The history of
Myanmar
Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar; and also referred to as Burma (the official English name until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and has ...
( ) covers the period from the time of first-known human settlements 13,000 years ago to the present day. The earliest inhabitants of
recorded history
Recorded history or written history describes the historical events that have been recorded in a written form or other documented communication which are subsequently evaluated by historians using the historical method. For broader world h ...
were a
Tibeto-Burman-speaking people who established the
Pyu city-states
The Pyu city-states ( ) were a group of city-states that existed from about the 2nd century BCE to the mid-11th century in present-day Upper Myanmar. The city-states were founded as part of the southward migration by the Tibeto-Burman languages, ...
ranged as far south as
Pyay
Pyay, and formerly anglicised as Prome, is the principal town of Pyay Township in the Bago Region in Myanmar. Pyay is located on the bank of the Irrawaddy River, north-west of Yangon. It is an important trade center for the Ayeyarwady Delta, Centr ...
and adopted
Theravada Buddhism
''Theravāda'' (; 'School of the Elders'; ) is Buddhism's oldest existing school. The school's adherents, termed ''Theravādins'' ( anglicized from Pali ''theravādī''), have preserved their version of the Buddha's teaching or '' Dhamma'' in ...
.
Another group, the
Bamar people
The Bamar people ( Burmese: ဗမာလူမျိုး, ''ba. ma lu myui:'' ) (formerly known as Burmese people or Burmans) are a Sino-Tibetan-speaking ethnic group native to Myanmar (formerly known as Burma). With an estimated population ...
, entered the upper Irrawaddy valley in the early 9th century. They went on to establish the
Pagan Kingdom (1044–1297), the first-ever unification of the Irrawaddy valley and its periphery. The
Burmese language
Burmese (; ) is a Tibeto-Burman languages, Tibeto-Burman language spoken in Myanmar, where it is the official language, lingua franca, and the native language of the Bamar people, Bamar, the country's largest ethnic group. Burmese dialects are a ...
and culture slowly came to replace Pyu norms during this period. After the
First Mongol invasion of Burma
The first Mongol invasions of Burma ( Burmese: မွန်ဂို–မြန်မာ စစ် (၁၂၇၇–၁၂၈၇); Chinese: 元緬戰爭) were a series of military conflicts between Kublai Khan's Yuan dynasty, a division of t ...
in 1287, several small kingdoms, of which the
Kingdom of Ava
The Ava Kingdom (, ; INN-wa pyi) also known as Inwa Kingdom or Kingdom of Ava was the dominant kingdom that ruled upper Burma (Myanmar) from 1365 to 1555. Founded in 1365, the kingdom was the successor state to the petty kingdoms of Myinsa ...
, the
Hanthawaddy Kingdom, the
Kingdom of Mrauk U
The Kingdom of Mrauk-U (Arakanese language, Arakanese: မြောက်ဦး ဘုရင့်နိုင်ငံတော်) was a kingdom that existed on the Arakan coastal plain from 1429 to 1785. Based in the capital Mrauk-U, near t ...
and the
Shan States
The Shan States were a collection of minor Shan people, Shan kingdoms called ''mueang, möng'' whose rulers bore the title ''saopha'' (''sawbwa''). In British rule in Burma, British Burma, they were analogous to the princely states of Britis ...
were principal powers, came to dominate the landscape, replete with ever-shifting alliances and constant wars. From this time, the history of this region has been characterised by geopolitical struggles between the Bamar ethnic group, and the multitude of smaller ethnic groups surrounding them.
In the second half of the 16th century, the
Toungoo dynasty
''taungnguumainn saat''
, conventional_long_name = Toungoo dynasty
, common_name = Taungoo dynasty
, status = Empire/Monarchy, Kingdom
, event_start = Independence from Kingdom of Ava, Ava Kingdom
, yea ...
(1510–1752) reunified the country, and founded the largest empire in the history of Southeast Asia for a brief period. Later Taungoo kings instituted several key administrative and economic reforms that gave rise to a smaller, more peaceful and prosperous kingdom in the 17th and early 18th centuries. In the second half of the 18th century, the
Konbaung dynasty
The Konbaung dynasty (), also known as the Third Burmese Empire (တတိယမြန်မာနိုင်ငံတော်), was the last dynasty that ruled Burma from 1752 to 1885. It created the second-largest empire in history of Mya ...
(1752–1885) restored the kingdom, and continued the Taungoo reforms that increased central rule in peripheral regions and produced one of the most literate states in Asia. The dynasty also went to war with all its neighbors. The
Anglo-Burmese wars
The Anglo-Burmese people, also known as the Anglo-Burmans, are a community of Eurasians of Burmese and European descent; they emerged as a distinct community through mixed relationships (sometimes permanent, sometimes temporary) between the B ...
(1824–85) eventually led to British colonial rule.
British rule
The British Raj ( ; from Hindustani , 'reign', 'rule' or 'government') was the colonial rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent,
*
* lasting from 1858 to 1947.
*
* It is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
* or dire ...
brought several enduring social, economic, cultural and administrative changes that completely transformed the once-agrarian society. British rule highlighted out-group differences among the country's myriad ethnic groups. Since independence in 1948, the country has been in
one of the longest running civil wars involving insurgent groups representing political and ethnic minority groups and successive central governments. The country was under military rule under various guises from 1962 to 2010 and again from 2021–present, and in the seemingly cyclical process has become one of the least developed nations in the world.
Early history (to the 9th century)
Prehistory
The earliest archaeological evidence suggests that cultures existed in Burma as early as 11,000 BCE. Most indications of early settlement have been found in the central dry zone, where scattered sites appear in close proximity to the Irrawaddy River. The ''Anyathian'', Burma's Stone Age, existed at a time thought to parallel the
Lower Paleolithic
The Lower Paleolithic (or Lower Palaeolithic) is the earliest subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. It spans the time from around 3.3 million years ago when the first evidence for stone tool production and use by hominins appears ...
and
Middle Paleolithic
The Middle Paleolithic (or Middle Palaeolithic) is the second subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age as it is understood in Europe, Africa and Asia. The term Middle Stone Age is used as an equivalent or a synonym for the Middle P ...
in Europe. The Neolithic or New Stone Age, when plants and animals were first domesticated and polished stone tools appeared, is evidenced in Burma by three caves located near Taunggyi at the edge of the Shan plateau that are dated to 10000 to 6000 BC.
[Cooler 2002: Chapter 1: Prehistoric and Animist Periods]
About 1500 BCE, people in the region were turning copper into bronze, growing rice, and domesticating chickens and pigs; they were among the first people in the world to do so. By 500 BCE, iron-working settlements emerged in an area south of present-day
Mandalay
Mandalay is the second-largest city in Myanmar, after Yangon. It is located on the east bank of the Irrawaddy River, 631 km (392 mi) north of Yangon. In 2014, the city had a population of 1,225,553.
Mandalay was founded in 1857 by Ki ...
. Bronze-decorated coffins and burial sites filled with earthenware remains have been excavated.
[Myint-U 2006: 45] Archaeological evidence at Samon Valley south of Mandalay suggests rice growing settlements that traded with China between 500 BC and 200 CE.
[Hudson 2005: 1] During the Iron Age, archaeological evidence also out of Samon Valley reveals changes in infant burial practices that were greatly influenced by India. These changes include burying infants in jars whose size depicts their family status.
Pyu city-states
The Pyu entered the Irrawaddy valley from present-day Yunnan, c. 2nd century BCE, and went on to found city-states throughout the Irrawaddy valley. The original home of the Pyu is reconstructed to be
Qinghai Lake
Qinghai Lake is the list of lakes by area, largest lakes of China, lake in China. Located in an endorheic basin in Qinghai Province, to which it gave its name, Qinghai Lake is classified as an alkaline lake, alkaline saline lake, salt lake. The ...
in present-day
Qinghai
Qinghai is an inland Provinces of China, province in Northwestern China. It is the largest provinces of China, province of China (excluding autonomous regions) by area and has the third smallest population. Its capital and largest city is Xin ...
and
Gansu
Gansu is a provinces of China, province in Northwestern China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeastern part of the province. The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibetan Plateau, Ti ...
.
[Moore 2007: 236] The Pyu were the earliest inhabitants of Burma of whom records are extant.
[Hall 1960: 8–10] During this period, Burma was part of an overland trade route from China to India. Trade with India brought Buddhism from India By the 4th century, many in the Irrawaddy valley had converted to Buddhism.
[Myint-U 2006: 51–52] Of the many city-states, the largest and most important was the
Sri Ksetra Kingdom
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of Sri Ksetra
, common_name = Kingdom of Sri Ksetra
, era = Classical Antiquity
, status = City-state
, event_start = Founding of kingdom
, year_start = c. 3rd – 9th century CE
, date_start =
, ...
southeast of modern Pyay, also thought to once be the capital city.
[Luce et al. 1939: 264–282] In March 638, the Pyu of Sri Ksetra launched a new calendar that later became the
Burmese calendar
The Burmese calendar (, , or , ; Burmese Era (BE) or Myanmar Era (ME)) is a lunisolar calendar in which the months are based on lunar months and years are based on sidereal years. The calendar is largely based on an older version of the Hind ...
.
[
Eighth-century Chinese records identify 18 Pyu states throughout the Irrawaddy valley, and describe the Pyu as a humane and peaceful people to whom war was virtually unknown and who wore silk cotton instead of actual silk so that they would not have to kill ]silkworm
''Bombyx mori'', commonly known as the domestic silk moth, is a moth species belonging to the family Bombycidae. It is the closest relative of '' Bombyx mandarina'', the wild silk moth. Silkworms are the larvae of silk moths. The silkworm is of ...
s. The Chinese records also report that the Pyu knew how to make astronomical calculations, and that many Pyu boys entered the monastic life at seven to the age of 20.[
It was a long-lasting civilisation that lasted nearly a millennium to the early 9th century until a new group of "swift horsemen" from the north, the Bamars, entered the upper Irrawaddy valley. In the early 9th century, the Pyu city-states of Upper Burma came under constant attacks by ]Nanzhao
Nanzhao ( zh, t=南詔, s=南诏, p=Nánzhào), also spelled Nanchao, , Yi language: ꂷꏂꌅ, ''Mashynzy'') was a dynastic kingdom that flourished in what is now southwestern China and northern Southeast Asia during the 8th and 9th centuri ...
(in modern Yunnan
Yunnan; is an inland Provinces of China, province in Southwestern China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 47.2 million (as of 2020). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the Chinese provinces ...
). In 832, the Nanzhao sacked Halingyi, which had overtaken Prome as the chief Pyu city-state and informal capital. Archaeologists interpret early Chinese texts detailing the plundering of Halingyi in 832 to detail the capturing of 3000 Pyu prisoners, later becoming Nanzhao slaves at Kunming
Kunming is the capital and largest city of the province of Yunnan in China. The political, economic, communications and cultural centre of the province, Kunming is also the seat of the provincial government. During World War II, Kunming was a Ch ...
.
While Pyu settlements remained in Upper Burma until the advent of the Pagan Empire in the mid 11th century, the Pyu gradually were absorbed into the expanding Burman kingdom of Pagan in the next four centuries. The Pyu language still existed until the late 12th century. By the 13th century, the Pyu had assumed Bamar ethnicity. The histories/legends of the Pyu were also incorporated to those of the Bamars.[
]
Mon kingdoms
According to the colonial era scholarship, as early as the 6th century, another people called the Mon began to enter the present-day Lower Burma from the Mon kingdoms of Haribhunjaya and Dvaravati in modern-day Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
. By the mid 9th century, the Mon had founded at least two small kingdoms (or large city-states) centred around Bago and Thaton. The earliest external reference to a Mon kingdom in Lower Burma was in 844–848 by Arab geographers.[Hall 1960: 11–12] But recent research shows that there is no evidence (archaeological or otherwise) to support colonial period conjectures that a Mon-speaking polity existed in Lower Burma until the late 13th century, and the first recorded claim that the kingdom of Thaton existed came only in 1479.
Bagan dynasty (849–1297)
Early Bagan
The Burmans who had come down with the early 9th Nanzhao raids of the Pyu states remained in Upper Burma. (Trickles of Burman migrations into the upper Irrawaddy valley might have begun as early as the 7th century.[Htin Aung 1967: 329]) In the mid-to-late 9th century, Pagan was founded as a fortified settlement along a strategic location on the Irrawaddy near the confluence of the Irrawaddy and its main tributary the Chindwin River
The Chindwin River (), also known as the Ningthi River (), is a river in Myanmar and is the largest tributary of the Irrawaddy River.
Sources
The Chindwin originates in the broad Hukawng Valley of Kachin State of Burma, roughly
, where the Tanai, ...
.[Lieberman 2003: 90–91]
It may have been designed to help the Nanzhao pacify the surrounding countryside.[Myint-U 2006: 56] Over the next two hundred years, the small principality gradually grew to include its immediate surrounding areas— to about 200 miles north to south and 80 miles from east to west by Anawrahta
Anawrahta Minsaw (, ; 11 May 1014 – 11 April 1077) was the founder of the Pagan Empire. Considered the father of the Burmese nation, Anawrahta turned a small principality in the dry zone of Upper Burma into the first Burmese Empire that ...
's accession in 1044.[Harvey 1925: 24–25]
Pagan Empire (1044–1297)
 Over the next 30 years, Anawrahta founded the Pagan Kingdom, unifying for the first time the regions that would later constitute the modern-day Burma. Anawrahta's successors by the late 12th century had extended their influence farther south into the upper
Over the next 30 years, Anawrahta founded the Pagan Kingdom, unifying for the first time the regions that would later constitute the modern-day Burma. Anawrahta's successors by the late 12th century had extended their influence farther south into the upper Malay Peninsula
The Malay Peninsula is located in Mainland Southeast Asia. The landmass runs approximately north–south, and at its terminus, it is the southernmost point of the Asian continental mainland. The area contains Peninsular Malaysia, Southern Tha ...
, at least to the Salween River
The Salween is a Southeast Asian river, about long, flowing from the Tibetan Plateau south into the Andaman Sea. The Salween flows primarily within southwest China and eastern Myanmar, with a short section forming the border of Myanmar and Tha ...
in the east, below the current China border in the farther north, and to the west, northern Arakan
Arakan ( or ; , ), formerly anglicised as Aracan, is the historical geographical name for the northeastern coastal region of the Bay of Bengal, covering present-day Bangladesh and Myanmar. The region was called "Arakan" for centuries. It is ...
and the Chin Hills.[Harvey 1925: 21] The Burmese Chronicles claim Pagan's suzerainty over the entire Chao Phraya Valley, and the Thai chronicles include the lower Malay Peninsula down to the Strait of Malacca
The Strait of Malacca is a narrow stretch of water, long and from wide, between the Malay Peninsula to the northeast and the Indonesian island of Sumatra to the southwest, connecting the Andaman Sea (Indian Ocean) and the South China Sea (Pa ...
to Pagan's realm.[Htin Aung 1967: 34]
By the early 12th century, Pagan had emerged as a major power alongside the Khmer Empire
The Khmer Empire was an empire in Southeast Asia, centered on Hydraulic empire, hydraulic cities in what is now northern Cambodia. Known as Kambuja (; ) by its inhabitants, it grew out of the former civilization of Chenla and lasted from 802 t ...
in Southeast Asia, recognised by Song China and the Chola dynasty
The Chola dynasty () was a Tamil dynasty originating from Southern India. At its height, it ruled over the Chola Empire, an expansive maritime empire. The earliest datable references to the Chola are from inscriptions dated to the 3rd cen ...
of India. Well into the mid-13th century, most of mainland Southeast Asia was under some degree of control of either the Pagan Empire or the Khmer Empire.
Anawrahta also implemented a series of key social, religious and economic reforms that would have a lasting impact in Burmese history. His social and religious reforms later developed into the modern-day culture of Myanmar
The culture of Myanmar (Burma) ( ) has been heavily influenced by Buddhism. Owing to its history, Burmese culture has significant influence over neighboring countries such as Laos, Siam, Assam in India, and Xishuangbanna regions in China. It h ...
. The most important development was the introduction of Theravada Buddhism to Upper Burma after Pagan's conquest of the Thaton Kingdom in 1057. Supported by royal patronage, the Buddhist school gradually spread to the village level in the next three centuries although Vajrayana Buddhist, Mahayana
Mahāyāna ( ; , , ; ) is a term for a broad group of Buddhist traditions, Buddhist texts#Mahāyāna texts, texts, Buddhist philosophy, philosophies, and practices developed in ancient India ( onwards). It is considered one of the three main ex ...
, Hindu
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ...
, and animism
Animism (from meaning 'breath, spirit, life') is the belief that objects, places, and creatures all possess a distinct spiritual essence. Animism perceives all things—animals, plants, rocks, rivers, weather systems, human handiwork, and in ...
remained heavily entrenched at all social strata.[Lieberman 2003: 112–119]
Pagan's economy was primarily based on the Kyaukse agricultural basin northeast of the capital, and Minbu, south of Bagan, where the Bamars had built a large number of new weirs and diversionary canals. It also benefited from external trade through its coastal ports. The wealth of the kingdom was devoted to building over 10,000 Buddhist temples in the Pagan capital zone between 11th and 13th centuries (of which 3000 remain to the present day). The wealthy donated tax-free land to religious authorities.
The Burmese language
Burmese (; ) is a Tibeto-Burman languages, Tibeto-Burman language spoken in Myanmar, where it is the official language, lingua franca, and the native language of the Bamar people, Bamar, the country's largest ethnic group. Burmese dialects are a ...
and culture gradually became dominant in the upper Irrawaddy valley, eclipsing the Pyu and Pali
Pāli (, IAST: pāl̤i) is a Classical languages of India, classical Middle Indo-Aryan languages, Middle Indo-Aryan language of the Indian subcontinent. It is widely studied because it is the language of the Buddhist ''Pali Canon, Pāli Can ...
norms by the late 12th century. By then, the Bamar leadership of the kingdom was unquestioned. The Pyu had largely assumed the Bamar ethnicity in Upper Burma. The Burmese language, once an alien tongue, was now the lingua franca of the kingdom.
The kingdom went into decline in the 13th century as the continuous growth of tax-free religious wealth—by the 1280s, two-thirds of Upper Burma's cultivable land had been alienated to the religion—affected the crown's ability to retain the loyalty of courtiers and military servicemen. This ushered in a vicious circle of internal disorders and external challenges by Mons, Mongols and Shans.[Lieberman 2003: 119–123]
Beginning in the early 13th century, the Shan began to encircle the Pagan Empire from the north and the east. The Mongols
Mongols are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, China ( Inner Mongolia and other 11 autonomous territories), as well as the republics of Buryatia and Kalmykia in Russia. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family o ...
, who had conquered Yunnan, the former homeland of the Bamar, in 1253, began their invasion in 1277 in response to an embassy crisis, and in 1287 sacked Pagan, ending the Pagan Kingdom's 250-year rule of the Irrawaddy valley and its periphery when the Pagan king of that time abandoned his palace on the news of the Mongol march. Pagan's rule of central Burma came to an end ten years later in 1297 when it was toppled by the Myinsaing Kingdom
The Myinsaing Kingdom ( ) also known as Myainsaing Regency was the regency that ruled central Burma (Myanmar) from 1297 to 1313. It was founded by three brothers— Athinkhaya, Yazathingyan and Thihathu from Myinsaing—Coedès 1968: 209 and ...
of Shan rulers.
Small kingdoms
 After the fall of Pagan, the Mongols left the searing Irrawaddy valley but the Pagan Kingdom was irreparably broken up into several small kingdoms. By the mid-14th century, the country had become organised along four major power centres: Upper Burma, Lower Burma, Shan States and Arakan. Many of the power centres were themselves made up of (often loosely held) minor kingdoms or princely states. This era was marked by a series of wars and switching alliances. Smaller kingdoms played a precarious game of paying allegiance to more powerful states, sometimes simultaneously.
After the fall of Pagan, the Mongols left the searing Irrawaddy valley but the Pagan Kingdom was irreparably broken up into several small kingdoms. By the mid-14th century, the country had become organised along four major power centres: Upper Burma, Lower Burma, Shan States and Arakan. Many of the power centres were themselves made up of (often loosely held) minor kingdoms or princely states. This era was marked by a series of wars and switching alliances. Smaller kingdoms played a precarious game of paying allegiance to more powerful states, sometimes simultaneously.
Ava (1364–1555)
Founded in 1364, Kingdom of Ava
The Ava Kingdom (, ; INN-wa pyi) also known as Inwa Kingdom or Kingdom of Ava was the dominant kingdom that ruled upper Burma (Myanmar) from 1365 to 1555. Founded in 1365, the kingdom was the successor state to the petty kingdoms of Myinsa ...
(Inwa) was the successor state to earlier, even smaller kingdoms based in central Burma: Taungoo
Taungoo (, ''Tauñngu myoú''; ), also spelled Toungoo and formerly Toung-ngú, is a district-level city in the Bago Region of Myanmar, 220 km from Yangon, towards the north-eastern end of the division, with mountain ranges to the east a ...
(1287–1318), Myinsaing– Pinya Kingdom (1297–1364), and Sagaing Kingdom (1315–64). In its first years of existence, Ava, which viewed itself as the rightful successor to the Pagan Kingdom, tried to reassemble the former empire. While it was able to pull the Taungoo-ruled kingdom and peripheral Shan states (Kalay
Kalay (; , ''Kalü''), also known as Kale, is a town in the Sagaing Region of Myanmar. It is located upstream from Mandalay and Monywa on the Myittha River, a tributary of the Chindwin River. The town is the district headquarters of the Kalay Distr ...
, Mohnyin
Mohnyin (, ; ) is a town in Kachin State, Myanmar. It is the administrative center for both Mohnyin Township and Mohnyin District
Mohnyin District () is a Districts of Burma, district of the Kachin State in northern Myanmar. The administrative c ...
, Mogaung
Mogaung ( ; ) is a town in Kachin State, Myanmar. It is situated on the Mandalay-Myitkyina railway line.
History
Mogaung or Möng Kawng was the name and capital (royal seat) of a relatively major one of the petty Shan (ethnic Tai) princ ...
, Hsipaw) into its fold at the peak of its power, it failed to reconquer the rest.
The Forty Years' War
The Forty Years' War (; 1385 – 1423; also Ava–Pegu War or the Mon–Burmese War) was a military war fought between the Burmese-speaking Kingdom of Ava and the Mon-speaking Kingdom of Hanthawaddy. The war was fought during two separat ...
(1385–1424) with Hanthawaddy left Ava exhausted, and its power plateaued. Its kings regularly faced rebellions in its vassal regions but were able to put them down until the 1480s. In the late 15th century, the Prome Kingdom and its Shan States successfully broke away, and in the early 16th century, Ava itself came under attacks from its former vassals. In 1510, Taungoo also broke away. In 1527, the Confederation of Shan States led by Mohnyin captured Ava. The Confederation's rule of Upper Burma, though lasted until 1555, was marred by internal fighting between Mohnyin and Thibaw houses. The kingdom was toppled by Taungoo forces in 1555.
The Burmese language and culture came into its own between the last period of the Pagan Kingdom (Old Burmese starts in the XII° century) and the Ava period.
Hanthawaddy Pegu (1287–1539, 1550–52)
The Mon- kingdom was founded as Ramannadesa right after Pagan's collapse in 1297. In the beginning, the Lower-Burma-based kingdom was a loose federation of regional power centre in the Mottama
Mottama (, ; Muttama , ; formerly Martaban) is a town in the Thaton District of Mon State, Myanmar. Located on the west bank of the Thanlwin river (Salween), on the opposite side of Mawlamyaing, Mottama was the capital of the Martaban Kingdo ...
, the Pegu and the Irrawaddy Delta
The Irrawaddy Delta or Ayeyarwady Delta lies in the Irrawaddy Division, the lowest expanse of land in Myanmar (Burma) that fans out from the limit of tidal influence at Myan Aung to the Bay of Bengal and Andaman Sea, to the south at the mout ...
. The energetic reign of Razadarit
Razadarit (, ; , or ; also spelled Yazadarit, "king of kings"; 1368–1421) was king of Kingdom of Hanthawaddy, Hanthawaddy Pegu from 1384 to 1421. He successfully unified his Mon language, Mon-speaking kingdom, and fended off major assaults ...
(1384–1421) cemented the kingdom's existence. Razadarit firmly unified the three Mon-speaking regions together, and successfully held off Ava in the Forty Years' War (1385–1424).
After the war, Hanthawaddy entered its golden age whereas its rival Ava gradually went into decline. From the 1420s to the 1530s, Hanthawaddy was the most powerful and prosperous kingdom of all post-Pagan kingdoms. Under a string of especially gifted monarchs, the kingdom enjoyed a long golden age, profiting from foreign commerce. The kingdom, with a flourishing the Mon language and culture, became a Centre of commerce and Theravada Buddhism.
Due to the inexperience of its last ruler, the powerful kingdom was conquered by the upstart Taungoo dynasty in 1539. The kingdom was briefly revived between 1550 and 1552. It effectively controlled only Pegu and was crushed by Taungoo in 1552.
Shan States (1287–1563)
The Shans, ethnic Tai peoples
Tai peoples are the populations who speak (or formerly spoke) the Tai languages. There are a total of about 93 million people of Tai ancestry worldwide, with the largest ethnic groups being Dai people, Dai, Thai people, Thai, Isan people, Isan, ...
who came down with the Mongols, stayed and quickly came to dominate much of northern to eastern arc of Burma, from northwestern Sagaing Division to Kachin Hills to the present day Shan Hills.
The most powerful Shan states were Mohnyin
Mohnyin (, ; ) is a town in Kachin State, Myanmar. It is the administrative center for both Mohnyin Township and Mohnyin District
Mohnyin District () is a Districts of Burma, district of the Kachin State in northern Myanmar. The administrative c ...
and Mogaung
Mogaung ( ; ) is a town in Kachin State, Myanmar. It is situated on the Mandalay-Myitkyina railway line.
History
Mogaung or Möng Kawng was the name and capital (royal seat) of a relatively major one of the petty Shan (ethnic Tai) princ ...
in present-day Kachin State
Kachin State (; Jingpho language, Kachin: ) is the northernmost administrative divisions of Myanmar, state of Myanmar. It is bordered by China to the north and east (Tibet Autonomous Region, Tibet and Yunnan, respectively), Shan State to the sou ...
, followed by Hsenwi (Theinni) (split up in a northern and a southern state in 1988), Thsipaw (Thibaw) and Momeik
Momeik (), also known as Möng Mit (), is a town situated on the Shweli River in northern Shan State. It is the capital of Mongmit District and the principal town of Mongmit Township, Myanmar.
Transport
It is connected by road to Mogok and its r ...
in present-day northern Shan State.[Fernquest 2005: 20–50]
Minor states included Kalay, Bhamo (Wanmaw or Manmaw), Hkamti Long (Kantigyi), Hopong (Hopon), Hsahtung (Thaton), Hsamönghkam (Thamaingkan), Hsawnghsup (Thaungdut), Hsihkip (Thigyit), Hsumhsai (Hsum Hsai), Kehsi Mangam (Kyithi Bansan), Kengcheng (Kyaingchaing), Kenghkam (Kyaingkan), Kenglön (Kyainglon), Kengtawng, Kengtung (Kyaington), Kokang (Kho Kan), Kyawkku Hsiwan (Kyaukku), Kyong (Kyon), Laihka (Legya), Lawksawk (Yatsauk), Loi-ai (Lwe-e), Loilong (Lwelong), Loimaw (Lwemaw), Nyaung Shwe and many more.
Mohnyin, in particular, constantly raided Ava's territory in the early 16th century. The Monhyin-led Confederation of Shan States, in alliance with Prome Kingdom, captured Ava itself in 1527. The Confederation defeated its erstwhile ally Prome in 1532, and ruled all of Upper Burma except Taungoo. But the Confederation was marred by internal bickering, and could not stop Taungoo, which conquered Ava in 1555 and all of the Shan States by 1563.
Arakan (1287–1785)
 Although Arakan had been de facto independent since the late Pagan period, the Laungkyet dynasty of Arakan was ineffectual. Until the founding of the Mrauk-U Kingdom in 1429, Arakan was often caught between bigger neighbours, and found itself a battlefield during the Forty Years' War between Ava and Pegu. Mrauk-U went on to be a powerful kingdom in its own right between 15th and 17th centuries, including East Bengal between 1459 and 1666. Arakan was the only post-Pagan kingdom not to be annexed by the Taungoo dynasty.
Although Arakan had been de facto independent since the late Pagan period, the Laungkyet dynasty of Arakan was ineffectual. Until the founding of the Mrauk-U Kingdom in 1429, Arakan was often caught between bigger neighbours, and found itself a battlefield during the Forty Years' War between Ava and Pegu. Mrauk-U went on to be a powerful kingdom in its own right between 15th and 17th centuries, including East Bengal between 1459 and 1666. Arakan was the only post-Pagan kingdom not to be annexed by the Taungoo dynasty.
Toungoo dynasty (1510–1752)
First Toungoo Empire (1510–99)
Beginning in the 1480s, Ava faced constant internal rebellions and external attacks from the Shan States, and began to disintegrate. In 1510, Taungoo, located in the remote southeastern corner of the Ava kingdom, also declared independence.[ When the Confederation of Shan States conquered Ava in 1527, many refugees fled southeast to Taungoo, the only kingdom in peace, and one surrounded by larger hostile kingdoms.
Taungoo, led by its ambitious king ]Tabinshwehti
Tabinshwehti (, ; 16 April 1516 – 30 April 1550) was King of Burma from 1530 to 1550, and the founder of the First Toungoo Empire. His military campaigns (1534–1549) created the largest kingdom in Burma since the fall of the Pagan Empire ...
and his deputy general Bayinnaung
, title = King of Toungoo
, image = Bayinnaung.JPG
, caption = Statue of Bayinnaung in front of the National Museum of Myanmar
, reign = 30 April 1550 – 10 October 1581
, coronation = 11 January 1551 at Taungoo, ...
, would go on to reunify the petty kingdoms that had existed since the fall of the Pagan Empire, and found the largest empire in the history of Southeast Asia. First, the upstart kingdom defeated a more powerful Hanthawaddy in the Taungoo–Hanthawaddy War (1534–41). Tabinshwehti moved the capital to newly captured Bago in 1539.
Taungoo had expanded its authority up to Pagan by 1544 but failed to conquer Arakan in 1545–47 and Siam in 1547–49. Tabinshwehti's successor Bayinnaung continued the policy of expansion, conquering Ava in 1555, Nearer/Cis-Salween Shan States (1557), Lan Na (1558), Manipur
Manipur () is a state in northeastern India with Imphal as its capital. It borders the Indian states of Assam to the west, Mizoram to the south, and Nagaland to the north and shares the international border with Myanmar, specifically t ...
(1560), Farther/Trans-Salween Shan states (1562–63), the Siam
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
(1564, 1569), and Lan Xang
Lan Xang () or Lancang was a Lao people, Lao kingdom that held the area of present-day Laos from 1353 to 1707. For three and a half centuries, Lan Xang was one of the largest kingdoms in Southeast Asia. The kingdom is the basis for Laos's nat ...
(1565–74), and bringing much of western and central mainland Southeast Asia under his rule.
Bayinnaung put in place a lasting administrative system that reduced the power of hereditary Shan chiefs, and brought Shan customs in line with low-land norms.[Htin Aung 1967: 117–118] But he could not replicate an effective administrative system everywhere in his far flung empire. His empire was a loose collection of former sovereign kingdoms, whose kings were loyal to him as the Cakkavatti (, ; Universal Ruler), not the kingdom of Taungoo.
The overextended empire unravelled soon after Bayinnaung's death in 1581. Siam broke away in 1584 and went to war with Burma until 1605. By 1597, the kingdom had lost all its possessions, including Taungoo, the ancestral home of the dynasty. In 1599, the Arakanese forces aided by Portuguese mercenaries, and in alliance with the rebellious Taungoo forces, sacked Pegu. The country fell into chaos, with each region claiming a king. Portuguese mercenary Filipe de Brito e Nicote
Filipe de Brito e Nicote or Burmese honorifics, Nga Zinga (, ; c. 1566 – April 1613) was a Portuguese people, Portuguese adventurer and mercenary in the service of the Rakhine people, Arakanese kingdom of Mrauk U, and later of the Thai people, ...
promptly rebelled against his Arakanese masters, and established Goa
Goa (; ; ) is a state on the southwestern coast of India within the Konkan region, geographically separated from the Deccan highlands by the Western Ghats. It is bound by the Indian states of Maharashtra to the north, and Karnataka to the ...
-backed Portuguese rule at Thanlyin
Thanlyin (; or ; , ; formerly Syriam) is a major port city of Myanmar, located across Bago River from the city of Yangon. Thanlyin comprises 17 quarters. It surrounding Thanlyin Township is home to the largest port in the country, Thilawa port ...
in 1603.
 Despite being a tumultuous time for Myanmar, the Taungoo expansions increased the international reach of the nation. Newly rich merchants from Myanmar traded as far as the
Despite being a tumultuous time for Myanmar, the Taungoo expansions increased the international reach of the nation. Newly rich merchants from Myanmar traded as far as the Rajahnate of Cebu
Cebu, also called Sugbu, informally referred to as the Rajahnate of Cebu, was an Indianized mandala (polity) monarchy on the island of Cebu in the Philippines prior to the arrival of the Spanish conquistadors. It is known in ancient Chi ...
in the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
where they sold Burmese Sugar (''śarkarā'') for Cebuano gold.[Santarita, J. B. (2018). Panyupayana: The Emergence of Hindu Polities in the Pre-Islamic Philippines. Cultural and Civilisational Links Between India and Southeast Asia, 93–105.] Filipinos also had merchant communities in Myanmar, historian William Henry Scott, quoting the Portuguese manuscript Summa Orientalis, noted that Mottama
Mottama (, ; Muttama , ; formerly Martaban) is a town in the Thaton District of Mon State, Myanmar. Located on the west bank of the Thanlwin river (Salween), on the opposite side of Mawlamyaing, Mottama was the capital of the Martaban Kingdo ...
in Burma
Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar; and also referred to as Burma (the official English name until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and ha ...
(Myanmar) had a large presence of merchants from Mindanao, Philippines. The Lucoes, a rival to the other Filipino group, the Mindanaoans, who instead came from the island of Luzon
Luzon ( , ) is the largest and most populous List of islands in the Philippines, island in the Philippines. Located in the northern portion of the List of islands of the Philippines, Philippine archipelago, it is the economic and political ce ...
, were also hired as mercenaries and soldiers for both Siam (Thailand) and Burma (Myanmar), in the Burmese-Siamese Wars, the same case as the Portuguese, who were also mercenaries for both sides.
Restored Taungoo kingdom (Nyaungyan restoration) (1599–1752)
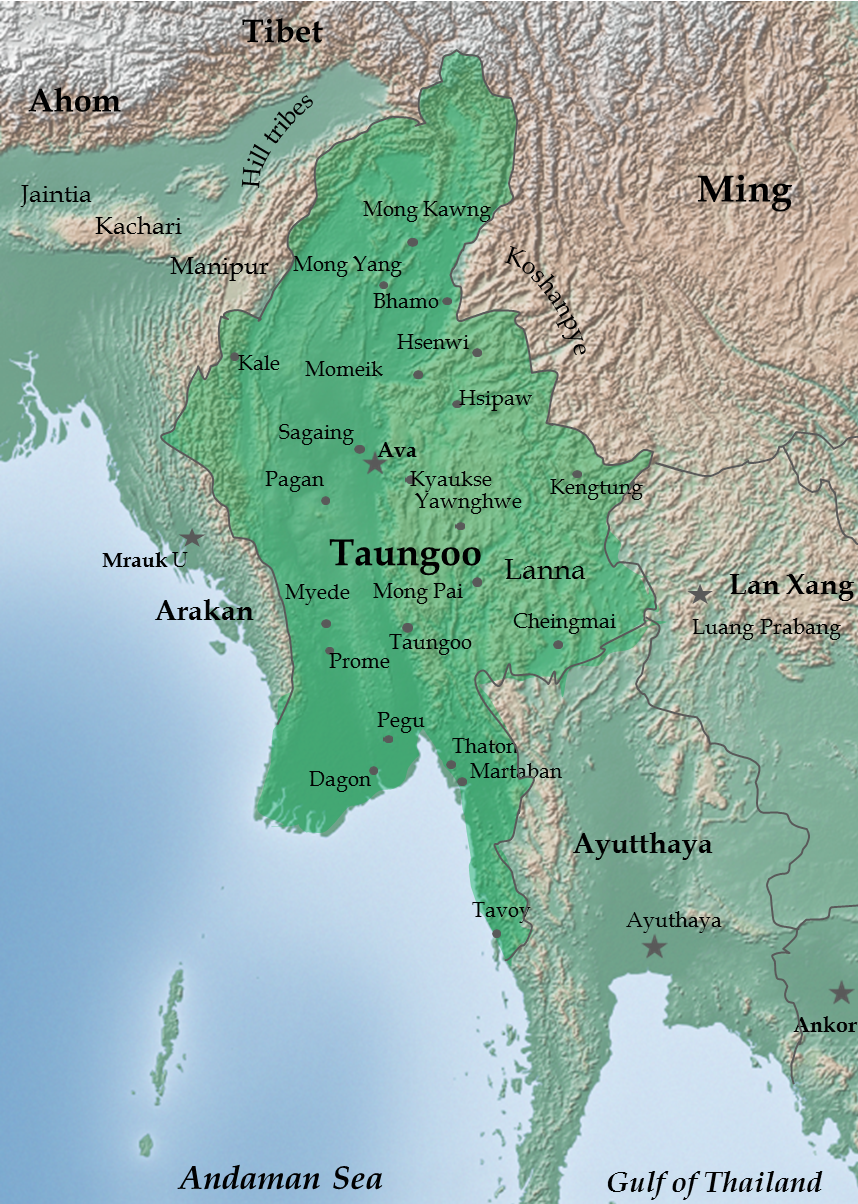 While the interregnum that followed the fall of the Pagan empire lasted over 250 years (1287–1555), that following the fall of First Taungoo was relatively short-lived. One of Bayinnaung's sons,
While the interregnum that followed the fall of the Pagan empire lasted over 250 years (1287–1555), that following the fall of First Taungoo was relatively short-lived. One of Bayinnaung's sons, Nyaungyan Min
Nyaungyan Min ( ; 8 November 1555 – ) was king of the Toungoo dynasty of Burma (Myanmar) from 1599 to 1605. He is also referred to as the founder of the restored Toungoo dynasty or Nyaungyan dynasty for starting the reunification process fol ...
, immediately began the reunification effort, successfully restoring central authority over Upper Burma and nearer Shan states by 1606.
In 1535, King Tabinshwehti reunified Burma and founded the second Burmese empire (Taungû dynasty, 1535–1752). This empire is almost constantly at war with the kingdom of Ayutthaya, in present-day Thailand. Faced with revolts and Portuguese incursions, the Taungû dynasty retreated to central Burma.
In the middle of the 16th century, King Tabinshwehti, originally from a southern province, and his son succeeded, with the help of the Portuguese, in reunifying the country. From 1599, the Kingdom of Pegu was under the management of the eastern Portuguese empire.
She reunified the country again in 1613 and definitively repelled attempts at Portuguese conquest. But the revolt of the Mons in the south of the country, encouraged by the French in India, weakened the kingdom which finally collapsed in 1752.
His successor Anaukpetlun
Anaukbaklun ( ; 21 January 1578 – 9 July 1628) was the sixth king of Taungoo Burma and was largely responsible for restoring the kingdom after it collapsed at the end of 16th century. In his 22-year reign from 1606 to 1628, Anaukpetlun comple ...
defeated the Portuguese at Thanlyin in 1613. He recovered the upper Tanintharyi
Tanintharyi may refer to:
* Tanintharyi (town) or Taninthayi (known during the British occupation as Tenasserim), a town in Tanintharyi Township, Myeik District, in the Tanintharyi Region of Burma (Myanmar)
* Tanintharyi Region, formerly Tenasseri ...
coast to Dawei
Dawei (, ; , ; , RTGS: ''Thawai'', ; formerly known as Tavoy) is a city in south-eastern Myanmar and is the capital of the Tanintharyi Region, formerly known as the Tenasserim Division, on the eastern bank of the Dawei River. The city is about ...
and Lan Na from the Siamese by 1614. He also captured the trans-Salween Shan states (Kengtung and Sipsongpanna) in 1622–26.
His brother Thalun
Thalun (, ; 17 June 1584 – 27 August 1648) was the eighth king of Toungoo dynasty of Burma (Myanmar). During his 19-year reign, Thalun successfully rebuilt the war-torn country which had been under constant warfare for nearly a century since ...
rebuilt the war-torn country. He ordered the first ever census in Burmese history in 1635, which showed that the kingdom had about two million people. By 1650, the three able kings–Nyaungyan, Anaukpetlun, and Thalun–had successfully rebuilt a smaller but far more manageable kingdom.
More importantly, the new dynasty proceeded to create a legal and political system whose basic features would continue under the Konbaung dynasty
The Konbaung dynasty (), also known as the Third Burmese Empire (တတိယမြန်မာနိုင်ငံတော်), was the last dynasty that ruled Burma from 1752 to 1885. It created the second-largest empire in history of Mya ...
well into the 19th century. The crown completely replaced the hereditary chieftainships with appointed governorships in the entire Irrawaddy valley, and greatly reduced the hereditary rights of Shan chiefs. It also reined in the continuous growth of monastic wealth and autonomy, giving a greater tax base. Its trade and secular administrative reforms built a prosperous economy for more than 80 years.[Liberman 2003: 158–164] Except for a few occasional rebellions and an external war—Burma defeated Siam's attempt to take Lan Na and Mottama in 1662–64—the kingdom was largely at peace for the rest of the 17th century.
The kingdom entered a gradual decline, and the authority of the "palace kings" deteriorated rapidly in the 1720s. From 1724 onwards, the Meitei people
The Meitei people, also known as Meetei people,P.20: "historically, academically and conventionally Manipuri prominently refers to the Meetei people."P.24: "For the Meeteis, Manipuris comprise Meeteis, Lois, Kukis, Nagas and Pangal." are a Ti ...
began raiding the upper Chindwin River
The Chindwin River (), also known as the Ningthi River (), is a river in Myanmar and is the largest tributary of the Irrawaddy River.
Sources
The Chindwin originates in the broad Hukawng Valley of Kachin State of Burma, roughly
, where the Tanai, ...
. In 1727, southern Lan Na (Chiang Mai
Chiang Mai, sometimes written as Chiengmai or Chiangmai, is the largest city in northern Thailand, the capital of Chiang Mai province and the List of municipalities in Thailand#Largest cities by urban population, second largest city in Thailan ...
) successfully revolted, leaving just northern Lan Na ( Chiang Saen) under an increasingly nominal Burmese rule. Meitei raids intensified in the 1730s, reaching increasingly deeper parts of central Burma.
In 1740, the Mon in lower Burma began a rebellion, and founded the restored Hanthawaddy kingdom
The Restored Hanthawaddy Kingdom (), also known as the Neo-Ramanic State () was the kingdom that ruled Lower Burma and parts of Upper Burma from 1740 to 1757. The kingdom grew out of a rebellion by the Mon led population of Pegu, who then ra ...
, and by 1745 controlled much of lower Burma. The Siamese also moved their authority up the Tanintharyi coast by 1752. Hanthawaddy invaded Upper Burma in November 1751, and captured Ava on 23 March 1752, ending the 266-year-old Taungoo dynasty.
Konbaung dynasty (1752–1885)
Reunification
Soon after the fall of Ava, a new dynasty rose in Shwebo
Shwebo ( ) is a city in Sagaing Region, Burma, 110 km north-west of Mandalay between the Irrawaddy and the Mu rivers. The city was the origin of the Konbaung Dynasty, established by King Alaungpaya in 1752, that was the dominant politic ...
to challenge the authority of Hanthawaddy. Over the next 70 years, the highly militaristic Konbaung dynasty went on to create the largest Burmese empire, second only to the empire of Bayinnaung
, title = King of Toungoo
, image = Bayinnaung.JPG
, caption = Statue of Bayinnaung in front of the National Museum of Myanmar
, reign = 30 April 1550 – 10 October 1581
, coronation = 11 January 1551 at Taungoo, ...
. By 1759, King Alaungpaya
Alaungpaya (, ; also spelled Alaunghpaya or Alaung-Phra; 11 May 1760) was the founder and first emperor of the Konbaung dynasty of Burma. By the time of his death from illness during his Burmese–Siamese War (1759–60), campaign in Siam, this ...
's Konbaung forces had reunited all of Burma (and Manipur), extinguished the Mon-led Hanthawaddy dynasty once and for all, and driven out the European powers who provided arms to Hanthawaddy—the French from Thanlyin
Thanlyin (; or ; , ; formerly Syriam) is a major port city of Myanmar, located across Bago River from the city of Yangon. Thanlyin comprises 17 quarters. It surrounding Thanlyin Township is home to the largest port in the country, Thilawa port ...
and the English from Cape Negrais.[Phayre 1967: 153]
Wars with Siam and China
The kingdom then went to war with the Ayutthaya Kingdom
The Ayutthaya Kingdom or the Empire of Ayutthaya was a Thai people, Thai kingdom that existed in Southeast Asia from 1351 to 1767, centered around the city of Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya (city), Ayutthaya, in Siam, or present-day Thailand. Europe ...
, which had occupied up the Tanintharyi coast to Mottama during the Burmese civil war (1740–1757), and had provided shelter to the Mon refugees. By 1767, the Konbaung armies had subdued much of Laos and defeated Siam. But they could not finish off the remaining Siamese resistance as they were forced to defend against four invasions by Qing China (1765–1769).[Lieberman 2003: 184–187] While the Burmese defences held in "the most disastrous frontier war the Qing dynasty had ever waged", the Burmese were preoccupied with another impending invasion by the world's largest empire for years. The Qing kept a heavy military line-up in the border areas for about one decade in an attempt to wage another war while imposing a ban on inter-border trade for two decades.[Dai 2004: 145–189]
The Ayutthaya Kingdom used the Konbaung preoccupation with the Qing to recover their lost territories by 1770
Events January– March
* January 1 – The foundation of Fort George, Bombay is laid by Colonel Keating, principal engineer, on the site of the former Dongri Fort.
* February 1 – Thomas Jefferson's home at Shadwell, Vi ...
, and in addition, went on to capture much of Lan Na by 1775, ending over two centuries of Burmese suzerainty over the region.[Wyatt 2003: 125] They went to war again in 1775–1776, 1785–1786, 1787, 1792
Events
January–March
* January 9 – The Treaty of Jassy ends the Russian Empire's war with the Ottoman Empire over Crimea.
* January 25 – The London Corresponding Society is founded.
* February 18 – Thomas Holcrof ...
, 1803–1808, 1809–1812 and 1849–1855, but these all resulted in a stalemate. After decades of war, the two countries essentially exchanged Tanintharyi (to Burma) and Lan Na (to Siam).
Westward expansion and wars with British Empire
Faced with a powerful China in the northeast and a resurgent Siam in the southeast, King Bodawpaya turned westward for expansion.[Myint-U 2006: 109] He conquered Arakan
Arakan ( or ; , ), formerly anglicised as Aracan, is the historical geographical name for the northeastern coastal region of the Bay of Bengal, covering present-day Bangladesh and Myanmar. The region was called "Arakan" for centuries. It is ...
in 1785, annexed Manipur
Manipur () is a state in northeastern India with Imphal as its capital. It borders the Indian states of Assam to the west, Mizoram to the south, and Nagaland to the north and shares the international border with Myanmar, specifically t ...
in 1814, and captured Assam
Assam (, , ) is a state in Northeast India, northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra Valley, Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . It is the second largest state in Northeast India, nor ...
in 1817–1819, leading to a long ill-defined border with British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance in South Asia. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another ...
. Bodawpaya's successor King Bagyidaw was left to put down British instigated rebellions in Manipur in 1819 and Assam in 1821–1822. Cross-border raids by rebels from the British protected territories and counter-cross-border raids by the Burmese led to the First Anglo-Burmese War (1824–26).[Marx 1853: 201–202]
Lasting 2 years and costing 13 million pounds, the first Anglo-Burmese War was the longest and most expensive war in British Indian history,[Myint-U 2006: 113] but ended in a decisive British victory. Burma ceded all of Bodawpaya's western acquisitions (Arakan, Manipur and Assam) plus Tenasserim. Burma was crushed for years by repaying a large indemnity of one million pounds (then US$5 million).[Htin Aung 1967: 214–215] In 1852, the British unilaterally and easily seized the Pegu province in the Second Anglo-Burmese War.[Myint-U 2006: 133]
After the war, King Mindon Min
Mindon Min (, ; 1808 – 1878), born Maung Lwin, was the penultimate king of Burma (Myanmar) from 1853 to 1878. He was one of the most popular and revered kings of Burma because of his role in the Fifth Buddhist Council. Under his half brothe ...
tried to modernise the Burmese state and economy, and made trade and territorial concessions to stave off further British encroachments, including ceding the Karenni States to the British in 1875. Nonetheless, the British, alarmed by the consolidation of French Indochina
French Indochina (previously spelled as French Indo-China), officially known as the Indochinese Union and after 1941 as the Indochinese Federation, was a group of French dependent territories in Southeast Asia from 1887 to 1954. It was initial ...
, annexed the remainder of the country in the Third Anglo-Burmese War
The Third Anglo-Burmese War (), also known as the Third Burma War, took place during 7–29 November 1885, with sporadic resistance continuing into 1887. It was the final of three wars fought in the 19th century between the Burmese and the Br ...
in 1885,[Marx 1853: 656] and sent the last Burmese king Thibaw Min and his family to exile in India.
Administrative and economic reforms
Konbaung kings extended administrative reforms first begun in the Restored Taungoo dynasty period (1599–1752), and achieved unprecedented levels of internal control and external expansion. Konbaung kings tightened control in the low lands and reduced the hereditary privileges of Shan saophas (chiefs). Konbaung officials, particularly after 1780, began commercial reforms that increased government income and rendered it more predictable. Money economy continued to gain ground. In 1857, the crown inaugurated a full-fledged system of cash taxes and salaries, assisted by the country's first standardised silver coinage.[
]
Culture
Cultural integration continued. For the first time in history, the Burmese language and culture came to predominate the entire Irrawaddy valley, with the Mon language and ethnicity completely eclipsed by 1830. The nearer Shan principalities adopted more lowland norms. The evolution and growth of Burmese literature and theatre continued, aided by an extremely high adult male literacy rate for the era (half of all males and 5% of females).[Lieberman 2003: 202–206] Monastic and lay elites around the Konbaung kings, particularly from Bodawpaya's reign, also launched a major reformation of Burmese intellectual life and monastic organisation and practice known as the Sudhamma Reformation. It led to amongst other things Burma's first proper state histories.[Charney 2006: 96–107]
British rule
Britain made Burma a province of India in 1886 with the capital at Rangoon. Traditional Burmese society was drastically altered by the demise of the monarchy and the separation of religion and state. Though war officially ended after only a couple of weeks, resistance continued in northern Burma until 1890, with the British finally resorting to a systematic destruction of villages and appointment of new officials to finally halt all guerrilla activity. The economic nature of society also changed dramatically. After the opening of the Suez Canal
The Suez Canal (; , ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, Indo-Mediterranean, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia (and by extension, the Sinai Peninsula from the rest ...
, the demand for Burmese rice grew and vast tracts of land were opened up for cultivation. However, to prepare the new land for cultivation, farmers were forced to borrow money from Indian moneylenders called chettiar
Chettiar (also spelt as Chetti and Chetty) is a title used by many traders, weaving, agricultural and land-owning castes in South India, especially in the Indian states of Tamil Nadu, Kerala and Karnataka.
Etymology
Chettiar/Chetty is deri ...
s at high interest rates and were often foreclosed on and evicted losing land and livestock. Most of the jobs also went to indentured Indian labourers, and whole villages became outlawed as they resorted to ' dacoity' (armed robbery). While the Burmese economy grew, most of the power and wealth remained in the hands of several British firms, Anglo-Burmese people
The Anglo-Burmese people, also known as the Anglo-Burmans, are a community of Eurasians of Burmese and European descent; they emerged as a distinct community through mixed relationships (sometimes permanent, sometimes temporary) between the B ...
, and migrants from India. The civil service was largely staffed by the Anglo-Burmese community and Indians, and Bamars were largely excluded almost entirely from military service.
By around the start of the 20th century, a nationalist movement began to take shape in the form of the Young Men's Buddhist Association (YMBA), modelled on the YMCA
YMCA, sometimes regionally called the Y, is a worldwide youth organisation based in Geneva, Switzerland, with more than 64 million beneficiaries in 120 countries. It has nearly 90,000 staff, some 920,000 volunteers and 12,000 branches w ...
, as religious associations were allowed by the colonial authorities. They were later superseded by the General Council of Burmese Associations (GCBA) which was linked with ''Wunthanu athin'' or National Associations that sprang up in villages throughout Burma proper. Between 1900 – 1911 the "Irish Buddhist" U Dhammaloka challenged Christianity and British rule on religious grounds. A new generation of Burmese leaders arose in the early 20th century from amongst the educated classes that were permitted to go to London to study law. They came away from this experience with the belief that the Burmese situation could be improved through reform. Progressive constitutional reform in the early 1920s led to a legislature with limited powers, a university and more autonomy for Burma within the administration of India. Efforts were also undertaken to increase the representation of Burmese in the civil service. Some people began to feel that the rate of change was not fast enough and the reforms not expansive enough.
 In 1920 the first university students strike in history broke out in protest against the new University Act which the students believed would only benefit the elite and perpetuate colonial rule. 'National Schools' sprang up across the country in protest against the colonial education system, and the strike came to be commemorated as ' National Day'.
In 1920 the first university students strike in history broke out in protest against the new University Act which the students believed would only benefit the elite and perpetuate colonial rule. 'National Schools' sprang up across the country in protest against the colonial education system, and the strike came to be commemorated as ' National Day'.Arakan
Arakan ( or ; , ), formerly anglicised as Aracan, is the historical geographical name for the northeastern coastal region of the Bay of Bengal, covering present-day Bangladesh and Myanmar. The region was called "Arakan" for centuries. It is ...
who subsequently led an armed rebellion against the British and later the nationalist government after independence, and U Wisara, the first martyr of the movement to die after a protracted hunger strike in prison.Yangon
Yangon, formerly romanized as Rangoon, is the capital of the Yangon Region and the largest city of Myanmar. Yangon was the List of capitals of Myanmar, capital of Myanmar until 2005 and served as such until 2006, when the State Peace and Dev ...
is named after U Wisara.) In December 1930, a local tax protest by Saya San in Tharrawaddy quickly grew into first a regional and then a national insurrection against the government. Lasting for two years, the Galon Rebellion, named after the mythical garuda
Garuda (; ; Vedic Sanskrit: , ) is a Hindu deity who is primarily depicted as the mount (''vahana'') of the Hindu god Vishnu. This divine creature is mentioned in the Hindu, Buddhist, and Jain faiths. Garuda is also the half-brother of the D ...
— the enemy of the nāga
In various Asian religious traditions, the Nāgas () are a divine, or semi-divine, race of half-human, half-serpent beings that reside in the netherworld (Patala), and can occasionally take human or part-human form, or are so depicted in art. ...
s (i.e., the British) – emblazoned on the pennants the rebels carried, required thousands of British troops to suppress along with promises of further political reform. The eventual trial of Saya San, who was executed, allowed several future national leaders, including Ba Maw and U Saw, who participated in his defence, to rise to prominence.Aung San
Aung San (, ; 13 February 191519 July 1947), known honorifically as '' Bogyoke'' Aung San, was a Burmese politician, independence activist and revolutionary. He was instrumental in Myanmar's struggle for independence from British rule, but he w ...
and Ko Nu, leaders of the Rangoon University Students Union (RUSU), for refusing to reveal the name of the author who had written an article in their university magazine, making a scathing attack on one of the senior university officials. It spread to Mandalay
Mandalay is the second-largest city in Myanmar, after Yangon. It is located on the east bank of the Irrawaddy River, 631 km (392 mi) north of Yangon. In 2014, the city had a population of 1,225,553.
Mandalay was founded in 1857 by Ki ...
leading to the formation of the All Burma Students Union (ABSU). Aung San and Nu subsequently joined the Thakin movement progressing from student to national politics.Rangoon
Yangon, formerly romanized as Rangoon, is the capital of the Yangon Region and the largest city of Myanmar. Yangon was the List of capitals of Myanmar, capital of Myanmar until 2005 and served as such until 2006, when the State Peace and Dev ...
student protesters, after successfully picketing the Secretariat, the seat of the colonial government, were charged by mounted police
Mounted police are police who patrol on horseback or camelback. Their day-to-day function is typically picturesque or ceremonial, but they are also employed in crowd control because of their mobile mass and height advantage and increasingly in th ...
from the Indian Imperial Police wielding batons, which killed a Rangoon University student called Aung Kyaw. In Mandalay, the colonial police shot into a crowd of protesters led by Buddhist monks, killing 17 people. The movement became known as ''Htaung thoun ya byei ayeidawbon'' (the '1300 Revolution
The 1300 Revolution (; also called the 1300 Movement or Year 1300 Strikes) was a nationwide general strike in Myanmar in 1938–1939, beginning with oilfield strikes. It is named for the year it occurred: 1300 in the Myanmar calendar. The strike's ...
' named after the Burmese calendar year),
World War II
Some Burmese nationalists saw the outbreak of World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
as an opportunity to extort concessions from the British in exchange for support in the war effort. Other Burmese, such as the Thakin movement, opposed Burma's participation in the war under any circumstances. Aung San co-founded the Communist Party of Burma
The Communist Party of Burma (CPB), also known as the Burma Communist Party (BCP), is an underground communist party in Myanmar (formerly Burma). It is the oldest existing political party in the country.
Founded in 1939, the CPB initially fo ...
(CPB) with other Thakins in August 1939.Marxist
Marxism is a political philosophy and method of socioeconomic analysis. It uses a dialectical and materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to analyse class relations, social conflic ...
literature as well as tracts from the Sinn Féin
Sinn Féin ( ; ; ) is an Irish republican and democratic socialist political party active in both the Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland.
The History of Sinn Féin, original Sinn Féin organisation was founded in 1905 by Arthur Griffit ...
movement in Ireland had been widely circulated and read among political activists. Aung San also co-founded the People's Revolutionary Party (PRP), renamed the Socialist Party after World War II. He was also instrumental in founding the Freedom Bloc by forging an alliance of the Dobama, ABSU, politically active monks and Ba Maw's Poor Man's Party.Chinese Communist Party
The Communist Party of China (CPC), also translated into English as Chinese Communist Party (CCP), is the founding and One-party state, sole ruling party of the People's Republic of China (PRC). Founded in 1921, the CCP emerged victorious in the ...
but he was detected by the Japanese authorities who offered him support by forming a secret intelligence unit called the ''Minami Kikan'' headed by Colonel Suzuki with the objective of closing the Burma Road and supporting a national uprising. Aung San briefly returned to Burma to enlist twenty-nine young men who went to Japan with him to receive military training on Hainan Island
Hainan is an island province and the southernmost province of China. It consists of the eponymous Hainan Island and various smaller islands in the South China Sea under the province's administration. The name literally means "South of the Sea ...
, China, and they came to be known as the " Thirty Comrades". When the Japanese occupied Bangkok
Bangkok, officially known in Thai language, Thai as Krung Thep Maha Nakhon and colloquially as Krung Thep, is the capital and most populous city of Thailand. The city occupies in the Chao Phraya River delta in central Thailand and has an estim ...
in December 1941, Aung San announced the formation of the Burma Independence Army
The Burma Independence Army (BIA), was a Collaboration with Imperial Japan, pro-Japanese and revolutionary army that fought for the end of British rule in Burma by assisting the Empire of Japan, Japanese in Japanese conquest of Burma, their c ...
(BIA) in anticipation of the Japanese invasion of Burma in 1942. The BIA formed a provisional government in some areas of the country in the spring of 1942, but there were differences within the Japanese leadership over the future of Burma. While Colonel Suzuki encouraged the Thirty Comrades to form a provisional government, the Japanese Military leadership had never formally accepted such a plan. Eventually the Japanese Army turned to Ba Maw to form a government. During the war in 1942, the BIA had grown in an uncontrolled manner, and in many districts officials and even criminals appointed themselves to the BIA. It was reorganised as the Burma Defence Army (BDA) under the Japanese but still headed by Aung San. While the BIA had been an irregular force, the BDA was recruited by selection and trained as a conventional army by Japanese instructors. Ba Maw was afterwards declared head of state, and his cabinet included both Aung San as War Minister and the Communist leader Thakin Than Tun as Minister of Land and Agriculture as well as the Socialist leaders Thakins Nu and Mya. When the Japanese declared Burma, in theory, independent in 1943, the Burma Defence Army (BDA) was renamed the Burma National Army (BNA).
The BIA formed a provisional government in some areas of the country in the spring of 1942, but there were differences within the Japanese leadership over the future of Burma. While Colonel Suzuki encouraged the Thirty Comrades to form a provisional government, the Japanese Military leadership had never formally accepted such a plan. Eventually the Japanese Army turned to Ba Maw to form a government. During the war in 1942, the BIA had grown in an uncontrolled manner, and in many districts officials and even criminals appointed themselves to the BIA. It was reorganised as the Burma Defence Army (BDA) under the Japanese but still headed by Aung San. While the BIA had been an irregular force, the BDA was recruited by selection and trained as a conventional army by Japanese instructors. Ba Maw was afterwards declared head of state, and his cabinet included both Aung San as War Minister and the Communist leader Thakin Than Tun as Minister of Land and Agriculture as well as the Socialist leaders Thakins Nu and Mya. When the Japanese declared Burma, in theory, independent in 1943, the Burma Defence Army (BDA) was renamed the Burma National Army (BNA).
Joining the Allies
It soon became apparent that Japanese promises of independence were merely a sham and that Ba Maw was deceived. As the war turned against the Japanese, they declared Burma a fully sovereign state on 1 August 1943, but this was just another facade. Disillusioned, Aung San
Aung San (, ; 13 February 191519 July 1947), known honorifically as '' Bogyoke'' Aung San, was a Burmese politician, independence activist and revolutionary. He was instrumental in Myanmar's struggle for independence from British rule, but he w ...
began negotiations with Communist leaders Thakin Than Tun and Thakin Soe
Thakin Soe (, ; 1906 – 6 May 1989) was a founding member of the Communist Party of Burma and a leader of the Anti-Fascist Organisation. He is regarded as one of Burma's most prominent communist leaders.
Early life
Soe was an ethnic Mon peop ...
, and Socialist leaders Ba Swe and Kyaw Nyein which led to the formation of the Anti-Fascist Organisation
The Anti-Fascist Organisation (AFO) was a resistance movement against the Japanese occupation of Burma and independence of Burma during World War II. It was the forerunner of the Anti-Fascist People's Freedom League.
History
The AFO was formed ...
(AFO) in August 1944 at a secret meeting of the CPB, the PRP and the BNA in Pegu
Bago (formerly spelled Pegu; , ), formerly known as Hanthawaddy, is a city and the capital of the Bago Region in Myanmar. It is located north-east of Yangon.
Etymology
The Burmese name Bago (ပဲခူး) is likely derived from the Mon lang ...
. The AFO was later renamed the Anti-Fascist People's Freedom League (AFPFL).Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
. Soe had already gone underground to organise resistance against the Japanese occupation, and Thakin Than Tun was able to pass on Japanese intelligence to Soe, while other Communist leaders Thakin Thein Pe
Thein Pe Myint ( ; also ''Thakin'' Thein Pe ( ); 10 July 1914 – 15 January 1978) was a Burmese politician, writer, and journalist. He wrote several politically and socially prominent books and founded the influential newspaper, ''The Botataung. ...
and Tin Shwe made contact with the exiled colonial government in Simla
Shimla, also known as Simla (List of renamed Indian cities and states#Himachal Pradesh, the official name until 1972), is the capital and the largest city of the northern Indian state of Himachal Pradesh. In 1864, Shimla was declared the summe ...
, India.Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not an explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are calle ...
in 1944 and 1945 through the British organisation Force 136
Force 136 was a far eastern branch of the British World War II intelligence organisation, the Special Operations Executive (SOE). Originally set up in 1941 as the India Mission with the cover name of GSI(k), it absorbed what was left of SOE's O ...
. On 27 March 1945 the Burma National Army rose up in a countrywide rebellion against the Japanese.Tatmadaw
The Tatmadaw, also known as the Sit-Tat, is the armed forces of Myanmar (formerly Burma). It is administered by the Ministry of Defence and composed of the Myanmar Army, the Myanmar Navy and the Myanmar Air Force. Auxiliary services include ...
(Armed Forces) Day'. Aung San
Aung San (, ; 13 February 191519 July 1947), known honorifically as '' Bogyoke'' Aung San, was a Burmese politician, independence activist and revolutionary. He was instrumental in Myanmar's struggle for independence from British rule, but he w ...
and others subsequently began negotiations with Lord Mountbatten
Admiral of the Fleet (Royal Navy), Admiral of the Fleet Louis Francis Albert Victor Nicholas Mountbatten, 1st Earl Mountbatten of Burma (born Prince Louis of Battenberg; 25 June 1900 – 27 August 1979), commonly known as Lord Mountbatten, was ...
and officially joined the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not an explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are calle ...
as the Patriotic Burmese Forces (PBF). At the first meeting, the AFO represented itself to the British as the provisional government of Burma with Thakin Soe as chairman and Aung San as a member of its ruling committee. The Japanese were routed from most of Burma by May 1945. Negotiations then began with the British over the disarming of the AFO and the participation of its troops in a post-war Burma Army. Some veterans had been formed into a paramilitary force under Aung San, called the ''Pyithu yèbaw tat'' or People's Volunteer Organisation (PVO), and were openly drilling in uniform.Kandy
Kandy (, ; , ) is a major city located in the Central Province, Sri Lanka, Central Province of Sri Lanka. It was the last capital of the Sinhalese monarchy from 1469 to 1818, under the Kingdom of Kandy. The city is situated in the midst of ...
conference in Ceylon
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
in September 1945.
Following World War II
The surrender of the Japanese brought a military administration to Burma and demands to try Aung San for his involvement in a murder during military operations in 1942. Lord Mountbatten realised that this was an impossibility considering Aung San's popular appeal.Hubert Rance
Major-General Sir Hubert Elvin Rance, (17 July 1898 – 24 January 1974) was a British politician who was the last Governor of British Burma between 1946 and 1948, during the transition from Japanese to British colonial administration. Later h ...
as the new governor, and almost immediately after his appointment the Rangoon Police went on strike. The strike, starting in September 1946, then spread from the police to government employees and came close to becoming a general strike.
Rance calmed the situation by meeting with Aung San and convincing him to join the Governor's Executive Council along with other members of the AFPFL.Aung San
Aung San (, ; 13 February 191519 July 1947), known honorifically as '' Bogyoke'' Aung San, was a Burmese politician, independence activist and revolutionary. He was instrumental in Myanmar's struggle for independence from British rule, but he w ...
-Attlee
Clement Richard Attlee, 1st Earl Attlee (3 January 18838 October 1967) was a British statesman who was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1945 to 1951 and Leader of the Labour Party from 1935 to 1955. Attlee was Deputy Prime Minister d ...
Agreement on 27 January 1947.Thakin Soe
Thakin Soe (, ; 1906 – 6 May 1989) was a founding member of the Communist Party of Burma and a leader of the Anti-Fascist Organisation. He is regarded as one of Burma's most prominent communist leaders.
Early life
Soe was an ethnic Mon peop ...
underground and the conservatives into opposition.
Aung San also succeeded in concluding an agreement with ethnic minorities for a unified Burma at the Panglong Conference
The Panglong Conference (), held in February 1947, was a historic meeting that took place at Panglong, Southern Shan State, Panglong in the Shan States in Burma between the Shan people, Shan, Kachin people, Kachin and Chin people, Chin ethnic mi ...
on 12 February, celebrated since as 'Union Day'. U Aung Zan Wai, U Pe Khin, Myoma U Than Kywe, Major Aung, Sir Maung Gyi and Dr. Sein Mya Maung. were most important negotiators and leaders of the historical pinlon (panglong) Conference negotiated with Burma national top leader General Aung San and other top leaders in 1947. All these leaders decided to join to form the Union of Burma. Union day celebration is one of the greatest in the history of Burma. The popularity of the AFPFL, now dominated by Aung San and the Socialists, was eventually confirmed when it won an overwhelming victory in the April 1947 constituent assembly elections.Martyrs' Day
Martyrs' Day are days observed in or by some countries, including the United States, Japan, India, Brazil, Canada and Australia, to recognise martyrs such as soldiers, revolutionaries or victims of genocide. Below is a list of various Martyrs' Days ...
. Shortly after, rebellion broke out in the Arakan led by the veteran monk U Seinda, and it began to spread to other districts.Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, often referred to as the British Commonwealth or simply the Commonwealth, is an International organization, international association of member states of the Commonwealth of Nations, 56 member states, the vast majo ...
, unlike India or Pakistan.
Independent Myanmar
1948–1962
Civil war broke out almost immediately following independence, as the Communist Party of Burma withdrew from the government and began its insurrection, while the Karen insurgency began the following year.Thakin Soe
Thakin Soe (, ; 1906 – 6 May 1989) was a founding member of the Communist Party of Burma and a leader of the Anti-Fascist Organisation. He is regarded as one of Burma's most prominent communist leaders.
Early life
Soe was an ethnic Mon peop ...
, the White Flag Communists led by Thakin Than Tun, the '' Yebaw Hpyu'' or (White Band) People's Volunteer Organisation led by Bo La Yaung, a member of the Thirty Comrades, army rebels calling themselves the Revolutionary Burma Army (RBA) led by Communist officers Bo Zeya, Bo Yan Aung and Bo Yè Htut – all three of them members of the Thirty Comrades, Arakanese Muslims or the Mujahid, and the Karen National Union (KNU).Bandung Conference
The first large-scale Asian–African or Afro–Asian Conference (), also known as the Bandung Conference, was a meeting of Asian and African states, most of which were newly independent, which took place on 18–24 April 1955 in Bandung, We ...
of 1955.Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
and the People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
.
By 1958, the country was beginning to recover economically, but was beginning to fall apart politically due to a split in the AFPFL into two factions. One faction was led by Thakins Nu and Tin, and the other was led by Ba Swe and Kyaw Nyein.
1962–1988
On 2 March 1962, Ne Win, with sixteen other senior military officers, staged a 1962 Burmese coup d'état, coup d'état, arrested U Nu, Sao Shwe Thaik and several others, and declared a socialist state to be run by their ''Union Revolutionary Council''. Sao Shwe Thaik's son, Sao Mye Thaik, was shot dead in what was generally described as a "bloodless" coup. Hsipaw, Thibaw Sawbwa Sao Kya Seng also disappeared mysteriously after being stopped at a checkpoint near Taunggyi.[Boudreau, Vincent (2004) ''Resisting Dictatorship: Repression and Protest in Southeast Asia'' Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, U.K.]
pp. 37–39
However, on 7 July 1962, a peaceful student protest on Rangoon University campus was suppressed by the military, killing over 100 students. The next day, the army blew up the Students Union building.Arakan
Arakan ( or ; , ), formerly anglicised as Aracan, is the historical geographical name for the northeastern coastal region of the Bay of Bengal, covering present-day Bangladesh and Myanmar. The region was called "Arakan" for centuries. It is ...
, called the King Dragon operation in Arakan, King Dragon operation, causing 250,000 refugees to flee to neighbouring Bangladesh.
U Nu, after his release from prison in October 1966, had left Burma in April 1969, and formed the Parliamentary Democracy Party (PDP) the following August in Bangkok
Bangkok, officially known in Thai language, Thai as Krung Thep Maha Nakhon and colloquially as Krung Thep, is the capital and most populous city of Thailand. The city occupies in the Chao Phraya River delta in central Thailand and has an estim ...
, Thailand with the former Thirty Comrades, Bo Let Ya, co-founder of the CPB and former Minister of Defence and deputy prime minister, Bo Yan Naing, and U Thwin, ex-BIA and former Minister of Trade. Another member of the Thirty Comrades, Bohmu Aung, former Minister of Defence, joined later. The fourth, Bo Setkya, who had gone underground after the 1962 coup, died in Bangkok shortly before U Nu arrived.
Crisis and the 1988 Uprising
Ne Win retired as president in 1981, but remained in power as Chairman of the BSPP until his sudden unexpected announcement to step down on 23 July 1988.Communist Party of Burma
The Communist Party of Burma (CPB), also known as the Burma Communist Party (BCP), is an underground communist party in Myanmar (formerly Burma). It is the oldest existing political party in the country.
Founded in 1939, the CPB initially fo ...
through its underground organisation. Although there had inevitably been some underground CPB presence as well as that of ethnic insurgent groups, there was no evidence of their being in charge to any extent.
1990–2006
The military government announced a change of name for the country in English from ''Burma'' to ''Myanmar'' in 1989. It also continued the economic reforms started by the old regime and called for a Constituent Assembly to revise the 1974 Constitution. This led to multiparty elections in May 1990 in which the newly formed National League for Democracy (NLD) won a landslide victory over the National Unity Party (Burma), National Unity Party (NUP, the successor to the BSPP) and about a dozen smaller parties.Yangon
Yangon, formerly romanized as Rangoon, is the capital of the Yangon Region and the largest city of Myanmar. Yangon was the List of capitals of Myanmar, capital of Myanmar until 2005 and served as such until 2006, when the State Peace and Dev ...
to an unnamed location near Kyatpyay just outside Pyinmana, to a newly designated capital city. This public action follows a long term unofficial policy of moving critical military and government infrastructure away from Yangon to avoid a repetition of the events of 8888 Uprising, 1988. On Armed Forces Day (27 March 2006), the capital was officially named Naypyidaw, Naypyidaw Myodaw (lit. Royal City of the Seat of Kings).
In November 2006, the International Labour Organization (ILO) announced it will be seeking – at the International Court of Justice – "to prosecute members of the ruling Myanmar junta for crimes against humanity" over the continuous forced labour of its citizens by the military. According to the ILO, an estimated 800,000 people are subject to forced labour in Myanmar.
2007 anti-government protests
 The 2007 Burmese anti-government protests were a series of anti-government protests that started in Burma on 15 August 2007. The immediate cause of the protests was mainly the unannounced decision of the ruling military junta, junta, the State Peace and Development Council, to remove fuel subsidies, which caused the price of Diesel fuel, diesel and gasoline, petrol to suddenly rise as much as 100%, and the price of compressed natural gas for buses to increase fivefold in less than a week.
The 2007 Burmese anti-government protests were a series of anti-government protests that started in Burma on 15 August 2007. The immediate cause of the protests was mainly the unannounced decision of the ruling military junta, junta, the State Peace and Development Council, to remove fuel subsidies, which caused the price of Diesel fuel, diesel and gasoline, petrol to suddenly rise as much as 100%, and the price of compressed natural gas for buses to increase fivefold in less than a week.[UN envoy warns of Myanmar crisis](_blank)
During the crackdown, there were rumours of disagreement within the Burmese military, but none were confirmed. At the time, independent sources reported, through pictures and accounts, 30 to 40 monks and 50 to 70 civilians killed as well as 200 beaten. However, other sources reveal more dramatic figures. In a White House statement President Bush said: "Monks have been beaten and killed ... Thousands of pro-democracy protesters have been arrested". Some news reports referred to the protests as the Saffron Revolution.
On 7 February 2008, SPDC announced that a referendum for the Constitution would be held, and Elections by 2010. The 2008 Burmese constitutional referendum was held on 10 May and promised a "discipline-flourishing democracy" for the country in the future.
Cyclone Nargis
On 3 May 2008, Cyclone Nargis devastated the country when winds of up to 215 km/h (135 mph) touched land in the densely populated, rice-farming delta of the Irrawaddy Division. It is estimated that more than 130,000 people died or went missing and damage totalled 10 billion US dollars; it was the worst natural disaster in Burmese history. The World Food Programme reported that, "Some villages have been almost totally eradicated and vast rice-growing areas are wiped out."
The United Nations estimated that as many as 1 million were left homeless and the World Health Organization "received reports of malaria outbreaks in the worst-affected area."[The Associated Press: Official: UN plane lands in Myanmar with aid after cyclone](_blank)
Yet in the critical days following this disaster, Burma's isolationist regime complicated recovery efforts by delaying the entry of United Nations planes delivering medicine, food, and other supplies. The government's failure to permit entry for large-scale international relief efforts was described by the United Nations as "unprecedented."
2011–2016
The 2011–2012 Burmese democratic reforms were an ongoing series of political, economic and administrative changes in Burma undertaken by the military-backed government. These reforms included the release of pro-democracy leader Aung San Suu Kyi from house arrest and subsequent dialogues with her, establishment of the Myanmar National Human Rights Commission, National Human Rights Commission, general amnesties of more than 200 political prisoners, institution of new labour laws that allow labour unions and strikes, relaxation of press censorship, and regulations of currency practices.
As a consequence of the reforms, ASEAN approved Burma's bid for the chairmanship in 2014. United States Secretary of State Hillary Clinton visited Burma on 1 December 2011, to encourage further progress; it was the first visit by a US Secretary of State in more than fifty years. United States President Barack Obama visited one year later, becoming the first US president to visit the country.
Suu Kyi's party, the National League for Democracy, participated in 2012 Burmese by-elections, by-elections held on 1 April 2012 after the government abolished laws that led to the NLD's boycott of the 2010 Burmese general election, 2010 general election. She led the NLD in winning the by-elections in a landslide, winning 41 out of 44 of the contested seats, with Suu Kyi herself winning a seat representing Kawhmu Constituency in the House of Representatives (Burma), lower house of the Pyidaungsu Hluttaw, Burmese Parliament.
2015 Myanmar general election, 2015 election results gave the National League for Democracy an absolute majority of seats in both chambers of the Burmese parliament, enough to ensure that its candidate would become President of Myanmar, president, while NLD leader Aung San Suu Kyi is constitutionally barred from the presidency. However, clashes between Burmese troops and Internal conflict in Burma, local insurgent groups continued.
2016–2021
The new parliament convened on 1 February 2016 and, on 15 March 2016, Htin Kyaw was elected as the first non-military president of the country since the 1962 Burmese coup d'état, 1962 coup d'état. Aung San Suu Kyi assumed the newly created role of the State Counsellor of Myanmar, State Counsellor, a position similar to Prime Minister, on 6 April 2016.
The resounding victory of Aung San Suu Kyi's National League for Democracy in 2015 general elections raised hope for a successful transition of Myanmar from a closely held military rule to a free democratic system. However, internal political turmoil, crumbling economy and ethnic strife continued to make the transition to democracy a painful one. The 2017 murder of Ko Ni, a prominent Muslim lawyer and a key member of Myanmar's governing National League for Democracy party is seen as a serious blow to the country's fragile democracy. Mr. Ko Ni's murder deprived Aung San Suu Kyi of his perspective as an adviser, particularly on reforming Myanmar's military-drafted Constitution and ushering the country to democracy.
There was a Rohingya genocide, military crackdown against Rohingya that occurred from October 2016 to January 2017, and the second has been occurring since August 2017. The crisis forced over a million Rohingya to flee to other countries. Most fled to Bangladesh, resulting in the creation of Kutupalong refugee camp, the world's largest refugee camp.
At the 2020 Myanmar general election, general election on 8 November 2020 the National League for Democracy (NLD) won 396 out of 476 seats in parliament, an even larger margin of victory than in the 2015 election. The military's proxy party, the Union Solidarity and Development Party, won only 33 seats.
2021–present
 On February 1, 2021, Myanmar's military, the
On February 1, 2021, Myanmar's military, the Tatmadaw
The Tatmadaw, also known as the Sit-Tat, is the armed forces of Myanmar (formerly Burma). It is administered by the Ministry of Defence and composed of the Myanmar Army, the Myanmar Navy and the Myanmar Air Force. Auxiliary services include ...
detained the state counsellor Aung San Suu Kyi and other government members. The military handed power to the military chief Min Aung Hlaing and a state of emergency was declared for one year.
 On 2 February 2021, healthcare workers and civil servants across the country, including in the national capital, Naypyidaw, launched a national civil disobedience movement (), in opposition to the coup d'état. Protesters have employed peaceful and Nonviolence, nonviolent forms of protest, which include acts of civil disobedience, labour strikes, a military boycott campaign, a Cacerolazo, pot-banging movement, a red ribbon campaign, public protests, and formal recognition of the election results by elected representatives.
On 20 February, two people were shot dead and at least two dozens more were injured in
On 2 February 2021, healthcare workers and civil servants across the country, including in the national capital, Naypyidaw, launched a national civil disobedience movement (), in opposition to the coup d'état. Protesters have employed peaceful and Nonviolence, nonviolent forms of protest, which include acts of civil disobedience, labour strikes, a military boycott campaign, a Cacerolazo, pot-banging movement, a red ribbon campaign, public protests, and formal recognition of the election results by elected representatives.
On 20 February, two people were shot dead and at least two dozens more were injured in Mandalay
Mandalay is the second-largest city in Myanmar, after Yangon. It is located on the east bank of the Irrawaddy River, 631 km (392 mi) north of Yangon. In 2014, the city had a population of 1,225,553.
Mandalay was founded in 1857 by Ki ...
by the military in violent crackdown. These people were residents of Maha Aung Myay Township guarding government shipyard workers involved in the civil disobedience movement from the police who were forcing them back to work. In addition to firing live rounds, the police and military personnel also beat, arrested, used water cannon, and threw various objects such as marbles and stones at civilians.
As of 26 March 2021, at least 3,070 people have been detained, and at least 423 protesters have been killed by military or police forces.
Myanmar civil war (2021–present), Armed insurgencies by the People's Defence Force (Myanmar), People's Defence Force of the National Unity Government of Myanmar, National Unity Government have erupted throughout Myanmar. In many villages and towns junta forces attacks drove out tens of thousands of people at least. UNOCHA said that as of early September 2022, 974,000 people had been internally displaced since the coup. In addition, between the February 2021 coup and June 2022 over 40,000 people fled into neighboring countries, including many from communities close to the borders that came under regime attacks.
See also
* History of Asia
* List of Burmese monarchs
** Burmese monarchs' family tree
* List of presidents of Burma
* Politics of Burma
* Prime Minister of Burma
* Timeline of Burmese history
Notes
References and further reading
* Aung-Thwin, Michael, and Maitrii Aung-Thwin. ''A history of Myanmar since ancient times: Traditions and transformations'' (Reaktion Books, 2013
online
*
* Brown, Ian. ''Burma's Economy in the Twentieth Century'' (Cambridge University Press, 2013) 229 pp
online review at http://eh.net/book-reviews
*
* Cameron, Ewan. "The State of Myanmar," ''History Today'' (May 2020), 70#4 pp 90–93.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
online free to borrow
*
* Kipgen, Nehginpao. ''Myanmar: A political history'' (Oxford University Press, 2016
online
*
*
*
* Mahmood, Syed S., et al. "The Rohingya people of Myanmar: health, human rights, and identity." ''The Lancet'' 389.10081 (2017): 1841–1850
online
*
*
*
*
*
* Seekins, Donald M. ''Historical Dictionary of Burma (Myanmar)'' (Rowman & Littlefield, 2017).
*
*
*
* Topich, William J., and Keith A. Leitich. ''The history of Myanmar'' (ABC-CLIO, 2013)
online
*
Historiography
* Englehart, Neil A. "Liberal Leviathan or Imperial Outpost? J. S. Furnivall on Colonial Rule in Burma", ''Modern Asian Studies'' (2011) 45#4 pp 759–790.
External links
Webproject in English and Myanmar about the history of Burma/Myanmar
by historian Thant Myint-U and webdesigners in Myanmar
Factfile: Burma's history of repression
University of Washington Library papers by Burmese historians Than Tun, Yi Yi, U Pe Maung Tin, Ba Shin
by Bob Hudson
The Changing Nature of Conflict Between Burma and Siam as seen from the Growth and Development of Burmese States from the 16th to the 19th Centuries
Pamaree Surakiat, Asia Research Institute, Singapore, March 2006
Online Burma/Myanmar Library
a veritable mine of information
The Bloodstrewn Path:Burma's Early Journey to Independence
BBC Burmese, 30 September 2005, Retrieved 2006-10-28
The Nu-Attlee Treaty and Let Ya-Freeman Agreement, 1947
Online Burma/Myanmar Library
Federalism in Burma
Online Burma/Myanmar Library
Burma Communist Party's Conspiracy to take over State Power and related information
Online Burma/Myanmar Library
Understanding Burma's SPDC Generals
''Mizzima'', Retrieved 2006-10-31
Strangers in a Changed Land
Thalia Isaak, ''The Irrawaddy'', March–April 2001, Retrieved 2006-10-29
Behold a New Empire
Aung Zaw,''The Irrawaddy'', October 2006, Retrieved 2006-10-19
Daewoo — A Serial Suitor of the Burmese Regime
Clive Parker, ''The Irrawaddy'', 7 December 2006, Retrieved on 2006-12-08
Heroes and Villains
''The Irrawaddy'', March 2007
Lion City Lament
Kyaw Zwa Moe, ''The Irrawaddy'', March 2007
Pyu Homeland in Samon Valley
Bob Hudson 2005
The History of India, as Told by Its Own Historians. The Muhammadan Period
by Sir H. M. Elliot; Edited by John Dowson; London Trubner Company 1867–1877
The Packard Humanities Institute
Persian Texts in Translation.
* http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/asia-pacific/7543347.stm Was the uprising of 1988 worth it?
{{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Burma
History of Myanmar,
bn:মায়ানমার#ইতিহাস
 After the fall of Pagan, the Mongols left the searing Irrawaddy valley but the Pagan Kingdom was irreparably broken up into several small kingdoms. By the mid-14th century, the country had become organised along four major power centres: Upper Burma, Lower Burma, Shan States and Arakan. Many of the power centres were themselves made up of (often loosely held) minor kingdoms or princely states. This era was marked by a series of wars and switching alliances. Smaller kingdoms played a precarious game of paying allegiance to more powerful states, sometimes simultaneously.
After the fall of Pagan, the Mongols left the searing Irrawaddy valley but the Pagan Kingdom was irreparably broken up into several small kingdoms. By the mid-14th century, the country had become organised along four major power centres: Upper Burma, Lower Burma, Shan States and Arakan. Many of the power centres were themselves made up of (often loosely held) minor kingdoms or princely states. This era was marked by a series of wars and switching alliances. Smaller kingdoms played a precarious game of paying allegiance to more powerful states, sometimes simultaneously.
 Although Arakan had been de facto independent since the late Pagan period, the Laungkyet dynasty of Arakan was ineffectual. Until the founding of the Mrauk-U Kingdom in 1429, Arakan was often caught between bigger neighbours, and found itself a battlefield during the Forty Years' War between Ava and Pegu. Mrauk-U went on to be a powerful kingdom in its own right between 15th and 17th centuries, including East Bengal between 1459 and 1666. Arakan was the only post-Pagan kingdom not to be annexed by the Taungoo dynasty.
Although Arakan had been de facto independent since the late Pagan period, the Laungkyet dynasty of Arakan was ineffectual. Until the founding of the Mrauk-U Kingdom in 1429, Arakan was often caught between bigger neighbours, and found itself a battlefield during the Forty Years' War between Ava and Pegu. Mrauk-U went on to be a powerful kingdom in its own right between 15th and 17th centuries, including East Bengal between 1459 and 1666. Arakan was the only post-Pagan kingdom not to be annexed by the Taungoo dynasty.
 Despite being a tumultuous time for Myanmar, the Taungoo expansions increased the international reach of the nation. Newly rich merchants from Myanmar traded as far as the
Despite being a tumultuous time for Myanmar, the Taungoo expansions increased the international reach of the nation. Newly rich merchants from Myanmar traded as far as the  While the interregnum that followed the fall of the Pagan empire lasted over 250 years (1287–1555), that following the fall of First Taungoo was relatively short-lived. One of Bayinnaung's sons,
While the interregnum that followed the fall of the Pagan empire lasted over 250 years (1287–1555), that following the fall of First Taungoo was relatively short-lived. One of Bayinnaung's sons,  In 1920 the first university students strike in history broke out in protest against the new University Act which the students believed would only benefit the elite and perpetuate colonial rule. 'National Schools' sprang up across the country in protest against the colonial education system, and the strike came to be commemorated as ' National Day'. There were further strikes and anti-tax protests in the later 1920s led by the ''Wunthanu athin''s. Prominent among the political activists were Buddhist monks (''pongyi''), such as U Ottama and U Seinda in the
In 1920 the first university students strike in history broke out in protest against the new University Act which the students believed would only benefit the elite and perpetuate colonial rule. 'National Schools' sprang up across the country in protest against the colonial education system, and the strike came to be commemorated as ' National Day'. There were further strikes and anti-tax protests in the later 1920s led by the ''Wunthanu athin''s. Prominent among the political activists were Buddhist monks (''pongyi''), such as U Ottama and U Seinda in the  The BIA formed a provisional government in some areas of the country in the spring of 1942, but there were differences within the Japanese leadership over the future of Burma. While Colonel Suzuki encouraged the Thirty Comrades to form a provisional government, the Japanese Military leadership had never formally accepted such a plan. Eventually the Japanese Army turned to Ba Maw to form a government. During the war in 1942, the BIA had grown in an uncontrolled manner, and in many districts officials and even criminals appointed themselves to the BIA. It was reorganised as the Burma Defence Army (BDA) under the Japanese but still headed by Aung San. While the BIA had been an irregular force, the BDA was recruited by selection and trained as a conventional army by Japanese instructors. Ba Maw was afterwards declared head of state, and his cabinet included both Aung San as War Minister and the Communist leader Thakin Than Tun as Minister of Land and Agriculture as well as the Socialist leaders Thakins Nu and Mya. When the Japanese declared Burma, in theory, independent in 1943, the Burma Defence Army (BDA) was renamed the Burma National Army (BNA).
The BIA formed a provisional government in some areas of the country in the spring of 1942, but there were differences within the Japanese leadership over the future of Burma. While Colonel Suzuki encouraged the Thirty Comrades to form a provisional government, the Japanese Military leadership had never formally accepted such a plan. Eventually the Japanese Army turned to Ba Maw to form a government. During the war in 1942, the BIA had grown in an uncontrolled manner, and in many districts officials and even criminals appointed themselves to the BIA. It was reorganised as the Burma Defence Army (BDA) under the Japanese but still headed by Aung San. While the BIA had been an irregular force, the BDA was recruited by selection and trained as a conventional army by Japanese instructors. Ba Maw was afterwards declared head of state, and his cabinet included both Aung San as War Minister and the Communist leader Thakin Than Tun as Minister of Land and Agriculture as well as the Socialist leaders Thakins Nu and Mya. When the Japanese declared Burma, in theory, independent in 1943, the Burma Defence Army (BDA) was renamed the Burma National Army (BNA).
 The 2007 Burmese anti-government protests were a series of anti-government protests that started in Burma on 15 August 2007. The immediate cause of the protests was mainly the unannounced decision of the ruling military junta, junta, the State Peace and Development Council, to remove fuel subsidies, which caused the price of Diesel fuel, diesel and gasoline, petrol to suddenly rise as much as 100%, and the price of compressed natural gas for buses to increase fivefold in less than a week. The protest demonstrations were at first dealt with quickly and harshly by the junta, with dozens of protesters arrested and detained. Starting 18 September, the protests had been led by thousands of Bhikkhu, Buddhist monks, and those protests had been allowed to proceed until a renewed government crackdown on 26 September.UN envoy warns of Myanmar crisis
The 2007 Burmese anti-government protests were a series of anti-government protests that started in Burma on 15 August 2007. The immediate cause of the protests was mainly the unannounced decision of the ruling military junta, junta, the State Peace and Development Council, to remove fuel subsidies, which caused the price of Diesel fuel, diesel and gasoline, petrol to suddenly rise as much as 100%, and the price of compressed natural gas for buses to increase fivefold in less than a week. The protest demonstrations were at first dealt with quickly and harshly by the junta, with dozens of protesters arrested and detained. Starting 18 September, the protests had been led by thousands of Bhikkhu, Buddhist monks, and those protests had been allowed to proceed until a renewed government crackdown on 26 September.UN envoy warns of Myanmar crisis On February 1, 2021, Myanmar's military, the
On February 1, 2021, Myanmar's military, the