Hagia Sophia (; ; ; ; ), officially the Hagia Sophia Grand Mosque (; ), is a
mosque
A mosque ( ), also called a masjid ( ), is a place of worship for Muslims. The term usually refers to a covered building, but can be any place where Salah, Islamic prayers are performed; such as an outdoor courtyard.
Originally, mosques were si ...
and former
church
Church may refer to:
Religion
* Church (building), a place/building for Christian religious activities and praying
* Church (congregation), a local congregation of a Christian denomination
* Church service, a formalized period of Christian comm ...
serving as a major cultural and historical site in
Istanbul
Istanbul is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, constituting the country's economic, cultural, and historical heart. With Demographics of Istanbul, a population over , it is home to 18% of the Demographics ...
,
Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
. The last of three church buildings to be successively erected on the site by the
Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
, it was completed in AD 537, becoming the world's largest interior space and among
the first The First or The 1st may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Albums
* The 1st (album), ''The 1st'' (album), by Willow, 2017
* The First (Shinee album), ''The First'' (Shinee album), 2011
* The First (single album), by NCT Dream, 2017
Television
* T ...
to employ a fully
pendentive
In architecture, a pendentive is a constructional device permitting the placing of a circular dome over a square room or of an elliptical dome over a rectangular room. The pendentives, which are triangular segments of a sphere, taper to point ...
dome. It is considered the epitome of
Byzantine architecture
Byzantine architecture is the architecture of the Byzantine Empire, or Eastern Roman Empire, usually dated from 330 AD, when Constantine the Great established a new Roman capital in Byzantium, which became Constantinople, until the Fall of Cons ...
and is said to have "changed the history of architecture".
From its dedication in 360 until 1453 Hagia Sophia served as the
cathedral
A cathedral is a church (building), church that contains the of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, Annual conferences within Methodism, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually s ...
of
Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
in the
Byzantine liturgical tradition, except for the period 1204‑1261 when the
Latin Crusaders installed their own
hierarchy
A hierarchy (from Ancient Greek, Greek: , from , 'president of sacred rites') is an arrangement of items (objects, names, values, categories, etc.) that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another. Hierarchy ...
. After the
fall of Constantinople
The Fall of Constantinople, also known as the Conquest of Constantinople, was the capture of Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire by the Ottoman Empire. The city was captured on 29 May 1453 as part of the culmination of a 55-da ...
in 1453, it served as a mosque, having its
minarets
A minaret is a type of tower typically built into or adjacent to mosques. Minarets are generally used to project the Muslim call to prayer (''adhan'') from a muezzin, but they also served as landmarks and symbols of Islam's presence. They can h ...
added shortly later. The site became a museum in 1935, and was redesignated as a mosque in 2020. In 2024, the upper floor of the mosque began to serve as a museum once again.
The current structure was built by the
Byzantine emperor
The foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, which Fall of Constantinople, fell to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as legitimate rulers and exercised s ...
Justinian I as the Christian cathedral of Constantinople between 532–537 and was designed by the Greek
geometers
A geometer is a mathematician whose area of study is the historical aspects that define geometry, instead of the analytical geometric studies that becomes conducted from geometricians.
Some notable geometers and their main fields of work, chr ...
Isidore of Miletus
Isidore of Miletus (; Medieval Greek pronunciation: ; ) was one of the two main Byzantine Greek mathematician, physicist and architects ( Anthemius of Tralles was the other) that Emperor Justinian I commissioned to design the cathedral Hagia Sop ...
and
Anthemius of Tralles
Anthemius of Tralles (, Medieval Greek: , ''Anthémios o Trallianós''; – 533 558) was a Byzantine Greek from Tralles who worked as a geometer and architect in Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire. With Isidor ...
. It was formally called the Church of God's Holy Wisdom, ()
the third church of the same name to occupy the site, as the prior one had been destroyed in the
Nika riots
The Nika riots (), Nika revolt or Nika sedition took place against Byzantine emperor Justinian I in Constantinople over the course of a week in 532 AD. They are often regarded as the most violent riots in the city's history, with nearly half of ...
. As the
episcopal see
An episcopal see is the area of a bishop's ecclesiastical jurisdiction.
Phrases concerning actions occurring within or outside an episcopal see are indicative of the geographical significance of the term, making it synonymous with ''diocese'' ...
of the
ecumenical patriarch of Constantinople
The ecumenical patriarch of Constantinople () is the List of ecumenical patriarchs of Constantinople, archbishop of Constantinople and (first among equals) among the heads of the several autocephalous churches that comprise the Eastern Orthodox ...
, it remained the world's largest cathedral for nearly a thousand years, until the
Seville Cathedral
The Cathedral of Saint Mary of the See (), better known as Seville Cathedral (), is a Catholic cathedral and former mosque in Seville, Andalusia, Spain. It was registered in 1987 by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site, along with the adjoining Alc� ...
was completed in 1520.
Hagia Sophia became the quintessential model for
Eastern Orthodox church architecture
Eastern Orthodox church architecture constitutes a distinct, recognizable family of styles among church architectures. These styles share a cluster of fundamental similarities, having been influenced by the common legacy of Byzantine architecture ...
, and its architectural style was emulated by
Ottoman mosques
Ottoman may refer to:
* Osman I, historically known in English as "Ottoman I", founder of the Ottoman Empire
* Osman II, historically known in English as "Ottoman II"
* Ottoman Empire 1299–1922
** Ottoman dynasty, ruling family of the Ottoman Em ...
a thousand years later.
The Hagia Sophia served as an architectural inspiration for many other religious buildings including the
Hagia Sophia in Thessaloniki,
Panagia Ekatontapiliani
Panagia Ekatontapiliani (); literally ''the church with 100 gates'') or Panagia Katapoliani () is a historic Byzantine church complex in Parikia town, on the island of Paros in Greece. The church complex contains a main chapel surrounded by two ...
, the
Şehzade Mosque
The Şehzade Mosque () is a 16th-century Ottoman imperial mosque located in the district of Fatih, on the third hill of Istanbul, Turkey. It was commissioned by Suleiman the Magnificent as a memorial to his son Şehzade Mehmed who died in 1543 ...
, the
Süleymaniye Mosque
The Süleymaniye Mosque (, ) is an Ottoman imperial mosque located on the Seven hills of Istanbul, Third Hill of Istanbul, Turkey. The mosque was commissioned by Suleiman the Magnificent () and designed by the imperial architect Mimar Sinan. An ...
, the
Rüstem Pasha Mosque
The Rüstem Pasha Mosque () is an Ottoman mosque located in the Hasırcılar Çarşısı (Strawmat Weavers Market) in the Tahtakale neighborhood of the Fatih district of Istanbul, Turkey, near the Spice Bazaar. Named after Rüstem Pasha, who ...
and the
Kılıç Ali Pasha Complex
The Kılıç Ali Pasha Mosque () is a mosque at the heart of a complex designed and built between 1580 and 1587 by Mimar Sinan, who at the time was in his 90s. The mosque itself was constructed in 1578–1580.
The complex is located in the Toph ...
.
As the religious and spiritual centre of the
Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, officially the Orthodox Catholic Church, and also called the Greek Orthodox Church or simply the Orthodox Church, is List of Christian denominations by number of members, one of the three major doctrinal and ...
for nearly one thousand years, the church was
dedicated to
Holy Wisdom
Holy Wisdom (, ) is a concept in Christian theology.
Christian theology received the Old Testament personification of Wisdom (Hebrew ''Chokmah'') as well as the concept of Sophia (wisdom), Wisdom (''Sophia'') from Greek philosophy, especially ...
.
[Janin (1953), p. 471.] The church has been described as "holding a unique position in the
Christian world
The terms Christendom or Christian world commonly refer to the global Christian community, Christian states, Christian-majority countries or countries in which Christianity is dominant or prevails.SeMerriam-Webster.com : dictionary, "Christen ...
",
and as "an architectural and cultural icon of Byzantine and Eastern Orthodox civilization".
[.] It was where the
excommunication
Excommunication is an institutional act of religious censure used to deprive, suspend, or limit membership in a religious community or to restrict certain rights within it, in particular those of being in Koinonia, communion with other members o ...
of Patriarch
Michael I Cerularius
Michael I of Constantinople (''Cerularius'' or ''Keroularios''; ; 1000 – 21 January 1059) was the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople from 1043 to 1059. His disputes with Pope Leo IX over church practices in the 11th century played a ro ...
was officially delivered by
Humbert of Silva Candida
Humbert of Silva Candida, O.S.B., also known as Humbert of Moyenmoutier ( 1000 to 1015 – 5 May 1061) was a French Benedictine abbot and later cardinal. It was his act of excommunicating the Patriarch of Constantinople, Michael I Cerularius ...
, the envoy of
Pope Leo IX
Pope Leo IX (, , 21 June 1002 – 19 April 1054), born Bruno von Egisheim-Dagsburg, was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 12 February 1049 to his death in 1054. Leo IX is considered to be one of the most historica ...
in 1054, an act considered the start of the
East–West Schism
The East–West Schism, also known as the Great Schism or the Schism of 1054, is the break of communion (Christian), communion between the Catholic Church and the Eastern Orthodox Church. A series of Eastern Orthodox – Roman Catholic eccle ...
. In 1204, it was converted during the
Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid S ...
into a Catholic cathedral under the
Latin Empire
The Latin Empire, also referred to as the Latin Empire of Constantinople, was a feudal Crusader state founded by the leaders of the Fourth Crusade on lands captured from the Byzantine Empire. The Latin Empire was intended to replace the Byzantin ...
, before being restored to the Eastern Orthodox Church upon the restoration of the Byzantine Empire in 1261.
Enrico Dandolo
Enrico Dandolo (Anglicised as Henry Dandolo, and Latinised as Henricus Dandulus; – May/June 1205) was the doge of Venice from 1192 until his death in 1205. He is remembered for his avowed piety, longevity, and shrewdness, and his role in the ...
, the
doge of Venice
The Doge of Venice ( ) – in Italian, was the doge or highest role of authority within the Republic of Venice (697–1797). The word derives from the Latin , meaning 'leader', and Venetian Italian dialect for 'duke', highest official of the ...
who led the
Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid S ...
and the 1204
Sack of Constantinople
The sack of Constantinople occurred in April 1204 and marked the culmination of the Fourth Crusade. Crusaders sacked and destroyed most of Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire. After the capture of the city, the Latin Empire ( ...
, was buried in the church.
After the fall of Constantinople to the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
in 1453,
[Müller-Wiener (1977), p. 112.] it was
converted to a mosque by
Mehmed the Conqueror
Mehmed II (; , ; 30 March 14323 May 1481), commonly known as Mehmed the Conqueror (; ), was twice the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from August 1444 to September 1446 and then later from February 1451 to May 1481.
In Mehmed II's first reign, ...
and became the
principal mosque of Istanbul until the 1616 construction of the
Sultan Ahmed Mosque
The Blue Mosque, officially the Sultan Ahmed Mosque (), is an Ottoman-era historical imperial mosque located in Istanbul, Turkey. It was constructed between 1609 and 1617 during the rule of Ahmed I and remains a functioning mosque today. It al ...
.
The patriarchate moved to the
Church of the Holy Apostles
The Church of the Holy Apostles (, ''Agioi Apostoloi''; ), also known as the Imperial Polyandrion (imperial cemetery), was a Byzantine Eastern Orthodox church in Constantinople, capital of the Eastern Roman Empire. The first structure dated to ...
, which became the city's cathedral. The complex remained a mosque until 1931, when it was closed to the public for four years. It was re-opened in 1935 as a museum under the
secular
Secularity, also the secular or secularness (from Latin , or or ), is the state of being unrelated or neutral in regards to religion. The origins of secularity can be traced to the Bible itself. The concept was fleshed out through Christian hi ...
Republic of Turkey, and the building was Turkey's most visited tourist attraction . In 2020, the
Council of State
A council of state is a governmental body in a country, or a subdivision of a country, with a function that varies by jurisdiction. It may be the formal name for the cabinet or it may refer to a non-executive advisory body associated with a head ...
annulled the 1934 decision to establish the museum, and the Hagia Sophia was reclassified as a mosque. The decision was highly controversial, sparking divided opinions and drawing condemnation from the Turkish opposition,
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
, the
World Council of Churches
The World Council of Churches (WCC) is a worldwide Christian inter-church organization founded in 1948 to work for the cause of ecumenism. Its full members today include the Assyrian Church of the East, most jurisdictions of the Eastern Orthodo ...
and the
International Association of Byzantine Studies International Association of Byzantine Studies (, AIEB) was launched in 1948. It is an international co-ordinating body that links national Byzantine Studies member groups.
Background and Activities
The AIEB was established in 1948 as an outgrowt ...
, as well as numerous international leaders, while several Muslim leaders in Turkey and other countries welcomed its conversion.
History
Church of Constantius II

The first church on the site was known as the ()
[Müller-Wiener (1977), p. 84.] because of its size compared to the sizes of the contemporary churches in the city.
According to the ''
Chronicon Paschale
''Chronicon Paschale'' (the ''Paschal'' or ''Easter Chronicle''), also called ''Chronicum Alexandrinum'', ''Constantinopolitanum'' or ''Fasti Siculi'', is the conventional name of a 7th-century Greek Christian chronicle of the world. Its name com ...
'', the church was
consecrated
Sacred describes something that is dedicated or set apart for the service or worship of a deity; is considered worthy of spiritual respect or devotion; or inspires awe or reverence among believers. The property is often ascribed to objects (a ...
on 15 February 360, during the reign of the emperor
Constantius II
Constantius II (; ; 7 August 317 – 3 November 361) was Roman emperor from 337 to 361. His reign saw constant warfare on the borders against the Sasanian Empire and Germanic peoples, while internally the Roman Empire went through repeated civ ...
() by the
Arian
Arianism (, ) is a Christological doctrine which rejects the traditional notion of the Trinity and considers Jesus to be a creation of God, and therefore distinct from God. It is named after its major proponent, Arius (). It is considered he ...
bishop
Eudoxius of Antioch
Eudoxius of Antioch (; died 370) was the fifth archibishop of Constantinople from 27 January 360 to early 370, previously bishop of Germanicia and of Antioch. Eudoxius was one of the most influential Arians.
Biography
Eudoxius was from A ...
.
[Janin (1953), p. 472.] It was built next to the area where the
Great Palace
The Great Palace of Constantinople (, ''Méga Palátion''; ), also known as the Sacred Palace (, ''Hieròn Palátion''; ), was the large imperial Byzantine palace complex located in the south-eastern end of the peninsula today making up the Fati ...
was being developed. According to the 5th-century ecclesiastical historian
Socrates of Constantinople
Socrates of Constantinople ( 380 – after 439), also known as Socrates Scholasticus (), was a 5th-century Greek Christian church historian, a contemporary of Sozomen and Theodoret.
He is the author of a ''Historia Ecclesiastica'' ("Church Hist ...
, the emperor Constantius had "constructed the Great Church alongside that called Irene which because it was too small, the emperor's father
onstantinehad enlarged and beautified".
A tradition which is not older than the 7th or 8th century reports that the edifice was built by Constantius' father,
Constantine the Great
Constantine I (27 February 27222 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was a Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337 and the first Roman emperor to convert to Christianity. He played a Constantine the Great and Christianity, pivotal ro ...
().
Hesychius of Miletus
Hesychius of Miletus (), Greek chronicler and biographer, surnamed Illustrius, son of an advocate, lived in Constantinople in the 6th century AD during the reign of Justinian. His writings contain more references to pagan Greek culture than Christi ...
wrote that Constantine built Hagia Sophia with a wooden roof and removed 427 (mostly pagan) statues from the site. The 12th-century chronicler
Joannes Zonaras
Joannes or John Zonaras ( ; 1070 – 1140) was a Byzantine Roman historian, chronicler and theologian who lived in Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul, Turkey). Under Emperor Alexios I Komnenos he held the offices of head justice and private s ...
reconciles the two opinions, writing that Constantius had repaired the edifice consecrated by
Eusebius of Nicomedia
Eusebius of Nicomedia (; ; died 341) was an Arian priest who baptised Constantine the Great on his deathbed in 337. A fifth-century legend evolved that Pope Sylvester I was the one to baptise Constantine, but this is dismissed by scholars as ...
, after it had collapsed.
Since Eusebius was the
bishop
A bishop is an ordained member of the clergy who is entrusted with a position of Episcopal polity, authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance and administration of di ...
of Constantinople from 339 to 341, and Constantine died in 337, it seems that the first church was erected by Constantius.
The nearby
Hagia Irene
Hagia Irene () or Hagia Eirene ( , "Holy Peace", ), sometimes known also as Saint Irene, is a former Eastern Orthodox church located in the outer courtyard of Topkapı Palace in Istanbul. It is the oldest known church structure in the city and on ...
("Holy Peace") church was completed earlier and served as cathedral until the Great Church was completed. Besides Hagia Irene, there is no record of major churches in the city-centre before the late 4th century.
Rowland Mainstone argued the 4th-century church was not yet known as Hagia Sophia.
The church is known to have had a timber roof, curtains, columns, and an entrance that faced west.
It likely had a
narthex
The narthex is an architectural element typical of Early Christian art and architecture, early Christian and Byzantine architecture, Byzantine basilicas and Church architecture, churches consisting of the entrance or Vestibule (architecture), ve ...
and is described as being shaped like a
Roman circus
A Roman circus (from the Latin word that means "circle") was a large open-air venue used mainly for chariot races, although sometimes serving other purposes. It was similar to the ancient Greek hippodrome. Along with theatres and amphitheatres, ...
. This may mean that it had a U-shaped plan like the basilicas of
San Marcellino e Pietro and
Sant'Agnese fuori le mura
The church of Saint Agnes Outside the Walls () is a Titular church, titular churches of Rome, church, a minor basilica in Rome, on a site sloping down from the Via Nomentana, which runs north-east out of the city, still under its ancient name. W ...
in
Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
.
However, it may also have been a more conventional three-, four-, or five-aisled basilica, perhaps resembling the original
Church of the Holy Sepulchre
The Church of the Holy Sepulchre, also known as the Church of the Resurrection, is a fourth-century church in the Christian Quarter of the Old City of Jerusalem, Old City of Jerusalem. The church is the seat of the Greek Orthodox Patriarchat ...
in
Jerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and ...
or the
Church of the Nativity
The Church of the Nativity, or Basilica of the Nativity, is a basilica located in Bethlehem, West Bank, Palestine. The grotto holds a prominent religious significance to Christianity, Christians of various denominations as the Nativity of Jesus, ...
in
Bethlehem
Bethlehem is a city in the West Bank, Palestine, located about south of Jerusalem, and the capital of the Bethlehem Governorate. It had a population of people, as of . The city's economy is strongly linked to Tourism in the State of Palesti ...
.
The building was likely preceded by an
atrium
Atrium may refer to:
Anatomy
* Atrium (heart), an anatomical structure of the heart
* Atrium, the genital structure next to the genital aperture in the reproductive system of gastropods
* Atrium of the ventricular system of the brain
* Pulmona ...
, as in the later churches on the site.
According to
Ken Dark
Kenneth Rainsbury Dark (born in Brixton, London in 1961) is a British archaeologist who works on the 1st millennium AD in Europe (including Roman and immediately post-Roman Britain) and the Roman and Byzantine Middle East, on the archaeology o ...
and Jan Kostenec, a further remnant of the 4th century basilica may exist in a wall of alternating brick and stone banded masonry immediately to the west of the Justinianic church.
The top part of the wall is constructed with bricks stamped with brick-stamps dating from the 5th century, but the lower part is of constructed with bricks typical of the 4th century.
This wall was probably part of the
propylaeum at the west front of both the Constantinian and Theodosian Great Churches.
The building was accompanied by a
baptistery
In Church architecture, Christian architecture the baptistery or baptistry (Old French ''baptisterie''; Latin ''baptisterium''; Greek language, Greek , 'bathing-place, baptistery', from , baptízein, 'to baptize') is the separate centrally planned ...
and a ''
skeuophylakion''.
A
hypogeum
A hypogeum or hypogaeum ( ; plural hypogea or hypogaea; literally meaning "underground") is an underground temple or tomb.
Hypogea will often contain niches for cremated human remains or loculi for buried remains. Occasionally tombs of th ...
, perhaps with an
martyrium
A ''martyrium'' (Latin) or ''martyrion'' (Greek) (: ''martyria)'', sometimes anglicized martyry (: "martyries"), is a church or shrine built over the tomb of a Christian martyr. It is associated with a specific architectural form, centered on a ...
above it, was discovered before 1946, and the remnants of a brick wall with traces of marble revetment were identified in 2004.
The hypogeum was a tomb which may have been part of the 4th-century church or may have been from the pre-Constantinian city of
Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion () was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' continued to be used as a n ...
.
The ''skeuophylakion'' is said by
Palladius to have had a circular floor plan, and since some U-shaped basilicas in Rome were funerary churches with attached circular mausolea (the
Mausoleum of Constantina
The Mausoleum of Constantina, also known as the ''Mausoleum of Santa Costanza'', was built in the 4th century AD for Constantina (also known as Constantia), the daughter of the emperor Constantine I. It later became a church. It is located in Ro ...
and the
Mausoleum of Helena
The Mausoleum of Helena is an ancient building in Rome, Italy, located on the Via Casilina, corresponding to the 3rd mile of the Ancient Rome, ancient Via Labicana. It was built by the Roman emperor Constantine I between 326 and 330, originall ...
), it is possible it originally had a funerary function, though by 405 its use had changed.
A later account credited a woman called Anna with donating the land on which the church was built in return for the right to be buried there.
Excavations on the western side of the site of the first church under the propylaeum wall reveal that the first church was built atop a road about wide.
According to early accounts, the first Hagia Sophia was built on the site of an ancient pagan temple, although there are no artefacts to confirm this.
The Patriarch of Constantinople
John Chrysostom
John Chrysostom (; ; – 14 September 407) was an important Church Father who served as archbishop of Constantinople. He is known for his preaching and public speaking, his denunciation of abuse of authority by both ecclesiastical and p ...
came into a conflict with Empress
Aelia Eudoxia
Aelia Eudoxia (; ; died 6 October 404) was Eastern Roman empress by marriage to the Roman emperor Arcadius. The marriage was arranged by Eutropius, one of the eunuch court officials, who was attempting to expand his influence. As Empress, sh ...
, wife of the emperor
Arcadius
Arcadius ( ; 377 – 1 May 408) was Roman emperor from 383 to his death in 408. He was the eldest son of the ''Augustus'' Theodosius I () and his first wife Aelia Flaccilla, and the brother of Honorius (). Arcadius ruled the eastern half of ...
(), and was sent into exile on 20 June 404. During the subsequent riots, this first church was largely burnt down.
Palladius noted that the 4th-century ''skeuophylakion'' survived the fire.
According to Dark and Kostenec, the fire may only have affected the main basilica, leaving the ancillary buildings intact.
Church of Theodosius II
A second church on the site was ordered by
Theodosius II
Theodosius II ( ; 10 April 401 – 28 July 450), called "the Calligraphy, Calligrapher", was Roman emperor from 402 to 450. He was proclaimed ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' as an infant and ruled as the Eastern Empire's sole emperor after the ...
(), who inaugurated it on 10 October 415. The ''
Notitia Urbis Constantinopolitanae
The ''Notitia Urbis Constantinopolitanae'' is an ancient "regionary", i.e., a list of monuments, public buildings and civil officials in Constantinople during the mid-5th century (between 425 and the 440s), during the reign of the emperor Theodosi ...
,'' a fifth-century list of monuments, names Hagia Sophia as , while the former cathedral Hagia Irene is referred to as . At the time of Socrates of Constantinople around 440, "both churches
ere
Ere or ERE may refer to:
* ''Environmental and Resource Economics'', a peer-reviewed academic journal
* ERE Informatique, one of the first French video game companies
* Ere language, an Austronesian language
* Ebi Ere (born 1981), American-Nigeria ...
enclosed by a single wall and served by the same clergy".
Thus, the complex would have encompassed a large area including the future site of the
Hospital of Samson.
If the fire of 404 destroyed only the 4th-century main basilica church, then the 5th century Theodosian basilica could have been built surrounded by a complex constructed primarily during the fourth century.
During the reign of Theodosius II, the emperor's elder sister, the ''Augusta''
Pulcheria
Aelia Pulcheria (; ; 19 January 398 or 399 – 453) was an Eastern Roman empress who advised her brother, the emperor Theodosius II, during his minority and then became wife to emperor Marcian from November 450 to her death in 453.
She was th ...
() was challenged by the patriarch
Nestorius
Nestorius of Constantinople (; ; ) was an early Christian prelate who served as Archbishop of Constantinople from 10 April 428 to 11 July 431. A Christian theologian from the Catechetical School of Antioch, several of his teachings in the fi ...
().
The patriarch denied the ''Augusta'' access to the sanctuary of the "Great Church", likely on 15 April 428.
According to the anonymous ''Letter to Cosmas'', the virgin empress, a promoter of the
cult of the Virgin Mary
Cults are social groups which have unusual, and often extreme, religious, spiritual, or philosophical beliefs and rituals. Extreme devotion to a particular person, object, or goal is another characteristic often ascribed to cults. The term ha ...
who habitually partook in the
Eucharist
The Eucharist ( ; from , ), also called Holy Communion, the Blessed Sacrament or the Lord's Supper, is a Christianity, Christian Rite (Christianity), rite, considered a sacrament in most churches and an Ordinance (Christianity), ordinance in ...
at the sanctuary of Nestorius's predecessors, claimed right of entry because of her equivalent position to the ''
Theotokos
''Theotokos'' ( Greek: ) is a title of Mary, mother of Jesus, used especially in Eastern Christianity. The usual Latin translations are or (approximately "parent (fem.) of God"). Familiar English translations are "Mother of God" or "God-beare ...
'' – the Virgin Mary – "having given birth to God".
Pulcheria along with
Pope Celestine I and Patriarch
Cyril of Alexandria
Cyril of Alexandria (; or ⲡⲓ̀ⲁⲅⲓⲟⲥ Ⲕⲓⲣⲓⲗⲗⲟⲥ; 376–444) was the Patriarch of Alexandria from 412 to 444. He was enthroned when the city was at the height of its influence and power within the Roman Empire ...
had Nestorius overthrown, condemned at the ecumenical council, and exiled.
The area of the western entrance to the Justinianic Hagia Sophia revealed the western remains of its Theodosian predecessor, as well as some fragments of the Constantinian church.
German archaeologist
Alfons Maria Schneider began conducting
archaeological excavations
In archaeology, excavation is the exposure, processing and recording of archaeological remains. An excavation site or "dig" is the area being studied. These locations range from one to several areas at a time during a project and can be condu ...
during the mid-1930s, publishing his final report in 1941.
Excavations in the area that had once been the 6th-century atrium of the Justinianic church revealed the monumental western entrance and atrium, along with columns and sculptural fragments from both 4th- and 5th-century churches.
Further digging was abandoned for fear of harming the structural integrity of the Justinianic building, but parts of the excavation trenches remain uncovered, laying bare the foundations of the Theodosian building.
The basilica was built by architect Rufinus. The church's main entrance, which may have had gilded doors, faced west, and there was an additional entrance to the east.
There was a central
pulpit
A pulpit is a raised stand for preachers in a Christian church. The origin of the word is the Latin ''pulpitum'' (platform or staging). The traditional pulpit is raised well above the surrounding floor for audibility and visibility, accesse ...
and likely an upper gallery, possibly employed as a
matroneum
A triforium is an interior gallery, opening onto the tall central space of a building at an upper level. In a church, it opens onto the nave from above the side aisles; it may occur at the level of the clerestory windows, or it may be locate ...
(women's section).
The exterior was decorated with elaborate carvings of rich Theodosian-era designs, fragments of which have survived, while the floor just inside the portico was embellished with polychrome mosaics.
The surviving carved gable end from the centre of the western façade is decorated with a cross-roundel.
Fragments of a
frieze
In classical architecture, the frieze is the wide central section of an entablature and may be plain in the Ionic order, Ionic or Corinthian order, Corinthian orders, or decorated with bas-reliefs. Patera (architecture), Paterae are also ...
of
relief
Relief is a sculpture, sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces remain attached to a solid background of the same material. The term ''wikt:relief, relief'' is from the Latin verb , to raise (). To create a sculpture in relief is to give ...
s with 12 lambs representing the
12 apostles
In Christian theology and ecclesiology, the apostles, particularly the Twelve Apostles (also known as the Twelve Disciples or simply the Twelve), were the primary disciples of Jesus according to the New Testament. During the life and ministr ...
also remain; unlike Justinian's 6th-century church, the Theodosian Hagia Sophia had both colourful floor mosaics and external decorative sculpture.
At the western end, surviving stone fragments of the structure show there was
vaulting
In architecture, a vault (French ''voûte'', from Italian ''volta'') is a self-supporting arched form, usually of stone or brick, serving to cover a space with a ceiling or roof. As in building an arch, a temporary support is needed while ring ...
, at least at the western end.
The Theodosian building had a monumental propylaeum hall with a portico that may account for this vaulting, which was thought by the original excavators in the 1930s to be part of the western entrance of the church itself.
The propylaeum opened onto an atrium which lay in front of the basilica church itself. Preceding the propylaeum was a steep monumental staircase following the contours of the ground as it sloped away westwards in the direction of the
Strategion, the Basilica, and the harbours of the
Golden Horn
The Golden Horn ( or ) is a major urban waterway and the primary inlet of the Bosphorus in Istanbul, Turkey. As a natural estuary that connects with the Bosphorus Strait at the point where the strait meets the Sea of Marmara, the waters of the ...
.
This arrangement would have resembled the steps outside the atrium of the Constantinian
Old St Peter's Basilica in Rome.
Near the staircase, there was a cistern, perhaps to supply a fountain in the atrium or for worshippers to wash with before entering.
The 4th-century ''skeuophylakion'' was replaced in the 5th century by the present-day structure, a
rotunda
A rotunda () is any roofed building with a circular ground plan, and sometimes covered by a dome. It may also refer to a round room within a building (an example being the one below the dome of the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C.). ...
constructed of banded masonry in the lower two levels and of plain brick masonry in the third.
Originally this rotunda, probably employed as a treasury for liturgical objects, had a second-floor internal gallery accessed by an external spiral staircase and two levels of niches for storage.
A further row of windows with marble window frames on the third level remain bricked up.
The gallery was supported on monumental
consoles with carved
acanthus
Acanthus (: acanthus, rarely acanthuses in English, or acanthi in Latin), its feminine form acantha (plural: acanthae), the Latinised form of the ancient Greek word acanthos or akanthos, or the prefix acantho-, may refer to:
Biology
*Acanthus ...
designs, similar to those used on the late 5th-century
Column of Leo.
A large
lintel
A lintel or lintol is a type of beam (a horizontal structural element) that spans openings such as portals, doors, windows and fireplaces. It can be a decorative architectural element, or a combined ornamented/structural item. In the case ...
of the ''skeuophylakion''
's western entrance – bricked up during the Ottoman era – was discovered inside the rotunda when it was archaeologically cleared to its foundations in 1979, during which time the brickwork was also
repointed.
The ''skeuophylakion'' was again restored in 2014 by the
Vakıflar.
A fire started during the tumult of the
Nika Revolt
The Nika riots (), Nika revolt or Nika sedition took place against Byzantine emperor Justinian I in Constantinople over the course of a week in 532 AD. They are often regarded as the most violent riots in the city's history, with nearly half of ...
, which had begun nearby in the
Hippodrome of Constantinople
The Hippodrome of Constantinople (; ; ) was a Roman circus, circus that was the sporting and social centre of Constantinople, capital of the Byzantine Empire. Today it is a square in Istanbul, Turkey, known as Sultanahmet Square ().
The word ...
, and the second Hagia Sophia was burnt to the ground on 13–14 January 532. The court historian
Procopius
Procopius of Caesarea (; ''Prokópios ho Kaisareús''; ; – 565) was a prominent Late antiquity, late antique Byzantine Greeks, Greek scholar and historian from Caesarea Maritima. Accompanying the Roman general Belisarius in Justinian I, Empe ...
wrote:
Greek cross
The Christian cross, with or without a figure of Jesus, Christ included, is the main religious symbol of Christianity. A cross with a figure of Christ affixed to it is termed a crucifix and the figure is often referred to as the ''corpus'' (La ...
File:Theodosius's Hagia Sophia 3.jpg, Porphyry
Porphyry (; , ''Porphyrios'' "purple-clad") may refer to:
Geology
* Porphyry (geology), an igneous rock with large crystals in a fine-grained matrix, often purple, and prestigious Roman sculpture material
* Shoksha porphyry, quartzite of purple c ...
column; column capital; impost block
File:Hagia Sophia Theodosius 2007 007.jpg, Soffits and cornice
In architecture, a cornice (from the Italian ''cornice'' meaning "ledge") is generally any horizontal decorative Moulding (decorative), moulding that crowns a building or furniture element—for example, the cornice over a door or window, ar ...
File:CapCorBizPil1SSofiaTeod-19Lato.jpg, Theodosian capital
File:CapCorBizPil1SSofiaTeod-19.jpg, Theodosian capital for a pilaster
In architecture, a pilaster is both a load-bearing section of thickened wall or column integrated into a wall, and a purely decorative element in classical architecture which gives the appearance of a supporting column and articulates an ext ...
, one of the few remains of the church of Theodosius II
File:Theodosius's Hagia Sophia 17.jpg, Soffit
A soffit is an exterior architectural feature, generally the horizontal, aloft underside of the roof edge. Its archetypal form, sometimes incorporating or implying the projection of rafters or trusses over the exterior of supporting walls, is t ...
s
Church of Justinian I (current structure)
On 23 February 532, only a few weeks after the destruction of the second basilica, Emperor
Justinian I inaugurated the construction of a third and entirely different basilica, larger and more majestic than its predecessors. Justinian appointed two architects, mathematician
Anthemius of Tralles
Anthemius of Tralles (, Medieval Greek: , ''Anthémios o Trallianós''; – 533 558) was a Byzantine Greek from Tralles who worked as a geometer and architect in Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire. With Isidor ...
and geometer and engineer
Isidore of Miletus
Isidore of Miletus (; Medieval Greek pronunciation: ; ) was one of the two main Byzantine Greek mathematician, physicist and architects ( Anthemius of Tralles was the other) that Emperor Justinian I commissioned to design the cathedral Hagia Sop ...
, to design the building.
Construction of the church began in 532 during the short tenure of Phocas as
praetorian prefect
The praetorian prefect (; ) was a high office in the Roman Empire. Originating as the commander of the Praetorian Guard, the office gradually acquired extensive legal and administrative functions, with its holders becoming the Emperor's chief ai ...
.
According to
John the Lydian
John the Lydian or John Lydus (; ) ( AD 490 – 565) was a Byzantine administrator and writer. He is considered a key figure in antiquarian studies from the fourth to the sixth century A.D. Although he is a secondary author, his works are signific ...
, Phocas was responsible for funding the initial construction of the building with 4,000
Roman pound
The units of measurement of ancient Rome were generally consistent and well documented.
Length
The basic unit of Roman linear measurement was the ''pes'' (plural: ''pedes'') or Roman foot. Investigation of its relation to the English foot goes ...
s of gold, but he was dismissed from office in October 532.
[John Lydus, ''De Magistratibus reipublicae Romanae'' III.76] John the Lydian wrote that Phocas had acquired the funds by moral means, but
Evagrius Scholasticus
Evagrius Scholasticus () was a Syrian scholar and intellectual living in the 6th century AD, and an aide to the patriarch Gregory of Antioch. His surviving work, ''Ecclesiastical History'' (), comprises a six-volume collection concerning the Chu ...
later wrote that the money had been obtained unjustly.
According to
Anthony Kaldellis
Anthony Kaldellis ( ; born 29 November 1971) is a Greek-American historian and Byzantinist who is a professor of classics at the University of Chicago. He is a specialist in Greek historiography, Plato, and Byzantine studies.
As the author of mon ...
, both of Hagia Sophia's architects named by Procopius were associated with the
school
A school is the educational institution (and, in the case of in-person learning, the Educational architecture, building) designed to provide learning environments for the teaching of students, usually under the direction of teachers. Most co ...
of the pagan philosopher
Ammonius of Alexandria
Ammonius () of Alexandria, son of Ammonius, was an ancient Greek grammarian who lived around the 1st century BCE.
He was a pupil of a teacher named "Alexander" (possibly Alexander Polyhistor), and became one of the chief teachers in the grammatic ...
.
It is possible that both they and John the Lydian considered Hagia Sophia a great temple for the supreme
Neoplatonist
Neoplatonism is a version of Platonic philosophy that emerged in the 3rd century AD against the background of Hellenistic philosophy and religion. The term does not encapsulate a set of ideas as much as a series of thinkers. Among the common id ...
deity
A deity or god is a supernatural being considered to be sacred and worthy of worship due to having authority over some aspect of the universe and/or life. The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' defines ''deity'' as a God (male deity), god or god ...
who manifestated through light and the sun. John the Lydian describes the church as the "''
temenos
A ''temenos'' ( Greek: ; plural: , ''temenē''). is a piece of land cut off and assigned as an official domain, especially to kings and chiefs, or a piece of land marked off from common uses and dedicated to a god, such as a sanctuary, holy g ...
'' of the Great God" ().
Originally the exterior of the church was covered with
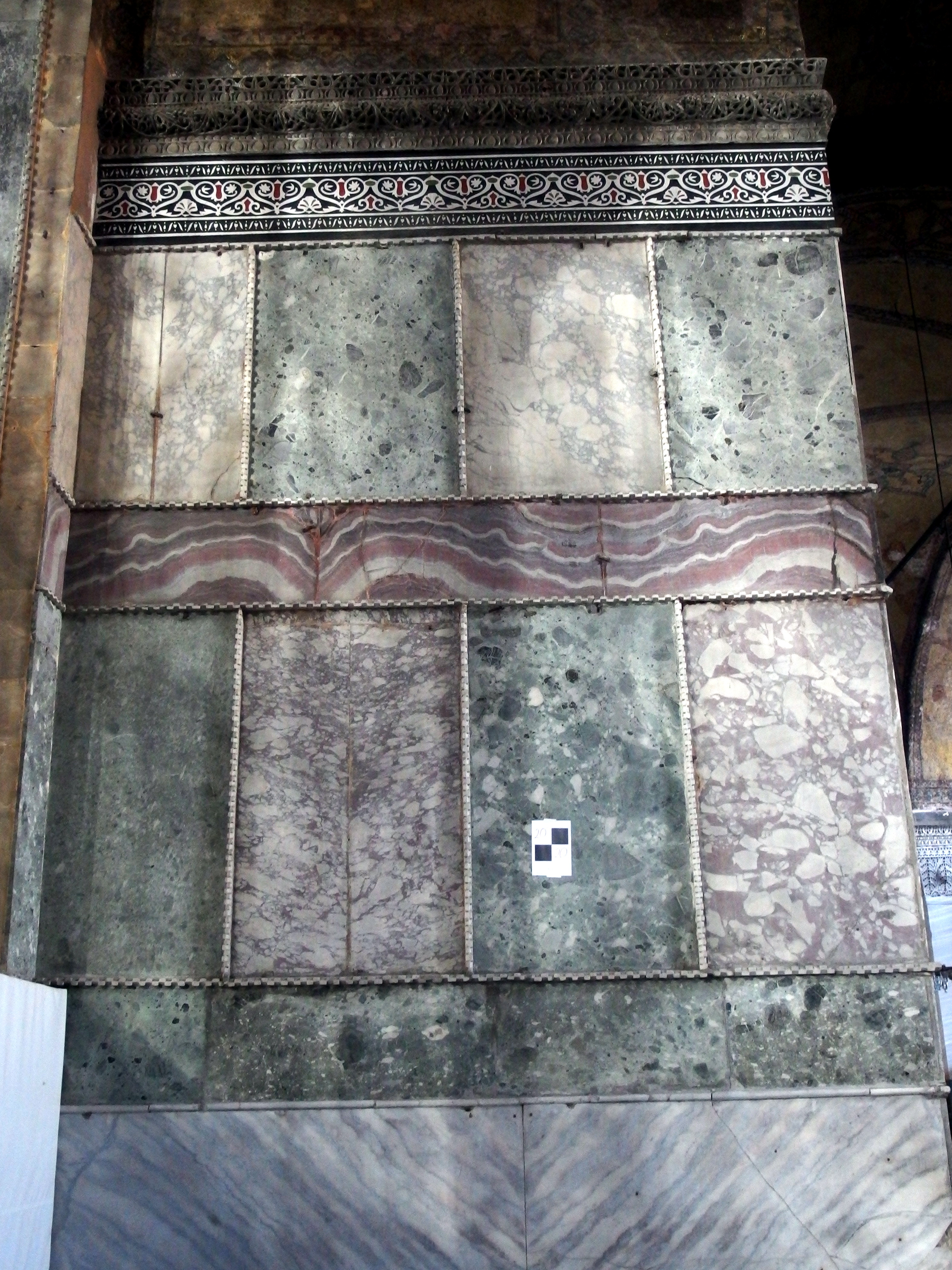
marble veneer, as indicated by remaining pieces of marble and surviving attachments for lost panels on the building's western face.
The white marble
cladding of much of the church, together with
gilding
Gilding is a decorative technique for applying a very thin coating of gold over solid surfaces such as metal (most common), wood, porcelain, or stone. A gilded object is also described as "gilt". Where metal is gilded, the metal below was tradi ...
of some parts, would have given Hagia Sophia a shimmering appearance quite different from the brick- and plaster-work of the modern period, and would have significantly increased its visibility from the sea.
The cathedral's interior surfaces were sheathed with polychrome marbles, green and white with purple
porphyry
Porphyry (; , ''Porphyrios'' "purple-clad") may refer to:
Geology
* Porphyry (geology), an igneous rock with large crystals in a fine-grained matrix, often purple, and prestigious Roman sculpture material
* Shoksha porphyry, quartzite of purple c ...
, and gold mosaics. The exterior was clad in
stucco
Stucco or render is a construction material made of aggregates, a binder, and water. Stucco is applied wet and hardens to a very dense solid. It is used as a decorative coating for walls and ceilings, exterior walls, and as a sculptural and ...
that was tinted yellow and red during the 19th-century restorations by the
Fossati architects.
The construction is described by Procopius in ''On Buildings'' (, ).
Columns and other marble elements were imported from throughout the Mediterranean, although the columns were once thought to be
spoils from cities such as Rome and Ephesus. Even though they were made specifically for Hagia Sophia, they vary in size. More than ten thousand people were employed during the construction process. This new church was contemporaneously recognized as a major work of architecture. Outside the church was an elaborate array of monuments around the bronze-plated
Column of Justinian
The Column of Justinian was a Roman triumphal column erected in Constantinople by the Byzantine emperor Justinian I in honour of his victories in 543. It stood in the western side of the great square of the Augustaeum, between the Hagia Sophia a ...
, topped by an equestrian statue of the emperor which dominated the
Augustaeum
The ''Augustaion'' () or, in Latin language, Latin, ''Augustaeum'', was an important ceremonial square in ancient and medieval Constantinople (modern Istanbul, Turkey), roughly corresponding to the modern ''Aya Sofya Meydanı'' (Turkish language, ...
, the open square outside the church which connected it with the
Great Palace
The Great Palace of Constantinople (, ''Méga Palátion''; ), also known as the Sacred Palace (, ''Hieròn Palátion''; ), was the large imperial Byzantine palace complex located in the south-eastern end of the peninsula today making up the Fati ...
complex through the
Chalke Gate
The Chalke Gate (), was the main ceremonial entrance ( vestibule) to the Great Palace of Constantinople in the Byzantine period. The name, which means "the Bronze Gate", was given to it either because of the bronze portals or from the gilded bro ...
. At the edge of the Augustaeum was the
Milion
The Milion ( or , ''Mílion''; ) was a marker from which all distances across the Roman Empire were measured. Erected by Septimius Severus in the 3rd century AD in the city of Byzantium, it became the zero-mile marker for the empire upon the r ...
and the Regia, the first stretch of Constantinople's main thoroughfare, the
''Mese''. Also facing the Augustaeum were the enormous Constantinian ''
thermae
In ancient Rome, (from Greek , "hot") and (from Greek ) were facilities for bathing. usually refers to the large Roman Empire, imperial public bath, bath complexes, while were smaller-scale facilities, public or private, that existed i ...
'', the
Baths of Zeuxippus
The Baths of Zeuxippus were popular public baths in the city of Constantinople. The origin of their name was disputed already in antiquity and could go back either to the god Zeus or to the artist Zeuxis. Constructed between 100 and 200, the Bat ...
, and the Justinianic civic basilica under which was the vast
cistern
A cistern (; , ; ) is a waterproof receptacle for holding liquids, usually water. Cisterns are often built to catch and store rainwater. To prevent leakage, the interior of the cistern is often lined with hydraulic plaster.
Cisterns are disti ...
known as the
Basilica Cistern
The Basilica Cistern, or Cisterna Basilica (, or , "Subterranean Cistern" or "Subterranean Palace"), is the largest of several hundred ancient cisterns that lie beneath the city of Istanbul, Turkey. The cistern, located southwest of the Hagi ...
. On the opposite side of Hagia Sophia was the former cathedral, Hagia Irene.
Procopius lauded the Justinianic building, writing in ''De aedificiis'':
Upon seeing the finished building, the Emperor reportedly said: "Solomon, I have surpassed thee".
Justinian and
Patriarch Menas
Menas of Constantinople (also ''Minas''; ; died 25 August 552), considered a saint in the Chalcedonian-affirming Church and by extension both the Eastern Orthodox Church and Catholic Church of modern times, was born in Alexandria, and enters ...
inaugurated the new basilica on 27 December 537, 5 years and 10 months after construction started, with much pomp.
[Müller-Wiener (1977), p. 86.] Hagia Sophia was the seat of the Patriarchate of Constantinople and a principal setting for Byzantine imperial ceremonies, such as
coronation
A coronation ceremony marks the formal investiture of a monarch with regal power using a crown. In addition to the crowning, this ceremony may include the presentation of other items of regalia, and other rituals such as the taking of special v ...
s. The basilica offered
sanctuary from persecution to criminals, although there was disagreement about whether Justinian had intended for murderers to be eligible for asylum.

Earthquakes in 553 and on
557
__NOTOC__
Year 557 ( DLVII) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 557 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe f ...
caused cracks in the main dome and eastern
semi-dome
In architecture, a semi-dome (or half-dome) is a half dome that covers a semi-circular area in a building.
Architecture
Semi-domes are a common feature of apses in Ancient Roman and traditional church architecture, and in mosques and iwans in Isla ...
. According to the ''Chronicle'' of
John Malalas
John Malalas (; ; – 578) was a Byzantine chronicler from Antioch in Asia Minor.
Life
Of Syrian descent, Malalas was a native speaker of Syriac who learned how to write in Greek later in his life. The name ''Malalas'' probably derive ...
, during a subsequent earthquake in 558,
the eastern semi-dome collapsed, destroying the
ambon, altar, and
ciborium. The collapse was due mainly to the excessive
bearing load and to the enormous
shear load
Shear may refer to:
Textile production
*Animal shearing, the collection of wool from various species
**Sheep shearing
*The removal of nap during wool cloth production
*Scissors, a hand-operated cutting equipment
Science and technology Engineerin ...
of the dome, which was too flat.
These caused the deformation of the piers which sustained the dome.
Justinian ordered an immediate restoration. He entrusted it to Isidorus the Younger, who used lighter materials. The entire vault had to be taken down and rebuilt 20 Byzantine feet () higher than before, giving the building its current interior height of . Moreover, Isidorus changed the dome type, erecting a ribbed dome with
pendentives
In architecture, a pendentive is a constructional device permitting the placing of a circular dome over a square room or of an elliptical dome over a rectangular room. The pendentives, which are triangular segments of a sphere, taper to point ...
whose diameter was between 32.7 and 33.5 m.
Under Justinian's orders, eight
Corinthian columns
The Corinthian order (, ''Korinthiakós rythmós''; ) is the last developed and most ornate of the three principal classical orders of Ancient Greek architecture and Roman architecture. The other two are the Doric order, which was the earliest, ...
were disassembled from
Baalbek
Baalbek (; ; ) is a city located east of the Litani River in Lebanon's Beqaa Valley, about northeast of Beirut. It is the capital of Baalbek-Hermel Governorate. In 1998, the city had a population of 82,608. Most of the population consists of S ...
, Lebanon and shipped to Constantinople around 560. This reconstruction, which gave the church its present 6th-century form, was completed in 562. The poet
Paul the Silentiary
Paul the Silentiary, also known as Paulus Silentiarius (, died AD 575–580), was a Greeks, Greek Byzantine poet and courtier to the emperor Justinian I, Justinian at Constantinople.
Life
What little we know of Paul's life comes largely from th ...
composed an ''
ekphrasis
Ekphrasis or ecphrasis (from the Greek) is a rhetorical device indicating the written description of a work of art. It is a vivid, often dramatic, verbal description of a visual work of art, either real or imagined. Thus, "an ekphrastic poem ...
'', or long visual poem, for the re-dedication of the basilica presided over by
Patriarch Eutychius on 24 December 562.
According to the history of the patriarch
Nicephorus I and the chronicler
Theophanes the Confessor
Theophanes the Confessor (; 759 – 817 or 818) was a member of the Byzantine aristocracy who became a monk and chronicler. He served in the court of Emperor Leo IV the Khazar before taking up the religious life. Theophanes attended the Second C ...
, various liturgical vessels of the cathedral were melted down on the order of the emperor
Heraclius
Heraclius (; 11 February 641) was Byzantine emperor from 610 to 641. His rise to power began in 608, when he and his father, Heraclius the Elder, the Exarch of Africa, led a revolt against the unpopular emperor Phocas.
Heraclius's reign was ...
() during the
Byzantine–Sasanian War of 602–628
The Byzantine–Sasanian War of 602–628, also called the Last Great War of Antiquity, was fought between the Byzantine Empire and the Sasanian Empire. It was the final and most devastating conflict of the Roman–Persian wars (54 BCAD&n ...
.
Theophanes states that these were made into gold and silver coins, and a tribute was paid to the
Avars.
The Avars attacked the extramural areas of Constantinople in 623, causing the Byzantines to move the "garment" relic () of Mary, mother of Jesus to Hagia Sophia from its usual shrine of the
Church of the ''Theotokos'' at
Blachernae
Blachernae () was a suburb in the northwestern section of Constantinople, the capital city of the Byzantine Empire. It is the site of a water source and a number of prominent churches were built there, most notably the great Church of St. Mary of ...
just outside the
Theodosian Walls
The Walls of Constantinople (; ) are a series of defensive wall, defensive stone walls that have surrounded and protected the city of Constantinople (modern Fatih district of Istanbul) since its founding as the new capital of the Roman Empire b ...
. On 14 May 626, the ''
Scholae Palatinae
The ''Scholae Palatinae'' (; ) were an elite military imperial guard unit, usually ascribed to the Roman Emperor Constantine the Great as a replacement for the '' equites singulares Augusti'', the cavalry arm of the Praetorian Guard. The ''Scho ...
'', an elite body of soldiers, protested in Hagia Sophia against a planned increase in bread prices. The Persians under
Shahrbaraz
Shahrbaraz (also spelled Shahrvaraz or Shahrwaraz; New Persian: ) was shah (king) of the Sasanian Empire from 27 April 630 to 9 June 630. He usurped the throne from Ardashir III, and was killed by Iranian nobles after forty days. Before usurp ...
and the Avars together laid the
siege of Constantinople
Constantinople (part of modern Istanbul, Turkey) was built on the land that links Europe to Asia through Bosporus and connects the Sea of Marmara and the Black Sea. As a transcontinental city within the Silk Road, Constantinople had a strategic ...
in 626; according to the ''
Chronicon Paschale
''Chronicon Paschale'' (the ''Paschal'' or ''Easter Chronicle''), also called ''Chronicum Alexandrinum'', ''Constantinopolitanum'' or ''Fasti Siculi'', is the conventional name of a 7th-century Greek Christian chronicle of the world. Its name com ...
'', on 2 August 626,
Theodore Syncellus
Theodore Synkellos (Greek: Θεόδωρος Σύγκελλος) was a Byzantine clergyman, diplomat and writer who flourished in the first half of the 7th century. He wrote in Greek.
Theodore was a high-ranking clergyman in Constantinople in the 6 ...
, a
deacon
A deacon is a member of the diaconate, an office in Christian churches that is generally associated with service of some kind, but which varies among theological and denominational traditions.
Major Christian denominations, such as the Cathol ...
and
presbyter
Presbyter () is an honorific title for Christian clergy. The word derives from the Greek ''presbyteros'', which means elder or senior, although many in Christian antiquity understood ''presbyteros'' to refer to the bishop functioning as overseer ...
of Hagia Sophia, was among those who negotiated unsuccessfully with the ''
khagan
Khagan or Qaghan (Middle Mongol:; or ''Khagan''; ) or zh, c=大汗, p=Dàhán; ''Khāqān'', alternatively spelled Kağan, Kagan, Khaghan, Kaghan, Khakan, Khakhan, Khaqan, Xagahn, Qaghan, Chagan, Қан, or Kha'an is a title of empire, im ...
'' of the Avars.
A
homily
A homily (from Greek ὁμιλία, ''homilía'') is a commentary that follows a reading of scripture, giving the "public explanation of a sacred doctrine" or text. The works of Origen and John Chrysostom (known as Paschal Homily) are considered ...
, attributed by existing
manuscripts
A manuscript (abbreviated MS for singular and MSS for plural) was, traditionally, any document written by hand or typewritten, as opposed to mechanically printed or reproduced in some indirect or automated way. More recently, the term has c ...
to Theodore Syncellus and possibly delivered on the anniversary of the event, describes the translation of the Virgin's garment and its ceremonial re-translation to Blachernae by the patriarch
Sergius I after the threat had passed.

In 726, the emperor
Leo the Isaurian
Leo III the Isaurian (; 685 – 18 June 741), also known as the Syrian, was the first Byzantine emperor of the Isaurian dynasty from 717 until his death in 741. He put an end to the Twenty Years' Anarchy, a period of great instability in the ...
issued a series of edicts against the veneration of images, ordering the army to destroy all icons – ushering in the period of
Byzantine iconoclasm
The Byzantine Iconoclasm () are two periods in the history of the Byzantine Empire when the use of religious images or icons was opposed by religious and imperial authorities within the Ecumenical Patriarchate (at the time still comprising the ...
. At that time, all religious pictures and statues were removed from the Hagia Sophia. Following a brief hiatus during the reign of Empress
Irene
Irene is a name derived from εἰρήνη (eirēnē), Greek for "peace".
Irene, and related names, may refer to:
* Irene (given name)
Places
* Irene, Gauteng, South Africa
* Irene, South Dakota, United States
* Irene, Texas, United States
...
(797–802), the iconoclasts returned. Emperor
Theophilus
Theophilus is a male given name with a range of alternative spellings. Its origin is the Greek word Θεόφιλος from θεός (''theós'', "God") and φιλία (''philía'', "love or affection") can be translated as "Love of God" or "Friend ...
() had two-winged bronze doors with his
monogram
A monogram is a motif (visual arts), motif made by overlapping or combining two or more letters or other graphemes to form one symbol. Monograms are often made by combining the initials of an individual or a company, used as recognizable symbo ...
s installed at the southern entrance of the church.
The basilica suffered damage, first in a great fire in 859, and again in an earthquake in 869 that caused the collapse of one of the half-domes.
Emperor
Basil I
Basil I, nicknamed "the Macedonian" (; 811 – 29 August 886), was Byzantine emperor from 867 to 886. Born to a peasant family in Macedonia, he rose to prominence in the imperial court after gaining the favour of Emperor Michael III, whose mist ...
ordered repair of the tympanas, arches, and vaults.
In his book ''
De Ceremoniis
The or (fully ) is the conventional Latin name for a Greek book of ceremonial protocol at the court of the Byzantine emperors in Constantinople. Its Greek title is often cited as ("Explanation of the Order of the Palace"), taken from the work' ...
'' ("Book of Ceremonies"), the emperor
Constantine VII
Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus (; 17 May 905 – 9 November 959) was the fourth Byzantine emperor of the Macedonian dynasty, reigning from 6 June 913 to 9 November 959. He was the son of Emperor Leo VI and his fourth wife, Zoe Karbonopsina, an ...
() wrote a detailed account of the ceremonies held in the Hagia Sophia by the emperor and the patriarch.
Early in the 10th century, the pagan ruler of the
Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rus', also known as Kyivan Rus,.
* was the first East Slavs, East Slavic state and later an amalgam of principalities in Eastern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical At ...
sent emissaries to his neighbors to learn about Judaism, Islam, and Roman and Orthodox Christianity. After visiting Hagia Sophia his emissaries reported back: "We were led into a place where they serve their God, and we did not know where we were, in heaven or on earth."
In the 940s or 950s, probably around 954 or 955, after the
Rus'–Byzantine War of 941 and the death of the
Grand Prince of Kiev
The Grand Prince of Kiev (sometimes also Grand Duke) was the title of the monarch of Kievan Rus', residing in Kiev (modern Kyiv) from the 10th to 13th centuries. In the 13th century, Kiev became an appanage principality first of the grand prin ...
,
Igor I (), his widow
Olga of Kiev
Olga (; ; – 11 July 969) was a regent of Kievan Rus' for her son Sviatoslav from 945 until 957. Following her baptism, Olga took the name Elenа. She is known for her subjugation of the Drevlians, a tribe that had killed her husband Igor. E ...
– regent for her infant son
Sviatoslav I () – visited the emperor Constantine VII and was received as queen of the
Rus'
Rus or RUS may refer to:
People
* East Slavic historical peoples (). See Names of Rus', Russia and Ruthenia
** Rus' people, the people of Rus'
** Rus, a legendary eponymous ancestor, see Lech, Czech and Rus
* Rus (surname), a surname found in Ro ...
in Constantinople.
She was probably baptized in Hagia Sophia's baptistery, taking the name of the reigning ''augusta'',
Helena Lecapena, and receiving the titles
''zōstē patrikía'' and the styles of ''
archon
''Archon'' (, plural: , ''árchontes'') is a Greek word that means "ruler", frequently used as the title of a specific public office. It is the masculine present participle of the verb stem , meaning "to be first, to rule", derived from the same ...
tissa'' and
hegemon
Hegemony (, , ) is the political, economic, and military predominance of one state over other states, either regional or global.
In Ancient Greece (ca. 8th BC – AD 6th c.), hegemony denoted the politico-military dominance of the ''hegemon'' ...
of the Rus'.
Her baptism was an important step towards the
Christianization of the Kievan Rus', though the emperor's treatment of her visit in ''De caerimoniis'' does not mention baptism.
According to an early 14th-century source, the second church in Kiev,
Saint Sophia's, was founded in ''
anno mundi
(from Latin 'in the year of the world'; ), abbreviated as AM or A.M., or Year After Creation, is a calendar era based on biblical accounts of the creation of the world and subsequent history. Two such calendar eras of notable use are:
* Sin ...
'' 6460 in the
Byzantine calendar
The Byzantine calendar, also called the Roman calendar, the Creation Era of Constantinople or the Era of the World (, also or ; 'Roman year since the creation of the universe', abbreviated as ε.Κ.), was the calendar used by the Eastern Orth ...
, or .
The name of this future cathedral of Kiev probably commemorates Olga's baptism.
After an earthquake in 989 collapsed the western dome arch, Emperor
Basil II
Basil II Porphyrogenitus (; 958 – 15 December 1025), nicknamed the Bulgar Slayer (, ), was the senior Byzantine emperor from 976 to 1025. He and his brother Constantine VIII were crowned before their father Romanos II died in 963, but t ...
asked for the Armenian architect
Trdat, creator of the
Cathedral of Ani
The Cathedral of Ani (, ''Anii mayr tačar''; ) is the largest standing building in Ani, the capital city of medieval Bagratid Armenia, located in present-day eastern Turkey, on the border with modern Armenia. Its construction was completed in t ...
, to direct the repairs. He erected again and reinforced the fallen dome arch, and rebuilt the west side of the dome with 15 dome ribs.
[Müller-Wiener (1977), p. 87.] The extent of the damage required six years of repair and reconstruction; the church was re-opened on 13 May 994. At the end of the reconstruction, the church's decorations were renovated, including the addition of four immense paintings of cherubs; a new depiction of Christ on the dome; a burial cloth of Christ shown on Fridays, and on the
apse
In architecture, an apse (: apses; from Latin , 'arch, vault'; from Ancient Greek , , 'arch'; sometimes written apsis; : apsides) is a semicircular recess covered with a hemispherical Vault (architecture), vault or semi-dome, also known as an ' ...
a new depiction of the Virgin Mary holding Jesus, between the apostles Peter and Paul.
[Mamboury (1953) p. 287] On the great side arches were painted the prophets and the teachers of the church.
In 1181, the daughter of the emperor Manuel I,
Maria Comnena, and her husband, the ''
caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (12 or 13 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war. He ...
''
Renier of Montferrat
Renier of Montferrat (; ) (1162–1183) was the fifth son of William V of Montferrat and Judith of Babenberg. He became son-in-law of the Byzantine Emperor Manuel I Komnenos and ''Caesar'' in 1180, and was later murdered in a Byzantine power-strug ...
, fled to Hagia Sophia at the culmination of their dispute with the empress
Maria of Antioch
Maria of Antioch (; 1145–1182) was a Byzantine empress by marriage to Byzantine Emperor Manuel I Komnenos, and regent during the minority of her son porphyrogennetos Alexios II Komnenos from 1180 until 1182.
Early life
Maria of Antioch wa ...
, regent for her son, the emperor
Alexius II Comnenus.
Maria Comnena and Renier occupied the cathedral with the support of the patriarch, refusing the imperial administration's demands for a peaceful departure.
According to Niketas Choniates, they "transformed the sacred courtyard into a military camp", garrisoned the entrances to the complex with locals and mercenaries, and despite the strong opposition of the patriarch, made the "house of prayer into a den of thieves or a well-fortified and precipitous stronghold", while "all the dwellings adjacent to Hagia Sophia and adjoining the Augusteion were demolished by
aria'smen".
[Niketas Choniates, ''Annals,'' CCXXX–CCXLII. ] A battle ensued in the Augustaion and around the
Milion
The Milion ( or , ''Mílion''; ) was a marker from which all distances across the Roman Empire were measured. Erected by Septimius Severus in the 3rd century AD in the city of Byzantium, it became the zero-mile marker for the empire upon the r ...
, during which the defenders fought from the "gallery of the Catechumeneia (also called the Makron)" facing the Augusteion, from which they eventually retreated and took up positions in the exonarthex of Hagia Sophia itself.
At this point, "the patriarch was anxious lest the enemy troops enter the temple, with unholy feet trample the holy floor, and with hands defiled and dripping with blood still warm plunder the all-holy dedicatory offerings".
After a successful sally by Renier and his knights, Maria requested a truce, the imperial assault ceased, and an amnesty was negotiated.
Greek historian
Niketas Choniates
Niketas or Nicetas Choniates (; – 1217), whose actual surname was Akominatos (), was a Byzantine Greek historian and politician. He accompanied his brother Michael Akominatos to Constantinople from their birthplace Chonae (from which came h ...
compared the preservation of the cathedral to the efforts made by the 1st-century emperor
Titus
Titus Caesar Vespasianus ( ; 30 December 39 – 13 September AD 81) was Roman emperor from 79 to 81. A member of the Flavian dynasty, Titus succeeded his father Vespasian upon his death, becoming the first Roman emperor ever to succeed h ...
to avoid the destruction of the
Second Temple
The Second Temple () was the Temple in Jerusalem that replaced Solomon's Temple, which was destroyed during the Siege of Jerusalem (587 BC), Babylonian siege of Jerusalem in 587 BCE. It was constructed around 516 BCE and later enhanced by Herod ...
during the
siege of Jerusalem in the
First Jewish–Roman War
The First Jewish–Roman War (66–74 CE), also known as the Great Jewish Revolt, the First Jewish Revolt, the War of Destruction, or the Jewish War, was the first of three major Jewish rebellions against the Roman Empire. Fought in the prov ...
.
Choniates reports that in 1182, a white
hawk
Hawks are birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. They are very widely distributed and are found on all continents, except Antarctica.
The subfamily Accipitrinae includes goshawks, sparrowhawks, sharp-shinned hawks, and others. This ...
wearing
jesses was seen to fly from the east to Hagia Sophia, flying three times from the "building of the ''Thōmaitēs''" (a basilica erected on the southeastern side of the Augustaion) to the
Palace of the Kathisma
A palace is a large residence, often serving as a royal residence or the home for a head of state or another high-ranking dignitary, such as a bishop or archbishop. The word is derived from the Latin name palātium, for Palatine Hill in Rome whi ...
in the
Great Palace
The Great Palace of Constantinople (, ''Méga Palátion''; ), also known as the Sacred Palace (, ''Hieròn Palátion''; ), was the large imperial Byzantine palace complex located in the south-eastern end of the peninsula today making up the Fati ...
, where new emperors were
acclaimed
An acclamation is a form of election that does not use a ballot. It derives from the ancient Roman word ''acclamatio'', a kind of ritual greeting and expression of approval towards imperial officials in certain social contexts.
Voting Voice vot ...
.
[Niketas Choniates, ''Annals,'' CCLI–CCLII. ] This was supposed to presage the end of the reign of
Andronicus I Comnenus ().
Choniates writes that in 1203, during the
Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid S ...
, the emperors
Isaac II Angelus and
Alexius IV Angelus stripped Hagia Sophia of all gold ornaments and silver oil-lamps to pay off the Crusaders who had ousted
Alexius III Angelus
Alexios III Angelos (; 1211), Latinized as Alexius III Angelus, was Byzantine Emperor from March 1195 to 17/18 July 1203. He reigned under the name Alexios Komnenos (; Aléxios Komnēnós) associating himself with the Komnenos dynasty (from whi ...
and helped Isaac return to the throne. In the
Sack of Constantinople
The sack of Constantinople occurred in April 1204 and marked the culmination of the Fourth Crusade. Crusaders sacked and destroyed most of Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire. After the capture of the city, the Latin Empire ( ...
in 1204, the church was further ransacked and desecrated by the Crusaders, as described by Choniates, though he did not witness the events in person. According to his account, Hagia Sophia was stripped of its remaining metal ornaments, its altar was smashed into pieces, and a "woman laden with sins" sang and danced on the
synthronon
''Synthronon'' (; plural: σύνθρονα, ''synthrona'') is a semicircular tiered structure at the back of the altar in the liturgical apse of an Eastern Orthodox church that combines benches reserved for the clergy, with the bishop's throne in t ...
.
He adds that mules and donkeys were brought into the cathedral's sanctuary to carry away the spoils, and that one of them slipped on the marble floor and was accidentally disembowelled, further contaminating the place.
According to
Ali ibn al-Athir, whose treatment of the Sack of Constantinople was probably dependent on a Christian source, the Crusaders massacred some clerics who had surrendered. Much of the interior was damaged and would not be repaired until its return to Orthodox control in 1261.
The sack of Hagia Sophia, and Constantinople in general, remained a sore point in
Catholic–Eastern Orthodox relations
The Catholic Church and Eastern Orthodox Church broke communion during the East–West Schism, East–West Schism of 1054. While an informal divide between the East and West existed prior to the split, these were internal disputes, under the umb ...
.
During the
Latin occupation
The Frankish Occupation (; anglicized as ), also known as the Latin Occupation () and, for the Venetian domains, Venetian Occupation (), was the period in Greek history after the Fourth Crusade (1204), when a number of primarily French ...
of Constantinople (1204–1261), the church became a Latin Catholic cathedral.
Baldwin I of Constantinople () was crowned emperor on 16 May 1204 in Hagia Sophia in a ceremony which closely followed Byzantine practices.
Enrico Dandolo
Enrico Dandolo (Anglicised as Henry Dandolo, and Latinised as Henricus Dandulus; – May/June 1205) was the doge of Venice from 1192 until his death in 1205. He is remembered for his avowed piety, longevity, and shrewdness, and his role in the ...
, the
Doge
Doge, DoGE or DOGE may refer to:
Internet culture
* Doge (meme), an Internet meme primarily associated with the Shiba Inu dog breed
** Dogecoin, a cryptocurrency named after the meme
** Kabosu (dog), the dog portrayed in the original Doge image ...
of
Venice
Venice ( ; ; , formerly ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are li ...
who commanded the sack and invasion of the city in 1204, is buried inside the church, probably in the upper eastern
gallery
Gallery or The Gallery may refer to:
* Gallery (surname), a surname
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Art gallery
** Contemporary art gallery
** Online art gallery
Music
* Gallery (band), an American soft rock band of the 1970s
Albums
* ' ...
. In the 19th century, an Italian restoration team placed a
cenotaph
A cenotaph is an empty grave, tomb or a monument erected in honor of a person or group of people whose remains are elsewhere or have been lost. It can also be the initial tomb for a person who has since been reinterred elsewhere. Although t ...
marker, frequently mistaken as being a medieval artifact, near the probable location and is still visible. The original tomb was destroyed by the Ottomans during the conversion of the church into a mosque.
Upon the capture of Constantinople in 1261 by the
Empire of Nicaea
The Empire of Nicaea (), also known as the Nicene Empire, was the largest of the three Byzantine Greeks, Byzantine Greek''A Short history of Greece from early times to 1964'' by Walter Abel Heurtley, W. A. Heurtley, H. C. Darby, C. W. Crawley, C ...
and the emperor
Michael VIII Palaeologus
Michael VIII Palaiologos or Palaeologus (; 1224 – 11 December 1282) reigned as Byzantine emperor from 1261 until his death in 1282, and previously as the co-emperor of the Empire of Nicaea from 1259 to 1261. Michael VIII was the founder of th ...
, (), the church was in a dilapidated state. In 1317, emperor
Andronicus II Palaeologus
Andronikos II Palaiologos (; 25 March 1259 – 13 February 1332), Latinized as Andronicus II Palaeologus, reigned as Byzantine emperor from 1282 to 1328. His reign marked the beginning of the recently restored empire's final decline. ...
() ordered four new
buttress
A buttress is an architectural structure built against or projecting from a wall which serves to support or reinforce the wall. Buttresses are fairly common on more ancient (typically Gothic) buildings, as a means of providing support to act ...
es () to be built in the eastern and northern parts of the church, financing them with the inheritance of his late wife,
Irene of Montferrat
Yolande of Montferrat ( – 1317 in Drama) (also known as Violante, then Empress Irene) was the second wife of Andronikos II Palaiologos and thus Empress of the Byzantine Empire. She was the heiress of the Margraviate of Montferrat.
Life
Born ...
(1314).
[Müller-Wiener (1977), p. 91.] New cracks developed in the dome after the earthquake of October 1344, and several parts of the building collapsed on 19 May 1346. Repairs by architects
Astras
Astras () is a mountain village of the Elis region in West Greece. A formerly independent community, it became part of the municipality of Lampeia as a result of the 1997 Kapodistrias reform. At the 2011 Kallikratis reform, Lampeia became a munici ...
and Peralta began in 1354.
On 12 December 1452,
Isidore of Kiev
Isidore or Isidor of Kiev, also known as Isidore of Thessalonica (1385 – 27 April 1463), was a prelate of Byzantine Greek origin. From 1437 to 1441, he served as the metropolitan of Kiev and all Rus', based in Moscow, after being chosen by ...
proclaimed in Hagia Sophia the long-anticipated ecclesiastical union between the western Catholic and eastern Orthodox Churches as decided at the
Council of Florence
The Council of Florence is the seventeenth ecumenical council recognized by the Catholic Church, held between 1431 and 1445. It was convened in territories under the Holy Roman Empire. Italy became a venue of a Catholic ecumenical council aft ...
and decreed by the
papal bull
A papal bull is a type of public decree, letters patent, or charter issued by the pope of the Catholic Church. It is named after the leaden Seal (emblem), seal (''bulla (seal), bulla'') traditionally appended to authenticate it.
History
Papal ...
''
Laetentur Caeli'', though it would be short-lived. The union was unpopular among the Byzantines, who had already expelled the Patriarch of Constantinople,
Gregory III, for his pro-union stance. A new patriarch was not installed until after the Ottoman conquest. According to the Greek historian
Doukas
The House of Doukas ( pl. Doukai; , pl. , feminine form Doukaina; ), Latinized as Ducas, was a Byzantine Greek noble family, whose branches provided several notable generals and rulers to the Byzantine Empire in the 9th–11th centuries. A mat ...
, the Hagia Sophia was tainted by these Catholic associations, and the anti-union Orthodox faithful avoided the cathedral, considering it to be a haunt of
demon
A demon is a malevolent supernatural entity. Historically, belief in demons, or stories about demons, occurs in folklore, mythology, religion, occultism, and literature; these beliefs are reflected in Media (communication), media including
f ...
s and a "Hellenic" temple of
Roman paganism
Religion in ancient Rome consisted of varying imperial and provincial religious practices, which were followed both by the people of Rome as well as those who were brought under its rule.
The Romans thought of themselves as highly religious, ...
. Doukas also notes that after the ''Laetentur Caeli'' was proclaimed, the Byzantines dispersed discontentedly to nearby venues where they drank toasts to the
Hodegetria
A Hodegetria, or Virgin Hodegetria, is an iconography, iconographic depiction of the Theotokos (Virgin Mary) holding the Child Jesus at her side while pointing to him as the source of salvation for humankind. The Virgin's head usually inclines t ...
icon, which had, according to late Byzantine tradition, interceded to save them in the former
sieges of Constantinople
Constantinople (part of modern Istanbul, Turkey) was built on the land that links Europe to Asia through Bosporus and connects the Sea of Marmara and the Black Sea. As a transcontinental city within the Silk Road, Constantinople had a strategic ...
by the
Avar Khaganate
The Pannonian Avars ( ) were an alliance of several groups of Eurasian nomads of various origins. The peoples were also known as the Obri in the chronicles of the Rus' people, Rus, the Abaroi or Varchonitai (), or Pseudo-Avars in Byzantine Empi ...
and the
Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate or Umayyad Empire (, ; ) was the second caliphate established after the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and was ruled by the Umayyad dynasty. Uthman ibn Affan, the third of the Rashidun caliphs, was also a member o ...
.
According to ''
Nestor Iskander's Tale on the Taking of Tsargrad
Nestor may refer to:
* Nestor (mythology), King of Pylos in Greek mythology
Arts and entertainment
* "Nestor" (''Ulysses'' episode) an episode in James Joyce's novel ''Ulysses''
* Nestor Studios, first-ever motion picture studio in Hollywood, L ...
'', the Hagia Sophia was the focus of an alarming
omen
An omen (also called ''portent'') is a phenomenon that is believed to foretell the future, often signifying the advent of change. It was commonly believed in ancient history, and still believed by some today, that omens bring divine messages ...
interpreted as the
Holy Spirit
The Holy Spirit, otherwise known as the Holy Ghost, is a concept within the Abrahamic religions. In Judaism, the Holy Spirit is understood as the divine quality or force of God manifesting in the world, particularly in acts of prophecy, creati ...
abandoning Constantinople on 21 May 1453, in the final days of the Siege of Constantinople.
The sky lit up, illuminating the city, and
many people gathered and saw on the Church of the Wisdom, at the top of the window, a large flame of fire issuing forth. It encircled the entire neck of the church for a long time. The flame gathered into one; its flame altered, and there was an indescribable light. At once it took to the sky. ... The light itself has gone up to heaven; the gates of heaven were opened; the light was received; and again they were closed.
The eventual fall of Constantinople had long been predicted in
apocalyptic literature
Apocalyptic literature is a genre of prophetical writing that developed in post- Exilic Jewish culture and was popular among millennialist early Christians. '' Apocalypse'' () is a Greek word meaning "revelation", "an unveiling or unfolding o ...
.
Hagia Sophia is mentioned in a hagiography of uncertain date detailing the life of the Eastern Orthodox saint
Andrew the Fool
Andrew of Constantinople (Andrew the Fool-for-Christ or Andrew, the Fool; ; died 936) is considered a saint by the Eastern Orthodox Church, and is revered as a fool for Christ.
Biography
Andrew, a Scythian by birth, was a slave of Theognostus, ...
.
The text is self-attributed to Nicephorus, a priest of Hagia Sophia, and contains a description of the
end time in the form of a dialogue, in which the interlocutor, upon being told by the saint that Constantinople will be sunk in a flood and that "the waters as they gush forth will irresistibly deluge her and cover her and surrender her to the terrifying and immense sea of the abyss", says "some people say that the Great Church of God will not be submerged with the city but will be suspended in the air by an invisible power".
The reply is given that "When the whole city sinks into the sea, how can the Great Church remain? Who will need her? Do you think God dwells in temples made with hands?"
The
Column of Constantine
The Column of Constantine (; ; ) is a monumental column commemorating the dedication of Constantinople by Roman emperor Constantine the Great on 11 May 330 AD. Completed , it is the oldest Constantinian monument to survive in Istanbul. The colu ...
, however, is prophesied to endure.
According to
Laonicus Chalcocondyles
Laonikos Chalkokondyles (; – ), also latinized as Laonicus Chalcocondyles, was a Byzantine Greek historian from Athens. He is known for his '' Demonstrations of Histories'' in ten books, which record the last 150 years of the Byzantine Empi ...
, Hagia Sophia was a refuge for the population during the city's capture.
Despite the ill-repute and empty state of Hagia Sophia after December 1452, Doukas writes that after the Theodosian Walls were breached, the Byzantines took refuge there as the Turks advanced through the city.
He attributes their change of heart to a prophecy.
In accordance with the traditional custom of the time, Sultan
Mehmed II allowed three full days of unbridled pillage in the city shortly after it was captured. This period saw the destruction of many Orthodox churches; Hagia Sophia itself was looted as the invaders believed it to contain the greatest treasures of the city.
[Nicol. ''The End of the Byzantine Empire'', p. 90.] Shortly after the defence of the
Walls of Constantinople
The Walls of Constantinople (; ) are a series of defensive wall, defensive stone walls that have surrounded and protected the city of Constantinople (modern Fatih district of Istanbul) since its founding as the new capital of the Roman Empire b ...
collapsed and the victorious Ottoman troops entered the city, the pillagers and looters made their way to the Hagia Sophia and battered down its doors before storming inside.
Once the three days passed, Mehmed was to claim the city's remaining contents for himself.
However, by the end of the first day, he proclaimed that the looting should cease as he felt profound sadness when he toured the city.
Throughout the siege of Constantinople, the trapped people of the city participated in the
Divine Liturgy
Divine Liturgy () or Holy Liturgy is the usual name used in most Eastern Christian rites for the Eucharistic service.
The Eastern Catholic Churches, Eastern Lutheranism, Eastern Lutheran Churches and the Eastern Orthodox Church believe the Divi ...
and the Prayer of the Hours at the Hagia Sophia, and the church was a refuge for many of those who were unable to contribute to the city's defence, including women, children, elderly, the sick and the wounded.
[Runciman. ''The Fall of Constantinople'', pp. 133–34.][Nicol, Donald M. ''The Last Centuries of Byzantium 1261–1453''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1972, p. 389.] As they were trapped in the church, the many congregants and other refugees became spoils-of-war to be divided amongst the triumphant invaders. The building was desecrated and looted, and those who sought shelter within the church were enslaved.
While most of the elderly and the infirm, injured, and sick were killed, the remainder (mainly teenage males and young boys) were chained and sold into
slavery in the Ottoman Empire
Chattel slavery was a major institution and a significant part of the Ottoman Empire's economy and traditional society.
The main sources of slaves were wars and politically organized enslavement expeditions in the Caucasus, Eastern Europe, S ...
.
Mosque (1453–1935)
Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
fell to the attacking Ottoman forces on 29 May 1453.
Sultan Mehmed II entered the city and performed the
Friday prayer
Friday prayer, or congregational prayer (), is the meeting together of Muslims for communal prayer and service at midday every Friday. In Islam, the day itself is called ''Yawm al-Jum'ah'' (shortened to ''Jum'ah''), which translated from Arabic me ...
and ''
khutbah
''Khutbah'' (, ''khuṭbah''; , ''khotbeh''; ) serves as the primary formal occasion for public sermon, preaching in the Islamic tradition.
Such sermons occur regularly, as prescribed by the teachings of all legal schools. The Islamic traditio ...
'' (sermon) in Hagia Sophia. The church's priests and religious personnel continued to perform Christian rites, prayers, and ceremonies until they were compelled to stop by the invaders.
When Mehmed and his entourage entered the church, he ordered that it be converted into a mosque immediately. One of the
''ʿulamāʾ'' (Islamic scholars) present climbed onto the church's ambo and recited the ''
shahada
The ''Shahada'' ( ; , 'the testimony'), also transliterated as ''Shahadah'', is an Islamic oath and creed, and one of the Five Pillars of Islam and part of the Adhan. It reads: "I bear witness that there is no Ilah, god but God in Islam, God ...
'' ("There is no god but Allah, and
Muhammad
Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious and political leader and the founder of Islam. Muhammad in Islam, According to Islam, he was a prophet who was divinely inspired to preach and confirm the tawhid, monotheistic teachings of A ...
is his messenger"), thus marking the
conversion of the church into a mosque.
Mehmed is reported to have taken a sword to a soldier who tried to pry up one of the paving slabs of the Proconnesian marble floor.
As described by Western visitors before 1453, such as the
Córdoban nobleman
Pero Tafur and the
Florentine geographer
Cristoforo Buondelmonti
Cristoforo Buondelmonti () was an Italian Franciscan priest, traveler, and was a pioneer in promoting first-hand knowledge of Greece and its antiquities throughout the Western world.
Biography
Cristoforo Buondelmonti was born around 1385 into an ...
, the church was in a dilapidated state, with several of its doors fallen from their hinges. Mehmed II ordered a renovation of the building. Mehmed attended the first Friday prayer in the mosque on 1 June 1453.
[Mamboury (1953), p. 288.] Aya Sofya became the first imperial mosque of Istanbul.
[Necipoĝlu (2005), p. 13] Most of the existing houses in the city and the area of the future
Topkapı Palace
The Topkapı Palace (; ), or the Seraglio, is a large museum and library in the east of the Fatih List of districts of Istanbul, district of Istanbul in Turkey. From the 1460s to the completion of Dolmabahçe Palace in 1856, it served as the ad ...
were endowed to the corresponding
waqf
A (; , plural ), also called a (, plural or ), or ''mortmain'' property, is an Alienation (property law), inalienable charitable financial endowment, endowment under Sharia, Islamic law. It typically involves donating a building, plot ...
.
From 1478, 2,360 shops, 1,300 houses, 4
caravanserai
A caravanserai (or caravansary; ) was an inn that provided lodging for travelers, merchants, and Caravan (travellers), caravans. They were present throughout much of the Islamic world. Depending on the region and period, they were called by a ...
s, 30 ''
boza
Boza, also bosa, is a fermented beverage originating from Central Asia and made in parts of the Balkans, Turkey, Central Asia, the Caucasus, and North Africa. It is a malt drink made by fermenting various grains: maize (corn) and wheat in Turkey ...
'' shops, and 23 shops of sheep heads and trotters gave their income to the foundation.
[Boyar & Fleet (2010), p. 145] Through the imperial charters of 1520 and 1547, shops and parts of the
Grand Bazaar and other markets were added to the foundation.
Before 1481, a small
minaret
A minaret is a type of tower typically built into or adjacent to mosques. Minarets are generally used to project the Muslim call to prayer (''adhan'') from a muezzin, but they also served as landmarks and symbols of Islam's presence. They can h ...
was erected on the southwest corner of the building, above the stair tower.
Mehmed's successor
Bayezid II () later built another minaret at the northeast corner.
One of the minarets collapsed after the
earthquake of 1509,
and around the middle of the 16th century they were both replaced by two diagonally opposite minarets built at the east and west corners of the edifice.
In 1498,
Bernardo Bonsignori was the last Western visitor to Hagia Sophia to report seeing the ancient Justinianic floor; shortly afterwards the floor was covered over with carpet and not seen again until the 19th century.
In the 16th century, Sultan
Suleiman the Magnificent
Suleiman I (; , ; 6 November 14946 September 1566), commonly known as Suleiman the Magnificent in the Western world and as Suleiman the Lawgiver () in his own realm, was the List of sultans of the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman sultan between 1520 a ...
() brought two colossal candlesticks from his
conquest
Conquest involves the annexation or control of another entity's territory through war or Coercion (international relations), coercion. Historically, conquests occurred frequently in the international system, and there were limited normative or ...
of the
Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from 1000 to 1946 and was a key part of the Habsburg monarchy from 1526-1918. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the Coro ...
and placed them on either side of the ''
mihrab
''Mihrab'' (, ', pl. ') is a niche in the wall of a mosque that indicates the ''qibla'', the direction of the Kaaba in Mecca towards which Muslims should face when praying. The wall in which a ''mihrab'' appears is thus the "''qibla'' wall".
...
''. During Suleiman's reign, the mosaics above the
narthex
The narthex is an architectural element typical of Early Christian art and architecture, early Christian and Byzantine architecture, Byzantine basilicas and Church architecture, churches consisting of the entrance or Vestibule (architecture), ve ...
and imperial gates depicting Jesus, Mary, and various Byzantine emperors were covered by whitewash and plaster, which were removed in 1930 under the Turkish Republic.

During the reign of
Selim II (), the building started showing signs of fatigue and was extensively strengthened with the addition of structural supports to its exterior by Ottoman architect
Mimar Sinan
Mimar Sinan (; , ; – 17 July 1588) also known as Koca Mi'mâr Sinân Âğâ, ("Sinan Agha (title), Agha the Grand Architect" or "Grand Sinan") was the chief Ottoman Empire, Ottoman architect, engineer and mathematician for sultans Suleiman ...
, who was also an earthquake engineer.
In addition to strengthening the historic Byzantine structure, Sinan built two additional large minarets at the western end of the building, the original sultan's lodge and the
türbe
''Türbe'' refers to a Muslim mausoleum, tomb or grave often in the Turkish-speaking areas and for the mausolea of Ottoman sultans, nobles and notables. A typical türbe is located in the grounds of a mosque or complex, often endowed by the ...
(mausoleum) of Selim II to the southeast of the building in 1576–1577. In order to do that, parts of the Patriarchate at the south corner of the building were pulled down the previous year.
Moreover, the golden
crescent
A crescent shape (, ) is a symbol or emblem used to represent the lunar phase (as it appears in the northern hemisphere) in the first quarter (the "sickle moon"), or by extension a symbol representing the Moon itself.
In Hindu iconography, Hind ...
was mounted on the top of the dome,
and a respect zone 35 ''
arşın
The arshin or arşın is an old Turkish and Russian unit of length ( or )
The Turkish "market arşın" was about long. The masonry arşın was 75.774 cm on average (mason's arşın = 24 parmak = 240 ḫaṭṭ) The usage of arşın was gradual ...
'' (about 24 m) wide was imposed around the building, leading to the demolition of all houses within the perimeter.
The türbe became the location of the tombs of 43 Ottoman princes.
Murad III
Murad III (; ; 4 July 1546 – 16 January 1595) was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1574 until his death in 1595. His rule saw battles with the Habsburg monarchy, Habsburgs and exhausting wars with the Safavid Iran, Safavids. The long-inde ...
() imported two large
alabaster
Alabaster is a mineral and a soft Rock (geology), rock used for carvings and as a source of plaster powder. Archaeologists, geologists, and the stone industry have different definitions for the word ''alabaster''. In archaeology, the term ''alab ...
Hellenistic
urns
An urn is a vase, often with a cover, with a typically narrowed neck above a rounded body and a footed pedestal. Describing a vessel as an "urn", as opposed to a vase or other terms, generally reflects its use rather than any particular shape ...
from
Pergamon
Pergamon or Pergamum ( or ; ), also referred to by its modern Greek form Pergamos (), was a rich and powerful ancient Greece, ancient Greek city in Aeolis. It is located from the modern coastline of the Aegean Sea on a promontory on the north s ...
(
Bergama
Bergama is a municipality and district of İzmir Province, Turkey. Its area is 1,544 km2, and its population is 105,754 (2022). By excluding İzmir's metropolitan area, it is one of the prominent districts of the province in terms of populatio ...
) and placed them on two sides of the nave.
In 1594 ''Mimar'' (court architect)
Davud Ağa
Davud Agha was the chief imperial architect of the Ottoman Empire from 1588, after the death of his predecessor Sinan, until his death in 1598 or 1599. His works include various monuments from the classical period of Ottoman architecture.
Caree ...
built the türbe of Murad III, where the Sultan and his
''valide'',
Safiye Sultan were buried.
The octagonal mausoleum of their son
Mehmed III
Mehmed III (, ''Meḥmed-i sālis''; ; 26 May 1566 – 22 December 1603) was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1595 until his death in 1603. Mehmed was known for ordering the execution of his brothers and leading the army in the Long Turkish ...
() and his ''valide'' was built next to it in 1608 by royal architect Dalgiç Mehmet Aĝa.
[Müller-Wiener (1977), p. 93.] His son
Mustafa I () converted the baptistery into his türbe.
In 1717, under the reign of Sultan
Ahmed III
Ahmed III (, ''Aḥmed-i sālis''; was sultan of the Ottoman Empire and a son of sultan Mehmed IV (r. 1648–1687). His mother was Gülnuş Sultan, originally named Evmania Voria, who was an ethnic Greek. He was born at Hacıoğlu Pazarcık, ...
(), the crumbling plaster of the interior was renovated, contributing indirectly to the preservation of many mosaics, which otherwise would have been destroyed by mosque workers.
It was usual for the mosaic's
tesserae
A tessera (plural: tesserae, diminutive ''tessella'') is an individual tile, usually formed in the shape of a square, used in creating a mosaic. It is also known as an abaciscus or abaculus.
Historical tesserae
In early antiquity, mo ...
—believed to be
talisman
A talisman is any object ascribed with religious or magical powers intended to protect, heal, or harm individuals for whom they are made. Talismans are often portable objects carried on someone in a variety of ways, but can also be installed perm ...
s—to be sold to visitors.
Sultan
Mahmud I ordered the restoration of the building in 1739 and added a ''
medrese
Madrasa (, also , ; Arabic: مدرسة , ), sometimes Romanization of Arabic, romanized as madrasah or madrassa, is the Arabic word for any Educational institution, type of educational institution, secular or religious (of any religion), whet ...
'' (a Koranic school, subsequently the library of the museum), an ''
imaret
Imaret, sometimes also known as a ''darüzziyafe'', is one of several names used to identify the public soup kitchens built throughout the Ottoman Empire from the 14th to the 19th centuries. These public kitchens were often part of a larger comp ...
'' (soup kitchen for distribution to the poor) and a library, and in 1740 he added a ''
Şadirvan'' (fountain for ritual ablutions), thus transforming it into a ''
külliye
A külliye () is a complex of buildings associated with Turkish architecture centered on a mosque and managed within a single institution, often based on a waqf (charitable foundation) and composed of a madrasa, a Dar al-Shifa (clinic), kitchens ...
'', or social complex. A new sultan's lodge and a new mihrab were built inside.
Renovation of 1847–1849
The 19th-century restoration of the Hagia Sophia was ordered by Sultan
Abdulmejid I () and completed between 1847 and 1849 by eight hundred workers under the supervision of the
Swiss-Italian architect brothers
Gaspare and Giuseppe Fossati. The brothers consolidated the dome with a restraining iron chain and strengthened the vaults, straightened the columns, and revised the decoration of the exterior and the interior of the building.
The mosaics in the upper gallery were exposed and cleaned, although many were recovered "for protection against further damage".
Eight new gigantic circular-framed discs or
medallions were hung from the
cornice
In architecture, a cornice (from the Italian ''cornice'' meaning "ledge") is generally any horizontal decorative Moulding (decorative), moulding that crowns a building or furniture element—for example, the cornice over a door or window, ar ...
, on each of the four piers and at either side of the apse and the west doors. These were designed by the calligrapher
Kazasker Mustafa Izzet Efendi
Kazasker Mustafa Izzet Efendi (, Turkish language, Modern Turkish: ''Kazasker Mustafa Izzet Efendi'') (alternative: Kadiasker Mustafa Izzet Efendi, Seyyid Mustafa) (b. 1801 Tosya – d. 16 November 1876 Istanbul), was an Ottoman Empire, Ottoman com ...
and painted with the names of
Allah
Allah ( ; , ) is an Arabic term for God, specifically the God in Abrahamic religions, God of Abraham. Outside of the Middle East, it is principally associated with God in Islam, Islam (in which it is also considered the proper name), althoug ...
,
Muhammad
Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious and political leader and the founder of Islam. Muhammad in Islam, According to Islam, he was a prophet who was divinely inspired to preach and confirm the tawhid, monotheistic teachings of A ...
, the
Rashidun
The Rashidun () are the first four caliphs () who led the Muslim community following the death of Muhammad: Abu Bakr (), Umar (), Uthman (), and Ali ().
The reign of these caliphs, called the Rashidun Caliphate (632–661), is considered i ...
(the first four caliphs), and the two grandsons of Muhammad. In 1850, the architects Fossati built a new
maqsura
''Maqsurah'' (, literally "closed-off space") is an enclosure, box, or wooden screen near the ''mihrab'' or the center of the ''qibla'' wall in a mosque. It was typically reserved for a Muslim ruler and his entourage, and was originally designed ...
or caliphal loge in
Neo-Byzantine
Neo-Byzantine architecture (also referred to as Byzantine Revival) was a Revivalism (architecture), revival movement, most frequently seen in religious, institutional and public buildings. It incorporates elements of the Byzantine architecture, ...
columns and an Ottoman–Rococo style marble grille connecting to the royal pavilion behind the mosque.
The new maqsura was built at the extreme east end of the northern aisle, next to the north-eastern pier. The existing maqsura in the apse, near the mihrab, was demolished.
A new entrance was constructed for the sultan: the .
The Fossati brothers also renovated the
minbar
A minbar (; sometimes romanized as ''mimber'') is a pulpit in a mosque where the imam (leader of prayers) stands to deliver sermons (, ''khutbah''). It is also used in other similar contexts, such as in a Hussainiya where the speaker sits and le ...
and
mihrab
''Mihrab'' (, ', pl. ') is a niche in the wall of a mosque that indicates the ''qibla'', the direction of the Kaaba in Mecca towards which Muslims should face when praying. The wall in which a ''mihrab'' appears is thus the "''qibla'' wall".
...
.
Outside the main building, the minarets were repaired and altered so that they were of equal height.
A clock building, the , was built by the Fossatis for use by the
muwaqqit
In the history of Islam, a ''muwaqqit'' (, more rarely ''mīqātī''; ) was an astronomer tasked with the timekeeping and the regulation of prayer times in an Islamic institution like a mosque or a madrasa. Unlike the muezzin (reciter of the ...
(the mosque timekeeper), and a new
madrasa
Madrasa (, also , ; Arabic: مدرسة , ), sometimes Romanization of Arabic, romanized as madrasah or madrassa, is the Arabic word for any Educational institution, type of educational institution, secular or religious (of any religion), whet ...
(Islamic school) was constructed. The was also built under their direction.
When the restoration was finished, the mosque was re-opened with a ceremony on 13 July 1849. An edition of
lithographs
Lithography () is a planographic method of printing originally based on the miscibility, immiscibility of oil and water. The printing is from a stone (lithographic limestone) or a metal plate with a smooth surface. It was invented in 1796 by ...
from drawings made during the Fossatis' work on Hagia Sophia was published in
London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
in 1852, entitled: ''Aya Sophia of Constantinople as Recently Restored by Order of H.M. The Sultan Abdulmejid''.
Louis Haghe
Louis Haghe (17 March 1806 – 9 March 1885) was a lithographer and watercolourist from the Netherlands and then the United Kingdom.
His father and grandfather had practised as architects. Training in his teens in watercolour painting, he found ...
after Gaspard Fossati (1852).
File:Aya Sofia, Constantinople (BM 1889,0603.107).jpg, South-eastern side, seen from the Imperial Gate of the Topkapı Palace
The Topkapı Palace (; ), or the Seraglio, is a large museum and library in the east of the Fatih List of districts of Istanbul, district of Istanbul in Turkey. From the 1460s to the completion of Dolmabahçe Palace in 1856, it served as the ad ...
, with the Fountain of Ahmed III on the left and the Sultan Ahmed Mosque
The Blue Mosque, officially the Sultan Ahmed Mosque (), is an Ottoman-era historical imperial mosque located in Istanbul, Turkey. It was constructed between 1609 and 1617 during the rule of Ahmed I and remains a functioning mosque today. It al ...
in the distance. Lithograph by Louis Haghe after Gaspard Fossati (1852).
File:Vue de la nouvelle tribune impériale, prise entre les colonnes d'Ephèze, et ensuite de face - Fossati Gaspard - 1852.jpg, The imperial lodge ( 1850)
File:Aya Sofia, Constantinople (BM 1889,0603.120).jpg, Gaspare Fossati
The Fossati brothers, Gaspare (7 October 1809 – 5 September 1883) and Giuseppe (1822–1891), were Swiss architects. They completed more than 50 projects in Turkey (then the Ottoman Empire) during the Tanzimat era. They belonged to the Morcot ...
's 1852 depiction of the Hagia Sophia, after his and his brother's renovation. Lithograph by Louis Haghe
Louis Haghe (17 March 1806 – 9 March 1885) was a lithographer and watercolourist from the Netherlands and then the United Kingdom.
His father and grandfather had practised as architects. Training in his teens in watercolour painting, he found ...
.
File:L'intérieur et l'extérieur de la mosquée, avant sa restauration - Fossati Gaspard - 1852.jpg, Nave before restoration, facing east
File:Vue générale de la grande nef, en regardant l'orient - Fossati Gaspard - 1852.jpg, Nave and apse after restoration, facing east
File:Gaspare Fossati - Louis Haghe - Vue générale de la grande nef, en regardant l'occident (Hagia Sophia - Ayasofya Mosque nave).jpg, Nave and entrance after restoration, facing west
File:Nartex, ou Porche - Fossati Gaspard - 1852.jpg, Narthex, facing north
File:Entrée principale de la mosquée - Fossati Gaspard - 1852.jpg, Exonarthex, facing north
File:Vue de l'entrée du côté du nord - Fossati Gaspard - 1852.jpg, North aisle from the entrance, facing east
File:Vue prise du même point, en regardant le porche - Fossati Gaspard - 1852.jpg, North aisle, facing west
File:Vue centrale de la nef du nord - Fossati Gaspard - 1852.jpg, Nave and south aisle from the north aisle
File:Entrée du gynécée, ou galerie supérieure - Fossati Gaspard - 1852.jpg, Northern gallery and entrance to the ''matroneum'' from the north-west
File:Vues dans la même gallerie, prises dans l'angle sud-ouest - Fossati Gaspard - 1852.jpg, Southern gallery from the south-west
File:Vue du fond de la galerie, du côté oriental - Fossati Gaspard - 1852.jpg, Southern gallery from the Marble Door facing west
File:Centre de la galerie - Fossati Gaspard - 1852.jpg, Southern gallery from the Marble Door facing east
Occupation of Istanbul (1918–1923)

In the aftermath of the defeat of the Ottoman Empire in World War I, Constantinople was
occupied
' ( Norwegian: ') is a Norwegian political thriller TV series that premiered on TV2 on 5 October 2015. Based on an original idea by Jo Nesbø, the series is co-created with Karianne Lund and Erik Skjoldbjærg. Season 2 premiered on 10 October ...
by British, French, Italian, and Greek forces. On , the Greek Orthodox Christian military priest
Eleftherios Noufrakis
Archimandrite Eleftherios Noufrakis (; born ''Emmanuel Noufrakis'' (), 1872 or 1874, Alones, Rethymno, Crete; died 5 August 1941, Athens) was a Greek Orthodox military priest. He is known for performing the first and only Divine Liturgy in the Ha ...
performed an unauthorized
Divine Liturgy
Divine Liturgy () or Holy Liturgy is the usual name used in most Eastern Christian rites for the Eucharistic service.
The Eastern Catholic Churches, Eastern Lutheranism, Eastern Lutheran Churches and the Eastern Orthodox Church believe the Divi ...
in the Hagia Sophia, the only such instance since the 1453 fall of Constantinople.
The anti-occupation
Sultanahmet demonstrations were held next to Hagia Sophia from March to May 1919. In Greece, the 500
drachma
Drachma may refer to:
* Ancient drachma, an ancient Greek currency
* Modern drachma
The drachma ( ) was the official currency of modern Greece from 1832 until the launch of the euro in 2001.
First modern drachma
The drachma was reintroduce ...
banknotes issued in 1923 featured Hagia Sophia.
Museum (1935–2020)


In 1935, the first
Turkish President
The president of Turkey, officially the president of the Republic of Türkiye (), is the head of state and head of government of Turkey. The president directs the executive branch of the national government and is the commander-in-chief of the ...
and founder of the Republic of Turkey,
Mustafa Kemal Atatürk
Mustafa Kemal Atatürk ( 1881 – 10 November 1938) was a Turkish field marshal and revolutionary statesman who was the founding father of the Republic of Turkey, serving as its first President of Turkey, president from 1923 until Death an ...
, transformed the building into a museum. During the Second World War, the minarets of the museum housed
MG 08
The MG 08 ( 08) is a heavy machine gun (HMG) which served as the standard HMG of the Imperial German Army during World War I. It was an adaptation of Hiram Maxim's 1884 Maxim gun design, and was produced in a number of variants during the war. Th ...
machine guns. The carpet and the layer of mortar underneath were removed and marble floor decorations such as the ''
omphalion'' appeared for the first time since the
Fossatis' restoration, when the white plaster covering many of the mosaics had been removed. Due to neglect, the condition of the structure continued to deteriorate, prompting the
World Monuments Fund
World Monuments Fund (WMF) is a private, international, non-profit organization dedicated to the preservation of historic architecture and cultural heritage sites around the world through fieldwork, advocacy, grantmaking, education, and training ...
(WMF) to include the Hagia Sophia
in their 1996 and
1998 Watch Lists. The building's copper roof had cracked, causing water to leak down over the fragile frescoes and mosaics. Moisture entered from below as well. Rising
ground water
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available fresh water in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidat ...
increased the level of humidity within the monument, creating an unstable environment for stone and paint. The WMF secured a series of grants from 1997 to 2002 for the restoration of the dome. The first stage of work involved the structural stabilization and repair of the cracked roof, which was undertaken with the participation of the
Turkish Ministry of Culture and Tourism
The Ministry of Culture and Tourism () is a government ministry of the Republic of Turkey, responsible for culture and tourism affairs in Turkey. Revolving fund management of the ministry is carried by DÖSİMM. On July 9, 2018, the newly electe ...
. The second phase, the preservation of the dome's interior, afforded the opportunity to employ and train young Turkish
conservators In certain areas of England, conservators are statutory bodies which manage areas of countryside for the use of the public.
Establishment, role and powers
Conservators are bodies corporate generally established, and granted their powers, by a ...
in the care of mosaics. By 2006, the WMF project was complete, though many areas of Hagia Sophia continue to require significant stability improvement, restoration, and conservation.
In 2014, Hagia Sophia was the second most visited museum in Turkey, attracting almost 3.3 million visitors annually.

While use of the complex as a place of worship (mosque or church) was strictly prohibited, in 1991 the Turkish government allowed the allocation of a pavilion in the museum complex (''Ayasofya Müzesi Hünkar Kasrı'') for use as a prayer room, and, since 2013, two of the museum's minarets had been used for voicing the call to prayer (the
ezan) regularly.

From the early 2010s, several campaigns and government high officials, notably Turkey's deputy prime minister
Bülent Arınç
Bülent Arınç (; born 25 May 1948) is a conservative Turkish politician. He served as the 22nd Speaker of the Parliament of Turkey from 2002 to 2007 and as a Deputy Prime Minister of Turkey between 2009 and 2015. He also co-founded the Just ...
in November 2013, demanded the Hagia Sophia be converted back into a mosque. In 2015,
Pope Francis
Pope Francis (born Jorge Mario Bergoglio; 17 December 1936 – 21 April 2025) was head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 13 March 2013 until Death and funeral of Pope Francis, his death in 2025. He was the fi ...
publicly acknowledged the
Armenian genocide
The Armenian genocide was the systematic destruction of the Armenians, Armenian people and identity in the Ottoman Empire during World War I. Spearheaded by the ruling Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), it was implemented primarily t ...
, which is
officially denied in Turkey. In response, the mufti of Ankara, Mefail Hızlı, said he believed the Pope's remarks would accelerate the conversion of Hagia Sophia into a mosque.
On 1 July 2016, Muslim prayers were held again in the Hagia Sophia for the first time in 85 years. That November, a Turkish
NGO
A non-governmental organization (NGO) is an independent, typically nonprofit organization that operates outside government control, though it may get a significant percentage of its funding from government or corporate sources. NGOs often focus ...
, the ''Association for the Protection of Historic Monuments and the Environment'', filed a lawsuit for converting the museum into a mosque.
The court decided it should stay as a 'monument museum'. In October 2016, Turkey's
Directorate of Religious Affairs
Directorate may refer to:
Contemporary
*Directorates of the Scottish Government
* Directorate-General, a type of specialised administrative body in the European Union
* Directorate-General for External Security, the French external intelligence ag ...
(''Diyanet'') appointed, for the first time in 81 years, a designated
imam
Imam (; , '; : , ') is an Islamic leadership position. For Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslims, Imam is most commonly used as the title of a prayer leader of a mosque. In this context, imams may lead Salah, Islamic prayers, serve as community leaders, ...
, Önder Soy, to the Hagia Sophia mosque. Since then, the
adhan
The (, ) is the Islamic call to prayer, usually recited by a muezzin, traditionally from the minaret of a mosque, shortly before each of the five obligatory daily prayers. The adhan is also the first phrase said in the ear of a newborn baby, ...
has been regularly called out from the Hagia Sophia's minarets five times a day.
On 13 May 2017, a large group of people, organized by the Anatolia Youth Association, gathered in front of Hagia Sophia and prayed the morning prayer with a call for the re-conversion of the museum into a mosque. On 21 June 2017 the
Directorate of Religious Affairs
Directorate may refer to:
Contemporary
*Directorates of the Scottish Government
* Directorate-General, a type of specialised administrative body in the European Union
* Directorate-General for External Security, the French external intelligence ag ...
(') organized a special programme, broadcast live by state-run television
TRT, which included the recitation of the
Quran
The Quran, also Romanization, romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a Waḥy, revelation directly from God in Islam, God (''Allah, Allāh''). It is organized in 114 chapters (, ) which ...
and prayers in Hagia Sophia, to mark the
Laylat al-Qadr
In Islamic belief, Laylat al-Qadr () or Night of Power is an Islamic holidays, Islamic festival in memory of the night when the Quran was first sent down from Heaven in Islam, heaven to the world, the first Waḥy, revelation the Islamic proph ...
.
Reversion to mosque (2018–present)


Since 2018,
Turkish president
The president of Turkey, officially the president of the Republic of Türkiye (), is the head of state and head of government of Turkey. The president directs the executive branch of the national government and is the commander-in-chief of the ...
Recep Tayyip Erdoğan
Recep Tayyip Erdoğan (born 26 February 1954) is a Turkish politician who is the 12th and current president of Turkey since 2014. He previously served as the 25th prime minister of Turkey, prime minister from 2003 to 2014 as part of the Jus ...
had talked of reverting the status of the Hagia Sophia back to a mosque, as a populist gesture.
On 31 March 2018 Erdoğan recited the first verse of the
Quran
The Quran, also Romanization, romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a Waḥy, revelation directly from God in Islam, God (''Allah, Allāh''). It is organized in 114 chapters (, ) which ...
in the Hagia Sophia, dedicating the prayer to the "souls of all who left us this work as inheritance, especially Istanbul's
conqueror," strengthening the political movement to make the Hagia Sophia a mosque once again. In March 2019 Erdoğan said that he would change the status of Hagia Sophia from a museum to a mosque, adding that it had been a "very big mistake" to turn it into a museum. As a UNESCO World Heritage site, this change would require approval from UNESCO's
World Heritage Committee
The World Heritage Committee is a committee of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization that selects the sites to be listed as UNESCO World Heritage Sites, including the World Heritage List and the List of World Her ...
. In late 2019 Erdoğan's office took over the administration and upkeep of the nearby
Topkapı Palace Museum
Topkapı ("cannonball gate"), sometimes spelled Topkapi outside of Turkey, is a Turkish word that may refer to:
Places
* Topkapı, Besni, a village in the district of Besni, Adıyaman Province, Turkey
* Topkapı, Fatih, a neighbourhood of Istanbul ...
, transferring responsibility for the site from the
Ministry of Culture and Tourism by presidential decree.
In 2020, Turkey's government celebrated the 567th anniversary of the Conquest of Constantinople with an Islamic prayer in Hagia Sophia. In May, during the anniversary events, passages from the Quran were read in the Hagia Sophia. Greece condemned this action, while Turkey in response accused Greece of making "futile and ineffective statements".
In June, the head of Turkey's Directorate of Religious Affairs said that "we would be very happy to open Hagia Sophia for worship" and that if it happened "we will provide our religious services as we do in all our mosques".
On 25 June,
John Haldon
John Frederick Haldon FBA (born 23 October 1948 in Newcastle upon Tyne) is a British historian, and Shelby Cullom Davis '30 Professor of European History emeritus, professor of Byzantine history and Hellenic Studies emeritus, as well as former ...
, president of the
International Association of Byzantine Studies International Association of Byzantine Studies (, AIEB) was launched in 1948. It is an international co-ordinating body that links national Byzantine Studies member groups.
Background and Activities
The AIEB was established in 1948 as an outgrowt ...
, wrote an open letter to Erdoğan asking that he "consider the value of keeping the Aya Sofya as a museum".
On 10 July 2020, the decision of the Council of Ministers from 1935 to transform the Hagia Sophia into a museum was annulled by the Council of State, decreeing that Hagia Sophia cannot be used "for any other purpose" than being a mosque and that the Hagia Sophia was property of the Fatih Sultan Mehmet Han Foundation. The council reasoned Ottoman Sultan Mehmet II, who conquered Istanbul, deemed the property to be used by the public as a mosque without any fees and was not within the jurisdiction of the Parliament or a ministry council. Despite secular and global criticism, Erdoğan signed a decree annulling the Hagia Sophia's museum status, reverting it to a mosque.
The call to prayer was broadcast from the minarets shortly after the announcement of the change and rebroadcast by major Turkish news networks.
A presidential spokesperson said it would become a working mosque, open to anyone similar to the
Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
ian churches
Sacré-Cœur and
Notre-Dame. The spokesperson also said that the change would not affect the status of the Hagia Sophia as a UNESCO World Heritage site, and that "Christian
icon
An icon () is a religious work of art, most commonly a painting, in the cultures of the Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, Catholic Church, Catholic, and Lutheranism, Lutheran churches. The most common subjects include Jesus, Mary, mother of ...
s" within it would continue to be protected.
A presidential spokesperson claimed that all political parties in Turkey supported Erdoğan's decision,
but the
Peoples' Democratic Party had previously released a statement denouncing the decision, saying "decisions on human heritage cannot be made on the basis of political games played by the government". The
mayor of Istanbul
The mayor of Istanbul is the head of the Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality. The mayor is elected popularly every five years. Nuri Aslan has served as interim mayor of Istanbul since 26 March 2025.
This article covers the Ottoman Empire to the ...
,
Ekrem İmamoğlu
Ekrem İmamoğlu (born 4 June 1970) is a Turkish politician and businessman who has served as the 32nd Mayor of Istanbul since 2019. He is currently suspended from office temporarily. He is the Republican People's Party (CHP) candidate for the ...
, said that he supports the conversion "as long as it benefits Turkey", adding that he felt that Hagia Sophia has been a mosque since 1453.
Ali Babacan
Ali Babacan (; born 4 April 1967) is a Turkish politician, economist, and engineer. He is the founder and current leader of the Democracy and Progress Party (DEVA). He served 13 years as the Minister of Foreign Affairs, Minister of Economy, Chie ...
attacked the policy of his former ally Erdoğan, saying the Hagia Sophia issue "has come to the agenda now only to cover up other problems".
Orhan Pamuk
Ferit Orhan Pamuk (born 7 June 1952; ) is a Turkish novelist, screenwriter, academic, and recipient of the 2006 Nobel Prize in Literature. One of Turkey's most prominent novelists, he has sold over 13 million books in 63 languages, making him ...
, Turkish
novelist
A novelist is an author or writer of novels, though often novelists also write in other genres of both fiction and non-fiction. Some novelists are professional novelists, thus make a living wage, living writing novels and other fiction, while other ...
and
Nobel laureate
The Nobel Prizes (, ) are awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, the Swedish Academy, the Karolinska Institutet, and the Norwegian Nobel Committee to individuals and organizations who make outstanding contributions in th ...
, publicly denounced the move, saying "Kemal Atatürk changed... Hagia Sophia from a mosque to a museum, honouring all previous Greek Orthodox and Latin Catholic history, making it as a sign of Turkish modern secularism".
On 17 July, Erdoğan announced that the first prayers in the Hagia Sophia would be open to between 1,000 and 1,500 worshippers, stating that Turkey had
sovereign power
Sovereignty can generally be defined as supreme authority. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within a state as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the person, body or institution that has the ultimate au ...
over Hagia Sophia and was not obligated to bend to international opinion.
While the Hagia Sophia has now been rehallowed as a mosque, the place remains open for visitors outside of prayer times. Entrance was initially free, but starting from 15 January 2024, foreign nationals have to pay an entrance fee.
On 22 July, a turquoise-coloured carpet was laid to prepare the mosque for worshippers.
The mosque opened for
Friday prayer
Friday prayer, or congregational prayer (), is the meeting together of Muslims for communal prayer and service at midday every Friday. In Islam, the day itself is called ''Yawm al-Jum'ah'' (shortened to ''Jum'ah''), which translated from Arabic me ...
s on 24 July, the 97th anniversary of the signature of the
Treaty of Lausanne
The Treaty of Lausanne (, ) is a peace treaty negotiated during the Lausanne Conference of 1922–1923 and signed in the Palais de Rumine in Lausanne, Switzerland, on 24 July 1923. The treaty officially resolved the conflict that had initially ...
, which established the borders of the modern Turkish Republic.
The mosaics of the Virgin and Child in the apse were covered by white drapes.
, President of the
Directorate of Religious Affairs
Directorate may refer to:
Contemporary
*Directorates of the Scottish Government
* Directorate-General, a type of specialised administrative body in the European Union
* Directorate-General for External Security, the French external intelligence ag ...
, proclaimed during his
sermon
A sermon is a religious discourse or oration by a preacher, usually a member of clergy. Sermons address a scriptural, theological, or moral topic, usually expounding on a type of belief, law, or behavior within both past and present context ...
, "Sultan Mehmet the Conqueror dedicated this magnificent construction to believers to remain a mosque until the
Day of Resurrection
In Islam, "the promise and threat" () of Judgement Day ( or ),
is when "all bodies will be resurrected" from the dead, and "all people" are "called to account" for their deeds and their faith during their life on Earth. It has been called "the do ...
".
Erdoğan and some government ministers attended the midday prayers as many worshippers prayed outside; at one point the security cordon was breached and dozens of people broke through police lines.
Turkey invited foreign leaders and officials, including
Pope Francis
Pope Francis (born Jorge Mario Bergoglio; 17 December 1936 – 21 April 2025) was head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 13 March 2013 until Death and funeral of Pope Francis, his death in 2025. He was the fi ...
, for the prayers. It is the fourth Byzantine church converted from museum to a mosque during Erdoğan's rule.

Days before the final decision on the conversion was made, Ecumenical Patriarch
Bartholomew I of Constantinople stated in a sermon that "the conversion of Hagia Sophia into a mosque would disappoint millions of Christians around the world". The proposed conversion was decried by other Orthodox Christian leaders, the
Russian Orthodox Church
The Russian Orthodox Church (ROC; ;), also officially known as the Moscow Patriarchate (), is an autocephaly, autocephalous Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox Christian church. It has 194 dioceses inside Russia. The Primate (bishop), p ...
's
Patriarch Kirill of Moscow
Kirill or Cyril (, , secular name Vladimir Mikhailovich Gundyayev, ; born 20 November 1946) is a Russian Orthodox bishop. He became Patriarch of Moscow and all Rus' and Primate of the Russian Orthodox Church on 1 February 2009.
Prior to beco ...
stating that "a threat to Hagia Sophia
a a threat to all of Christian civilization".
Following the Turkish government's decision, UNESCO announced it "deeply regret
ed the conversion "made without prior discussion", and asked Turkey to "open a dialogue without delay", stating that the lack of negotiation was "regrettable".
UNESCO further announced that the "state of conservation" of Hagia Sophia would be "examined" at the next session of the
World Heritage Committee
The World Heritage Committee is a committee of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization that selects the sites to be listed as UNESCO World Heritage Sites, including the World Heritage List and the List of World Her ...
, urging Turkey "to initiate dialogue without delay, in order to prevent any detrimental effect on the universal value of this exceptional heritage".
, UNESCO's Assistant Director-General for Culture said "It is important to avoid any implementing measure, without prior discussion with UNESCO, that would affect physical access to the site, the structure of the buildings, the site's moveable property, or the site's management".
The
World Council of Churches
The World Council of Churches (WCC) is a worldwide Christian inter-church organization founded in 1948 to work for the cause of ecumenism. Its full members today include the Assyrian Church of the East, most jurisdictions of the Eastern Orthodo ...
condemned the decision to convert the building into a mosque, saying that would "inevitably create uncertainties, suspicions and mistrust".
At the recitation of the Sunday
Angelus
FIle:Jean-François Millet (II) 001.jpg, ''The Angelus (painting), The Angelus'' (1857–1859) by Jean-François Millet
The Angelus (; Latin for "angel") is a Catholic devotion commemorating the Incarnation (Christianity), Incarnation of Jesus ...
prayer at
St Peter's Square
St. Peter's Square (, ) is a large plaza located directly in front of St. Peter's Basilica in Vatican City, the papal enclave in Rome, directly west of the neighborhood (rione) of Borgo. Both the square and the basilica are named after Saint ...
on 12 July
Pope Francis
Pope Francis (born Jorge Mario Bergoglio; 17 December 1936 – 21 April 2025) was head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 13 March 2013 until Death and funeral of Pope Francis, his death in 2025. He was the fi ...
said, "My thoughts go to Istanbul. I think of Santa Sophia and I am very pained" ().
Josep Borrell
Josep Borrell Fontelles (; born 24 April 1947) is a Spanish politician who served as High Representative of the Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy and Vice-President of the European Commission from 2019 to 2024. A member of the Spani ...
, the
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
's
High Representative for Foreign Affairs and
Vice-President of the European Commission
A Vice-President of the European Commission is a member of the European Commission who leads the commission's work in particular focus areas in which multiple European Commissioners participate.
Currently, the European Commission has a total of ...
, released a statement calling the decisions by the Council of State and Erdoğan "regrettable" and pointing out that "as a founding member of the
Alliance of Civilisations, Turkey has committed to the promotion of inter-religious and inter-cultural dialogue and to fostering of tolerance and co-existence." According to Borrell, the
European Union member states
The European Union (EU) is a political and economic union of Lists of member states of the European Union, 27 member states that are party to the EU's Treaties of the European Union, founding treaties, and thereby subject to the privileges and ...
' twenty-seven foreign ministers "condemned the Turkish decision to convert such an emblematic monument as the Hagia Sophia" at meeting on 13 July, saying it "will inevitably fuel the mistrust, promote renewed division between religious communities and undermine our efforts at dialog and cooperation" and that "there was a broad support to call on the Turkish authorities to urgently reconsider and reverse this decision".
Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
denounced the conversion and considered it a breach of the UNESCO World Heritage titling.
Greek culture minister Lina Mendoni called it an "open provocation to the civilised world" which "absolutely confirms that there is no independent justice" in Erdoğan's Turkey, and that his
Turkish nationalism
Turkish nationalism () is nationalism among the people of Turkey and individuals whose national identity is Turkish. Turkish nationalism consists of political and social movements and sentiments prompted by a love for Turkish culture, Turkish ...
"takes his country back six centuries".
Greece and
Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
called for EU sanctions on Turkey.
Morgan Ortagus
Morgan Deann Ortagus (born July 10, 1982) is an American diplomat, intelligence analyst, political advisor, United States Navy, naval officer, and former television commentator serving as deputy Ambassadors of the United States#Special envoys, re ...
, the
spokesperson for the United States Department of State
The Spokesperson for the United States Department of State is a U.S. government official whose primary responsibility is to serve as the spokesperson for the United States Department of State and the U.S. government's foreign policies. The posi ...
, noted: "We are disappointed by the decision by the government of Turkey to change the status of the Hagia Sophia."
Jean-Yves Le Drian
Jean-Yves Le Drian (; born 30 June 1947) is a French politician who served as Minister of Europe and Foreign Affairs in the governments of Prime Ministers Édouard Philippe and Jean Castex (2017–2022) and as Minister of Defence under Preside ...
,
foreign minister
In many countries, the ministry of foreign affairs (abbreviated as MFA or MOFA) is the highest government department exclusively or primarily responsible for the state's foreign policy and relations, diplomacy, bilateral, and multilateral r ...
of
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, said his country "deplores" the move, saying "these decisions cast doubt on one of the most symbolic acts of modern and secular Turkey".
Vladimir Dzhabarov, deputy head of the foreign affairs committee of the Russian
Federation Council
The Federation Council, unofficially Senate, is the upper house of the Federal Assembly of Russia, with the lower house being the State Duma. It was established by the Constitution of the Russian Federation in 1993.
Each of the 89 federal s ...
, said that it "will not do anything for the Muslim world. It does not bring nations together, but on the contrary brings them into collision" and calling the move a "mistake".
The former
deputy prime minister of Italy
The deputy prime minister of Italy, officially the vice-president of the Council of Ministers of the Italian Republic (Italian language, Italian: ''Vicepresidente del Consiglio dei ministri della Repubblica Italiana''), is a senior member of th ...
,
Matteo Salvini
Matteo Salvini (; born 9 March 1973) is an Italian politician who has been serving as Deputy Prime Minister of Italy and Italian Minister of Infrastructure and Transport, Minister of Infrastructure and Transport since 2022. He has been List of F ...
, held a demonstration in protest outside the Turkish consulate in
Milan
Milan ( , , ; ) is a city in northern Italy, regional capital of Lombardy, the largest city in Italy by urban area and the List of cities in Italy, second-most-populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of nea ...
, calling for all plans for
accession of Turkey to the European Union
Turkey is negotiating its accession to the European Union (EU) as a member state, following its application to become a full member of the European Economic Community (EEC), the predecessor of the EU, on 14 April 1987.
After the ten founding ...
to be terminated "once and for all".
In
East Jerusalem
East Jerusalem (, ; , ) is the portion of Jerusalem that was Jordanian annexation of the West Bank, held by Jordan after the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, as opposed to West Jerusalem, which was held by Israel. Captured and occupied in 1967, th ...
, a protest was held outside the Turkish consulate on 13 July, with the burning of a
Turkish flag
The national flag of Turkey, officially the Turkish flag (), is a red flag featuring a white crescent and star on its emblem, based on the 18th-century Ottoman Empire flag. The flag is often called "the red flag" (), and is referred to as "the ...
and the display of the
Greek flag
The national flag of Greece, popularly referred to as the Blue-and-White (, ) or the Cyan-and-White (, ), is officially recognised by Greece as one of its national symbols and has 5 equal horizontal stripes of blue alternating with white. There ...
and
flag of the Greek Orthodox Church
The Ecumenical Patriarchate and Mount Athos, and also the Greek Orthodox Churches in the diaspora under the Patriarchate use a black double-headed eagle in a yellow field as their flag or emblem.
The eagle is depicted as clutching a sword and an ...
.
Ersin Tatar
Ersin Tatar (born 7 September 1960) is a Turkish Cypriot politician who has served as the fifth President of Northern Cyprus since 2020. He previously served as the fourth Prime Minister of Northern Cyprus following the collapse of Tufan Erhü ...
, prime minister of the Turkish Republic of
Northern Cyprus
Northern Cyprus, officially the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus (TRNC), is a ''de facto'' state that comprises the northeastern portion of the Geography of Cyprus, island of Cyprus. It is List of states with limited recognition, recognis ...
, which is
recognized only by Turkey, welcomed the decision, calling it "sound" and "pleasing".
Through a spokesman the
Foreign Ministry
In many countries, the ministry of foreign affairs (abbreviated as MFA or MOFA) is the highest government department exclusively or primarily responsible for the state's foreign policy and relations, diplomacy, bilateral, and multilateral re ...
of
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
welcomed the change, saying the decision was an "issue that should be considered as part of Turkey's national sovereignty" and "Turkey's internal affair".
Sergei Vershinin
Sergius is a male given name of Ancient Roman origin after the name of the Latin ''gens'' Sergia or Sergii of regal and republican ages. It is a common Christian name, in honour of Saint Sergius, or in Kyivan Rus', of Sergius of the Holy Caves ...
, deputy foreign minister of
Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
, said that the matter was of one of "internal affairs, in which, of course, neither we nor others should interfere." The
Arab Maghreb Union
The Arab Maghreb Union ( '; AMU/UMA) is a political union and economic union trade agreement aiming for economic and future political unity among Arab countries that are located primarily in the Maghreb in North Africa. Its members are the natio ...
was supportive.
Ekrema Sabri, imam of the
al-Aqsa Mosque
The Aqsa Mosque, also known as the Qibli Mosque or Qibli Chapel is the main congregational mosque or Musalla, prayer hall in the Al-Aqsa mosque compound in the Old City (Jerusalem), Old City of Jerusalem. In some sources the building is also n ...
, and
Ahmed bin Hamad al-Khalili
Sheikh Ahmad bin Hamad Al-Khalili ( NP) (; born 1942) is the Grand Mufti of the Sultanate of Oman.
Opinions
The Grand Mufti appears regularly on TV, where he answers the public's questions on Islam. He urged the government to ban alcohol in Oman ...
, grand mufti of
Oman
Oman, officially the Sultanate of Oman, is a country located on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in West Asia and the Middle East. It shares land borders with Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. Oman’s coastline ...
, both congratulated Turkey on the move.
The
Muslim Brotherhood
The Society of the Muslim Brothers ('' ''), better known as the Muslim Brotherhood ( ', is a transnational Sunni Islamist organization founded in Egypt by Islamic scholar, Imam and schoolteacher Hassan al-Banna in 1928. Al-Banna's teachings s ...
was also in favour of the news.
A spokesman for the Palestinian
Islamist movement
Hamas
The Islamic Resistance Movement, abbreviated Hamas (the Arabic acronym from ), is a Palestinian nationalist Sunni Islam, Sunni Islamism, Islamist political organisation with a military wing, the Qassam Brigades. It has Gaza Strip under Hama ...
called the verdict "a proud moment for all Muslims". Pakistani politician
Chaudhry Pervaiz Elahi
Chaudhry Parvez Elahi Warraich (Urdu, ; born 1 November 1945) is a Pakistani politician who was the Chief Minister of Punjab from late 2002 to late 2007 and again from late 2022 to early 2023. He was a member of the Provincial Assembly of ...
of the
Pakistan Muslim League (Q)
The Pakistan Muslim League (Quaid e Azam Group) ; ''Pākistān Muslim Līg (Qāf)'', Acronyms: PML(Q), PML-Q, PMLQ, "Q League" (officially registered as the Pakistan Muslim League) is a political party in Pakistan. As of the 2024 parliamentary e ...
welcomed the ruling, claiming it was "not only in accordance with the wishes of the people of Turkey but the entire Muslim world". The
Muslim Judicial Council
The Muslim Judicial Council SA (MJC), a non-profit umbrella body of Sunni Islamic clerics in South Africa, is headquartered in Cape Town, South Africa. It was established in 1945 by the Muslim Progressive Society. As of 2009, approximately 150 mo ...
group in
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
praised the move, calling it "a historic turning point". In
Nouakchott
Nouakchott ( ) is the capital and largest city of Mauritania. Located in the southwestern part of the country, it is one of the largest cities in the Sahara. The city also serves as the administrative and economic center of Mauritania.
Once a ...
, capital of
Mauritania
Mauritania, officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania, is a sovereign country in Maghreb, Northwest Africa. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Western Sahara to Mauritania–Western Sahara border, the north and northwest, ...
, there were prayers and celebrations topped by the sacrifice of a
camel
A camel (from and () from Ancient Semitic: ''gāmāl'') is an even-toed ungulate in the genus ''Camelus'' that bears distinctive fatty deposits known as "humps" on its back. Camels have long been domesticated and, as livestock, they provid ...
. On the other hand,
Shawki Allam
Shawki Ibrahim Abdel-Karim Allam () is the 19th Grand Mufti of Egypt through Dar al-Ifta al-Misriyyah, succeeding Ali Gomaa. He is succeeded by Nazeer Ayyad on the 11th of August 2024, following a presidential decree.
Biography
Allam was born in ...
, grand mufti of
Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, ruled that conversion of the Hagia Sophia to a mosque is "impermissible".
When President Erdoğan announced that the first Muslim prayers would be held inside the building on 24 July, he added that "like all our mosques, the doors of Hagia Sophia will be wide open to locals and foreigners, Muslims and non-Muslims." Presidential spokesman
İbrahim Kalın
İbrahim Kalın (born 15 September 1971) is a Turkish bureaucrat and academic who is the current director of the National Intelligence Organization (MİT). An academic specialising in Islamic philosophy, Kalın received his doctorate under the su ...
said that the icons and mosaics of the building would be preserved, and that "in regards to the arguments of secularism, religious tolerance and coexistence, there are more than four hundred churches and synagogues open in Turkey today." The Turkish foreign minister,
Mevlüt Çavuşoğlu
Mevlüt Çavuşoğlu (; born 5 February 1968) is a Turkish diplomat and politician who is currently a member of the Grand National Assembly of Turkey, Grand National Assembly. He also served as the Minister of Foreign Affairs (Turkey), Minister o ...
, told
TRT Haber
TRT Haber ( English: TRT News) is a Turkish news and current affairs television channel. It was listed by Anadolu Agency
Anadolu Agency (, ; abbreviated AA) is a state-run news agency headquartered in Ankara, Turkey.
History
The Anadolu Agenc ...
on 13 July that the government was surprised at the reaction of UNESCO, saying that "We have to protect our ancestors' heritage. The function can be this way or that way – it does not matter".
On 14 July the prime minister of Greece,
Kyriakos Mitsotakis
Kyriakos Mitsotakis (, ; born 4 March 1968) is a Greek politician currently serving as the prime minister of Greece since July 2019, except for a month between May and June 2023. Mitsotakis has been president of the New Democracy (Greece), New ...
, said his government was "considering its response at all levels" to what he called Turkey's "unnecessary, petty initiative", and that "with this backward action, Turkey is opting to sever links with
western world
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to various nations and state (polity), states in Western Europe, Northern America, and Australasia; with some debate as to whether those in Eastern Europe and Latin America also const ...
and its values".
In relation to both Hagia Sophia and the
Cyprus–Turkey maritime zones dispute, Mitsotakis called for European sanctions against Turkey, referring to it as "a regional troublemaker, and which is evolving into a threat to the stability of the whole south-east Mediterranean region".
Dora Bakoyannis
Theodora "Dora" Bakoyanni (, ; née Mitsotaki, ; born May 6, 1954) is a Greek politician. From 2006 to 2009 she was Minister of Foreign Affairs of Greece, the highest position ever to have been held by a woman in the Cabinet of Greece at the ti ...
, Greek former foreign minister, said Turkey's actions had "crossed the Rubicon", distancing itself from the West.
Armenia's Foreign Ministry expressed "deep concern" about the move, adding that it brought to a close Hagia Sophia's symbolism of "cooperation and unity of humankind instead of clash of civilizations." Catholicos
Karekin II
Catholicos Garegin II (, also spelled Karekin; born 21 August 1951) is the Catholicos of All Armenians, the supreme head of the Armenian Apostolic Church, since 1999. In 2013 he was unanimously elected the Oriental Orthodox head of the World Cou ...
, the head of the Armenian Apostolic Church, said the move "violat
dthe rights of national religious minorities in Turkey."
Sahak II Mashalian
Archbishop Sahag II Mashalian (, ), also known as Sahak Mashalyan in Eastern Armenian transliteration (born 17 March 1962) became the 85th Armenian Patriarch of Constantinople in 2019.
The Armenian Patriarchate of Constantinople is one of the f ...
, the Armenian Patriarch of Constantinople, perceived as loyal to the Turkish government, endorsed the decision to convert the museum into a mosque. He said, "I believe that believers' praying suits better the spirit of the temple instead of curious tourists running around to take pictures."
In July 2021, UNESCO asked for an updated report on the state of conservation and expressed "grave concern". There were also some concerns about the future of its World Heritage status. Turkey responded that the changes had "no negative impact" on UNESCO standards and the criticism is "biased and political".
Architecture
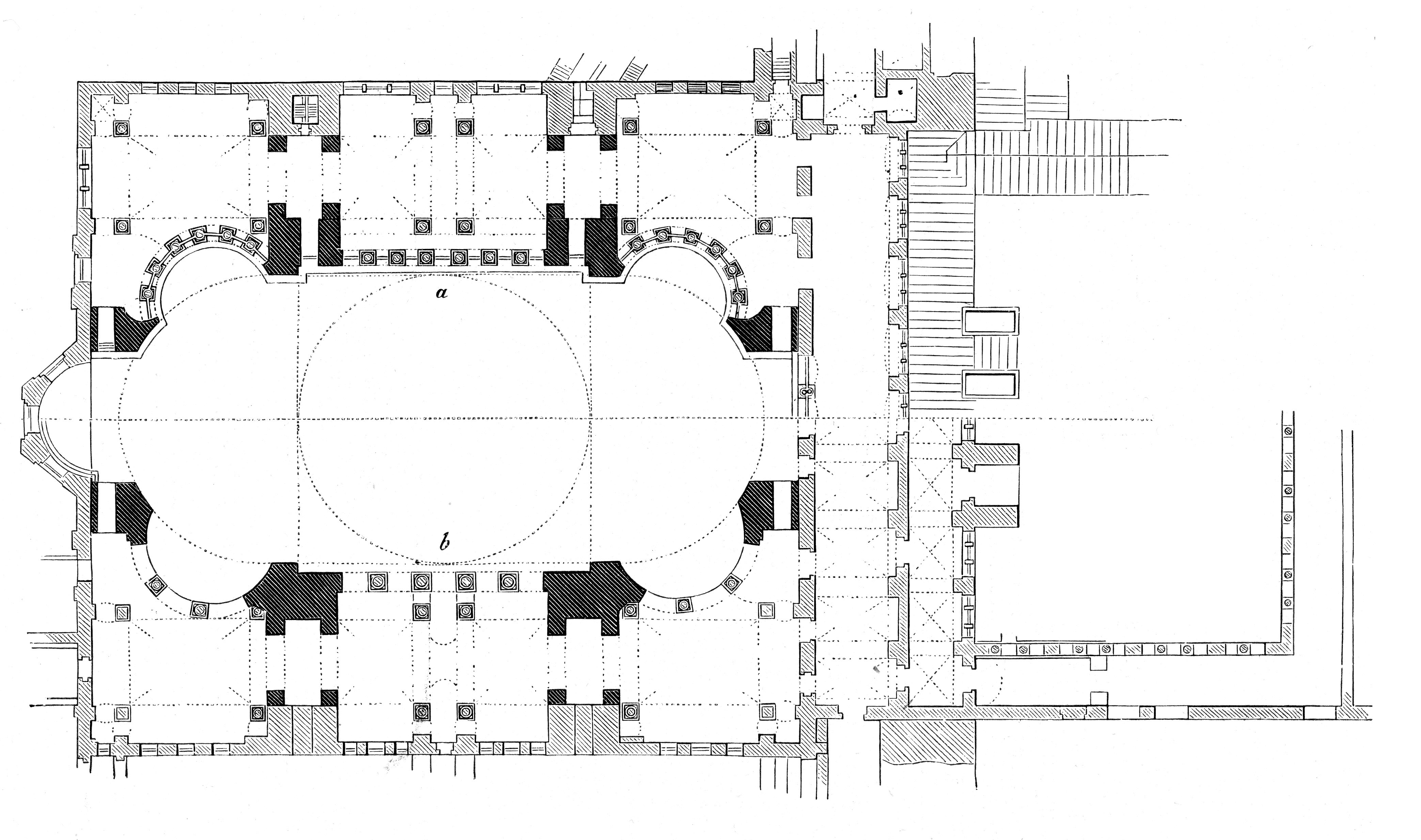
Hagia Sophia is one of the greatest surviving examples of
Byzantine architecture
Byzantine architecture is the architecture of the Byzantine Empire, or Eastern Roman Empire, usually dated from 330 AD, when Constantine the Great established a new Roman capital in Byzantium, which became Constantinople, until the Fall of Cons ...
.
Its interior is decorated with
mosaic
A mosaic () is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/Mortar (masonry), mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and ...
s,
marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock consisting of carbonate minerals (most commonly calcite (CaCO3) or Dolomite (mineral), dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2) that have recrystallized under the influence of heat and pressure. It has a crystalline texture, and is ty ...
pillars, and coverings of great artistic value. Justinian had overseen the completion of the greatest cathedral ever built up to that time, and it was to remain the largest cathedral for 1,000 years until the completion of the
cathedral in Seville in Spain.
The Hagia Sophia uses masonry construction. The structure has brick and
mortar
Mortar may refer to:
* Mortar (weapon), an indirect-fire infantry weapon
* Mortar (masonry), a material used to fill the gaps between blocks and bind them together
* Mortar and pestle, a tool pair used to crush or grind
* Mortar, Bihar, a village i ...
joints that are 1.5 times the width of the bricks. The mortar joints are composed of a combination of sand and minute ceramic pieces distributed evenly throughout the mortar joints. This combination of sand and
potsherds
This page is a glossary of archaeology, the study of the human past from material remains.
A
B
C
D
E
F
...
was often used in
Roman concrete
Roman concrete, also called , was used in construction in ancient Rome. Like its modern equivalent, Roman concrete was based on a hydraulic-setting cement added to an aggregate.
Many buildings and structures still standing today, such as br ...
, a predecessor to modern
concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of aggregate bound together with a fluid cement that cures to a solid over time. It is the second-most-used substance (after water), the most–widely used building material, and the most-manufactur ...
. A considerable amount of iron was used as well, in the form of cramps and ties.
Justinian's basilica was at once the culminating architectural achievement of
late antiquity
Late antiquity marks the period that comes after the end of classical antiquity and stretches into the onset of the Early Middle Ages. Late antiquity as a period was popularized by Peter Brown (historian), Peter Brown in 1971, and this periodiza ...
and the first masterpiece of Byzantine architecture. Its influence, both architecturally and liturgically, was widespread and enduring in the
Eastern Christianity
Eastern Christianity comprises Christianity, Christian traditions and Christian denomination, church families that originally developed during Classical antiquity, classical and late antiquity in the Eastern Mediterranean region or locations fu ...
,
Western Christianity
Western Christianity is one of two subdivisions of Christianity (Eastern Christianity being the other). Western Christianity is composed of the Latin Church and Protestantism, Western Protestantism, together with their offshoots such as the O ...
, and
Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
alike.

The vast interior has a complex structure. The
nave
The nave () is the central part of a church, stretching from the (normally western) main entrance or rear wall, to the transepts, or in a church without transepts, to the chancel. When a church contains side aisles, as in a basilica-type ...
is covered by a central dome which at its maximum is from floor level and rests on an arcade of 40 arched windows. Repairs to its structure have left the dome somewhat elliptical, with the diameter varying between .
At the western entrance and eastern liturgical side, there are arched openings extended by half domes of identical diameter to the central dome, carried on smaller
semi-dome
In architecture, a semi-dome (or half-dome) is a half dome that covers a semi-circular area in a building.
Architecture
Semi-domes are a common feature of apses in Ancient Roman and traditional church architecture, and in mosques and iwans in Isla ...
d
exedrae
An exedra (: exedras or exedrae) is a semicircular architectural recess or platform, sometimes crowned by a semi-dome, and either set into a building's façade or free-standing. The original Greek word ''ἐξέδρα'' ('a seat out of doors') w ...
, a hierarchy of dome-headed elements built up to create a vast oblong interior crowned by the central dome, with a clear span of .
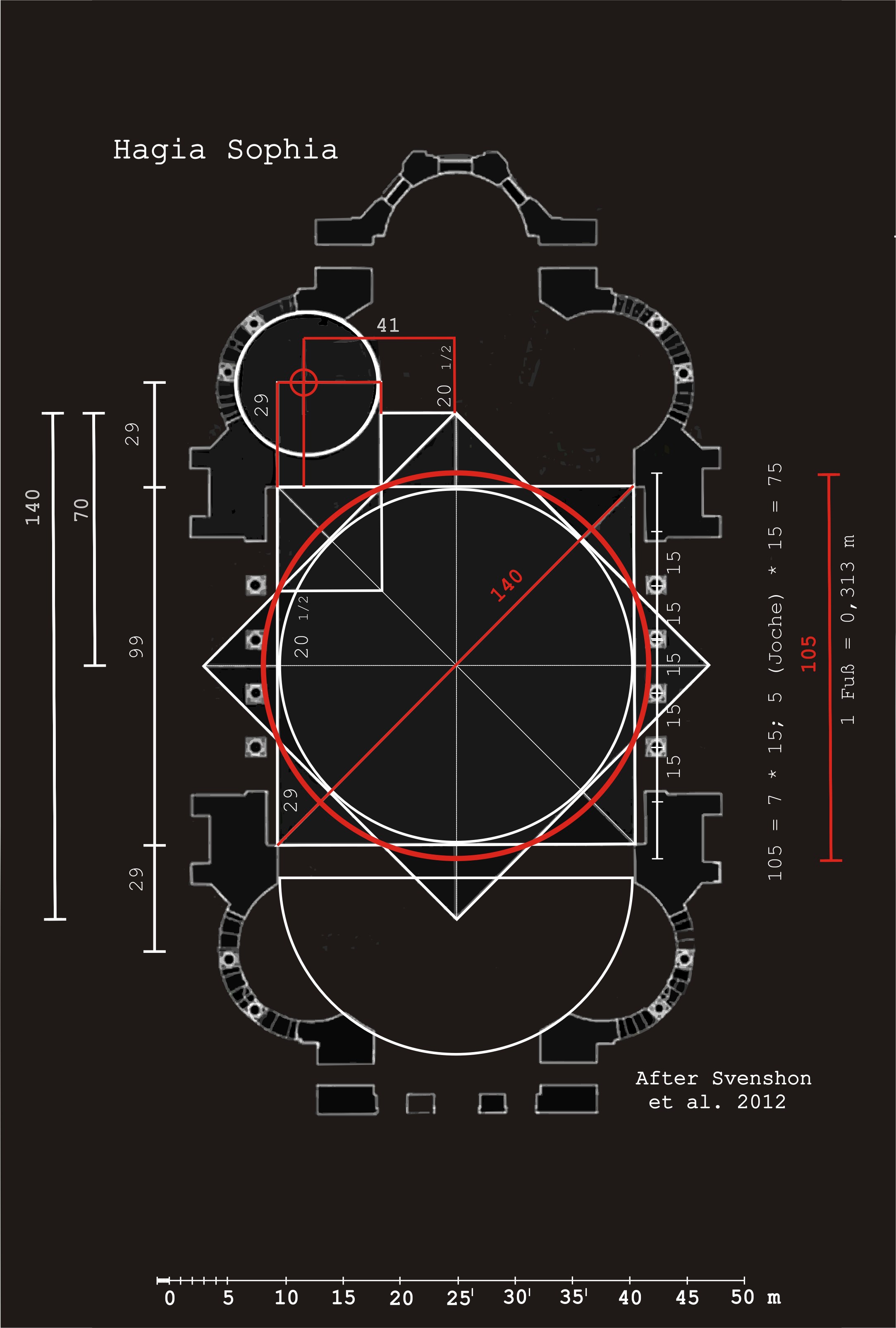
The theories of
Hero of Alexandria
Hero of Alexandria (; , , also known as Heron of Alexandria ; probably 1st or 2nd century AD) was a Greek mathematician and engineer who was active in Alexandria in Egypt during the Roman era. He has been described as the greatest experimental ...
, a
Hellenistic mathematician of the 1st century AD, may have been utilized to address the challenges presented by building such an expansive dome over so large a space. Svenshon and Stiffel proposed that the architects used Hero's proposed values for constructing vaults. The square measurements were calculated using the side-and-diagonal number progression, which results in squares defined by the numbers 12 and 17, wherein 12 defines the side of the square and 17 its diagonal, which have been used as standard values as early as in cuneiform Babylonian texts.
[Svenshon, Helge Olaf: Heron of Alexandria and the Dome of Hagia Sophia in Istanbul. In: Proceedings of the Third Congress on Construction History. Brandenburg University of Technology Cottbus, 20th – 24th May 2009. NEUNPLUS1, Berlin, S. 1387–1394. ]
Each of the four sides of the great square Hagia Sophia is approximately 31 m long, and it was previously thought that this was the equivalent of 100
Byzantine feet.
Svenshon suggested that the size of the side of the central square of Hagia Sophia is not 100 Byzantine feet but instead 99 feet. This measurement is not only rational, but it is also embedded in the system of the side-and-diagonal number progression (70/99) and therefore a usable value by the applied mathematics of antiquity. It gives a diagonal of 140 which is manageable for constructing a huge dome.
Floor
The stone floor of Hagia Sophia dates from the 6th century. After the first collapse of the vault, the broken dome was left ''in situ'' on the original Justinianic floor and a new floor was laid above the rubble when the dome was rebuilt in 558.
From the installation of this second Justinianic floor, the floor became part of the
liturgy
Liturgy is the customary public ritual of worship performed by a religious group. As a religious phenomenon, liturgy represents a communal response to and participation in the sacred through activities reflecting praise, thanksgiving, remembra ...
, with significant locations and spaces demarcated in various ways using different-coloured stones and marbles.
The floor is predominantly made up of
Proconnesian marble, quarried on
Proconnesus
Marmara Island () is a Turkish island in the Sea of Marmara. With an area of , it is the largest island in the Sea of Marmara and the second-largest island of Turkey - after Gökçeada (formerly ; ''Imvros''). It is the center of Marmara Dist ...
(Marmara Island) in the
Propontis
The Sea of Marmara, also known as the Sea of Marmora or the Marmara Sea, is a small inland sea entirely within the borders of Turkey. It links the Black Sea and the Aegean Sea via the Bosporus and Dardanelles straits, separating Turkey's E ...
(Sea of Marmara). This was the main white marble used in the monuments of Constantinople. Other parts of the floor, like the Thessalian
verd antique
Verd antique (obsolete French, from Italian, ''verde antico'', "ancient green"), also called verde antique, ''marmor thessalicum'', or Ophite, is a serpentinite breccia popular since ancient times as a decorative facing stone. It is a dark, du ...
"marble", were quarried in
Thessaly
Thessaly ( ; ; ancient Aeolic Greek#Thessalian, Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic regions of Greece, geographic and modern administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient Thessaly, a ...
in
Roman Greece
Greece in the Roman era (, ) describes the Roman conquest of ancient Greece (roughly, the territory of the modern nation-state of Greece) as well as that of the Greek people and the areas they inhabited and ruled historically. It covers the peri ...
. The Thessalian verd antique bands across the nave floor were often likened to rivers.
The floor was praised by numerous authors and repeatedly compared to a sea.
The Justinianic poet
Paul the Silentiary
Paul the Silentiary, also known as Paulus Silentiarius (, died AD 575–580), was a Greeks, Greek Byzantine poet and courtier to the emperor Justinian I, Justinian at Constantinople.
Life
What little we know of Paul's life comes largely from th ...
likened the ambo and the solea connecting it to the sanctuary with an island in a sea, with the sanctuary itself a harbour.
The 9th-century ''Narratio'' writes of it as "like the sea or the flowing waters of a river".
Michael the Deacon
Abba Mikaʾel (), also known as Michael the Deacon, was an Ethiopian deacon, best known for holding theological discussions with Martin Luther in 1534.
Stanislau Paulau suggested that Mikaʾel, who was able to speak broken Italian, may be a membe ...
in the 12th century also described the floor as a sea in which the ambo and other liturgical furniture stood as islands.
During the 15th-century conquest of Constantinople, the Ottoman caliph Mehmed is said to have ascended to the dome and the galleries in order to admire the floor, which according to
Tursun Beg
Tursun Beg (; probably born in mid-1420s in Edirne)Woodhead, Christine. "Ṭūrsūn Beg." Encyclopaedia of Islam, Second Edition. Brill, 2011. was an Ottoman bureaucrat and historian who wrote a chronicle dedicated to Mehmed II.
Tursun Beg's l ...
resembled "a sea in a storm" or a "petrified sea".
Other Ottoman-era authors also praised the floor;
Tâcîzâde Cafer Çelebi
Nişancı Tâcîzâde Cafer Çelebi or Nīshāndji Tādji-Zādah Djā'far Chālabī (c. 1459–1515), known for short as Câ’fer Çelebi#Title, Çelebi or Ja'far, Jā’far Çelebi#Title, Chālabī was an Ottoman Empire, Ottoman statesman and ...
compared it to waves of marble.
The floor was hidden beneath a carpet on 22 July 2020.
Narthex and portals
The Imperial Gate, or Imperial Door, was the main entrance between the exo- and esonarthex, and it was originally exclusively used by the emperor.
A long ramp from the northern part of the outer narthex leads up to the upper gallery.

Upper gallery
The upper gallery, or
matroneum
A triforium is an interior gallery, opening onto the tall central space of a building at an upper level. In a church, it opens onto the nave from above the side aisles; it may occur at the level of the clerestory windows, or it may be locate ...
, is horseshoe-shaped; it encloses the nave on three sides and is interrupted by the apse. Several mosaics are preserved in the upper gallery, an area traditionally reserved for the Empress and her court. The best-preserved mosaics are located in the southern part of the gallery.
The northern first floor gallery contains
runic graffiti believed to have been left by members of the
Varangian Guard
The Varangian Guard () was an elite unit of the Byzantine army from the tenth to the fourteenth century who served as personal bodyguards to the Byzantine emperors. The Varangian Guard was known for being primarily composed of recruits from Nort ...
. Structural damage caused by natural disasters is visible on the Hagia Sophia's exterior surface. To ensure that the Hagia Sophia did not sustain any damage on the interior of the building, studies have been conducted using ground penetrating radar within the gallery of the Hagia Sophia. With the use of
ground-penetrating radar
Ground-penetrating radar (GPR) is a geophysical method that uses radar pulses to image the subsurface. It is a non-intrusive method of surveying the sub-surface to investigate underground utilities such as concrete, asphalt, metals, pipes, cables ...
(GPR), teams discovered weak zones within the Hagia Sophia's gallery and also concluded that the curvature of the vault dome has been shifted out of proportion, compared to its original angular orientation.
Dome

The
dome
A dome () is an architectural element similar to the hollow upper half of a sphere. There is significant overlap with the term cupola, which may also refer to a dome or a structure on top of a dome. The precise definition of a dome has been a m ...
of Hagia Sophia has spurred particular interest for many art historians, architects, and engineers because of the innovative way the original architects envisioned it. The dome is carried on four spherical triangular
pendentive
In architecture, a pendentive is a constructional device permitting the placing of a circular dome over a square room or of an elliptical dome over a rectangular room. The pendentives, which are triangular segments of a sphere, taper to point ...
s, making the Hagia Sophia one of the first large-scale uses of this element. The pendentives are the corners of the square base of the dome, and they curve upwards into the dome to support it, thus restraining the lateral forces of the dome and allowing its weight to flow downwards. The main dome of the Hagia Sophia was the largest pendentive dome in the world until the completion of
St Peter's Basilica
The Papal Basilica of Saint Peter in the Vatican (), or simply St. Peter's Basilica (; ), is a church of the Italian Renaissance architecture, Italian High Renaissance located in Vatican City, an independent microstate enclaved within the cit ...
, and it has a much lower height than any other dome of such a large diameter.
The great dome at the Hagia Sophia is in diameter and is only thick. The main building materials for the original Hagia Sophia were brick and mortar. Brick aggregate was used to make roofs easier to construct. Due to the material's plasticity, it was chosen over cut stone due to the fact that aggregate can be used over a longer distance. According to Rowland Mainstone, "it is unlikely that the vaulting-shell is anywhere more than one normal brick in thickness".
The weight of the dome remained a problem for most of the building's existence. The original cupola collapsed entirely after the earthquake of 558; in 563 a new dome was built by
Isidore the Younger
Isidore of Miletus the Younger or simply Isidore the Younger ( – 563) was a Byzantine architect and a nephew of the architect Isidore of Miletus. Like his uncle, he was a native of Miletus.
According to Procopius' ''Buildings'', Isidore in his ...
. Unlike the original, this included 40 ribs and was raised 6.1 meters (20 feet), in order to lower the lateral forces on the church walls. A larger section of the second dome collapsed as well, over two episodes, so that as of 2021, only two sections of the present dome, the north and south sides, are from the 562 reconstructions. Of the whole dome's 40 ribs, the surviving north section contains eight ribs, while the south section includes six ribs.
Although this design stabilizes the dome and the surrounding walls and arches, the actual construction of the walls of Hagia Sophia weakened the overall structure. The
bricklayer
A bricklayer, which is related to but different from a mason, is a craftsperson and tradesperson who lays bricks to construct brickwork. The terms also refer to personnel who use blocks to construct blockwork walls and other forms of maso ...
s used more
mortar
Mortar may refer to:
* Mortar (weapon), an indirect-fire infantry weapon
* Mortar (masonry), a material used to fill the gaps between blocks and bind them together
* Mortar and pestle, a tool pair used to crush or grind
* Mortar, Bihar, a village i ...
than brick, which is more effective if the mortar was allowed to settle, as the building would have been more flexible; however, the builders did not allow the mortar to cure before they began the next layer. When the dome was erected, its weight caused the walls to lean outward because of the wet mortar underneath. When Isidore the Younger rebuilt the fallen cupola, he had first to build up the interior of the walls to make them vertical again. Additionally, the architect raised the height of the rebuilt dome by approximately so that the lateral forces would not be as strong and its weight would be transmitted more effectively down into the walls. Moreover, he shaped the new cupola like a
scallop
Scallop () is a common name that encompasses various species of marine bivalve molluscs in the taxonomic family Pectinidae, the scallops. However, the common name "scallop" is also sometimes applied to species in other closely related famili ...
ed shell or the inside of an umbrella, with
ribs
The rib cage or thoracic cage is an endoskeletal enclosure in the thorax of most vertebrates that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum, which protect the vital organs of the thoracic cavity, such as the heart, lungs and great vessels ...
that extend from the top down to the base. These ribs allow the weight of the dome to flow between the windows, down the pendentives, and ultimately to the foundation.
Hagia Sophia is famous for the light that reflects everywhere in the interior of the nave, giving the dome the appearance of hovering. This effect was achieved by inserting forty windows around the base of the original structure, which also reduced its weight.
Buttresses
Numerous
buttress
A buttress is an architectural structure built against or projecting from a wall which serves to support or reinforce the wall. Buttresses are fairly common on more ancient (typically Gothic) buildings, as a means of providing support to act ...
es have been added throughout the centuries. The flying buttresses to the west of the building, although thought to have been constructed by the Crusaders upon their visit to Constantinople, were actually built during the Byzantine era. This shows that the Romans had prior knowledge of flying buttresses, which can also be seen at in Greece, at the Arch of Galerius and Rotunda, Rotunda of Galerius in Thessaloniki, at the monastery of Hosios Loukas in Boeotia, and in Italy at the octagonal basilica of Basilica of San Vitale, San Vitale in Ravenna.
Other buttresses were constructed during the Ottoman times under the guidance of the architect Mimar Sinan, Sinan. A total of 24 buttresses were added.
Minarets
The
minaret
A minaret is a type of tower typically built into or adjacent to mosques. Minarets are generally used to project the Muslim call to prayer (''adhan'') from a muezzin, but they also served as landmarks and symbols of Islam's presence. They can h ...
s were an Ottoman addition and not part of the original church's Byzantine design. Mehmed had built a wooden minaret over one of the half domes soon after Hagia Sophia's conversion from a cathedral to a mosque. This minaret does not exist today. One of the minarets (at southeast) was built from red brick and can be dated back from the reign of Mehmed or his successor Bayezid II, Beyazıd II. The other three were built from white limestone and sandstone, of which the slender northeast column was erected by Bayezid II and the two identical, larger minarets to the west were erected by
Selim II and designed by the famous Ottoman architect
Mimar Sinan
Mimar Sinan (; , ; – 17 July 1588) also known as Koca Mi'mâr Sinân Âğâ, ("Sinan Agha (title), Agha the Grand Architect" or "Grand Sinan") was the chief Ottoman Empire, Ottoman architect, engineer and mathematician for sultans Suleiman ...
. Both are in height, and their thick and massive patterns complete Hagia Sophia's main structure. Many ornaments and details were added to these minarets on repairs during the 15th, 16th, and 19th centuries, which reflect each period's characteristics and ideals.
Notable elements and decorations
Originally, under Justinian's reign, the interior decorations consisted of abstract designs on marble slabs on the walls and floors as well as mosaics on the curving vaults. Of these mosaics, the two archangels Gabriel and Michael (archangel), Michael are still visible in the spandrels (corners) of the bema. There were already a few figurative decorations, as attested by the late 6th-century ''
ekphrasis
Ekphrasis or ecphrasis (from the Greek) is a rhetorical device indicating the written description of a work of art. It is a vivid, often dramatic, verbal description of a visual work of art, either real or imagined. Thus, "an ekphrastic poem ...
'' of
Paul the Silentiary
Paul the Silentiary, also known as Paulus Silentiarius (, died AD 575–580), was a Greeks, Greek Byzantine poet and courtier to the emperor Justinian I, Justinian at Constantinople.
Life
What little we know of Paul's life comes largely from th ...
, the ''Description of Hagia Sophia''. The spandrels of the gallery are faced in inlaid thin slabs (''opus sectile''), showing patterns and figures of flowers and birds in precisely cut pieces of white marble set against a background of black marble. In later stages, figurative mosaics were added, which were destroyed during the Byzantine Iconoclasm, iconoclastic controversy (726–843). Present mosaics are from the post-iconoclastic period.
Apart from the mosaics, many figurative decorations were added during the second half of the 9th century: an image of Christ in the central dome; Eastern Orthodox saints, prophets and Church Fathers in the Tympanum (architecture), tympana below; historical figures connected with this church, such as Patriarch Ignatius of Constantinople, Patriarch Ignatius; and some scenes from the Gospels in the galleries. Basil II, Basil II let artists paint a giant six-winged seraph on each of the four pendentives.
The Ottomans covered their faces with golden stars,
but in 2009, one of them was restored to its original state.
[Ronchey (2010), p. 157]
File: Empress loge Hagia Sophia 2007 002.jpg, The Loge of the Empress. The columns are made of green Thessalian stone.
File:Empress loge Hagia Sophia 2007 006.jpg, Verd antique columns and disc in the empress's loggia
File: Marble jar Hagia Sophia 2007 001.jpg, Lustration urn brought from Pergamon
Pergamon or Pergamum ( or ; ), also referred to by its modern Greek form Pergamos (), was a rich and powerful ancient Greece, ancient Greek city in Aeolis. It is located from the modern coastline of the Aegean Sea on a promontory on the north s ...
by Murad III
Murad III (; ; 4 July 1546 – 16 January 1595) was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1574 until his death in 1595. His rule saw battles with the Habsburg monarchy, Habsburgs and exhausting wars with the Safavid Iran, Safavids. The long-inde ...
. Carved from a single block of marble in the 2nd century BC.
File: Marble door Hagia Sophia 2007 003.jpg, Marble Door
File: Istanbul.Hagia Sophia052.jpg, The wishing column
Loggia of the Empress
The loggia of the empress is located in the centre of the gallery of the Hagia Sophia, above the Imperial Gate and directly opposite the apse. From this
matroneum
A triforium is an interior gallery, opening onto the tall central space of a building at an upper level. In a church, it opens onto the nave from above the side aisles; it may occur at the level of the clerestory windows, or it may be locate ...
(women's gallery), the Byzantine Empress, empress and the court-ladies would watch the proceedings down below. A green stone disc of
verd antique
Verd antique (obsolete French, from Italian, ''verde antico'', "ancient green"), also called verde antique, ''marmor thessalicum'', or Ophite, is a serpentinite breccia popular since ancient times as a decorative facing stone. It is a dark, du ...
marks the spot where the throne of the empress stood.
Lustration urns
Two huge marble lustration (ritual purification) urns were brought from
Pergamon
Pergamon or Pergamum ( or ; ), also referred to by its modern Greek form Pergamos (), was a rich and powerful ancient Greece, ancient Greek city in Aeolis. It is located from the modern coastline of the Aegean Sea on a promontory on the north s ...
during the reign of Sultan
Murad III
Murad III (; ; 4 July 1546 – 16 January 1595) was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1574 until his death in 1595. His rule saw battles with the Habsburg monarchy, Habsburgs and exhausting wars with the Safavid Iran, Safavids. The long-inde ...
. They are from the Hellenistic period and carved from single blocks of marble.
Marble Door
The Marble Door inside the Hagia Sophia is located in the southern upper enclosure or gallery. It was used by the participants in synods, who entered and left the meeting chamber through this door. It is said that each side is symbolic and that one side represents heaven while the other represents hell. Its panels are covered in fruits and fish motifs. The door opens into a space that was used as a venue for solemn meetings and important resolutions of patriarchate officials.
Nice Door
The Nice Door is the oldest architectural element found in the Hagia Sophia dating back to the 2nd century BC. The decorations are of reliefs of geometric shapes as well as plants that are believed to have come from a pagan temple in Tarsus, Mersin, Tarsus in Cilicia (Roman province), Cilicia, part of the Cibyrrhaeot Theme in modern-day Mersin Province in south-eastern Turkey. It was incorporated into the building by Emperor Theophilos in 838 where it is placed in the south exit in the inner narthex.
Imperial Gate
The Imperial Gate is the door that was used solely by the Emperor and his personal bodyguard and retinue.
At it is the largest door in the Hagia Sophia and has been dated to the 6th century. Byzantine sources say it was made with wood from Noah's Ark.
In April 2022, the door was vandalised by unknown assailant(s).
Wishing column
At the northwest of the building, there is a column with a hole in the middle covered by bronze plates. This column goes by different names; the "perspiring" or "sweating column", the "crying column", or the "wishing column". Legend states that it has been moist since the appearance of Gregory Thaumaturgus near the column in 1200. It is believed that touching the moisture cures many illnesses.
Viking inscription
In the southern section of Hagia Sophia, a 9th-century Vikings, Viking inscription has been discovered, which reads, "Halvdan was here." It is theorized that the inscription was created by a Viking soldier serving as a mercenary in the Eastern Roman Empire.
Mosaics

The first mosaics which adorned the church were completed during the reign of Justin II. Many of the non-figurative mosaics in the church come from this period. Most of the mosaics, however, were created in the 10th and 12th centuries, following the periods of Byzantine Iconoclasm.
During the Fourth Crusade, Sack of Constantinople in 1204, the Latin Crusaders vandalized valuable items in every important Byzantine structure of the city, including the golden mosaics of the Hagia Sophia. Many of these items were shipped to Venice, whose
Doge
Doge, DoGE or DOGE may refer to:
Internet culture
* Doge (meme), an Internet meme primarily associated with the Shiba Inu dog breed
** Dogecoin, a cryptocurrency named after the meme
** Kabosu (dog), the dog portrayed in the original Doge image ...
Enrico Dandolo
Enrico Dandolo (Anglicised as Henry Dandolo, and Latinised as Henricus Dandulus; – May/June 1205) was the doge of Venice from 1192 until his death in 1205. He is remembered for his avowed piety, longevity, and shrewdness, and his role in the ...
had organized the invasion and sack of Constantinople after an agreement with Prince Alexios IV Angelos, Alexios Angelos, the son of a deposed Isaac II Angelus, Byzantine emperor.
19th-century restoration
Following the building's conversion into a mosque in 1453, many of its mosaics were covered with plaster, due to Aniconism in Islam, Islam's ban on representational imagery. This process was not completed at once, and reports exist from the 17th century in which travellers note that they could still see Christian images in the former church. In 1847–1849, the building was restored by
Gaspare and Giuseppe Fossati, and Sultan
Abdulmejid I allowed them to also document any mosaics they might discover during this process, which were later archived in Swiss libraries. This work did not include repairing the mosaics, and after recording the details about an image, the Fossatis painted it over again. The Fossatis restored the mosaics of the two ''hexapteryga'' (six-winged angels; it is uncertain whether they are seraphim or cherubim) located on the two east pendentives, and covered their faces again before the end of the restoration.
[Hoffman (1999), p. 207] The other two mosaics, placed on the west pendentives, are copies in paint created by the Fossatis since they could find no surviving remains of them.
As in this case, the architects reproduced in paint damaged decorative mosaic patterns, sometimes redesigning them in the process. The Fossati records are the primary sources about a number of mosaic images now believed to have been completely or partially destroyed in the 1894 Istanbul earthquake. These include a mosaic over a now-unidentified ''Door of the Poor'', a large image of a jewel-encrusted cross, and many images of angels, saints, patriarchs, and church fathers. Most of the missing images were located in the building's two tympana.
One mosaic they documented is Christ Pantocrator in a circle, which would indicate it to be a ceiling mosaic, possibly even of the main dome, which was later covered and painted over with Islamic calligraphy that expounds God as the light of the universe. The Fossatis' drawings of the Hagia Sophia mosaics are today kept in the Archive of the Canton of Ticino.
File:Hagia Sophia Imperial Gate mosaic 2.jpg, Imperial gate mosaic
File:Hagia Sophia Southwestern entrance mosaics 2.jpg, Southwestern entrance mosaic with Justinian I, Justinian the Great (left) and Constantine the Great (right) with the Mary, mother of Jesus, Virgin Mary in the center
File:Apse mosaic Hagia Sophia Virgin and Child.jpg, Apse mosaic of the Mary, mother of Jesus, Virgin Mary and Christ Child, Christ the Child
File:Empress Zoe mosaic Hagia Sophia.jpg, The Zoë Porphyrogenita, Empress Zoe mosaic
File:Comnenus mosaics Hagia Sophia.jpg, The John II Komnenos, Comnenus mosaic
File:Deesis mosaic Hagia Sophia.jpg, The Deësis mosaic
File:Johnchrysostom.jpg, Mosaic in the northern tympanum depicting Saint John Chrysostom
John Chrysostom (; ; – 14 September 407) was an important Church Father who served as archbishop of Constantinople. He is known for his preaching and public speaking, his denunciation of abuse of authority by both ecclesiastical and p ...
File:Jesus-Christ-from-Hagia-Sophia.jpg, Detail of the Christ Pantocrator mosaic, also known as the Deesis, Deësis mosaic
File:2. Seraph angel. 13th century CE. Ceiling mosaics, Hagia Sophia, Istanbul, Turkey.jpg, A Seraph angel. 13th century CE.
20th-century restoration
Many mosaics were uncovered in the 1930s by a team from the Byzantine Institute of America led by Thomas Whittemore. The team chose to let a number of simple cross images remain covered by plaster but uncovered all major mosaics found.
Because of its long history as both a church and a mosque, a particular challenge arises in the restoration process. Christian iconography, iconographic mosaics can be uncovered, but often at the expense of important and historic Islamic art. Restorers have attempted to maintain a balance between both Christian and Islamic cultures. In particular, much controversy rests upon whether the Islamic calligraphy on the dome of the cathedral should be removed, to permit the underlying Pantocrator mosaic of Christ as Master of the World to be exhibited (assuming the mosaic still exists).
The Hagia Sophia has been a victim of natural disasters that have caused deterioration to the buildings structure and walls. The deterioration of the Hagia Sophia's walls can be directly attributed to salt crystallization. The crystallization of salt is due to an intrusion of rainwater that causes the Hagia Sophia's deteriorating inner and outer walls. Diverting excess rainwater is the main solution to the deteriorating walls at the Hagia Sophia.
Built between 532 and 537, a subsurface structure under the Hagia Sophia has been under investigation, using LaCoste-Romberg gravimeters to determine the depth of the subsurface structure and to discover other hidden cavities beneath the Hagia Sophia. The hidden cavities have also acted as a support system against earthquakes. With these findings using the LaCoste-Romberg gravimeters, it was also discovered that the Hagia Sophia's foundation is built on a slope of natural rock.
Imperial Gate mosaic
The Imperial Gate mosaic is located in the Tympanum (architecture), tympanum above that gate, which was used only by the emperors when entering the church. Based on style analysis, it has been dated to the late 9th or early 10th century. The emperor with a Halo (religious iconography), nimbus or halo could possibly represent emperor Leo VI the Wise or his son Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus bowing down before Christ Pantocrator, seated on a jewelled throne, giving his blessing and holding in his left hand an open book.
Southwestern entrance mosaic
The southwestern entrance mosaic, situated in the tympanum of the southwestern entrance, dates from the reign of
Basil II
Basil II Porphyrogenitus (; 958 – 15 December 1025), nicknamed the Bulgar Slayer (, ), was the senior Byzantine emperor from 976 to 1025. He and his brother Constantine VIII were crowned before their father Romanos II died in 963, but t ...
. It was rediscovered during the restorations of 1849 by the Fossatis. The Virgin sits on a throne without a back, her feet resting on a pedestal, embellished with precious stones. The Christ Child sits on her lap, giving his blessing and holding a scroll in his left hand. On her left side stands emperor Constantine in ceremonial attire, presenting a model of the city to Mary. On her right side stands emperor
Justinian I, offering a model of the Hagia Sophia. The composition of the figure of the Virgin enthroned was probably copied from the mosaic inside the semi-dome of the apse inside the liturgical space.
Apse mosaics
The mosaic in the
semi-dome
In architecture, a semi-dome (or half-dome) is a half dome that covers a semi-circular area in a building.
Architecture
Semi-domes are a common feature of apses in Ancient Roman and traditional church architecture, and in mosques and iwans in Isla ...
above the apse at the east end shows Mary, mother of Jesus holding the Christ Child and seated on a jewelled ''thokos'' backless throne.
Since its rediscovery after a period of concealment in the Ottoman era, it "has become one of the foremost monuments of Byzantium".
The infant Jesus's garment is depicted with golden ''
tesserae
A tessera (plural: tesserae, diminutive ''tessella'') is an individual tile, usually formed in the shape of a square, used in creating a mosaic. It is also known as an abaciscus or abaculus.
Historical tesserae
In early antiquity, mo ...
''.
Guillaume-Joseph Grelot, who had travelled to Constantinople, in 1672 engraved and in 1680 published in Paris an image of the interior of Hagia Sophia which shows the apse mosaic indistinctly.
Together with a picture by Cornelius Loos drawn in 1710, these images are early attestations of the mosaic before it was covered towards the end of the 18th century.
The mosaic of the Virgin and Child was rediscovered during the restorations of the Fossati brothers in 1847–1848 and revealed by the restoration of Thomas Whittemore in 1935–1939.
It was studied again in 1964 with the aid of scaffolding.
It is not known when this mosaic was installed.
According to Cyril Mango, the mosaic is "a curious reflection on how little we know about Byzantine art". The work is generally believed to date from after the end of Byzantine Iconoclasm and usually dated to the patriarchate of Photius I, Photius I () and the time of the emperors Michael III () and
Basil I
Basil I, nicknamed "the Macedonian" (; 811 – 29 August 886), was Byzantine emperor from 867 to 886. Born to a peasant family in Macedonia, he rose to prominence in the imperial court after gaining the favour of Emperor Michael III, whose mist ...
().
Most specifically, the mosaic has been connected with a surviving
homily
A homily (from Greek ὁμιλία, ''homilía'') is a commentary that follows a reading of scripture, giving the "public explanation of a sacred doctrine" or text. The works of Origen and John Chrysostom (known as Paschal Homily) are considered ...
known to have been written and delivered by Photius in the cathedral on 29 March 867.
Other scholars have favoured earlier or later dates for the present mosaic or its composition. Nikolaos Oikonomides pointed out that Photius's homily refers to a standing portrait of the ''Theotokos'' – a ''
Hodegetria
A Hodegetria, or Virgin Hodegetria, is an iconography, iconographic depiction of the Theotokos (Virgin Mary) holding the Child Jesus at her side while pointing to him as the source of salvation for humankind. The Virgin's head usually inclines t ...
'' – while the present mosaic shows her seated.
Likewise, a biography of the patriarch Isidore I of Constantinople, Isidore I () by his successor Philotheus I of Constantinople, Philotheus I () composed before 1363 describes Isidore seeing a standing image of the Virgin at Epiphany (holiday), Epiphany in 1347.
Serious damage was done to the building by earthquakes in the 14th century, and it is possible that a standing image of the Virgin that existed in Photius's time was lost in the earthquake of 1346, in which the eastern end of Hagia Sophia was partly destroyed.
This interpretation supposes that the present mosaic of the Virgin and Child enthroned is of the late 14th century, a time in which, beginning with Nilus of Constantinople (), the patriarchs of Constantinople began to have official Seal (emblem), seals depicting the ''Theotokos'' enthroned on a ''thokos''.
Still other scholars have proposed an earlier date than the later 9th century. According to George Galavaris, the mosaic seen by Photius was a ''Hodegetria'' portrait which after the earthquake of 989 was replaced by the present image not later than the early 11th century.
According to Oikonomides however, the image in fact dates to before the Triumph of Orthodoxy, having been completed , during the iconodule interlude between the First Iconoclast (726–787) and the Second Iconoclast (814–842) periods.
Having been plastered over in the Second Iconoclasm, Oikonomides argues a new, standing image of the Virgin ''Hodegetria'' was created above the older mosaic in 867, which then fell off in the earthquakes of the 1340s and revealed again the late 8th-century image of the Virgin enthroned.
More recently, analysis of a hexaptych menologion icon panel from Saint Catherine's Monastery at Mount Sinai has determined that the panel, showing numerous scenes from the life of the Virgin and other theologically significant iconic representations, contains an image at the centre very similar to that in Hagia Sophia.
The image is labelled in Greek merely , but in the Georgian language the inscription reveals the image is labelled "of the semi-dome of Hagia Sophia".
This image is therefore the oldest depiction of the apse mosaic known and demonstrates that the apse mosaic's appearance was similar to the present day mosaic in the late 11th or early 12th centuries, when the hexaptych was inscribed in Georgian by a Georgian monk, which rules out a 14th-century date for the mosaic.
The portraits of the archangels Gabriel and Michael (largely destroyed) in the bema of the arch also date from the 9th century. The mosaics are set against the original golden background of the 6th century. These mosaics were believed to be a reconstruction of the mosaics of the 6th century that were previously destroyed during the iconoclastic era by the Byzantines of that time, as represented in the inaugural sermon by the patriarch Photios. However, no record of figurative decoration of Hagia Sophia exists before this time.
Emperor Alexander mosaic
The Emperor Alexander mosaic is not easy to find for the first-time visitor, located on the second floor in a dark corner of the ceiling. It depicts the emperor Alexander (Byzantine emperor), Alexander in full regalia, holding a scroll in his right hand and a globus cruciger in his left. A drawing by the Fossatis showed that the mosaic survived until 1849 and that Thomas Whittemore, founder of the Byzantine Institute of America who was granted permission to preserve the mosaics, assumed that it had been destroyed in the earthquake of 1894. Eight years after his death, the mosaic was discovered in 1958 largely through the researches of Robert Van Nice. Unlike most of the other mosaics in Hagia Sophia, which had been covered over by ordinary plaster, the Alexander mosaic was simply painted over and reflected the surrounding mosaic patterns and thus was well hidden. It was duly cleaned by the Byzantine Institute's successor to Whittemore, Paul A. Underwood.
Empress Zoe mosaic
The Empress Zoe mosaic on the eastern wall of the southern gallery dates from the 11th century. Christ Pantocrator, clad in the dark blue robe (as is the custom in Byzantine art), is seated in the middle against a golden background, giving his blessing with the right hand and holding the Bible in his left hand. On either side of his head are the ''nomina sacra'' ' and ', meaning ''Iēsous Christos''. He is flanked by Constantine IX Monomachus and Empress Zoe, both in ceremonial costumes. He is offering a purse, as a symbol of donation, he made to the church, while she is holding a scroll, symbol of the donations she made. The previous heads have been scraped off and replaced by the three present ones. Perhaps the earlier mosaic showed her first husband Romanos III, Romanus III Argyrus or her second husband Michael IV the Paphlagonian, Michael IV. Another theory is that this mosaic was made for an earlier emperor and empress, with their heads changed into the present ones.
Comnenus mosaic
The Comnenus mosaic, also located on the eastern wall of the southern gallery, dates from 1122. The Virgin Mary is standing in the middle, depicted, as usual in Byzantine art, in a dark blue gown. She holds the Christ Child on her lap. He gives his blessing with his right hand while holding a scroll in his left hand. On her right side stands emperor John II Comnenus, represented in a garb embellished with precious stones. He holds a purse, symbol of an imperial donation to the church. His wife, the empress Irene of Hungary stands on the left side of the Virgin, wearing ceremonial garments and holding an eiletarion scroll. Their eldest son Alexios Komnenos (co-emperor), Alexius Comnenus is represented on an adjacent pilaster. He is shown as a beardless youth, probably representing his appearance at his coronation aged seventeen. In this panel, one can already see a difference with the Empress Zoe mosaic that is one century older. There is a more realistic expression in the portraits instead of an idealized representation. The Empress Irene, daughter of Ladislaus I of Hungary, Ladislaus I of Hungary, is shown with plaited blond hair, rosy cheeks, and grey eyes, revealing her Hungarians, Hungarian descent. The emperor is depicted in a dignified manner.
Deësis mosaic
The Deësis mosaic (, "Entreaty") probably dates from 1261. It was commissioned to mark the end of 57 years of Latin Catholic use and the return to the Eastern Orthodox faith. It is the third panel situated in the imperial enclosure of the upper galleries. It is widely considered the finest in Hagia Sophia, because of the softness of the features, the humane expressions and the tones of the mosaic. The style is close to that of the Italian painters of the late 13th or early 14th century, such as Duccio. In this panel the Virgin Mary and John the Baptist are imploring the intercession of Christ Pantocrator for humanity on Last Judgment, Judgment Day. The bottom part of this mosaic is badly deteriorated. This mosaic is considered as the beginning of a renaissance in Byzantine Pictorial artist, pictorial art.
Northern tympanum mosaics
The northern Tympanum (architecture), tympanum mosaics feature various saints. They have been able to survive due to their high and inaccessible location. They depict Patriarchs of Constantinople
John Chrysostom
John Chrysostom (; ; – 14 September 407) was an important Church Father who served as archbishop of Constantinople. He is known for his preaching and public speaking, his denunciation of abuse of authority by both ecclesiastical and p ...
and Ignatios of Constantinople standing, clothed in white robes with crosses, and holding richly jewelled Bibles. The figures of each patriarch, revered as saints, are identifiable by labels in Greek. The other mosaics in the other tympana have not survived probably due to the frequent earthquakes, as opposed to any deliberate destruction by the Ottoman conquerors.
Dome mosaic
The dome was decorated with four non-identical figures of the six-winged angels which protect the Throne of God; it is uncertain whether they are seraphim or cherubim. The mosaics survive in the eastern part of the dome, but since the ones on the western side were damaged during the Byzantine period, they have been renewed as frescoes. During the Ottoman period each face was covered with metallic lids in the shape of stars, but these were removed to reveal the faces during renovations in 2009.
Other burials
* Selim II (1524 – 15 December 1574)
*
Murad III
Murad III (; ; 4 July 1546 – 16 January 1595) was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1574 until his death in 1595. His rule saw battles with the Habsburg monarchy, Habsburgs and exhausting wars with the Safavid Iran, Safavids. The long-inde ...
1546–1595
* Mustafa I ( – 20 January 1639), in the courtyard.
*
Enrico Dandolo
Enrico Dandolo (Anglicised as Henry Dandolo, and Latinised as Henricus Dandulus; – May/June 1205) was the doge of Venice from 1192 until his death in 1205. He is remembered for his avowed piety, longevity, and shrewdness, and his role in the ...
( – June 1205), in the east gallery.
* Gli ( – 7 November 2020), in the garden.
Works influenced by the Hagia Sophia
Many buildings have been modeled on the Hagia Sophia's core structure of a large central dome resting on pendentives and buttressed by two semi-domes.
Byzantine architecture, Byzantine churches influenced by the Hagia Sophia include the
Hagia Sophia in Thessaloniki, and the
Hagia Irene
Hagia Irene () or Hagia Eirene ( , "Holy Peace", ), sometimes known also as Saint Irene, is a former Eastern Orthodox church located in the outer courtyard of Topkapı Palace in Istanbul. It is the oldest known church structure in the city and on ...
. The latter was remodeled to have a dome similar to the Hagia Sophia's during the reign of Justinian. Neo-Byzantine churches modeled on the Hagia Sophia include the Kronstadt Naval Cathedral, Holy Trinity Cathedral, Sibiu
and Poti Cathedral. Each closely replicates the internal geometry of the Hagia Sophia. The layout of the Kronstadt Naval Cathedral is nearly identical to the Hagia Sophia in size and geometry. Its marble revetment also mimics the style of the Hagia Sophia. The Catedral Metropolitana Ortodoxa in São Paulo and the Église du Saint-Esprit (Paris) both replace the two large tympanum (architecture), tympanums beneath the main dome with two shallow semi-domes. Several churches combine elements of the Hagia Sophia with a Latin cross plan. For instance, the transept of the Cathedral Basilica of Saint Louis (St. Louis) is formed by two semi-domes surrounding the main dome. The church's column capitals and mosaics also emulate the style of the Hagia Sophia. Other examples include the Alexander Nevsky Cathedral, Sofia, St Sophia's Cathedral, London, Saint Clement Catholic Church, Chicago, and the Basilica of the National Shrine of the Immaculate Conception. Several mosques commissioned by the Ottoman dynasty have plans based on the Hagia Sophia, including the
Süleymaniye Mosque
The Süleymaniye Mosque (, ) is an Ottoman imperial mosque located on the Seven hills of Istanbul, Third Hill of Istanbul, Turkey. The mosque was commissioned by Suleiman the Magnificent () and designed by the imperial architect Mimar Sinan. An ...
and the Bayezid II Mosque, Istanbul, Bayezid II Mosque.
Synagogues based on the Hagia Sophia include the Congregation Emanu-El (San Francisco),
Great Synagogue of Florence, and Hurva Synagogue.
Gallery
File:Hagia Sophia (15468276434).jpg, Detail of the columns
File:20131203 Istanbul 048.jpg, Detail of the columns
File:Fossati 003.JPG, Six patriarchs mosaic in the southern tympanum as drawn by the Fossati brothers
File:Fossati 002.JPG, Moasics as drawn by the Fossati brothers
File:Nikea-arius.png, The Hagia Sophia in the background of an icon from the Monastery of Great Meteoron
File:Relation nouvelle d'un voyage de Constantinople - enrichie de plans levez par l'auteur sur les lieux, and des figures de tout ce qu'il y a de plus remarquable dans cette ville (1680) (14773026492).jpg, Guillaume-Joseph Grelot's engraving 1672, looking east and showing the apse mosaic
File:Relation nouvelle d'un voyage de Constantinople - enrichie de plans levez par l'auteur sur les lieux, and des figures de tout ce qu'il y a de plus remarquable dans cette ville (1680) (14586659270).jpg, Guillaume-Joseph Grelot's engraving 1672, looking west
File:Interior of the Hagia Sophia.jpg, ''Interior of the Hagia Sophia'' by John Singer Sargent, 1891
File:Sébah and Joaillier - Interior of Ayasofya Mosque.jpg, Photograph by Sébah & Joaillier,
File:Philippe Chaperon Sainte-Sophie, 1893 (collection particulière).jpg, Watercolour of the interior by Philippe Chaperon, 1893
File:Detail of Sculptural Relief on the Marble Door of the Hagia Sophia in Istanbul, Turkey.jpg, Detail of relief
Relief is a sculpture, sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces remain attached to a solid background of the same material. The term ''wikt:relief, relief'' is from the Latin verb , to raise (). To create a sculpture in relief is to give ...
on the Marble Door.
File:Hagia Sophia (16064799696).jpg, Imperial Gate from the nave
File:Henricus Dandolo grób RB1.jpg, 19th-century cenotaph of Enrico Dandolo
Enrico Dandolo (Anglicised as Henry Dandolo, and Latinised as Henricus Dandulus; – May/June 1205) was the doge of Venice from 1192 until his death in 1205. He is remembered for his avowed piety, longevity, and shrewdness, and his role in the ...
, Doge
Doge, DoGE or DOGE may refer to:
Internet culture
* Doge (meme), an Internet meme primarily associated with the Shiba Inu dog breed
** Dogecoin, a cryptocurrency named after the meme
** Kabosu (dog), the dog portrayed in the original Doge image ...
of Venice
Venice ( ; ; , formerly ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are li ...
, and commander of the 1204 Fourth Crusade, Sack of Constantinople
File:Gate of the mosque of Saint Sophia - Lewis John F - 1838.jpg, Gate of the ''külliye'', by John Frederick Lewis, 1838
File:Fountain of the gate of Eski (Old) Serai - Lewis John F - 1838.jpg, Fountain of Ahmed III from the gate of the ''külliye'', by John Frederick Lewis, 1838
File:Saint Sophia and distant view of Sultan Achmet (Mosques) - Lewis John F - 1838.jpg, Southern side of Hagia Sophia, looking east, by John Frederick Lewis, 1838
File:Adriaan-Reland-Verhandeling-van-de-godsdienst-der-Mahometaanen MG 0720.tif, From ''Verhandeling van de godsdienst der Mahometaanen'', by Adriaan Reland, 1719
File:Interior of Haghia Sophia.jpg, Interior of Haghia Sophia
File:Voyage en Orient (bgw20 0447).jpg, Hagia Sophia from the south-west, 1914
File:Hagia Sophia and its faithful tourists (24238189635).jpg, Hagia Sophia in the snow, December 2015
File:MG08 on the minaret of the Ayasofya Museum 1941.jpg, Maschinengewehr 08, ''Maschinengewehr'' 08 mounted on a minaret during World War II
See also
*Runic inscriptions in Hagia Sophia
*List of Byzantine inventions
*List of tallest domes
*List of largest monoliths
*List of oldest church buildings
*List of tallest structures built before the 20th century
*List of Turkish Grand Mosques
*Conversion of non-Islamic places of worship into mosques
Notes
References
Citations
Sources
*
*
*
* ''Hagia Sophia''
Hagia Sophia. Accessed 23 September 2014.
*
*
*
* .
*
*
*
*
*
* Runciman, Steven (1965)
The Fall of Constantinople, 1453. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 145. .
*
*
*
Further reading
:''See also the thematically organised full bibliography in Stroth (2021), pp. 137–183.''
*
*
*
*
*
* Harris, Jonathan, ''Constantinople: Capital of Byzantium''. Hambledon/Continuum (2007).
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Scharf, Joachim: "Der Kaiser in Proskynese. Bemerkungen zur Deutung des Kaisermosaiks im Narthex der Hagia Sophia von Konstantinopel". In: ''Festschrift Percy Ernst Schramm zu seinem siebzigsten Geburtstag von Schülern und Freunden zugeeignet'', Wiesbaden 1964, pp. 27–35.
*
*
* Kurt Weitzmann, Weitzmann, Kurt, ed.,
Age of spirituality: late antique and early Christian art, third to seventh century'', no. 592, 1979, Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York,
*
*
Articles
*
*
*Bordewich, Fergus M.
"A Monumental Struggle to Preserve Hagia Sophia" ''Smithsonian (magazine), Smithsonian'' magazine, December 2008
*Calian, Florian
The Hagia Sophia and Turkey's Neo-Ottomanism, ''Armenian Weekly''.
*
*Ousterhout, Robert G.
Museum or Mosque? Istanbul's Hagia Sophia has been a monument to selective readings of history." ''History Today'' (Sept 2020).
*Suchkov, Maxim
Why did Moscow call Ankara's Hagia Sophia decision "Turkey's internal affair"?, ''Middle East Institute''.
Mosaics
*''Hagia Sophia''
hagiasophia.com: Mosaics
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
*
360 Degree Virtual Tour of Hagia Sophia Mosque MuseumGigapixel of Hagia Sophia Dome (214 Billion Pixel)* [http://en.istanbul.gov.tr/the-most-visited-museums-of-turkey-hagia-sophia-museum The Most Visited Museums of Turkey: Hagia Sophia Museum, Governorship of Istanbul]
{{Authority control
Hagia Sophia,
537 establishments
6th-century churches
15th-century mosques in Turkey
Buildings converted to Catholic church buildings
Byzantine church buildings in Istanbul
Church buildings converted to a different denomination
Church buildings with domes
Churches in Istanbul
Religion in Constantinople
Churches and monasteries of Constantinople
Constantius II
Eastern Orthodox church buildings
Eastern Orthodox pilgrimage sites
Fatih
Former cathedrals in Turkey
Greece–Turkey relations
Greek Orthodox cathedrals in Europe
Historic Civil Engineering Landmarks
Historic sites in Turkey
Justinian I
Mosques converted from churches in Turkey
Mosques in Istanbul
Theodosius II
World Heritage Sites in Turkey
Mosques converted from Byzantine churches
 The first church on the site was known as the ()Müller-Wiener (1977), p. 84. because of its size compared to the sizes of the contemporary churches in the city. According to the ''
The first church on the site was known as the ()Müller-Wiener (1977), p. 84. because of its size compared to the sizes of the contemporary churches in the city. According to the '' Earthquakes in 553 and on
Earthquakes in 553 and on  In 726, the emperor
In 726, the emperor  During the reign of Selim II (), the building started showing signs of fatigue and was extensively strengthened with the addition of structural supports to its exterior by Ottoman architect
During the reign of Selim II (), the building started showing signs of fatigue and was extensively strengthened with the addition of structural supports to its exterior by Ottoman architect  In the aftermath of the defeat of the Ottoman Empire in World War I, Constantinople was
In the aftermath of the defeat of the Ottoman Empire in World War I, Constantinople was 
 In 1935, the first
In 1935, the first  While use of the complex as a place of worship (mosque or church) was strictly prohibited, in 1991 the Turkish government allowed the allocation of a pavilion in the museum complex (''Ayasofya Müzesi Hünkar Kasrı'') for use as a prayer room, and, since 2013, two of the museum's minarets had been used for voicing the call to prayer (the ezan) regularly.
While use of the complex as a place of worship (mosque or church) was strictly prohibited, in 1991 the Turkish government allowed the allocation of a pavilion in the museum complex (''Ayasofya Müzesi Hünkar Kasrı'') for use as a prayer room, and, since 2013, two of the museum's minarets had been used for voicing the call to prayer (the ezan) regularly.
 From the early 2010s, several campaigns and government high officials, notably Turkey's deputy prime minister
From the early 2010s, several campaigns and government high officials, notably Turkey's deputy prime minister 
 Since 2018,
Since 2018,  Days before the final decision on the conversion was made, Ecumenical Patriarch Bartholomew I of Constantinople stated in a sermon that "the conversion of Hagia Sophia into a mosque would disappoint millions of Christians around the world". The proposed conversion was decried by other Orthodox Christian leaders, the
Days before the final decision on the conversion was made, Ecumenical Patriarch Bartholomew I of Constantinople stated in a sermon that "the conversion of Hagia Sophia into a mosque would disappoint millions of Christians around the world". The proposed conversion was decried by other Orthodox Christian leaders, the  Hagia Sophia is one of the greatest surviving examples of
Hagia Sophia is one of the greatest surviving examples of  The theories of
The theories of 
 The
The  The first mosaics which adorned the church were completed during the reign of Justin II. Many of the non-figurative mosaics in the church come from this period. Most of the mosaics, however, were created in the 10th and 12th centuries, following the periods of Byzantine Iconoclasm.
During the Fourth Crusade, Sack of Constantinople in 1204, the Latin Crusaders vandalized valuable items in every important Byzantine structure of the city, including the golden mosaics of the Hagia Sophia. Many of these items were shipped to Venice, whose
The first mosaics which adorned the church were completed during the reign of Justin II. Many of the non-figurative mosaics in the church come from this period. Most of the mosaics, however, were created in the 10th and 12th centuries, following the periods of Byzantine Iconoclasm.
During the Fourth Crusade, Sack of Constantinople in 1204, the Latin Crusaders vandalized valuable items in every important Byzantine structure of the city, including the golden mosaics of the Hagia Sophia. Many of these items were shipped to Venice, whose