Buttock Implant on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Gluteoplasty (from
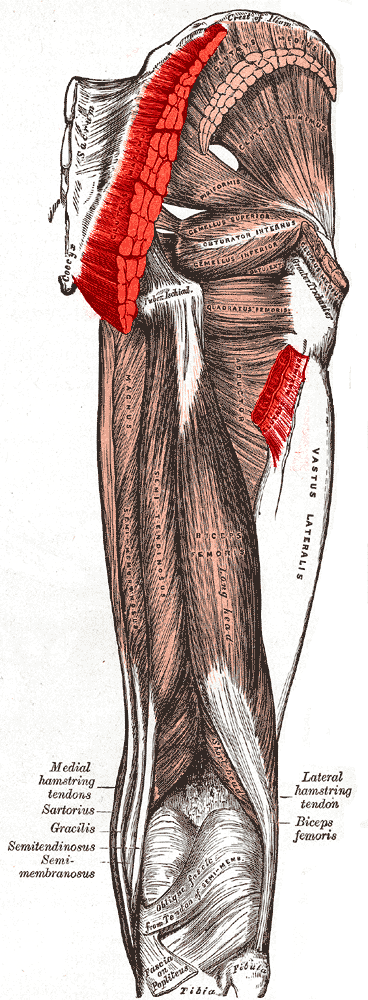 Anatomically, the mass of each
Anatomically, the mass of each
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
: , 'rump' + , 'shaped, formed, moulded') denotes the plastic surgery and the liposuction
Liposuction, or simply lipo, is a type of fat-removal procedure used in plastic surgery. Evidence does not support an effect on weight beyond a couple of months and does not appear to affect obesity-related problems. In the United States, lip ...
procedures for the correction of congenital
A birth defect is an abnormal condition that is present at childbirth, birth, regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disability, disabilities that may be physical disability, physical, intellectual disability, intellectual, or dev ...
, traumatic, and acquired defects/deformities of the buttocks and the anatomy of the gluteal region; and for the aesthetic enhancement (by augmentation or by reduction) of the contour of the buttocks
The buttocks (: buttock) are two rounded portions of the exterior anatomy of most mammals, located on the posterior of the pelvic region. In humans, the buttocks are located between the lower back and the perineum. They are composed of a lay ...
.
The procedures for buttock augmentation and buttock repair include the surgical
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery ...
emplacement of a gluteal implant (buttock prosthesis); liposculpture (fat transfer and liposuction
Liposuction, or simply lipo, is a type of fat-removal procedure used in plastic surgery. Evidence does not support an effect on weight beyond a couple of months and does not appear to affect obesity-related problems. In the United States, lip ...
); and body contouring (surgery, liposculpture, and Sculptra injections) to resolve the patient's particular concern or deformity of the gluteal region.
Background
The functional purpose of the buttocks musculature is to establish a stablegait
Gait is the pattern of Motion (physics), movement of the limb (anatomy), limbs of animals, including Gait (human), humans, during Animal locomotion, locomotion over a solid substrate. Most animals use a variety of gaits, selecting gait based on s ...
(balanced walk) for the person who requires the surgical correction of either a defect or a deformity of the gluteal region; therefore, the restoration of anatomic functionality is the therapeutic consideration that determines which gluteoplasty procedure will effectively correct the damaged muscles of the buttocks. The applicable techniques for surgical
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery ...
and correction include the surgical emplacement of gluteal implants; autologous tissue-flaps; the excision (cutting and removal) of damaged tissues; lipoinjection augmentation; and liposuction
Liposuction, or simply lipo, is a type of fat-removal procedure used in plastic surgery. Evidence does not support an effect on weight beyond a couple of months and does not appear to affect obesity-related problems. In the United States, lip ...
reduction—to resolve the defect or deformity caused by a traumatic injury (blunt
Blunt may refer to:
* Blunt (surname), a surname (and list of people with the name)
* Blunt (cigar), a term used in the cigar industry to designate blunt-tipped, usually factory-rolled cigars
* Blunt (cannabis), a slang term used in cannabis cult ...
, penetrating, blast
Blast or The Blast may refer to:
*Explosion, a rapid increase in volume and release of energy in an extreme manner
*Detonation, an exothermic front accelerating through a medium that eventually drives a shock front
*A planned explosion in a mine, ...
) to the buttocks muscles (gluteus maximus
The gluteus maximus is the main extensor muscle of the hip in humans. It is the largest and outermost of the three gluteal muscles and makes up a large part of the shape and appearance of each side of the hips. It is the single largest muscle in ...
, gluteus medius
The gluteus medius, one of the three gluteal muscles, is a broad, thick, radiating muscle. It is situated on the outer surface of the pelvis.
Its posterior third is covered by the gluteus maximus, its anterior two-thirds by the gluteal aponeuros ...
, gluteus minimus
The gluteus minimus, or glutæus minimus, the smallest of the three gluteal muscles, is situated immediately beneath the gluteus medius.
Structure
It is fan-shaped, arising from the outer surface of the ilium, between the anterior and infe ...
), and any deformation of the anatomic contour of the buttocks. Likewise, the corrective techniques apply to resolving the sagging skin of the body, and the muscle and bone deformities presented by the formerly obese
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classified as obese when ...
patient, after a massive weight loss (MWL) bariatric surgery
Bariatric surgery (also known as metabolic surgery or weight loss surgery) is a surgical procedure used to manage obesity and obesity-related conditions. Long term weight loss with bariatric surgery may be achieved through alteration of gut ho ...
procedure; and for resolving congenital defects
A birth defect is an abnormal condition that is present at birth, regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can range from mild to severe. Birth def ...
and congenital deformities of the gluteal region.
Surgical anatomy of the buttocks
;Muscular origins and insertionsbuttock
The buttocks (: buttock) are two rounded portions of the exterior anatomy of most mammals, located on the posterior of the pelvic region. In humans, the buttocks are located between the lower back and the perineum. They are composed of a laye ...
principally comprises two muscles—the gluteus maximus muscle
The gluteus maximus is the main extensor muscle of the hip in humans. It is the largest and outermost of the three gluteal muscles and makes up a large part of the shape and appearance of each side of the hips. It is the single largest muscle i ...
and the gluteus medius muscle
The gluteus medius, one of the three gluteal muscles, is a broad, thick, radiating muscle. It is situated on the outer surface of the pelvis.
Its posterior third is covered by the gluteus maximus, its anterior two-thirds by the gluteal aponeuros ...
—which are covered by a layer of adipose body fat. The upper aspects of the buttocks end at the iliac crest
The crest of the ilium (or iliac crest) is the superior border of the wing of ilium and the superolateral margin of the greater pelvis.
Structure
The iliac crest stretches posteriorly from the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS) to the posterio ...
(the upper edges of the wings of the ilium, and the upper lateral margins of the greater pelvis
The pelvic cavity is a body cavity that is bounded by the bones of the pelvis. Its oblique roof is the pelvic inlet (the superior opening of the pelvis). Its lower boundary is the pelvic floor.
The pelvic cavity primarily contains the reproduc ...
), and the lower aspects of the buttocks end at the horizontal gluteal crease
The gluteal sulcus (also known as the gluteal fold, tuck, fold of the buttock, horizontal gluteal crease, or gluteal furrow) is an area of the body of humans and anthropoid apes, described by a horizontal crease formed by the inferior aspect of t ...
, where the buttocks anatomy joins the rear, upper portion of the thighs. The gluteus maximus muscle has two points of insertion: (i) the one-third superior portion of the (coarse line) linea aspera
The linea aspera () is a ridge of roughened surface on the posterior surface of the shaft of the femur. It is the site of attachments of muscles and the intermuscular septum.
Its margins diverge above and below.
The linea aspera is a prominent ...
of the thigh bone (femur
The femur (; : femurs or femora ), or thigh bone is the only long bone, bone in the thigh — the region of the lower limb between the hip and the knee. In many quadrupeds, four-legged animals the femur is the upper bone of the hindleg.
The Femo ...
), and (ii) the superior portion of the iliotibial tract
The iliotibial tract or iliotibial band (ITB; also known as Maissiat's band or the IT band) is a longitudinal fibrous reinforcement of the fascia lata. The action of the muscles associated with the ITB ( tensor fasciae latae and some fibers of g ...
(a long, fibrous reinforcement of the deep fascia lata
The fascia lata is the deep fascia of the thigh. It encloses the thigh muscles and forms the outer limit of the fascial compartments of thigh, which are internally separated by the medial intermuscular septum and the lateral intermuscular sept ...
of the thigh). The left and the right gluteus maximus muscles (the butt cheeks) are vertically divided by the intergluteal cleft
The intergluteal cleft or just gluteal cleft, also known by a number of synonyms, including natal cleft and cluneal cleft, is the groove between the buttocks that runs from just below the sacrum to the perineum, so named because it forms the vis ...
(the butt-crack) which contains the anus
In mammals, invertebrates and most fish, the anus (: anuses or ani; from Latin, 'ring' or 'circle') is the external body orifice at the ''exit'' end of the digestive tract (bowel), i.e. the opposite end from the mouth. Its function is to facil ...
.
The gluteus maximus muscle
The gluteus maximus is the main extensor muscle of the hip in humans. It is the largest and outermost of the three gluteal muscles and makes up a large part of the shape and appearance of each side of the hips. It is the single largest muscle i ...
is a large and very thick muscle (6–7 cm) located on the sacrum
The sacrum (: sacra or sacrums), in human anatomy, is a triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1S5) between ages 18 and 30.
The sacrum situates at the upper, back part of the pelvic cavity, ...
, which is the large, triangular bone located at the base of the vertebral column
The spinal column, also known as the vertebral column, spine or backbone, is the core part of the axial skeleton in vertebrates. The vertebral column is the defining and eponymous characteristic of the vertebrate. The spinal column is a segmente ...
, and at the upper- and back-part of the pelvic cavity
The pelvic cavity is a body cavity that is bounded by the bones of the pelvis. Its oblique roof is the pelvic inlet (the superior opening of the pelvis). Its lower boundary is the pelvic floor.
The pelvic cavity primarily contains the reproduc ...
, where it is inserted (like a wedge) between the two hip bone
The hip bone (os coxae, innominate bone, pelvic bone or coxal bone) is a large flat bone, constricted in the center and expanded above and below. In some vertebrates (including humans before puberty) it is composed of three parts: the Ilium (bone) ...
s. The upper part of the sacrum is connected to the final lumbar vertebra
The lumbar vertebrae are located between the thoracic vertebrae and pelvis. They form the lower part of the back in humans, and the tail end of the back in quadrupeds. In humans, there are five lumbar vertebrae. The term is used to describe the ...
(L5), and to the bottom of the coccyx
The coccyx (: coccyges or coccyxes), commonly referred to as the tailbone, is the final segment of the vertebral column in all apes, and analogous structures in certain other mammals such as horse anatomy, horses. In tailless primates (e.g. hum ...
(tailbone). At its origin, the gluteus maximus muscle extends to include parts of the iliac bone, the sacrum, the coccyx, the sacrosciatic ligament, and the tuberosity of the ischium
The ischial tuberosity (or tuberosity of the ischium, tuber ischiadicum), also known colloquially as the sit bones or sitz bones, or as a pair the sitting bones, is a large posterior (anatomy), posterior bone, bony protuberance on the superior r ...
.
Like every pelvic-area muscle, the gluteus maximus muscle originates from the pelvis; nonetheless, it is the sole pelvic muscle not inserted to the trochanter
A trochanter is a tubercle of the femur near its joint with the hip bone. In humans and most mammals, the trochanters serve as important muscle attachment sites. Humans have two, sometimes three, trochanters.
Etymology
The anatomical term ' ...
(head of the femur), and is approximately aligned to the femur
The femur (; : femurs or femora ), or thigh bone is the only long bone, bone in the thigh — the region of the lower limb between the hip and the knee. In many quadrupeds, four-legged animals the femur is the upper bone of the hindleg.
The Femo ...
and the fascia lata
The fascia lata is the deep fascia of the thigh. It encloses the thigh muscles and forms the outer limit of the fascial compartments of thigh, which are internally separated by the medial intermuscular septum and the lateral intermuscular sept ...
(the deep fascia
Deep fascia (or investing fascia) is a fascia, a layer of dense connective tissue that can surround individual muscles and groups of muscles to separate into fascial compartments.
This fibrous connective tissue interpenetrates and surrounds the m ...
of the thigh); the tissues of the gluteus maximus muscle cover only the rear, lateral face of the trochanter, and there form a bursa (purse) that faces the interior of the thigh
In anatomy, the thigh is the area between the hip (pelvis) and the knee. Anatomically, it is part of the lower limb.
The single bone in the thigh is called the femur. This bone is very thick and strong (due to the high proportion of bone tissu ...
.
Innervation
The motor innervation of the gluteus maximus muscle is performed by theinferior gluteal nerve
The inferior gluteal nerve is the main motor neuron that innervates the gluteus maximus muscle. It is responsible for the movement of the gluteus maximus in activities requiring the hip to extend the thigh, such as climbing stairs. Injury to this ...
(a branch nerve of the sacral plexus
In human anatomy, the sacral plexus is a nerve plexus which provides motor and sensory nerves for the posterior thigh, most of the lower leg and foot, and part of the pelvis. It is part of the lumbosacral plexus and emerges from the lumbar verteb ...
) and extends from the pelvis to the gluteal region, then traverses the greater sciatic foramen
The greater sciatic foramen is an opening (:wikt:foramen, foramen) in the posterior human pelvis. It is formed by the sacrotuberous ligament, sacrotuberous and sacrospinous ligaments. The piriformis muscle passes through the foramen and occupies ...
(opening) from behind and to the middle to then join the sciatic nerve
The sciatic nerve, also called the ischiadic nerve, is a large nerve in humans and other vertebrate animals. It is the largest branch of the sacral plexus and runs alongside the hip joint and down the right lower limb. It is the longest and widest ...
. The inferior gluteal nerve divides into three collateral branches: (i) the gluteus branch, (ii) the perineal branch, and (iii) the femoral branch. The first ramification—the gluteus branch—is a branch nerve that is very close to the emergence of the inferior gluteal nerve to the area, next to the inferior border of the pyramidalis muscle
The pyramidalis muscle is a small triangular muscle, anterior to the rectus abdominis muscle, and contained in the rectus sheath.
Structure
The pyramidalis muscle is part of the anterior abdominal wall. Inferiorly, the pyramidalis muscle attache ...
.
In surgical and body contouring praxis, the plastic surgeon creates the implant-pocket—either for the gluteal prosthesis or for the injections of autologous fat—by undermining the gluteus maximus muscle with a dissection technique that avoids the sacrum
The sacrum (: sacra or sacrums), in human anatomy, is a triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1S5) between ages 18 and 30.
The sacrum situates at the upper, back part of the pelvic cavity, ...
, the sacrotuberous ligament
The sacrotuberous ligament (great or posterior sacrosciatic ligament) is situated at the lower and back part of the pelvis. It is flat, and triangular in form; narrower in the middle than at the ends.
Structure
It runs from the sacrum (the lowe ...
, and the tuberosity of the ischium
The ischial tuberosity (or tuberosity of the ischium, tuber ischiadicum), also known colloquially as the sit bones or sitz bones, or as a pair the sitting bones, is a large posterior (anatomy), posterior bone, bony protuberance on the superior r ...
; which, if accidentally cut, might isolate the posterior (back) portion of the muscle and lead to denervation, the loss of nerve function and of innervation.
Vascularization
Thesuperior gluteal artery
The superior gluteal artery is the terminal branch of the posterior division of the internal iliac artery. It exits the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen before splitting into a superficial branch and a deep branch.
Structure
Origin
Th ...
, the inferior gluteal artery
The inferior gluteal artery (sciatic artery) is a terminal branch of the anterior trunk of the internal iliac artery. It exits the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen. It is distributed chiefly to the buttock and the back of the thigh.
Ana ...
, the superior gluteal veins, and the inferior gluteal veins irrigate the gluteus maximus muscle with arterial
An artery () is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in ...
and venous
Veins () are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and fetal c ...
blood. The vascularization, the entrance of the blood vessels to the muscle tissues, occurs at the anterior (front) face of the muscle, very close to the sacrum
The sacrum (: sacra or sacrums), in human anatomy, is a triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1S5) between ages 18 and 30.
The sacrum situates at the upper, back part of the pelvic cavity, ...
. As the arteries and the veins enter the mass of the gluteal muscle, they divide into narrower blood-vessel ramifications (configured like the horizontal branches of a tree), most of which travel parallel to the muscle fibres.
In surgical and body contouring praxis, the plastic surgeon effects the implant-pocket undermining of the gluteus maximus muscle by carefully separating the muscle fibres to avoid severing the pertinent blood vessels, which would interfere with the blood irrigation of the muscle tissue. Therefore, to create an implant-pocket, either for a gluteal prosthesis or for lipoinjection, a low-angle muscle-dissection is performed in order to avoid the risk of severing any major branch—superior
Superior may refer to:
*Superior (hierarchy), something which is higher in a hierarchical structure of any kind
Places
* Superior (proposed U.S. state), an unsuccessful proposal for the Upper Peninsula of Michigan to form a separate state
*Lak ...
or inferior—of the gluteal artery, which travels very close to the sacrum
The sacrum (: sacra or sacrums), in human anatomy, is a triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1S5) between ages 18 and 30.
The sacrum situates at the upper, back part of the pelvic cavity, ...
and to the sacrotuberous ligament
The sacrotuberous ligament (great or posterior sacrosciatic ligament) is situated at the lower and back part of the pelvis. It is flat, and triangular in form; narrower in the middle than at the ends.
Structure
It runs from the sacrum (the lowe ...
.
Surgical procedures
Surgical therapy
While the resolution of the defects and deformities of the gluteal region can be realized surgically, the assessment of the degree of severity of the injury organizes treatment therapies into three types: (i) buttocks augmentation, (ii) buttocks reduction, and (iii) contour irregularity treatments that combine surgery and liposculpture (liposuction
Liposuction, or simply lipo, is a type of fat-removal procedure used in plastic surgery. Evidence does not support an effect on weight beyond a couple of months and does not appear to affect obesity-related problems. In the United States, lip ...
and fat-injection).
Buttocks augmentation treatments
Gluteal implants
The augmentation of the buttocks is realized with a gluteal implant, which is emplaced under eachgluteus maximus muscle
The gluteus maximus is the main extensor muscle of the hip in humans. It is the largest and outermost of the three gluteal muscles and makes up a large part of the shape and appearance of each side of the hips. It is the single largest muscle i ...
; the insertion of the buttock prosthesis is through a midline incision (5–8-cm-wide) over the tailbone (coccyx
The coccyx (: coccyges or coccyxes), commonly referred to as the tailbone, is the final segment of the vertebral column in all apes, and analogous structures in certain other mammals such as horse anatomy, horses. In tailless primates (e.g. hum ...
). Augmentation with a gluteal implant is the method most effective for enlarging the buttocks of a patient whose body possesses few stores of excess adipose fat in the lower portion of the trunk, the buttocks
The buttocks (: buttock) are two rounded portions of the exterior anatomy of most mammals, located on the posterior of the pelvic region. In humans, the buttocks are located between the lower back and the perineum. They are composed of a lay ...
and thigh
In anatomy, the thigh is the area between the hip (pelvis) and the knee. Anatomically, it is part of the lower limb.
The single bone in the thigh is called the femur. This bone is very thick and strong (due to the high proportion of bone tissu ...
s, the anatomic regions where the human body usually stores excess body fat. Post-operatively, because of the cutting (incising) into the flesh of the tailbone muscles, the full healing of the augmented tissues can be approximately 6–8 months, in the course of which the gluteal-muscle tissues relax, and the settled buttocks prostheses are integrated to the gluteal region. The implantation procedure can be performed upon a patient who is either sedated or anaesthetized, either under general anaesthesia
General anaesthesia (UK) or general anesthesia (US) is medically induced loss of consciousness that renders a patient unarousable even by painful stimuli. It is achieved through medications, which can be injected or inhaled, often with an analges ...
or under local anaesthesia
Local anesthesia is any technique to induce the absence of sensation in a specific part of the body, generally for the aim of inducing local analgesia, i.e. local insensitivity to pain, although other local senses may be affected as well. It all ...
. The usual operating-room time for a buttocks augmentation procedure is approximately two hours. The procedure can be managed either as an overnight in-patient treatment or as a hospital outpatient treatment. Given the nature of the surgical incisions to the gluteus maximus muscles, the therapeutic management of post-surgical pain (at the surgical-wound sites) and normal tissue-healing usually require a four to six-week convalescence, after which the patient resumes their normal-life activities.
Lipoinjection
The augmentation and contouring of the buttocks with autologous fat transfer (lipoinjection) therapy is realized with the excess adipose-fat tissue harvested from theabdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the gut, belly, tummy, midriff, tucky, or stomach) is the front part of the torso between the thorax (chest) and pelvis in humans and in other vertebrates. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal ...
, flanks, and thigh
In anatomy, the thigh is the area between the hip (pelvis) and the knee. Anatomically, it is part of the lower limb.
The single bone in the thigh is called the femur. This bone is very thick and strong (due to the high proportion of bone tissu ...
s of the patient. In 1987 Dr. Eduardo Krulig, a Venezuelan plastic surgeon, described the technique, using the name "lipoinjection" for the first time, mentioning the regions of the body where the technique is useful. The gentle liposuction applied to harvest the autologous fat minimally disturbs the local tissues, especially the connective-tissue layer between the skin and the immediate subcutaneous muscle tissues. Then, the harvested fat is injected to the pertinent body area of the gluteal region, through a fine-gauge cannula
A cannula (; Latin meaning 'little reed'; : cannulae or cannulas) is a tube that can be inserted into the body, often for the delivery or removal of fluid or for the gathering of samples. In simple terms, a cannula can surround the inner or out ...
inserted through a small surgical incision, which produces a short and narrow scar
A scar (or scar tissue) is an area of fibrosis, fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin after an injury. Scars result from the biological process of wound repair in the skin, as well as in other Organ (anatomy), organs, and biological tissue, t ...
. Lipoinjection contouring and augmentation with the patient's own body fat avoids the possibility of tissue rejection, and is physically less invasive than buttocks-implant surgery. Therefore, depending upon the health of the patient, the convalescence period allows them to resume daily, normal-life activities at two days post-operative, and the full spectrum of physical activity at two weeks post-operative. Furthermore, the liposuction harvesting of the patient's excess body fat improves the aesthetic appearance of the body fat donor-sites. Nonetheless, physiologically, the human body's normal, health-management chemistry does resorb (break down and eliminate) some of the injected adipose-fat tissue, and so might diminish the augmentation. According to the degree of diminishment of the volume and contour caused by the fat-resorption, the patient might require additional sessions of fat-transfer therapy to achieve the desired size, shape, and contour of the buttocks.
In common parlance, lipoinjection into the buttocks for aesthetic purposes is often called a "Brazilian butt lift" (BBL). This name is suggested to originate from the Brazilian surgeon Ivo Pitanguy
Ivo Hélcio Jardim de Campos Pitanguy (July 5, 1926 – August 6, 2016) was a pioneering Brazilian plastic surgeon renowned globally for his significant contributions to the field of aesthetic and reconstructive surgery. Based in Rio de Janeiro, ...
, who pioneered the surgery in the 1960s. The popularity of the surgery significantly increased during the 2010s as a result of social media trends.
Body contouring
The augmentation of the buttocks, by rearranging and enhancing the pertinent muscle and fat tissues of the gluteal region, is realized with a combined gluteoplasty procedure of surgery (subcutaneous dermal-fat flaps) and liposculpture (fat-suction, fat-injection). Therapeutically, such a combined correction-and-enhancement procedure is a realistic and feasible lower-body-lift treatment for the patient who has undergone massiveweight loss
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health, or physical fitness, refers to a reduction of the total body mass, by a mean loss of fluid, body fat (adipose tissue), or lean mass (namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon, and other conn ...
(MWL) in the course of resolving obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classifi ...
with bariatric surgery
Bariatric surgery (also known as metabolic surgery or weight loss surgery) is a surgical procedure used to manage obesity and obesity-related conditions. Long term weight loss with bariatric surgery may be achieved through alteration of gut ho ...
. In the case of the patient who presents under-projected, flat buttocks ( gluteal hypoplasia), and a degree of gluteal-muscle ptosis (prolapsation, falling forward), wherein neither gluteal-implant surgery nor lipoinjection would be adequate to restoring the natural anatomic contour of the gluteal region, the application of a combined treatment of autologous dermal-fat flap surgery and lipoinjection can achieve the required functional correction and aesthetic contour.
Buttocks reduction treatments
The methods for reducing the size of the buttocks include the varieties ofliposuction
Liposuction, or simply lipo, is a type of fat-removal procedure used in plastic surgery. Evidence does not support an effect on weight beyond a couple of months and does not appear to affect obesity-related problems. In the United States, lip ...
, such as lipectomy (with and without ultrasonic
Ultrasound is sound with frequencies greater than 20 kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply to any frequency range, includi ...
enhancement) to reduce excess body fat, and superficial liposculpture, to reshape, refine, and re-establish the natural contour of the body. The usual buttocks-reduction treatment is lipectomy with applied tumescence
Tumescence is the quality or state of being tumescent or swollen. Tumescence usually refers to the normal engorgement with blood ( vascular congestion) of the erectile tissues, marking sexual excitation, and possible readiness for sexual activity. ...
and anaesthesia
Anesthesia (American English) or anaesthesia (British English) is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prev ...
, wherein the body fat is harvested by aspiration (suction) through a small-gauge cannula (2–4 mm) that is inserted through a small incision, either to the intergluteal sulcus (the butt-crack), or to the upper area of the gluteus maximus muscle
The gluteus maximus is the main extensor muscle of the hip in humans. It is the largest and outermost of the three gluteal muscles and makes up a large part of the shape and appearance of each side of the hips. It is the single largest muscle i ...
proper.
Ultrasonic lipectomy
Ultrasonically assisted liposuction can quickly remove a large volume ofbody fat
Adipose tissue (also known as body fat or simply fat) is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. It also contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, Blood vessel, vascular endothel ...
for the correction of a notable occurrence of lipodystrophy
Lipodystrophy syndromes are a group of genetic or acquired disorders in which the body is unable to produce and maintain healthy fat tissue. The medical condition is characterized by abnormal or degenerative conditions of the body's adipose tissu ...
, a deposit of adipose fat to the buttocks and related anatomic areas. The ultrasonic
Ultrasound is sound with frequencies greater than 20 kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply to any frequency range, includi ...
liposuction machine liquefies the excess fat tissue, and so more readily facilitates its removal with conventional suction-lipectomy. The quick fat-harvesting allowed by the ultrasonic lipectomy technique has eliminated the larger (long and wide) surgical incisions that once were required for removing a large volume of adipose tissue. Nonetheless, because of the sensitivity of the gluteal-region tissues, the skin of the pertinent donor-site is cooled in order to prevent ultrasonic heat damage caused by the liquefying and removal of the excess adipose fat.
Superficial liposculpture
Reshaping the buttocks with liposculpture is performed with a small cannula (2 mm) specifically for contouring superficial body fat, the configuration of which (number of open ports) is determined by the type and the degree of gluteal correction to be realized. To sculpt rounded contours to square-shaped buttocks muscles, superficial liposculpture allows the plastic surgeon to control the injection-rate of the fat-volume. Moreover, superficialliposuction
Liposuction, or simply lipo, is a type of fat-removal procedure used in plastic surgery. Evidence does not support an effect on weight beyond a couple of months and does not appear to affect obesity-related problems. In the United States, lip ...
can be combined with other treatment methods for contouring the gluteal region to achieve the required functional, anatomic correction, and the aesthetic enhancement sought by the patient, such as reshaping the lateral area of the buttocks into an athletic form. The study ''Contouring the Gluteal Region with Tumescent Liposculpture'' (2011) indicated that effective, gluteal-region contouring is best achieved by tailoring the liposuction-reduction and the lipoinjection-augmentation techniques to the anatomic topography of the body areas to be corrected. Furthermore, the study ''Contouring of the Gluteal Region in Women: Enhancement and Augmentation'' (2011) indicated that natural contours of the buttocks and the thighs are effectively achieved with a combined gluteoplasty of selective liposuction and lipoinjection, which reduces the need for aggressive surgical procedures, decreases the risk of medical complications, abbreviates wound-recovery-time, and lessens post-operative scarring. Combined with any buttocks-correction method, superficial liposculpture facilitates the treatment of contour irregularities, the surgical revision of scars, and the correction of gluteal-region contour depressions.
Surgical technique
Pre-operative matters
To meet the functional requirements and the aesthetic expectations (body image
Body image is a person's thoughts, feelings and perception of the aesthetics or sexual attractiveness of their own body. The concept of body image is used in several disciplines, including neuroscience, psychology, medicine, psychiatry, psycho ...
) of the patient, the plastic surgeon establishes a realistic and feasible surgery plan by which to correct the anatomic contour deficiencies of the gluteal region. The surgeon and the patient determine the location of the surgical-wound scar
A scar (or scar tissue) is an area of fibrosis, fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin after an injury. Scars result from the biological process of wound repair in the skin, as well as in other Organ (anatomy), organs, and biological tissue, t ...
s, and determine the best operative position, to allow the proper exposure of the pertinent anatomy to be corrected. Because the surgical procedure requires the tumescence
Tumescence is the quality or state of being tumescent or swollen. Tumescence usually refers to the normal engorgement with blood ( vascular congestion) of the erectile tissues, marking sexual excitation, and possible readiness for sexual activity. ...
and anaesthesia
Anesthesia (American English) or anaesthesia (British English) is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prev ...
of the gluteal-region area to be corrected, the physician and the anaesthesiologist
Anesthesiology, anaesthesiology or anaesthesia is the medical specialty concerned with the total perioperative care of patients before, during and after surgery. It encompasses anesthesia, intensive care medicine, critical emergency medicine, an ...
determine the volumes of the anaesthetic and tumescent fluids to be administered to the patient during the procedure, and so avoid the risks of drugs overdose and toxicity.
Operative matters
For a lipoinjection augmentation, the surgeon first dissects and prepares the augmentation-pocket to which will be injected the autologous fat-tissue. The surgical creation (muscle dissection) of the augmentation-pocket avoids the gluteal innervation (superior gluteal nerve
The superior gluteal nerve is a mixed (motor and sensory) nerve of the sacral plexus that originates in the pelvis. It provides motor innervation to the gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, tensor fasciae latae; it also has a cutaneous branch.
Str ...
and inferior gluteal nerve
The inferior gluteal nerve is the main motor neuron that innervates the gluteus maximus muscle. It is responsible for the movement of the gluteus maximus in activities requiring the hip to extend the thigh, such as climbing stairs. Injury to this ...
) and the vascular system (venous
Veins () are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and fetal c ...
and arterial
An artery () is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in ...
) of the gluteus maximus muscle
The gluteus maximus is the main extensor muscle of the hip in humans. It is the largest and outermost of the three gluteal muscles and makes up a large part of the shape and appearance of each side of the hips. It is the single largest muscle i ...
. Afterwards, the surgeon sutures the dissection-incision and secures it with adhesive tape to ensure that the augmentation-pocket remains open, as dissected, ready to receive the injections of adipose fat. For the revision of scars, with surgery and injections of autologous fat, or with allopathic synthetic fillers, the surgeon applies subcuticular closures to the incision wounds, which then are bandaged.
Post-operative matters
After completing the surgical corrections and the lipoinjection contouring of the pertinent area(s) of the gluteal region, the surgeon thoroughly examines the patient to ensure his or her general recovery from the operation, and examines each surgical incision to ascertain that it is correctly sutured and taped, in order to facilitate the uneventful healing of the gluteus-muscle tissues, without medical complications. The patient is advised to avoid exercise and strenuous physical activity until three weeks post-operative, how to properly care for surgical-incision wounds, and how to wear a compression garment that will keep in place the surgically corrected tissues, and so ensure their healing as a whole anatomic unit of the gluteal region. When a patient has undergone a surgical contouring of the buttocks with gluteal implants, the final, corrected body contour usually is observed at six months post-operative or at one year post-operative, depending upon the tissue-healing capabilities of the patient's body. The liposculpture patient usually requires approximately six months, and occasionally one year before producing the final, corrected body contour. For both procedures, at approximately one month post-operative, marked aesthetic improvement is noticeable in the corrected body areas, as is the elimination of the initial, post-operative weight gain caused by the body's retention of the infiltratedanaesthetic
An anesthetic (American English) or anaesthetic (British English; see spelling differences) is a drug used to induce anesthesia — in other words, to result in a temporary loss of sensation or awareness. They may be divided into t ...
and tumescent
Tumescence is the quality or state of being tumescent or swollen. Tumescence usually refers to the normal engorgement with blood ( vascular congestion) of the erectile tissues, marking sexual excitation, and possible readiness for sexual activity. ...
fluids. The patient is advised to wear a compression garment to contain swelling and to immobilize the corrected tissues, so that they heal as one anatomic unit of the gluteal region. Moreover, throughout the convalescence, to facilitate shrinking the skin to the new, corrected body contour, and to resolve unevenness, wrinkles to the skin, and localized swelling, the continual application of massage and (occasional) ultrasound treatments can facilitate the diminishment of the post-operative conditions.
Dangers and complications
Of the three general methods of gluteal augmentation procedures, including implants, flaps and fat graft, a 2019 systemic literature review with meta-analysis of 46 publications revealed fat graft with the least complication rate (7%) while implants associated with highest complication rate (31%). The surgical and liposculpture contouring of the human body presents possible medical complications such as: the psychological—unmetbody image
Body image is a person's thoughts, feelings and perception of the aesthetics or sexual attractiveness of their own body. The concept of body image is used in several disciplines, including neuroscience, psychology, medicine, psychiatry, psycho ...
expectations of aesthetic improvement; the physical—uneven contour, local and general; the physiologic—toxic reactions to the anaesthesic and the tumescent
Tumescence is the quality or state of being tumescent or swollen. Tumescence usually refers to the normal engorgement with blood ( vascular congestion) of the erectile tissues, marking sexual excitation, and possible readiness for sexual activity. ...
drugs; and the nervous—paresthesia
Paresthesia is a sensation of the skin that may feel like numbness (''hypoesthesia''), tingling, pricking, chilling, or burning. It can be temporary or Chronic condition, chronic and has many possible underlying causes. Paresthesia is usually p ...
, localized areas of perduring numbness in the corrected portion(s) of the gluteal region. The medical complications possible to a surgical buttocks augmentation procedure, the submuscular emplacement of a gluteal implant, include infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
, surgical-wound dehiscence that exposes the implant, revision surgery, rupture of the implant, seroma
A seroma is a pocket of clear serous fluid (filtered blood plasma). They may sometimes develop in the body after surgery, particularly after breast surgery, abdominal surgery, and reconstructive surgery. They can be diagnosed by physical sign ...
(a pocket of clear serous fluid), capsular contracture, asymmetry of the corrected area, shifting of the implant, surgical over-correction, injury to the sciatic nerve
The sciatic nerve, also called the ischiadic nerve, is a large nerve in humans and other vertebrate animals. It is the largest branch of the sacral plexus and runs alongside the hip joint and down the right lower limb. It is the longest and widest ...
, and paresthesia
Paresthesia is a sensation of the skin that may feel like numbness (''hypoesthesia''), tingling, pricking, chilling, or burning. It can be temporary or Chronic condition, chronic and has many possible underlying causes. Paresthesia is usually p ...
(tingling skin). The medical complications possible to a liposculpture buttocks augmentation include the bodily resorption of some of the injected adipose fat, asymmetric contour of the corrected body area, an irregular contour to the body, seroma, abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body, usually caused by bacterial infection. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pre ...
(pus enclosed by inflamed tissue), cellulitis
Cellulitis is usually a bacterial infection involving the inner layers of the skin. It specifically affects the dermis and subcutaneous fat. Signs and symptoms include an area of redness which increases in size over a few days. The borders of ...
(subcutaneous connective-tissue inflammation), and paresthesia.
Like most medical procedures, buttock augmentation comes with risks, some of which can be life-threatening. A total of 413 Mexican plastic surgeons reported 64 deaths related to liposuction, with 13 deaths caused by gluteal lipoinjection. In Colombia, nine deaths were documented. Of the 13 deaths in Mexico, eight (61.6 percent) occurred during lipoinjection, whereas the remaining five (38.4 percent) occurred within the first 24 hours. In Colombia, six deaths (77.7 percent) occurred during surgery and three occurred (22.2 percent) immediately after surgery. Secondary lymphoedema of the lower extremities has been reported as an unusual side effect of liquid silicone injection on the hips and buttock while thromboembolism, implant displacement and explosion have also been listed as some of the dangers.
Unmet expectations
In the surgical praxis of body contouring therapy, the patient's body-image expectations can be different from the contoured body that is the outcome of the performed surgical operation. Such unmet aesthetic expectations can be avoided at the pre-operative consultation stage, whereby, with informed consent, the physician and the patient jointly establish a realistic and feasible surgery plan to achieve a mutually satisfactory corrective outcome (functional and aesthetic) of the operation to the gluteal region, the buttock- and thigh-areas.Contour problems
Contour problems of the corrected gluteal region can be prevented with the operational use of small-gauge cannulas (ca. 2.0 mm) specifically for superficial liposuction; and with the application of cross-pattern harvesting of the excess body fat, to avoid removing too much adipose fat tissue, which might disfigure the contour of the patient's fat-donor area. The possible contour problems that might arise from ultrasonic liposuction are skin burns and hypertrophic scarring, which might occur if the fat-donor area skin is not cooled and protected during the fat harvest. To that end, the infusion of a tumescence-inducing solution to the fat-donor area(s) assists in cooling the patient's skin during the ultrasonic lipo-harvesting; likewise, the application of moist towels, a skin protector, and the constant cooling-fluid infiltration of the cannula in an integrated sheath.Drug complications (anaesthetic and tumescent)
The infiltration of a solution ofanaesthesia
Anesthesia (American English) or anaesthesia (British English) is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prev ...
- and tumescence
Tumescence is the quality or state of being tumescent or swollen. Tumescence usually refers to the normal engorgement with blood ( vascular congestion) of the erectile tissues, marking sexual excitation, and possible readiness for sexual activity. ...
-inducing drugs can present medical complications such as a fluid overload of the tissues, the inadequate replacement of the infiltrated solution, and the partitioning (separation) of a single infiltration into several pools, which then are removed by suction lipectomy. Moreover, during anaesthesia, maintaining the patient's stable blood pressure can be difficult, which increases the possibility of bleeding, and the possibility that anaesthetic toxicity can occur if excessive doses are administered by infiltration; the symptoms are manifested as central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
(CNS) occurrences of drug-induced anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion characterised by an unpleasant state of inner wikt:turmoil, turmoil and includes feelings of dread over Anticipation, anticipated events. Anxiety is different from fear in that fear is defined as the emotional response ...
, apprehension, restlessness, nervousness, disorientation, confusion, dizziness, blurred vision, tremors, nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. It can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the throat.
Over 30 d ...
, vomiting, shivering, and seizures; likewise, as manifestations of drowsiness, unconsciousness, respiratory depression, and respiratory arrest. Furthermore, the toxicity symptoms of a tumescence-inducing drug (e.g. epinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands a ...
) might cause such CNS symptoms, for which reason the operative application of a tumescent drug is limited throughout the operation.
Numbness (paresthesia)
Post-operatively, local areas of numbness (paresthesia
Paresthesia is a sensation of the skin that may feel like numbness (''hypoesthesia''), tingling, pricking, chilling, or burning. It can be temporary or Chronic condition, chronic and has many possible underlying causes. Paresthesia is usually p ...
) might occur in the contoured portion(s) of the gluteal region, and might perdure for a long time after the surgery. Hence, the patient is advised to facilitate the re-sensitizing of the numb area(s) with applications of gentle massage, to prevent the development of a neuroma
A neuroma (; plural: neuromata or neuromas) is a growth or tumor of nerve tissue. Neuromas tend to be benign (i.e. not cancerous); many nerve tumors, including those that are commonly malignant, are nowadays referred to by other terms.
Neuromas ...
complication, and to alleviate pain. Nonetheless, depending upon the tissue-healing capabilities of the patient, he or she can recover in full at two years post-operative.
Outcomes
The outcome of a buttocks-contouring procedure depends upon the specific defect or deformity. Depressed scars and deep morphological defects are difficult to correct because of the curvature of the buttocks as an anatomic unit, and because of the scar-contracting elements of the tissues across the gluteal curvature. In such a case, although the injection of (autologous or artificial) tissue fillers to correct the defect or the deformity might be impermanent, that injection usually will remedy the functional and aesthetic shortcoming(s) required by the patient and will thus serve the therapeutic purpose of gluteoplasty.Popularity
In common parlance, "Brazilian butt lift" (BBL) is often used to describe lipoinjection into the buttocks for aesthetic purposes. This name is suggested to originate from the Brazilian surgeonIvo Pitanguy
Ivo Hélcio Jardim de Campos Pitanguy (July 5, 1926 – August 6, 2016) was a pioneering Brazilian plastic surgeon renowned globally for his significant contributions to the field of aesthetic and reconstructive surgery. Based in Rio de Janeiro, ...
, who pioneered the surgery in the 1960s. The popularity of the surgery significantly increased during the 2010s as a result of social media trends.
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Buttock Augmentation Cosmetic surgery Implants (medicine) Plastic surgical procedures Prosthetics