An armoured fighting vehicle (
British English
British English is the set of Variety (linguistics), varieties of the English language native to the United Kingdom, especially Great Britain. More narrowly, it can refer specifically to the English language in England, or, more broadly, to ...
) or armored fighting vehicle (
American English
American English, sometimes called United States English or U.S. English, is the set of variety (linguistics), varieties of the English language native to the United States. English is the Languages of the United States, most widely spoken lang ...
) (AFV) is an armed
combat vehicle
A ground combat vehicle, also known as a land assault vehicle or simply a combat vehicle or an assault vehicle, is a land-based military vehicle intended to be used for combat operations. They differ from non-combat military vehicles such as M ...
protected by
armour
Armour (Commonwealth English) or armor (American English; see American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, spelling differences) is a covering used to protect an object, individual, or vehicle from physical injury or damage, e ...
, generally combining
operational mobility
In the field of military theory, the operational level of war (also called operational art, as derived from , or operational warfare) represents the level of command that connects the details of tactics with the goals of strategy.
In U.S. ...
with
offensive and
defensive
Defense or defence may refer to:
Tactical, martial, and political acts or groups
* Defense (military), forces primarily intended for warfare
* Civil defense, the organizing of civilians to deal with emergencies or enemy attacks
* Defense indust ...
capabilities. AFVs can be wheeled or
tracked. Examples of AFVs are
tank
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful engine; ...
s,
armoured cars
Armored (or armoured) car may refer to:
Wheeled armored vehicles
* Armored car (military), a wheeled armoured fighting vehicle
* Armored car (valuables), an armored van or truck used to transport valuables
* Armored car (VIP), a civilian vehic ...
,
assault gun
An assault gun (from , , meaning "assault gun") is a type of armored infantry support vehicle and self-propelled artillery, mounting an infantry support gun on a protected self-propelled chassis, intended for providing infantry with heavy di ...
s,
self-propelled artilleries,
infantry fighting vehicle
An infantry fighting vehicle (IFV), also known as a mechanized infantry combat vehicle (MICV), is a type of armoured fighting vehicle and armoured personnel carrier used to carry infantry into battle and provide direct fire, direct-fire suppo ...
s (IFV), and
armoured personnel carrier
An armoured personnel carrier (APC) is a broad type of armoured military vehicle designed to transport personnel and equipment in combat zones. Since World War I, APCs have become a very common piece of military equipment around the world.
Acc ...
s (APC).
Armoured fighting vehicles are classified according to their characteristics and intended role on the battlefield. The classifications are not absolute; two countries may classify the same vehicle differently, and the criteria change over time. For example, relatively lightly armed armoured personnel carriers were largely superseded by infantry fighting vehicles with much heavier armament in a similar role.
Successful designs are often adapted to a wide variety of applications. For example, the
MOWAG Piranha
The Mowag Piranha is a family of armoured fighting vehicles designed by the Swiss company Mowag (since 2010 General Dynamics European Land Systems – Mowag GmbH).
Five generations of vehicles have been produced, manufactured by Mowag or under ...
, originally designed as an APC, has been adapted to fill numerous roles such as a
mortar carrier, infantry fighting vehicle, and assault gun.
Armoured fighting vehicles began to appear in use in World War I with the armoured car, the tank, the self-propelled gun, and the personnel carrier seeing use. By World War II, armies had large numbers of AFVs, together with other vehicles to carry troops this permitted highly mobile
manoeuvre warfare
Maneuver warfare, or manoeuvre warfare, is a military strategy which emphasizes movement, initiative and surprise to achieve a position of advantage. Maneuver seeks to inflict losses indirectly by envelopment, encirclement and disruption, while ...
.
Evolution
The concept of a highly mobile and protected fighting unit has been around for centuries; from
Hannibal
Hannibal (; ; 247 – between 183 and 181 BC) was a Punic people, Carthaginian general and statesman who commanded the forces of Ancient Carthage, Carthage in their battle against the Roman Republic during the Second Punic War.
Hannibal's fat ...
's
war elephant
A war elephant is an elephant that is Animal training, trained and guided by humans for combat purposes. Historically, the war elephant's main use was to charge (warfare), charge the enemy, break their ranks, and instill terror and fear. Elep ...
s to
Leonardo's
contraptions, military strategists endeavoured to maximize the mobility and survivability of their soldiers.
Armoured fighting vehicles were not possible until
internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal comb ...
s of sufficient power became available at the start of the 20th century.
History
Pre-modern

Modern armoured fighting vehicles represent the realization of an ancient concept – that of providing troops with mobile protection and firepower. Armies have deployed war machines and cavalries with rudimentary armour in battle for millennia. Use of these animals and engineering designs sought to achieve a balance between the conflicting needs of mobility, firepower and protection.
= Siege machine
=

Siege engine
A siege engine is a device that is designed to break or circumvent heavy castle doors, thick city walls and other fortifications in siege warfare. Some are immobile, constructed in place to attack enemy fortifications from a distance, while othe ...
s, such as
battering ram
A battering ram is a siege engine that originated in ancient times and was designed to break open the masonry walls of fortifications or splinter their wooden gates. In its simplest form, a battering ram is just a large, heavy log carried ...
s and
siege tower
A Roman siege tower or breaching tower (or in the Middle Ages, a belfry''Castle: Stephen Biesty's Cross-Sections''. Dorling Kindersley Pub (T); 1st American edition (September 1994). Siege towers were invented in 300 BC. ) is a specialized siege ...
s, would often be armoured in order to protect their crews from enemy action.
Polyidus of Thessaly
Polyidus of Thessaly (also Polyides, Polydus; , , English translation: "much beauty", from ''polus'', "many, much" and ''eidos'', "form, appearance, beauty") was an ancient Greek military engineer of Philip, who made improvements in the covered b ...
developed a very large movable siege tower, the ''
helepolis
Helepolis (, meaning: "Taker of Cities") is the Greek name for a movable siege tower.
The most famous was that invented by Polyidus of Thessaly, and improved by Demetrius I of Macedon and Epimachus of Athens, for the Siege of Rhodes (305 BC ...
'', as early as 340 BC, and Greek forces used such structures in the
Siege of Rhodes (305 BC).
The idea of a protected fighting vehicle has been known since antiquity. Frequently cited is
Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 1452 - 2 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially rested o ...
's 15th-century sketch of a
mobile, protected gun-platform; the drawings show a conical, wooden shelter with apertures for cannons around the circumference. The machine was to be mounted on four wheels which would be turned by the crew through a system of
hand cranks and
cage (or "lantern") gears. Leonardo claimed: "I will build armoured wagons which will be safe and invulnerable to enemy attacks. There will be no obstacle which it cannot overcome." Modern replicas have demonstrated that the human crew would have been able to move it over only short distances.
= War wagon
=
Hussite
file:Hussitenkriege.tif, upright=1.2, Battle between Hussites (left) and Crusades#Campaigns against heretics and schismatics, Catholic crusaders in the 15th century
file:The Bohemian Realm during the Hussite Wars.png, upright=1.2, The Lands of the ...
forces in
Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
developed
war wagon
A war wagon is any of several historical types of early fighting vehicle involving an armed or armored animal-drawn cart or wagon.
China
One of the earliest example of using conjoined wagons in warfare as fortification is described in the Chine ...
s –
medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
horse-drawn
wagon
A wagon (or waggon) is a heavy four-wheeled vehicle pulled by Working animal#Draft animals, draft animals or on occasion by humans, used for transporting goods, commodities, agricultural materials, supplies and sometimes people.
Wagons are i ...
s that doubled as
wagon fort
A wagon fort, wagon fortress, wagenburg or corral, often referred to as circling the wagons, is a temporary fortification made of wagons arranged into a rectangle, circle, or other shape and possibly joined with each other to produce an improvis ...
s – around 1420 during the
Hussite Wars
The Hussite Wars, also called the Bohemian Wars or the Hussite Revolution, were a series of civil wars fought between the Hussites and the combined Catholic forces of Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor, Holy Roman Emperor Sigismund, the Papacy, a ...
. These heavy wagons were given protective sides with firing slits; their heavy firepower came from either a cannon or from a force of
hand-gunners and
crossbowmen
An arbalist, also spelled arbelist, is one who shoots a crossbow.
Background
An extensive list of archaic words for medieval crossbowmen is given by Payne-Gallwey. Richardson, in his 1839 dictionary, did not make specific reference to the cross ...
, supported by
light cavalry
Light cavalry comprised lightly armed and body armor, armored cavalry troops mounted on fast horses, as opposed to heavy cavalry, where the mounted riders (and sometimes the warhorses) were heavily armored. The purpose of light cavalry was p ...
and
infantry
Infantry, or infantryman are a type of soldier who specialize in ground combat, typically fighting dismounted. Historically the term was used to describe foot soldiers, i.e. those who march and fight on foot. In modern usage, the term broadl ...
using
pike
Pike, Pikes or The Pike may refer to:
Fish
* Blue pike or blue walleye, an extinct color morph of the yellow walleye ''Sander vitreus''
* Ctenoluciidae, the "pike characins", some species of which are commonly known as pikes
* ''Esox'', genus of ...
s and
flail
Flail may refer to:
* Flail (tool), an agricultural implement for threshing
* Flail (weapon)
A flail is a weapon consisting of a striking head attached to a handle by a flexible rope, strap, or chain. The chief tactical virtue of the flail i ...
s. Heavy
arquebus
An arquebus ( ) is a form of long gun that appeared in Europe and the Ottoman Empire during the 15th century. An infantryman armed with an arquebus is called an arquebusier.
The term ''arquebus'' was applied to many different forms of firearms ...
es mounted on wagons were called ''arquebus à croc''. These carried a ball of about .

Modern
By the end of
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, most modern armies had vehicles to carry infantry, artillery and
anti-aircraft weapon
Anti-aircraft warfare (AAW) is the counter to aerial warfare and includes "all measures designed to nullify or reduce the effectiveness of hostile air action".AAP-6 It encompasses surface-based, subsurface (Submarine#Armament, submarine-lau ...
ry. Most modern AFVs are superficially similar in design to their World War II counterparts, but with significantly better armour, weapons, engines, electronics, and suspension. The increase in the capacity of
transport aircraft Transport aircraft is a broad category of aircraft that includes:
* Airliners, aircraft, usually large and most often operated by airlines, intended for carrying multiple passengers or cargo in commercial service
* Cargo aircraft or freighters, fix ...
makes possible and practicable the transport of AFVs by air. Many armies are replacing some or all of their traditional heavy vehicles with lighter airmobile versions, often with wheels instead of tracks.
= Armed and armoured car
=
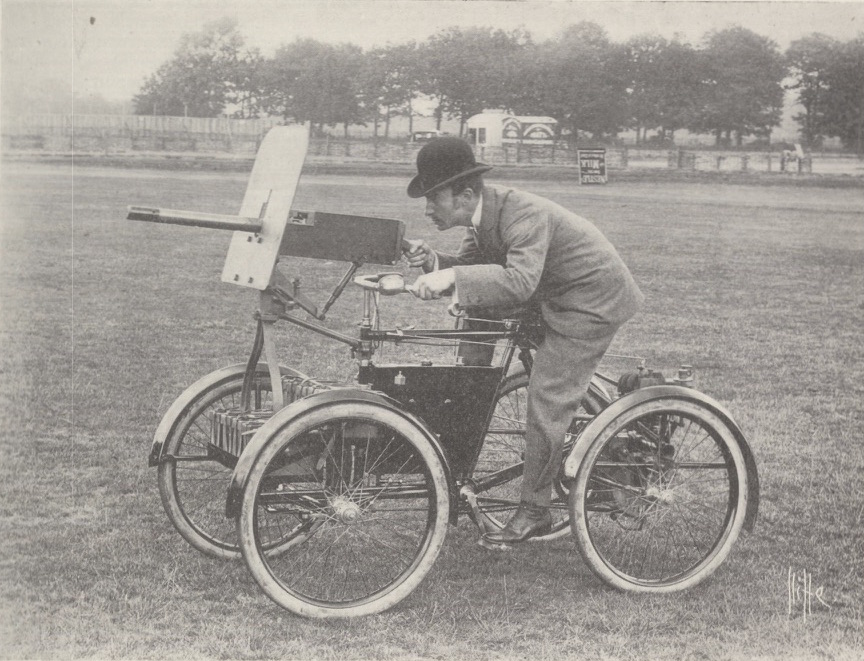
The first modern AFVs were armed cars, dating back virtually to the invention of the
motor car
A car, or an automobile, is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of cars state that they run primarily on roads, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport people rather than cargo. There are around one bil ...
. The British inventor
F. R. Simms designed and built the
Motor Scout
The Motor Scout was the first armed petrol engine powered vehicle ever built. It was not intended for running over ploughed fields or charging, but it was designed to provide a cover or to support infantry and cavalry wherever good roads were a ...
in 1898. It was the first armed, petrol-engine powered vehicle ever built. It consisted of a
De Dion-Bouton
De Dion-Bouton was a French automobile manufacturer and railcar manufacturer, which operated from 1883 to 1953. The company was founded by the Marquis Jules-Albert de Dion, Georges Bouton, and Bouton's brother-in-law Charles Trépardoux.
Ste ...
quadracycle
A quadracycle (also spelled quadricycle) is a four-wheeled human-powered land vehicle. It is also referred to as a quadcycle, pedal car or four-wheeled bicycle amongst other terms.
Quadracycles have been in use since 1853 and have grown int ...
with a
Maxim machine gun
The Maxim gun is a Recoil operation, recoil-operated machine gun invented in 1884 by Hiram Maxim, Hiram Stevens Maxim. It was the first automatic firearm, fully automatic machine gun in the world.
The Maxim gun has been called "the weapon most ...
mounted on the front bar. An iron shield offered some protection for the driver from the front, but it lacked all-around protective armour.
The
armoured car was the first modern fully armoured fighting vehicle. The first of these was the
Simms's Motor War Car, also designed by Simms and built by
Vickers, Sons & Maxim
Vickers was a British engineering company that existed from 1828 until 1999. It was formed in Sheffield as a steel foundry by Edward Vickers and his father-in-law, and soon became famous for casting church bells. The company went public in 18 ...
in 1899.
The vehicle had Vickers armour 6 mm thick and was powered by a four-cylinder 3.3-litre
16
hp Cannstatt Daimler engine giving it a maximum speed of around . The armament, consisting of two Maxim guns, was carried in two turrets with 360° traverse.

Another early armoured car of the period was the French
Charron, Girardot et Voigt 1902
The Charron, Girardot et Voigt 1902 was a French armoured car (French: ''Automitrailleuse blindée'') developed in 1902 by the company Charron, Girardot et Voigt. It was equipped with a Hotchkiss machine gun, and with 7 mm armour for the g ...
, presented at the ''Salon de l'Automobile et du cycle'' in
Brussels
Brussels, officially the Brussels-Capital Region, (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) is a Communities, regions and language areas of Belgium#Regions, region of Belgium comprising #Municipalit ...
, on 8 March 1902. The vehicle was equipped with a
Hotchkiss machine gun
The Hotchkiss machine gun was any of a line of products developed and sold by Hotchkiss et Cie, (full name Société Anonyme des Anciens Etablissements Hotchkiss et Cie), established by United States gunsmith Benjamin B. Hotchkiss. Hotchkiss mo ...
, and with 7 mm armour for the gunner. Armoured cars were first used in large numbers on both sides during
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
as scouting vehicles.
= Tank
=
In 1903,
H. G. Wells
Herbert George Wells (21 September 1866 – 13 August 1946) was an English writer, prolific in many genres. He wrote more than fifty novels and dozens of short stories. His non-fiction output included works of social commentary, politics, hist ...
published the short story "
The Land Ironclads
"The Land Ironclads" is a short story by British writer H. G. Wells, which originally appeared in the December 1903 issue of the ''Strand Magazine''. It features tank-like "land ironclads," armoured fighting vehicles that carry riflemen, engin ...
," positing indomitable war machines that would bring a new age of land warfare, the way steam-powered
ironclad warship
An ironclad was a steam-propelled warship protected by steel or iron armor constructed from 1859 to the early 1890s. The ironclad was developed as a result of the vulnerability of wooden warships to explosive or incendiary shells. The firs ...
s had ended the
age of sail
The Age of Sail is a period in European history that lasted at the latest from the mid-16th (or mid-15th) to the mid-19th centuries, in which the dominance of sailing ships in global trade and warfare culminated, particularly marked by the int ...
.
Wells's literary vision was realized in 1916, when, amidst the pyrrhic standstill of the
Great War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, the British
Landship Committee
The Landship Committee was a small British committee formed during the First World War to develop armoured fighting vehicles for use on the Western Front. The eventual outcome was the creation of what is now called the tank. Established in Febr ...
deployed revolutionary armoured vehicles to break the stalemate. The tank was envisioned as an armoured machine that could cross ground under fire from
machine guns and reply with its own mounted machine guns and
naval artillery
Naval artillery is artillery mounted on a warship, originally used only for naval warfare and then subsequently used for more specialized roles in surface warfare such as naval gunfire support (NGFS) and anti-aircraft warfare (AAW) engagements. ...
. These first
British tanks of World War I moved on
caterpillar track
Continuous track or tracked treads are a system of vehicle propulsion used in tracked vehicles, running on a continuous band of treads or track plates driven by two or more wheels. The large surface area of the tracks distributes the w ...
s that had substantially lower ground pressure than wheeled vehicles, enabling them to pass the muddy, pocked terrain and slit trenches of the
Battle of the Somme
The Battle of the Somme (; ), also known as the Somme offensive, was a battle of the First World War fought by the armies of the British Empire and the French Third Republic against the German Empire. It took place between 1 July and 18 Nove ...
.
= Troop transport
=
The tank eventually proved highly successful and, as technology improved, it became a weapon that could cross large distances at much higher speeds than supporting
infantry
Infantry, or infantryman are a type of soldier who specialize in ground combat, typically fighting dismounted. Historically the term was used to describe foot soldiers, i.e. those who march and fight on foot. In modern usage, the term broadl ...
and
artillery
Artillery consists of ranged weapons that launch Ammunition, munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, and l ...
. The need to provide the units that would fight alongside the tank led to the development of a wide range of specialised AFVs, especially during the
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
(1939–1945).
The armoured personnel carrier, designed to transport infantry troops to the frontline, emerged towards the end of World War I. During the first actions with
tank
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful engine; ...
s, it had become clear that close contact with infantry was essential in order to secure ground won by the tanks. Troops on foot were vulnerable to enemy fire, but they could not be transported in the tank because of the intense heat and noxious atmosphere. In 1917, Lieutenant G. J. Rackham was ordered to design an armoured vehicle that could fight and carry troops or supplies. The
Mark IX tank
The Mark IX tank was a British armoured fighting vehicle from the First World War. It was the world's first specialised armoured personnel carrier (APC).
Development
During the first actions with tanks, it became clear that infantry often coul ...
was built by
Armstrong, Whitworth & Co., although just three vehicles had been finished at the time of the
Armistice
An armistice is a formal agreement of warring parties to stop fighting. It is not necessarily the end of a war, as it may constitute only a cessation of hostilities while an attempt is made to negotiate a lasting peace. It is derived from t ...
in November 1918, and only 34 were built in total.
= Tankette
=

Different tank classifications emerged in the interwar period. The
tankette
A tankette is a tracked armoured fighting vehicle that resembles a small tank, roughly the size of a car. It is mainly intended for light infantry support and scouting. was conceived as a mobile, two-man model, mainly intended for reconnaissance. In 1925,
Sir John Carden
Sir John Valentine Carden, 6th Baronet MBE (6 February 1892 – 10 December 1935) was an English tank and vehicle designer. He was the sixth baronet of Templemore, County Tipperary, from 1931.
Work
Born in London, Carden ran a company from 1 ...
and
Vivian Loyd
Captain Vivian Graham Loyd MC (13 May 18941972) was an English soldier and engineer who designed armoured vehicles including the Carden Loyd tankette and Loyd Carrier.
Early years
Vivian Graham Loyd was born in Windsor, Berkshire, to a fam ...
produced the first such design to be adopted – the
Carden Loyd tankette
The Carden Loyd tankettes were a series of British tankettes of the period between the World Wars, the most successful of which was the Mark VI, the only version built in significant numbers. It became a classic tankette design worldwide, was ...
. Tankettes saw use in the
Royal Italian Army
The Royal Italian Army () (RE) was the land force of the Kingdom of Italy, established with the proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy. During the 19th century Italy started to unify into one country, and in 1861 Manfredo Fanti signed a decree c ...
during the
Italian invasion of Ethiopia (1935–1936), the
Spanish Civil War
The Spanish Civil War () was a military conflict fought from 1936 to 1939 between the Republican faction (Spanish Civil War), Republicans and the Nationalist faction (Spanish Civil War), Nationalists. Republicans were loyal to the Left-wing p ...
(1936–1939), and during
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. The
Imperial Japanese Army
The Imperial Japanese Army (IJA; , ''Dai-Nippon Teikoku Rikugun'', "Army of the Greater Japanese Empire") was the principal ground force of the Empire of Japan from 1871 to 1945. It played a central role in Japan’s rapid modernization during th ...
used tankettes in
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
for infantry support, reconnaissance and later for
jungle warfare
Jungle warfare or woodland warfare is warfare in forests, jungles, or similar environments. The term encompasses military operations affected by the terrain, climate, vegetation, and wildlife of densely-wooded areas, as well as the strategies a ...
.
= Self-propelled artillery
=
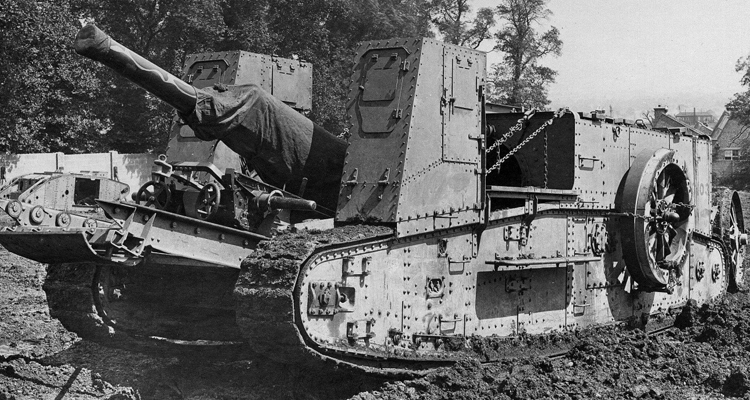

The British
Gun Carrier Mark I
The Gun Carrier Mark I was a British vehicle of the First World War. The gun carrier was designed to transport a 6-inch howitzer or a 60-pounder gun forward soon after an attack to support infantry in advanced positions. Gun carriers were first ...
, the first
Self-propelled artillery
Self-propelled artillery (also called locomotive artillery) is artillery equipped with its own propulsion system to move toward its firing position. Within the terminology are the self-propelled gun, self-propelled howitzer, self-propelled mo ...
, was fielded in 1917. It was based on the first tank, the British
Mark I
Mark I or Mark 1 often refers to the first version of a weapon or military vehicle, and is sometimes used in a similar fashion in civilian product development. In some instances, the Arabic numeral "1" is substituted for the Roman numeral "I". " ...
, and carried a heavy field-gun. The next major advance was the
Birch gun (1925), developed for the British motorised warfare experimental brigade (the
Experimental Mechanized Force
The Experimental Mechanized Force (EMF) was a brigade-sized formation of the British Army. It was officially formed on 1 May 1927 to investigate and develop the techniques and equipment required for armoured warfare and was the first armoured fo ...
). This mounted a field gun, capable of the usual artillery trajectories and even anti-aircraft use, on a tank chassis.
During World War II, most major military powers developed self-propelled artillery vehicles. These had guns mounted on a tracked chassis (often that of an obsolete or superseded tank) and provided an armoured superstructure to protect the gun and its crew. The first British design,
"Bishop", carried the
25 pdr gun-howitzer in an extemporised mounting on a tank chassis that severely limited the gun's performance. It was replaced by the more effective
Sexton. The Germans built many lightly armoured
self-propelled anti-tank gun
Self-propelled may refer to
* Human-powered transport, humans moving themselves (and their cargo) via their own muscle energy
* Machines that power their own movement:
** Automobile (from ''auto-'' + ''mobile'', "self-moving")
** Locomotive (from ...
s using captured French equipment (for example
Marder I
The ''Marder I'' "Marten" (Sd.Kfz. 135) was a German World War II tank destroyer, armed with a 75 mm Pak-40 anti-tank gun. Most Marder Is were built on the base of the ''Tracteur Blindé'' 37L (Lorraine), a French artillery tractor/armou ...
), their own obsolete light tank chassis (
Marder II
The ''Marder'' II ("marten" in English) was a German tank destroyer of World War II based on the Panzer II chassis. There were two versions, the first mounted a modified Soviet 7.62 cm gun firing German ammunition, while the other mounted the ...
), or ex-Czech chassis (
Marder III
''Marder'' III was the name for a series of World War II German tank destroyers. They mounted either the modified ex-Soviet 76.2 mm F-22 Model 1936 divisional field gun, or the German 7.5 cm PaK 40, in an open-topped fighting compartment o ...
). These led to better-protected tank destroyers, built on a medium-tank chassis such as the
Jagdpanzer IV
The ''Jagdpanzer'' IV / Sd.Kfz. 162, was a German tank destroyer based on the Panzer IV chassis and built in three main variants. As one of the casemate-style turretless Jagdpanzer (tank destroyer, literally "hunting tank") designs, it was devel ...
or the
Jagdpanther
The (German: "hunting Panther"), Sd.Kfz. 173, was a tank destroyer (, a self-propelled anti-tank gun) built by Germany during World War II.
The combined the 8.8 cm Pak 43 anti-tank gun, similar to the main gun of the Tiger II, with the armor ...
.
= Anti-aircraft vehicle
=
The
Self-propelled anti-aircraft weapon
An anti-aircraft vehicle, also known as a self-propelled anti-aircraft gun (SPAAG) or self-propelled air defense system (SPAD), is a mobile vehicle with a dedicated anti-aircraft warfare, anti-aircraft capability.
Specific weapon systems used ...
debuted in WWI. The
German 88 mm anti-aircraft gun was truck-mounted and used to great effect against British tanks, and the British
QF 3-inch 20 cwt
The QF 3-inch 20 cwt anti-aircraft gun became the standard anti-aircraft gun used in the home defence of the United Kingdom against German Zeppelins airships and bombers and on the Western Front in World War I. It was also common on British warsh ...
was mounted on trucks for use on the
Western Front. Although the
Birch gun was a general purpose artillery piece on an armoured tracked chassis, it was capable of elevation for anti-aircraft use.
Vickers Armstrong
Vickers-Armstrongs Limited was a British engineering conglomerate formed by the merger of the assets of Vickers Limited and Sir W G Armstrong Whitworth & Company in 1927. The majority of the company was nationalised in the 1960s and 1970s, wi ...
developed one of the first SPAAGs based on the chassis of the Mk.E 6-ton light tank/
Dragon Medium Mark IV tractor, mounting a Vickers QF-1 "Pom-Pom" gun of 40 mm. The Germans fielded the Sd.Kfz. 10/4 and 6/2, cargo halftracks mounting single 20 mm or 37 mm AA guns (respectively) by the start of the war.
= Self-propelled multiple rocket-launcher
=
Rocket launchers such as the Soviet
Katyusha
Katyusha () is a diminutive of the Russian name Ekaterina or Yekaterina, the Russian form of Katherine
Katherine (), also spelled Catherine and Catherina, other variations, is a feminine given name. The name and its variants are popular in c ...
originated in the late 1930s. The
Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the German Army (1935–1945), ''Heer'' (army), the ''Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmac ...
fielded self-propelled rocket artillery in World War II – the
Panzerwerfer
The German ''Panzerwerfer'' refers to either of two different types of half-tracked multiple rocket launchers employed by Nazi Germany during the Second World War. The two self-propelled artillery vehicles are the ''15 cm Panzerwerfer 42 ...
and
Wurfrahmen 40 equipped half-track armoured fighting vehicles. Many modern
multiple rocket launchers
A multiple rocket launcher (MRL) or multiple launch rocket system (MLRS) is a type of rocket artillery system that contains multiple launchers which are fixed to a single platform, and shoots its rocket ordnance in a fashion similar to a vol ...
are self propelled by either truck or tank chassis.
Design
Survivability
The level of armour protection between AFVs varies greatly – a
main battle tank
A main battle tank (MBT), also known as a battle tank or universal tank or simply tank,Ogorkiewicz 2018 p222 is a tank that fills the role of armour-protected direct fire and maneuver in many modern armies. Cold War-era development of more po ...
will normally be designed to take hits from other
tank gun
A tank gun is the main armament of a tank. Modern tank guns are high-velocity, large-caliber artilleries capable of firing kinetic energy penetrators, high-explosive anti-tank, and cannon-launched guided projectiles. Anti-aircraft guns can also ...
s and
anti-tank missiles
An anti-tank guided missile (ATGM), anti-tank missile, anti-tank guided weapon (ATGW) or anti-armor guided weapon is a guided missile primarily designed to hit and destroy heavily armored military vehicles. ATGMs range in size from shoulder- ...
, whilst light
reconnaissance
In military operations, military reconnaissance () or scouting is the exploration of an area by military forces to obtain information about enemy forces, the terrain, and civil activities in the area of operations. In military jargon, reconnai ...
vehicles are often only armoured "just in case". Whilst heavier armour provides better protection, it makes vehicles less mobile (for a given engine power), limits its air-transportability, increases cost, uses more fuel and may limit the places it can go – for example, many bridges may be unable to support the weight of a main battle tank. A trend toward
composite armour
Composite armour is a type of vehicle armour consisting of layers of different materials such as metals, plastics, ceramics or air. Most composite armours are lighter than their all-metal equivalent, but instead occupy a larger volume for the sa ...
is taking the place of steel – composites are stronger for a given weight, allowing the tank to be lighter for the same protection as steel armour, or better protected for the same weight. Armour is being supplemented with
active protection system
An active protection system (APS) is a system designed to actively prevent certain anti-tank weapons from destroying a vehicle.
Countermeasures that either conceal the vehicle from or disrupt the guidance of an incoming guided missile threat are ...
s on a number of vehicles, allowing the AFV to protect itself from incoming projectiles.

The level of protection also usually varies considerably throughout the individual vehicle too, depending on the role of the vehicle and the likely direction of attack. For example, a main battle tank will usually have the heaviest armour on the hull front and the turret, lighter armour on the sides of the hull and the thinnest armour on the top and bottom of the tank. Other vehicles – such as the
MRAP
Mine-Resistant Ambush Protected Vehicle (MRAPV), also known as MRAP vehicle, is a type of armoured personnel carrier that is designed specifically to withstand land mines, improvised explosive device (IED) attacks, and ambushes to save troops' li ...
family – may be primarily armoured against the threat from
IEDs
An improvised explosive device (IED) is a bomb constructed and deployed in ways other than in conventional military action. It may be constructed of conventional military explosives, such as an artillery shell, attached to a detonating mechan ...
and so will have heavy,
sloped armour
Sloped armour is armour that is oriented neither Vertical and horizontal, vertically nor horizontally. Such angled armour is typically mounted on tanks and other armoured fighting vehicles (AFVs), as well as Naval ship, naval vessels such as battl ...
on the bottom of the hull.
Firepower
Weaponry varies by a very wide degree between AFVs – lighter vehicles for infantry carrying, reconnaissance or specialist roles may have only a
autocannon
An autocannon, automatic cannon or machine cannon is a automatic firearm, fully automatic gun that is capable of rapid-firing large-caliber ( or more) armour-piercing, explosive or incendiary ammunition, incendiary shell (projectile), shells, ...
or
machine gun (or no armament at all), whereas heavy self-propelled artillery will carry
howitzer
The howitzer () is an artillery weapon that falls between a cannon (or field gun) and a mortar. It is capable of both low angle fire like a field gun and high angle fire like a mortar, given the distinction between low and high angle fire break ...
s,
mortars
Mortar may refer to:
* Mortar (weapon), an indirect-fire infantry weapon
* Mortar (masonry), a material used to fill the gaps between blocks and bind them together
* Mortar and pestle, a tool pair used to crush or grind
* Mortar, Bihar, a village i ...
or
rocket
A rocket (from , and so named for its shape) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using any surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely ...
launchers. These weapons may be mounted on a
pintle
A pintle is a pin or bolt, usually inserted into a gudgeon, which is used as part of a pivot or hinge. Other applications include pintle and lunette ring for towing, and pintle pins securing casters in furniture.
Use
Pintle/gudgeon sets have ...
, affixed directly to the vehicle or placed in a
turret
Turret may refer to:
* Turret (architecture), a small tower that projects above the wall of a building
* Gun turret, a mechanism of a projectile-firing weapon
* Optical microscope#Objective turret (revolver or revolving nose piece), Objective turre ...
or cupola.
The greater the recoil of the weapon on an AFV, the larger the turret ring needs to be. A larger turret ring necessitates a larger vehicle. To avoid listing to the side, turrets on amphibious vehicles are usually located at the centre of the vehicle.
Grenade launcher
A grenade launcher is a weapon that fires a specially designed, large caliber projectile, often with an explosive, Smoke screen, smoke, or tear gas, gas warhead. Today, the term generally refers to a class of dedicated firearms firing unitary gre ...
s provide a versatile launch platform for a plethora of munitions including,
smoke
Smoke is an aerosol (a suspension of airborne particulates and gases) emitted when a material undergoes combustion or pyrolysis, together with the quantity of air that is entrained or otherwise mixed into the mass. It is commonly an unwante ...
, phosphorus,
tear gas
Tear gas, also known as a lachrymatory agent or lachrymator (), sometimes colloquially known as "mace" after the Mace (spray), early commercial self-defense spray, is a chemical weapon that stimulates the nerves of the lacrimal gland in the ey ...
, illumination, anti-personnel, infrared and radar-jamming rounds.
Turret stabilization is an important capability because it enables firing on the move and prevents crew fatigue.
Maneuverability
Modern AFVs have primarily used either petrol (gasoline) or diesel piston engines. More recently, gas turbines have been used. Most early AFVs used
petrol engine
A petrol engine (gasoline engine in American and Canadian English) is an internal combustion engine designed to run on petrol (gasoline). Petrol engines can often be adapted to also run on fuels such as liquefied petroleum gas and ethanol blends ...
s, as they offer a good
power-to-weight ratio
Power-to-weight ratio (PWR, also called specific power, or power-to-mass ratio) is a calculation commonly applied to engines and mobile power sources to enable the comparison of one unit or design to another. Power-to-weight ratio is a measurement ...
. However, they fell out of favour during World War II due to the flammability of the fuel.
Most current AFVs are powered by a
diesel engine
The diesel engine, named after the German engineer Rudolf Diesel, is an internal combustion engine in which Combustion, ignition of diesel fuel is caused by the elevated temperature of the air in the cylinder due to Mechanics, mechanical Compr ...
; modern technology, including the use of
turbo-charging, helps to overcome the lower power-to-weight ratio of diesel engines compared to petrol.
Gas turbine
A gas turbine or gas turbine engine is a type of Internal combustion engine#Continuous combustion, continuous flow internal combustion engine. The main parts common to all gas turbine engines form the power-producing part (known as the gas gene ...
(turboshaft) engines offer a very high power-to-weight ratio and were starting to find favour in the late 20th century – however, they offer very poor fuel consumption and as such some armies are switching from gas turbines back to diesel engines (i.e. the Russian
T-80
The T-80 is a main battle tank (MBT) that was designed and manufactured in the former Soviet Union and manufactured in Russia. The T-80 is based on the T-64, while incorporating features from the later T-72 and changing the engine to a gas turbi ...
used a gas turbine engine, whereas the later
T-90
The T-90 is a third-generation Russian main battle tank developed from, and designed to replace the T-72. It uses a 125mm 2A46 smoothbore main gun, the 1A45T fire-control system, an upgraded engine, and gunner's thermal sight. Standard p ...
does not). The US
M1 Abrams
The M1 Abrams () is a third-generation American main battle tank designed by Chrysler Defense (now General Dynamics Land Systems) and named for General Creighton Abrams. Conceived for modern armored ground warfare, it is one of the heavies ...
is a notable example of a gas turbine powered tank.
Modern classification by type and role
Notable armoured fighting vehicles extending from post-World War I to today.
Tank
The
tank
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful engine; ...
is an all terrain AFV incorporating artillery which is designed to fill almost all battlefield roles and to engage enemy forces by the use of
direct fire
Direct fire or line-of-sight fire refers to firing of a ranged weapon whose projectile is launched directly at a target within the line-of-sight of the user. The firing weapon must have a sighting device and an unobstructed view to the target, ...
in the frontal assault role. Though several configurations have been tried, particularly in the early experimental "golden days" of tank development, a standard, mature design configuration has since emerged to a generally accepted pattern. This features a main
tank gun
A tank gun is the main armament of a tank. Modern tank guns are high-velocity, large-caliber artilleries capable of firing kinetic energy penetrators, high-explosive anti-tank, and cannon-launched guided projectiles. Anti-aircraft guns can also ...
or
artillery gun
Artillery consists of ranged weapons that launch Ammunition, munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, and l ...
, mounted in a fully rotating
turret
Turret may refer to:
* Turret (architecture), a small tower that projects above the wall of a building
* Gun turret, a mechanism of a projectile-firing weapon
* Optical microscope#Objective turret (revolver or revolving nose piece), Objective turre ...
atop a tracked automotive hull, with various additional secondary weapon systems throughout.
Philosophically, the tank is, by its very nature, an offensive weapon. Being a protective encasement with at least one gun position, it is essentially a
pillbox Pillbox may refer to:
* Pill organizer, a container for medicine
* Pillbox hat, a woman's hat with a flat crown, straight upright sides, and no brim
* Pillbox (military)
A pillbox is a type of blockhouse, or concrete dug-in guard-post, often ...
or small
fortress
A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from L ...
(though these are static fortifications of a purely defensive nature) that can move toward the enemy – hence its offensive utility. Psychologically, the tank is a
force multiplier
In military science, force multiplication or a force multiplier is a factor or a combination of factors that gives personnel or weapons (or other hardware) the ability to accomplish greater feats than without it. The expected size increase requ ...
that has a positive morale effect on the infantry it accompanies.
It also instills fear in the opposing force who can often hear and even feel their arrival.
Tank classifications
Tanks were classified either by size or by role.
File:Ripsaw M5.webp, alt=Ripsaw Ground Combat Vehicle, Ripsaw M5 unmanned light tank
A light tank is a Tank classification, tank variant initially designed for rapid movements in and out of combat, to outmaneuver heavier tanks. It is smaller with thinner vehicle armour, armor and a less powerful tank gun, main gun, tailored for ...
File:PanzerIISaumur.jpg, A WWII German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
Panzer II
The Panzer II is the common name used for a family of Nazi Germany, German tanks used in World War II. The official German designation was ''Panzerkampfwagen'' II (abbreviated ''Pz.Kpfw. II'').
Although the vehicle had originally been designed a ...
light tank
File:T-34-76 RB8.JPG, Soviet-made Polish T-34
The T-34 is a Soviet medium tank from World War II. When introduced, its 76.2 mm (3 in) tank gun was more powerful than many of its contemporaries, and its 60-degree sloped armour provided good protection against Anti-tank warfare, ...
medium tank Model 1942 in Poznań
Poznań ( ) is a city on the Warta, River Warta in west Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business center and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint John's ...
, Poland. The model 1942's hexagonal turret distinguishes it from earlier models.
File:T29 Heavy Tank.png, American
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, p ...
T29 Heavy Tank
Classification by relative size was common, as this also tended to influence the tanks' role.
*
Light tank
A light tank is a Tank classification, tank variant initially designed for rapid movements in and out of combat, to outmaneuver heavier tanks. It is smaller with thinner vehicle armour, armor and a less powerful tank gun, main gun, tailored for ...
s are smaller tanks with thinner armour and lower-powered guns, allowing for better tactical mobility and ease of strategic transport. These are intended for
armoured reconnaissance
Armoured reconnaissance also Combat reconnaissance vehicle is the combination of terrestrial reconnaissance with armoured warfare by soldiers using tanks and wheeled or tracked armoured reconnaissance vehicles. While the mission of reconnaissan ...
,
skirmishing
Skirmishers are light infantry or light cavalry soldiers deployed as a vanguard, flank guard or rearguard to screen a tactical position or a larger body of friendly troops from enemy advances. They may be deployed in a skirmish line, an irreg ...
,
artillery observation,
expeditionary warfare
Expeditionary warfare is a military invasion of a foreign territory, especially away from established bases. Expeditionary forces were in part the antecedent of the modern concept of rapid deployment forces. Traditionally, expeditionary forces we ...
and supplementing
airborne or naval landings. Light tanks are typically cheaper to build and maintain, but fare poorly against heavier tanks. They may be held in reserve for exploiting any breakthroughs in enemy lines, with the goal of disrupting communications and supply lines.
*
Medium tank
A medium tank is a classification of tanks, particularly prevalent during World War II, which represented a compromise between the mobility oriented light tanks and the armour and armament oriented heavy tanks. A medium tank's classification ...
s are mid-sized tanks with adequate armour and guns, and fair mobility, allowing for a balance of fighting abilities, mobility, cost-effectiveness, and transportability. Medium tanks are effective in groups when used against enemy tanks.
*
Heavy tank
A heavy tank is a tank classification produced from World War I to the end of the Cold War. These tanks generally sacrificed mobility and maneuverability for better armour protection and equal or greater firepower than tanks of lighter classes.
...
s are larger tanks with thick armour and more powerful guns, but less mobile and more difficult to transport. They were intended to be more than a match for typical enemy medium tanks, easily penetrating their armour while being much less susceptible to their attacks. Heavy tanks cost more to both build and maintain, and their heavy armour proved most effective when deployed in support infantry assaulting entrenched fortifications.
Over time, tanks tended to be designed with heavier armour and weapons, increasing the weight of all tanks, so these classifications are relative to the average for the nation's tanks for any given period. An older tank design might be reclassified over time, such as a tank being first deployed as a medium tank, but in later years relegated to light tank roles.
Tanks were also classified by roles that were independent of size, such as
cavalry tank
The cruiser tank (sometimes called cavalry tank or fast tank) was a British tank concept of the interwar period for tanks designed as modernised armoured and mechanised cavalry, as distinguished from infantry tanks. Cruiser tanks were develop ...
,
cruiser tank
The cruiser tank (sometimes called cavalry tank or fast tank) was a British tank concept of the interwar period for tanks designed as modernised armoured and mechanised cavalry, as distinguished from infantry tanks. Cruiser tanks were develop ...
,
fast tank,
infantry tank
The infantry tank was a tank concept developed by the United Kingdom and France in the years leading up to World War II. Infantry tanks were designed to support infantrymen in an attack. To achieve this, the vehicles were generally heavily arm ...
, "assault" tank, or "breakthrough" tank. Military theorists initially tended to assign tanks to traditional military infantry, cavalry, and artillery roles, but later developed more specialized roles unique to tanks.
In modern use, the heavy tank has fallen out of favour, being supplanted by more heavily armed and armoured descendant of the medium tanks – the universal
main battle tank
A main battle tank (MBT), also known as a battle tank or universal tank or simply tank,Ogorkiewicz 2018 p222 is a tank that fills the role of armour-protected direct fire and maneuver in many modern armies. Cold War-era development of more po ...
. The light tank has, in many armies, lost favour to cheaper, faster, lighter
armoured cars
Armored (or armoured) car may refer to:
Wheeled armored vehicles
* Armored car (military), a wheeled armoured fighting vehicle
* Armored car (valuables), an armored van or truck used to transport valuables
* Armored car (VIP), a civilian vehic ...
; however, light tanks (or similar vehicles with other names) are still in service with a number of forces as
reconnaissance vehicle
A reconnaissance vehicle, also known as a scout vehicle, is a military vehicle used for forward reconnaissance. Both tracked and wheeled reconnaissance vehicles are in service. In some nations, light tanks such as the M551 Sheridan and AMX-13 h ...
s, most notably the
Russian Marines
The Russian Naval Infantry (), often referred to as Russian Marines in the West, operate as the naval infantry of the Russian Navy. Established in 1705, they are capable of conducting amphibious operations as well as operating as more traditiona ...
with the
PT-76
The PT-76 is a Soviet Union, Soviet amphibious vehicle, amphibious light tank that was introduced in the early 1950s and soon became the standard reconnaissance tank of the Soviet Army and the other Warsaw Pact armed forces. It was widely exporte ...
, the
British Army
The British Army is the principal Army, land warfare force of the United Kingdom. the British Army comprises 73,847 regular full-time personnel, 4,127 Brigade of Gurkhas, Gurkhas, 25,742 Army Reserve (United Kingdom), volunteer reserve perso ...
with the
Scimitar
A scimitar ( or ) is a single-edged sword with a convex curved blade of about 75 to 90 cm (30 to 36 inches) associated with Middle Eastern, South Asian, or North African cultures. A European term, ''scimitar'' does not refer to one specific swor ...
, and the
Chinese Army
The People's Liberation Army (PLA) is the military of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) and the People's Republic of China (PRC). It consists of four services— Ground Force, Navy, Air Force, and Rocket Force—and four arms— Aerospac ...
with the
Type 63.
Main battle tank
File:Karelian_Lock_23_(7827362).jpg, United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
third-generation M1 Abrams
The M1 Abrams () is a third-generation American main battle tank designed by Chrysler Defense (now General Dynamics Land Systems) and named for General Creighton Abrams. Conceived for modern armored ground warfare, it is one of the heavies ...
tank
File:2013_Moscow_Victory_Day_Parade_(28).jpg, Russian
Russian(s) may refer to:
*Russians (), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*A citizen of Russia
*Russian language, the most widely spoken of the Slavic languages
*''The Russians'', a b ...
T-90
The T-90 is a third-generation Russian main battle tank developed from, and designed to replace the T-72. It uses a 125mm 2A46 smoothbore main gun, the 1A45T fire-control system, an upgraded engine, and gunner's thermal sight. Standard p ...
main battle tank with 2A46
The 2A46 (also called D-81TM) is a 125 mm/L48 smoothbore cannon of Soviet origin used in several main battle tanks. It was designed by OKB-9 (Artillery Plant No. 9) in Yekaterinburg.
Description
It was developed by the Spetstekhnika Design ...
smoothbore gun
File:Leopard_2A6,_PzBtl_104.jpg, Modern Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
Leopard 2
The Leopard 2 is a third generation German main battle tank (MBT). Developed by Krauss-Maffei in the 1970s, the tank entered service in 1979 and replaced the earlier Leopard 1 as the main battle tank of the West German army. Various iterat ...
main battle tank
File:ZTZ-99A_MBT_20170902.jpg, Chinese
Chinese may refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people identified with China, through nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**Han Chinese, East Asian ethnic group native to China.
**'' Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic ...
Type 99 main battle tank
Modern
main battle tanks
A main battle tank (MBT), also known as a battle tank or universal tank or simply tank,Ogorkiewicz 2018 p222 is a tank that fills the role of armour-protected direct fire and maneuver in many modern armies. Cold War-era development of more po ...
or "universal tanks" incorporate recent advances in automotive, artillery, armour, and electronic technology to combine the best characteristics of the historic medium and heavy tanks into a single, all-around type. They are also the most expensive to mass-produce. A main battle tank is distinguished by its high level of firepower, mobility and armour protection relative to other vehicles of its era. It can cross comparatively rough terrain at high speeds, but its heavy dependency on fuel, maintenance, and ammunition makes it
logistically demanding. It has the heaviest
armour
Armour (Commonwealth English) or armor (American English; see American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, spelling differences) is a covering used to protect an object, individual, or vehicle from physical injury or damage, e ...
of any AFVs on the battlefield, and carries a powerful
precision-guided munition
A precision-guided munition (PGM), also called a smart weapon, smart munition, or smart bomb, is a type of weapon system that integrates advanced guidance and control systems, such as Global Positioning System, GPS, laser guidance, or Infrared ...
weapon systems that may be able to engage a wide variety of both ground targets and air targets. Despite significant advances in
anti-tank warfare
Anti-tank warfare refers to the military strategies, tactics, and weapon systems designed to counter and destroy enemy armored vehicles, particularly tanks. It originated during World War I following the first deployment of tanks in 1916, and ...
, it still remains the most versatile and fearsome land-based weapon-systems of the 21st-century, valued for its
shock action and high
survivability
Survivability is the ability to remain alive or continue to exist. The term has more specific meaning in certain contexts.
Ecological
Following disruptive forces such as flood, fire, disease, war, or climate change some species of flora, faun ...
.
Tankette
A tankette is a tracked armed and armoured vehicle resembling a small "ultra-light tank" or "super-light tank" roughly the size of a car, mainly intended for light infantry support or
scouting
Scouting or the Scout Movement is a youth social movement, movement which became popularly established in the first decade of the twentieth century. It follows the Scout method of informal education with an emphasis on practical outdoor activi ...
. Tankettes were introduced in the mid-1920s as a reconnaissance vehicle and a mobile machine gun position They were one or two-man vehicles armed with a machine gun. Colloquially it may also simply mean a "small tank".
Tankettes were designed and built by several nations between the 1920s and 1940s following the British
Carden Loyd tankette
The Carden Loyd tankettes were a series of British tankettes of the period between the World Wars, the most successful of which was the Mark VI, the only version built in significant numbers. It became a classic tankette design worldwide, was ...
which was a successful implementation of "one man tank" ideas from
Giffard Le Quesne Martel
Lieutenant-General Sir Giffard Le Quesne Martel (10 October 1889 – 3 September 1958) was a British Army officer who served in both the First and Second World Wars. Familiarly known as "Q Martel" or just "Q", he was a pioneering British mili ...
, a British Army engineer. They were very popular with smaller countries. Some saw some combat (with limited success) in World War II. However, the vulnerability of their light armour eventually caused the concept to be abandoned. However, the
German Army
The German Army (, 'army') is the land component of the armed forces of Federal Republic of Germany, Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German together with the German Navy, ''Marine'' (G ...
uses a modern design of air-transportable armoured weapons carriers, the
Wiesel AWC
The Wiesel Armoured Weapons Carrier (AWC; ) is a German light air-transportable armoured fighting vehicle, more specifically a lightly armoured weapons carrier, produced by Rheinmetall.
The Wiesel has been used in several of the Bundeswehr's mis ...
, which resembles the concept of a tankette.
''Super''-heavy tank
The term "super-heavy tank" has been used to describe armoured fighting vehicles of extreme size, generally over 75 tonnes. Programs have been initiated on several occasions with the aim of creating an invincible
siegeworks
A siege () . is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or by well-prepared assault. Siege warfare (also called siegecrafts or poliorcetics) is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characte ...
/
breakthrough vehicle for penetrating enemy formations and fortifications without fear of being destroyed in combat. Examples were designed in World War I and World War II (such as the
Panzer VIII Maus
''Panzerkampfwagen'' VIII ''Maus'' (English: 'mouse') was a German World War II super-heavy tank completed in July of 1944. As of 2025, it is the heaviest fully enclosed armored fighting vehicle ever built. Five were ordered, but only two hulls ...
), along with a few in the
Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
. However, few working prototypes were built and there is no clear evidence any of these vehicles saw combat, as their immense size would have made most designs impractical.
File:TOG II.jpg, British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
TOG II
The TOG 2, officially known as the Heavy Tank, TOG II, was a British super-heavy tank design produced during the early stages of World War II for a scenario where the battlefields of northern France and Belgium devolved into a morass of mud, tr ...
File:Metro-maus1.jpg, German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
Panzer VIII Maus
''Panzerkampfwagen'' VIII ''Maus'' (English: 'mouse') was a German World War II super-heavy tank completed in July of 1944. As of 2025, it is the heaviest fully enclosed armored fighting vehicle ever built. Five were ordered, but only two hulls ...
Missile tank

A
missile tank
A missile tank is an armoured fighting vehicle fulfilling the role of a main battle tank, but using only guided missiles for main armament. Several nations have experimented with prototypes, notably the Soviet Union during the tenure of Nikita ...
is a tank fulfilling the role of a main battle tank, but using only
anti-tank
Anti-tank warfare refers to the military strategies, tactics, and weapon systems designed to counter and destroy enemy armored vehicles, particularly tanks. It originated during World War I following the first deployment of tanks in 1916, and ...
surface-to-surface missile
A surface-to-surface missile (SSM) is a missile designed to be launched from the ground or the sea and strike targets on land or at sea. They may be fired from hand-held or vehicle mounted devices, from fixed installations, or from a ship. They ar ...
s for main armament. Several nations have experimented with prototypes, notably the Soviet Union during the tenure of Nikita Khrushchev (projects Object 167, Object 137Ml, Object 155Ml, Object 287, Object 775),
Flame tank

A flame tank is an otherwise-standard
tank
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful engine; ...
equipped with a
flamethrower
A flamethrower is a ranged incendiary device designed to project a controllable jet of fire. First deployed by the Byzantine Empire in the 7th century AD, flamethrowers saw use in modern times during World War I, and more widely in World W ...
, most commonly used to supplement
combined arms
Combined arms is an approach to warfare that seeks to integrate different combat arms of a military to achieve mutually complementary effects—for example, using infantry and armoured warfare, armour in an Urban warfare, urban environment in ...
attacks against
fortification
A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Lati ...
s, confined spaces, or other obstacles. The type only reached significant use in the
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, during which the United States,
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
,
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
,
Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
,
Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
and the United Kingdom (including members of the
British Commonwealth
The Commonwealth of Nations, often referred to as the British Commonwealth or simply the Commonwealth, is an international association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire
The B ...
) all produced flamethrower-equipped tanks. Usually, the flame projector replaced one of the tank's machineguns, however, some flame projectors replaced the tank's main gun. Fuel for the flame weapon was generally carried inside the tank, although a few designs mounted the fuel externally, such as the armoured trailer used on the
Churchill Crocodile
The Churchill Crocodile was a British flame-throwing tank of late Second World War. It was a variant of the Tank, Infantry, Mk IV (A22) Churchill Mark VII, although the Churchill Mark IV was initially chosen to be the base vehicle.
The Croco ...
.
Flame tanks have been superseded by
thermobaric weapon
A thermobaric weapon, also called an aerosol bomb, or a vacuum bomb, is a type of explosive munition that works by dispersing an aerosol cloud of gas, liquid or powdered explosive. The fuel is usually a single compound, rather than a mixture o ...
s such as the Russian
TOS-1
TOS-1 Buratino (, Heavy Flamethrower System) is a Soviet 220 mm 30-barrel (original system, Object 634 or TOS-1M) or 24-barrel (Object 634B or TOS-1A Solntsepyok) multiple rocket launcher capable of using thermobaric warheads, mounted on a ...
.
Infantry tank

The idea for this tank was developed during World War I by British and French. The
infantry
Infantry, or infantryman are a type of soldier who specialize in ground combat, typically fighting dismounted. Historically the term was used to describe foot soldiers, i.e. those who march and fight on foot. In modern usage, the term broadl ...
tank was designed to work in concert with infantry in the assault, moving mostly at a walking pace, and carrying heavy armour to survive defensive fire. Its main purpose was to suppress enemy fire, crush obstacles such as barbed-wire entanglements, and protect the infantry on their advance into and through enemy lines by giving mobile
overwatch
''Overwatch'' (abbreviated as OW) is a multimedia franchise centered on a series of multiplayer first-person shooter (FPS) video games developed by Blizzard Entertainment. ''Overwatch (video game), Overwatch'' was released in 2016 with a success ...
and
cover
Cover or covers may refer to:
Packaging
* Another name for a lid
* Cover (philately), generic term for envelope or package
* Album cover, the front of the packaging
* Book cover or magazine cover
** Book design
** Back cover copy, part of c ...
. The French
Renault FT
The Renault FT (frequently referred to in post-World War I literature as the FT-17, FT17, or similar) is a French light tank that was among the most revolutionary and influential tank designs in history. The FT was the first production tank to h ...
was the first iteration of this concept.
The British and French retained the concept between the wars and into the Second World War era. Because infantry tanks did not need to be fast, they could carry heavy armour. One of the best-known infantry tanks was the
Matilda II
The Infantry Tank Mark II, better known as the Matilda, is a British infantry tank of the Second World War.Jentz, p. 11.
The design began as the A12 specification in 1936, as a gun-armed counterpart to the first British infantry tank, the mac ...
of World War II. Other examples include the French
R-35, the British
Valentine, and the British
Churchill.
Cruiser tank
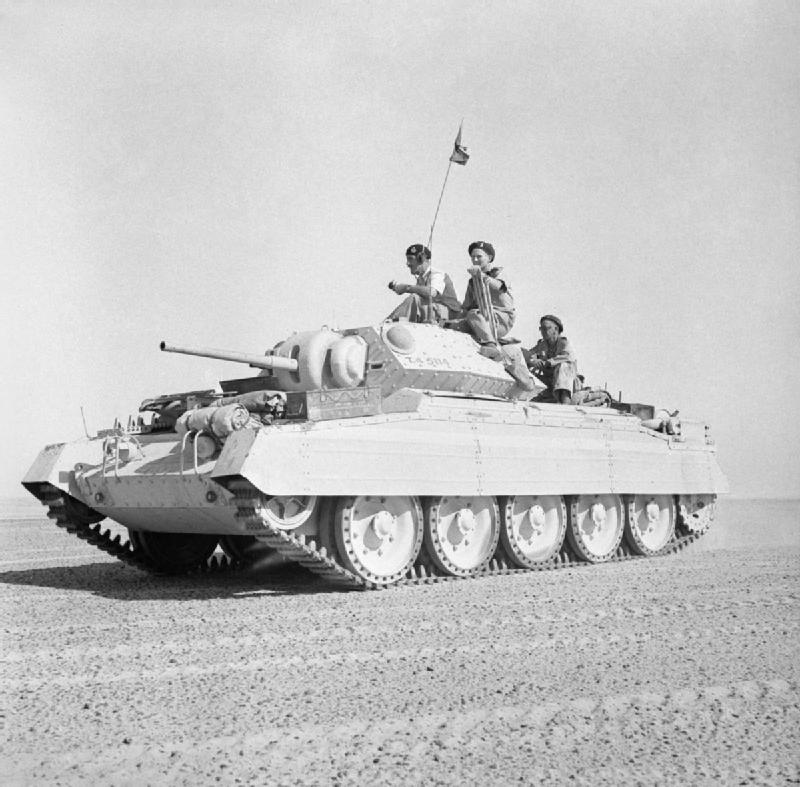

A cruiser tank, or cavalry tank, was designed to move fast and exploit penetrations of the enemy front. The idea originated in "
Plan 1919
Plan 1919 was a military strategy drawn up by British Army officer J. F. C. Fuller in 1918 during World War I. His plan criticised the practice of physically destroying the enemy, and instead called for tanks to rapidly advance into the enemy's ...
", a British plan to break the trench deadlock of
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
in part via the use of high-speed tanks. The first cruiser tank was the British
Whippet
The Whippet is a British breed of dog of sighthound type. It closely resembles the Greyhound and the smaller Italian Greyhound, and is intermediate between them in size. In the nineteenth century it was sometimes called "the poor man's raceh ...
.
Between the wars, this concept was implemented in the "fast tanks" pioneered by
J. Walter Christie. These led to the Soviet
BT tank series and the British
cruiser tank series.
During
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, British cruiser tanks were designed to complement
infantry tank
The infantry tank was a tank concept developed by the United Kingdom and France in the years leading up to World War II. Infantry tanks were designed to support infantrymen in an attack. To achieve this, the vehicles were generally heavily arm ...
s, exploiting gains made by the latter to attack and disrupt the enemy rear areas. In order to give them the required speed, cruiser designs sacrificed armour and armament compared to the infantry tanks. Pure British cruisers were generally replaced by more capable medium tanks such as the
US Sherman and, to a lesser extent, the
Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English statesman, politician and soldier, widely regarded as one of the most important figures in British history. He came to prominence during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms, initially a ...
by 1943.
The Soviet fast tank (''bistrokhodniy tank'', or
BT tank
The BT tank (, lit. "fast moving tank" or "high-speed tank") was one of a series of Soviet light tanks produced in large numbers between 1932 and 1941. They were lightly armoured, but reasonably well-armed for their time, and had the best mobil ...
) classification also came out of the infantry/cavalry concept of armoured warfare and formed the basis for the British cruisers after 1936. The T-34 was a development of this line of tanks as well, though their armament, armour, and all-round capability places them firmly in the medium tank category.
Armoured car
The
armoured car is a wheeled, often lightly armoured, vehicle adapted as a fighting machine. Its earliest form consisted of a motorised ironside chassis fitted with firing ports. By
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, this had evolved into a mobile fortress equipped with command equipment, searchlights, and machine guns for self-defence. It was soon proposed that the requirements for the armament and layout of armoured cars be somewhat similar to those on naval craft, resulting in turreted vehicles. The first example carried a single revolving cupola with a
Vickers gun
The Vickers machine gun or Vickers gun is a water-cooled .303 British (7.7 mm) machine gun produced by Vickers Limited, originally for the British Army. The gun was operated by a three-man crew but typically required more men to move and ...
; modern armoured cars may boast heavier armament – ranging from twin machine guns to large calibre cannon.
Some multi-axled wheeled fighting vehicles can be quite heavy, and superior to older or smaller tanks in terms of armour and armament. Others are often used in military marches and processions, or for the escorting of important figures. Under peacetime conditions, they form an essential part of most standing armies. Armoured car units can move without the assistance of transporters and cover great distances with fewer logistical problems than tracked vehicles.
During
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, armoured cars were used for reconnaissance alongside scout cars. Their guns were suitable for some defence if they encountered enemy armoured fighting vehicles, but they were not intended to engage enemy
tank
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful engine; ...
s.
Armoured cars
Armored (or armoured) car may refer to:
Wheeled armored vehicles
* Armored car (military), a wheeled armoured fighting vehicle
* Armored car (valuables), an armored van or truck used to transport valuables
* Armored car (VIP), a civilian vehic ...
have since been used in the offensive role against tanks with varying degrees of success, most notably during the
South African Border War
The South African Border War, also known as the Namibian War of Independence, and sometimes denoted in South Africa as the Angolan Bush War, was a largely asymmetric conflict that occurred in Namibia (then South West Africa), Zambia, and Angol ...
,
Toyota War
The Toyota War (, ), also known as the Great Toyota War, which took place in 1987 in Northern Chad and on the Chad–Libya border, was the last phase of the Chadian–Libyan War. It takes its name from the Toyota pickup trucks, primarily the Toyo ...
, the
Invasion of Kuwait
The Iraqi invasion of Kuwait, codenamed Project 17, began on 2 August 1990 and marked the beginning of the Gulf War. After defeating the Kuwait, State of Kuwait on 4 August 1990, Ba'athist Iraq, Iraq went on to militarily occupy the country fo ...
, and other
lower-intensity conflicts.
File:Rolls Royce 1920 Mk1 1 Bovington.jpg, Rolls-Royce Armoured Car
The Rolls-Royce armoured car is a British armoured car developed in 1914 and used during the First World War, Irish Civil War, the inter-war period in Imperial Air Control in Transjordan, Palestine and Mesopotamia, and in the early stages of the ...
in The Tank Museum, Bovington
File:T 17 Staghound Armored Car (1).jpg, American T17E1 Staghound
The T17E1 armored car was an American Armored car (military), armored car manufactured during the Second World War. It saw service with United Kingdom, British and other Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth forces during the war under the nam ...
armoured car of World War II
File:SATORY 9 JANVIER 2014 021 bis.jpg, French Renault VBC-90 six-wheeled armoured car.
Aerosledge
An ''aerosledge'' is a type of propeller-driven
snowmobile
A snowmobile, also known as a snowmachine (chiefly Alaskan), motor sled (chiefly Canadian), motor sledge, skimobile, snow scooter, or simply a sled is a motorized vehicle designed for winter travel and recreation on snow.
Their engines normally ...
, running on skis, used for communications, mail deliveries, medical aid, emergency recovery and border patrolling in northern Russia, as well as for recreation. Aerosledges were used by the Soviet
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People ...
during the
Winter War
The Winter War was a war between the Soviet Union and Finland. It began with a Soviet invasion of Finland on 30 November 1939, three months after the outbreak of World War II, and ended three and a half months later with the Moscow Peac ...
and
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
.
Some early aerosledges were built by young
Igor Sikorsky
Igor Ivanovich Sikorsky, (25 May 1889 – 26 October 1972) was a Russian-American aviation pioneer in both helicopters and fixed-wing aircraft. His first success came with the Sikorsky S-2, the second aircraft of his design and construc ...
in 1909–10, before he built multi-engine airplanes and helicopters. They were very light
plywood
Plywood is a composite material manufactured from thin layers, or "plies", of wood veneer that have been stacked and glued together. It is an engineered wood from the family of manufactured boards, which include plywood, medium-density fibreboa ...
vehicles on skis, propelled by old airplane engines and propellers.
Scout car
A ''scout car'' is a military armoured
reconnaissance vehicle
A reconnaissance vehicle, also known as a scout vehicle, is a military vehicle used for forward reconnaissance. Both tracked and wheeled reconnaissance vehicles are in service. In some nations, light tanks such as the M551 Sheridan and AMX-13 h ...
, capable of off-road mobility and often carrying mounted weapons such as
machine guns for offensive capabilities and crew protection. They often only carry an operational crew aboard, which differentiates them from wheeled armoured personnel carriers (APCs) and
infantry mobility vehicle
An infantry mobility vehicle (IMV) is a four-wheel drive armored personnel carrier (APC) serving as an armed military transport, military patrol, reconnaissance or security vehicle. Those IMVs are distinct from 8-, 6-, and 4-wheeled APCs (su ...
s (IMVs), but early scout cars, such as the open-topped US
M3 scout car could carry a crew of seven. The term is often used synonymously with the more general term armoured car, which also includes armoured civilian vehicles. They are also differentiated by being designed and built for purpose, as opposed to improvised "
technicals
Technicals may refer to:
* Technical (vehicle), an improvised fighting vehicle often used in civil conflict
* TECHNICALS, a clothing brand owned by Blacks Leisure Group
See also
* Technical (disambiguation)
Technical may refer to:
* Technical ...
" which might serve in the same role.
File:Verkhnyaya Pyshma Tank Museum 2011 140.jpg, BA-64
The BA-64 (, from , ''Bronirovaniy Avtomobil'', literally "armoured car") was a Soviet four-wheeled scout car, armoured scout car. Built on the chassis of a GAZ-64 or GAZ-67 jeep, it incorporated a hull loosely modeled after that of the Leichter ...
at the UMMC Museum
File:BRDM-2 (1964) owned by James Stewart pic1.JPG, Soviet BRDM-2
The BRDM-2 (''Boyevaya Razvedyvatelnaya Dozornaya Mashina'', Боевая Разведывательная Дозорная Машина, literally "Combat Reconnaissance/Patrol Vehicle") is an amphibious armoured scout car designed and developed ...
amphibious scout car.
Reconnaissance vehicle
A ''reconnaissance vehicle'', also known as a ''scout vehicle'', is a
military vehicle
A military vehicle is any vehicle for land-based military transport and activity, including combat vehicles, both specifically designed for or significantly used by military. Most military vehicles require Off-road vehicle, off-road capabilities ...
used for forward
reconnaissance
In military operations, military reconnaissance () or scouting is the exploration of an area by military forces to obtain information about enemy forces, the terrain, and civil activities in the area of operations. In military jargon, reconnai ...
. Both tracked and wheeled reconnaissance vehicles are in service. In some countries, light tanks such as the
M551 Sheridan
The M551 "Sheridan" AR/AAV (Reconnaissance vehicle, Armored Reconnaissance/Airborne Assault Vehicle) was a light tank developed by the United States and named after General (United States), General Philip Sheridan, of American Civil War fame. It ...
and
AMX-13
The AMX-13 is a French light tank produced from 1952 to 1987. It served with the French Army, as the Char 13t-75 Modèle 51, and was exported to more than 26 other nations. Named after its initial weight of 13 tonnes, and featuring a tough and re ...
are also used by scout platoons. Reconnaissance vehicles are usually designed with a low profile or small size and are lightly armoured, relying on speed and cover to escape detection. Their armament ranges from a
medium machine gun
A medium machine gun (MMG), in modern terms, usually refers to a belt-fed machine gun firing a full-powered rifle cartridge, and is considered "medium" in weight (). Medium machine guns are light enough to be infantry-portable (as opposed to ...
to an
autocannon
An autocannon, automatic cannon or machine cannon is a automatic firearm, fully automatic gun that is capable of rapid-firing large-caliber ( or more) armour-piercing, explosive or incendiary ammunition, incendiary shell (projectile), shells, ...
. Modern examples are often fitted with
ATGM
An anti-tank guided missile (ATGM), anti-tank missile, anti-tank guided weapon (ATGW) or anti-armor guided weapon is a guided missile primarily designed to hit and destroy heavily armored military vehicles. ATGMs range in size from shoulder ...
s and a wide range of sensors.
Armoured reconnaissance is the combination of
terrestrial reconnaissance Ground reconnaissance (also terrestrial reconnaissance, ground recon), is a type of reconnaissance that is employed along the elements of ground warfare
Land warfare or ground warfare is the process of military operations eventuating in combat t ...
with
armoured warfare
Armoured warfare or armored warfare (American English; American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, see spelling differences), is the use of armoured fighting vehicles in modern warfare. It is a major component of modern Milita ...
by using tanks and wheeled or tracked armoured reconnaissance vehicles. While the mission of reconnaissance is to gather intelligence about the enemy with the use of reconnaissance vehicles, armoured reconnaissance adds the ability to fight for information, and to have an effect on and to shape the enemy through the performance of traditional armoured tasks. Some
armoured personnel carrier
An armoured personnel carrier (APC) is a broad type of armoured military vehicle designed to transport personnel and equipment in combat zones. Since World War I, APCs have become a very common piece of military equipment around the world.
Acc ...
s and
infantry mobility vehicle
An infantry mobility vehicle (IMV) is a four-wheel drive armored personnel carrier (APC) serving as an armed military transport, military patrol, reconnaissance or security vehicle. Those IMVs are distinct from 8-, 6-, and 4-wheeled APCs (su ...
, such as the
M113
The M113 is a fully tracked armored personnel carrier (APC) that was developed and produced by the FMC Corporation. The M113 was sent to United States Army Europe in 1961 to replace the mechanized infantry's M59 APCs. The M113 was first used ...
,
TPz Fuchs
The TPz Fuchs from Transportpanzer Fuchs is a German armoured personnel carrier originally developed by Daimler-Benz, and manufactured and further developed by Rheinmetall MAN Military Vehicles (RMMV). Fuchs was the second wheeled armoured vehic ...
, and
Cadillac Gage Commando
The Cadillac Gage Commando, frequently denoted as the M706 in U.S. military service, is an American armored car designed to be amphibious. It was engineered by Cadillac Gage specifically for the United States Military Police Corps during the ...
double in the reconnaissance role.
File:Stryker RV front q.jpg, United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the primary Land warfare, land service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is designated as the Army of the United States in the United States Constitution.Article II, section 2, clause 1 of th ...
M1127
The M1127 reconnaissance vehicle (RV) is a wheeled armored personnel carrier in the Stryker family, developed and produced by General Dynamics Land Systems Canada (GDLS-C) and is currently in service with the US Army.
General
The RV provides an e ...
File:Scimitar Light Tank MOD 45149231.jpg, British FV107 Scimitar
The FV107 Scimitar is an armoured tracked military reconnaissance vehicle (sometimes classed as a light tank) formerly used by the British Army, until it was retired from active service in April 2023. It was manufactured by Alvis in Coventry. ...
tracked reconnaissance vehicle in the Salisbury Plain Training Area
The Salisbury Plain Training Area is a large expanse of land on Salisbury Plain in Wiltshire, England, which is managed by the Defence Infrastructure Organisation on behalf of the Ministry of Defence.
History
The British Army's Salisbury Pla ...
Internal security vehicle

An internal security vehicle (ISV), also known as an armoured security vehicle (ASV), is a combat vehicle used for suppressing civilian unrest. Security vehicles are typically armed with a turreted
heavy machine gun
A heavy machine gun (HMG) is significantly larger than light, medium or general-purpose machine guns. HMGs are typically too heavy to be man-portable (carried by one person) and require mounting onto a weapons platform to be operably stable or ...
and auxiliary
medium machine gun
A medium machine gun (MMG), in modern terms, usually refers to a belt-fed machine gun firing a full-powered rifle cartridge, and is considered "medium" in weight (). Medium machine guns are light enough to be infantry-portable (as opposed to ...
. The vehicle is designed to minimize firepower dead space.
Non-lethal
Non-lethal weapons, also called nonlethal weapons, less-lethal weapons, less-than-lethal weapons, non-deadly weapons, compliance weapons, or pain-inducing weapons are weapons intended to be less likely to kill a living target than convention ...
water cannon
A water cannon is a device that shoots a high-velocity stream of water. Typically, a water cannon can deliver a large volume of water, often over dozens of meters. They are used in firefighting, large vehicle washing, riot control, and mining. ...
s and
tear gas
Tear gas, also known as a lachrymatory agent or lachrymator (), sometimes colloquially known as "mace" after the Mace (spray), early commercial self-defense spray, is a chemical weapon that stimulates the nerves of the lacrimal gland in the ey ...
cannons can provide suppressive fire in lieu of unnecessary deadly fire.
The vehicle must be protected against weapons typical of riots. Protection from
improvised incendiary devices is achieved though coverage of the air intake and exhaust ports as well as a strong locking mechanism on the fuel opening. Turret and door locks prevent access to the interior of the vehicle by rioters. Vision blocks, ballistic glass and window shutters and outside
surveillance cameras
Closed-circuit television (CCTV), also known as video surveillance, is the use of closed-circuit television cameras to transmit a signal to a specific place on a limited set of monitors. It differs from broadcast television in that the signal ...
allow protected observation from within the vehicle. Wheeled 4x4 and 6x6 configurations are typical of security vehicles. Tracked security vehicles are often cumbersome and leave negative political connotations for being perceived as an imperial invading force.
Military light utility vehicle
Military light utility vehicles are the lightest weight class of military vehicles. It refers to light
4x4
A four-wheel drive, also called 4×4 ("four by four") or 4WD, is a two-axled vehicle drivetrain capable of providing torque to all of its wheels simultaneously. It may be full-time or on-demand, and is typically linked via a transfer case provi ...
military vehicles with light or no armour and all-terrain mobility. This type of vehicle originated in the first half of the 20th century when horses and other
draft animal
A working animal is an animal, usually domesticated, that is kept by humans and trained to perform tasks. Some are used for their physical strength (e.g. oxen and draft horses) or for transportation (e.g. riding horses and camels), while othe ...
s were replaced with mechanization. Light utility vehicles such as the
Willys Jeep
The Willys MB and the Ford GPW, both formally called the U.S. Army truck, ton, 4×4, command reconnaissance, commonly known as the Willys Jeep, Jeep, or jeep, and sometimes referred to by its Standard Army vehicle supply number G-503,According ...
were frequently mounted with .50-calibre machineguns and other small weapons for
hit-and-run tactics
Hit-and-run tactics are a Military tactics, tactical doctrine of using short surprise attacks, withdrawing before the enemy can respond in force, and constantly maneuvering to avoid full engagement with the enemy. The purpose is not to decisive ...
in World War II, especially by the
British Special Air Service who used Jeeps to raid
Axis
An axis (: axes) may refer to:
Mathematics
*A specific line (often a directed line) that plays an important role in some contexts. In particular:
** Coordinate axis of a coordinate system
*** ''x''-axis, ''y''-axis, ''z''-axis, common names ...
airfields during the
North Africa campaign
The North African campaign of World War II took place in North Africa from 10 June 1940 to 13 May 1943, fought between the Allies and the Axis Powers. It included campaigns in the Libyan and Egyptian deserts (Western Desert campaign, Desert Wa ...
. After the war, vehicles like the
Toyota Mega Cruiser
The is a large, heavy-duty four-wheel-drive SUV introduced by Toyota in 1995. As the largest 4WD vehicle ever built by Toyota, its design resembles that of the Humvee and Hummer H1.
Like the Humvee, the Mega Cruiser was originally designed pri ...
and
Humvee
The High Mobility Multipurpose Wheeled Vehicle (HMMWV; colloquial: Humvee) is a family of Military light utility vehicle, light, four-wheel drive Military vehicle#Military trucks, military trucks and utility vehicles produced by AM General. It ...
filled this role. In the 21st century,
improvised explosive devices
An improvised explosive device (IED) is a bomb constructed and deployed in ways other than in conventional warfare, conventional military action. It may be constructed of conventional military explosives, such as an artillery shell, attached t ...
continue to pose threat to mobile infantry resulting in light utility vehicles being made heavier and with more armour.
File:1942Jeep.jpg, Willys Jeep
The Willys MB and the Ford GPW, both formally called the U.S. Army truck, ton, 4×4, command reconnaissance, commonly known as the Willys Jeep, Jeep, or jeep, and sometimes referred to by its Standard Army vehicle supply number G-503,According ...
with a 37 mm gun M3 and M1917A1 machinegun of the US Army's 3rd Infantry 3rd Division may refer to:
Air divisions
*3d Air Division, United States
* 3d Attack Wing, United States
Anti-air divisions
* 3rd Flak Division, Nazi Germany
Armoured divisions
*3rd Armoured Division (Australia)
*3rd Armored Division (Fr ...
in Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of . As of 2025 the population ...
File:USMC-04325 (cropped).jpg, American Humvee
The High Mobility Multipurpose Wheeled Vehicle (HMMWV; colloquial: Humvee) is a family of Military light utility vehicle, light, four-wheel drive Military vehicle#Military trucks, military trucks and utility vehicles produced by AM General. It ...
, the main US light utility vehicle since the 1980s
Improvised fighting vehicle
An improvised fighting vehicle is a combat vehicle resulting from modifications to a civilian or military non-combat vehicle in order to give it a fighting capability. Such modifications usually consist of the grafting of
armour plating
Military vehicles are commonly armoured (or armored; see spelling differences) to withstand the impact of shrapnel, bullets, shells, rockets, and missiles, protecting the personnel inside from enemy fire. Such vehicles include armoured fightin ...
and
weapon systems. Various militaries have procured such vehicles, ever since the introduction of the first
automobile
A car, or an automobile, is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of cars state that they run primarily on roads, Car seat, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport private transport#Personal transport, peopl ...
s into military service.
During the early days, the absence of a doctrine for the military use of automobiles or of an industry dedicated to producing them, lead to much improvisation in the creation of early armoured cars, and other such vehicles. Later, despite the advent of
arms industries
Arms or ARMS may refer to:
* Arm or arms, the upper limbs of the body
Arm, Arms, or ARMS may also refer to:
People
* Ida A. T. Arms (1856–1931), American missionary-educator, temperance leader
Coat of arms or weapons
*Armaments or weapons
** ...
in many countries, several armies still resorted to using ad hoc contraptions, often in response to unexpected military situations, or as a result of the development of new
tactics
Tactic(s) or Tactical may refer to:
* Tactic (method), a conceptual action implemented as one or more specific tasks
** Military tactics, the disposition and maneuver of units on a particular sea or battlefield
** Chess tactics
In chess, a tac ...
for which no available vehicle was suitable. The construction of improvised fighting vehicles may also reflect a lack of means for the force that uses them. This is especially true in
underdeveloped countries
The least developed countries (LDCs) are developing countries listed by the United Nations that exhibit the lowest indicators of socioeconomic development. The concept of LDCs originated in the late 1960s and the first group of LDCs was listed b ...
and even in
developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a less-developed Secondary sector of the economy, industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to developed countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. ...
, where various armies and
guerrilla
Guerrilla warfare is a form of unconventional warfare in which small groups of irregular military, such as rebels, Partisan (military), partisans, paramilitary personnel or armed civilians, which may include Children in the military, recruite ...
forces have used them, as they are more affordable than military-grade combat vehicles.
Modern examples include military gun truck used by units of regular armies or other official government armed forces, based on a conventional
military cargo truck, that is able to carry a large weight of weapons and armour. They have mainly been used by regular armies to escort military convoys in regions subject to ambush by
guerrilla
Guerrilla warfare is a form of unconventional warfare in which small groups of irregular military, such as rebels, Partisan (military), partisans, paramilitary personnel or armed civilians, which may include Children in the military, recruite ...
forces. "
Narco tank
A narco tank, also called rhino trucks or , is a type of improvised fighting vehicle used by drug cartels. The vehicles are primarily civilian trucks with improvised vehicle armour, which adds operational mobility, tactical offensive, and defe ...
s", used by
Mexican
Mexican may refer to:
Mexico and its culture
*Being related to, from, or connected to the country of Mexico, in North America
** People
*** Mexicans, inhabitants of the country Mexico and their descendants
*** Mexica, ancient indigenous people ...
drug cartels in the
Mexican drug war
The Mexican drug war is an List of ongoing armed conflicts, ongoing Asymmetric warfare, asymmetric armed conflict between the Federal government of Mexico, Mexican government and various Drug cartel#Mexico, drug trafficking syndicates. When the ...
, are built from such trucks, which combines
operational mobility
In the field of military theory, the operational level of war (also called operational art, as derived from , or operational warfare) represents the level of command that connects the details of tactics with the goals of strategy.
In U.S. ...
,
tactical
Tactic(s) or Tactical may refer to:
* Tactic (method), a conceptual action implemented as one or more specific tasks
** Military tactics, the disposition and maneuver of units on a particular sea or battlefield
** Chess tactics
** Political tact ...
offensive, and
defensive
Defense or defence may refer to:
Tactical, martial, and political acts or groups
* Defense (military), forces primarily intended for warfare
* Civil defense, the organizing of civilians to deal with emergencies or enemy attacks
* Defense indust ...
capabilities.
File:Na KhTZ-16.jpg, Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
NI tank
The NI tank also known as the Odessa tank (; ''tank NI'', abbr. , , literally "for fright"), was a Soviet Union, Soviet improvised fighting vehicle, based on an STZ-5 agricultural tractor, manufactured in Odessa during the Siege of Odessa (1941) ...
improvised fighting tractor of WWII
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
.
File:Free Syrian Army technical in the eastern Qalamoun Mountains (cropped).jpg, Technical armed with a ZPU-2 heavy machine gun
A heavy machine gun (HMG) is significantly larger than light, medium or general-purpose machine guns. HMGs are typically too heavy to be man-portable (carried by one person) and require mounting onto a weapons platform to be operably stable or ...
operated by the Free Syrian Army
The Free Syrian Army (FSA; ) is a Big tent, big-tent coalition of decentralized Syrian opposition (2011–2024), Syrian opposition rebel groups in the Syrian civil war founded on 29 July 2011 by Colonel Riad al-Asaad and six officers who defe ...
during clashes with ISIS
Isis was a major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion whose worship spread throughout the Greco-Roman world. Isis was first mentioned in the Old Kingdom () as one of the main characters of the Osiris myth, in which she resurrects her sla ...
in the eastern Qalamoun Mountains
The Qalamoun Mountains () are the northeastern portion of the Anti-Lebanon Mountains, and they are northeast of the Syrian capital Damascus. They run from Barada River Valley in the southwest to the city of Hisyah in the northeast.
Western Q ...
, southern Syria, 2017
File:Gun Truck.jpg, A gun truck of the type used in Iraq, based on an M939 five-ton truck
File:Narco-tank-1.jpg, "Monstruo 2010", a narco tank based on a Ford F-350
The Ford Super Duty (also known as the Ford F-Series Super Duty) is a series of heavy-duty pickup trucks produced by the Ford Motor Company since the 1999 model year. Slotted above the consumer-oriented Ford F-150, the Super Duty trucks are an e ...
with a turret
Turret may refer to:
* Turret (architecture), a small tower that projects above the wall of a building
* Gun turret, a mechanism of a projectile-firing weapon
* Optical microscope#Objective turret (revolver or revolving nose piece), Objective turre ...
captured by Mexican
Mexican may refer to:
Mexico and its culture
*Being related to, from, or connected to the country of Mexico, in North America
** People
*** Mexicans, inhabitants of the country Mexico and their descendants
*** Mexica, ancient indigenous people ...
Authorities in Jalisco
Jalisco, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Jalisco, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. It is located in western Mexico and is bordered by s ...
Troop carriers
Troop-carrying AFVs are divided into three main types – armoured personnel carriers (APCs), infantry fighting vehicles (IFVs) and infantry mobility vehicles (IMV). The main difference between the three is their intended role – the APC is designed purely to transport troops and is armed for self-defence only – whereas the IFV is designed to provide close-quarters and anti-armour fire support to the infantry it carries. IMV is a wheeled armoured personnel carrier serving as a military patrol, reconnaissance or security vehicle.
Armoured personnel carrier
Armoured personnel carriers (APCs) are intended to carry infantry quickly and relatively safely to the point where they are deployed. In the
Battle of Amiens, 8 August 1918, the British
Mk V* tank (a lengthened Mark V) carried a small number of machine gunners as an experiment, but the men were debilitated by the conditions inside the vehicle. Later that year the first purpose-built APC, the British
Mk IX tank (Mark Nine), appeared. In 1944, the Canadian general
Guy Simonds
Lieutenant-general (Canada), Lieutenant-General Guy Granville Simonds, (April 23, 1903 – May 15, 1974) was a senior Canadian Army officer who served with distinction during World War II. Acknowledged by many military historians and senior comm ...
ordered the conversion of redundant armoured vehicles to carry troops (generically named "
Kangaroos
Kangaroos are marsupials from the family Macropodidae (macropods, meaning "large foot"). In common use, the term is used to describe the largest species from this family, the red kangaroo, as well as the antilopine kangaroo, eastern grey ...
"). This proved highly successful, even without training, and the concept was widely used in the
21st Army Group
The 21st Army Group was a British headquarters formation formed during the Second World War. It controlled two field armies and other supporting units, consisting primarily of the British Second Army and the First Canadian Army. Established ...
. Post-war, specialised designs were built, such as the Soviet
BTR-60
The BTR-60 is the first vehicle in a series of Soviet Union, Soviet eight-wheeled armoured personnel carriers (APCs). It was developed in the late 1950s as a replacement for the BTR-152 and was seen in public for the first time in 1961. BTR (vehi ...
and US
M113
The M113 is a fully tracked armored personnel carrier (APC) that was developed and produced by the FMC Corporation. The M113 was sent to United States Army Europe in 1961 to replace the mechanized infantry's M59 APCs. The M113 was first used ...
.
File:Bundesarchiv Bild 101I-801-0664-37, Berlin, Unter den Linden, Schützenpanzer.jpg, German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
WWII Sd.Kfz. 251
The Sd.Kfz. 251 (''Sonderkraftfahrzeug 251'') was a World War II German half-tracked armoured personnel carrier. Designed by the Hanomag company to transport the ''Panzergrenadier'' (German mechanized infantry) into battle, the Sd.Kfz. 251 was bas ...
half-track
A half-track is a civilian or military vehicle with wheels at the front for steering and continuous tracks at the back to propel the vehicle and carry most of the load. A half-track combines the soft-ground traction of a tank with the Car handl ...
ed APC
File:IM000656.jpg, Israeli Namer
Namer (, ; meaning "leopard," and also a syllabic abbreviation of "Nagmash" (APC) and "Merkava") is an Israeli armoured personnel carrier based on a Merkava#Merkava Mark IV, Merkava Mark IV tank chassis. Namer was developed by and is being asse ...
tracked APC
File:GTK_Boxer_Fuehrungsfahrzeug_front.jpg, The ARTEC Boxer armoured personnel carrier
Infantry fighting vehicle
An ''infantry fighting vehicle'' (''IFV''), also known as a ''mechanized infantry combat vehicle'' (''MICV''), is a type of armoured fighting vehicle used to carry
infantry
Infantry, or infantryman are a type of soldier who specialize in ground combat, typically fighting dismounted. Historically the term was used to describe foot soldiers, i.e. those who march and fight on foot. In modern usage, the term broadl ...
into battle and provide
direct
Direct may refer to:
Mathematics
* Directed set, in order theory
* Direct limit of (pre), sheaves
* Direct sum of modules, a construction in abstract algebra which combines several vector spaces
Computing
* Direct access (disambiguation), ...
fire support
Fire support is a military tactics term used to describe weapons fire used to support friendly forces by engaging, suppressing, or destroying enemy forces, facilities, or materiel in combat. It is often provided through indirect fire, though th ...
.
The first example of an IFV was the
West German
West Germany was the common English name for the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) from its formation on 23 May 1949 until its reunification with East Germany on 3 October 1990. It is sometimes known as the Bonn Republic after its capital c ...
Schützenpanzer Lang HS.30 which served in the
Bundeswehr
The (, ''Federal Defence'') are the armed forces of the Germany, Federal Republic of Germany. The is divided into a military part (armed forces or ''Streitkräfte'') and a civil part, the military part consists of the four armed forces: Germ ...
from 1958 until the early 1980s.
IFVs are similar to armoured personnel carriers (APCs) and
infantry carrier vehicles (ICVs), designed to transport a
section
Section, Sectioning, or Sectioned may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media
* Section (music), a complete, but not independent, musical idea
* Section (typography), a subdivision, especially of a chapter, in books and documents
** Section sig ...
or
squad
In military terminology, a squad is among the smallest of Military organization, military organizations and is led by a non-commissioned officer. NATO and United States, U.S. doctrine define a squad as an organization "larger than a fireteam, ...
of infantry (generally between five and ten men) and their equipment. They are differentiated from APCswhich are purely "troop-transport" vehicles armed only for self-defencebecause they are designed to give direct fire support to the dismounted infantry and so usually have significantly enhanced armament. IFVs also often have improved
armour
Armour (Commonwealth English) or armor (American English; see American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, spelling differences) is a covering used to protect an object, individual, or vehicle from physical injury or damage, e ...
and some have firing ports (allowing the infantry to fire
personal weapons
A service pistol (also known as a standard-issue pistol or a personal ordnance weapon) is any handgun issued to regular military personnel or law enforcement officers. Typically, service pistols are semi-automatic pistols (previously revolvers) ...
while mounted).
They are typically armed with an
autocannon
An autocannon, automatic cannon or machine cannon is a automatic firearm, fully automatic gun that is capable of rapid-firing large-caliber ( or more) armour-piercing, explosive or incendiary ammunition, incendiary shell (projectile), shells, ...
of 20 to 57 mm calibre, 7.62mm machine guns,
anti-tank guided missile
An anti-tank guided missile (ATGM), anti-tank missile, anti-tank guided weapon (ATGW) or anti-armor guided weapon is a guided missile primarily designed to hit and destroy heavily armored military vehicles. ATGMs range in size from shoulde ...
s (ATGMs) and/or
surface-to-air missile
A surface-to-air missile (SAM), also known as a ground-to-air missile (GTAM) or surface-to-air guided weapon (SAGW), is a missile designed to be launched from the ground or the sea to destroy aircraft or other missiles. It is one type of anti-ai ...
s (SAMs). IFVs are usually
tracked, but some wheeled vehicles fall into this category. IFVs are generally less heavily armed and armoured than
main battle tank
A main battle tank (MBT), also known as a battle tank or universal tank or simply tank,Ogorkiewicz 2018 p222 is a tank that fills the role of armour-protected direct fire and maneuver in many modern armies. Cold War-era development of more po ...
s. They sometimes carry anti-tank missiles to protect and support infantry against armoured threats, such as the NATO
TOW missile and Soviet
Bastion
A bastion is a structure projecting outward from the curtain wall of a fortification, most commonly angular in shape and positioned at the corners of the fort. The fully developed bastion consists of two faces and two flanks, with fire from the ...
, which offer a significant threat to tanks. Specially equipped IFVs have taken on some of the roles of light tanks; they are used by reconnaissance organizations, and light IFVs are used by airborne units which must be able to fight without the heavy firepower of tanks.
File:Puma, first series.jpg, The German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
Puma infantry fighting vehicle
File:BMP-2M.jpg, Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
BMP-2
The BMP-2 (''Boyevaya Mashina Pekhoty'', , literally "combat machine/vehicle f theinfantry") is an amphibious infantry fighting vehicle introduced in the 1980s in the Soviet Union, following on from the BMP-1 of the 1960s.
Development his ...
M amphibious IFV
File:Royal Tank Museum 157.jpg, South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
n Wheeled Ratel IFV
The Ratel is a South African infantry fighting vehicle. It was the first wheeled infantry fighting vehicle to enter service worldwide and was built on a modified MAN Truck & Bus, MAN truck chassis. The Ratel was designed in response to a South Af ...
Infantry mobility vehicle

An ''infantry mobility vehicle'' (''IMV'') or ''protected patrol vehicle'' (''PPV'') is a wheeled armoured personnel carrier (APC) serving as a military patrol, reconnaissance or security vehicle. Examples include the
ATF Dingo
The ATF Dingo is a German heavily armored military MRAP infantry mobility vehicle based on a Unimog chassis with a V-hull design, produced by the company KNDS Deutschland (formerly Krauss-Maffei Wegmann (KMW)). The first prototype of the Dingo 1 ...
,
AMZ Dzik
Dzik () is a Poland, Polish-made multi-purpose infantry mobility vehicle. Produced by the AMZ-KUTNO Ltd, AMZ works in Kutno, it is designed for serving both the patrol and intervention roles, as well as an armoured personnel carrier for use by va ...
,
AMZ Tur
Tur (Tur 1) () is a light infantry mobility vehicle designed by the Polish factory AMZ-Kutno in 2007. The Tur was designed for intervention and patrol tasks behind front lines, specially equipped for operations in dangerous areas. It has a five ...
,
Mungo ESK
The Mungo ESK (Einsatzfahrzeug Spezialisierte Kräfte) is an air-transportable, armoured multirole transport vehicle operated by the Airmobile Operations Division and the Rapid Forces Division of the German Army.
The Mungo is based on the Mul ...
, and
Bushmaster IMV
The Bushmaster Protected Mobility Vehicle or Infantry Mobility Vehicle is an Australian-built four-wheel drive armoured vehicle. The Bushmaster was primarily designed by the then government-owned Australian Defence Industries (ADI), and is curr ...
. This term also applies to the vehicles currently being fielded as part of the
MRAP
Mine-Resistant Ambush Protected Vehicle (MRAPV), also known as MRAP vehicle, is a type of armoured personnel carrier that is designed specifically to withstand land mines, improvised explosive device (IED) attacks, and ambushes to save troops' li ...
program.
IMVs were developed in response to the threats of modern counterinsurgency warfare, with an emphasis on
Ambush
An ambush is a surprise attack carried out by people lying in wait in a concealed position. The concealed position itself or the concealed person(s) may also be called an "". Ambushes as a basic military tactics, fighting tactic of soldi ...
Protection and
Mine
Mine, mines, miners or mining may refer to:
Extraction or digging
*Miner, a person engaged in mining or digging
*Mining, extraction of mineral resources from the ground through a mine
Grammar
*Mine, a first-person English possessive pronoun
M ...
-Resistance. Similar vehicles existed long before the term IMV was coined, such as the French
VAB and South African
Buffel
The Buffel (English: ''Buffalo'') is an infantry mobility vehicle used by the South African Defence Force during the South African Border War. The Buffel was also used as an armoured fighting vehicle and proved itself in this role. It replaced ...
. The term is coming more into use to differentiate light 4x4 wheeled APCs from the traditional 8x8 wheeled APCs. It is a
neologism
In linguistics, a neologism (; also known as a coinage) is any newly formed word, term, or phrase that has achieved popular or institutional recognition and is becoming accepted into mainstream language. Most definitively, a word can be considered ...
for what might have been classified in the past as an armoured
scout car
A scout car is a light wheeled armored military vehicle, purpose-built and used for passive reconnaissance. Scout cars are either unarmed or lightly armed for self-defense, and do not carry large-caliber weapons systems. This differentiates them ...
, such as the
BRDM
BRDM is an initialism for ''Boyevaya Razvedyvatelnaya Dozornaya Mashina'', (RU Боевая Разведывательная Дозорная Машина), literally "Combat Reconnaissance Patrol Vehicle". The BRDM is a eight-wheeled amphibious ...
, but the IMV is distinguished by having a requirement to carry dismountable infantry. The up-armoured
M1114 Humvee variant can be seen as an adaptation of the unarmoured Humvee to serve in the IMV role.
File:CV9035 assessment (cropped).jpg, A CV-9035 Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
infantry fighting vehicle used by U.S. Army
File:M113IraqiFreedom.jpg, The M113
The M113 is a fully tracked armored personnel carrier (APC) that was developed and produced by the FMC Corporation. The M113 was sent to United States Army Europe in 1961 to replace the mechanized infantry's M59 APCs. The M113 was first used ...
, one of the most common tracked APCs, on duty during the Iraq War
The Iraq War (), also referred to as the Second Gulf War, was a prolonged conflict in Iraq lasting from 2003 to 2011. It began with 2003 invasion of Iraq, the invasion by a Multi-National Force – Iraq, United States-led coalition, which ...
File:Dingo 2.jpg, An ATF Dingo
The ATF Dingo is a German heavily armored military MRAP infantry mobility vehicle based on a Unimog chassis with a V-hull design, produced by the company KNDS Deutschland (formerly Krauss-Maffei Wegmann (KMW)). The first prototype of the Dingo 1 ...
of the German Army
The German Army (, 'army') is the land component of the armed forces of Federal Republic of Germany, Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German together with the German Navy, ''Marine'' (G ...
is a mine-resistant and ambush-protected infantry mobility vehicle used by several European armed forces
File:278th MP Company's new ASVs.jpg, A United States Army National Guard
The Army National Guard (ARNG) is an organized Militia (United States), militia force and a Reserve components of the United States Armed Forces, federal military reserve force of the United States Army. It is simultaneously part of two differen ...
M1117 armoured security vehicle
The M1117 armored security vehicle (ASV; nicknamed Guardian) is an internal security vehicle based on the Cadillac Gage Commando, V-100 and V-150 Commando series of Armored car (military), armored cars. It was developed in the late 1990s for ser ...
File:Nexter Aravis, place Jeanne Helbling, Strasbourg 2010 (2).jpg, A French Nexter Aravis in Strasbourg
Strasbourg ( , ; ; ) is the Prefectures in France, prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est Regions of France, region of Geography of France, eastern France, in the historic region of Alsace. It is the prefecture of the Bas-Rhin Departmen ...
File:Norwegian Iveco LMV 02.jpg, Norwegian soldiers running operations in an Iveco LMV
The Iveco LMV (Light Multirole Vehicle) is a 4WD tactical vehicle developed by Iveco, and in service with several countries. After its adoption by the Italian Army as the ''Veicolo-Tattico-Leggero-Multiruolo'' (VTLM) ''Lince'' ("Light tactical m ...
in Faryab province, Afghanistan. The Iveco LMV is widely used by European militaries.
File:Saxony State Police Survivor R (1).jpg, An RMMV Survivor R used by the Saxony
Saxony, officially the Free State of Saxony, is a landlocked state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, and Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic. Its capital is Dresden, and ...
State Police. In this configuration, it does not feature the .50 machine gun and grenade launcher remote weapon station used in the standard military configuration.
Amphibious vehicles
Many modern military vehicles, ranging from light wheeled command and reconnaissance, through armoured personnel carriers and tanks, are manufactured with amphibious capabilities. Contemporary wheeled armoured amphibians include the French
Véhicule de l'Avant Blindé
The or VAB (literally meaning "Armoured Forward Vehicle"; but more appropriately translated: "Armoured Vanguard Vehicle") is a French armoured personnel carrier and support vehicle designed and manufactured by ''Renault Trucks Defense'' (now kno ...
and
Véhicule Blindé Léger
The Panhard Véhicule Blindé Léger ("Light armoured vehicle"), also known by its acronym Panhard VBL or simply VBL, is a French wheeled 4×4 all-terrain vehicle built by Panhard. The vehicle is offered in various configurations, and was design ...
. The latter is a small, lightly armoured
4×4
A four-wheel drive, also called 4×4 ("four by four") or 4WD, is a two-axled vehicle drivetrain capable of providing torque to all of its wheels simultaneously. It may be full-time or on-demand, and is typically linked via a transfer case pro ...
all-terrain vehicle that is fully amphibious and can swim at 5.4 km/h. The VAB (''Véhicule de l'Avant Blindé'' – 'armoured vanguard vehicle') is a fully amphibious armoured personnel carrier powered in the water by two water jets, that entered service in 1976 and produced in numerous configurations, ranging from basic personnel carrier, anti-tank missile platform.
During the
Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
the
Soviet bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc (Combloc), the Socialist Bloc, the Workers Bloc, and the Soviet Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of communist states of Central and Eastern Europe, Asia, Africa, and Latin America that were a ...
states developed a number of amphibious APCs, fighting vehicles and tanks, both wheeled and tracked. Most of the vehicles the Soviets designed were amphibious, or could ford deep water. Wheeled examples are the
BRDM-1
The BRDM-1 (''Bronirovannaya Razvedyvatelnaya Dozornaya Mashina'', Бронированная Разведывательная Дозорная Машина, literally "armored reconnaissance/patrol vehicle") is a Soviet amphibious armored scout c ...
and
BRDM-2
The BRDM-2 (''Boyevaya Razvedyvatelnaya Dozornaya Mashina'', Боевая Разведывательная Дозорная Машина, literally "Combat Reconnaissance/Patrol Vehicle") is an amphibious armoured scout car designed and developed ...
4x4
A four-wheel drive, also called 4×4 ("four by four") or 4WD, is a two-axled vehicle drivetrain capable of providing torque to all of its wheels simultaneously. It may be full-time or on-demand, and is typically linked via a transfer case provi ...
armoured scout cars, as well as the
BTR-60
The BTR-60 is the first vehicle in a series of Soviet Union, Soviet eight-wheeled armoured personnel carriers (APCs). It was developed in the late 1950s as a replacement for the BTR-152 and was seen in public for the first time in 1961. BTR (vehi ...
,
BTR-70
The BTR-70 is an eight-wheeled armored personnel carrier () originally developed by the Soviet Union during the late 1960s under the manufacturing code GAZ-4905. On August 21, 1972, it was accepted into Soviet service and would later be widely exp ...
,
BTR-80
The BTR-80 () is an 8×8 wheeled Amphibious vehicle, amphibious armoured personnel carrier (APC) designed in the Soviet Union. It was adopted in 1985 and replaced the previous vehicles, the BTR-60 and BTR-70, in the Soviet Army. It was first de ...
,
BTR-94
The BTR-94 is a Ukrainian amphibious armoured personnel carrier ('' Bronetransporter''), a modification of the Soviet eight-wheeled BTR-80.
Description
The BTR-94's turret BAU-23x2 is larger than the BTR-80's BPU-1. It is fitted with a twin ...
and
BTR-90 8x8 armoured personnel carriers.

During the 1930s and 1940s, Japan produced a number of amphibious tank designs, including prototypes such as the
Sumida amphibious armored car (AMP),
SR I-Go
The was the first amphibious tank of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN). The Type 2 Ka-Mi was based on the Imperial Japanese Army's Type 95 Ha-Go light tank with major modifications. It first saw combat service during the Guadalcanal campaign in l ...
,
SR II Ro-Go,
SR III Ha-Go
The was the first amphibious vehicle, amphibious tank of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN). The Type 2 Ka-Mi was based on the Imperial Japanese Army's Type 95 Ha-Go light tank with major modifications. It first saw combat service during the Guadal ...
,
Type 1 Mi-Sha (a/k/a Type 1 Ka-Mi) and
Type 5 To-Ku. Production amphibious tanks during World War II included the
Type 2 Ka-Mi
The was the first amphibious tank of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN). The Type 2 Ka-Mi was based on the Imperial Japanese Army's Type 95 Ha-Go light tank with major modifications. It first saw combat service during the Guadalcanal campaign in l ...
, and
Type 3 Ka-Chi
The was an amphibious medium tank developed by the Imperial Japanese Navy in World War II. The Type 3 Ka-Chi was based on an extensively modified Imperial Japanese Army Type 1 Chi-He medium tank (it had 2 more road-wheels and two more return ro ...
; production amphibious transports included the
F B swamp vehicle
The F B was an Imperial Japanese Army (IJA) military transport/personnel carrier used for crossing difficult swampy terrain. It was part of a series of vehicles developed by the army in its effort to mechanize and give mobility to their forces. A ...
and
Type 4 Ka-Tsu APC. All production units were for use by the
Japanese Special Naval Landing Forces
The Special Naval Landing Forces (SNLF; ) were standalone naval infantry units in the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) and were a part of the IJN land forces. They saw extensive service in the Second Sino-Japanese War and in the Pacific theatre o ...
in campaigns in the Pacific with amphibious operations.
The United States started developing a long line of
Landing Vehicle Tracked
The Amphibious Vehicle, Tracked (LVT or AMTRAC) is an amphibious warfare vehicle and Amphibious vehicle, amphibious landing craft, introduced by the United States Navy and United States Marine Corps. (The USN and USMC use ''L'' to designate ...
(LVT) designs from . The US Marine Corps currently uses the AAV7-A1
Assault Amphibious Vehicle
The Assault Amphibious Vehicle (AAV)—official designation AAVP-7A1 (formerly known as Landing Vehicle, Tracked, Personnel-7 abbr. LVTP-7)—is a fully tracked amphibious landing vehicle manufactured by BAE Systems Platforms & Services (prev ...
, which was to be succeeded by the
Expeditionary Fighting Vehicle
The Expeditionary Fighting Vehicle (EFV) (formerly known as the Advanced Amphibious Assault Vehicle (AAAV)) was an amphibious assault vehicle developed by General Dynamics during the 1990s and 2000s for use by the US Marine Corps. It would ha ...
, which was capable of planing on water and can achieve water speeds of 37–46 km/h. The EFV project has been cancelled.
A significant number of tracked armoured vehicles that are primarily intended for land-use, have some amphibious capability, tactically useful inland, reducing dependence on bridges. They use their tracks, sometimes with added propeller or water jets for propulsion. As long as the banks have a shallow enough slopes to enter or leave the water they can cross rivers and water obstacles.
Some heavy tanks can operate amphibiously with a fabric skirt to add
buoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is the force exerted by a fluid opposing the weight of a partially or fully immersed object (which may be also be a parcel of fluid). In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of t ...
. The
Sherman
Sherman most commonly refers to:
*Sherman (name), including a list of people and fictional characters with the given name or surname
** William Tecumseh Sherman (1820–1891), American Civil War General
*M4 Sherman, a World War II American tank
S ...
DD tank
DD or duplex drive tanks, nicknamed "Donald Duck tanks", were a type of amphibious vehicle, amphibious swimming tank developed by the British during the Second World War. The phrase is mostly used for the Duplex Drive variant of the M4 Sherman ...
used in the
Normandy landings
The Normandy landings were the landing operations and associated airborne operations on 6 June 1944 of the Allies of World War II, Allied invasion of Normandy in Operation Overlord during the Second World War. Codenamed Operation Neptune and ...
had this setup. When in water the waterproof float screen was raised and propellers deployed. Some modern vehicles use a similar skirt.
File:DD-Tank.jpg, M4 Sherman
The M4 Sherman, officially medium tank, M4, was the medium tank most widely used by the United States and Western Allies in World War II. The M4 Sherman proved to be reliable, relatively cheap to produce, and available in great numbers. I ...
DD tank
DD or duplex drive tanks, nicknamed "Donald Duck tanks", were a type of amphibious vehicle, amphibious swimming tank developed by the British during the Second World War. The phrase is mostly used for the Duplex Drive variant of the M4 Sherman ...
during WWII
File:BTR-80 coming ashore.jpg, BTR-80
The BTR-80 () is an 8×8 wheeled Amphibious vehicle, amphibious armoured personnel carrier (APC) designed in the Soviet Union. It was adopted in 1985 and replaced the previous vehicles, the BTR-60 and BTR-70, in the Soviet Army. It was first de ...
s coming ashore, engine snorkels and waterjet deployed
File:AAV-australia.jpg, Two U.S. Marine Corps
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines or simply the Marines, is the maritime land force service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is responsible for conducting expeditionary ...
Assault Amphibious Vehicle
The Assault Amphibious Vehicle (AAV)—official designation AAVP-7A1 (formerly known as Landing Vehicle, Tracked, Personnel-7 abbr. LVTP-7)—is a fully tracked amphibious landing vehicle manufactured by BAE Systems Platforms & Services (prev ...
s emerge from the surf onto the sand of Freshwater Beach
Freshwater Beach is a beach located in Freshwater, New South Wales, a suburb of Sydney, Australia. Freshwater Beach is the first beach north of Manly, New South Wales, on the Peninsula. The beach is flanked by a headland at each end and can pr ...
, Australia
File:PKP trailer attached to the amphibian carrier PTS-2 in Military-historical Museum of Artillery, Engineer and Signal Corps in Saint-Petersburg, Russia.jpg, PKP trailer
File:PTS-M.jpg, Soviet PTS-M landing craft
Airborne vehicles

Lightweight armoured fighting vehicles designed or modified to be
carried by aircraft and delivered by air drop, helicopter lift, glider, or air landing with infantry to provide heavier tactical firepower and mobility. The air-equivalent to amphibious vehicles, the main advantage of airborne forces is their ability to be deployed into combat zones without land passage, as long as the
airspace
Airspace is the portion of the atmosphere controlled by a country above its territory, including its territorial waters or, more generally, any specific three-dimensional portion of the atmosphere. It is not the same as outer space which is t ...
is accessible. Airborne vehicles are limited only by the tonnage capacity of their
transport aircraft Transport aircraft is a broad category of aircraft that includes:
* Airliners, aircraft, usually large and most often operated by airlines, intended for carrying multiple passengers or cargo in commercial service
* Cargo aircraft or freighters, fix ...
. Airborne vehicles typically lack the armour and supplies necessary for prolonged combat, so they are utilized for establishing an
airhead
An airhead is a designated area in a hostile or threatened territory which, when seized and held, allows the air landing of further teams and materiel via an airbridge, and provides the maneuver and preparation space necessary for projected oper ...
to bring in larger forces before carrying out other combat objectives. One modern example is the German
Wiesel AWC
The Wiesel Armoured Weapons Carrier (AWC; ) is a German light air-transportable armoured fighting vehicle, more specifically a lightly armoured weapons carrier, produced by Rheinmetall.
The Wiesel has been used in several of the Bundeswehr's mis ...
. The USA also created the
M22 Locust
The M22 Locust, officially Light Tank (Airborne), M22, was an American-designed airborne light tank which was produced during World War II. The Locust began development in 1941 after the British War Office requested that the American governmen ...
as a way to aid paratroopers/ being paradropped in as it was very lightly armoured and very small.
Armoured engineering vehicle
Modern engineering AFV's utilize chassis based on main battle tank platforms: these vehicles are as well armoured and protected as tanks, designed to keep up with tanks, breach obstacles to help tanks get to wherever it needs to be, perform utility functions necessary to expedite mission objectives of tanks, and to conduct other earth-moving and engineering work on the battlefield. These vehicles go by different names depending upon the country of use or manufacture. In the United States the term "combat engineer vehicle (CEV)" is used, in the United Kingdom the term "
Armoured Vehicle Royal Engineers
Armoured Vehicle Royal Engineers (AVRE), also known as Assault Vehicle Royal Engineers, is the title given to a series of armoured military engineering vehicles operated by the Royal Engineers (RE) for the purpose of protecting engineers duri ...
(AVRE)" is used, while in Canada and other commonwealth nations the term "armoured engineer vehicle (AEV)" is used. There is no set template for what such a vehicle will look like, yet likely features include a large dozer blade or mine ploughs, a large calibre demolition cannon, augers, winches, excavator arms and cranes, or lifting booms.
Although the term "armoured engineer vehicle" is used specifically to describe these multi-purpose tank-based engineering vehicles, that term is also used more generically in British and Commonwealth militaries to describe all heavy tank-based engineering vehicles used in the support of mechanized forces. Thus, "armoured engineer vehicle" used generically would refer to AEV, AVLB, Assault Breachers, and so on. Good examples of this type of vehicle include the UK
Trojan AVRE, the Russian IMR, and the US
M728 Combat Engineer Vehicle.
Breaching vehicle
A breaching vehicle is especially designed to clear pathways for troops and other vehicles through
minefields
A land mine, or landmine, is an explosive weapon often concealed under or camouflaged on the ground, and designed to destroy or disable enemy targets as they pass over or near it. Land mines are divided into two types: anti-tank mines, whic ...
and along
roadside bomb
An improvised explosive device (IED) is a bomb constructed and deployed in ways other than in conventional warfare, conventional military action. It may be constructed of conventional military explosives, such as an artillery shell, attached t ...
s and other
improvised explosive device
An improvised explosive device (IED) is a bomb constructed and deployed in ways other than in conventional warfare, conventional military action. It may be constructed of conventional military explosives, such as an artillery shell, attached t ...
s. These vehicles are equipped with mechanical or other means for the breaching of man-made obstacles. Common types of breaching vehicles include mechanical
flails, mine plough vehicles, and mine roller vehicles.
Armoured bulldozer

The armoured bulldozer is a basic tool of
combat engineering
A combat engineer (also called pioneer or sapper) is a type of soldier who performs military engineering tasks in support of land forces combat operations. Combat engineers perform a variety of military engineering, tunnel and mine warfare tas ...
. These
combat engineering vehicle
A military engineering vehicle is a vehicle built for construction work or for the transportation of combat engineering, combat engineers on the battlefield. These vehicles may be modified civilian equipment (such as the Armored bulldozer, armo ...
s combine the earth moving capabilities of the bulldozer with armour which protects the vehicle and its operator in or near combat. Most are civilian bulldozers modified by addition of
vehicle armour
Military vehicles are commonly armoured (or armored; American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, see spelling differences) to withstand the impact of Fragmentation (weaponry), shrapnel, bullets, Shell (projectile), shells, Rocke ...
/military equipment, but some are
tank
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful engine; ...
s stripped of armament and fitted with a dozer blade. Some tanks have bulldozer blades while retaining their armament, but this does not make them armoured bulldozers as such, because combat remains the primary role – earth moving is a secondary task.
Armoured recovery vehicle
An ''armoured recovery vehicle'' (''ARV'') is a type of
vehicle recovery
Vehicle recovery is the recovery of any vehicle to another place, generally speaking with a commercial vehicle known as a ''recovery vehicle'', tow truck or spectacle lift.
Recovery can take the form of general recovery, normally of broken dow ...
armoured fighting vehicle used to repair battle- or mine-damaged as well as broken-down armoured vehicles during combat, or to tow them out of the danger zone for more extensive repairs. To this end the term ''armoured repair and recovery vehicle'' (''ARRV'') is also used.
ARVs are normally built on the
chassis
A chassis (, ; plural ''chassis'' from French châssis ) is the load-bearing framework of a manufactured object, which structurally supports the object in its construction and function. An example of a chassis is a vehicle frame, the underpart ...
of a main battle tank (MBT), but some are also constructed on the basis of other armoured fighting vehicles, mostly armoured personnel carriers (APCs). ARVs are usually built on the basis of a vehicle in the same class as they are supposed to recover; a tank-based ARV is used to recover tanks, while an APC-based one recovers APCs, but does not have the power to tow a much heavier tank.
Armoured vehicle-launched bridge
An ''armoured vehicle-launched bridge'' (''AVLB'') is a combat support vehicle, sometimes regarded as a subtype of
combat engineering vehicle
A military engineering vehicle is a vehicle built for construction work or for the transportation of combat engineering, combat engineers on the battlefield. These vehicles may be modified civilian equipment (such as the Armored bulldozer, armo ...
, designed to assist militaries in rapidly deploying
tank
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful engine; ...
s and other armoured fighting vehicles across rivers. The AVLB is usually a tracked vehicle converted from a tank chassis to carry a folding metal bridge instead of weapons. The AVLB's job is to allow armoured or infantry units to cross water, when a river too deep for vehicles to wade through is reached, and no bridge is conveniently located (or sufficiently sturdy, a substantial concern when moving 60-ton tanks).
The bridge layer unfolds and launches its cargo, providing a ready-made bridge across the obstacle in only minutes. Once the span has been put in place, the AVLB vehicle detaches from the bridge, and moves aside to allow traffic to pass. Once all of the vehicles have crossed, it crosses the bridge itself and reattaches to the bridge on the other side. It then retracts the span ready to move off again. A similar procedure can be employed to allow crossings of small chasms or similar obstructions. AVLBs can carry bridges of or greater in length. By using a tank chassis, the bridge layer is able to cover the same terrain as main battle tanks, and the provision of armour allows them to operate even in the face of enemy fire. However, this is not a universal attribute: some exceptionally sturdy 6x6 or 8x8 truck chassis have lent themselves to bridge-layer applications.
Combat engineer section carriers
''Combat engineer section carriers'' are used to transport
sapper
A sapper, also called a combat engineer, is a combatant or soldier who performs a variety of military engineering duties, such as breaching fortifications, demolitions, bridge-building, laying or clearing minefields, preparing field defenses ...
s (
combat engineer
A combat engineer (also called pioneer or sapper) is a type of soldier who performs military engineering tasks in support of land forces combat operations. Combat engineers perform a variety of military engineering, Tunnel warfare, tunnel and l ...
s) and can be fitted with
bulldozer
A bulldozer or dozer (also called a crawler) is a large tractor equipped with a metal #Blade, blade at the front for pushing material (soil, sand, snow, rubble, or rock) during construction work. It travels most commonly on continuous tracks, ...
s' blades and other mine-breaching devices. They are often used as APCs because of their carrying ability and heavy protection. They are usually armed with
machine guns and grenade launchers and usually tracked to provide enough tractive force to push blades and rakes. Some examples are the U.S.
M113 APC,
IDF Puma
The Puma (Hebrew: פומ"ה פורץ מכשולים הנדסי) is a heavily armored Combat engineering vehicle and armored personnel carrier that the Engineering Corps of the Israeli Defence Forces has used since the early 1990s. The vehicle c ...
,
Nagmachon
Nagmachon is a heavily armoured infantry fighting vehicle fielded by the Israel Defense Forces. The Nagmachon evolved from the ''NagmaSho't'' armoured personnel carrier (APC), which in turn was based on Centurion tank Sho't hulls from the 1970s a ...
, Husky, and U.S.
M1132 ESV (a
Stryker
The Stryker is a family of Eight-wheel drive, eight-wheeled armored fighting vehicles derived from the Canadian LAV III. Stryker vehicles are produced by General Dynamics Land Systems-Canada (GDLS-C) for the United States Army in a plant in L ...
variant).
File:French_army_EFA_DSC00859.jpg#/media/File:French_army_EFA_DSC00859.jpg, French EFA Amphibious float bridge
File:M60-panther-mcgovern-base.jpg, A remotely controlled Panther armoured mine clearing vehicle leads a column down a road in Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina, sometimes known as Bosnia-Herzegovina and informally as Bosnia, is a country in Southeast Europe. Situated on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula, it borders Serbia to the east, Montenegro to the southeast, and Croatia to th ...
, 16 May 1996.
File:M1 Assault Breacher Vehicle.jpg, Marines with 2nd Combat Engineer Battalion launch a M58 MICLIC
The M58 mine-clearing line charge (MICLIC) is a rocket-projected mine-clearing line charge used to provide a "close-in" demining capability for maneuver forces of the United States Army and Marine Corps.
First fielded in 1988 with United State ...
from an M1150 Assault Breacher Vehicle
File:D9-IDF-2018-Zachi-Evenor-1.jpg, An armoured IDF Caterpillar D9
The IDF Caterpillar D9 — nicknamed ''Doobi'' (, for teddy bear) — is a Caterpillar D9 armored bulldozer used by the Israel Defense Forces (IDF). It is supplied by Caterpillar Inc. and modified by the Israel Defense Forces, Israeli Milita ...
bulldozer
A bulldozer or dozer (also called a crawler) is a large tractor equipped with a metal #Blade, blade at the front for pushing material (soil, sand, snow, rubble, or rock) during construction work. It travels most commonly on continuous tracks, ...
, nicknamed "דובי" ('Teddy bear
A teddy bear, or simply a teddy, is a stuffed toy in the form of a bear. The teddy bear was named by Morris Michtom after the 26th president of the United States, Theodore Roosevelt; it was developed apparently simultaneously in the first deca ...
') in Israel. Its armour allows it to work under heavy fire.
File:Bergepanzer Bueffel.jpg, BPz3 "Büffel" armoured recovery vehicle, German Army
The German Army (, 'army') is the land component of the armed forces of Federal Republic of Germany, Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German together with the German Navy, ''Marine'' (G ...
File:M60A1 Armored Vehicle Landing Bridge.jpg, An M60A1 armoured vehicle-launched bridge (AVLB), deploying its scissors-type bridge
File:Stryker ESV front q.jpg, An M1132 engineer squad vehicle (ESV) issued to combat engineer squads in the US Army Stryker brigade combat teams
Air defence vehicles
An anti-aircraft vehicle, also known as a self-propelled anti-aircraft gun (SPAAG) or self-propelled air defense system (SPAD), is a mobile vehicle with a dedicated anti-aircraft capability.
Specific weapon systems used include
machine guns,
anti-aircraft autocannons, larger anti-air guns, or
surface-to-air-missiles, and some mount both guns and longer-ranged missiles (e.g. the Pantsir-S1). Platforms used include both trucks and heavier combat vehicles such as armored personnel carriers and tanks, which add protection from aircraft, artillery, and small arms fire for front line deployment.
Anti-aircraft guns are usually mounted in a quickly-traversing turret with a high rate of elevation, for tracking fast-moving aircraft. They are often in dual or quadruple mounts, allowing a high rate of fire. In addition, most anti-aircraft guns can be used in a direct-fire role against surface targets to great effect. In the early 21st century, missiles (generally mounted on similar turrets) largely supplanted anti-aircraft guns, though guns have recently shown revived utility against slow, low-flying drones.
File:Brno, Řečkovice, transportér Praga V33 II.JPG, Czechoslovak
Czechoslovak may refer to:
*A demonym or adjective pertaining to Czechoslovakia (1918–93)
**First Czechoslovak Republic (1918–38)
**Second Czechoslovak Republic (1938–39)
**Third Czechoslovak Republic (1948–60)
** Fourth Czechoslovak Repu ...
self-propelled anti-aircraft gun M53/59 Praga developed in the late 1950s.
Image:Wirbelwind CFB Borden 2.jpg, German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
Wirbelwind
The ''Flakpanzer'' IV "''Wirbelwind''" (Whirlwind in English) was a German self-propelled anti-aircraft gun based on the Panzer IV tank. It was developed in 1944 as a successor to the earlier '' Möbelwagen'' self-propelled anti-aircraft gun.
H ...
- a 20 mm ''Flakvierling'' quadmount on a Panzer IV
The IV (Pz.Kpfw. IV), commonly known as the Panzer IV, is a German medium tank developed in the late 1930s and used extensively during the Second World War. Its ordnance inventory designation was Sd.Kfz. 161.
The Panzer IV was the most numer ...
chassis.
File:Gepard 1a2 overview.jpg, Flakpanzer Gepard
The ''Flugabwehrkanonenpanzer Gepard'' ("anti-aircraft-gun tank 'Cheetah, better known as the Flakpanzer Gepard) is an all-weather-capable West German Self-propelled anti-aircraft weapon, self-propelled anti-aircraft gun (SPAAG) based on the hu ...
, Germany
File:JLTV 1.jpg, At AUSA 2017, a JLTV Utility variant mounting Boeing
The Boeing Company, or simply Boeing (), is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and product support s ...
's SHORAD Launcher
File:2008 Moscow Victory Day Parade - 9K22 Tunguska.jpg, Typical of more modern designs, the Tunguska-M1
The 2K22 Tunguska () is a Soviet Union, Soviet Caterpillar track, tracked self-propelled anti-aircraft gun armed with a Surface-to-air missile, surface-to-air gun and missile system. It is designed to provide day and night protection for infantry ...
mounts both missile
A missile is an airborne ranged weapon capable of self-propelled flight aided usually by a propellant, jet engine or rocket motor.
Historically, 'missile' referred to any projectile that is thrown, shot or propelled towards a target; this ...
s and autocannon
An autocannon, automatic cannon or machine cannon is a automatic firearm, fully automatic gun that is capable of rapid-firing large-caliber ( or more) armour-piercing, explosive or incendiary ammunition, incendiary shell (projectile), shells, ...
s.
Self-propelled artillery
Self-propelled
artillery
Artillery consists of ranged weapons that launch Ammunition, munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, and l ...
vehicles give mobility to
artillery
Artillery consists of ranged weapons that launch Ammunition, munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, and l ...
. Within the term are covered
self-propelled gun
Self-propelled artillery (also called locomotive artillery) is artillery equipped with its own propulsion system to move toward its firing position. Within the terminology are the self-propelled gun, self-propelled howitzer, self-propelled mo ...
s (or
howitzer
The howitzer () is an artillery weapon that falls between a cannon (or field gun) and a mortar. It is capable of both low angle fire like a field gun and high angle fire like a mortar, given the distinction between low and high angle fire break ...
s) and
rocket artillery
Rocket artillery is artillery that uses rockets as the projectile. The use of rocket artillery dates back to medieval China where devices such as fire arrows were used (albeit mostly as a psychological weapon). Fire arrows were also used in mult ...
. They are highly mobile, usually based on tracked chassis carrying either a large howitzer or other field gun or alternatively a
mortar or some form of rocket or missile launcher. They are usually used for long-range
indirect bombardment support on the battlefield.
In the past, self-propelled artillery has included direct-fire "Gun Motor Carriage" vehicles, such as
assault gun
An assault gun (from , , meaning "assault gun") is a type of armored infantry support vehicle and self-propelled artillery, mounting an infantry support gun on a protected self-propelled chassis, intended for providing infantry with heavy di ...
s and
tank destroyer
A tank destroyer, tank hunter or tank killer is a type of armoured fighting vehicle, predominantly intended for anti-tank duties. They are typically armed with a direct fire anti-tank gun, artillery gun, also known as a self-propelled anti-ta ...
s (also known as self-propelled anti-tank guns). These have been heavily armoured vehicles, the former providing danger-close fire-support for infantry and the latter acting as specialized anti-tank vehicles.
Modern self-propelled artillery vehicles may superficially resemble tanks, but they are generally lightly armoured, too lightly to survive in direct-fire combat. However, they protect their crews against
shrapnel and
small arms
A firearm is any type of gun that uses an explosive charge and is designed to be readily carried and operated by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see legal definitions).
The first firearms originate ...
and are therefore usually included as armoured fighting vehicles. Many are equipped with
machine guns for defence against enemy infantry.
The key advantage of self-propelled over towed artillery is that it can be brought into action much faster. Before towed artillery can be used, it has to stop, unlimber and the guns set up. To move position, the guns must be limbered up again and brought – usually towed – to the new location. By comparison, self-propelled artillery in combination with modern communications, can stop at a chosen location and begin firing almost immediately, then quickly move on to a new position. This ability is very useful in a mobile conflict and particularly on the advance.
Conversely, towed artillery was and remains cheaper to build and maintain. It is also lighter and can be taken to places that self-propelled guns cannot reach, so despite the advantages of the self-propelled artillery, towed guns remain in the
arsenal
An arsenal is a place where arms and ammunition are made, maintained and repaired, stored, or issued, in any combination, whether privately or publicly owned. Arsenal and armoury (British English) or armory (American English) are mostly ...
s of many modern armies.
File:Destroyed german self-propelled gun carriage.jpg, A Wespe
The Sd.Kfz. 124 ''Wespe'' (German for "wasp"), also known as ''Leichte Feldhaubitze 18/2 auf Fahrgestell Panzerkampfwagen II (Sf.)'' ("Light field howitzer 18 on Panzer II chassis (self-propelled)"), is a German self-propelled gun developed and ...
destroyed in Normandy
Normandy (; or ) is a geographical and cultural region in northwestern Europe, roughly coextensive with the historical Duchy of Normandy.
Normandy comprises Normandy (administrative region), mainland Normandy (a part of France) and insular N ...
, 1944.
File:G6 Howitzer2.JPG, G6 howitzer
The G6, sometimes denoted as the G6 ''Rhino'', is a South African self-propelled howitzer. It was developed as a turreted, self-propelled variant of the G5 howitzer series, mating the gun to a six-wheeled mine-protected armoured chassis. Des ...
wheeled SPG
File:Slovak Ground Forces Zuzana 2 first time outside Slovakia (1) (cropped).jpg, Slovak Self-propelled 155mm Howitzer model 2000 Zuzana
Zuzana is a common female given name in the Czech Republic and Slovakia. It is often translated to other languages as Zuzanna (Polish), Zsuzsanna (Hungarian), Suzanne, Susan, or Susannah – all commonly derived from the Hebrew language name Shosh ...
File:April 9th rehearsal in Alabino of 2014 Victory Day Parade (558-34).jpg, A Russian 2S19 Msta-S in 2014
Assault gun
An assault gun is a gun or howitzer mounted on a motor vehicle or armoured chassis, designed for use in the
direct fire
Direct fire or line-of-sight fire refers to firing of a ranged weapon whose projectile is launched directly at a target within the line-of-sight of the user. The firing weapon must have a sighting device and an unobstructed view to the target, ...
role in support of
infantry
Infantry, or infantryman are a type of soldier who specialize in ground combat, typically fighting dismounted. Historically the term was used to describe foot soldiers, i.e. those who march and fight on foot. In modern usage, the term broadl ...
when attacking other infantry or
fortified
A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Lat ...
positions.
Historically, the custom-built fully armoured assault guns usually mounted the gun or howitzer in a fully enclosed
casemate
A casemate is a fortified gun emplacement or armoured structure from which guns are fired, in a fortification, warship, or armoured fighting vehicle.Webster's New Collegiate Dictionary
When referring to antiquity, the term "casemate wall" ...
on a tank chassis. The use of a
casemate
A casemate is a fortified gun emplacement or armoured structure from which guns are fired, in a fortification, warship, or armoured fighting vehicle.Webster's New Collegiate Dictionary
When referring to antiquity, the term "casemate wall" ...
instead of a
gun turret
A gun turret (or simply turret) is a mounting platform from which weapons can be fired that affords protection, visibility and ability to turn and aim. A modern gun turret is generally a rotatable weapon mount that houses the crew or mechanis ...
limited these weapons'
field of fire
The field of fire or zone of fire (ZF) of a weapon, or group of weapons, is the area around it that can easily and effectively be reached by projectiles from a given position.
Field of fire
The term originally came from the ''field of fire'' in f ...
, but allowed a larger gun to be fitted relative to the chassis, more armour to be fitted for the same weight, and provided a cheaper construction. In most cases, these turretless vehicles also presented a lower profile as a target for the enemy.
File:ISU-152 at Victory Park in Moscow.jpg, ISU-152
The ISU-152 (, meaning " IS tank based self-propelled installation with 152mm caliber gun") is a Soviet self-propelled gun developed and used during World War II. It was unofficially nicknamed ''Zveroboy'' (; "beast killer") in response to seve ...
K, Victory Park, Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
, Russia
File:Ikv 91 a.jpg, Infanterikanonvagn 91
The infanterikanonvagn 91 (ikv 91), , was a high mobility assault gun that was developed to meet the operational requirements of the Swedish Army. It was designed and manufactured by Hägglund & Söner (whose military vehicle business is now B ...
, Swedish turreted amphibious assault gun
Self-propelled siege gun
Self-Propelled siege guns often carry cannons or mortars in excess of 400mm. The carrying platform could be multiple vehicles, built for use on train rails, or a purpose-built chassis.
Mortar carrier
A mortar carrier, or self-propelled mortar, is a
self-propelled artillery
Self-propelled artillery (also called locomotive artillery) is artillery equipped with its own propulsion system to move toward its firing position. Within the terminology are the self-propelled gun, self-propelled howitzer, self-propelled mo ...
vehicle carrying one or more
mortar as its primary weapon. Mortar carriers cannot be fired while on the move and some must be dismounted to fire. In U.S. Army doctrine, mortar carriers provide close and immediate indirect fire support for maneuver units while allowing for rapid displacement and quick reaction to the tactical situation. The ability to relocate not only allows fire support to be provided where it is needed faster, but also allows these units to avoid
counter-battery fire
Counter-battery fire (sometimes called counter-fire) is a battlefield tactic employed to defeat the enemy's indirect fire elements ( multiple rocket launchers, artillery and mortars), including their target acquisition, as well as their command ...
. Mortar carriers have traditionally avoided direct contact with the enemy. Many units report never using secondary weapons in combat.
Prior to the
Iraq War
The Iraq War (), also referred to as the Second Gulf War, was a prolonged conflict in Iraq lasting from 2003 to 2011. It began with 2003 invasion of Iraq, the invasion by a Multi-National Force – Iraq, United States-led coalition, which ...
, American 120 mm mortar platoons reorganized from six
M1064 mortar carrier
The M1064 mortar carrier is an American vehicle, consisting of the M121 mortar – a version of the M120 mortar – mounted on an M113 chassis. The M1287 mortar carrier vehicle will replace the M1064 in U.S. Army service.
Design
The design co ...
s and two M577 fire direction centres (FDC) to four M1064 and one FDC.
The urban environment of Iraq made it difficult to utilize mortars. New technologies such as mortar ballistic computers and communication equipment and are being integrated. Modern era combat is becoming more reliant on
direct fire
Direct fire or line-of-sight fire refers to firing of a ranged weapon whose projectile is launched directly at a target within the line-of-sight of the user. The firing weapon must have a sighting device and an unobstructed view to the target, ...
support from mortar carrier
machine guns.
File:T5E1-motar-carrier-4.2inch-haugh.jpg, T5E1 4.2inch mortar carrier variant of the M3 Scout Car.
File:ParkPatriot2015part11-150.jpg, 2S9 Nona
The 2S9 ''NONA'' () is a self-propelled and air-droppable 120 mm mortar designed in the Soviet Union, which entered service in 1981. The 2S9 chassis is designated the S-120 and based on the aluminium hull of the BTR-D airborne multi-purpose ...
-S 120 mm Soviet self-propelled mortar
A mortar carrier, or self-propelled mortar, is a self-propelled artillery piece in which a mortar (weapon), mortar is the primary weapon. Simpler vehicles carry a standard infantry mortar while in more complex vehicles the mortar is fully in ...
, 2016.
File:Stryker MCV-B.jpg, An American M1129 mortar carrier
Multiple rocket launcher
A multiple rocket launcher is a type of unguided
rocket artillery
Rocket artillery is artillery that uses rockets as the projectile. The use of rocket artillery dates back to medieval China where devices such as fire arrows were used (albeit mostly as a psychological weapon). Fire arrows were also used in mult ...
system. Like other
rocket
A rocket (from , and so named for its shape) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using any surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely ...
artillery, multiple rocket launchers are less accurate and have a much lower (sustained) rate of fire than batteries of traditional
artillery
Artillery consists of ranged weapons that launch Ammunition, munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, and l ...
guns. However, they have the capability of simultaneously dropping many hundreds of kilograms of explosive, with devastating effect.
The
Korean
Korean may refer to:
People and culture
* Koreans, people from the Korean peninsula or of Korean descent
* Korean culture
* Korean language
**Korean alphabet, known as Hangul or Korean
**Korean dialects
**See also: North–South differences in t ...
Hwacha
The ''hwacha'' or ''hwach'a'' () was a multiple rocket launcher and an organ gun of similar design which were developed in fifteenth century Korea. It resembled a wooden cart with a launch pad attached, and it had up to 200 tiny Sin'gijŏn, sing ...
is an example of an early weapon system with a resemblance to the modern-day multiple rocket launcher. The first self-propelled multiple rocket launchers – and arguably the most famous – were the
Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
BM-13 Katyushas, first used during World War II and exported to Soviet allies afterwards. They were simple systems in which a rack of launch rails was mounted on the back of a truck. This set the template for modern multiple rocket launchers. The first modern multiple rocket launcher was the
German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
''
15 cm Nebelwerfer 41
The 15 cm Nebelwerfer 41 (15 cm NbW 41) was a German multiple rocket launcher used in the Second World War. It served with units of the ''Nebeltruppen'', German Chemical Corps units that had the responsibility for poison gas and smoke w ...
'' of the 1930s, a small towed artillery piece. Only later in
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
did the British deploy similar weapons in the form of the
Land Mattress.The Americans mounted tubular launchers atop
M4 Sherman
The M4 Sherman, officially medium tank, M4, was the medium tank most widely used by the United States and Western Allies in World War II. The M4 Sherman proved to be reliable, relatively cheap to produce, and available in great numbers. I ...
tanks to create the
T34 Calliope
The Rocket Launcher T34 (Calliope) was a tank-mounted multiple rocket launcher used by the United States Army during World War II. The launcher was placed atop the M4 Sherman, with its prominent vertical side frames anchored to the turret's si ...
rocket launching tank, only used in small numbers, as their closest equivalent to the Katyusha.
File:Panzerwerfer alias Maultier.jpg, German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
Panzerwerfer
The German ''Panzerwerfer'' refers to either of two different types of half-tracked multiple rocket launchers employed by Nazi Germany during the Second World War. The two self-propelled artillery vehicles are the ''15 cm Panzerwerfer 42 ...
half-tracked MRLS.
File:BM-31-12 on ZIS-12 chassis at the Museum on Sapun Mountain Sevastopol 4.jpg, Katyusha rocket launcher
The Katyusha ( rus, Катю́ша, p=kɐˈtʲuʂə, a=Ru-Катюша.ogg) is a type of rocket artillery first built and fielded by the Soviet Union in World War II. Multiple rocket launchers such as these deliver explosives to a target area m ...
at the Museum (Diorama
A diorama is a replica of a scene, typically a three-dimensional model either full-sized or miniature. Sometimes dioramas are enclosed in a glass showcase at a museum. Dioramas are often built by hobbyists as part of related hobbies like mili ...
) on Sapun Mountain, Sevastopol
Sevastopol ( ), sometimes written Sebastopol, is the largest city in Crimea and a major port on the Black Sea. Due to its strategic location and the navigability of the city's harbours, Sevastopol has been an important port and naval base th ...
File:9a52 smerch.jpg, BM-30 Smerch
The BM-30 ''Smerch'' (, 'whirlwind'), 9K58 Smerch or 9A52-2 Smerch-M is a heavy Self-propelled artillery, self-propelled 300 mm multiple rocket launcher designed in the Soviet Union to fire a full load of 12 solid-fuelled projectiles. The ...
300 mm rocket launcher in raised position
File:Army mlrs 1982 02.jpg, The M270
The M270 Multiple Launch Rocket System (M270 MLRS) is an American armored self-propelled multiple launch rocket system.
The U.S. Army variant of the M270 is based on the chassis of the Bradley Fighting Vehicle. The first M270s were delivere ...
MLRS conducts a rocket launch.
Missile vehicle
Missile vehicle
A missile vehicle, also known as a missile carrier, missile truck, or (if capable of launching) missile launcher vehicle, is a military vehicle that is purpose-built and designed to carry missiles, either for safe transportation or for launching ...
s are trucks or tractor units designed to carry rockets or missiles. The missile vehicle may be a self-propelled unit, or the missile holder/launcher may be on a trailer towed by a prime mover. They are used in the military forces of a number of countries in the world. Long missiles are commonly transported parallel to the ground on these vehicles, but elevated into an inclined or vertical position for launching.
* A
Transporter erector launcher
A transporter erector launcher (TEL) is a missile vehicle with an integrated tractor unit that can transport, elevate to a firing position and launch one or more rockets or missiles.
History
Such vehicles exist for both surface-to-air missiles ...
(TEL) is a missile vehicle with an integrated prime mover (tractor unit) that can carry, elevate to firing position and launch one or more missiles. Such vehicles exist for both surface-to-air missiles and surface-to-surface missiles.
File:19-03-2012-Parade-rehearsal - Topol-M.jpg, Missile truck MZKT
MZKT (''МЗКТ'' or ''МЗКЦ'', , , Minsk Wheel(ed) Tractor Plant (MWTP)) is a manufacturer of heavy off-road vehicles, especially military trucks, based in Minsk, in Belarus; it was formerly a division of MAZ. MZKT civilian trucks are bran ...
79221 under missile Topol-M
The RT-2PM2 «Topol-M» (, NATO reporting name: SS-27 "Sickle B", other designations: SS-27 Mod 1, RS-12M1, RS-12M2, formerly incorrectly RT-2UTTKh) is one of the most recent intercontinental ballistic missiles to be deployed by Russia, and the f ...
Image:sa-4.jpg, A Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
2K11 Krug
The 2K11 ''Krug'' (; English: 'circle') is a Soviet Union, Soviet and now Russian medium-range, medium-to-high altitude surface-to-air missile (SAM) system. The system was designed by NPO Novator and produced by Kalinin Machine Building Plant. I ...
TEL
TEL or Tel may refer to:
Businesses and organisations
* Tokyo Electron, a semiconductor equipment manufacturer
* TE Connectivity, a technology company, NYSE stock ticker TEL
* The European Library, an Internet service
Place names
* Tel, Azerbaij ...
File:MoscowParade2009 7.jpg, S-300 missile system
The S-300 (NATO reporting name SA-10 Grumble) is a series of long-range surface-to-air missile systems developed by the former Soviet Union. It was produced by NPO Almaz for the Soviet Air Defence Forces to defend against air raids and cruise ...
.
Tank destroyer
Tank destroyers and tank hunters are armed with an
anti-tank gun
An anti-tank gun is a form of artillery designed to destroy tanks and other armoured fighting vehicles, normally from a static defensive position. The development of specialized anti-tank munitions and anti-tank guns was prompted by the appearance ...
or
anti-tank missile
An anti-tank guided missile (ATGM), anti-tank missile, anti-tank guided weapon (ATGW) or anti-armor guided weapon is a missile guidance, guided missile primarily designed to hit and destroy armoured fighting vehicle, heavily armored military v ...
launcher, and are designed specifically to engage enemy armoured vehicles. Many have been based on a tracked tank chassis, while others are wheeled. Since World War II, main battle tanks have largely replaced gun-armed tank destroyers; although lightly armoured anti-tank guided missile (ATGM) carriers are commonly used for supplementary long-range anti-tank engagements.
In post-
Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
conflict, the resurgence of
expeditionary warfare
Expeditionary warfare is a military invasion of a foreign territory, especially away from established bases. Expeditionary forces were in part the antecedent of the modern concept of rapid deployment forces. Traditionally, expeditionary forces we ...
has seen the emergence of gun-armed wheeled vehicles, sometimes called "protected gun systems", which may bear a superficial resemblance to tank destroyers, but are employed as direct fire support units typically providing support in low intensity operations such as Iraq and Afghanistan. These have the advantage of easier deployment, as only the largest air transports can carry a main battle tank, and their smaller size makes them more effective in urban combat.
Many forces' IFVs carry anti-tank missiles in every infantry platoon, and attack helicopters have also added anti-tank capability to the modern battlefield. But there are still dedicated anti-tank vehicles with very heavy long-range missiles, or intended for airborne use. There have also been dedicated anti-tank vehicles built on ordinary armoured personnel carrier or armoured car chassis. Examples include the U.S. M901 ITV (Improved TOW Vehicle) and the Norwegian NM142, both on an
M113
The M113 is a fully tracked armored personnel carrier (APC) that was developed and produced by the FMC Corporation. The M113 was sent to United States Army Europe in 1961 to replace the mechanized infantry's M59 APCs. The M113 was first used ...
chassis, several Soviet ATGM launchers based on the
BRDM scout car, the British FV438
Swingfire
Swingfire was a British wire-guided anti-tank missile developed in the 1960s and produced from 1966 until 1993. The name refers to its ability to make a rapid turn of up to ninety degrees after firing to bring it onto the line of the sighting ...
and
FV102 Striker
The FV102 Striker was the anti-tank guided missile carrier in the CVR(T) family and served in the British Army.
Overview
FV102 Striker was the Swingfire wire-guided anti-tank missile carrying member of the CVR(T) family. The FV102 Striker wa ...
and the
German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
''Raketenjagdpanzer'' series built on the chassis of the
HS 30 and
Mardar IFVs.
File:M3 75mm gun motor carriage.jpg, American M3 GMC half-track
A half-track is a civilian or military vehicle with wheels at the front for steering and continuous tracks at the back to propel the vehicle and carry most of the load. A half-track combines the soft-ground traction of a tank with the Car handl ...
ed tank destroyer
Image:M-36 tank destroyer at Dudelange, Luxembourg, 3 January 1945 (SC 198612).jpg, 90 mm GMC M36 during the Battle of the Bulge in January, 1945
File:Jagdtiger 1 Bovington.jpg, British-captured German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
Jagdtiger
The ''Jagdtiger'' ("Hunting Tiger"; officially designated ''Panzerjäger Tiger Ausf. B'') is a German casemate-type heavy tank destroyer (''Jagdpanzer'') of World War II. It was built upon the slightly lengthened chassis of a Tiger II. Its ordn ...
in The Tank Museum
The Tank Museum (previously the Bovington Tank Museum) is a collection of armoured fighting vehicles at Bovington Camp in Dorset, South West England. It is about north of the village of Wool and west of the major port of Poole. The collectio ...
, the UK
File:NM142 x 3.jpg, A Norwegian anti-tank platoon equipped with NM142
The NM142 (''Norwegian Model'') is an anti-tank missile carrier variant of the American M113 Armored Personnel Carrier, which has been fitted with a TOW2 turret developed in Norway by Kværner Eureka.
Armament
The NM-142 mounts a turret conta ...
TOW missile launchers
File:Panzermuseum Munster 2010 0915.JPG, West German
West Germany was the common English name for the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) from its formation on 23 May 1949 until its reunification with East Germany on 3 October 1990. It is sometimes known as the Bonn Republic after its capital c ...
missile tank destroyer Raketenjagdpanzer 2
The Raketenjagdpanzer 2 or Raketenjagdpanzer SS-11 was a West German tank destroyer employed from 1967 to 1982 and equipped with Nord SS.11 guided anti tank missiles. It was developed at the same time as the Kanonenjagdpanzer and the Marder (IFV), ...
.
Armoured train
An ''armoured train'' is a railway train protected with
armour
Armour (Commonwealth English) or armor (American English; see American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, spelling differences) is a covering used to protect an object, individual, or vehicle from physical injury or damage, e ...
. They are usually equipped with rail cars armed with
artillery
Artillery consists of ranged weapons that launch Ammunition, munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, and l ...
,
autocannon
An autocannon, automatic cannon or machine cannon is a automatic firearm, fully automatic gun that is capable of rapid-firing large-caliber ( or more) armour-piercing, explosive or incendiary ammunition, incendiary shell (projectile), shells, ...
s,
machine guns, tank
turret
Turret may refer to:
* Turret (architecture), a small tower that projects above the wall of a building
* Gun turret, a mechanism of a projectile-firing weapon
* Optical microscope#Objective turret (revolver or revolving nose piece), Objective turre ...
s and
anti-aircraft gun
Anti-aircraft warfare (AAW) is the counter to aerial warfare and includes "all measures designed to nullify or reduce the effectiveness of hostile air action".AAP-6 It encompasses surface-based, subsurface ( submarine-launched), and air-ba ...
s. They were mostly used during the late 19th to mid-20th century, when they offered an innovative way to quickly move large amounts of firepower. Their use was discontinued in most countries when road vehicles became much more powerful and offered more flexibility, and because armoured trains were too vulnerable to track sabotage and attacks from the air. However, the
Russian Federation
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
used improvised armoured trains in the
Second Chechen War
Names
The Second Chechen War is also known as the Second Chechen Campaign () or the Second Russian Invasion of Chechnya from the Chechens, Chechen insurgents' point of view.Федеральный закон № 5-ФЗ от 12 января 19 ...
in the late 1990s and 2000s. Armoured trains carrying ballistic missiles have also been used.
The rail cars on an armoured train were designed for many tasks, such as carrying artillery and machine guns, infantry units, anti-tank and anti-aircraft guns. During World War II, the Germans would sometimes put a ''Fremdgerät'' (captured AFVs such as the French
Somua S-35 or Czech
PzKpfw 38(t)), or obsolescent
Panzer II
The Panzer II is the common name used for a family of Nazi Germany, German tanks used in World War II. The official German designation was ''Panzerkampfwagen'' II (abbreviated ''Pz.Kpfw. II'').
Although the vehicle had originally been designed a ...
light tanks on a flatbed rail car, which could quickly be offloaded by means of a ramp and used away from the railway line to chase down enemy
partisans
Partisan(s) or The Partisan(s) may refer to:
Military
* Partisan (military), paramilitary forces engaged behind the front line
** Francs-tireurs et partisans, communist-led French anti-fascist resistance against Nazi Germany during WWII
** Itali ...
.
Different types of armour were used to protect armoured trains from attack. In addition to various metal plates, concrete and sandbags were used in some cases on armoured trains.
Armoured trains were sometimes escorted by a kind of rail-tank called a
draisine
A draisine () is a light auxiliary rail vehicle, driven by service personnel, equipped to transport crew and material necessary for the maintenance of railway infrastructure.
The eponymous term is derived from the German inventor Baron Karl D ...
. One such example was the Italian 'Littorina' armoured trolley, which had a cab in the front and rear, each with a control set so it could be driven down the tracks in either direction. Littorina mounted two dual 7.92mm
MG13 machine gun turrets from
Panzer I
The Panzer I was a light tank produced by Nazi Germany in the 1930s. Its name is short for ( German for " armored fighting vehicle mark I"), abbreviated as . The tank's official German ordnance inventory designation was '' Sd.Kfz. 101 ...
light tanks.
File:MÁV armoured train.jpg, Hungarian MÁVAG
MÁVAG (''Magyar Királyi Állami Vas-, Acél- és Gépgyárak''; ''Hungarian Royal State Iron, Steel and Machine Factories'') was the largest Hungarian rail vehicle producer. MÁVAG company was the second largest industrial enterprise after the ...
armoured train in 1914
File:Pancierovy vlak-Zvolen.jpg, Replica of the "Hurban" armoured train located in Zvolen, Slovakia
File:Obrněná drezína Tatra T 18.gif, Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Polish people, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
* Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin ...
armoured draisine
A draisine () is a light auxiliary rail vehicle, driven by service personnel, equipped to transport crew and material necessary for the maintenance of railway infrastructure.
The eponymous term is derived from the German inventor Baron Karl D ...
Tatra T18.
A missile vehicle, also known as a missile carrier, missile truck, or (if capable of launching) missile launcher vehicle, is a military vehicle that is purpose-built and designed to carry missiles, either for safe transportation or for launching missiles in combat. Missile vehicles include transporter erector launchers (TEL) and multiple rocket launchers (MRL).
See also
References
Sources
*
*
*
*
*
External links
US Wheeled armoured fighting vehicles
{{Post-Cold War tanks, style=wide
Military vehicles by type
 Modern armoured fighting vehicles represent the realization of an ancient concept – that of providing troops with mobile protection and firepower. Armies have deployed war machines and cavalries with rudimentary armour in battle for millennia. Use of these animals and engineering designs sought to achieve a balance between the conflicting needs of mobility, firepower and protection.
Modern armoured fighting vehicles represent the realization of an ancient concept – that of providing troops with mobile protection and firepower. Armies have deployed war machines and cavalries with rudimentary armour in battle for millennia. Use of these animals and engineering designs sought to achieve a balance between the conflicting needs of mobility, firepower and protection.


 The first modern AFVs were armed cars, dating back virtually to the invention of the
The first modern AFVs were armed cars, dating back virtually to the invention of the  Another early armoured car of the period was the French
Another early armoured car of the period was the French  The British
The British  The level of protection also usually varies considerably throughout the individual vehicle too, depending on the role of the vehicle and the likely direction of attack. For example, a main battle tank will usually have the heaviest armour on the hull front and the turret, lighter armour on the sides of the hull and the thinnest armour on the top and bottom of the tank. Other vehicles – such as the
The level of protection also usually varies considerably throughout the individual vehicle too, depending on the role of the vehicle and the likely direction of attack. For example, a main battle tank will usually have the heaviest armour on the hull front and the turret, lighter armour on the sides of the hull and the thinnest armour on the top and bottom of the tank. Other vehicles – such as the  A
A  A flame tank is an otherwise-standard
A flame tank is an otherwise-standard  The idea for this tank was developed during World War I by British and French. The
The idea for this tank was developed during World War I by British and French. The  A cruiser tank, or cavalry tank, was designed to move fast and exploit penetrations of the enemy front. The idea originated in "
A cruiser tank, or cavalry tank, was designed to move fast and exploit penetrations of the enemy front. The idea originated in " An ''infantry mobility vehicle'' (''IMV'') or ''protected patrol vehicle'' (''PPV'') is a wheeled armoured personnel carrier (APC) serving as a military patrol, reconnaissance or security vehicle. Examples include the
An ''infantry mobility vehicle'' (''IMV'') or ''protected patrol vehicle'' (''PPV'') is a wheeled armoured personnel carrier (APC) serving as a military patrol, reconnaissance or security vehicle. Examples include the  During the 1930s and 1940s, Japan produced a number of amphibious tank designs, including prototypes such as the Sumida amphibious armored car (AMP),
During the 1930s and 1940s, Japan produced a number of amphibious tank designs, including prototypes such as the Sumida amphibious armored car (AMP),  Lightweight armoured fighting vehicles designed or modified to be carried by aircraft and delivered by air drop, helicopter lift, glider, or air landing with infantry to provide heavier tactical firepower and mobility. The air-equivalent to amphibious vehicles, the main advantage of airborne forces is their ability to be deployed into combat zones without land passage, as long as the
Lightweight armoured fighting vehicles designed or modified to be carried by aircraft and delivered by air drop, helicopter lift, glider, or air landing with infantry to provide heavier tactical firepower and mobility. The air-equivalent to amphibious vehicles, the main advantage of airborne forces is their ability to be deployed into combat zones without land passage, as long as the  The armoured bulldozer is a basic tool of
The armoured bulldozer is a basic tool of  Self-Propelled siege guns often carry cannons or mortars in excess of 400mm. The carrying platform could be multiple vehicles, built for use on train rails, or a purpose-built chassis.
Self-Propelled siege guns often carry cannons or mortars in excess of 400mm. The carrying platform could be multiple vehicles, built for use on train rails, or a purpose-built chassis.