
The bat virome is the
group of viruses associated with
bats. Bats host a diverse array of viruses, including all seven types described by the
Baltimore classification system
Baltimore classification is a system used to classify viruses based on their manner of messenger RNA (mRNA) synthesis. By organizing viruses based on their manner of mRNA production, it is possible to study viruses that behave similarly as a dis ...
: (I)
double-stranded DNA viruses; (II)
single-stranded DNA viruses; (III)
double-stranded RNA viruses; (IV)
positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses
In molecular biology and genetics, the sense of a nucleic acid molecule, particularly of a strand of DNA or RNA, refers to the nature of the roles of the strand and its complement in specifying a sequence of amino acids. Depending on the context ...
; (V)
negative-sense single-stranded RNA viruses
In molecular biology and genetics, the sense of a nucleic acid molecule, particularly of a strand of DNA or RNA, refers to the nature of the roles of the strand and its complement in specifying a sequence of amino acids. Depending on the context, ...
; (VI)
positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses that replicate through a DNA intermediate; and (VII)
double-stranded DNA viruses that replicate through a single-stranded RNA intermediate. The greatest share of bat-associated viruses identified as of 2020 are of type IV, in the family ''
Coronaviridae''.
Bats harbor several viruses that are
zoonotic, or capable of infecting humans, and some bat-borne viruses are considered important
emerging viruses.
These zoonotic viruses include the
rabies virus,
SARS-CoV,
MERS-CoV,
Marburg virus
Marburg virus (MARV) is a hemorrhagic fever virus of the ''Filoviridae'' family of viruses and a member of the species '' Marburg marburgvirus'', genus ''Marburgvirus''. It causes Marburg virus disease in primates, a form of viral hemorrhagic f ...
,
Nipah virus, and
Hendra virus. While research clearly indicates that
SARS-CoV-2 originated in bats,
it is unknown how it was transmitted to humans, or if an intermediate host was involved. It has been speculated that bats may have a role in the
ecology of the Ebola virus, though this is unconfirmed. While transmission of rabies from bats to humans usually occurs via biting, most other zoonotic bat viruses are transmitted by direct contact with infected bat fluids like urine,
guano
Guano (Spanish from qu, wanu) is the accumulated excrement of seabirds or bats. As a manure, guano is a highly effective fertilizer due to the high content of nitrogen, phosphate, and potassium, all key nutrients essential for plant growth. G ...
, or saliva, or through contact with an infected, non-bat
intermediate host
In biology and medicine, a host is a larger organism that harbours a smaller organism; whether a parasitic, a mutualistic, or a commensalist ''guest'' (symbiont). The guest is typically provided with nourishment and shelter. Examples include a ...
. There is no firm evidence that butchering or consuming
bat meat can lead to viral transmission, though this has been speculated.
Despite the abundance of viruses associated with bats, they rarely become ill from viral infections, and
rabies is the only viral illness known to kill bats. Much research has been conducted on bat
virology, particularly bat
immune response. Bats'
immune systems differ from other mammals in their lack of several
inflammasomes, which activate the body's inflammatory response, as well as a dampened
stimulator of interferon genes
Stimulator of interferon genes (STING), also known as transmembrane protein 173 (TMEM173) and MPYS/MITA/ERIS is a protein that in humans is encoded by the STING1 gene.
STING plays an important role in innate immunity. STING induces type I interfe ...
(STING) response, which helps control host response to pathogens. Preliminary evidence indicates bats are thus more tolerant of infection than other mammals. While much research has centered on bats as a source of zoonotic disease, reviews have found mixed results on whether bats harbor more zoonotic viruses than other groups. A 2015 review found that bats do not harbor more zoonotic viruses than
primates or
rodents, though the three groups harbored more than other mammal
orders
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of ...
.
In contrast, a 2020 review found that bats do not have more zoonotic viruses than any other bird or mammal group when viral diversity is measured relative to host diversity, as bats are the second-most diverse order of mammals.
Viral diversity
Viruses have been found in bat populations around the world. Bats harbor all groups of viruses in the
Baltimore classification,
representing at least 28 families of viruses.
Most of the viruses harbored by bats are
RNA virus
An RNA virus is a virusother than a retrovirusthat has ribonucleic acid (RNA) as its genetic material. The nucleic acid is usually single-stranded RNA ( ssRNA) but it may be double-stranded (dsRNA). Notable human diseases caused by RNA viruses ...
es, though they are also known to have
DNA viruses.
Bats are more tolerant of viruses than terrestrial mammals.
A single bat can host several different kinds of viruses without becoming ill.
Bats have also been shown to be more susceptible to reinfection with the same viruses, whereas other mammals, especially humans, have a greater propensity for developing varying degrees of immunity. Their behavior and life history also make them "exquisitely suitable hosts of viruses and other disease agents", with long lifespans, the ability to enter
torpor or hibernate, and their ability to traverse landscapes with daily and seasonal movement.
Though bats harbor diverse viruses, they are rarely lethal to the bat host. Only the rabies virus and a few other lyssaviruses have been confirmed to kill bats.
Various factors have been implicated in bats' ability to survive viral infections. One possibility is bats' use of flight. Flight produces a
fever-like response, resulting in elevated temperature (up to ) and metabolic rate. Additionally, this fever-like response may help them cope with actual fevers upon getting a viral infection.
Some research indicates that bats' immune systems have allowed them to cope with a variety of viruses. A 2018 study found that bats have a dampened
STING response compared to other mammals, which could allow them to respond to viral threats without over-responding.
STING is a
signaling molecule that helps coordinate various host defense genes against pathogens. The authors of the study concluded that "the weakened, but not entirely lost, functionality of STING may have profound impact for bats to maintain the balanced state of 'effective response' but not 'over response' against viruses."
Additionally, bats lack several
inflammasomes found in other mammals;
other inflammasomes are present with a greatly reduced response. While inflammation is an immune response to viruses, excessive inflammation is damaging to the body, and viruses like
severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 1 (SARS-CoV-1; or Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, SARS-CoV) is a strain of coronavirus that causes severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), the respiratory illness responsible for th ...
(SARS-CoV) are known to kill humans by inducing excessive inflammation. Bats' immune systems may have evolved to be more tolerant of stressors such as viral infections compared to other mammals.
Transmission to humans
The vast majority of bat viruses have no
zoonotic potential, meaning they cannot be transmitted to humans.
The zoonotic viruses have four possible routes of transmission to humans: contact with bat body fluids (blood, saliva, urine, feces); intermediate hosts; environmental exposure; and blood-feeding arthropods.
es like the
rabies virus are transmitted from bats to humans via biting. Transmission of most other viruses does not appear to take place via biting, however. Contact with bat fluids such as guano, urine, and saliva is an important source of
spillover from bats to humans. Other mammals may play a role in transmitting bat viruses to people, with
pig farms a source of bat-borne viruses in Malaysia and Australia.
Other possible transmission routes of bat-borne viruses are more speculative. It is possible but unconfirmed that hunting, butchering, and consuming bat meat can result in viral spillover. While
arthropods like
mosquitoes,
ticks, and
fleas may
transmit viral infections from other mammals to humans, it is highly speculative that arthropods play a role in mediating bat viruses to humans. There is little evidence of environmental transmission of viruses from bats to humans, meaning that bat-borne virus do not persist in the environment for long. However, a limited number of studies have been conducted on the subject.
Bats compared to other viral reservoirs
Bats and their viruses may be the subject of more research than viruses found in other mammal
orders
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of ...
, an example of research bias. A 2015 review found that from 1999 to 2013, there were 300–1200 papers published about bat viruses annually, compared to 12–45 publications for
marsupial viruses and only 1–9 studies for
sloth viruses. The same review found that bats do not have significantly greater viral diversity than other mammal groups. Bats, rodents, and primates all harbored significantly more zoonotic viruses than other mammal groups, though the differences among the aforementioned three groups were not significant (bats have no more zoonotic viruses than rodents and primates).
A 2020 review of mammals and birds found that the identity of the taxonomic groups did not have any impact on the probability of harboring zoonotic viruses. Instead, more diverse groups had greater viral diversity. Bat life history traits and immunity, while likely influential in determining bat viral communities, were not associated with a greater probability of viral spillover into humans.
Sampling
Bats are sampled for viruses in a variety of ways. They can be tested for seropositivity for a given virus using a method like
ELISA, which determines whether or not they have the corresponding
antibodies
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the ...
for the virus. They can also be surveyed using molecular detection techniques like
PCR PCR or pcr may refer to:
Science
* Phosphocreatine, a phosphorylated creatine molecule
* Principal component regression, a statistical technique
Medicine
* Polymerase chain reaction
** COVID-19 testing, often performed using the polymerase chain r ...
(polymerase chain reaction), which can be used to replicate and amplify viral sequences.
Histopathology
Histopathology (compound of three Greek words: ''histos'' "tissue", πάθος ''pathos'' "suffering", and -λογία '' -logia'' "study of") refers to the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Spe ...
, which is the microscopic examination of tissue, can also be used. Viruses have been isolated from bat blood, saliva, feces, tissue, and urine. Some sampling is non-invasive and does not require killing the bat for sampling, whereas other sampling requires sacrificing the animal first. A 2016 review found no significant difference in total number of viruses found and new viruses discovered between lethal and non-lethal studies. Several species of
threatened bat have been killed for viral sampling, including the
Comoro rousette,
Hildegarde's tomb bat,
Natal free-tailed bat
The Natal free-tailed bat (''Mormopterus acetabulosus'') is a species of bat in the family Molossidae, the free-tailed bats. It is endemic to the island of Mauritius. It is known from fewer than five locations in its range, but it is common at a ...
, and the
long-fingered bat
The long-fingered bat (''Myotis capaccinii'') is a carnivorous species of vesper bat. It is native to coastal areas around the Mediterranean Sea, as well as a few patches of land in western Iran. Due to the fact that its population is in decli ...
.
Double-stranded DNA viruses
Adenoviruses
Adenovirus
Adenoviruses (members of the family ''Adenoviridae'') are medium-sized (90–100 nm), nonenveloped (without an outer lipid bilayer) viruses with an icosahedral nucleocapsid containing a double-stranded DNA genome. Their name derives from the ...
es have been detected in bat guano, urine, and oral and rectal swabs. They have been found in both
megabats and
microbats across a large geographic area. Bat adenoviruses are closely related to those finds in
canids.
The greatest diversity of bat adenoviruses has been found in Eurasia, though the virus family may be undersampled in bats overall.
Herpesviruses
Diverse
herpesviruses have been found in bats in North and South America, Asia, Africa, and Europe,
including representatives of the three subfamilies,
alpha-,
beta-, and
gammaherpesviruses.
Bat-hosted herpesviruses include the species ''
Pteropodid alphaherpesvirus 1
''Pteropodid alphaherpesvirus 1'' (PtHV-1) is a species of virus in the genus ''Simplexvirus'', subfamily ''Alphaherpesvirinae'', family ''Herpesviridae'', and order ''Herpesvirales
The ''Herpesvirales'' is an order of dsDNA viruses (Baltimore ...
'' and ''
Vespertilionid gammaherpesvirus 1
''Vespertilionid gammaherpesvirus 1'' (VeGHV-1) is a species of virus in the genus ''Percavirus'', subfamily ''Gammaherpesvirinae'', family ''Herpesviridae'', and order ''Herpesvirales
The ''Herpesvirales'' is an order of dsDNA viruses (Baltim ...
''.
Papillomaviruses
Papillomaviruses were first detected in bats in 2006, in the
Egyptian fruit bat. They have since been identified in several other bat species, including the
serotine bat,
greater horseshoe bat, and the
straw-colored fruit bat
The straw-coloured fruit bat (''Eidolon helvum'') is a large fruit bat that is the most widely distributed of all the African megabats. It is quite common throughout its area ranging from the southwestern Arabian Peninsula, across forest and sav ...
. Five distinct lineages of bat papillomaviruses have been recognized.
Single-stranded DNA viruses
Anelloviruses
No
anellovirus is known to cause disease in humans.
The first bat anellovirus, a
Torque teno virus
''Alphatorquevirus'' is a genus of viruses in the family ''Anelloviridae'', in group II in the Baltimore classification. It encompasses many species of the virus formerly known as TTV, transfusion transmitted virus, or torque teno virus, SENV, S ...
, was found in a Mexican free-tailed bat. Novel anelloviruses have also been detected in two
leaf-nosed bat species: the
common vampire bat and
Seba's short-tailed bat. The bat anelloviruses and one opossum anellovirus have been included in the proposed genus ''Sigmatorquevirus''.
Circoviruses
Circoviruses, family ''Circoviridae'', are among the most diverse of all viruses.
Like anelloviruses, circoviruses are not associated with any disease in humans.
About a third of all circoviruses are associated with bats, found in North and South America, Europe, and Asia.
A study of
horseshoe
A horseshoe is a fabricated product designed to protect a horse hoof from wear. Shoes are attached on the palmar surface (ground side) of the hooves, usually nailed through the insensitive hoof wall that is anatomically akin to the human toen ...
and
vesper
Vesper means ''evening'' in Classical Latin. It may also refer to:
Places
* Vesper, Kansas, an unincorporated community in the United States
* Vesper, Oregon, an unincorporated community in the United States
* Vesper, Wisconsin, a village in the ...
bats in China identified circoviruses from the genera ''
Circovirus'' and ''
Cyclovirus''.
Parvoviruses
Several kinds of
parvoviruses are considered important for human and animal health. Several strains of parvovirus have been identified from bat guano in the US states of Texas and California. Serum analysis of the straw-colored fruit bat and
Jamaican fruit bat led to the identification of two new parvoviruses. Bat parvoviruses are in the subfamily ''
Parvovirinae
''Parvovirinae'' is a subfamily of viruses in the family '' Parvoviridae''. There are ten genera and 84 species assigned to this subfamily.
Taxonomy
The following 10 genera are recognized:
*''Amdoparvovirus''
*'' Artiparvovirus''
*''Aveparvovi ...
'', closely resembling the genera ''
Protoparvovirus'', ''
Erythrovirus
''Erythroparvovirus'' is a genus of viruses in subfamily '' Parvovirinae'' of the virus family ''Parvoviridae''. Primates serve as natural hosts. There are seven species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include fifth disease
...
'', and ''
Bocaparvovirus''.
Double-stranded RNA viruses
Reoviruses
Zoonotic
Some disease-causing reovirus species are associated with bats. One such virus is
Melaka virus
Melaka virus (MELV) is a bat-borne virus. It was first isolated in a human in Melaka, Malaysia in 2006. A bat reservoir was suspected because traceback analysis revealed that the patient had been exposed to a bat prior to the onset of infection. M ...
, which was linked to illness in a Malaysian man and his two children in 2006.
The man said that a bat had been in his home a week before he became ill, and the virus was closely related to other reoviruses linked to bats.
Kampar virus Kampar may refer to:
Indonesia
* Kampar Regency, Riau Province, eastern Sumatra
* Kampar River, a river in the same province
Malaysia
*Kampar District, Perak
*Kampar, Perak
Kampar ( Jawi: كمڤر, nicknamed ''Education City'') is the larges ...
was identified a few months later in another Malaysian man. Though he had no known contact with bats, Kampar virus is closely related to Melaka virus. Several other reovirus strains identified in ill humans are known as Miyazaki‐Bali/2007,
Sikamat virus
Sikamat is a small town in Seremban District, Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia. The area contains many government schools and is one of the denser locations for them; SMK Tunku Ampuan Durah, SMK Dato' Sheikh Ahmad, SMK Haji Mohd Redza, SM Sains Tuanku A ...
, and SI‐MRV01. No reoviruses linked to bats have caused death in humans.
Other
Reoviruses include many viruses that do not cause disease in humans, including several found in bats. One reovirus species associated with bats is ''
Nelson Bay orthoreovirus
''Nelson Bay orthoreovirus'', often called Nelson Bay virus (NBV) is a novel double-stranded RNA orthoreovirus species first isolated from a flying fox (Pteropus poliocephalus) near Nelson Bay in New South Wales, Australia.Gard G, Compans RW. Stru ...
'', sometimes called ''Pteropine orthoreovirus'' (PRV), which is an
orthoreovirus; several virus strains of it have been identified in bats. The type member of ''Nelson Bay orthoreovirus'' is Nelson Bay virus (NBV), which was first identified in 1970 from the blood of a
gray-headed flying fox
The grey-headed flying fox (''Pteropus poliocephalus'') is a megabat native to Australia. The species shares mainland Australia with three other members of the genus '' Pteropus'': the little red '' P. scapulatus'', spectacled '' P. conspicill ...
in
New South Wales, Australia. NBV was the first reovirus to be isolated from a bat species. Another strain of ''Nelson Bay orthoreovirus'' associated with bats is
Pulau virus, which was first identified from the
small flying fox
The small flying fox, island flying fox or variable flying fox (''Pteropus hypomelanus'') is a species of flying fox in the family Pteropodidae. It is found in Australia, Cambodia, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Maldives, Myanmar, Papua New Guinea, the ...
of
Tioman Island in 2006. Other viruses include ''
Broome orthoreovirus'' from the
little red flying fox of
Broome, Western Australia;
Xi River virus
Xi River virus (XRV) is a putative novel bat virus in the genus ''Orthoreovirus'' isolated from fruit bats in Guangdong Province in southern China. It is the first bat reovirus isolated in China.
Virology Genome
Only a partial sequence of XR ...
from
Leschenault's rousette in
Guangdong, China; and
Cangyuan virus also from Leschenault's rousette.
Several
mammalian orthoreovirus
''Mammalian orthoreovirus'' (MRV) is a double-stranded RNA virus. It is a part of the family ''Reoviridae'', as well as the subfamily ''Spinareovirinae''. As seen in the name, the Mammalian Ortheoreovirus infects numerous Mammalian Species, mamma ...
es are associated with bats, including at least three from Germany and 19 from Italy. These were found in
pipistrelles, the
brown long-eared bat, and the
whiskered bat.
es have been isolated from bats, including
Ife virus from the straw-colored fruit bat,
Japanaut virus from the
common blossom bat
The common blossom bat (''Syconycteris australis'') also known as the southern blossom bat or Queensland blossom bat, is a megabat in the family Pteropodidae. The common blossom bat feeds mostly on nectar and pollen rather than fruit.
It is one ...
, and
Fomédé virus from ''
Nycteris
''Nycteris'' comprises a genus of bats commonly called slit-faced or hollow-faced bats. They are grouped in the family Nycteridae. The bats are found in East Malaysia, Indonesia, and many parts of Africa.
Description
They are small bats, from i ...
'' species.
Positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses
Astroviruses
Astroviruses have been found in several genera of bat in the
Old World
The "Old World" is a term for Afro-Eurasia that originated in Europe , after Europeans became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia, which were previously thought of by the ...
, including ''
Miniopterus'', ''
Myotis'', ''
Hipposideros'', ''
Rhinolophus'', ''Pipistrellus'', ''
Scotophilus'', and ''
Taphozous'',
though none in Africa.
Bats have very high prevalence rates of astroviruses; studies in Hong Kong and mainland China found prevalence rates approaching 50% from anal swabs. No astroviruses identified in bats are associated with disease in humans.
Caliciviruses
Bat
caliciviruses were first identified in
Hong Kong in the
Pomona roundleaf bat
The Pomona roundleaf bat, Pomona leaf-nosed bat, or Andersen's leaf-nosed bat (''Hipposideros pomona'') is a species of bat in the family Hipposideridae that is endemic to India.
Taxonomy
It was described as a new species in 1918 by Danish mam ...
,
and were later identified from
tricolored bats in the US state of Maryland. Bat caliciviruses are similar to the genera ''
Sapovirus'' and ''
Valovirus'', with
noroviruses also detected from two microbat species in China.
Coronaviruses
SARS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2, and MERS-CoV
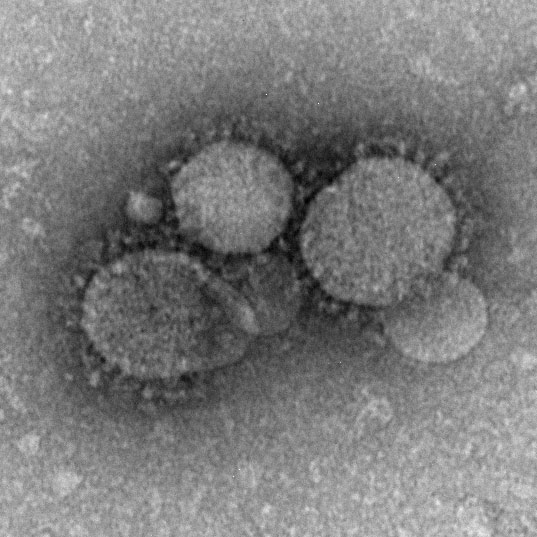
Several zoonotic coronaviruses are associated with bats, including severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and ''
Middle East respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus'' (MERS-CoV).
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019), the respiratory illness responsible for the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The virus previously had a No ...
is another zoonotic coronavirus likely originating in bats. SARS-CoV causes the disease
severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) in humans. The first documented case of SARS was in November 2002 in
Foshan
Foshan (, ), alternately romanized as Fatshan, is a prefecture-level city in central Guangdong Province, China. The entire prefecture covers and had a population of 9,498,863 as of the 2020 census. The city is part of the western side of the ...
, China.
It became an
epidemic, affecting 28 countries around the world with 8,096 cases and 774 deaths.
The natural reservoir of SARS-CoV was identified as bats, with the
Chinese rufous horseshoe bat
The Chinese rufous horseshoe bat (''Rhinolophus sinicus'') is a species of bat in the family Rhinolophidae. It is found in Bhutan, China, India, Nepal, and Vietnam.
The species is most easily confused with '' R. affinis'', from which it is bes ...
considered a particularly strong candidate after a coronavirus was recovered from a colony that had 95% nucleotide sequence similarity to SARS-CoV.
There is uncertainty on whether or not animals like
palm civets and
raccoon dogs were intermediate hosts that facilitated the spread of the virus from bats to humans, or if humans acquired the virus directly from bats.
The first human case of
Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) was in June 2012 in
Jeddah
Jeddah ( ), also spelled Jedda, Jiddah or Jidda ( ; ar, , Jidda, ), is a city in the Hejaz region of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) and the country's commercial center. Established in the 6th century BC as a fishing village, Jeddah's pro ...
, Saudi Arabia.
As of November 2019, 2,494 cases of MERS have been reported in twenty-seven countries, resulting in 858 fatalities. It is believed that MERS-CoV originated in bats, though
camel
A camel (from: la, camelus and grc-gre, κάμηλος (''kamēlos'') from Hebrew or Phoenician: גָמָל ''gāmāl''.) is an even-toed ungulate in the genus ''Camelus'' that bears distinctive fatty deposits known as "humps" on its back. C ...
s are likely the intermediate host through which humans became infected. Human-to-human transmission is possible, though does not easily occur.
The
SARS-CoV-2 outbreak in humans started in
Wuhan, China in 2019. Genetic analyses of SARS-COV-2 showed that it was highly similar to viruses found in horseshoe bats, with 96% similarity to a virus isolated from the
intermediate horseshoe bat
The intermediate horseshoe bat (''Rhinolophus affinis'') is a bat species of the family Rhinolophidae (“nose crest”) that is very widespread throughout much of the Indian subcontinent, southern and central China and Southeast Asia. It is li ...
. Due to similarity with known bat coronaviruses, data "clearly indicates" that the natural reservoirs of SARS-COV-2 are bats. It is yet unclear how the virus was transmitted to humans, though an intermediate host may have been involved.
Phylogenetic reconstruction of SARS-CoV-2 suggests that the strain that caused a human pandemic diverged from the strain found in bats decades ago, likely between 1950 and 1980.
Other
Bats harbor a great diversity of
coronavirus
Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the com ...
es, with sampling by the
EcoHealth Alliance in China alone identifying about 400 new strains of coronavirus. A study of coronavirus diversity harbored by bats in eastern Thailand revealed forty-seven coronaviruses.
Flaviviruses

Most
flaviviruses are transmitted via arthropods, but bats may play a role in the ecology of some species. Several strains of ''
Dengue virus
''Dengue virus'' (DENV) is the cause of dengue fever. It is a mosquito-borne, single positive-stranded RNA virus of the family ''Flaviviridae''; genus ''Flavivirus''. Four serotypes of the virus have been found, a reported fifth has yet to be co ...
'' have been found in bats in the Americas, and ''
West Nile virus'' has been identified in fruit bats in South India. Serological studies indicate that ''West Nile virus'' may also be present in bats in North America and the
Yucatán Peninsula. ''
Saint Louis encephalitis virus
In religious belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of holiness, likeness, or closeness to God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and denomination. In Catholic, Eastern Ortho ...
'' has been detected in bats in the US states of Texas and Ohio, as well as the Yucatán Peninsula. ''
Japanese encephalitis virus'' or its associated antibodies have been found in several bat species throughout Asia. Other flaviviruses detected in bats include ''
Sepik virus
''Sepik virus'' (SEPV) is an arthropod-borne virus (arbovirus) of the genus ''Flavivirus'' and family ''Flaviviridae''. ''Flaviviridae'' is one of the most well characterized viral families, as it contains many well-known viruses that cause disea ...
'', ''
Entebbe bat virus
''Entebbe bat virus'' is an infectious disease caused by a ''Flavivirus'' that is closely related to yellow fever.
Little is known about the symptoms caused by the Entebbe bat virus, and it is unknown if the virus can infect humans. Entebbe b ...
'',
Sokuluk virus
Sokuluk ( dng, Сохўлў, Sohwlw; Kyrgyz, russian: Сокулук) is a large village in the Chüy Region of Kyrgyzstan. Divided over two rural communities, its total population was 30,540 in 2021.
Sokuluk is the administrative center of Sokul ...
, ''
Yokose virus
''Yokose virus'' (YOKV) is in the genus Flavivirus of the family Flaviviridae. Flaviviridae are often found in arthropods, such as mosquitoes and ticks, and may also infect humans. The genus Flavivirus includes over 50 known viruses, including Ye ...
'', ''
Dakar bat virus'', ''
Bukalasa bat virus'', ''
Carey Island virus
Carey may refer to:
Names
* Carey (given name), a given name
* Carey (surname), a surname
** List of people with surname Carey
Places Canada
* Carey Group, British Columbia; in the Pacific
* Carey Island (Nunavut) in James Bay
United Kingdom
* ...
'', ''
Phnom Penh bat virus'', ''
Rio Bravo bat virus
Rio or Río is the Portuguese, Spanish, Italian, and Maltese word for "river". When spoken on its own, the word often means Rio de Janeiro, a major city in Brazil.
Rio or Río may also refer to:
Geography Brazil
* Rio de Janeiro
* Rio do Sul, a ...
'', ''
Montana myotis leukoencephalitis virus
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British ...
'', and
Tamana bat virus Tamana may refer to:
* Tamana, Kiribati, an island
* Tamana, Kumamoto, a city in Kumamoto Prefecture, Japan
* Tamana, Wallis and Futuna
Tamana is a village in Wallis and Futuna. It is located in Alo District
Alo (also known unofficially as Tu ...
.
Picornaviruses
Several genera of
picornaviruses have been found in bats, including ''
Kobuvirus'', ''
Sapelovirus
''Sapelovirus'' is a genus of viruses in the order ''Picornavirales'', in the family ''Picornaviridae
Picornaviruses are a group of related nonenveloped RNA viruses which infect vertebrates including fish, mammals, and birds. They are ...
'', ''
Cardiovirus'', and ''
Senecavirus''.
Picornaviruses have been identified from a diverse array of bat species around the world.
Negative-sense single-stranded RNA viruses
Arenaviruses
Arenaviruses are mainly associated with
rodents, though some can cause illness in humans. The first arenavirus identified in bats was ''
Tacaribe mammarenavirus'', which was isolated from Jamaican fruit bats and the
great fruit-eating bat. Antibody response associated with Tacaribe virus has also been found in the common vampire bat, the
little yellow-shouldered bat
The little yellow-shouldered bat (''Sturnira lilium'') is a bat species from South and Central America. It is a frugivore
A frugivore is an animal that thrives mostly on raw fruits or succulent fruit-like produce of plants such as roots, shoo ...
, and
Heller's broad-nosed bat. It is unclear if bats are the natural reservoir of Tacaribe virus. There has been one known human infection by Tacaribe virus, though it was accidentally acquired in a laboratory setting.
Hantaviruses
Hantaviruses, family ''Hantaviridae'', naturally occur in vertebrates. All bat-associated hantaviruses are in the subfamily ''Mammantavirinae''. Of the four genera within the subfamily, ''
Loanvirus'' and ''
Mobatvirus'' are the genera that have been documented in various bats. Almost all bat hantaviruses have been identified from microbats.
Mouyassue virus
Mouyassue virus is a novel, single-stranded, enveloped, negative-sense RNA orthohantavirus.
Natural reservoir
The banana pipistrelle (''Neoromicia nanus'') found in the Côte d'Ivoire is the natural reservoir of Mouyassue virus. It shares a c ...
has been identified from the
banana pipistrelle in
Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital is Yamoussoukro, in the centre of the country, while its largest city and economic centre is ...
and the
Cape serotine
The Cape serotine (''Laephotis capensis'') is a species of vesper bat occurring in Sub-Saharan Africa. 'Serotine' is from Latin 'serotinus' meaning ‘of the evening'.
It is found in Angola, Benin, Botswana, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Rep ...
in Ethiopia;
Magboi virus
Magboi virus (MGBV) is a novel, bat-borne Orthohantavirus discovered in a slit-faced bat trapped near the Magboi Stream in eastern Sierra Leone in 2011. It is a single-stranded, negative sense, RNA virus in the Bunyavirales order.
Molecular vi ...
from the
hairy slit-faced bat
The hairy slit-faced bat (''Nycteris hispida'') is a species of slit-faced bat widely distributed throughout forests and savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees ...
in
Sierra Leone;
Xuan Son virus
Xuan Son virus is a single-stranded, enveloped, negative-sense RNA virus of the genus '' Mobatvirus''.
Natural reservoir
It was isolated in Pomona roundleaf bats in Xuân Sơn National Park, a nature reserve in Thanh Sơn District, Phú Thọ ...
from the Pomona roundleaf bat in Vietnam;
Huangpi virus
Huangpi District () is one of 13 urban District (China), districts of the prefecture-level city of Wuhan, the capital of Hubei, Hubei Province, China, situated on the northern (left) bank of the Yangtze River. The Sheshui enters the Yangtze at Hu ...
from the
Japanese house bat in China; ''
Longquan loanvirus'' from several horseshoe bats in China;
Makokou virus
Makokou is the regional capital of the Ogooué-Ivindo province in Gabon. Its coordinates are . Its altitude is 308 m. Its population in 2004 is around 16,600.
The city lies on the Ivindo River and the N4 road. It grew around iron ore min ...
from
Noack's roundleaf bat
Noack's roundleaf bat (''Hipposideros ruber'') is a species of bat in the family Hipposideridae. It is found throughout tropical Africa. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests, moist savanna, and caves and other sub ...
in Gabon;
Đakrông virus from
Stoliczka's trident bat in Vietnam;
''
Brno loanvirus
Brno ( , ; german: Brünn ) is a city in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. Located at the confluence of the Svitava and Svratka rivers, Brno has about 380,000 inhabitants, making it the second-largest city in the Czech Republi ...
'' from the
common noctule in the Czech Republic;
and ''
Laibin mobatvirus
Laibin (, Zhuang: Laizbinh) is a prefecture-level city in the central part of the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China.
History
Laibin is an ancient town with more than 2000 years of history. The area was settled in prehistoric times, more tha ...
'' from the
black-bearded tomb bat in China. As of 2019, only ''
Quezon mobatvirus'' has been identified from a megabat, as it was identified from a
Geoffroy's rousette in the Philippines.
Bat hantaviruses are not associated with illness in humans.
Filoviruses
''Marburgvirus'' and ''Ebolavirus''

''
Filoviridae'' is a family of virus containing two genera associated with bats: ''
Marburgvirus
The genus ''Marburgvirus'' is the taxonomic home of ''Marburg marburgvirus'', whose members are the two known marburgviruses, Marburg virus (MARV) and Ravn virus (RAVV). Both viruses cause Marburg virus disease in humans and nonhuman prim ...
'' and ''
Ebolavirus'', which contain the species that cause
Marburg virus disease and
Ebola virus disease
Ebola, also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) and Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF), is a viral hemorrhagic fever in humans and other primates, caused by ebolaviruses. Symptoms typically start anywhere between two days and three weeks after becom ...
, respectively. Though relatively few disease outbreaks are caused by filoviruses, they are of high concern due to their extreme
virulence, or capacity to cause harm to their hosts. Filovirus outbreaks typically have high mortality rates in humans. Though the first filovirus was identified in 1967, it took more than twenty years to identify any natural reservoirs.
Ebola virus disease is a relatively rare but life-threatening illness in humans, with an average mortality rate of 50% (though individual outbreaks may be as high as 90% mortality). The first outbreaks were in 1976 in
South Sudan and
Democratic Republic of the Congo.
The natural reservoirs of ebolaviruses are unknown.
However, some evidence indicates that megabats may be natural reservoirs.
Several megabat species have tested
seropositive for
antibodies
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the ...
against ebolaviruses, including the
hammer-headed bat
The hammer-headed bat ('), also known as hammer-headed fruit bat and big-lipped bat, is a megabat widely distributed in West and Central Africa. It is the only member of the genus ''Hypsignathus'', which is part of the tribe Epomophorini along w ...
,
Franquet's epauletted fruit bat, and
little collared fruit bat.
Other possible reservoirs include non-human
primates,
rodents, shrews, carnivores, and ungulates. Definitively stating that fruit bats are natural reservoirs is problematic; as of 2017, researchers have been largely unable to isolate ebolaviruses or their viral RNA sequences from fruit bats. Additionally, bats typically have low level of ebolavirus-associated antibodies, and seropositivity in bats is not strongly correlated to human outbreaks.
Marburg virus disease (MVD) was first identified in 1967 during simultaneous outbreaks in
Marburg and
Frankfurt in Germany, and
Belgrade, Serbia. MVD is highly virulent, with an average human mortality rate of 50%, but as high as 88% for individual outbreaks.
MVD is caused by
Marburg virus
Marburg virus (MARV) is a hemorrhagic fever virus of the ''Filoviridae'' family of viruses and a member of the species '' Marburg marburgvirus'', genus ''Marburgvirus''. It causes Marburg virus disease in primates, a form of viral hemorrhagic f ...
and the closely related
Ravn virus, which was formerly considered synonymous with Marburg virus. Marburg virus was first detected in the
Egyptian fruit bat in 2007,
which is now recognized as the natural reservoir of the virus.
Marburg virus has been detected in Egyptian fruit bats in Gabon, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Kenya, and Uganda.
Spillover from Egyptian fruit bats occurs when humans spend prolonged time in mines or caves inhabited by the bats,
though the exact mechanism of transmission is unclear.
Human-to-human transmission occurs through direct contact with infected bodily fluids, including blood or semen, or indirectly through contact with bedding or clothing exposed to these fluids.
Other
Lloviu virus
The species ''Lloviu cuevavirus'' ( ) is the taxonomic home of a virus that forms filamentous virion, ''Lloviu virus'' (LLOV). The species is included in the genus ''Cuevavirus''. LLOV is a distant relative of the commonly known Ebola virus an ...
, a kind of filovirus in the genus ''
Cuevavirus'', has been identified from the
common bent-wing bat
The common bent-wing bat (''Miniopterus schreibersii''), also known as the Schreibers's long-fingered bat or Schreibers's bat, is a species of insectivorous bat. They appear to have dispersed from a subtropical origin and distributed throughout ...
in Spain.
Another filovirus, ''
Bombali ebolavirus'', has been isolated from
free-tailed bats, including the
little free-tailed bat and the
Angolan free-tailed bat
The Angolan free-tailed bat (''Mops condylurus'') is a species of bat in the family Molossidae. It is found in Angola, Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, the Republic of the Congo, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ivory Coast, ...
.
Neither Lloviu virus nor ''Bombali ebolavirus'' is associated with illness in humans.
Genomic RNA associated with ''
Mengla dianlovirus
''Mengla dianlovirus'' (MLAV, also written ''Měnglà virus'') is a type of filovirus identified in a ''Rousettus'' bat in Mengla County, Yunnan Province, China and first reported in January 2019. It is classified in the same family as ''Ebolav ...
'', though not the virus itself, has been identified from ''
Rousettus'' bats in China.
Rhabdoviruses
Rabies-causing viruses
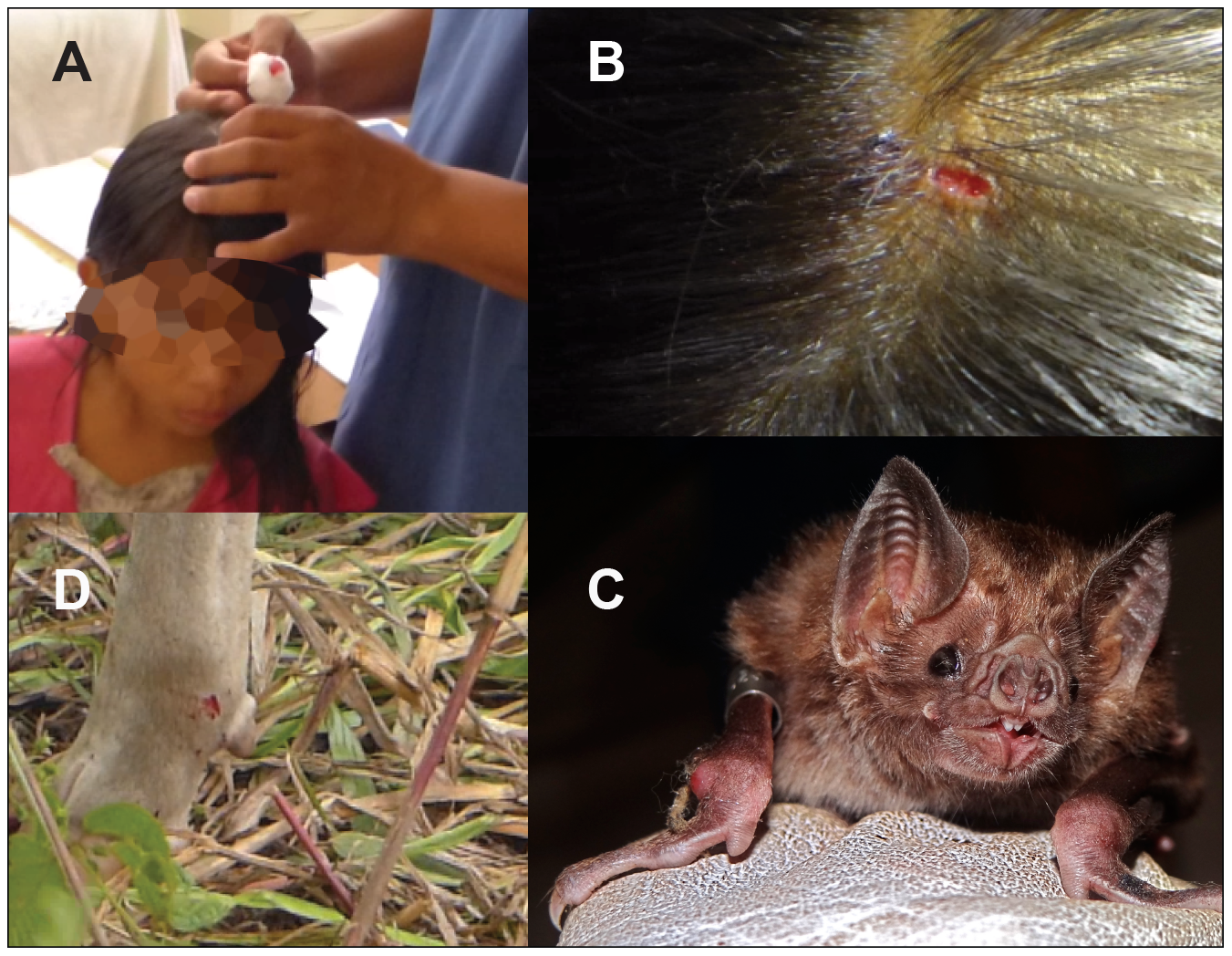 Lyssavirus
Lyssaviruses (from the genus ''Lyssavirus'' in the family ''
Rhabdoviridae'') include the
rabies virus, ''
Australian bat lyssavirus'', and other related viruses, many of which are also harbored by bats. Unlike most other viruses in the family ''Rhabdoviridae'', which are transmitted by arthropods, lyssaviruses are transmitted by mammals, most frequently through biting. All mammals are susceptible to lyssaviruses, though bats and carnivores are the most common natural reservoirs. The vast majority of human rabies cases are a result of the rabies virus, with only twelve other human cases attributed to other lyssaviruses as of 2015.
These rarer lyssaviruses associated with bats include ''
Duvenhage lyssavirus'' (three human cases as of 2015); ''
European bat 1 lyssavirus
European, or Europeans, or Europeneans, may refer to:
In general
* ''European'', an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to Europe
** Ethnic groups in Europe
** Demographics of Europe
** European cuisine
European cuisine co ...
'' (one human case as of 2015); ''
European bat 2 lyssavirus'' (two human cases as of 2015); and ''
Irkut lyssavirus Irkut may stand for:
* Irkut (river), a tributary of the Angara in Russia
* Irkut Corporation
The JSC Irkut Corporation () (russian: Иркут) is a Russian aircraft manufacturer, headquartered in the Aeroport District, Northern Administrative ...
'' (one human case as of 2015). Microbats are suspected as the reservoirs of these four uncommon lyssaviruses.
After transmission has occurred, the average human is asymptomatic for two months, though the incubation period can be as short as a week or as long as several years.
Italian scientist
Antonio Carini
Antonio Carini (1872–1950) was an Italian physician, bacteriologist and professor. He worked in the public health services of São Paulo, Brazil for over forty years.Hélder Queiroz
Hélder Lima de Queiroz () (born 1963) is a Brazilian conservation biologist, primatologist, and fish behaviorist.
He is the Director of the Instituto de Desenvolvimento Sustentável Mamirauá (MISD) in Amazonas state, dedicated to protect ...
in 1934 and
Joseph Lennox Pawan in 1936.
Vampire bats were the first to be documented with rabies; in 1953, an insectivorous bat in Florida was discovered with rabies, making it the first documented occurrence in an insectivorous species outside the vampire bats' ranges. Bats have an overall low prevalence of rabies virus, with a majority of surveys of apparently healthy individuals showing rabies incidence of 0.0–0.5%.
Sick bats are more likely to be submitted for rabies testing than apparently healthy bats, known as sampling bias, with most studies reporting rabies incidence of 5–20% in sick or dead bats.
Rabies virus exposure can be fatal in bats, though it is likely that the majority of individuals do not develop the disease after exposure.
In non-bat mammals, exposure to the rabies virus almost always leads to death.

Globally, dogs are by far the most common source of human rabies deaths. Bats are the most common source of rabies in humans in North and South America, Western Europe, and Australia.
Many
feeding guilds of bats may transmit rabies to humans, including insectivorous, frugivorous, nectarivorous, omnivorous, sanguivorous, and carnivorous species.
The common vampire bat is a source of human rabies in Central and South America, though the frequency at which humans are bitten is poorly understood. Between 1993 and 2002, the majority of human rabies cases associated with bats in the Americas were the result of non-vampire bats.
In North America, about half of human rabies instances are
cryptic
Cryptic may refer to:
In science:
* Cryptic species complex, a group of species that are very difficult to distinguish from one another
* Crypsis, the ability of animals to blend in to avoid observation
* Cryptic era, earliest period of the Earth
...
, meaning that the patient has no known bite history.
While it has been speculated that rabies virus could be transmitted through aerosols, studies of the rabies virus have concluded that this is only feasible in limited conditions. These conditions include a very large colony of bats in a hot and humid cave with poor ventilation. While two human deaths in 1956 and 1959 had been tentatively attributed to aerosolization of the rabies virus after entering a cave with bats, "investigations of the 2 reported human cases revealed that both infections could be explained by means other than aerosol transmission".
It is instead generally thought that most instances of cryptic rabies are the result of an unknown bat bite.
Bites from a bat can be so small that they are not visible without magnification equipment, for example. Outside of bites, rabies virus exposure can also occur if infected fluids come in contact with a
mucous membrane or a break in the skin.
Other
Many bat lyssaviruses are not associated with infection in humans. These include ''
Lagos bat lyssavirus'', ''
Shimoni bat lyssavirus'', ''
Khujand lyssavirus'', ''
Aravan lyssavirus Aravan may refer to:
*Aravan, Kyrgyzstan, a large village in Osh Region, Kyrgyzstan
*Aravan District, a district of Osh Region, Kyrgyzstan
*Aravan or Aravansay, a river in Kyrgyzstan and Uzbekistan
*Aravan (legendary), a legendary ruler of 5th cent ...
'', ''
Bokeloh bat lyssavirus'', ''
West Caucasian bat lyssavirus'', and ''
Lleida bat lyssavirus
Lleida (, ; Spanish: Lérida ) is a city in the west of Catalonia, Spain. It is the capital city of the province of Lleida.
Geographically, it is located in the Catalan Central Depression. It is also the capital city of the Segrià comarca, as ...
''.
''Lagos bat lyssavirus'', also known as Lagos bat virus (LBV), has been isolated from a megabat in sub-Saharan Africa.
This lyssavirus has four distinct lineages, all of which are found in the straw-colored fruit bat.
Rhabdoviruses from other genera have been identified in bats. This includes several from the genus ''
Ledantevirus'':
Kern Canyon virus, which was found in the
Yuma myotis
The Yuma myotis (''Myotis yumanensis'') is a species of vesper bat native to western North America.
Description
The Yuma myotis is a relatively small myotis, measuring in head-body length, with an average wingspan of and a weight of about . T ...
in California (US);
Kolente virus from the
Jones's roundleaf bat
Jones's roundleaf bat (''Hipposideros jonesi'') is a species of bat in the family Hipposideridae. It is endemic to southern West Africa. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical dry forest, savanna, subtropical or tropical dry lowland gra ...
in Guinea;
from the
eloquent horseshoe bat in Kenya;
Oita virus
Oita often refers to:
*Ōita Prefecture, Kyushu, Japan
*Ōita (city), the capital of the prefecture
Oita or Ōita may also refer to:
Places
*Ōita District, Ōita, a former district in Ōita Prefecture, Japan
*Ōita Stadium, a multi-use stadium ...
from the
little Japanese horseshoe bat
The little Japanese horseshoe bat (''Rhinolophus cornutus'') is a species of bat
Bats are mammals of the order Chiroptera.''cheir'', "hand" and πτερόν''pteron'', "wing". With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mam ...
; and
Fikirini virus from the
striped leaf-nosed bat
The striped leaf-nosed bat (''Macronycteris vittatus'') is a species of bat native to eastern and southern Africa. It was formerly considered part of '' M. commersoni'', which is now viewed as being restricted to Madagascar. Both ''commersoni'' an ...
in Kenya.
Orthomyxoviruses
 Orthomyxovirus
Orthomyxoviruses include
influenza
Influenza, commonly known as "the flu", is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These symptoms ...
viruses. While birds are the primary reservoir for the genus ''
Alphainfluenzavirus'', a few bat species in Central and South America have also tested positive for the viruses. These species include the little yellow-shouldered bat and the
flat-faced fruit-eating bat. Bat populations tested in Guatemala and Peru had high seropositivity rates, which suggests that influenza A infections are common among bats in the New World.
Paramyxoviruses
Hendra, Nipah, and Menangle viruses

''
Paramyxoviridae'' is a family that includes several zoonotic viruses naturally found in bats. Two are in the genus ''
Henipavirus''—
Hendra virus and
Nipah virus. Hendra virus was first identified in 1994 in
Hendra, Australia. Four different species of
flying fox have tested positive for Hendra virus: the gray-headed flying fox, little red flying fox,
spectacled flying fox, and
black flying fox
The black flying fox or black fruit bat (''Pteropus alecto'') is a bat in the family Pteropodidae. It is among the largest bats in the world, but is considerably smaller than the largest species in its genus, ''Pteropus''. The black flying fox ...
.
Horses are the intermediate host between flying foxes and humans. Between 1994 and 2014, there were fifty-five outbreaks of Hendra virus in Australia, resulting in the death or euthanization of eighty-eight horses. Seven humans are known to have been infected by Hendra virus, with four fatalities.
Six of the seven infected humans were directly exposed to the blood or other fluids of sick or dead horses (three were veterinarians), while the seventh case was a veterinary nurse who had recently irrigated the nasal cavity of a horse not yet exhibiting symptoms. It is unclear how horses become infected with Hendra virus, though it is believed to occur following direct exposure to flying fox fluids. There is also evidence of horse-to-horse transmission. In late 2012, a
vaccine was released to prevent infection in horses.
Vaccine uptake has been low, with an estimated 11–17% of Australian horses vaccinated by 2017.
The first human outbreak of Nipah virus was in 1998 in Malaysia.
It was determined that flying foxes were also the reservoir of the virus, with domestic pigs as the intermediate host between bats and humans. Outbreaks have also occurred in Bangladesh, India, Singapore, and the Philippines. In Bangladesh, the primary mode of transmission of Nipah virus to humans is through the consumption of
date palm sap
''Phoenix dactylifera'', commonly known as date or date palm, is a flowering plant species in the palm family, Arecaceae, cultivated for its edible sweet fruit called dates. The species is widely cultivated across northern Africa, the Middle Eas ...
. Pots set out to collect the sap are contaminated with flying fox urine and guano, and the bats also lick the sap streams flowing into the pots. It has been speculated that the virus may also be transmitted to humans by eating fruit partially consumed by flying foxes, or by coming into contact with their urine, though no definitive evidence supports this.
An additional zoonotic paramyxovirus that bats harbor is
Menangle virus, which was first identified at a hog farm in
New South Wales, Australia. Flying foxes were once again identified as the natural reservoirs of the virus, with the black, spectacled, and gray-headed
seropositive for the virus. Two employees of the hog farm became sick with flu-like illnesses, later shown to be a result of the virus.
''
Sosuga pararubulavirus'' is known to have infected one person—an American wildlife biologist who had conducted bat and rodent research in Uganda.
The
Egyptian fruit bat later tested positive for the virus, indicating that it is potentially a natural reservoir.
Other
Bats host several paramyxoviruses that are not known to affect humans. Bats are the reservoir of
Cedar virus
Cedar virus, officially ''Cedar henipavirus'', is a henipavirus known to be harboured by '' Pteropus spp''. Infectious virus was isolated from the urine of a mixed ''Pteropus alecto'' and '' P. poliocephalus'' in Queensland, Australia in 2009. Un ...
, a paramyxovirus first discovered in flying foxes
South East Queensland.
The zoonotic potential of Cedar virus is unknown. In Brazil in 1979, ''
Mapuera orthorubulavirus'' was isolated from the saliva of the little yellow-shouldered bat. Mapuera virus has never been associated with disease in other animals or humans, but experimental exposure of mice to the virus resulted in fatality.
''
Tioman pararubulavirus
Tioman Island ( ms, Pulau Tioman) is a mukim and an island in Rompin District, Pahang, Malaysia. It is located off the east coast of the state, and is some long and wide. It has seven villages, the largest and most populous being Kampung ...
'' has been isolated from the urine of the small flying fox, which causes fever in some domestic pigs after exposure, but no other symptoms.
Tukoko virus has been detected from Leschenault's rousette in China.
Bats have been suggested as the host of ''
Porcine orthorubulavirus'', though definitive evidence has not been collected.
Togaviruses
Togaviruses include
alphaviruses, which have been detected in bats. Alphaviruses cause
encephalitis
Encephalitis is inflammation of the brain. The severity can be variable with symptoms including reduction or alteration in consciousness, headache, fever, confusion, a stiff neck, and vomiting. Complications may include seizures, hallucinations, ...
in humans. Alphaviruses that have been detected in bats include ''
Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus'', ''
Eastern equine encephalitis virus'', and ''
Western equine encephalitis virus''. ''
Sindbis virus'' has been detected from horseshoe bats and
roundleaf bat
''Hipposideros'' is one of the most diverse genera of bats, with more than 70 species. They are collectively called roundleaf bats after the shape of their nasal ornament. It is the type genus of the family Hipposideridae. It is divided into spe ...
s. ''
Chikungunya virus'' has been isolated from Leschenault's rousette, the Egyptian fruit bat,
Sundevall's roundleaf bat
Sundevall's roundleaf bat (''Hipposideros caffer''), also called Sundevall's leaf-nosed bat, is a species of bat in the family Hipposideridae.
These bats are very similar in appearance to the closely related Noack's roundleaf bat, and the two hav ...
, the little free-tailed bat, and ''Scotophilus'' species.
Positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses that replicate through a DNA intermediate
Retroviruses
Bats can be infected with
retrovirus
A retrovirus is a type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell. Once inside the host cell's cytoplasm, the virus uses its own reverse transcriptase ...
es, including the
gammaretrovirus
Gammaretrovirus is a genus in the ''Retroviridae'' Family (biology), family. Example species are the murine leukemia virus and the feline leukemia virus. They cause various sarcomas, leukemias and immune deficiencies in mammals, reptiles and bird ...
found in horseshoe bats, Leschenault's rousette, and the
greater false vampire bat
The greater false vampire bat (''Lyroderma lyra'') is a species of bat in the family Megadermatidae, the false vampire bats. It is native to Asia. It is also known as the Indian false vampire bat or greater false-vampire
Description
This sp ...
. Several bat retroviruses have been identified that are similar to the ''
Reticuloendotheliosis virus'' found in birds. These retroviruses were found in
mouse-eared bats, horseshoe bats, and flying foxes. The discovery of varied and distinct gammaretroviruses in bat genomes indicates that bats likely played important roles in their diversification. Bats also host an extensive number of
betaretrovirus
''Betaretrovirus'' is a genus of the ''Retroviridae'' family. It has type B or type D morphology. The type B is common for a few exogenous, vertically transmitted and endogenous viruses of mice; some primate and sheep viruses are the type D.
Ex ...
es, including within mouse-eared bats, horseshoe bats, and flying foxes. Bat betaretroviruses span the entire breadth of betaretrovirus diversity, similar to those of rodents, which may indicate that bats and rodents are primary reservoirs of the viruses. Betaretroviruses have infected bats for a majority of bat evolutionary history, since at least 36 million years ago.
Double-stranded DNA viruses that replicate through a single-stranded RNA intermediate

Hepadnaviruses
Hepadnavirus
''Hepadnaviridae'' is a family of viruses. Humans, apes, and birds serve as natural hosts. There are currently 18 species in this family, divided among 5 genera. Its best-known member is hepatitis B virus. Diseases associated with this family i ...
es are also known to affect bats, with the
tent-making bat, Noack's roundleaf bat, and the
halcyon horseshoe bat
The halcyon horseshoe bat (''Rhinolophus alcyone'') is a species of bat in the family Rhinolophidae. It is found in Cameroon, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ivory Coast, Equatorial Guinea, Ghana, Guinea, Kenya, Liberia, ...
known to harbor several. The hepadnavirus found in the tent-making bat, which is a New World species, was the closest relative of human hepadnoviruses.
Though relatively few hepadnaviruses have been identified in bats, it is highly likely that additional strains will be discovered through further research. As of 2016, they had been found in four bat families:
Hipposideridae and
Rhinolophidae from the suborder
Yinpterochiroptera and
Molossidae and
Vespertilionidae from
Yangochiroptera. The high diversity of bat hosts suggests that bats share a long evolutionary history with hepadnaviruses, indicating bats may have had an important role in hepadnavirus evolution.
See also
*
Histoplasmosis
*
Human virome
References
{{Baltimore classification
Coronaviridae
Hantaviridae
Hemorrhagic fevers
 The bat virome is the group of viruses associated with bats. Bats host a diverse array of viruses, including all seven types described by the
The bat virome is the group of viruses associated with bats. Bats host a diverse array of viruses, including all seven types described by the  Several zoonotic coronaviruses are associated with bats, including severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and '' Middle East respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus'' (MERS-CoV).
Several zoonotic coronaviruses are associated with bats, including severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and '' Middle East respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus'' (MERS-CoV).  Most flaviviruses are transmitted via arthropods, but bats may play a role in the ecology of some species. Several strains of ''
Most flaviviruses are transmitted via arthropods, but bats may play a role in the ecology of some species. Several strains of '' '' Filoviridae'' is a family of virus containing two genera associated with bats: ''
'' Filoviridae'' is a family of virus containing two genera associated with bats: '' Lyssaviruses (from the genus ''Lyssavirus'' in the family '' Rhabdoviridae'') include the rabies virus, '' Australian bat lyssavirus'', and other related viruses, many of which are also harbored by bats. Unlike most other viruses in the family ''Rhabdoviridae'', which are transmitted by arthropods, lyssaviruses are transmitted by mammals, most frequently through biting. All mammals are susceptible to lyssaviruses, though bats and carnivores are the most common natural reservoirs. The vast majority of human rabies cases are a result of the rabies virus, with only twelve other human cases attributed to other lyssaviruses as of 2015. These rarer lyssaviruses associated with bats include '' Duvenhage lyssavirus'' (three human cases as of 2015); ''
Lyssaviruses (from the genus ''Lyssavirus'' in the family '' Rhabdoviridae'') include the rabies virus, '' Australian bat lyssavirus'', and other related viruses, many of which are also harbored by bats. Unlike most other viruses in the family ''Rhabdoviridae'', which are transmitted by arthropods, lyssaviruses are transmitted by mammals, most frequently through biting. All mammals are susceptible to lyssaviruses, though bats and carnivores are the most common natural reservoirs. The vast majority of human rabies cases are a result of the rabies virus, with only twelve other human cases attributed to other lyssaviruses as of 2015. These rarer lyssaviruses associated with bats include '' Duvenhage lyssavirus'' (three human cases as of 2015); '' Globally, dogs are by far the most common source of human rabies deaths. Bats are the most common source of rabies in humans in North and South America, Western Europe, and Australia. Many feeding guilds of bats may transmit rabies to humans, including insectivorous, frugivorous, nectarivorous, omnivorous, sanguivorous, and carnivorous species. The common vampire bat is a source of human rabies in Central and South America, though the frequency at which humans are bitten is poorly understood. Between 1993 and 2002, the majority of human rabies cases associated with bats in the Americas were the result of non-vampire bats. In North America, about half of human rabies instances are
Globally, dogs are by far the most common source of human rabies deaths. Bats are the most common source of rabies in humans in North and South America, Western Europe, and Australia. Many feeding guilds of bats may transmit rabies to humans, including insectivorous, frugivorous, nectarivorous, omnivorous, sanguivorous, and carnivorous species. The common vampire bat is a source of human rabies in Central and South America, though the frequency at which humans are bitten is poorly understood. Between 1993 and 2002, the majority of human rabies cases associated with bats in the Americas were the result of non-vampire bats. In North America, about half of human rabies instances are  Orthomyxoviruses include
Orthomyxoviruses include