|
Battle Of Amiens (1918)
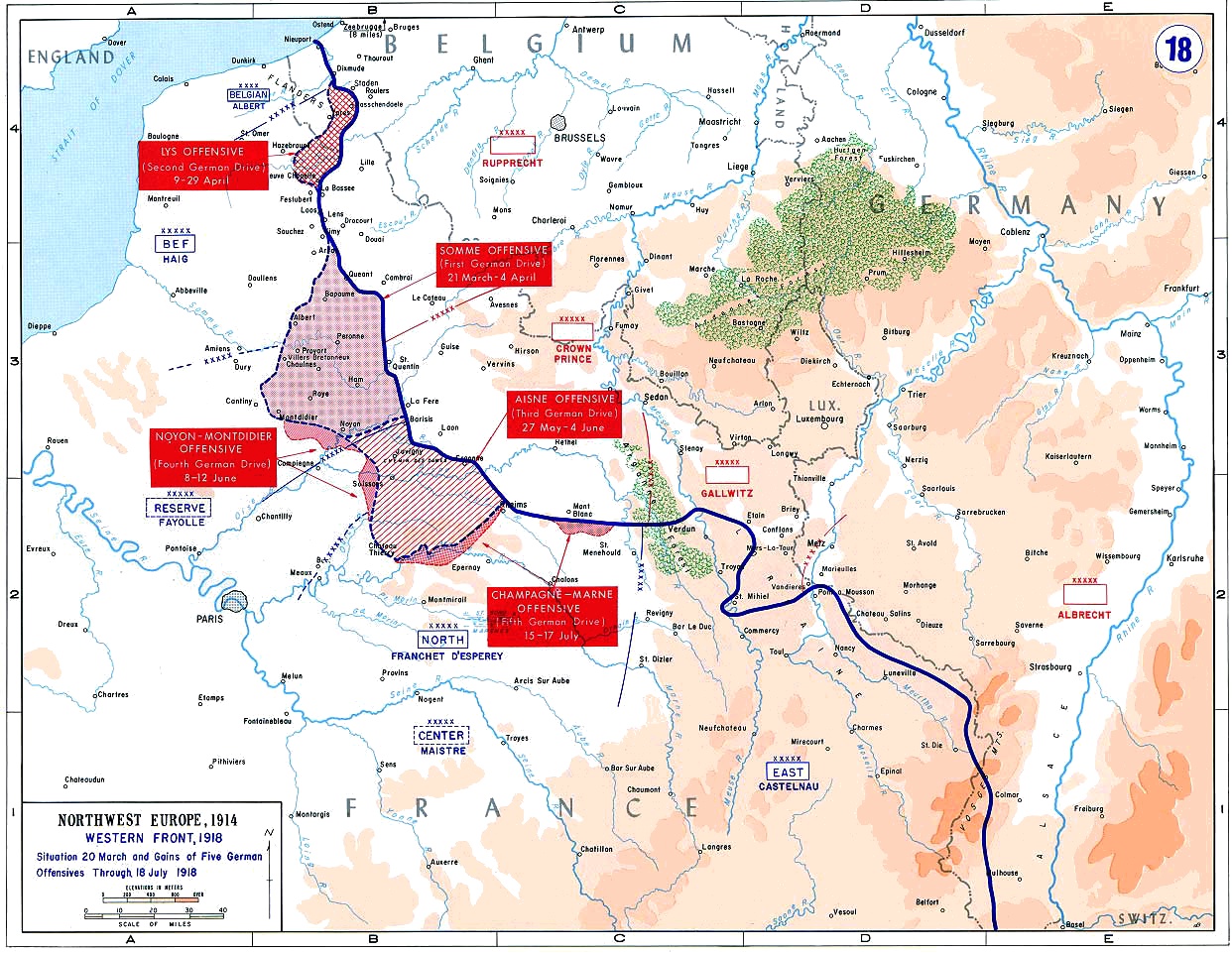
The Battle of Amiens, also known as the Third Battle of Picardy was the opening phase of the Allies of World War I, Allied offensive which began on 8 August 1918, later known as the Hundred Days Offensive, which ultimately led to the end of World War I. Allied forces advanced over on the first day, one of the greatest advances of the war, with Gen Henry Rawlinson, 1st Baron Rawlinson, Henry Rawlinson's British Fourth Army, with nine of its 19 Division (military), divisions supplied by the fast-moving Australian Corps of Lt General John Monash and Canadian Corps of Lt General Arthur Currie, and Gen Marie Eugène Debeney's French First Army playing a decisive role. The battle is also notable for its effects on both sides' morale and the large number of surrender (military), surrendering German Empire, German forces. This led Erich Ludendorff to later describe the first day of the battle as "the black day of the German Army". Amiens was one of the first major battles involving arm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Front (World War I)
The Western Front was one of the main Theatre (warfare), theatres of war during World War I. Following the outbreak of war in August 1914, the Imperial German Army, German Army opened the Western Front by German invasion of Belgium (1914), invading Luxembourg and Belgium, then gaining military control of important industrial regions in Third Republic of France, France. The German advance was halted with the First Battle of the Marne, Battle of the Marne. Following the Race to the Sea, both sides dug in along a meandering line of fortified trench warfare, trenches, stretching from the North Sea to the Swiss frontier with France, the position of which changed little except during early 1917 and again in 1918. Between 1915 and 1917 there were several offensives along this Front (military), front. The attacks employed massive artillery bombardments and massed infantry advances. Entrenchments, machine gun emplacements, barbed wire, and artillery repeatedly inflicted severe casualties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allies Of World War I
The Allies or the Entente (, ) was an international military coalition of countries led by the French Republic, the United Kingdom, the Russian Empire, the United States, the Kingdom of Italy, and the Empire of Japan against the Central Powers of the German Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Bulgaria in World War I (1914–1918). By the end of the first decade of the 20th century, the major European powers were divided between the Triple Entente and the Triple Alliance. The Triple Entente was made up of the United Kingdom, France, and Russia. The Triple Alliance was originally composed of Germany, Austria–Hungary, and Italy, but Italy remained neutral in 1914. As the war progressed, each coalition added new members. Japan joined the Entente in 1914 and, despite proclaiming its neutrality at the beginning of the war, Italy also joined the Entente in 1915. The term "Allies" became more widely used than "Entente", although the United Kingdom, Fran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Michael
Operation Michael () was a major German military offensive during World War I that began the German spring offensive on 21 March 1918. It was launched from the Hindenburg Line, in the vicinity of Saint-Quentin, France. Its goal was to break through the Allied (Entente) lines and advance in a north-westerly direction to seize the Channel Ports, which supplied the British Expeditionary Force (BEF), and to drive the BEF into the sea. Two days later General Erich Ludendorff, the chief of the German General Staff, adjusted his plan and pushed for an offensive due west, along the whole of the British front north of the River Somme. This was designed to first separate the French and British Armies before continuing with the original concept of pushing the BEF into the sea. The offensive ended at Villers-Bretonneux, to the east of the Allied communications centre at Amiens, where the Allies managed to halt the German advance; the German Army had suffered many casualties and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Army (German Empire)
The Imperial German Army (1871–1919), officially referred to as the German Army (), was the unified ground and air force of the German Empire. It was established in 1871 with the political unification of Germany under the leadership of Prussia, and was dissolved in 1919, after the defeat of the German Empire in World War I (1914–1918). In the Federal Republic of Germany, the term refers to the German Army, the land component of the . Formation and name The states that made up the German Empire contributed their armies; within the German Confederation, formed after the Napoleonic Wars, each state was responsible for maintaining certain units to be put at the disposal of the Confederation in case of conflict. When operating together, the units were known as the Federal Army (). The Federal Army system functioned during various conflicts of the 19th century, such as the First Schleswig War from 1848 to 1852. However, by the time of the Second Schleswig War of 1864, tensio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armoured Warfare
Armoured warfare or armored warfare (American English; American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, see spelling differences), is the use of armoured fighting vehicles in modern warfare. It is a major component of modern Military science, methods of war. The premise of armored warfare rests on the ability of troops to penetrate conventional Defense (military), defensive lines through use of Maneuver warfare, manoeuvre by armoured units. Much of the application of armoured warfare depends on the use of tanks and related vehicles used by other supporting arms such as infantry fighting vehicles, self-propelled artillery, and other combat vehicles, as well as mounted combat engineers and other support units. The Military doctrine, doctrine of armored warfare was developed to break the static nature of World War I trench warfare on the Western Front (World War I), Western Front, and return to the 19th century school of thought that advocated manoeuvre and Decisive vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperial Germany, the Second Reich or simply Germany, was the period of the German Reich; . from the unification of Germany in 1871 until the German revolution of 1918–1919, November Revolution in 1918, when the German Reich changed its form of government from a monarchy to a Weimar Republic, republic. The German Empire consisted of States of the German Empire, 25 states, each with its own nobility: four constituent Monarchy, kingdoms, six Grand duchy, grand duchies, five Duchy, duchies (six before 1876), seven Principality, principalities, three Free imperial city, free Hanseatic League, Hanseatic City-state, cities, and Alsace–Lorraine, one imperial territory. While Prussia was one of four kingdoms in the realm, it contained about two-thirds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surrender (military)
Surrender, in military terms, is the relinquishment of control over territory, combatants, fortifications, ships or armament to another power. A surrender may be accomplished peacefully or it may be the result of defeat in battle. A sovereign state may surrender following defeat in a war, usually by signing a peace treaty or capitulation (surrender), capitulation agreement. A battlefield surrender, either by individuals or when ordered by officer (armed forces), officers, normally results in those surrendering becoming prisoners of war. Definition and etymology Merriam-Webster defines "surrender" as "the action of yielding one's person or giving up the possession of something especially into the power of another", and traces the etymology to the Middle English ''surrendre'', from French ''sur-'' or ''sus-'', ''suz'' "under" + ''rendre'' "to give back"; this in turn is defined by the University of Michigan Middle English Dictionary as meaning "The giving up of an estate, a grant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French First Army
The First Army () was a field army of France that fought during World War I and World War II. It was also active during the Cold War. World War I On mobilization in August 1914, General Auguste Dubail was put in the charge of the First Army, which comprised the 7th, 8th, 13th, 14th, and 21st Army Corps, two divisions of cavalry and one reserve infantry division. It was massed between Belfort and the general line Mirecourt-Lunéville with headquarters at Epinal. First Army then took part, along with the French Second Army, in the Invasion of Lorraine. The First Army intended to take the strongly defended town of Sarrebourg. Bavarian Crown Prince Rupprecht, commander of the German Sixth Army, was tasked with stopping the French invasion. The French attack was repulsed by Rupprecht and his stratagem of pretending to retreat and then strongly attacking back. On 20 August Rupprecht launched a major counter-offensive, driving the French armies out. Dubail was replaced in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marie Eugène Debeney
Marie Eugène Debeney (5 May 1864 – 6 November 1943) was a French Army general who fought in the First World War. He commanded a corps at the Battle of the Somme in 1916 then, in the second half of 1917, served as chief of staff to the French Commander-in-Chief Philippe Pétain. He then commanded the First Army which, fighting alongside British Empire forces, played an important role in the mobile fighting of 1918, including at the Battle of Amiens and the Storming of the Hindenburg Line. He later served an important term as Chief of the General Staff of the French army in the 1920s. Early life Marie-Eugène Debeney was born in Bourg-en-Bresse, Ain. A student at Saint-Cyr, Marie-Eugène Debeney became Lieutenant des Chasseurs in 1886. Debeney was professor of infantry tactics at the ''École de Guerre''. He was an advocate of firepower, like Pétain and Fayolle, not a theorist of ''élan'' and the infantry offensive, like Grandmaison. First World War Early War He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Currie
General Sir Arthur William Currie, (5 December 187530 November 1933) was a senior officer of the Canadian Army who fought during World War I. He had the unique distinction of starting his military career on the very bottom rung as a pre-war militia gunner before rising through the ranks to become the first Canadian commander of the Canadian Corps. Currie's success was based on his ability to rapidly adapt brigade tactics to the exigencies of trench warfare, using set piece operations and bite-and-hold tactics. He is generally considered to be among the most capable commanders of the Western Front, and one of the finest commanders in Canadian military history. Currie began his military career in 1897 as a part-time soldier in the Canadian militia while making his living as a teacher and later as an insurance salesman and real estate speculator. Currie rose quickly through the ranks: commissioned as an officer in 1900, promoted to captain in 1901, then major in 1906 and becam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Corps
The Canadian Corps was a World War I corps formed from the Canadian Expeditionary Force in September 1915 after the arrival of the 2nd Canadian Division in France. The corps was expanded by the addition of the 3rd Canadian Division in December 1915 and the 4th Canadian Division in August 1916. The organization of a 5th Canadian Division began in February 1917 but it was still not fully formed when it was broken up in February 1918 and its men used to reinforce the other four divisions. The majority of soldiers of the Canadian Corps were British-born Canadians until near the end of the war, when the number of those of Canadian birth who had enlisted rose to 51 percent. They were mostly volunteers, as conscription was not implemented until the end of the war (''see'' Conscription Crisis of 1917). Ultimately, only 24,132 conscripts made it to France before 11 November 1918. In the later stages of the war the Canadian Corps was regarded by friend and foe alike as one of the most effec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Monash
General (Australia), General Sir John Monash (; 27 June 1865 – 8 October 1931) was an Australian civil engineer and military commander of the World War I, First World War. He commanded the 13th Brigade (Australia), 13th Infantry Brigade before the war and then, shortly after its outbreak, became commander of the 4th Brigade (Australia), 4th Brigade in Egypt, with which he took part in the Gallipoli campaign. In July 1916, he took charge of the newly raised 3rd Division (Australia), 3rd Division in north-western France and, in May 1918, became commander of the Australian Corps, at that time the largest corps on the Western Front (World War I), Western Front. According to historian A. J. P. Taylor, he was "the only general of creative originality produced by the First World War". Early life Monash was born in 58 Dudley Street, West Melbourne, Victoria, to Jewish parents, both from Krotoschin in the Prussian province of Province of Posen, Posen (now Krotoszyn County, Krotos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |