 |
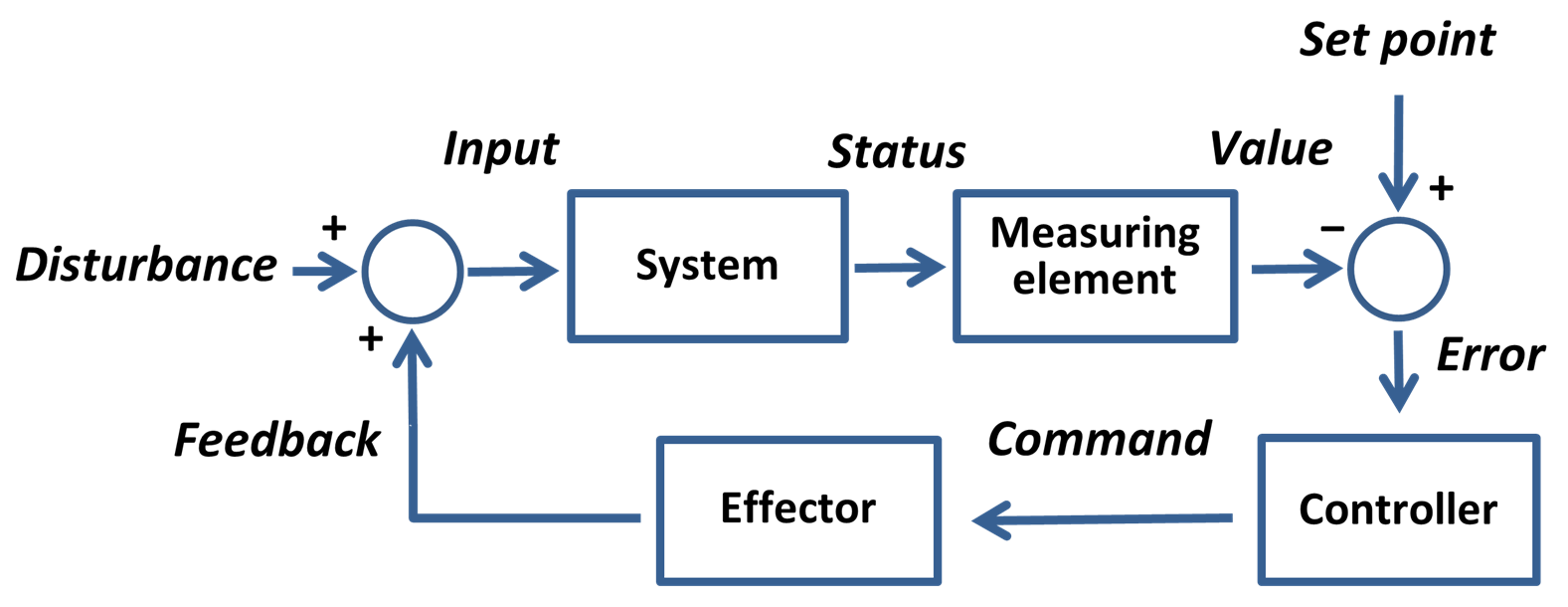
Setpoint (control System)
In cybernetics and control theory, a setpoint (SP; also set point) is the desired or target value for an essential variable, or process value (PV) of a control system, which may differ from the actual measured value of the variable. Departure of such a variable from its setpoint is one basis for error-controlled regulation using negative feedback for automatic control. A setpoint can be any physical quantity or parameter that a control system seeks to regulate, such as temperature, pressure, flow rate, position, speed, or any other measurable attribute. In the context of PID controller, the setpoint represents the reference or goal for the controlled process variable. It serves as the benchmark against which the actual process variable (PV) is continuously compared. The PID controller calculates an error signal by taking the difference between the setpoint and the current value of the process variable. Mathematically, this error is expressed as: :e(t) = SP - PV(t), where e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Set-point Control
Set point or setpoint may refer to: * Set point (tennis), a tennis term meaning one player is one point away from winning a set * Set point (endocrinology), a term encompassing a number of quantities (e.g. body weight, body temperature) where the endocrine system contributes to regulation and homeostasis. * Setpoint (control system), the target value that an automatic control system, for example PID controller, will aim to reach * Set point theory, a theory describing how the body maintains a consistent weight over time * Set Point (album), ''Set Point'' (album), the fourth studio album by Elka (singer), Yolka {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Cruise Control
Cruise control (also known as speed control, cruise command, autocruise, or tempomat) is a system that automatically controls the speed of an automobile. The system is a servomechanism that takes over the car's throttle to maintain a steady speed set by the driver. History Speed control existed in early automobiles such as the Wilson-Pilcher in the early 1900s. They had a lever on the steering column that could be used to set the speed to be maintained by the engine. In 1908, the Peerless included a governor to keep the speed of the engine through an extra throttle lever on the steering wheel. Peerless successfully used a flyball governor. They advertised their system as being able to "maintain speed whether uphill or down." A governor was used by James Watt and Matthew Boulton in 1788 to control steam engines, but the use of governors dates at least back to the 17th century. On an engine, the governor uses centrifugal force to adjust the throttle position to adapt the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Control Loop Theory
Control may refer to: Basic meanings Economics and business * Control (management), an element of management * Control, an element of management accounting * Comptroller (or controller), a senior financial officer in an organization * Controlling interest, a percentage of voting stock shares sufficient to prevent opposition * Foreign exchange controls, regulations on trade * Internal control, a process to help achieve specific goals typically related to managing risk Mathematics and science * Control (optimal control theory), a variable for steering a controllable system of state variables toward a desired goal * Controlling for a variable in statistics * Scientific control, an experiment in which "confounding variables" are minimised to reduce error * Control variables, variables which are kept constant during an experiment * Biological pest control, a natural method of controlling pests * Control network in geodesy and surveying, a set of reference points of known geospatial c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Control Engineering
Control engineering, also known as control systems engineering and, in some European countries, automation engineering, is an engineering discipline that deals with control systems, applying control theory to design equipment and systems with desired behaviors in control environments. The discipline of controls overlaps and is usually taught along with electrical engineering, chemical engineering and mechanical engineering at many institutions around the world. The practice uses sensors and detectors to measure the output performance of the process being controlled; these measurements are used to provide corrective feedback helping to achieve the desired performance. Systems designed to perform without requiring human input are called automatic control systems (such as cruise control for regulating the speed of a car). Multi-disciplinary in nature, control systems engineering activities focus on implementation of control systems mainly derived by mathematical modeling of a diver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Control Devices
Control may refer to: Basic meanings Economics and business * Control (management), an element of management * Control, an element of management accounting * Comptroller (or controller), a senior financial officer in an organization * Controlling interest, a percentage of voting stock shares sufficient to prevent opposition * Foreign exchange controls, regulations on trade * Internal control, a process to help achieve specific goals typically related to managing risk Mathematics and science * Control (optimal control theory), a variable for steering a controllable system of state variables toward a desired goal * Controlling for a variable in statistics * Scientific control, an experiment in which "confounding variables" are minimised to reduce error * Control variables, variables which are kept constant during an experiment * Biological pest control, a natural method of controlling pests * Control network in geodesy and surveying, a set of reference points of known geospatial c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Classical Control Theory
Classical control theory is a branch of control theory that deals with the behavior of dynamical systems with inputs, and how their behavior is modified by feedback, using the Laplace transform as a basic tool to model such systems. The usual objective of control theory is to control a system, often called the ''plant'', so its output follows a desired control signal, called the ''reference'', which may be a fixed or changing value. To do this a '' controller'' is designed, which monitors the output and compares it with the reference. The difference between actual and desired output, called the ''error'' signal, is applied as feedback to the input of the system, to bring the actual output closer to the reference. Classical control theory deals with linear time-invariant (LTI) single-input single-output (SISO) systems. The Laplace transform of the input and output signal of such systems can be calculated. The transfer function relates the Laplace transform of the input and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Process Control
Industrial process control (IPC) or simply process control is a system used in modern manufacturing which uses the principles of control theory and physical industrial control systems to monitor, control and optimize continuous Industrial processes, industrial production processes using control algorithms. This ensures that the industrial machines run smoothly and safely in factories and efficiently use energy to transform raw materials into high-quality finished products with reliable consistency while reducing Efficient energy use#Industry, energy waste and economic costs, something which could not be achieved purely by human manual control. In IPC, control theory provides the theoretical framework to understand system dynamics, predict outcomes and design control strategies to ensure predetermined objectives, utilizing concepts like feedback loops, stability analysis and controller design. On the other hand, the physical apparatus of IPC, based on automation technologies, cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
PID Controller
PID or Pid may refer to: Medicine * Pelvic inflammatory disease or pelvic inflammatory disorder, an infection of the upper part of the female reproductive system * Primary immune deficiency, disorders in which part of the body's immune system is missing or does not function properly * Prolapsed intervertebral disc, commonly called a herniated disc Science, technology and engineering * BBC Programme Identifier, a unique identifier for a BBC television or radio programme brand, a season or series, or an individual episode * OBD-II PIDs (on-board diagnostics parameter IDs), requests for data through an OBD connector in automotive repair * Packet Identifier, a field in a MPEG transport stream#Packet Identifier (PID), MPEG transport stream packet * Partial information decomposition, an extension of information theory * Passive infrared detector, a passive infrared sensor * Payload Interface Document (used on space engineering program for example) * Persistent identifier, a long-lastin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
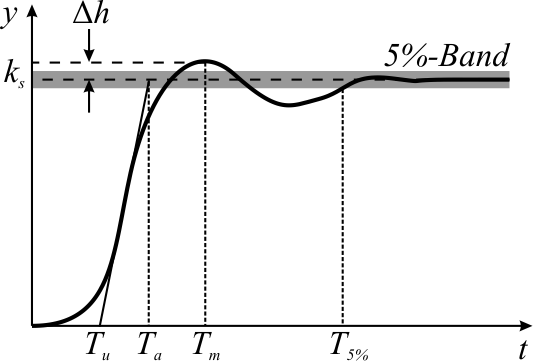 |
Overshoot (signal)
In signal processing, control theory, electronics, and mathematics, overshoot is the occurrence of a signal or function exceeding its target. Undershoot is the same phenomenon in the opposite direction. It arises especially in the step response of bandlimited systems such as low-pass filters. It is often followed by ringing (signal), ringing, and at times conflated with the latter. Definition Maximum overshoot is defined in Katsuhiko Ogata's ''Discrete-time control systems'' as "the maximum peak value of the response curve measured from the desired response of the system." Control theory In control theory, overshoot refers to an output exceeding its final, steady-state value. For a step response, step input, the ''percentage overshoot'' (PO) is the maximum value minus the step value divided by the step value. In the case of the unit step, the ''overshoot'' is just the maximum value of the step response minus one. Also see the definition of ''overshoot'' in an #Electronics, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Cybernetics
Cybernetics is the transdisciplinary study of circular causal processes such as feedback and recursion, where the effects of a system's actions (its outputs) return as inputs to that system, influencing subsequent action. It is concerned with general principles that are relevant across multiple contexts, including in engineering, ecological, economic, biological, cognitive and social systems and also in practical activities such as designing, learning, and managing. Cybernetics' transdisciplinary character has meant that it intersects with a number of other fields, leading to it having both wide influence and diverse interpretations. The field is named after an example of circular causal feedback—that of steering a ship (the ancient Greek κυβερνήτης (''kybernḗtēs'') refers to the person who steers a ship). In steering a ship, the position of the rudder is adjusted in continual response to the effect it is observed as having, forming a feedback loop throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Process Variable
In control theory, a process variable (PV; also process value or process parameter) is the current measured value of a particular part of a process which is being monitored or controlled. An example of this would be the temperature of a furnace. The current temperature is the process variable, while the desired temperature is known as the set-point (SP). Control system use Measurement of process variables is essential in control systems to controlling a process. The value of the process variable is continuously monitored so that control may be exerted. Four commonly measured variables that affect chemical and physical processes are: pressure, temperature, level and flow. but there are in fact a large number of measurement quantities which for international purposes use the International System of Units (SI) The SP-PV error is used to exert control on a process so that the value of PV equals the value of the SP. A classic use of this is in the PID controller PID or Pid ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Proportional–integral–derivative Controller
A proportional–integral–derivative controller (PID controller or three-term controller) is a feedback-based control loop mechanism commonly used to manage machines and processes that require continuous control and automatic adjustment. It is typically used in industrial control systems and various other applications where constant control through modulation is necessary without human intervention. The PID controller automatically compares the desired target value (Setpoint (control system), setpoint or SP) with the actual value of the system (process variable or PV). The difference between these two values is called the ''error value'', denoted as e(t). It then applies corrective actions automatically to bring the PV to the same value as the SP using three methods: The proportional () component responds to the current error value by producing an Output (computing), output that is directly proportional to the magnitude of the error. This provides immediate correction based on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |