.5% to 1% in many locations (including France, Netherlands, New Zealand, and Portugal), 1% to 2% in other locations (Australia, England, Lithuania, and Spain), and exceeded 2% in Italy.
A December 2020 systematic review and meta-analysis estimated that population IFR during the first wave of the pandemic was about 0.5% to 1% in many locations (including France, Netherlands, New Zealand, and Portugal), 1% to 2% in other locations (Australia, England, Lithuania, and Spain), and exceeded 2% in Italy.[ ] Text was copied from this source, which is available under
Text was copied from this source, which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
. That study also found that most of these differences in IFR reflected corresponding differences in the age composition of the population and age-specific infection rates; in particular, the metaregression estimate of IFR is very low for children and younger adults (e.g., 0.002% at age 10 and 0.01% at age 25) but increases progressively to 0.4% at age 55, 1.4% at age 65, 4.6% at age 75, and 15% at age 85.influenza
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These sympto ...
.
Earlier estimates of IFR
At an early stage of the pandemic, the World Health Organization reported estimates of IFR between 0.3% and 1%. On 2July, The WHO's chief scientist reported that the average IFR estimate presented at a two-day WHO expert forum was about 0.6%.Bergamo province
The province of Bergamo (; ) is a province in the Lombardy region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Bergamo. The province has a population of 1,103,768 (2023), an area of , and contains 242 ''comuni'' (municipalities).
Geography
The pro ...
, 0.6% of the population has died. In September 2020, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported preliminary estimates of age-specific IFRs for public health planning purposes.
Sex differences
COVID‑19 case fatality rate
In epidemiology, case fatality rate (CFR) – or sometimes more accurately case-fatality risk – is the proportion of people who have been diagnosed with a certain disease and end up dying of it. Unlike a disease's mortality rate, the CFR does ...
s are higher among men than women in most countries. However, in a few countries like India, Nepal, Vietnam, and Slovenia the fatality cases are higher in women than men.Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention
The Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CCDC; ) is an institution directly under the National Health Commission, based in Changping District, Beijing, China.
Established in 1983, it works to protect public health and safety ...
reported the death rate was 2.8% for men and 1.7% for women.
Ethnic differences
In the US, a greater proportion of deaths due to COVID‑19 have occurred among African Americans and other minority groups.health insurance
Health insurance or medical insurance (also known as medical aid in South Africa) is a type of insurance that covers the whole or a part of the risk of a person incurring medical expenses. As with other types of insurance, risk is shared among ma ...
and care of underlying conditions such as diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
,heart disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina pectoris, angina, myocardial infarction, heart attack), heart failure, ...
also increase their risk of death. Similar issues affect Native American and Latino communities.Black
Black is a color that results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without chroma, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness.Eva Heller, ''P ...
, Asian, and other ethnic minority background. More severe impacts upon patients including the relative incidence of the necessity of hospitalisation requirements, and vulnerability to the disease has been associated via DNA analysis to be expressed in genetic variants at chromosomal region 3, features that are associated with European Neanderthal
Neanderthals ( ; ''Homo neanderthalensis'' or sometimes ''H. sapiens neanderthalensis'') are an extinction, extinct group of archaic humans who inhabited Europe and Western and Central Asia during the Middle Pleistocene, Middle to Late Plei ...
heritage. That structure imposes greater risks that those affected will develop a more severe form of the disease.Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology
The Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology (, shortened to MPI EVA) is a research institute based in Leipzig, Germany, that was founded in 1997. It is part of the Max Planck Society network.
Well-known scientists currently based at ...
and the Karolinska Institutet
The Karolinska Institute (KI; ; sometimes known as the (Royal) Caroline Institute in English) is a research-led medical university in Solna within the Stockholm urban area of Sweden and one of the foremost medical research institutes globally. ...
.
Comorbidities
Biological
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, and distribution of ...
factors (immune response) and the general behaviour (habits) can strongly determine the consequences of COVID‑19.diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained hyperglycemia, high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or th ...
,cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina, heart attack), heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumati ...
.medical chart
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for patients, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care pract ...
s were available, 96.1% of people had at least one comorbidity
In medicine, comorbidity refers to the simultaneous presence of two or more medical conditions in a patient; often co-occurring (that is, concomitant or concurrent) with a primary condition. It originates from the Latin term (meaning "sicknes ...
with the average person having 3.4 diseases.ischaemic heart disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), or ischemic heart disease (IHD), is a type of heart disease involving the reduction of blood flow to the cardiac muscle due to a build-up of atheromatous plaque in the a ...
(27.6% of deaths), atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (AF, AFib or A-fib) is an Heart arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia) characterized by fibrillation, rapid and irregular beating of the Atrium (heart), atrial chambers of the heart. It often begins as short periods ...
(23.1% of deaths) and chronic renal failure
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a type of long-term kidney disease, defined by the sustained presence of abnormal kidney function and/or abnormal kidney structure. To meet criteria for CKD, the abnormalities must be present for at least three mo ...
(20.2% of deaths).
Most critical respiratory comorbidities according to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), are: moderate or severe asthma
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wh ...
, pre-existing COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by chronic respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. GOLD defines COPD as a heterogeneous lung condition characterized by chronic respiratory s ...
, pulmonary fibrosis
Pulmonary fibrosis is a condition in which the lungs become scarred over time. Symptoms include shortness of breath, a dry cough, feeling tired, weight loss, and nail clubbing. Complications may include pulmonary hypertension, respiratory ...
, cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder inherited in an autosomal recessive manner that impairs the normal clearance of Sputum, mucus from the lungs, which facilitates the colonization and infection of the lungs by bacteria, notably ''Staphy ...
.meta-analysis
Meta-analysis is a method of synthesis of quantitative data from multiple independent studies addressing a common research question. An important part of this method involves computing a combined effect size across all of the studies. As such, th ...
of several smaller research papers also suggests that smoking can be associated with worse outcomes. When someone with existing respiratory problems is infected with COVID‑19, they might be at greater risk for severe symptoms.amphetamine
Amphetamine (contracted from Alpha and beta carbon, alpha-methylphenethylamine, methylphenethylamine) is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, an ...
s, insofar as their drug use may have caused lung damage.
In August 2020, the CDC issued a caution that tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
(TB) infections could increase the risk of severe illness or death. The WHO recommended that people with respiratory symptoms be screened for both diseases, as testing positive for COVID‑19 could not rule out co-infections. Some projections have estimated that reduced TB detection due to the pandemic could result in 6.3 million additional TB cases and 1.4 million TB-related deaths by 2025.
History
The virus is thought to be of natural animal origin, most likely through spillover infection
Spillover infection, also known as pathogen spillover and spillover event, occurs when a reservoir population with a high pathogen prevalence comes into contact with a novel host population. The pathogen is transmitted from the reservoir population ...
.index case
The index case or patient zero is the first documented patient in a disease epidemic within a population, or the first documented patient included in an epidemiological study.
It can also refer to the first case of a condition or syndrome (no ...
originated and investigations into the origin of the pandemic are ongoing.Science
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which stu ...
'', virus transmission into humans occurred through two spillover events in November 2019 and was likely due to live wildlife trade on the Huanan wet market in the city of Wuhan
Wuhan; is the capital of Hubei, China. With a population of over eleven million, it is the most populous city in Hubei and the List of cities in China by population, eighth-most-populous city in China. It is also one of the nine National cent ...
(Hubei, China). Doubts about the conclusions have mostly centered on the precise site of spillover. Earlier phylogenetics
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical dat ...
estimated that SARS-CoV-2 arose in October or November 2019.Guangdong
) means "wide" or "vast", and has been associated with the region since the creation of Guang Prefecture in AD 226. The name "''Guang''" ultimately came from Guangxin ( zh, labels=no, first=t, t= , s=广信), an outpost established in Han dynasty ...
before Wuhan.
Most scientists believe the virus spilled into human populations through natural zoonosis
A zoonosis (; plural zoonoses) or zoonotic disease is an infectious disease of humans caused by a pathogen (an infectious agent, such as a virus, bacterium, parasite, fungi, or prion) that can jump from a non-human vertebrate to a human. When ...
, similar to the SARS-CoV-1
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 1 (SARS-CoV-1), previously known as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV), is a strain (biology), strain of coronavirus that causes severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), the ...
and MERS-CoV
Middle East respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus (MERS-CoV, ''Betacoronavirus cameli'') or EMC/2012 ( HCoV-EMC/2012), is the virus that causes Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS). It is a species of coronavirus which infects humans, ba ...
outbreaks, and consistent with other pandemics in human history.Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is an intergovernmental body of the United Nations. Its job is to "provide governments at all levels with scientific information that they can use to develop climate policies". The World Met ...
several social and environmental factors including climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
, natural ecosystem destruction and wildlife trade
Wildlife trade refers to the exchange of products derived from non-domesticated animals or plants usually extracted from their natural environment or raised under controlled conditions. It can involve the trade of living or dead individuals, tis ...
increased the likelihood of such zoonotic spillover.European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
found climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
increased the likelihood of the pandemic by influencing distribution of bat species.Huanan Seafood Market
The Wuhan Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market (), also known as the Huanan Seafood Market (''Huanan'' means 'South China') or simply the Wuhan Wet Market, was a live animal and seafood market in Jianghan District, Wuhan, the capital of Hubei Prov ...
in Wuhan
Wuhan; is the capital of Hubei, China. With a population of over eleven million, it is the most populous city in Hubei and the List of cities in China by population, eighth-most-populous city in China. It is also one of the nine National cent ...
in December 2019.Wuhan Institute of Virology
The Wuhan Institute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (WIV; zh, s=中国科学院武汉病毒研究所) is a research institute on virology under the Wuhan Branch of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Located in Jiangxia District, Wuh ...
.biological weapon
Biological agents, also known as biological weapons or bioweapons, are pathogens used as weapons. In addition to these living or replicating pathogens, toxins and Toxin#Biotoxins, biotoxins are also included among the bio-agents. More than 1,2 ...
and is unlikely to have been genetically engineered
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification or genetic manipulation, is the modification and manipulation of an organism's genes using technology. It is a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including th ...
. There is no evidence SARS-CoV-2 existed in any laboratory prior to the pandemic.Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market
The Wuhan Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market (), also known as the Huanan Seafood Market (''Huanan'' means 'South China') or simply the Wuhan Wet Market, was a live animal and fish market, seafood market in Jianghan District, Wuhan, the capital of ...
, which also sold live animals.superspreading event
A superspreading event (SSEV) is an event in which an infectious disease is spread much more than usual, while an unusually contagious organism infected with a disease is known as a superspreader. In the context of a human-borne illness, a super ...
, but that it was not the site of the initial outbreak. Traces of the virus have been found in wastewater samples that were collected in Milan
Milan ( , , ; ) is a city in northern Italy, regional capital of Lombardy, the largest city in Italy by urban area and the List of cities in Italy, second-most-populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of nea ...
and Turin
Turin ( , ; ; , then ) is a city and an important business and cultural centre in northern Italy. It is the capital city of Piedmont and of the Metropolitan City of Turin, and was the first Italian capital from 1861 to 1865. The city is main ...
, Italy, on 18 December 2019.
By December 2019, the spread of infection was almost entirely driven by human-to-human transmission.Wuhan Central Hospital
The Central Hospital of Wuhan () is a tertiary hospital located in Jiang'an District in Wuhan, Hubei, China. It was established in 1880 as a clinic under Hankou's Catholic church. In 1893, it was later expanded and renamed as Catholic Hospital.
...
sent a bronchoalveolar lavage fluid
Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL), also known as bronchoalveolar washing, is a diagnostic method of the lower respiratory system in which a bronchoscope is passed through the mouth or nose into an appropriate airway in the lungs, with a measured amou ...
(BAL) sample from an unresolved clinical case to sequencing company Vision Medicals. On 27 and 28 December, Vision Medicals informed the Wuhan Central Hospital and the Chinese CDC of the results of the test, showing a new coronavirus. A pneumonia cluster of unknown cause was observed on 26 December and treated by the doctor Zhang Jixian
Zhang Jixian ( zh, s=张继先, t=張繼先, p=Zhāng Jìxiān, born 1966) is a Chinese pulmonologist. She is known to have discovered SARS‑CoV‑2, and was the director of the Department of Respiratory Medicine of Hubei Provincial Hospital of ...
in Hubei Provincial Hospital, who informed the Wuhan Jianghan CDC on 27 December. On 30 December, a test report addressed to Wuhan Central Hospital, from company CapitalBio Medlab, stated an erroneous positive result for SARS
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is a viral respiratory disease of zoonotic origin caused by the virus SARS-CoV-1, the first identified strain of the SARS-related coronavirus. The first known cases occurred in November 2002, and the ...
, causing a group of doctors at Wuhan Central Hospital to alert their colleagues and relevant hospital authorities of the result. The Wuhan Municipal Health Commission issued a notice to various medical institutions on "the treatment of pneumonia of unknown cause" that same evening. Eight of these doctors, including Li Wenliang
Li Wenliang (; 12 October 19857 February 2020) was a Chinese ophthalmologist who warned his colleagues about early COVID-19 infections in Wuhan.
On 30 December 2019, Wuhan Centres for Disease Prevention and Control (Wuhan CDC) issued emerg ...
(punished on 3January), were later admonished by the police for spreading false rumours and another, Ai Fen
Ai Fen () is a Chinese doctor and director of the emergency department of Central Hospital of Wuhan. In December 2019, she was one of the first doctors to encounter pneumonia patients infected with the then-unknown virus, SARS-CoV-2. On 30 Dec ...
, was reprimanded by her superiors for raising the alarm.
The Wuhan Municipal Health Commission made the first public announcement of a pneumonia outbreak of unknown cause on 31 December, confirming 27 casesChinese provinces
Provinces ( zh, c=省, p=Shěng) are the most numerous type of province-level divisions in the People's Republic of China (PRC). There are currently 22 provinces administered by the PRC and one province that is claimed, but not administere ...
, helped by the Chinese New Year migration and Wuhan being a transport hub and major rail interchange.Shenzhen
Shenzhen is a prefecture-level city in the province of Guangdong, China. A Special economic zones of China, special economic zone, it is located on the east bank of the Pearl River (China), Pearl River estuary on the central coast of Guangdong ...
.New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
New York may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* ...
came from European travellers, rather than directly from China or any other Asian country.Reuters
Reuters ( ) is a news agency owned by Thomson Reuters. It employs around 2,500 journalists and 600 photojournalists in about 200 locations worldwide writing in 16 languages. Reuters is one of the largest news agencies in the world.
The agency ...
'' reported that it had estimated the worldwide total number of deaths due to COVID‑19 to have exceeded five million.
The Public Health Emergency of International Concern for COVID-19 ended on 5 May 2023. By this time, everyday life in most countries had returned to how it was before the pandemic.
Misinformation
After the initial outbreak of COVID19, misinformation
Misinformation is incorrect or misleading information. Misinformation and disinformation are not interchangeable terms: misinformation can exist with or without specific malicious intent, whereas disinformation is distinct in that the information ...
and disinformation
Disinformation is misleading content deliberately spread to deceive people, or to secure economic or political gain and which may cause public harm. Disinformation is an orchestrated adversarial activity in which actors employ strategic dece ...
regarding the origin, scale, prevention, treatment, and other aspects of the disease rapidly spread online.
Other species
Humans appear to be capable of spreading the virus to some other animals,ferret
The ferret (''Mustela furo'') is a small, domesticated species belonging to the family Mustelidae. The ferret is most likely a domesticated form of the wild European polecat (''Mustela putorius''), as evidenced by the ferret's ability to inter ...
s, can catch this virus from infected humans.respiratory
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies gr ...
(such as a cough) and digestive symptoms.pig
The pig (''Sus domesticus''), also called swine (: swine) or hog, is an omnivorous, domesticated, even-toed, hoofed mammal. It is named the domestic pig when distinguishing it from other members of the genus '' Sus''. Some authorities cons ...
s, duck
Duck is the common name for numerous species of waterfowl in the family (biology), family Anatidae. Ducks are generally smaller and shorter-necked than swans and goose, geese, which are members of the same family. Divided among several subfam ...
s, or chickens at all.Mice
A mouse (: mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus' ...
, rats, and rabbits, if they can be infected at all, are unlikely to be involved in spreading the virus.great ape
The Hominidae (), whose members are known as the great apes or hominids (), are a taxonomic family of primates that includes eight extant species in four genera: '' Pongo'' (the Bornean, Sumatran and Tapanuli orangutan); '' Gorilla'' (the ...
species such as orangutan
Orangutans are great apes native to the rainforests of Indonesia and Malaysia. They are now found only in parts of Borneo and Sumatra, but during the Pleistocene they ranged throughout Southeast Asia and South China. Classified in the genus ...
s can also be infected with the COVID‑19 virus.Mink
Mink are dark-colored, semiaquatic, carnivorous mammals of the genera ''Neogale'' and '' Mustela'' and part of the family Mustelidae, which also includes weasels, otters, and ferrets. There are two extant species referred to as "mink": the A ...
s, which are in the same family as ferrets, have been infected.mink farm
Fur farming is the practice of breeding or raising certain types of animals for their fur.
Most of the world's farmed fur was produced by European farmers. In 2018, there were 5,000 fur farms in the EU, located across 22 countries; these area ...
s.Denmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous a ...
, a major producer of mink pelts, ordered the slaughter of all minks over fears of viral mutations,Cluster 5
Cluster 5 is a designation used by the Danish Statens Serum Institut for a virus variant described by the institute in autumn 2020, in connection with investigations of SARS-CoV-2 infection among mink and humans in the north of Jutland, Denmark.
...
. A vaccine for mink and other animals is being researched.
Research
International research on vaccines and medicines in COVID19 is underway by government organisations, academic groups, and industry researchers.clinical trial
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human subject research, human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel v ...
s have been undertaken, with research happening on every continent except Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. ...
. , more than 200 possible treatments have been studied in humans.
Transmission and prevention research
Modelling
A model is an informative representation of an object, person, or system. The term originally denoted the plans of a building in late 16th-century English, and derived via French and Italian ultimately from Latin , .
Models can be divided into ...
research has been conducted with several objectives, including predictions of the dynamics of transmission, diagnosis and prognosis of infection, estimation of the impact of interventions, or allocation of resources. Modelling studies are mostly based on compartmental models in epidemiology
Compartmental models are a mathematical framework used to simulate how populations move between different states or "compartments." While widely applied in various fields, they have become particularly fundamental to the mathematical modelling of ...
, estimating the number of infected people over time under given conditions. Several other types of models have been developed and used during the COVID19 pandemic including computational fluid dynamics
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical analysis and data structures to analyze and solve problems that involve fluid dynamics, fluid flows. Computers are used to perform the calculations required ...
models to study the flow physics of COVID19, retrofits of crowd movement models to study occupant exposure, mobility-data based models to investigate transmission, or the use of macroeconomic
Macroeconomics is a branch of economics that deals with the performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of an economy as a whole. This includes regional, national, and global economies. Macroeconomists study topics such as output/ GDP ...
models to assess the economic impact of the pandemic.
Treatment-related research
 Repurposed
Repurposed antiviral drug
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Antiviral drugs are a class of antimicrobials ...
s make up most of the research into COVID‑19 treatments.vasodilator
Vasodilation, also known as vasorelaxation, is the widening of blood vessels. It results from relaxation of smooth muscle cells within the vessel walls, in particular in the large veins, large arteries, and smaller arterioles. Blood vessel wal ...
s, corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
s, immune therapies, lipoic acid
Lipoic acid (LA), also known as α-lipoic acid, alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) and thioctic acid, is an organosulfur compound derived from caprylic acid (octanoic acid). ALA, which is made in animals normally, is essential for aerobic metabolism. It i ...
, bevacizumab
Bevacizumab, sold under the brand name Avastin among others, is a monoclonal antibody medication used to treat a number of types of cancers and a specific eye disease. For cancer, it is given by slow injection into a vein (intravenous) and use ...
, and recombinant angiotensin-converting enzyme 2.Solidarity trial
The Solidarity trial for treatments is a multinational Phase III-IV clinical trial organized by the World Health Organization (WHO) and partners to compare four untested treatments for hospitalized people with severe COVID-19 illness. The tria ...
to assess the treatment effects of some promising drugs:experimental drug
An experimental drug is a medicinal product (a drug or vaccine) that has not yet received drug approval, approval from governmental regulatory agency, regulatory authorities for routine use in human medicine, human or veterinary medicine. A medicin ...
called remdesivir
Remdesivir, sold under the brand name Veklury, Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged. is a Broad-spectrum antiviral drug, broad-spectrum ...
* Anti-malarial
Antimalarial medications or simply antimalarials are a type of antiparasitic chemical agent, often naturally derived, that can be used to treat or to prevent malaria, in the latter case, most often aiming at two susceptible target groups, young c ...
drugs chloroquine
Chloroquine is an antiparasitic medication that treats malaria. It works by increasing the levels of heme in the blood, a substance toxic to the malarial parasite. This kills the parasite and stops the infection from spreading. Certain types ...
and hydroxychloroquine
Hydroxychloroquine, sold under the brand name Plaquenil among others, is a medication used to prevent and treat malaria in areas where malaria remains sensitive to chloroquine. Other uses include treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, an ...
* Two anti-HIV drugs, lopinavir/ritonavir
Lopinavir/ritonavir (LPV/r), sold under the brand name Kaletra among others, is a fixed-dose combination antiretroviral medication for the treatment and prevention of HIV/AIDS. It combines lopinavir with a low dose of ritonavir. It is gene ...
and interferon-beta
The type-I interferons (IFN) are cytokines which play essential roles in inflammation, immunoregulation, tumor cells recognition, and T-cell responses. In the human genome, a cluster of thirteen functional IFN genes is located at the 9p21.3 cyt ...
More than 300 active clinical trials are underway as of April 2020.RECOVERY Trial
The Randomised Evaluation of COVID-19 Therapy (RECOVERY Trial) is a large-enrollment clinical trial of possible treatments for people in the United Kingdom admitted to hospital with severe COVID-19 infection. The trial was later expanded to ...
in the United Kingdom showed that dexamethasone reduced mortality by one third for people who are critically ill on ventilators and one fifth for those receiving supplemental oxygen. Because this is a well-tested and widely available treatment, it was welcomed by the WHO, which is in the process of updating treatment guidelines to include dexamethasone and other steroids. Based on those preliminary results, dexamethasone treatment has been recommended by the NIH for peoples with COVID‑19 who are mechanically ventilated or who require supplemental oxygen but not in people with COVID‑19 who do not require supplemental oxygen.
In September 2020, the WHO released updated guidance on using corticosteroids for COVID‑19.European Medicines Agency
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) is an agency of the European Union (EU) in charge of the evaluation and supervision of pharmaceutical products. Prior to 2004, it was known as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products ...
(EMA) endorsed the use of dexamethasone in adults and adolescents from twelve years of age and weighing at least who require supplemental oxygen therapy.[ Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.] Dexamethasone can be taken by mouth
Oral administration is a route of administration whereby a substance is taken through the Human mouth, mouth, swallowed, and then processed via the digestive system. This is a common route of administration for many medications.
Oral administ ...
or given as an injection or infusion (drip) into a vein.Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respo ...
(FDA) issued an emergency use authorisation for the investigational monoclonal antibody therapy bamlanivimab
Bamlanivimab is a monoclonal antibody developed by AbCellera Biologics and Eli Lilly as a treatment for COVID-19. The medication was granted an emergency use authorization (EUA) by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in November 2020, and ...
for the treatment of mild-to-moderate COVID‑19.etesevimab
Bamlanivimab/etesevimab is a combination of two monoclonal antibody, monoclonal antibodies, bamlanivimab and etesevimab, administered together via intravenous infusion as a treatment for COVID-19. Both types of antibody target the coronavirus ...
administered together for the treatment of mild to moderate COVID‑19 in people twelve years of age or older weighing at least who test positive for SARS‑CoV‑2 and who are at high risk for progressing to severe COVID‑19. The authorised use includes treatment for those who are 65 years of age or older or who have certain chronic medical conditions.
Cytokine storm
 A
A cytokine storm
A cytokine storm, also called hypercytokinemia, is a pathological reaction in humans and other animals in which the innate immune system causes an uncontrolled and excessive release of pro-inflammatory signaling molecules called cytokines. Cytok ...
can be a complication in the later stages of severe COVID‑19. A cytokine storm is a potentially deadly immune reaction where a large amount of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokine
Chemokines (), or chemotactic cytokines, are a family of small cytokines or signaling proteins secreted by cells that induce directional movement of leukocytes, as well as other cell types, including endothelial and epithelial cells. In addit ...
s are released too quickly. A cytokine storm can lead to ARDS and multiple organ failure. Data collected from Jin Yin-tan Hospital in Wuhan, China indicates that people who had more severe responses to COVID‑19 had greater amounts of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in their system than people who had milder responses. These high levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines indicate presence of a cytokine storm.
Tocilizumab
Tocilizumab, sold under the brand name Actemra among others, is an immunosuppressive drug, used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis, polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis, giant cell arter ...
has been included in treatment guidelines by China's National Health Commission
The National Health Commission (NHC) is a Ministries of the People's Republic of China, cabinet-level executive department of the State Council of the People's Republic of China which is responsible for formulating national health policies. It ...
after a small study was completed.ferritin
Ferritin is a universal intracellular and extracellular protein that stores iron and releases it in a controlled fashion. The protein is produced by almost all living organisms, including archaea, bacteria, algae, higher plants, and animals. ...
blood test to identify a cytokine storm (also called cytokine storm syndrome, not to be confused with cytokine release syndrome
In immunology, cytokine release syndrome (CRS) is a form of systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) that can be triggered by a variety of factors such as infections and certain drugs. It refers to cytokine storm syndromes (CSS) and occur ...
), it is meant to counter such developments, which are thought to be the cause of death in some affected people.[Various sources:
*
*
* ] The interleukin-6 receptor
Interleukin 6 receptor (IL6R) also known as CD126 (Cluster of Differentiation 126) is a type I cytokine receptor.
Function
Interleukin 6 (IL6) is a potent pleiotropic cytokine that regulates cell growth and differentiation and plays an impor ...
(IL-6R) antagonist
An antagonist is a character in a story who is presented as the main enemy or rival of the protagonist and is often depicted as a villain.[CAR T cell
In biology, chimeric antigen receptors (CARs)—also known as chimeric immunoreceptors, chimeric T cell receptors or artificial T cell receptors—are receptor proteins that have been engineered to give T cells the new ability to target a specific ...](_b ...<br></span></div> was approved by the FDA to undergo a PhaseIII clinical trial assessing its effectiveness on COVID‑19 based on retrospective case studies for the treatment of steroid-refractory cytokine release syndrome induced by a different cause, <div class=)
therapy
A therapy or medical treatment is the attempted remediation of a health problem, usually following a medical diagnosis. Both words, ''treatment'' and ''therapy'', are often abbreviated tx, Tx, or Tx.
As a rule, each therapy has indications a ...
, in 2017.blood–brain barrier
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable membrane, semipermeable border of endothelium, endothelial cells that regulates the transfer of solutes and chemicals between the circulatory system and the central nervous system ...
, and exacerbating neurotoxicity
Neurotoxicity is a form of toxicity in which a biological, chemical, or physical agent produces an adverse effect on the structure or function of the central and/or peripheral nervous system. It occurs when exposure to a substance – specifical ...
while having no effect on the incidence of CRS.
Lenzilumab, an anti-GM-CSF monoclonal antibody
A monoclonal antibody (mAb, more rarely called moAb) is an antibody produced from a cell lineage made by cloning a unique white blood cell. All subsequent antibodies derived this way trace back to a unique parent cell.
Monoclonal antibodie ...
, is protective in murine models for CAR T cell-induced CRS and neurotoxicity and is a viable therapeutic option due to the observed increase of pathogenic GM-CSF secreting Tcells in hospitalised patients with COVID‑19.
Passive antibodies
 Transferring purified and concentrated
Transferring purified and concentrated antibodies
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as bacteria and viruses, including those that caus ...
produced by the immune systems of those who have recovered from COVID‑19 to people who need them is being investigated as a non-vaccine method of passive immunisation.mechanism of action
In pharmacology, the term mechanism of action (MOA) refers to the specific biochemical Drug interaction, interaction through which a Medication, drug substance produces its pharmacological effect. A mechanism of action usually includes mention o ...
by which passive antibody therapy can mediate defence against SARS-CoV-2. The spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 is the primary target for neutralising antibodies.phagocytosis
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell (biology), cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs ph ...
, may be possible.convalescent serum
In immunology, antiserum is a blood serum containing antibodies (either monoclonal or polyclonal) that is used to spread passive immunity to many diseases via blood donation (plasmapheresis). For example, convalescent serum, or passive antibod ...
, which consists of the liquid portion of the blood from people who recovered from the infection and contains antibodies specific to this virus, which is then administered to active patients.
Bioethics
Since the outbreak of the COVID‑19 pandemic, scholars have explored the bioethics
Bioethics is both a field of study and professional practice, interested in ethical issues related to health (primarily focused on the human, but also increasingly includes animal ethics), including those emerging from advances in biology, me ...
, normative economics
Normativity is the phenomenon in human societies of designating some actions or outcomes as good, desirable, or permissible, and others as bad, undesirable, or impermissible. A norm in this sense means a standard for evaluating or making judgme ...
, and political theories
Political philosophy studies the theoretical and conceptual foundations of politics. It examines the nature, scope, and legitimacy of political institutions, such as states. This field investigates different forms of government, ranging from de ...
of healthcare policies related to the public health crisis. Academics have pointed to the moral distress of healthcare workers, ethics of distributing scarce healthcare resources such as ventilators, and the global justice of vaccine diplomacies. The socio-economic inequalities between genders, races, groups with disabilities, communities, regions, countries, and continents have also drawn attention in academia and the general public.
See also
* Coronavirus diseases
Coronavirus diseases are caused by viruses in the coronavirus subfamily, a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, the group of viruses cause respiratory tract infections that can range from ...
, a group of closely related syndromes
* Disease X
Disease X is a placeholder name that was adopted by the World Health Organization (WHO) in February 2018 on their shortlist of blueprint priority diseases to represent a hypothetical, unknown pathogen. The WHO adopted the placeholder name to ...
, a WHO term
*
*
References
Further reading
*
*
*
Scholia
Scholia (: scholium or scholion, from , "comment", "interpretation") are grammatical, critical, or explanatory comments – original or copied from prior commentaries – which are inserted in the margin of the manuscript of ancient a ...
Q104287299.
External links
Health agencies
Coronavirus disease (COVID‑19)Facts
by the World Health Organization (WHO)
Coronavirus (COVID‑19)
by the UK National Health Service
The National Health Service (NHS) is the term for the publicly funded health care, publicly funded healthcare systems of the United Kingdom: the National Health Service (England), NHS Scotland, NHS Wales, and Health and Social Care (Northern ...
(NHS)
Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19)
by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the National public health institutes, national public health agency of the United States. It is a Federal agencies of the United States, United States federal agency under the United S ...
(CDC)
Directories
Coronavirus Resource Center
at the Center for Inquiry
The Center for Inquiry (CFI) is a U.S. nonprofit organization that works to mitigate belief in pseudoscience and the paranormal and to fight the influence of religion in government.
History
The Center for Inquiry was established in 1991 by ...
COVID‑19 Information on FireMountain.net
COVID‑19 Resource Directory on OpenMD
Medical journals
BMJ's Coronavirus (covid‑19) Hub
by the BMJ
''The BMJ'' is a fortnightly peer-reviewed medical journal, published by BMJ Publishing Group Ltd, which in turn is wholly-owned by the British Medical Association (BMA). ''The BMJ'' has editorial freedom from the BMA. It is one of the world' ...
Coronavirus (Covid‑19)
by ''The New England Journal of Medicine
''The New England Journal of Medicine'' (''NEJM'') is a weekly medical journal published by the Massachusetts Medical Society. Founded in 1812, the journal is among the most prestigious peer-reviewed medical journals. Its 2023 impact factor w ...
''
Coronavirus (COVID‑19) Research Highlights
by Springer Nature
Springer Nature or the Springer Nature Group is a German-British academic publishing company created by the May 2015 merger of Springer Science+Business Media and Holtzbrinck Publishing Group's Nature Publishing Group, Palgrave Macmillan, and Macm ...
Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID‑19)
by ''JAMA
''JAMA'' (''The Journal of the American Medical Association'') is a peer-reviewed medical journal published 48 times a year by the American Medical Association. It publishes original research, reviews, and editorials covering all aspects of b ...
''
COVID‑19 Resource Centre
by ''The Lancet
''The Lancet'' is a weekly peer-reviewed general medical journal, founded in England in 1823. It is one of the world's highest-impact academic journals and also one of the oldest medical journals still in publication.
The journal publishes ...
''
Covid‑19: Novel Coronavirus
by Wiley Publishing
John Wiley & Sons, Inc., commonly known as Wiley (), is an American multinational publishing company that focuses on academic publishing and instructional materials. The company was founded in 1807 and produces books, journals, and encyclop ...
Novel Coronavirus Information Center
by Elsevier
Elsevier ( ) is a Dutch academic publishing company specializing in scientific, technical, and medical content. Its products include journals such as ''The Lancet'', ''Cell (journal), Cell'', the ScienceDirect collection of electronic journals, ...
Treatment guidelines
*
*
*
*
*
*
{{#invoke:Authority control, authorityControl
Occupational safety and health
Vaccine-preventable diseases
Viral respiratory tract infections
Zoonotic viral diseases
Public health
Coronavirus-associated diseases
 Complications may include
Complications may include 
 The SARS-CoV-2 virus can infect a wide range of cells and systems of the body. COVID‑19 is most known for affecting the upper respiratory tract (sinuses, nose, and throat) and the lower respiratory tract (windpipe and lungs). The lungs are the organs most affected by COVID‑19 because the virus accesses host cells via the
The SARS-CoV-2 virus can infect a wide range of cells and systems of the body. COVID‑19 is most known for affecting the upper respiratory tract (sinuses, nose, and throat) and the lower respiratory tract (windpipe and lungs). The lungs are the organs most affected by COVID‑19 because the virus accesses host cells via the  Research conducted when Alpha was the dominant variant has suggested COVID-19 may cause brain damage. Later research showed that all variants studied (including Omicron) killed brain cells, but the exact cells killed varied by variant. It is unknown if such damage is temporary or permanent. Observed individuals infected with COVID-19 (most with mild cases) experienced an additional 0.2% to 2% of brain tissue lost in regions of the brain connected to the sense of smell compared with uninfected individuals, and the overall effect on the brain was equivalent on average to at least one extra year of normal ageing; infected individuals also scored lower on several cognitive tests. All effects were more pronounced among older ages.
Research conducted when Alpha was the dominant variant has suggested COVID-19 may cause brain damage. Later research showed that all variants studied (including Omicron) killed brain cells, but the exact cells killed varied by variant. It is unknown if such damage is temporary or permanent. Observed individuals infected with COVID-19 (most with mild cases) experienced an additional 0.2% to 2% of brain tissue lost in regions of the brain connected to the sense of smell compared with uninfected individuals, and the overall effect on the brain was equivalent on average to at least one extra year of normal ageing; infected individuals also scored lower on several cognitive tests. All effects were more pronounced among older ages.
 Although SARS-CoV-2 has a tropism for ACE2-expressing epithelial cells of the respiratory tract, people with severe COVID‑19 have symptoms of systemic hyperinflammation. Clinical laboratory findings of elevated IL2, IL6, IL7, as well as the following suggest an underlying immunopathology:
* Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GMCSF)
* Interferon gamma-induced protein10 (IP10)
* Monocyte chemoattractant protein1 (MCP1)
* Macrophage inflammatory protein 1alpha (MIP1alpha)
*
Although SARS-CoV-2 has a tropism for ACE2-expressing epithelial cells of the respiratory tract, people with severe COVID‑19 have symptoms of systemic hyperinflammation. Clinical laboratory findings of elevated IL2, IL6, IL7, as well as the following suggest an underlying immunopathology:
* Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GMCSF)
* Interferon gamma-induced protein10 (IP10)
* Monocyte chemoattractant protein1 (MCP1)
* Macrophage inflammatory protein 1alpha (MIP1alpha)
*  Multiple viral and host factors affect the pathogenesis of the virus. The S-protein, otherwise known as the spike protein, is the viral component that attaches to the host receptor via the
Multiple viral and host factors affect the pathogenesis of the virus. The S-protein, otherwise known as the spike protein, is the viral component that attaches to the host receptor via the  The severity of the inflammation can be attributed to the severity of what is known as the
The severity of the inflammation can be attributed to the severity of what is known as the 

 Chest CT scans may be helpful to diagnose COVID‑19 in individuals with a high clinical suspicion of infection but are not recommended for routine screening. Bilateral multilobar ground-glass opacities with a peripheral, asymmetric, and posterior distribution are common in early infection. Subpleural dominance,
Chest CT scans may be helpful to diagnose COVID‑19 in individuals with a high clinical suspicion of infection but are not recommended for routine screening. Bilateral multilobar ground-glass opacities with a peripheral, asymmetric, and posterior distribution are common in early infection. Subpleural dominance,  Preventive measures to reduce the chances of infection include getting vaccinated, staying at home, wearing a mask in public, avoiding crowded places, keeping distance from others, ventilating indoor spaces, managing potential exposure durations, washing hands with soap and water often and for at least twenty seconds, practising good respiratory hygiene, and avoiding touching the eyes, nose, or mouth with unwashed hands.
Those diagnosed with COVID‑19 or who believe they may be infected are advised by the CDC to stay home except to get medical care, call ahead before visiting a healthcare provider, wear a face mask before entering the healthcare provider's office and when in any room or vehicle with another person, cover coughs and sneezes with a tissue, regularly wash hands with soap and water and avoid sharing personal household items.
The first COVID‑19 vaccine was granted regulatory approval on 2December 2020 by the UK medicines regulator MHRA. It was evaluated for emergency use authorisation (EUA) status by the US
Preventive measures to reduce the chances of infection include getting vaccinated, staying at home, wearing a mask in public, avoiding crowded places, keeping distance from others, ventilating indoor spaces, managing potential exposure durations, washing hands with soap and water often and for at least twenty seconds, practising good respiratory hygiene, and avoiding touching the eyes, nose, or mouth with unwashed hands.
Those diagnosed with COVID‑19 or who believe they may be infected are advised by the CDC to stay home except to get medical care, call ahead before visiting a healthcare provider, wear a face mask before entering the healthcare provider's office and when in any room or vehicle with another person, cover coughs and sneezes with a tissue, regularly wash hands with soap and water and avoid sharing personal household items.
The first COVID‑19 vaccine was granted regulatory approval on 2December 2020 by the UK medicines regulator MHRA. It was evaluated for emergency use authorisation (EUA) status by the US 

 Thorough hand hygiene after any cough or sneeze is required. The WHO also recommends that individuals wash hands often with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, especially after going to the toilet or when hands are visibly dirty, before eating and after blowing one's nose. When soap and water are not available, the CDC recommends using an alcohol-based
Thorough hand hygiene after any cough or sneeze is required. The WHO also recommends that individuals wash hands often with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, especially after going to the toilet or when hands are visibly dirty, before eating and after blowing one's nose. When soap and water are not available, the CDC recommends using an alcohol-based  The
The  A December 2020 systematic review and meta-analysis estimated that population IFR during the first wave of the pandemic was about 0.5% to 1% in many locations (including France, Netherlands, New Zealand, and Portugal), 1% to 2% in other locations (Australia, England, Lithuania, and Spain), and exceeded 2% in Italy.
A December 2020 systematic review and meta-analysis estimated that population IFR during the first wave of the pandemic was about 0.5% to 1% in many locations (including France, Netherlands, New Zealand, and Portugal), 1% to 2% in other locations (Australia, England, Lithuania, and Spain), and exceeded 2% in Italy.  Repurposed
Repurposed  A
A  Transferring purified and concentrated
Transferring purified and concentrated