|
Ordnance QF 25 Pounder
The Ordnance QF 25-pounder, or more simply 25-pounder or 25-pdr, with a calibre of 3.45 inches (87.6 mm), was a piece of field artillery used by British and Commonwealth forces in the Second World War. Durable, easy to operate and versatile, it was the most produced and used British field gun and gun-howitzer during the war. It was introduced into service just before the War started and combined both high-angle and direct-fire abilities, a relatively high rate of fire, and a reasonably lethal shell, with a highly mobile piece. Initial production was slow, but by 1945, over 12,000 had been manufactured. It remained the British Army's primary artillery field piece well into the 1960s, with smaller numbers used in training units until the 1980s. Many Commonwealth countries used theirs in active or reserve service until about the 1970s, and ammunition for the weapon is currently (2020s) being produced by Pakistan Ordnance Factories. Design The design was the result of extended s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field Gun
A field gun is a field artillery piece. Originally the term referred to smaller guns that could accompany a field army on the march, that when in combat could be moved about the battlefield in response to changing circumstances (field artillery), as opposed to guns installed in a fort (Royal Garrison Artillery, garrison artillery or coastal artillery), or to siege cannons and mortar (weapon), mortars which are too large to be moved quickly, and would be used only in a prolonged siege. Perhaps the most famous use of the field gun in terms of advanced tactics was Napoleon Bonaparte's use of very large wheels on the guns that allowed them to be moved quickly even during a battle. By moving the guns from point to point during a battle, enemy formations could be broken up to be handled by the infantry or cavalry wherever they were massing, dramatically increasing the overall effectiveness of the attack. World War I As the evolution of artillery continued, almost all guns of any siz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
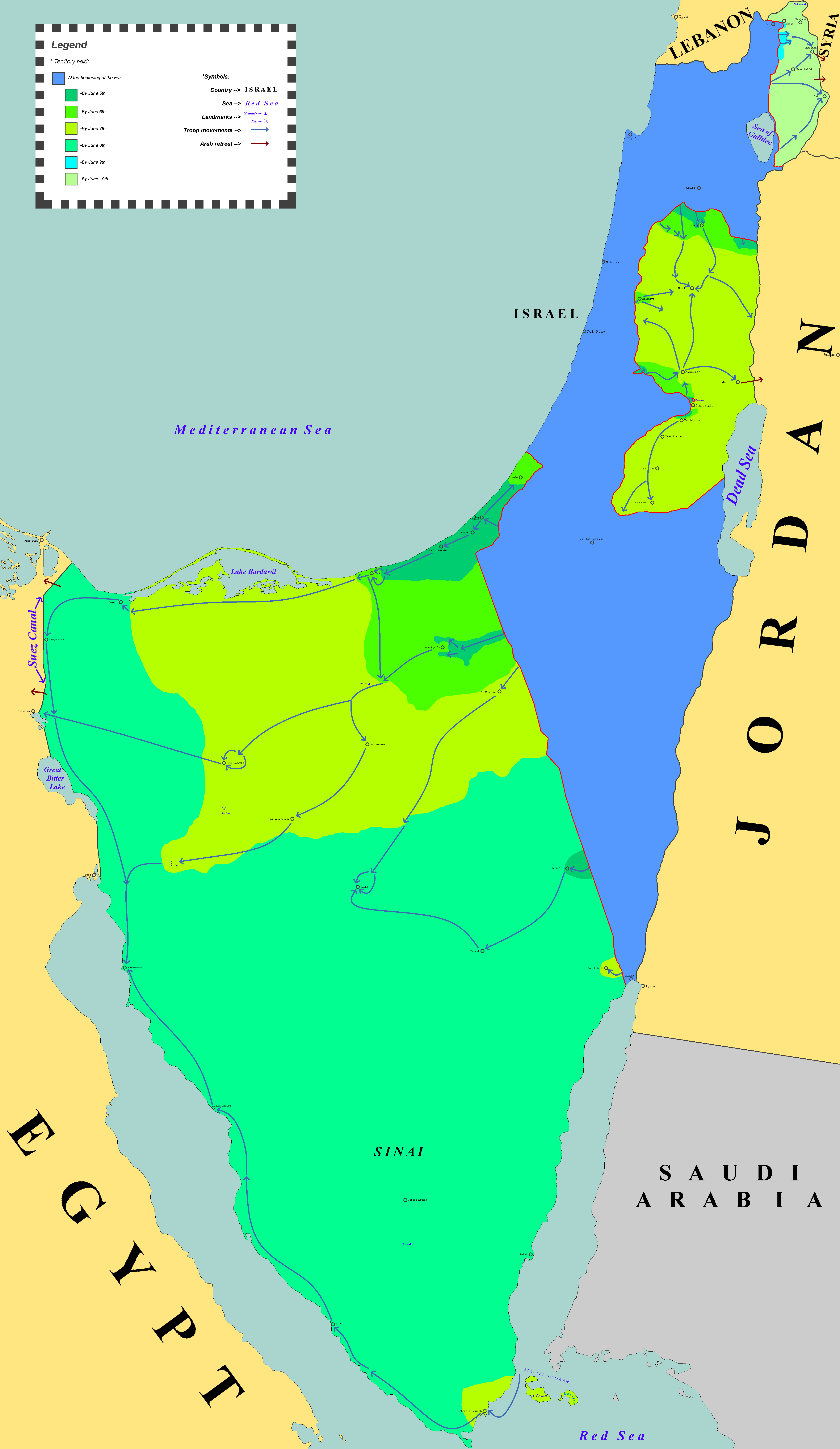
Six-Day War
The Six-Day War, also known as the June War, 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states, primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, Syria, and Jordan from 5 to 10June 1967. Military hostilities broke out amid poor relations between Israel and its Arab neighbors, which had been observing the 1949 Armistice Agreements signed at the end of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, First Arab–Israeli War. In 1956, regional tensions over the Straits of Tiran (giving access to Eilat, a port on the southeast tip of Israel) escalated in what became known as the Suez Crisis, when Israel invaded Egypt over the Israeli passage through the Suez Canal and Straits of Tiran, Egyptian closure of maritime passageways to Israeli shipping, ultimately resulting in the re-opening of the Straits of Tiran to Israel as well as the deployment of the United Nations Emergency Force (UNEF) along the Borders of Israel#Border with Egypt, Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonwealth Of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, often referred to as the British Commonwealth or simply the Commonwealth, is an International organization, international association of member states of the Commonwealth of Nations, 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territorial evolution of the British Empire, territories of the British Empire from which it developed. They are connected through their English in the Commonwealth of Nations, use of the English language and cultural and historical ties. The chief institutions of the organisation are the Commonwealth Secretariat, which focuses on intergovernmental relations, and the Commonwealth Foundation, which focuses on non-governmental relations between member nations. Numerous List of Commonwealth organisations, organisations are associated with and operate within the Commonwealth. The Commonwealth dates back to the first half of the 20th century with the decolonisation of the British Empire through increased self-governance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydraulic Recoil Mechanism
A hydraulic recoil mechanism is a way of limiting the effects of recoil and adding to the accuracy and firepower of an artillery piece. Description The idea of using a water brake to counteract the recoil of naval cannons was first suggested to the British Admiralty by Carl Wilhelm Siemens in the early 1870s, but it took about a decade for the idea to be commercialized, primarily by Josiah Vavasseur. The usual recoil system in modern quick-firing guns is the ''hydro-pneumatic recoil system''. In this system, the barrel is mounted on rails on which it can recoil to the rear, and the recoil is taken up by a cylinder which is similar in operation to an automotive gas-charged shock absorber. It is commonly mounted parallel to the barrel, but is shorter and smaller. The cylinder is charged with compressed air, as well as hydraulic oil; in operation, the barrel's energy is taken up in compressing the air as the barrel recoils backward, then is dissipated via hydraulic da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rifled Breech Loader
A rifled breech loader (RBL) is an artillery piece which, unlike the smoothbore cannon and rifled muzzle loader which preceded it, has rifling in the barrel and is loaded from the breech-loading weapon, breech at the rear of the gun. The spin imparted by the gun's rifling gives projectiles directional stability and increased range. Loading from the rear of the gun leaves the crew less exposed to enemy fire, allows smaller gun emplacements or turrets, and allows a faster rate of fire. These rapidly improving breech systems and the powerful new guns they facilitated led to an arms race in fortification and ironclad warship design that led to the battleship class of HMS Dreadnought (1906), HMS ''Dreadnought'' and continued until the start of World War I. Overview The major problem to be solved with breechloading artillery was obturation: the sealing of the breech after firing to ensure that none of the gases generated by the burning of the propellant (initially gunpowder) escaped r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variants
Variant may refer to: Arts and entertainment * ''Variant'' (magazine), a former British cultural magazine * Variant cover, an issue of comic books with varying cover art * ''Variant'' (novel), a novel by Robison Wells * " The Variant", 2021 episode of the TV series ''Loki'' **Sylvie (Marvel Cinematic Universe), a character who was originally referred to as the Variant **"Variant", a fictional term in the Marvel Cinematic Universe pertaining to the multiverse Gaming *Chess variant, a game derived from, related to or similar to chess in at least one respect *List of poker variants * List of ''Tetris'' variants Mathematics and computing * Loop variant, a decreasing value ensuring that a loop in a computer programme terminates * Variant (logic), a term or formula obtained from another one by consistently renaming all variables * Variant symlinks, a symbolic link to a file that has a variable name embedded in it * Variant type, in programming languages * Z-variant, unicode characters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Ordnance
Royal Ordnance plc was formed on 2 January 1985 as a public corporation, owning the majority of what until then were the remaining United Kingdom government-owned Royal Ordnance Factories (abbreviated ROFs) which manufactured explosives, ammunition, small arms including the Lee–Enfield rifle, guns and military vehicles such as tanks. It owned some 16 factories; and employed about 19,000 staff. Royal Ordnance plc was bought by British Aerospace (BAe) in April 1987, which became BAE Systems in 1999. The name Royal Ordnance was retained for almost another twenty years; and the sites retained their former names, either as ''Royal Ordnance'' or later ''RO Defence'' sites. The Royal Ordnance name was dropped in 2004 and after having traded as Land Systems, the division is now known as Land UK. History Royal Ordnance Factories The Royal Ordnance Factories (ROFs) can trace their history back to 1560 with the founding of the Royal Gunpowder Factory (RGPF) at Waltham Abbey, Essex. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operators
Operator may refer to: Mathematics * A symbol indicating a mathematical operation * Logical operator or logical connective in mathematical logic * Operator (mathematics), mapping that acts on elements of a space to produce elements of another space, e.g.: ** Linear operator ** Differential operator ** Integral operator (other) ** Operational calculus Computers * Computer operator, an occupation * Operator (computer programming) In computer programming, an operator is a programming language construct that provides functionality that may not be possible to define as a user-defined function (i.e. sizeof in C) or has syntax different than a function (i.e. infix addit ..., a type of computer program function * Operator (extension), an extension for the Firefox web browser, for reading microformats * Operator pattern, a provisioning automation and auto-scaling strategy for Kubernetes * Ableton Operator, a software synthesizer developed by Ableton Science * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iraqi Civil War (2014–2017)
Iraqi civil war may refer to: * Iraqi–Kurdish conflict (1918–2003), wars and rebellions by Iraqi Kurds against the government ** First Iraqi–Kurdish War (1961–70) ** Second Iraqi–Kurdish War (1974–75) * 1991 Iraqi uprisings, rebellions in Iraq during a ceasefire in the Gulf War * Iraqi Kurdish Civil War (1994–97), a conflict between rival Kurdish factions in Iraqi Kurdistan * Iraqi conflict (2003–present). See also: **Iraq War (2003–11), a war that began with the U.S. invasion of Iraq ***Iraqi insurgency (2003–2011) *** Occupation of Iraq (2003–2011) *** Iraqi civil war (2006–2008), a civil war between Sunni and Shia militias including the Iraqi government and Al-Qaeda in Iraq (now known as ISIL) **** Islamic Army–Al-Qaeda conflict ** Iraqi insurgency (2011–2013), an escalation of insurgent and sectarian violence after the U.S. withdrew ** War in Iraq (2013–2017), a war between ISIL and the Iraqi government and allies ** 2017 Iraqi–Kurdish conf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lebanese Civil War
The Lebanese Civil War ( ) was a multifaceted armed conflict that took place from 1975 to 1990. It resulted in an estimated 150,000 fatalities and led to the exodus of almost one million people from Lebanon. The religious diversity of the Lebanese people played a notable role in the lead-up to and during the conflict: Lebanese Christians and Lebanese Sunni Muslims comprised the majority in the coastal cities; Lebanese Shia Muslims were primarily based throughout southern Lebanon and in the Beqaa Valley in the east; and Lebanese Druze, Druze and Christians populated the country's mountainous areas. At the time, the Lebanese government was under the influence of elites within the Maronite Christian community. The link between politics and religion was reinforced under the Greater Lebanon, French Mandate from 1920 to 1943, and the country's parliamentary structure favoured a leading position for Lebanese Christians, who constituted the majority of the population. However, Leban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iran–Iraq War
The Iran–Iraq War, also known as the First Gulf War, was an armed conflict between Iran and Iraq that lasted from September 1980 to August 1988. Active hostilities began with the Iraqi invasion of Iran and lasted for nearly eight years, until the acceptance of United Nations Security Council Resolution 598 by both sides. Iraq's primary rationale for the attack against Iran cited the need to prevent Ruhollah Khomeini—who had spearheaded the Iranian revolution in 1979—from exporting the new Iranian ideology to Iraq. There were also fears among the Iraqi leadership of Saddam Hussein that Iran, a theocratic state with a population predominantly composed of Shia Muslims, would exploit sectarian tensions in Iraq by rallying Iraq's Shia majority against the Baʽathist government, which was officially secular but dominated by Sunni Muslims. Iraq also wished to replace Iran as the power player in the Persian Gulf, which was not seen as an achievable objective prior to the Is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |